Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT): Pathways to Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
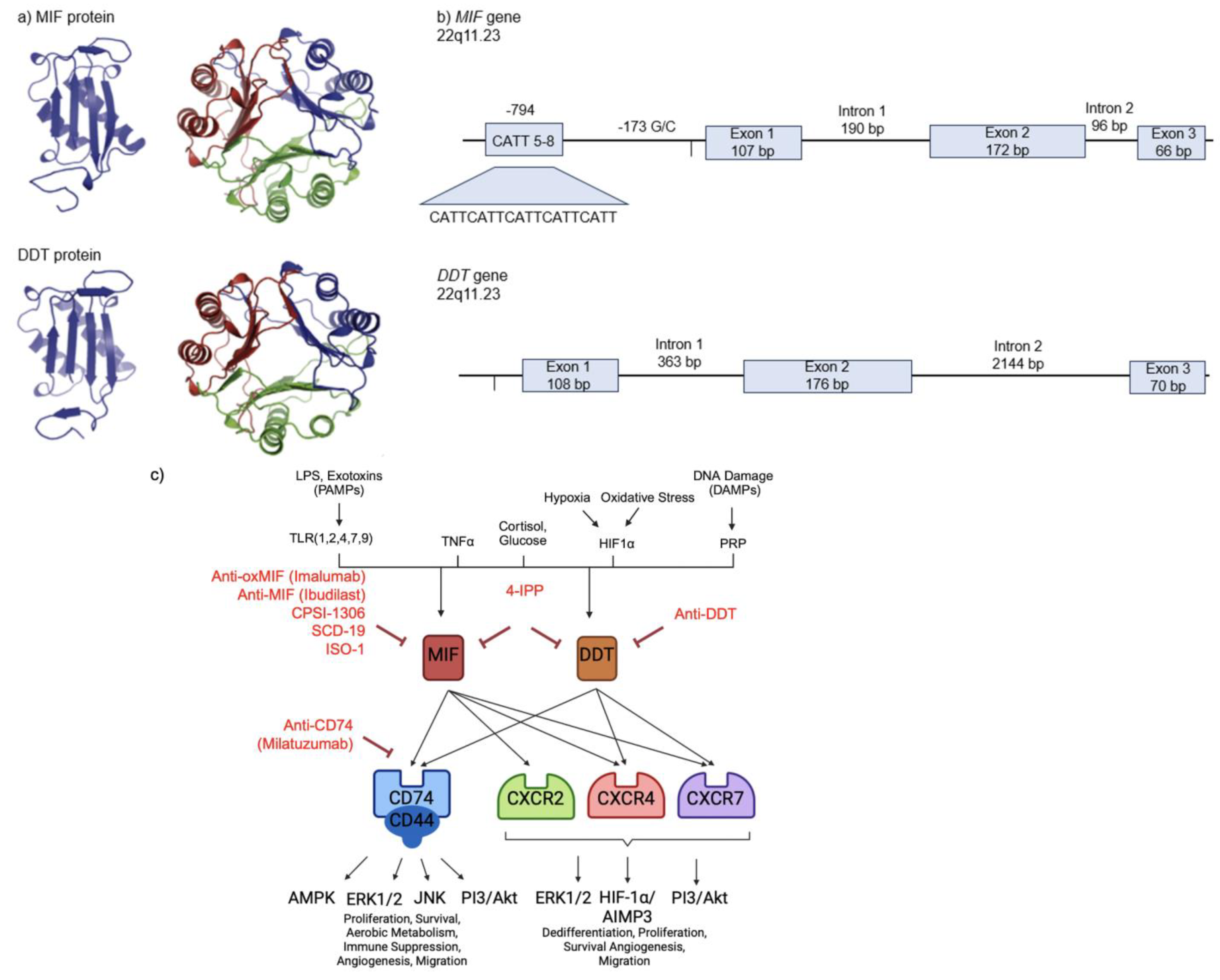
2. MIF and DDT Structure and Regulation
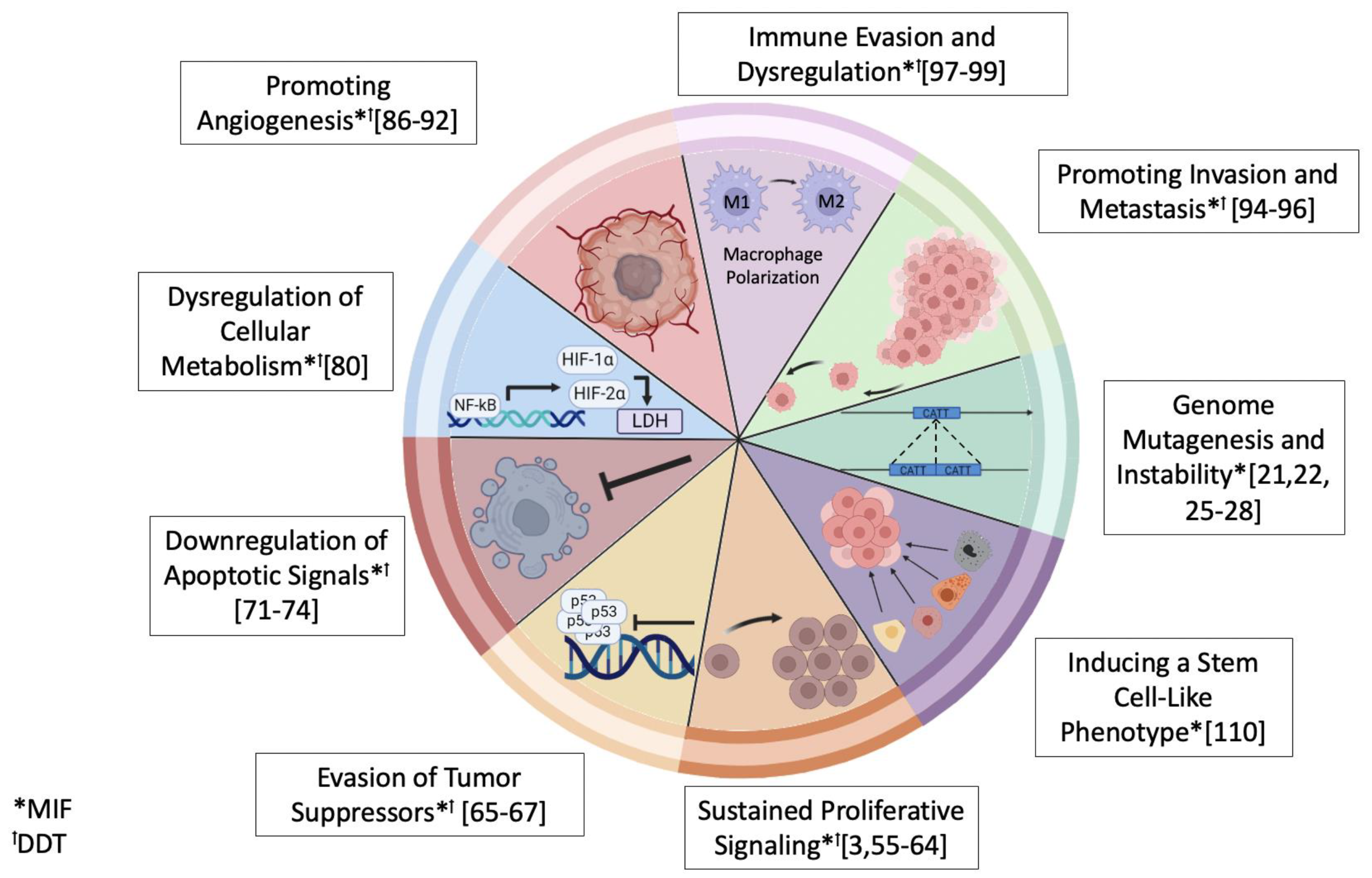
3. MIF and DDT Functions in Cancer Progression
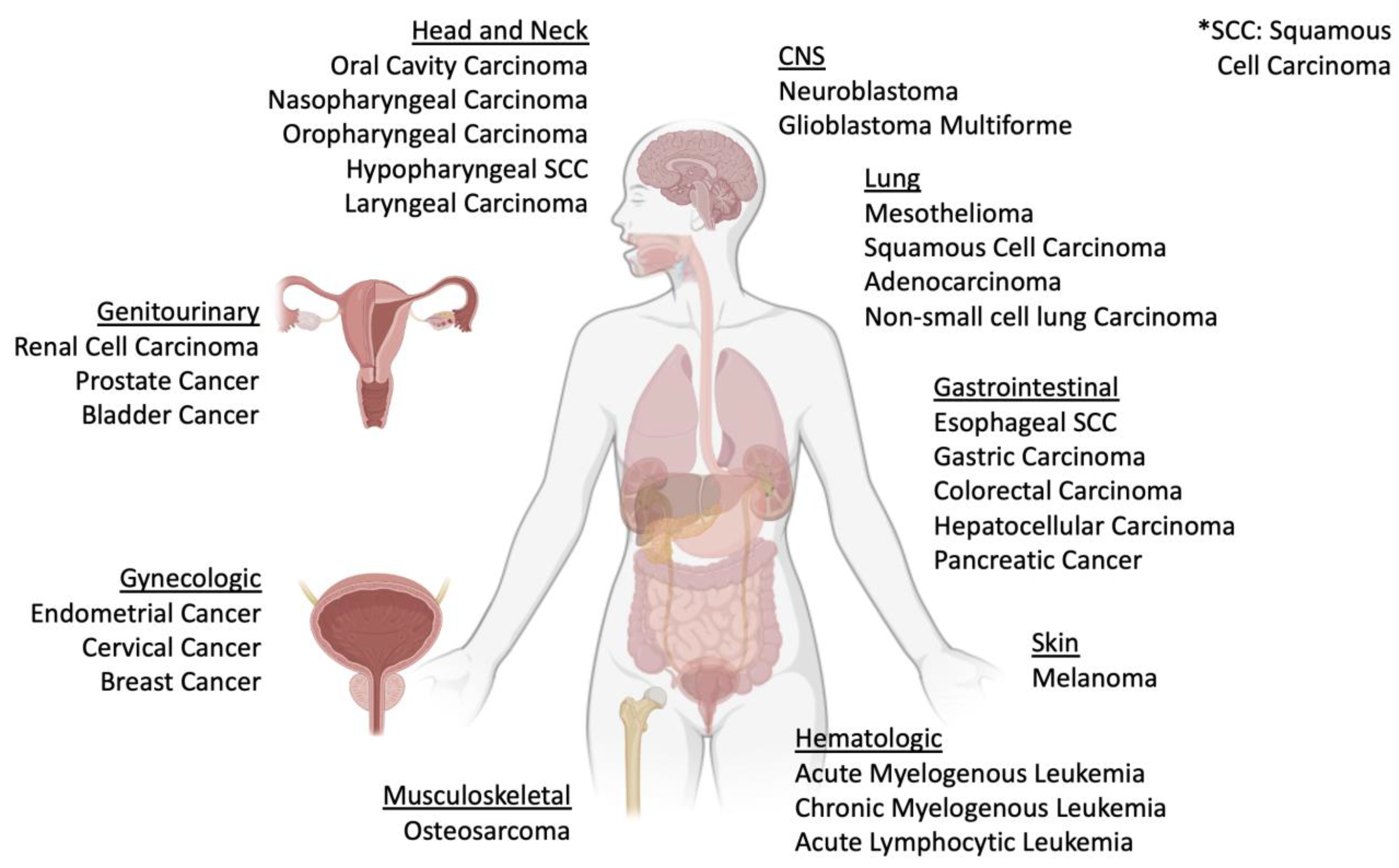
4. Evidence of MIF and DDT in Cancer
4.1. Hematologic Cancers
4.2. Osteosarcoma
4.3. Skin Cancers
4.4. Head and Neck Cancers
4.5. Lung Cancers
4.6. Gastrointestinal Cancers
4.6.1. Esophageal and Gastric Cancer
4.6.2. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
4.6.3. Pancreatic Carcinoma
4.6.4. Colorectal Carcinoma
4.7. Central Nervous System Cancers
4.8. Urogenital Cancers
4.8.1. Bladder Cancer
4.8.2. Prostate Cancer
4.8.3. Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.9. Breast Cancer
4.10. Gynecologic Cancers
4.10.1. Endometrial Carcinoma
4.10.2. Cervical Cancer
5. Current Therapeutic Applications and Clinical Trials
6. Future Directions
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, J.R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: Its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1966, 56, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, B.R.; Bennett, B. Mechanism of a Reaction in Vitro Associated with Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity. Science 1966, 153, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskas, S.S.; Wong, D.W.; Bucala, R.; Djudjaj, S.; Boor, P. Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal. 2019, 57, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaiya, K.; Langford, D.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Shanmughapriya, S. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Roger, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A regulator of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froidevaux, C.; Roger, T.; Martin, C.; Glauser, M.P.; Calandra, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and innate immune responses to bacterial infections. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, S13–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, K.N.; Templeton, D.J.; Cross, J.V. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor protects cancer cells from immunogenic cell death and impairs anti-tumor immune responses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Leng, L.; Sauler, M.; Fu, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, X.; Lee, P.; Bucala, R. Transcription factor ICBP90 regulates the MIF promoter and immune susceptibility locus. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.-A.; Leng, L.; Kim, B.-J.; Du, X.; Tilstam, P.V.; Kim, K.H.; Kong, J.-S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Liu, A.; Wang, T.; et al. MIF allele-dependent regulation of the MIF coreceptor CD44 and role in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7917–E7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Romero, R.; Benedek, G.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Vandenbark, A.A. Predicted structure of MIF/CD74 and RTL1000/CD74 complexes. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merk, M.; Zierow, S.; Leng, L.; Das, R.; Du, X.; Schulte, W.; Fan, J.; Lue, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, H.; et al. The D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT) gene product is a cytokine and functional homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E577–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomposo, O.I.; Illescas, O.; Pacheco-Fernández, T.; Laclette, J.P.; Rodriguez, T.; Rodriguez-Sosa, M. Immune modulation by the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) family: D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT) is not (always) a backup system. Cytokine 2020, 133, 155121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Hoti, S. Role of cysteine-58 and cysteine-95 residues in the thiol di-sulfide oxidoreductase activity of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor-2 of Wuchereria bancrofti. Acta Trop. 2016, 153, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Bernhagen, J.; Mitchell, R.A.; Bucala, R. The macrophage is an important and previously unrecognized source of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.P.W.; Foote, A.; Fan, H.; de Castro, C.P.; Lang, T.; Jones, S.A.; Gavrilescu, N.; Mills, K.H.G.; Leech, M.; Morand, E.F.; et al. Loss of autophagy enhances MIF/macrophage migration inhibitory factor release by macrophages. Autophagy 2016, 12, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellowe, A.S.; Sauler, M.; Hou, Y.; Merola, J.; Liu, R.; Calderon, B.; Lauridsen, H.M.; Harris, M.R.; Leng, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Endothelial cell-secreted MIF reduces pericyte contractility and enhances neutrophil extravasation. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.-T.; Guo, L.-L.; Feng, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, N.; Ma, L.-L.; Shen, L.; Tong, G.-H.; Yan, Q.-W.; Zhu, S.-J.; et al. MIF, secreted by human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, promotes chemotaxis and outgrowth of colorectal cancer in liver prometastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22410–22423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, D.; Grieb, G.; Hristov, M.; Pallua, N.; Weber, C.; Bernhagen, J.; Steffens, G. Hypoxia-induced endothelial secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and role in endothelial progenitor cell recruitment. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeber, G.; Calandra, T.; Roduit, R.; Haefliger, J.-A.; Bonny, C.; Thompson, N.; Thorens, B.; Temler, E.; Meinhardt, A.; Bacher, M.; et al. Insulin secretion is regulated by the glucose-dependent production of islet β cell macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4782–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Bucala, R. The immunobiology of MIF: Function, genetics and prospects for precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Siu, E.; Bucala, R. Genotyping Two Promoter Polymorphisms in the MIF Gene: A -794 CATT(5-8) Microsatellite Repeat and a -173 G/C SNP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2080, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matia-García, I.; Salgado-Goytia, L.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; García-Arellano, S.; Hernández-Bello, J.; Salgado-Bernabé, A.B.; Parra-Rojas, I. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Promoter Polymorphisms (−794 CATT5–8and −173 G>C): Relationship with mRNA Expression and Soluble MIF Levels in Young Obese Subjects. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 461208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, M.; Mitchell, R.A.; Endres, S.; Bucala, R. D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT or MIF-2): Doubling the MIF cytokine family. Cytokine 2012, 59, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, C.; He, H.; Zhang, X. UHRF1 regulates the transcriptional repressor HBP1 through MIF in T acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos-Navarro, G.; Del Toro-Arreola, A.; Daneri-Navarro, A.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Bautista-Herrera, L.A.; Topete, R.A.F.; Macias, B.U.A.; Castro, D.I.J.; Morán-Mendoza, A.d.J.; Oceguera-Villanueva, A.; et al. Association of the genetic variants (-794 CATT5-8 and -173 G > C) of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) with higher soluble levels of MIF and TNFα in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-W.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Tian, M.-M.; Feng, G.