Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrodeposition Process
3.2. Morphological Analysis
3.3. Elemental Analysis of the Samples
3.4. FTIR-ATR Analysis
3.5. Structural Analysisof the PB Films
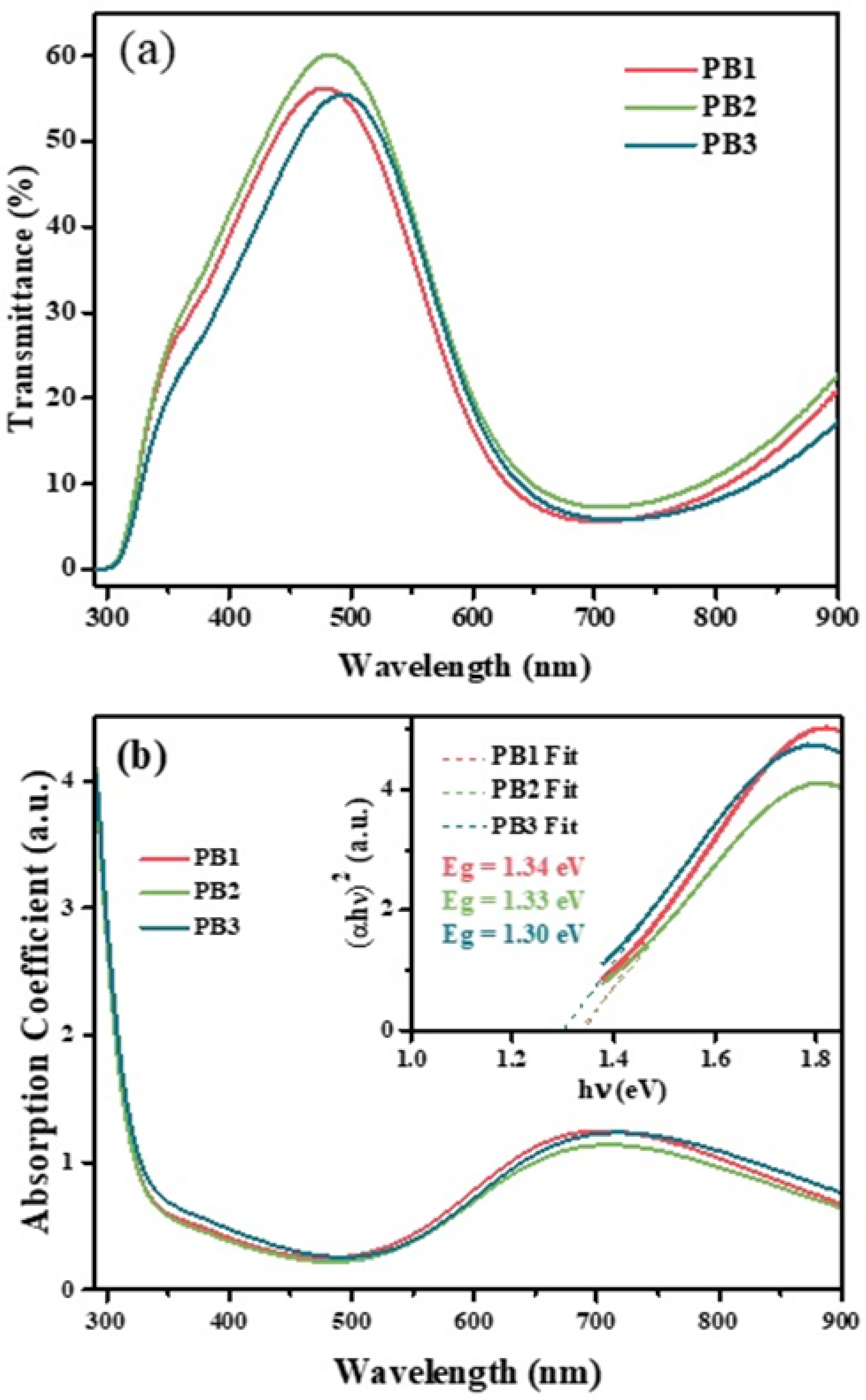
3.6. UV-Vis Spectroscopic Analysis
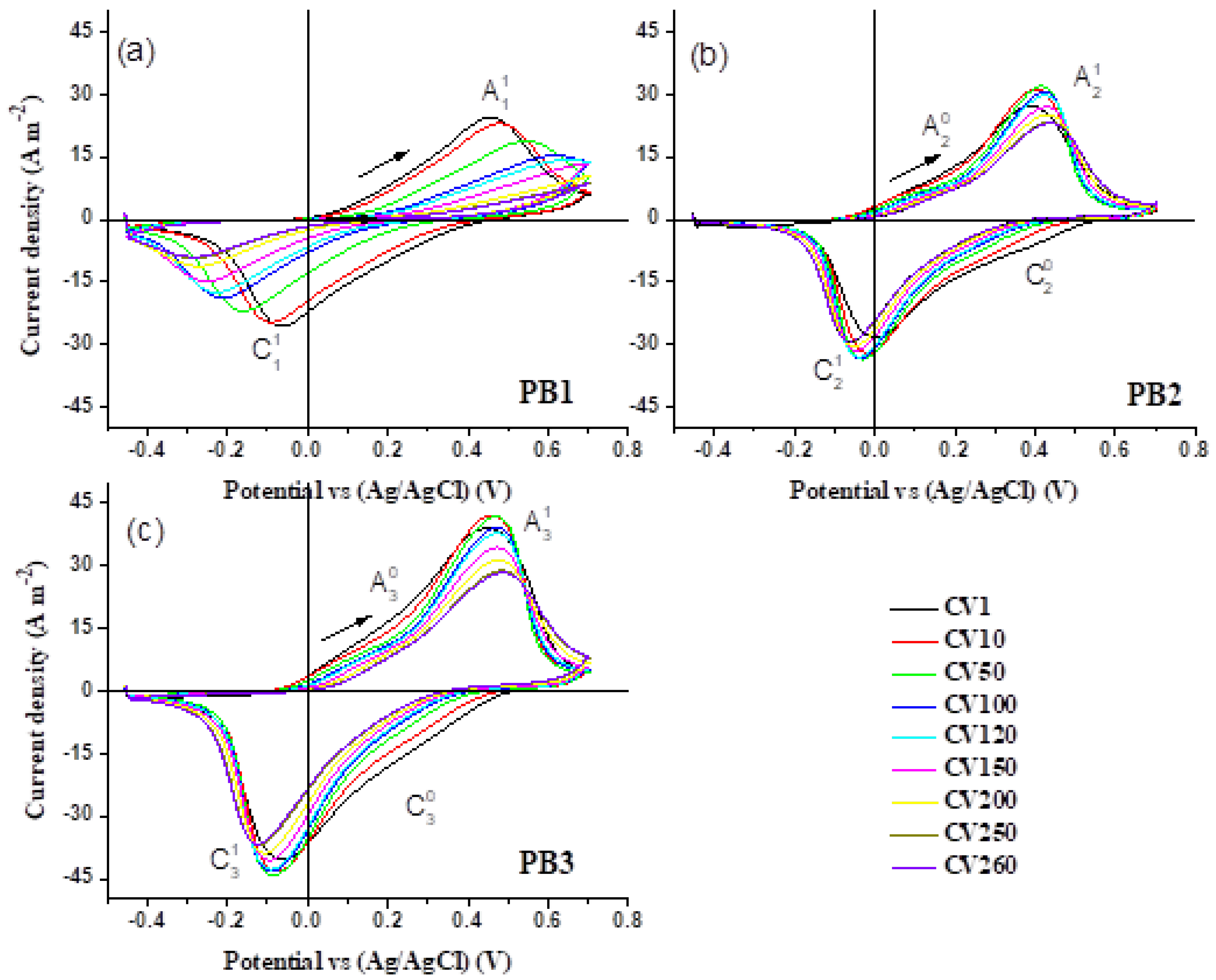
3.7. Cyclic Voltammetry Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monk, P.M.; Mortimer, R.J.; Rosseinsky, D.R. Electrochromism and Electrochromic Devices; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Volume 421. [Google Scholar]
- Isfahani, V.B.; Memarian, N.; Dizaji, H.R.; Arab, A.; Silva, M.M. The physical and electrochromic properties of Prussian Blue thin films electrodeposited on ITO electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 304, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, V.B.; Pereira, R.F.; Fernandes, M.; Sabadini, R.C.; Pereira, S.; Dizaji, H.R.; Arab, A.; Fortunato, E.; Pawlicka, A.; Rego, R. Gellan-Gum and LiTFSI-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Electrochromic Devices. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 5110–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, S.G.; Pech, D. Low Temperature Deposition of Highly Cyclable Porous Prussian Blue Cathode for Lithium-Ion Microbattery. Small 2021, 17, 2101615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Qin, R.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, F. Structure and properties of prussian blue analogues in energy storage and conversion applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, W. Recent progress in Prussian blue films: Methods used to control regular nanostructures for electrochemical biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Tacconi, N.R.; Rajeshwar, K.; Lezna, R.O. Metal hexacyanoferrates: Electrosynthesis, in situ characterization, and applications. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3046–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X. Vacancy modification of Prussian-blue nano-thin films for high energy-density micro-supercapacitors with ultralow RC time constant. