Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
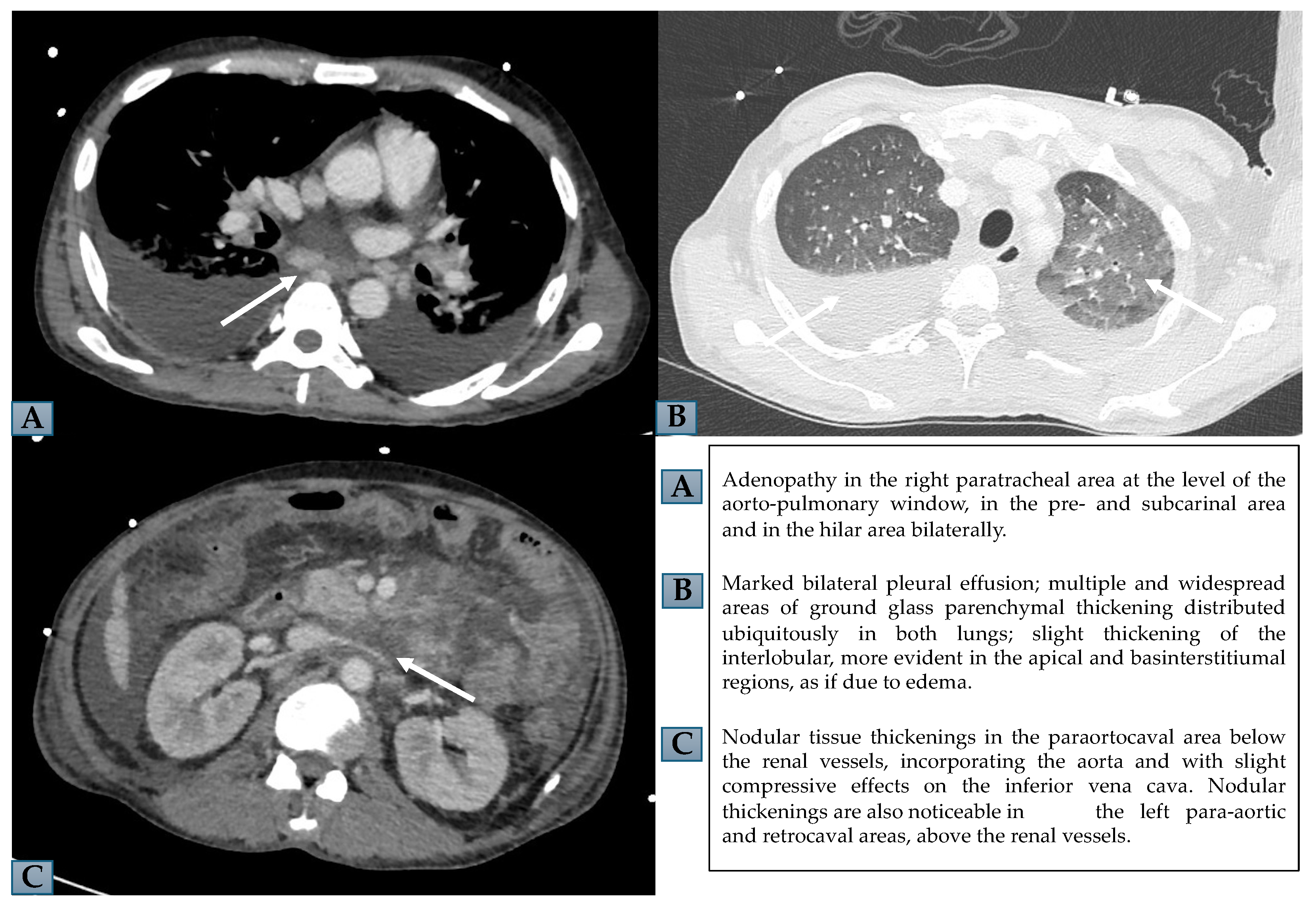
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrakasan, S.; Filipovich, A.H. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Advances in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Berliner, N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 24, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Schulert, G.S.; Volpi, S.; Lee, P.Y.; Kernan, K.F.; Caricchio, R.; Mahmud, S.; Hazen, M.M.; Halyabar, O.; et al. On the Alert for Cytokine Storm: Immunopathology in COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Cohen, D.N.; Greig, B.; Yenamandra, A.; Vnencak-Jones, C.; Thompson, M.A.; Kim, A.S. The ambiguous boundary between EBV-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and systemic EBV-driven T cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5738–5749. [Google Scholar]
- Grom, A.A.; Villanueva, J.; Lee, S.; Goldmuntz, E.A.; Passo, M.H.; Filipovich, A. Natural killer cell dysfunction in patients with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, G.; Knaak, C.; Vorderwülbecke, G.; La Rosée, P.; Balzer, F.; Schenk, T.; Schuster, F.S.; Nyvlt, P.; Janka, G.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; et al. Hyperferritinemia in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Lee, W.I.; Cook, M.C.; Smyth, L.; Talaulikar, D. Correlation of haemophagocytosis with clinical criteria of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and recommendations for bone marrow reporting. Pathology 2022, 54, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.I.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforow, S.; Berliner, N. The unique aspects of presentation and diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2015, 2015, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; Marsh, R.A. Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cron, R.Q.; Goyal, G.; Chatham, W.W. Cytokine Storm Syndrome. Annu. Rev. Med. 2023, 74, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoory, B.; Geerlinks, A.; Wilejto, M.; Kernan, K.; Hines, M.; Romano, M.; Piskin, D.; Ravelli, A.; Sinha, R.; Aletaha, D.; et al. The 2022 EULAR/ACR Points to Consider at the Early Stages of Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (HLH/MAS). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayne, C.B.; Albeituni, S.; Nichols, K.E.; Cron, R.Q. The Immunology of Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.M. Macrophage activation syndrome in rheumatic disease: What is the role of the antigen presenting cell? Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, R.D.; Suttles, J. Functional plasticity of macrophages: Reversible adaptation to changing microenvironments. J. Leuk. Biol. 2004, 76, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Schmidt, S.V.; Sander, J.; Draffehn, A.; Krebs, W.; Quester, I.; De Nardo, D.; Gohel, T.D.; Emde, M.; Schmidleithner, L.; et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity 2014, 40, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cron, R.Q.; Davi, S.; Minoia, F.; Ravelli, A. Clinical features and correct diagnosis of macrophage activation syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellotti, G.M.; Khan, F.B.; Nguyen, J.; Chen, C.; Bruzzone, C.M.; Bechtel, H.; Brown, G.; Nath, K.A.; Steer, C.J.; Hebbel, R.P.; et al. H-ferritin ferroxidase induces cytoprotective pathways and inhibits microvascular stasis in transgenic sickle mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, G.; Spies, C.; Schenk, T.