-S.; You, W.-C.; Li, J.-Y. Inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms increase the risk of atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf-Eldein, M.; Elghannam, D.; Abdel-Malak, C. MIF-173G/C (rs755622) polymorphism as a risk factor for acute lymphoblastic leukemia development in children. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, e3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Qin, J.; Lv, X.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. MIF promoter polymorphism increases peripheral blood expression levels, contributing to increased susceptibility and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizawa, N.; Yamaguchi, E.; Takahashi, D.; Nishihira, J.; Nishimura, M. Functional polymorphisms in the promoter region of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and atopy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Renner, P.; Roger, T.; Calandra, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: Gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to inflammatory diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41 (Suppl. S7), S513–S519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-B.; Leng, L.; Beitin, A.; Chen, R.; McDonald, C.; Hsiao, B.; Jenison, R.D.; Kang, I.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, A.; et al. Simultaneous detection of microsatellite repeats and SNPs in the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene by thin-film biosensor chips and application to rural field studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipyan, A.; Chen, D.; Dekker, F.J. Epigenetic regulation in macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-mediated signaling in cancer and inflammation. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, N.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, M.; Takano, H.; Hayashi, T.; Ota, M.; Nomura-Horita, T.; Hayashi, R.; Shimasaki, T.; Ostuka, T.; et al. Influence of MIF polymorphisms on CpG island hyper-methylation of CDKN2A in the patients with ulcerative colitis. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yao, L.; Yang, T.; Guo, L.; Gu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, K. MiR-451 suppresses the growth, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xu, Z.; Hao, D. MicroRNA-451 inhibits neuroblastoma proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandres, E.; Bitarte, N.; Arias, F.; Agorreta, J.; Fortes, P.; Agirre, X.; Zarate, R.; Diaz-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ramirez, N.; Sola, J.J.; et al. microRNA-451 Regulates Macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, E.; Zhu, J.; Feng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, W.; Fan, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-144/451a cluster contributes to HCC progression via paracrine HGF/MIF-mediated TAM remodeling. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, C.; Shao, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L. microRNA-1228⁎ impairs the pro-angiogenic activity of gastric cancer cells by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Life Sci. 2017, 180, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-X.; Wang, X.-M.; Han, X.-D.; Cao, B.-F. MiR-608 exerts tumor suppressive function in lung adenocarcinoma by directly targeting MIF. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4908–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Ma, J. miR-608 inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoori, A.; Gopalan, V.; Lu, C.-T.; Chua, T.C.; Morris, D.L.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Expression pattern of miR-451 and its target MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor) in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 70, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-B.; Wei, M.-X.; Han, J.-Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Lu, P.-H. MicroRNA-451 regulates AMPK/mTORC1 signaling and fascin1 expression in HT-29 colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; He, P.; Wang, J.; Schetter, A.; Tang, W.; Funamizu, N.; Yanaga, K.; Uwagawa, T.; Satoskar, A.R.; Gaedcke, J.; et al. A Novel MIF Signaling Pathway Drives the Malignant Character of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting NR3C2. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3838–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelmess, R.M.; Stijlemans, B.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Hallmarks of Cancer Affected by the MIF Cytokine Family. Cancers 2023, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guda, M.R.; Rashid, M.A.; Asuthkar, S.; Jalasutram, A.; Caniglia, J.L.; Tsung, A.J.; Velpula, K.K. Pleiotropic role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2760–2773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snyderman, R.; Pike, M.C. Macrophage migratory dysfunction in cancer. A mechanism for subversion of surveillance. Am. J. Pathol. 1977, 88, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, A.; Le Roy, D.; Théroude, C.; Bernhagen, J.; Roger, T.; Calandra, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes the migration of dendritic cells through CD74 and the activation of the Src/PI3K/myosin II pathway. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lou, C.; Ma, J.; Gong, Q.; Tian, Z.; You, Y.; Ren, G.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; He, K.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Changes of Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Chemotherapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 914120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Park, J.; Song, Y.; Kim, S.; Moon, J. HIF1α-mediated AIMP3 suppression delays stem cell aging via the induction of autophagy. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Tilstam, P.V.; Hwang, S.S.; Simons, D.; Schulte, W.; Leng, L.; Sauler, M.; Ganse, B.; Averdunk, L.; Kopp, R.; et al. D-dopachrome tautomerase in adipose tissue inflammation and wound repair. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilsborrow, J.B.; Doherty, E.; Tilstam, P.V.; Bucala, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Feng, Z.; Tao, S.; Gao, J.; Lin, Y.; Wei, X.; Zheng, B.; Huang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Destabilization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor by 4-IPP reduces NF-κB/P-TEFb complex-mediated c-Myb transcription to suppress osteosarcoma tumourigenesis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-alpha, IL-6 in the regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal. Interact. 2018, 18, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hussain, F.; Freissmuth, M.; Völkel, D.; Thiele, M.; Douillard, P.; Antoine, G.; Thurner, P.; Ehrlich, H.; Schwarz, H.-P.; Scheiflinger, F.; et al. Human Anti-Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Antibodies Inhibit Growth of Human Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Park, S.; Kim, C.I.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S.S.; Park, J.B.; Kwon, J.T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor 4-IPP downregulates stemness phenotype and mesenchymal trans-differentiation after irradiation in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Guo, J.; Yao, J.; Jiang, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Sun, W.; Jiang, X. D-dopachrome tautomerase is over-expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and acts cooperatively with macrophage migration inhibitory factor to promote cancer growth. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2056–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J. Combined Knockdown of D-dopachrome Tautomerase and Migration Inhibitory Factor Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Human Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotzomi-Ortega, I.; Nieto-Yañez, O.; Juárez-Avelar, I.; Rojas-Sanchez, G.; Montes-Alvarado, J.B.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Aguilar-Alonso, P.; Rodriguez-Sosa, M.; Maycotte, P. Autophagy inhibition in breast cancer cells induces ROS-mediated MIF expression and M1 macrophage polarization. Cell Signal. 2021, 86, 110075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-Q.; Xie, J.; Lei, X.-Y.; Zhang, L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulatesproliferation of gastric cancer cellsvia the PI3K/Akt pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5541–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.H.-X.; Lam, S.K.; Chan, A.O.; Lin, M.C.M.; Kung, H.F.; Ogura, K.; Berg, D.E.; Wong, B.C.Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor stimulated by Helicobacter pylori increases proliferation of gastric epithelial cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1946–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, E.J.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Minch, K.; Suarez, G.; Sierra, J.C.; Yamaoka, Y.; Reyes, V.E. The Helicobacter pylori urease B subunit binds to CD74 on gastric epithelial cells and induces NF-κB activation and Interleukin-8 production. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, S.E.; Rendon, B.E.; Xin, D.; Yaddanapudi, K.; Mitchell, R.A. MIF family members cooperatively inhibit p53 expression and activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.D.; Shoaibi, M.A.; Maestro, R.; Carnero, A.; Hannon, G.J.; Beach, D.H. A proinflammatory cytokine inhibits P53 Tumor suppressor activity. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, V.; Dash, P.; Suklabaidya, S.; Murmu, K.C.; Sasmal, P.K.; Jogdand, G.M.; Parida, D.; Sethi, M.; Das, B.; Mohapatra, D.; et al. MIF confers survival advantage to pancreatic CAFs by suppressing interferon pathway-induced p53-dependent apoptosis. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, R.; Ohta, S.; Yaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Sugihara, E.; Okano, H.; Saya, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Kawase, T.; Yoshida, K.; et al. MIF Maintains the Tumorigenic Capacity of Brain Tumor–Initiating Cells by Directly Inhibiting p53. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.A.; Liao, H.; Chesney, J.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Baugh, J.; David, J.; Bucala, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) sustains macrophage proinflammatory function by inhibiting p53: Regulatory role in the innate immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, O.; Moll, U.M. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Bae, S.H.; Yoo, M.R.; Kim, Y.Y.; Hong, I.K.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates macrophage migration inhibitory factor to protect neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-H.; Jian, W.-H.; Wu, Z.-F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Xia, J.-T. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppressed cyclin D1 expression and hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5570–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Bustos, M.A.; Cho, S.N.; Roszik, J.; Ryu, S.; Lopez, V.M.; Burks, J.K.; Lee, J.E.; Grimm, E.A.; Hoon, D.S.; et al. Interplay between soluble CD74 and macrophage-migration inhibitory factor drives tumor growth and influences patient survival in melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binsky, I.; Haran, M.; Starlets, D.; Gore, Y.; Lantner, F.; Harpaz, N.; Leng, L.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Shvidel, L.; Berrebi, A.; et al. IL-8 secreted in a macrophage migration-inhibitory factor- and CD74-dependent manner regulates B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13408–13413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucala, R.; Donnelly, S.C. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Probable Link between Inflammation and Cancer. Immunity 2007, 26, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Luo, F.; Yang, L.; Wu, W.; Liu, X. Hypoxia stimulates the expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human vascular smooth muscle cells via HIF-1α dependent pathway. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, F.; Peng, J.; Wu, X. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes Warburg effect via activation of the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway in lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, M.; Koong, A.C.; Rendon, B.E.; Zundel, W.; Mitchell, R.A. Amplification of tumor hypoxic responses by macrophage migration inhibitory factor–dependent hypoxia-inducible factor stabilization. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, R.C.; Desa, D.E.; Gillette, A.A.; Bartels, E.; Harari, P.M.; Skala, M.C.; Beebe, D.J.; Kerr, S.C. Microphysiological head and neck cancer model identifies novel role of lymphatically secreted monocyte migration inhibitory factor in cancer cell migration and metabolism. Biomaterials 2023, 298, 122136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, R.A.; Shoshan, E.; Whang, S.; Markel, G.; Jaiswal, A.R.; Liu, A.; Curran, M.A.; Travassos, L.R.; Bar-Eli, M. MIF inhibition as a strategy for overcoming resistance to immune checkpoint blockade therapy in melanoma. OncoImmunology 2020, 9, 1846915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, M.; Tanese, K.; Masugi, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Sakamoto, M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CD74 interaction regulates the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 in melanoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, J.A.; Gantier, M.; Li, L.; Byrne, A.; Buckley, A.; Donnelly, S.C. Dual regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression in hypoxia by CREB and HIF-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, M.; Schrader, J.; Thompson, N.; Kuschela, K.; Gemsa, D.; Waeber, G.; Schlegel, J. Up-regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene and protein expression in glial tumor cells during hypoxic and hypoglycemic stress indicates a critical role for angiogenesis in glioblastoma multiforme. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oda, S.; Oda, T.; Nishi, K.; Takabuchi, S.; Wakamatsu, T.; Tanaka, T.; Adachi, T.; Fukuda, K.; Semenza, G.L.; Hirota, K. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor activates hypoxia-inducible factor in a p53-dependent manner. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- No, Y.R.; Lee, S.-J.; Kumar, A.; Yun, C.C. HIF1α-Induced by Lysophosphatidic Acid Is Stabilized via Interaction with MIF and CSN5. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesney, J.; Metz, C.; Bacher, M.; Peng, T.; Meinhardt, A.; Bucala, R. An essential role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in angiogenesis and the growth of a murine lymphoma. Mol. Med. 1999, 5, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; He, S.; Feng, F.; Guo, L.; Jiang, W.; Lu, S. Macrophage inhibitory factor 1 acts as a potential biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and is a target for antibody-based therapy. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Hegde, P.; Pruitt, J.R.; Sielecki, T.M.; Choudhary, D.; Scarpato, K.; DeGraff, D.J.; Pilbeam, C.C.; Taylor, J.A. Macrophage migratory inhibitory factor promotes bladder cancer progression via increasing proliferation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.