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Mai, W. Visualized UV photodetectors based on prussian blue/TiO2 for smart irradiation monitoring application. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wu, F.; Yu, F.; Wu, M.; Zhu, X. Multifunctional theranostic agents based on prussian blue nanoparticles for tumor targeted and MRI—guided photodynamic/photothermal combined treatment. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 135101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hou, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xue, P. Indocyanine green-modified hollow mesoporous Prussian blue nanoparticles loading doxorubicin for fluorescence-guided tri-modal combination therapy of cancer. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5717–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseinsky, D.R.; Glidle, A. EDX, spectroscopy, and composition studies of electrochromic iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II) deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, C641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseinsky, D.R.; Glasser, L.; Jenkins, H.D.B. Thermodynamic clarification of the curious ferric/potassium ion exchange accompanying the electrochromic redox reactions of Prussian blue, iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10472–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Jareño, J.; Navarro-Laboulais, J.; Vicente, F. A numerical approach to the voltammograms of the reduction of Prussian Blue films on ITO electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Romero, D.; Agrisuelas, J.; García-Jareño, J.J.; Gregori, J.; Gabrielli, C.; Perrot, H.; Vicente, F. Electromechanical phase transition in hexacyanometallate nanostructure (Prussian blue). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7121–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, C.; Murray, R.W. Observations on the composition of Prussian blue films and their electrochemistry. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontova, E.; Daurat, M.; Long, J.; Godefroy, A.; Salles, F.; Guari, Y.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Larionova, J. Fashioning Prussian blue nanoparticles by adsorption of luminophores: Synthesis, properties, and in vitro imaging. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahu, M.; Ali, L.M.; Sene, S.; Long, J.; Camerel, F.; Ciancone, M.; Salles, F.; Chopineau, J.; Devoisselle, J.-M.; Felix, G. A rational study of the influence of Mn 2+-insertion in Prussian blue nanoparticles on their photothermal properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9670–9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-Y.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.-D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.-K.; Liu, W.; Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.-S.; Yao, T. Unconventional CN vacancies suppress iron-leaching in Prussian blue analogue pre-catalyst for boosted oxygen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Samain, L.; Long, G.J. Characterization and utilization of Prussian blue and its pigments. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 18018–18044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, P.R.; Ferreira, F.F.; Giménez-Romero, D.; Oliveira Setti, G.; Faria, R.C.; Gabrielli, C.; Perrot, H.; Garcia-Jareño, J.J.; Vicente, F. Synchrotron structural characterization of electrochemically synthesized hexacyanoferrates containing K+: A revisited analysis of electrochemical redox. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13264–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontova, E. Multifunctional Nanomaterials BASED on Coordination Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.B. Mixed-Valence Compounds: Theory and Applications in Chemistry, Physics, Geology, and Biology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Agrisuelas, J.; García-Jareño, J.J.; Gimenez-Romero, D.; Vicente, F. Insights on the mechanism of insoluble-to-soluble Prussian blue transformation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, P149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boergert, M.J. Crystal Structure, Thermal Expansion, and Water Occupancies in Prussian Blue Analogs: A Combined Neutron, X-ray, and Microscopy Study; New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Khan, M.A.N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, L. Core–shell prussian