Research Advances in the Immunomodulatory Functions of CD100/SEMA4D and Their Roles in Viral Infectious Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
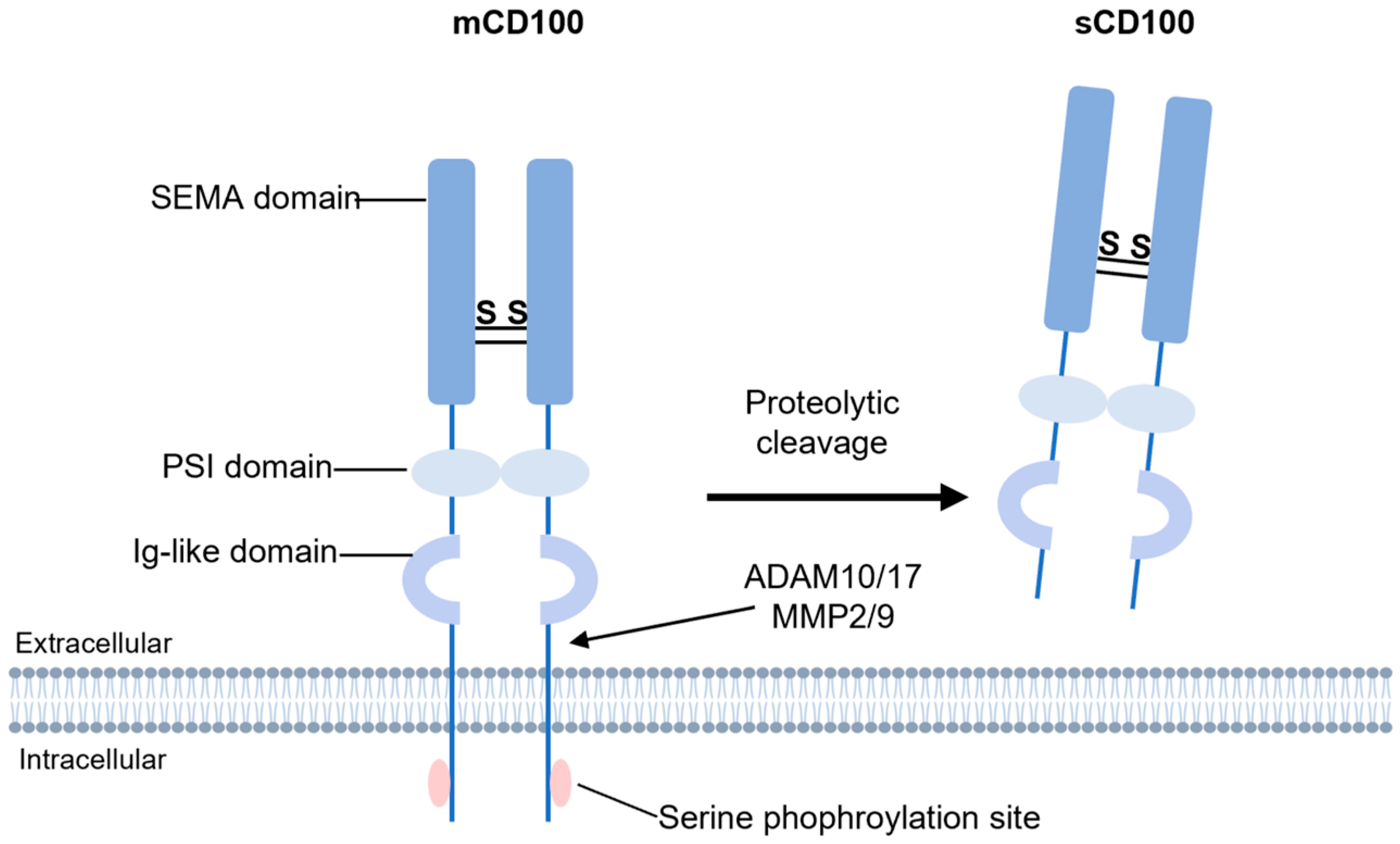
2. Structural Features and Expression Patterns of CD100
3. Regulatory Roles of CD100 in Immune Cells
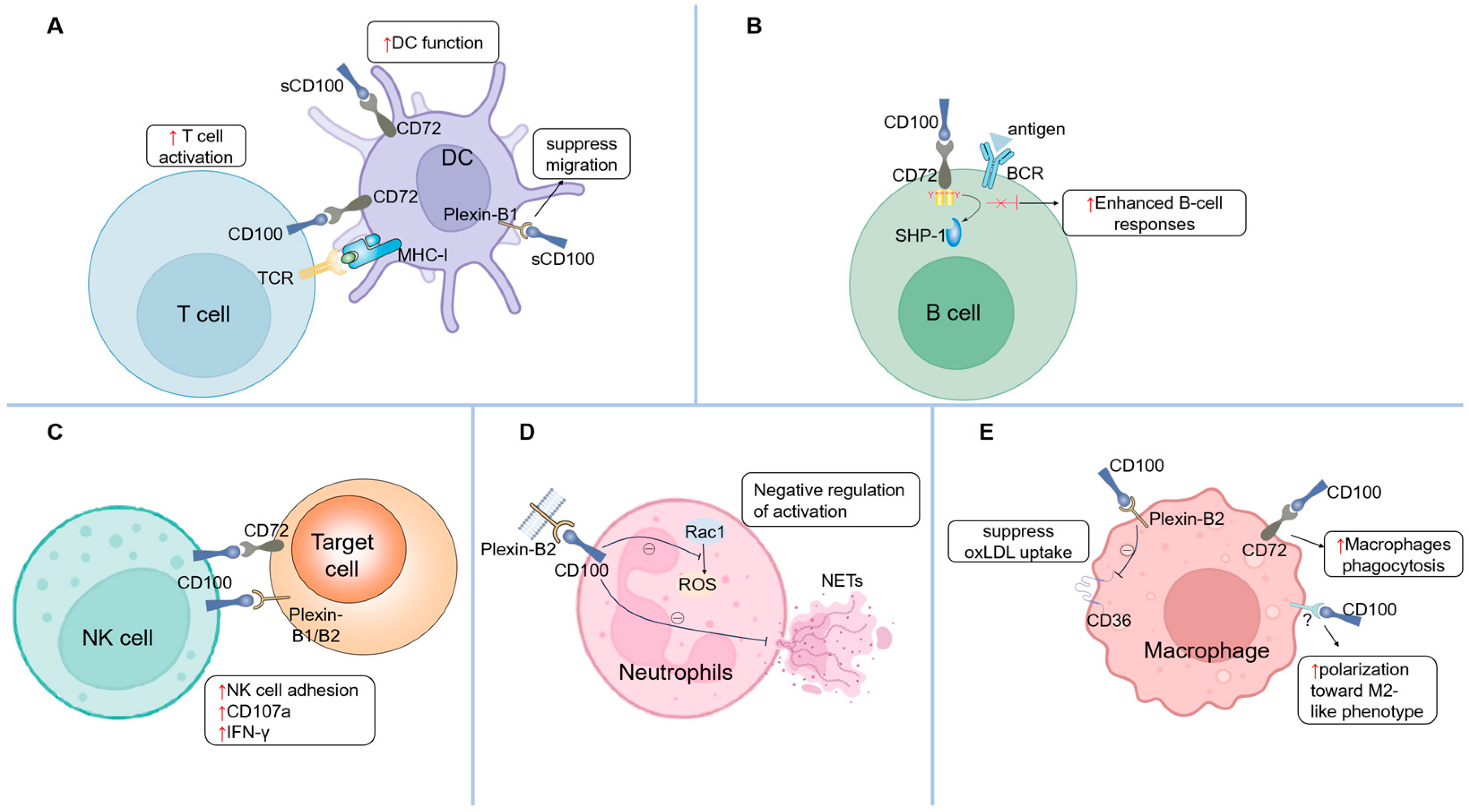
3.1. T Cells
3.2. B Cells
3.3. Dendritic Cells (DCs)
3.4. Natural Killer (NK) Cells
3.5. Neutrophils
3.6. Macrophages
4. CD100 in Viral Infectious Diseases
4.1. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
4.2. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
4.3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
4.4. Hantaan Virus (HTNV)
5. Clinical Prospects of CD100
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, K.T.; Boumsell, L.; Schultze, J.L.; Boussiotis, V.A.; Dorfman, D.M.; Cardoso, A.A.; Bensussan, A.; Nadler, L.M.; Freeman, G.J. Human CD100, a Novel Leukocyte Semaphorin That Promotes B-Cell Aggregation and Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11780–11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takegahara, N.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Semaphorins: A New Class of Immunoregulatory Molecules. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougeret, C.; Mansur, I.G.; Dastot, H.; Schmid, M.; Mahouy, G.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L. Increased Surface Expression of a Newly Identified 150-kDa Dimer Early after Human T Lymphocyte Activation. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuazo-Gaztelu, I.; Pàez-Ribes, M.; Carrasco, P.; Martín, L.; Soler, A.; Martínez-Lozano, M.; Pons, R.; Llena, J.; Palomero, L.; Graupera, M.; et al. Antitumor Effects of Anti-Semaphorin 4D Antibody Unravel a Novel Proinvasive Mechanism of Vascular-Targeting Agents. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5328–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, J.; Qi, F.; You, H. Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Pancreatic Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, M.; Kumanogoh, A. The Role of Semaphorins in Immune Responses and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Pan, W.; Bayer, W.; Thoens, C.; Heim, K.; Dittmer, U.; Timm, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; et al. MMP2/MMP9-Mediated CD100 Shedding Is Crucial for Inducing Intrahepatic Anti-HBV CD8 T Cell Responses and HBV Clearance. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-N.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Xi, F.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.-Z. Imbalance Between Soluble and Membrane-Bound CD100 Regulates Monocytes Activity in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Viral Immunol. 2021, 34, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Ji, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Lian, J.; Hao, C.; et al. CD100 Up-Regulation Induced by Interferon-α on B Cells Is Related to Hepatitis C Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.R.; Li, J.G.; Zuo, W.Z.; et al. Interferon-α-Induced CD100 on Naïve CD8+ T Cells Enhances Antiviral Responses to Hepatitis C Infection through CD72 Signal Transduction. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fan, C.