-X.; Chen, K.; Yang, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Gan, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Coleman, T.R.; Al-Abed, Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes colorectal cancer. Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, V.; Du, W.; Gupta, Y.; Yeh, I.-J.; Montano, M.; Magi-Galuzzi, C.; Welford, S.M. Dysregulated D-dopachrome tautomerase, a hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent gene, cooperates with macrophage migration inhibitory factor in renal tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3713–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Taylor, J.; A Kuchel, G.; Hegde, P.; Voznesensky, O.S.; Claffey, K.; Tsimikas, J.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Pilbeam, C. Null mutation for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is associated with less aggressive bladder cancer in mice. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chan, H.M.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Nicholls, J.; Chen, C.F.; Lee, P.Y.; Lui, V.; Bacher, M.; Tam, P.K.H. Upregulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to induced N-Myc expression by the activation of ERK signaling pathway and increased expression of interleukin-8 and VEGF in neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Qiao, J.; Li, T.; Yang, S.; Hong, Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal pathways in breast cancer MCF-7 cell. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Qian, M.; Qiu, W.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation induced by hypoxia via CXCR4/AKT/EMT pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80358–80372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.-N.; Moon, H.-H.; Ku, J.-L. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α and macrophage migration-inhibitory factor induce metastatic behavior in CXCR4-expressing colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.T.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J. Chronic macrophage migration inhibitory factor exposure induces mesenchymal epithelial transition and promotes gastric and colon cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanese, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Berkova, Z.; Wang, Y.; Samaniego, F.; Lee, J.E.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Grimm, E.A. Cell Surface CD74–MIF Interactions Drive Melanoma Survival in Response to Interferon-γ. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasama, T.; Ohtsuka, K.; Sato, M.; Takahashi, R.; Wakabayashi, K.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A multifunctional cytokine in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis 2010, 2010, 106202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Momcilovic, M.; Popadic, D.; Harhaji, L.; Miljkovic, D.; Metz, C.; Mangano, K.; Papaccio, G.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is necessary for progression of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 215, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, H.-R.; Leng, L.; Kang, I.; Jorgensen, W.L.; Cho, C.-S.; Bucala, R.; Kim, W.-U. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the regulatory t cell response of tumor-bearing Mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3905–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Baker, D.; Dijke, P.T. TGF-β-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, J.; Hagemann, T. Cancer-Related Inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Tang, Y.; Hua, S. Immunological Approaches Towards Cancer and Inflammation: A Cross Talk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, L.; Tang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Yu, H.; Liu, H. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor of Thelazia callipaeda induces M2-like macrophage polarization through TLR4-mediated activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-C.; Wu, T.-N.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Wabitsch, M.; Tian, Y.-F.; Hsieh, P.-S. Targeted inhibition of CD74 attenuates adipose COX-2-MIF-mediated M1 macrophage polarization and retards obesity-related adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-P.; Chien, C.-S.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Chan, M.-S.; Lee, A.C.-L.; Chen, Y.-W.; Huang, P.-I.; Ma, H.-I.; Lo, W.-L.; Chien, Y.; et al. Musashi-1 Regulates MIF1-Mediated M2 Macrophage Polarization in Promoting Glioblastoma Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoochani, A.; A Schwarz, M.; Yakubov, E.; Engelhorn, T.; Doerfler, A.; Buchfelder, M.; Bucala, R.; E Savaskan, N.; Eyüpoglu, I.Y. MIF-CD74 signaling impedes microglial M1 polarization and facilitates brain tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6246–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alban, T.J.; Bayik, D.; Otvos, B.; Rabljenovic, A.; Leng, L.; Jia-Shiun, L.; Roversi, G.; Lauko, A.; Momin, A.A.; Mohammadi, A.M.; et al. Glioblastoma Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Subsets Express Differential Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Receptor Profiles That Can Be Targeted to Reduce Immune Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Huang, T.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, S.; Wei, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Z. Human embryonic stem cells secrete macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A novel finding. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; He, H.; Fan, B.; Deng, R.; Hong, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor rejuvenates aged human mesenchymal stem cells and improves myocardial repair. Aging 2019, 11, 12641–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavayogarajah, T.; Sinitski, D.; El Bounkari, O.; Torres-Garcia, L.; Lewinsky, H.; Harjung, A.; Chen, H.-R.; Panse, J.; Vankann, L.; Shachar, I.; et al. CXCR4 and CD74 together enhance cell survival in response to macrophage migration-inhibitory factor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2022, 115, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Yao, J. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the pathogenesis of leukemia (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, D.; Aderka, D.; Livni, E.; Joshua, H.; Shaklai, M.; Pinkhas, J. Migration inhibition factor activity in sera of patients with chronic lymphatic leukemia. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1979, 63, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Mohamed, E.H.; Esa, E.; Kamaluddin, N.R.; Zain, S.M.; Yusoff, Y.M.; Assenov, Y.; Mohamed, Z.; Zakaria, Z. Circulating cytokines and small molecules follow distinct expression patterns in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf-Eldein, M.; Elghannam, D.; Elderiny, W.; Abdel-Malak, C. Prognostic Implication of MIF Gene Expression in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, H.; Rong, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Tong, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y. The MIF −173G/C polymorphism and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a Chinese population. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinart, N.; Nguyen, P.-H.; Boucas, J.; Rosen, N.; Kvasnicka, H.-M.; Heukamp, L.; Rudolph, C.; Ristovska, V.; Velmans, T.; Mueller, C.; et al. Delayed development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the absence of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Blood 2013, 121, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, K.; Friedlander, G.; Pellegrino, B.; Radomir, L.; Lewinsky, H.