blue analogs with compositional heterogeneity and open cages for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiri, S.; Najdoski, M.; Velevska, J. A simple chemical method for deposition of electrochromic Prussian blue thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncki, R.; Lenarczuk, T.; Radomska, A.; Głąb, S. Optical biosensors based on Prussian Blue films. Analyst 2001, 126, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrisuelas, J.; García-Jareño, J.J.; Vicente, F. Identification of processes associated with different iron sites in the Prussian Blue structure by in situ electrochemical, gravimetric, and spectroscopic techniques in the dc and ac regimes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A. Prussian blue and its analogues: Electrochemistry and analytical applications. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2001, 13, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duek, E.A.; De Paoli, M.A.; Mastragostino, M. A solid-state electrochromic device based on polyaniline, prussian blue and an elastomeric electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 1993, 5, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, M.; Ramadan, R.; Abdelhady, K. Preparation and characterization of spray-deposited efficient Prussian blue electrochromic thin film. Optik 2017, 129, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, V.B.; Dizaji, H.R.; Memarian, N.; Arab, A. Electrodeposition of Prussian Blue films: Study of deposition time effect on electrochemical properties. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 096449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelle, B.P.; Hagen, G. Performance of an electrochromic window based on polyaniline, prussian blue and tungsten oxide. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1999, 58, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotry, S.; Singh, P.; Joshi, A.G.; Singh, D.; Sood, K.; Shivaprasad, S. Electrodeposited Prussian blue films: Annealing effect. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Kamyabi, M.A. Electrochemical formation of Prussian blue films with a single ferricyanide solution on gold electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 584, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, R.; Muñoz, E.; Henríquez, R.; Córdova, R.; Kahlert, H.; Hasse, U.; Scholz, F. Irreversible electrostatic deposition of Prussian blue from colloidal solutions. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafisayar, P.; Bahrololoom, M. Pulse electrodeposition of Prussian Blue thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 542, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotukhina, E.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Vorotyntsev, M. One-stage periodical anodic-cathodic double pulse deposition of nanocomposite materials. Application to Prussian Blue/polypyrrole film coated electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 122, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Fundamentals and applications. Electrochem. Methods 2001, 2, 580–632. [Google Scholar]
- Baggio, B.F.; Vicente, C.; Pelegrini, S.; Pla Cid, C.C.; Brandt, I.S.; Tumelero, M.A.; Pasa, A.A. Morphology and structure of electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian white thin films. Materials 2019, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, P.J.; Malik, M.A.; Denca, A.; Strojek, J. In situ FT-IR/ATR spectroelectrochemistry of Prussian blue in the solid state. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesza, P.J.; Faszynska, M. Indium (III)-hexacyanof errate as a novel polynuclear mixed-valent inorganic material for preparation of thin zeolitic films on conducting substrates. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1988, 252, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhao, Z. A novel stable electrochromic thin film: A Prussian Blue analogue based on palladium hexacyanoferrate. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1990, 292, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.A.; Hamnett, A.; Higgins, S.J. A study of electrochemically grown prussian blue films using Fourier-transform infra-red spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1990, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumoorthi, M.; Thomas Joseph Prakash, J. Structure, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide ultra thin films prepared by jet nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, J.; Plivelic, T.; Rocha, R.; Tadokoro, S.; Torriani, I.; Muccillo, E. Synthesis of In2O3nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of a citrate gel precursor. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2005, 7, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyguist, R.; Kagel, R. Infrared Spectra of Inorganic Compounds; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Karpagavinayagam, P.; Vedhi, C. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Avicennia marina flower extract. Vacuum 2019, 160, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.M.; Thema, F.T.; Dikio, E.D. Electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide based on graphene oxide/prussian blue modified glassy carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2012, 7, 5069–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, A. Synthesis, characterization and the electrocatalytic application of prussian blue/titanate nanotubes nanocomposite. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Gomes, I.; Pereira, M.; Moura, C.; Mendes, J.; Almeida, B. Structural and dielectric properties of laser ablated BaTiO3 films deposited over electrophoretically dispersed CoFe2O4 grains. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 164112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.; Almeida, B.; Aguiar, M.; Mendes, J. Structural and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 thin films deposited by laser ablation on Si (001) substrates. Vacuum 2008, 82, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Perera, I.R.; Daeneke, T.; Makuta, S.; Tachibana, Y.; Jasieniak, J.J.; Mishra, A.; Bäuerle, P.; Spiccia, L.; Bach, U. Indium tin oxide as a semiconductor material in efficient p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.B. The color and electronic configurations of Prussian blue. Inorg. Chem. 1962, 1, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, M.F.; Cukiernik, F.D.; Forlano, P.; Olabe, J.A. Electronic structure of cyano-bridged dinuclear iron complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2001, 54, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavender, A.; Samantilleke, A.; Sa, P.; Almeida, B.; Vasilevskiy, M.; Hong, N.H. Simple way to make Anatase TiO2 films on FTO glass for promising solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2012, 69, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, M.; Peter, Y.Y. Fundamentals of Semiconductors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 619. [Google Scholar]
- Bayzi Isfahani, V.; Silva, M.M. Fundamentals and Advances of Electrochromic Systems: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, R.J.; Reynolds, J.R. In situ colorimetric and composite coloration efficiency measurements for electrochromic Prussian blue. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Talagaeva, N.V.; Zolotukhina, E.V.; Pisareva, P.A.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. Electrochromic properties of Prussian blue–polypyrrole composite films in dependence on parameters of synthetic procedure. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, F.; Fischer, P.; Ludi, A.; Hälg, W. Neutron diffraction study of Prussian Blue, Fe4 [Fe (CN) 6] 3. xH2O. Location of water molecules and long-range magnetic order. Inorg. Chem. 1980, 19, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, K.; Nakayama, M.; Nakaoka, K. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance and in situ infrared spectroscopic studies on the redox reaction of Prussian blue. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 474, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Hermes, M.; Scholz, F. Solid state electrochemical reactions in systems with miscibility gaps. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F.; Dostal, A. The formal potentials of solid metal hexacyanometalates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 34, 2685–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
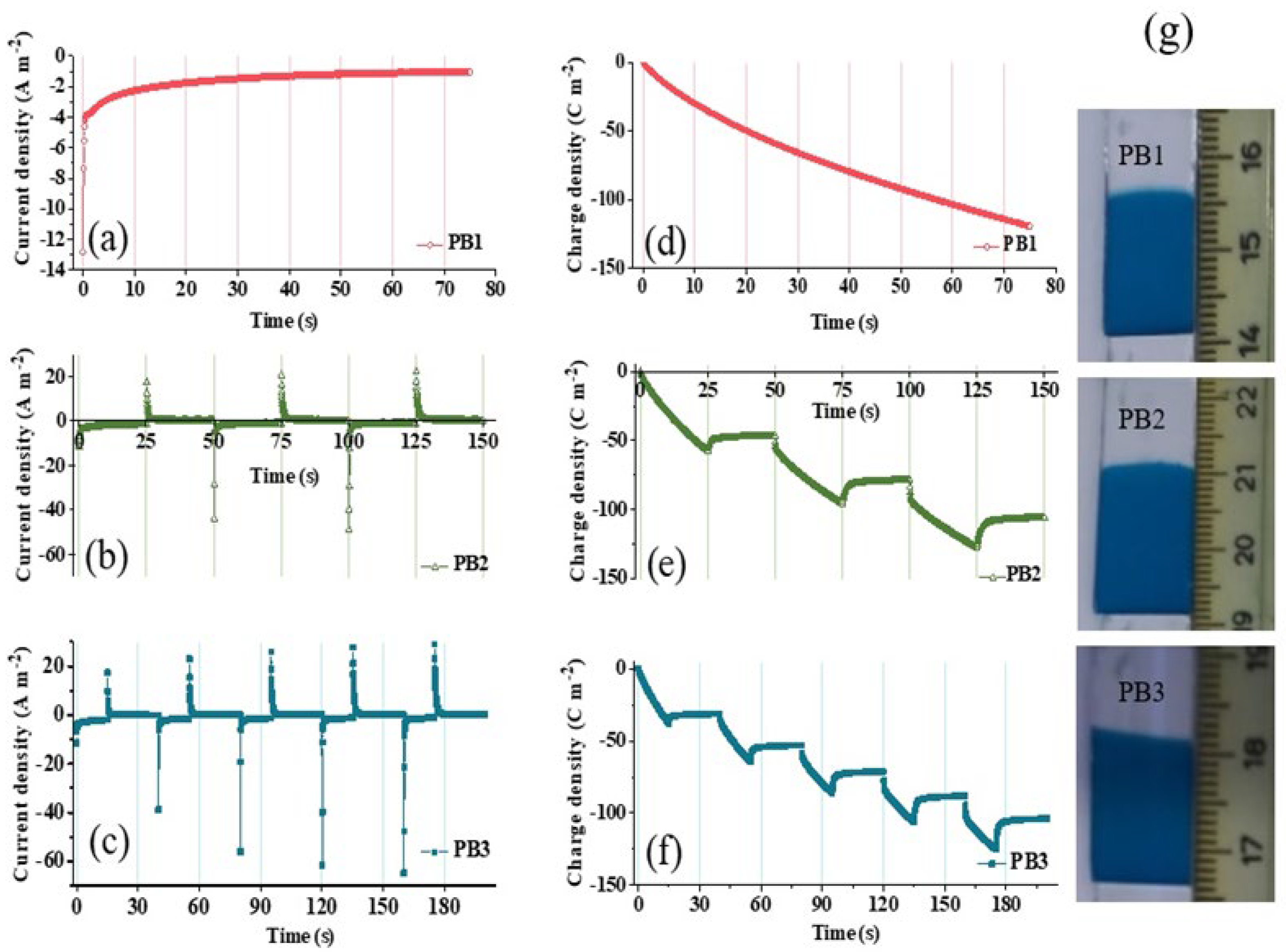
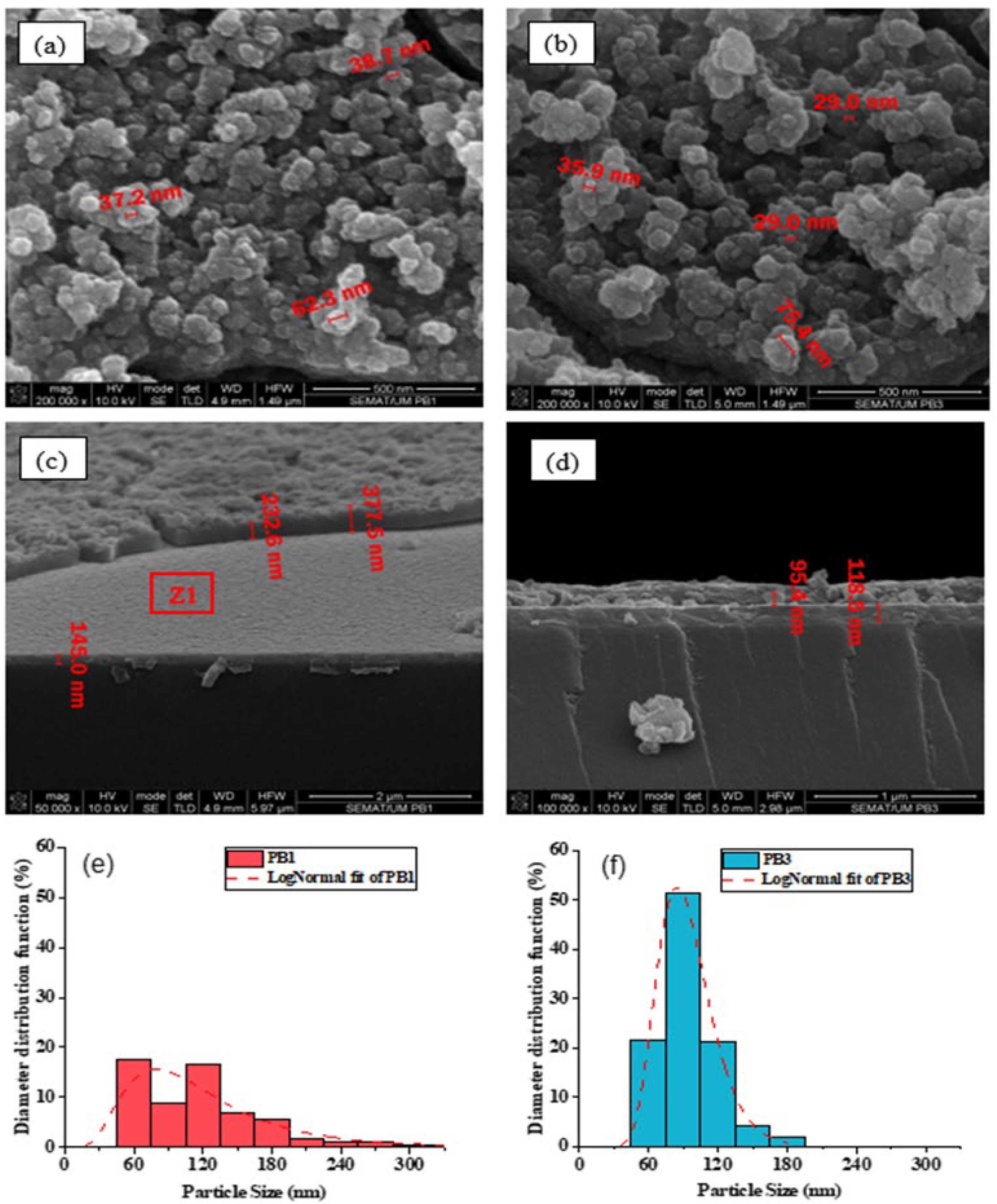

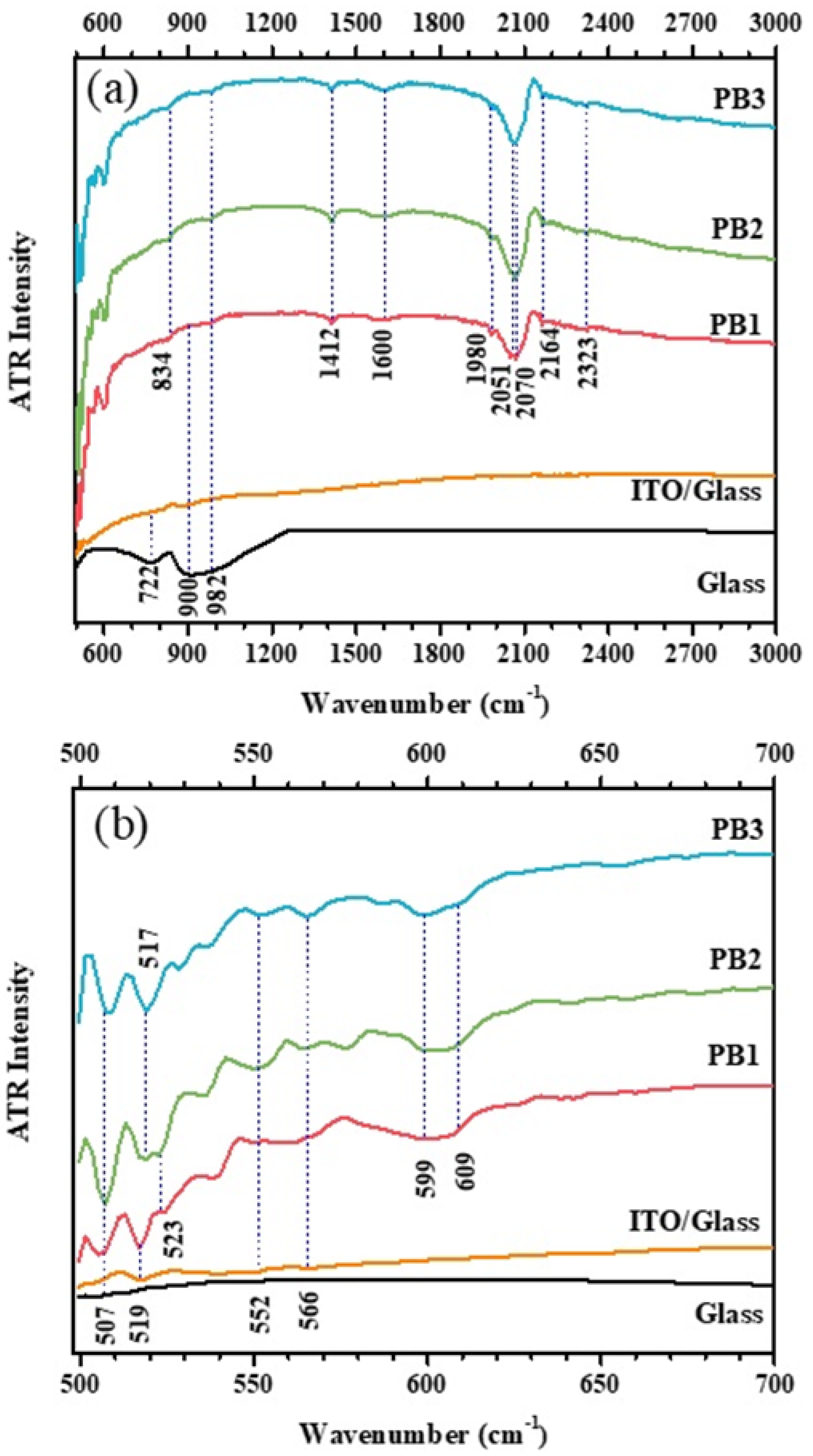
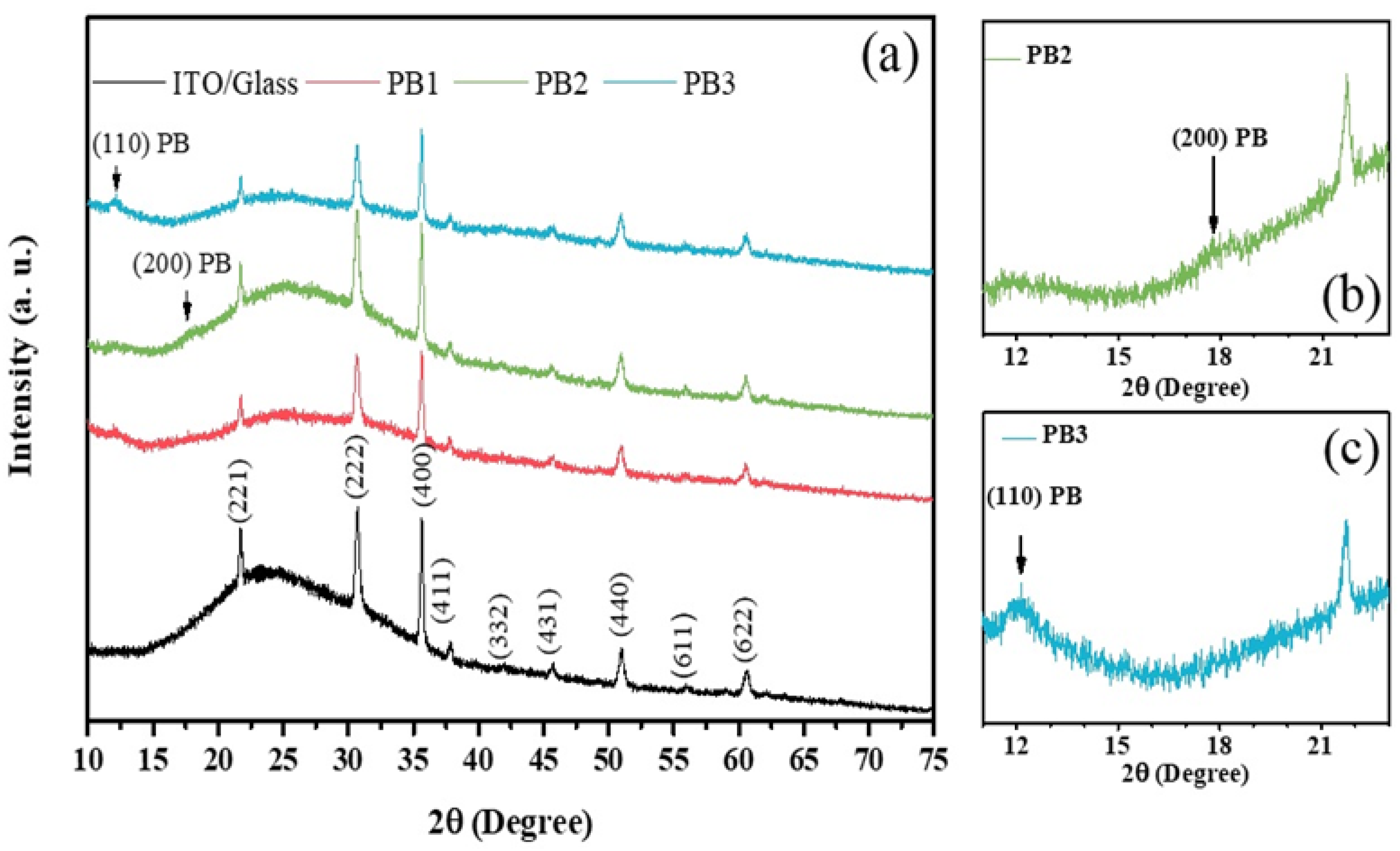

| Sample Name | PB1 | PB2 | PB3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | DC CHA | Symmetric Pulse | Non-Symmetric Pulse | |||||||||