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ye, C.; Ji, G.; Ma, L.; Lian, J.; et al. Interferon-α-Enhanced CD100/Plexin-B1/B2 Interactions Promote Natural Killer Cell Functions in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.M.; Milush, J.M.; Ho, E.L.; Batista, M.D.; Holditch, S.J.; Keh, C.E.; Norris, P.J.; Keating, S.M.; Deeks, S.G.; Hunt, P.W.; et al. Expansion of CD8+ T Cells Lacking Sema4D/CD100 during HIV-1 Infection Identifies a Subset of T Cells with Decreased Functional Capacity. Blood 2012, 119, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, Z.; Elbirt, D.; Radian, S.; Bezalel-Rosenberg, S.; Mahlab-Guri, K.; Toubi, E.; Asher, I.; Sthoeger, Z. Low Levels of the Immunoregulator Semaphorin 4D (CD100) in Sera of HIV Patients. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 191, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yi, J.; Zhuang, R.; Yu, H.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, B. CD8low CD100-T Cells Identify a Novel CD8 T Cell Subset Associated with Viral Control during Human Hantaan Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11834–11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Yi, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, C.; Zhuang, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, A.; et al. Elevated Plasma Soluble Sema4D/CD100 Levels Are Associated with Disease Severity in Patients of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, C.; Elhabazi, A.; Bismuth, G.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L. CD100 Is Associated with CD45 at the Surface of Human T Lymphocytes. Role in T Cell Homotypic Adhesion. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 5262–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.A.; Harlos, K.; Mavaddat, N.; Davis, S.J.; Stuart, D.I.; Jones, E.Y.; Esnouf, R.M. The Ligand-Binding Face of the Semaphorins Revealed by the High-Resolution Crystal Structure of SEMA4D. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.J.C.; Robinson, R.A.; Pérez-Brangulí, F.; Bell, C.H.; Mitchell, K.J.; Siebold, C.; Jones, E.Y. Structural Basis of Semaphorin-Plexin Signalling. Nature 2010, 467, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Nishide, M.; Maeda, Y.; Hayama, Y.; Koyama, S.; Nojima, S.; Takamatsu, H.; Okuzaki, D.; Morita, T.; Nakatani, T.; et al. Pathological and Therapeutic Implications of Eosinophil-Derived Semaphorin 4D in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 843–854.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ke, Y.; Dang, E.; Fang, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Shao, S.; Qiao, P.; Zhang, T.; et al. Semaphorin 4D from CD15+ Granulocytes via ADAM10-Induced Cleavage Contributes to Antibody Production in Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laber, A.; Gadermaier, E.; Wallwitz, J.; Berg, G.; Himmler, G. A High-Sensitivity Enzyme Immunoassay for the Quantification of Soluble Human Semaphorin 4D in Plasma. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 574, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, K.T.; Cornillet, M.; Björkström, N.K. Soluble SEMA4D/CD100: A Novel Immunoregulator in Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 163, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xu, D.Z.; Li, Q.; Mou, P.; Zeng, Z.; Brass, L.F.; Zhu, L. The Regulation of Sema4D Exodomain Shedding by Protein Kinase A in Platelets. Platelets 2016, 27, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaire, S.; Elhabazi, A.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L. CD100 Is a Leukocyte Semaphorin. CMLS Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granziero, L.; Circosta, P.; Scielzo, C.; Frisaldi, E.; Stella, S.; Geuna, M.; Giordano, S.; Ghia, P.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. CD100/Plexin-B1 Interactions Sustain Proliferation and Survival of Normal and Leukemic CD5+ B Lymphocytes. Blood 2003, 101, 1962–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, S.; Markel, G.; Porgador, A.; Bushkin, Y.; Mandelboim, O. CD100 on NK Cells Enhance IFNgamma Secretion and Killing of Target Cells Expressing CD72. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Watanabe, C.; Lee, I.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Araki, H.; Hirata, H.; Iwahori, K.; Uchida, J.; Yasui, T.; et al. Identification of CD72 as a Lymphocyte Receptor for the Class IV Semaphorin CD100: A Novel Mechanism for Regulating B Cell Signaling. Immunity 2000, 13, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabbert-de Ponnat, I.; Marie-Cardine, A.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Schiavon, V.; Tamagnone, L.; Thomasset, N.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L. Soluble CD100 Functions on Human Monocytes and Immature Dendritic Cells Require Plexin C1 and Plexin B1, Respectively. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagnone, L.; Artigiani, S.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Ming, G.I.; Song, H.; Chedotal, A.; Winberg, M.L.; Goodman, C.S.; Poo, M.; et al. Plexins Are a Large Family of Receptors for Transmembrane, Secreted, and GPI-Anchored Semaphorins in Vertebrates. Cell 1999, 99, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the Human Tissue-Specific Expression by Genome-Wide Integration of Transcriptomics and Antibody-Based Proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Immune Cell Interactions. Nat. Inmunol. 2008, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcón, V.L.; Luther, C.; Balce, D.; Takei, F. B-Cell Co-Receptor CD72 Is Expressed on NK Cells and Inhibits IFN-Gamma Production but Not Cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, Z.; Haj, T.; Balbir, A.; Peri, R.; Rosner, I.; Slobodin, G.; Kessel, A.; Toubi, E. A Regulatory Role for CD72 Expression on B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Bondada, S. CD72, a Coreceptor with Both Positive and Negative Effects on B Lymphocyte Development and Function. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklina, E.M.; Nekrasova, I.V. New Aspects of the Seam4D-Dependent Control of Lymphocyte Activation. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2017, 473, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau-Fauvarque, C.; Kumanogoh, A.; Camand, E.; Jaillard, C.; Barbin, G.; Boquet, I.; Love, C.; Jones, E.Y.; Kikutani, H.; Lubetzki, C.; et al. The Transmembrane Semaphorin Sema4D/CD100, an Inhibitor of Axonal Growth, Is Expressed on Oligodendrocytes and Upregulated after CNS Lesion. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9229–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Kumanogoh, A.; Watanabe, C.; Uchida, J.; Wang, X.; Yasui, T.; Yukawa, K.; Ikawa, M.; Okabe, M.; Parnes, J.R.; et al. The Class IV Semaphorin CD100 Plays Nonredundant Roles in the Immune System: Defective B and T Cell Activation in CD100-Deficient Mice. Immunity 2000, 13, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Suzuki, K.; Ch’ng, E.; Watanabe, C.; Marukawa, S.; Takegahara, N.; Ishida, I.; Sato, T.; Habu, S.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Requirement for the Lymphocyte Semaphorin, CD100, in the Induction of Antigen-Specific T Cells and the Maturation of Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, C.; Kumanogoh, A.; Shi, W.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, S.; Okabe, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kikutani, H. Enhanced Immune Responses in Transgenic Mice Expressing a Truncated Form of the Lymphocyte Semaphorin CD100. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklina, E.; Nekrasova, I.; Glebezdina, N. Signaling from Membrane Semaphorin 4D in T Lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 129, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Björkström, N.K.; Melum, E. Intact CD100–CD72 Interaction Necessary for TCR-Induced T Cell Proliferation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witherden, D.A.; Watanabe, M.; Garijo, O.; Rieder, S.E.; Sarkisyan, G.; Cronin, S.J.F.; Verdino, P.; Wilson, I.A.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H.; et al. The CD100 Receptor Interacts with Its Plexin-B2 Ligand to Regulate Epidermal Γδ T Cell Function. Immunity 2012, 37, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doody, G.M.; Justement, L.B.; Delibrias, C.C.; Matthews, R.J.; Lin, J.; Thomas, M.L.; Fearon, D.T. A Role in B Cell Activation for CD22 and the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP. Science 1995, 269, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonks, N.K.; Neel, B.G. From Form to Function: Signaling by Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases. Cell 1996, 87, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, A.K.; Yuen, K.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Branch, D.R.; Siminovitch, K.A. The SH2 Domain Containing Tyrosine Phosphatase-1 down-Regulates Activation of Lyn and Lyn-Induced Tyrosine Phosphorylation of the CD19 Receptor in B Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Baumgarth, N.; Parnes, J.R. CD72-Deficient Mice Reveal Nonredundant Roles of CD72 in B Cell Development and Activation. Immunity 1999, 11, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, I.; Kumanogoh, A.; Suzuki, K.; Akahani, S.; Noda, K.; Kikutani, H. Involvement of CD100, a Lymphocyte Semaphorin, in the Activation of the Human Immune System via CD72: Implications for the Regulation of Immune and Inflammatory Responses. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, M.; Nojima, S.; Ito, D.; Takamatsu, H.; Koyama, S.; Kang, S.; Kimura, T.; Morimoto, K.; Hosokawa, T.; Hayama, Y.; et al. Semaphorin 4D Inhibits Neutrophil Activation and Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Neutrophil-Mediated Autoimmune Vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhabazi, A.; Delaire, S.