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Becker-Herman, S.; Shachar, I. CD74 as a regulator of transcription in normal B cells. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Yarom, N.; Radomir, L.; Sever, L.; Kramer, M.P.; Lewinsky, H.; Bornstein, C.; Blecher-Gonen, R.; Barnett-Itzhaki, Z.; Mirkin, V.; Friedlander, G.; et al. CD74 is a novel transcription regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binsky, I.; Lantner, F.; Grabovsky, V.; Harpaz, N.; Shvidel, L.; Berrebi, A.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Alon, R.; et al. TAp63 regulates VLA-4 expression and chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell migration to the bone marrow in a CD74-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4761–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Tadros, V.; Hiramoto, B.; Leeper, K.; Hino, C.; Xiao, J.; Pham, B.; Kim, D.H.; Reeves, M.E.; Chen, C.-S.; et al. Targeting TKI-Activated NFKB2-MIF/CXCLs-CXCR2 Signaling Pathways in FLT3 Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia Reduced Blast Viability. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, I.; Lee, M.R.; Nam, K.W.; Oh, J.H.; Moon, K.C.; Kim, H.-S. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor relates to survival in high-grade osteosarcoma. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Gao, J.; Jin, K.; Chen, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhu, K.; Huang, W.; Liu, F.; Mei, L.; Lou, C.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor 4-IPP suppresses osteoclast formation and promotes osteoblast differentiation through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7667–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Zierow, S.; Syed, M.; Bucala, R.; Bhandari, V.; Lolis, E.J. Targeting distinct tautomerase sites of D-DT and MIF with a single molecule for inhibition of neutrophil lung recruitment. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4961–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Petrenko, O.; Metz, C.N.; Forsthuber, T.G.; Mitchell, R.; Huss, R.; Moll, U.; Müller, W.; Bucala, R. The p53-dependent effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by gene targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9354–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Yoshihisa, Y.; Yamakoshi, T.; Rehman, M.U.; Norisugi, O.; Hara, H.; Matsunaga, K.; Makino, T.; Nishihira, J.; Shimizu, T. UV-B Radiation induces macrophage migration inhibitory factor–mediated melanogenesis through activation of protease-activated receptor-2 and stem cell factor in keratinocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huth, S.; Huth, L.; Heise, R.; Marquardt, Y.; Lopopolo, L.; Piecychna, M.; Boor, P.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Kapurniotu, A.; Yazdi, A.S.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and its homolog D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT) are significant promotors of UVB- but not chemically induced non-melanoma skin cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Croce, M.; Reggiani, F.; Schinzari, G.; Ambrosio, M.; Gangemi, R.; Tortora, G.; Pfeffer, U.; Amaro, A. Uveal Melanoma Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repp, A.C.; Mayhew, E.S.; Apte, S.; Niederkorn, J.Y. Human uveal melanoma cells produce macrophage migration-inhibitory factor to prevent lysis by NK cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, M.; Rullan, A.J.; Piulats, J.M. Uveal melanoma as a target for immune-therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, C.; Roszik, J.; Grimm, E. Combined inhibition of SDHA and MIF in Uveal Melanoma cells effectively reduces cell survival. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 4959. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T.; Abe, R.; Nakamura, H.; Ohkawara, A.; Suzuki, M.; Nishihira, J. High expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human melanoma cells and its role in tumor cell growth and angiogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobold, S.; Merk, M.; Hofer, L.; Peters, P.; Bucala, R.; Endres, S. The macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-homologue D-dopachrome tautomerase is a therapeutic target in a murine melanoma model. Oncotarget 2013, 5, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midena, E.M.; Parrozzani, R.M.; Midena, G.; Trainiti, S.; Marchione, G.; Cosmo, E.; Londei, D.; Frizziero, L.M. In vivo intraocular biomarkers: Changes of aqueous humor cytokines and chemokines in patients affected by uveal melanoma. Medicine 2020, 99, e22091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Baird, A.W.; O’farrelly, C. Microanatomy of the liver immune system. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, G.; Rai, A.J.; Carvajal, R.D.; Schwartz, G.K. Uveal Melanoma Exosomes Induce a Prometastatic Microenvironment through Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Xin, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Rao, W.; Du, Z.; Bai, J.; Guo, Z.; Ruan, X.; et al. Mapping the single-cell landscape of acral melanoma and analysis of the molecular regulatory network of the tumor microenvironments. eLife 2022, 11, e78616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes the invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma through matrix metalloprotein-2/9. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Cen, X.; Liang, X.-H.; Tang, Y.-L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A potential driver and biomarker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 10650–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cludts, S.; Decaestecker, C.; Johnson, B.; Lechien, J.; Leroy, X.; Kindt, N.; Kaltner, H.; André, S.; Gabius, H.-J.; Saussez, S. Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during progression to hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2010, 30, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, R.; Franceschi, D.; Pan, H.; Wei, C.; Ogbuehi, A.C.; Lethaus, B.; Savkovic, V.; Gaus, S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Different Immune Signatures in HPV- and HPV + Driven Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 2079389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindt, N.; Lechien, J.; Decaestecker, C.; Rodriguez, A.; Chantrain, G.; Remmelink, M.; Laurent, G.; Gabius, H.-J.; Saussez, S. Expression of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor is correlated with progression in oral cavity carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4499–4505. [Google Scholar]