| Parameters | VR (V) | TR (s) | VR (V) | TR (s) | VO (V) | TO (s) | Cycles Number | VR (V) | TR (s) | VO (V) | TO (s) | Cycles Number |
| Values | 0.445 | 75 | 0.445 | 25 | 0.860 | 25 | 3 | 0.445 | 15 | 0.860 | 25 | 5 |
| EDX | C (at %) | N (at %) | O (at %) | K (at %) | Fe (at %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB1 | 28.22 | 33.12 | 30.40 | 3.78 | 4.48 |
| PB2 | 27.23 | 34.49 | 29.87 | 3.39 | 5.01 |
| PB3 | 26.76 | 34.45 | 30.96 | 3.36 | 4.46 |
| Sample | PB1 | PB2 | PB3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | QAnodic (C m−2) | QCathodic (C m−2) | QAnodic (C m−2) | QCathodic (C m−2) | QAnodic (C m−2) | QCathodic (C m−2) | |||
| Cycle Number | |||||||||
| 2 | 81 | 87 | 89 | 100 | 139 | 152 | |||
| 10 | 77 | 81 | 92 | 96 | 134 | 141 | |||
| 260 | 14 | 17 | 71 | 73 | 93 | 99 | |||
| Parameters | QTotal (C m−2) | χ (%) | QTotal (C m−2) | χ (%) | QTotal (C m−2) | χ (%) | |||
| Cycle Number | R2 | R10 | R2 | R0 | R2 | R0 | |||
| 2 | 169 | 82 | 81 | 189 | 24 | 23 | 291 | 39 | 30 |
| 10 | 158 | 187 | 274 | ||||||
| 260 | 31 | 144 | 192 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayzi Isfahani, V.; Arab, A.; Horta Belo, J.; Pedro Araújo, J.; Manuela Silva, M.; Gonçalves Almeida, B. Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods. Materials 2022, 15, 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248857
Bayzi Isfahani V, Arab A, Horta Belo J, Pedro Araújo J, Manuela Silva M, Gonçalves Almeida B. Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248857
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayzi Isfahani, Vahideh, Ali Arab, João Horta Belo, João Pedro Araújo, Maria Manuela Silva, and Bernardo Gonçalves Almeida. 2022. "Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods" Materials 15, no. 24: 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248857
APA StyleBayzi Isfahani, V., Arab, A., Horta Belo, J., Pedro Araújo, J., Manuela Silva, M., & Gonçalves Almeida, B. (2022). Comparison of Physical/Chemical Properties of Prussian Blue Thin Films Prepared by Different Pulse and DC Electrodeposition Methods. Materials, 15(24), 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248857