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L.; Bismuth, G. Biological Activity of Soluble CD100. I. The Extracellular Region of CD100 Is Released from the Surface of T Lymphocytes by Regulated Proteolysis. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4341–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, M.C.A.; Galuppo, M.K.; Capelli-Peixoto, J.; Stolf, B.S. CD100 Effects in Macrophages and Its Roles in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, M.C.A.; Gutierrez, P.S.; Debbas, V.; Kalil, J.; Stolf, B.S. CD100 and Plexins B2 and B1 Mediate Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Might Take Part in Atherogenesis. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppo, M.K.; de Rezende, E.; Forti, F.L.; Cortez, M.; Cruz, M.C.; Teixeira, A.A.; Giordano, R.J.; Stolf, B.S. CD100/Sema4D Increases Macrophage Infection by Leishmania (Leishmania) Amazonensis in a CD72 Dependent Manner. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebinoski, S.; Zhang, Q.; Cillo, A.R.; Manne, S.; Xiao, H.; Brunazzi, E.A.; Tabib, T.; Cardello, C.; Lian, C.G.; Murphy, G.F.; et al. Autoreactive CD8+ T Cells Are Restrained by an Exhaustion-like Program That Is Maintained by LAG3. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T Cells Mediate Viral Clearance and Disease Pathogenesis during Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Rocha, R.; Lopez-Abente, J.; Gutierrez, C.; Pérez-Fernández, V.A.; Prieto-Sánchez, A.; Moreno-Guillen, S.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.-Á.; Pion, M. CD72/CD100 and PD-1/PD-L1 Markers Are Increased on T and B Cells in HIV-1+ Viremic Individuals, and CD72/CD100 Axis Is Correlated with T-Cell Exhaustion. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.L.; Reilly, C.A.; Winter, L.A.; Pandina, T.; Jonason, A.; Scrivens, M.; Balch, L.; Bussler, H.; Torno, S.; Seils, J.; et al. Generation and Preclinical Characterization of an Antibody Specific for SEMA4D. MAbs 2016, 8, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaGanke, C.; Samkoff, L.; Edwards, K.; Jung Henson, L.; Repovic, P.; Lynch, S.; Stone, L.; Mattson, D.; Galluzzi, A.; Fisher, T.L.; et al. Safety/Tolerability of the Anti-Semaphorin 4D Antibody VX15/2503 in a Randomized Phase 1 Trial. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, A.; Evans, E.E.; Fisher, T.L.; Leonard, J.E.; Smith, E.S.; Reader, A.; Mishra, V.; Manber, R.; Walters, K.A.; Kowarski, L.; et al. Pepinemab Antibody Blockade of SEMA4D in Early Huntington’s Disease: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, A.; Evans, E.E.; Fisher, T.L.; Zauderer, M. Pepinemab: A SEMA4D Antagonist for Treatment of Huntington’s and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2025, 34, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besliu, A.; Banica, L.; Predeteanu, D.; Vlad, V.; Ionescu, R.; Pistol, G.; Opris, D.; Berghea, F.; Stefanescu, M.; Matache, C. Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes Analysis Detects CD100/SEMA4D Alteration in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Autoimmunity 2011, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ogata, A.; Kang, S.; Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Nojima, S.; Kimura, T.; Ito, D.; Morimoto, K.; Nishide, M.; et al. Semaphorin 4D Contributes to Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inducing Inflammatory Cytokine Production: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Dong, N.; Wang, Q.; Yi, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Jin, B.; et al. Increased Levels of Plasma Soluble Sema4D in Patients with Heart Failure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-S.; Jing, C.-Q.; Shan, K.-S.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Guo, X.-B.; Cao, Z.-X.; Mu, L.-J.; Peng, L.-P.; Zhou, M.-L.; Li, L.-P. Semaphorin 4D and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Overexpression Is Related to Prognosis in Colorectal Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Kang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Semaphorin 4D Expression Is Associated with a Poor Clinical Outcome in Cervical Cancer Patients. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infection | Cells Affected | Expression Pattern | Pathway | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV (Chronic) | CD8+ T cell B cell | ↑mCD100 ↓sCD100 | sCD100/CD72 | ↓IFN-γ, TNF-α ↓No. of CD100+ B cell | Yang et al. [7] |
| HBV (Acute) | CD8+ T cell | ↓mCD100 ↑sCD100 | sCD100/CD72 | ↑IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α | Yang et al. [7] |
| HBV (in vitro) | LSEC DC | sCD100/CD72 | ↓T cell suppression mediated by LSEC ↑CD80, CD86, IL-2 | Yang et al. [7] | |
| HBV-ACLF | CD14+ monocyte | ↑mCD100 ↓sCD100 | sCD100/CD72 | ↓IFN-γ, TNF-α ↓Granzyme B | Zhang et al. [8] |
| HCV (Chronic) | B cell | ↑mCD100 | He et al. [9] | ||
| CD8+ T cell | ↓mCD100 | mCD100/CD72 | ↓IFN-γ, TNF-α ↓Granzyme B, perforin | Li et al. [10] | |
| NK cell | ↓mCD100 | mCD100/PlexinB1, B2 | ↓CD107a ↓IFN-γ | He et al. [11] | |
| HIV | CD8+ T cell CD4+ T cell | ↓mCD100 ↓sCD100 | CD100/CD72 | ↓IFN-γ, TNF-α ↓perforin | Eriksson et al. [12] Vadasz et al. [13] |
| HTNV | CD8lo CD100− T cell | ↑sCD100 | ↑activation (CD38, HLA-DR) ↑IFN-γ, TNF-α ↑Granzyme B, perforin | Liu et al. [14] Liu et al. [15] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J. Research Advances in the Immunomodulatory Functions of CD100/SEMA4D and Their Roles in Viral Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094341
Zhao M, Chen L, Chen Y, Yang X, Feng X, Yang D, Zheng X, Liu J. Research Advances in the Immunomodulatory Functions of CD100/SEMA4D and Their Roles in Viral Infectious Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094341
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Mengxiao, Liwei Chen, Yuhang Chen, Xuecheng Yang, Xuemei Feng, Dongliang Yang, Xin Zheng, and Jia Liu. 2025. "Research Advances in the Immunomodulatory Functions of CD100/SEMA4D and Their Roles in Viral Infectious Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094341
APA StyleZhao, M., Chen, L., Chen, Y., Yang, X., Feng, X., Yang, D., Zheng, X., & Liu, J. (2025). Research Advances in the Immunomodulatory Functions of CD100/SEMA4D and Their Roles in Viral Infectious Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094341