- Kindt, N.; Preillon, J.; Kaltner, H.; Gabius, H.-J.; Chevalier, D.; Rodriguez, A.; Johnson, B.D.; Megalizzi, V.; Decaestecker, C.; Laurent, G.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical and experimental studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.-J.; Wu, T.-T.; Li, B.; Tian, X.-Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.-X. Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and DJ-1 contribute to cell invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; Burtness, B. Treating Head and Neck Cancer in the Age of Immunotherapy: A 2023 Update. Drugs 2023, 83, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindt, N.; Descamps, G.; Lechien, J.R.; Remmelink, M.; Colet, J.-M.; Wattiez, R.; Berchem, G.; Journe, F.; Saussez, S. Involvement of HPV Infection in the Release of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R. Serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 as a clinical marker for non–small cell lung cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, M.; Zhao, L.; Carskadon, S.; Arenberg, D. Expression of CD74, the receptor for macrophage migration inhibitory factor, in non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, A.M.; Rendon, B.E.; Zhao, M.; Qian, M.-W.; Bucala, R.; Xin, D.; Mitchell, R.A. Cooperative regulation of non-small cell lung carcinoma angiogenic potential by macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its homolog, d-dopachrome tautomerase. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Tu, S. Inhibition of CXCR4 regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition of NSCLC via the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Kuo, K.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Wang, Y. Cisplatin resistant lung cancer cells promoted M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via the Src/CD155/MIF functional pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, H.; Son, B.; Kim, W.; Jun, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kang, C.; Kim, J.; Youn, B. Dissociation of MIF-rpS3 complex and sequential NF-κB activation is involved in IR-induced metastatic conversion of NSCLC. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 2504–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.M.; Kim, D.C.; Kim, Y.; Song, D.H. Prognostic role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterstrom, C.; Soltermann, A.; Opitz, I.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Weder, W.; A Stahel, R.; Triponez, F.; Robert, J.H.; Serre-Beinier, V. CD74: A new prognostic factor for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhi, F.; Feng, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor may contribute to the occurrence of multiple primary lung adenocarcinomas. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawhinney, L.; Armstrong, M.E.; O’reilly, C.; Bucala, R.; Leng, L.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Fayne, D.; Keane, M.P.; Tynan, A.; Maher, L.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) enzymatic activity and lung cancer. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.R.; Wang, H.; Hudlikar, R.; Lu, X.; Zhang, M.R.; Hoang, C.D.; Yan, F.; Schrump, D.S. A Unique Gene Signature Predicting Recurrence-Free Survival In Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 165, 1554–1564.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Bi, G.; Shan, G.; Liang, J.; Yao, G.; Sui, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q. Identification of the relationship between single-cell N6-methyladenosine regulators and the infiltrating immune cells in esophageal carcinoma. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-M.; Sun, D.-N.; Jiao, Y.-L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.; Sun, M.; Gu, B.-L.; Chen, P.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes tumor aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via activation of Akt and inactivation of GSK3β. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Law, S.; Huang, X.; Lee, P.Y.; Bacher, M.; Srivastava, G.; Wong, J. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor stimulates angiogenic factor expression and correlates with differentiation and lymph node status in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.H.; Zhang, S.T.; Lam, S.K.; Lin, M.C.; Kung, H.F.; Wong, B.C. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and effects of bile acids and NSAIDs. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, S.-B.; Ma, G.; Tang, X.-F.; Chen, S.-P.; He, J.; Liu, W.-L.; Xie, D.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Li, J. The expressions of MIF and CXCR4 protein in tumor microenvironment are adverse prognostic factors in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Ye, W.; Uemura, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q.; et al. The level of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is negatively correlated with the efficacy of PD-1 blockade immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy as a neoadjuvant therapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 37, 101775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shun, C.-T.; Lin, J.-T.; Huang, S.-P.; Lin, M.-T.; Wu, M.-S. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is associated with enhanced angiogenesis and advanced stage in gastric carcinomas. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3767–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-P.; Yu, X.-H.; Zhang, S.-X. Expression and significance of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in gastric adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010, 90, 2625–2628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-X. CD74 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor as therapeutic targets in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisawa, T.; Tahara, T.; Shibata, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Nakamura, M.; Kamiya, Y.; Fujita, H.; Yoshioka, D.; Arima, Y.; Okubo, M.; et al. Functional promoter polymorphisms of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene in gastric carcinogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beswick, E.J.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Suarez, G.; Sierra, J.C.; Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pylori CagA-dependent macrophage migration inhibitory factor produced by gastric epithelial cells binds to CD74 and stimulates procarcinogenic events. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6794–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, D.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, W.; Sun, L.; et al. MAPK4 silencing in gastric cancer drives liver metastasis by positive feedback between cancer cells and macrophages. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Deng, X.; Kong, X.; Du, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D.; Guha, S.; Li, Z.; et al. ZFPM2-AS1, a novel lncRNA, attenuates the p53 pathway and promotes gastric carcinogenesis by stabilizing MIF. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5982–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, T.H.; Saal, A.; Bergmann, I.; Fischer, P.; Heinrichs, D.; Brandt, E.F.; Koenen, M.T.; Djudjaj, S.; Schneider, K.M.; Boor, P.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor exerts pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects via CD74 in murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4452–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-Q.; Tang, Z.; Huang, R.; Qu, W.-F.; Fang, Y.; Yang, R.; Tao, C.-Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.-L.; Sun, H.-X.; et al. CD36+ cancer-associated fibroblasts provide immunosuppressive microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma via secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denz, A.; Pilarsky, C.; Muth, D.; Rückert, F.; Saeger, H.-D.; Grützmann, R. Inhibition of MIF leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 160, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Q.; Zhi, F.-C.; Chen, X.-Q.; Wang, Y.-D. Expression of macrophage migration inhibition factor in pancreatic carcinoma tissue. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2004, 24, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, R.; Huang, A.; Fang, Z.; Wang, K.; He, M.; Xia, J.; Li, W. Upregulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes tumor metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2628–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funamizu, N.; Hu, C.; Lacy, C.; Schetter, A.; Zhang, G.; He, P.; Gaedcke, J.; Ghadimi, M.B.; Ried, T.; Yfantis, H.G.