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Balzer, F.; La Rosée, P. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Potentially Underdiagnosed in Intensive Care Units. Shock 2018, 50, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Serum ferritin is an important inflammatory disease marker, as it is mainly a leakage product from damaged cells. Metallomics 2014, 6, 748–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.R.; Shah, Y.M. Iron homeostasis in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kyriazopoulou, E.; Leventogiannis, K.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; Pantazi, A.; Orfanos, S.E.; Rovina, N.; Tsangaris, I.; Gkavogianni, T.; Botsa, E.; et al. Macrophage activation-like syndrome: An immunological entity associated with rapid progression to death in sepsis. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Bai, G.; Han, W.; Guo, R.; Cui, N. mTOR Modulates the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced CD4+ T Cell Apoptosis Mediated by ROS in Septic Immunosuppression. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 6077570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernan, K.F.; Carcillo, J.A. Hyperferritinemia and inflammation. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.A.; Connor, J.R. The significance of ferritin in cancer: Anti-oxidation, inflammation and tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1836, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, E.; Tomita, N.; Koyama, S.; Ogusa, E.; Ishii, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Miyashita, K.; Matsuura, S.; Tachibana, T.; Takasaki, H.; et al. Serum ferritin level is prognostic of patient outcome in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; López-Guillermo, A.; Khamashta, M.A.; Bosch, X. Adult haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet 2014, 383, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaak, C.; Nyvlt, P.; Schuster, F.S.; Spies, C.; Heeren, P.; Schenk, T.; Balzer, F.; La Rosée, P.; Janka, G.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients: Diagnostic reliability of HLH-2004 criteria and HScore. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaczka, M.; Vaktnäs, J.; Klimkowska, M.; Hägglund, H. Malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: A retrospective population-based analysis from a single center. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. A Novel Prognostic Index Model for Adult Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis in China. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Kobayashi, R.; Tanaka, J.; Hashino, S.; Ota, S.; Torimoto, Y.; Kakinoki, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Hatakeyama, N.; et al. Risk factor analysis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma-associated haemophagocytic syndromes: A multicentre study. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 165, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoref-Lorenz, A.; Murakami, J.; Hofstetter, L.; Iyer, S.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Mohamed, S.F.; Miller, P.G.; Guber, E.; Weinstein, S.; Yacobovich, J.; et al. An improved index for diagnosis and mortality prediction in malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2022, 139, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallawany, N.K.; Curry, C.V.; Allen, C.E. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Epstein-Barr virus: A complex relationship with diverse origins, expression and outcomes. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiadi, A.; Zoref-Lorenz, A.; Lee, C.Y.; Jordan, M.B.; Chen, L.Y.C. Malignancy-associated haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e217–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gars, E.; Purington, N.; Scott, G.; Chisholm, K.; Gratzinger, D.; Martin, B.A.; Ohgami, R.S. Bone marrow histomorphological criteria can accurately diagnose hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, A.M.; Campigotto, F.; Mullally, A.; Fogerty, A.; Massarotti, E.; Neuberg, D.; Berliner, N. Marked hyperferritinemia does not predict for HLH in the adult population. Blood 2015, 125, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Ruxolitinib for refractory/relapsed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 2020, 105, e210–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Ruxolitinib combined with doxorubicin, etoposide, and dexamethasone for the treatment of the lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bami, S.; Vagrecha, A.; Soberman, D.; Badawi, M.; Cannone, D.; Lipton, J.M.; Cron, R.Q.; Levy, C.F. The use of anakinra in the treatment of secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attygalle, A.D.; Cabeçadas, J.; Gaulard, P.; Jaffe, E.S.; de Jong, D.; Ko, Y.H.; Said, J.; Klapper, W. Peripheral T-cell and NK-cell lymphomas and their mimics; taking a step forward—Report on the lymphoma workshop of the XVIth meeting of the European Association for Haematopathology and the Society for Hematopathology. Histopathology 2014, 64, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Yamashita, D.; Nakamura, S. Nodal EBV+ cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma: A literature review based on the 2017 WHO classification. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2020, 60, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Asano, N.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Takata, K.; Elsayed, A.A.; Satou, A.; Takahashi, E.; Kinoshita, T.; Nakamura, S. T-cell receptor (TCR) phenotype of nodal Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma (CTL): A clinicopathologic study of 39 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, D.; Shimada, K.; Takata, K.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Kohno, K.; Satou, A.; Sakakibara, A.; Nakamura, S.; Asano, N.; Kato, S. Reappraisal of nodal Epstein-Barr Virus-negative cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma: Identification of indolent CD5+ diseases. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2599–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottestam, H.; Horne, A.; Aricò, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; Webb, D.; Janka, G.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Long-term results of the HLH-94 treatment protocol. Blood 2011, 118, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, P.; Gietka, P.; Książyk, J.B.; Machaczka, M. The influence of various therapeutic regimens on early clinical and laboratory response and outcome of children with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, B.; Angurana, S.K.; Awasthi, P.; Nallasamy, K.; Baranwal, A.; Bansal, A.; Bansal, D.; Rawat, A.; Varma, N.; Jayashree, M. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a PICU of a Developing Economy: Clinical Profile, Intensive Care Needs, Outcome, and Predictors of Mortality. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 22, e44–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaishi, T.; Takeshita, T.; Himori, N.; Takahashi, T.; Misu, T.; Ogawa, R.; Kaneko, K.; Fujimori, J.; Abe, M.; Ishii, T.; et al. Rapid Administration of High-Dose Intravenous Methylprednisolone Improves Visual Outcomes After Optic Neuritis in Patients With AQP4-IgG-Positive NMOSD. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoory, B.; Carcillo, J.A.; Chatham, W.W.; Amdur, R.L.; Zhao, H.; Dinarello, C.A.; Cron, R.Q.; Opal, S.M. Interleukin-1 Receptor Blockade Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in Sepsis Patients With Features of Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Reanalysis of a Prior Phase III Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamuth, N.J.; Nichols, K.E.; Paessler, M.; Teachey, D.T. Use of rituximab in conjunction with immunosuppressive chemotherapy as a novel therapy for Epstein Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2007, 29, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hot, A.; Toh, M.L.; Coppéré, B.; Perard, L.; Girard Madoux, M.H.; Mausservey, C.; Desmurs-Clavel, H.; French, M.; Ninet, J. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adult-onset Still disease: Clinical features and long-term outcome: A case-control study of 8 patients. Medicine 2010, 89, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Jordan, M.B.; Allen, C.; Cesaro, S.; Rizzari, C.; Rao, A.; Degar, B.; Garrington, T.P.; Sevilla, J.; Putti, M.C.; et al. Emapalumab in Children with Primary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, P.S.; Ahmed, A.; Merrill, S.A.; Wilcox, R.A. Ruxolitinib in adult patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, E103–E105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | In Medicine Department | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.60 | 0.70–1.20 |
| Na+ (mmol/L) | 124 | 136–145 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 4.5 | 3.4–5.5 |
| Ca++ (mmol/L) | 1.70 | 2.10–2.50 |
| Proteins (g/dL) | 4.2 | 6.0–8.2 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 1.9 | 3.5–5.5 |
| Amylase (U/L) | 141 | 28–100 |
| Lipase (U/L) | 102 | 13–60 |
| AST (U/L) | 508 | 9–45 |
| ALT (U/L) | 148 | 10–40 |
| γGT (U/L) | 130 | 8–61 |
| CPK (U/L) | 1544 | 20–200 |
| LDH (U/L) | 2049 | 135–225 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 391 | 45–236 |
| Ferritin (µg/L) | >8000 | 30–400 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 3.82 | 0–0.5 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 5 | 0–25 |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 11.56 | 0.02–0.064 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 11.1 | 13.5–16.5 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 3.16 | 4.40–11.30 |
| N (×109/L) | 2.64 | 1.80–7.70 |
| L (×109/L) | 0.30 | 1.80–4.80 |
| PLT (×109/L) | 60 | 150–450 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 84 | 150–400 |
| INR | 1.30 | 0.81–1.20 |
| aPTT ratio | 1.31 | 0.8–1.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gioia, C.; Paroli, M.; Izzo, R.; Di Sanzo, L.; Rossi, E.; Pignatelli, P.; Accapezzato, D. Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115921
Gioia C, Paroli M, Izzo R, Di Sanzo L, Rossi E, Pignatelli P, Accapezzato D. Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115921
Chicago/Turabian StyleGioia, Chiara, Marino Paroli, Raffaella Izzo, Lorenzo Di Sanzo, Elisabetta Rossi, Pasquale Pignatelli, and Daniele Accapezzato. 2024. "Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115921
APA StyleGioia, C., Paroli, M., Izzo, R., Di Sanzo, L., Rossi, E., Pignatelli, P., & Accapezzato, D. (2024). Pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115921