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition, enhances tumor aggressiveness and predicts clinical outcome in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Xi, J.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Long, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, G.-H.; et al. The Tautomerase Activity of Tumor exosomal MIF promotes pancreatic cancer progression by modulating mdsc differentiation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 12, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Yang, Y.M.; Pandol, S.J.; Seki, E. Exosome Migration Inhibitory Factor as a Marker and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Weeks, A.; Lim, S.; Yuzhalin, A.; Jones, K.; Muschel, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A key cytokine and therapeutic target in colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasasever, V.; Camlica, H.; Duranyildiz, D.; Oguz, H.; Tas, F.; Dalay, N. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer. Cancer Investig. 2007, 25, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramireddy, L.; Chen, W.T.; Peng, C.; Hu, R.; Ke, T.; Chiang, H.; Chang, S.; Tsai, F.; Lo, W. Association Between Genetic Polymorphism of the MIF Gene and Colorectal Cancer in Taiwan. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2015, 29, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-X.; Wu, L.-H.; Xia, H.H.-X.; Ma, W.-Q.; Zhong, H.-J.; Xu, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, R.-J.; Wang, L.-J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor siRNA inhibits hepatic metastases of colorectal cancer cells. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, S.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.; Jang, J.; Lim, Y.; Song, S.; Han, S.; Kim, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes resistance to MEK blockade in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, H.; Lu, Q.; Yu, S. PCSK9 promotes the progression and metastasis of colon cancer cells through regulation of EMT and PI3K/AKT signaling in tumor cells and phenotypic polarization of macrophages. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.; Rendon, B.E.; Zhao, M.; Winner, M.; Coleman, A.M.; Mitchell, R.A. The MIF homologue D-dopachrome tautomerase promotes COX-2 expression through β-catenin–dependent and –independent mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, L.; Jing, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yao, X.; Sun, X. Autophagic flux is essential for the downregulation of D-dopachrome tautomerase by atractylenolide I to ameliorate intestinal adenoma formation. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Basile, M.S.; Lombardo, S.D.; Mangano, K.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Overexpression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and Its Homologue D-Dopachrome Tautomerase as Negative Prognostic Factor in Neuroblastoma. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Ciurleo, R.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Bella, R.; Mangano, K.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Basile, M.S. Emerging Role of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Family of Cytokines in Neuroblastoma. Pathogenic Effectors and Novel Therapeutic Targets? Molecules 2020, 25, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gerique, L.; García, M.; Garrido-Garcia, A.; Gómez-González, S.; Torrebadell, M.; Prada, E.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; Muñoz, O.; Perez-Jaume, S.; Lemos, I.; et al. MIF/CXCR4 signaling axis contributes to survival, invasion, and drug resistance of metastatic neuroblastoma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, N.; Deuster, O.; Noelker, C.; Stüer, C.; Strik, H.; Schaller, C.; Dodel, R.; Meyer, B.; Bacher, M. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in primary glioblastoma multiforme cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, K.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Mammana, S.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F. Pathogenic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in glioblastoma and its targeting with specific inhibitors as novel tailored therapeutic approach. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17951–17970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presti, M.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, A.; Colletti, G.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in glioblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-B.; Tian, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Z. Elevated expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor correlates with tumor recurrence and poor prognosis of patients with gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 106, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.B.; Lee, S.; Harmanci, A.S.; Patel, R.; Latha, K.; Yang, Y.; Marisetty, A.; Lee, H.; Heimberger, A.B.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. CXCR4 expression is associated with proneural-to-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, B.; Silver, D.J.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Alvarado, A.G.; Turaga, S.M.; Sorensen, M.D.; Rayman, P.; Flavahan, W.A.; Hale, J.S.; Stoltz, K.; et al. Cancer Stem Cell-Secreted Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Stimulates Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cell Function and Facilitates Glioblastoma Immune Evasion. STEM CELLS 2016, 34, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Castro, B.; Flanigan, P.; Jahangiri, A.; Hoffman, D.; Chen, W.; Kuang, R.; De Lay, M.; Yagnik, G.; Wagner, J.R.; Mascharak, S.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor downregulation: A novel mechanism of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Rajendran, G.; Abbott, E.; Martin, A.; Amalraj, S.; Dennis, K.; Li, X.; Warrick, J.; A Taylor, J. Role of MIF1/MIF2/CD74 interactions in bladder cancer. J. Pathol. 2023, 259, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-S.; Dai, Y.-P.; Li, W.; Liu, L.-D. Expression and significance of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in bladder urothelial cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2011, 33, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y. CD74 expression is increased in high-grade, invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, J.; Wahafu, W.; Song, L.; Ping, H.; Wang, M.; Yang, F.; Niu, Y.; Qing, W.; Xing, N. Expression of CD74 in bladder cancer and its suppression in association with cancer proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis in HT-1376 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7631–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penticuff, J.C.; Woolbright, B.L.; Sielecki, T.M.; Weir, S.J.; Taylor, J.A. MIF family proteins in genitourinary cancer: Tumorigenic roles and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Siegler, K.L.; Leifheit, E.C.; Vera, P.L. Inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor decreases proliferation and cytokine expression in bladder cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Siegler, K.L.; Vera, P.L.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Bifulco, C.; Lee, A.; Gregersen, P.K.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene polymorphisms are associated with increased prostate cancer incidence. Genes Immun. 2007, 8, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Siegler, K.L.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Vera, P.L. Inhibition of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor or Its Receptor (CD74) Attenuates Growth and Invasion of DU-145 Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8730–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiei, S.; Gui, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.S.; Kibel, A.S.; Jia, L. Targeting the MIF/CXCR7/AKT Signaling Pathway in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Siegler, K.; Hudson, P.B. Enhanced expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma metastases. Urology 1996, 48, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, V.; Kindt, N.; Decaestecker, C.; Gabius, H.-J.; Laurent, G.; Noël, J.-C.; Saussez, S. Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptor (CD74) in human breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Ye, C.; Yao, C.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces angiogenesis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008, 261, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Chen, N.; Lin, Y.; Ma, H.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Tian, X. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes breast cancer metastasis via activation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF kappa B axis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans, E.; Noetzel, E.; Bektas, N.; Schütz, A.K.; Lue, H.; Lennartz, B.; Hartmann, A.; Dahl, E.; Bernhagen, J. Dual role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charan, M.; Das, S.; Mishra, S.; Chatterjee, N.; Varikuti, S.; Kaul, K.; Misri, S.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Satoskar, A.R.; Ganju, R.K. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibition as a novel therapeutic approach against triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Dong, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, S.; Nie, R.; Zhang, X.; An, R. Expression of MIF and c-erbB-2 in endometrial cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3828–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannice, R.; Erreni, M.; Allavena, P.; Buscaglia, M.; Tozzi, R. Chemokines mRNA expression in relation to the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) mRNA and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) mRNA expression in the microenvironment of endometrial cancer tissue and normal endometrium: A pilot study. Cytokine 2013, 64, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Jin, O.; Han, S.; Nie, R.; Zhu, L.; Gao, X.; Li, L. Correlations of leukemia inhibitory factor and macrophage migration inhibitory factor with endometrial carcinoma. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2015, 36, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Bondza, P.K.; Metz, C.N.; Akoum, A. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor up-regulates alpha(v)beta(3) integrin and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line Ishikawa. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2008, 77, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Tian, W.-Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Guo, F.; Zhao, J.; Gao, C.; Xue, F.-X. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the progression of endometrial cancer via the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.-J.; Deng, W.-G.; Niu, C.-B.; Li, Y.-Y.; Fu, Y. Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and cd74 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2011, 21, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krockenberger, M.; Engel, J.B.; Kolb, J.; Dombrowsky, Y.; Häusler, S.F.M.; Kohrenhagen, N.; Dietl, J.; Wischhusen, J.; Honig, A. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in cervical cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lian, J.; Tao, H.; Shang, H.; Zhang, L. Correlation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene polymorphism with the risk of early-stage cervical cancer and lymphatic metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinagl, A.; Thiele, M.; Douillard, P.; Völkel, D.; Kenner, L.; Kazemi, Z.; Freissmuth, M.; Scheiflinger, F.; Kerschbaumer, R.J. Oxidized macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential new tissue marker and drug target in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73486–73496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.; Donnelly, S.C.; A Mitchell, R. OxMIF: A druggable isoform of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer and inflammatory diseases. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, D.; Patel, M.R.; Sachdev, J.C.; Hart, L.L.; Halama, N.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Völkel, D.; Youssef, A.; de Jong, F.A.; et al. Phase I study of imalumab (BAX69), a fully human recombinant antioxidized macrophage migration inhibitory factor antibody in advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolan, P.; Gibbons, J.A.; He, L.; Chang, E.; Jones, D.; Gross, M.I.; Davidson, J.B.; Sanftner, L.M.; Johnson, K.W. Ibudilast in healthy volunteers: Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics with single and multiple doses. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 66, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Conwit, R.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Gleason, T.; Goodman, A.; Klawiter, E.C.; Matsuda, K.; McGovern, M.; Naismith, R.T.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Ibudilast in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, W.; Sevim-Nalkiran, H.; Zaman, A.M.; Matsuda, K.; Khasraw, M.; Nowak, A.K.; Chung, L.; Baxter, R.C.; McDonald, K.L. Ibudilast sensitizes glioblastoma to temozolomide by targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, S.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Sharkey, R.M.; Tat, F.; Gold, D.V.; Goldenberg, D.M. Milatuzumab–SN-38 Conjugates for the Treatment of CD74+ Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, M.; Mirkin, V.; Braester, A.; Harpaz, N.; Shevetz, O.; Shtreiter, M.; Greenberg, S.; Mordich, O.; Amram, O.; Binsky-Ehrenreich, I.; et al. A phase I-II clinical trial of the anti-CD74 monoclonal antibody milatuzumab in frail patients with refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A patient based approach. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiechen, Z.C.; Stromnes, I.M. Mechanisms Governing Immunotherapy Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 613815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Cai, W.; Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Putha, L.; Xia, Q.; Windsor, J.A.; Phillips, A.R.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Du, D.; et al. Targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Acute Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdez, C.N.; Sánchez-Zuno, G.A.; Bucala, R.; Tran, T.T. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT): Pathways to Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094849
Valdez CN, Sánchez-Zuno GA, Bucala R, Tran TT. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT): Pathways to Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094849
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdez, Caroline Naomi, Gabriela Athziri Sánchez-Zuno, Richard Bucala, and Thuy T. Tran. 2024. "Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT): Pathways to Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094849
APA StyleValdez, C. N., Sánchez-Zuno, G. A., Bucala, R., & Tran, T. T. (2024). Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT): Pathways to Tumorigenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094849





