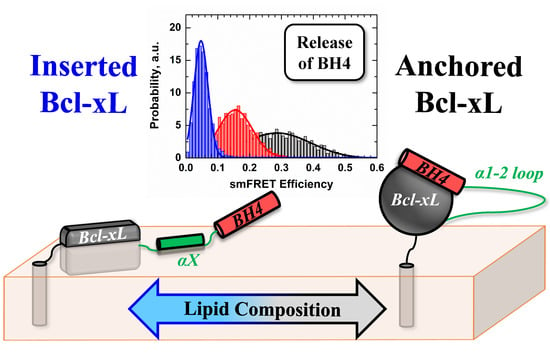
Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
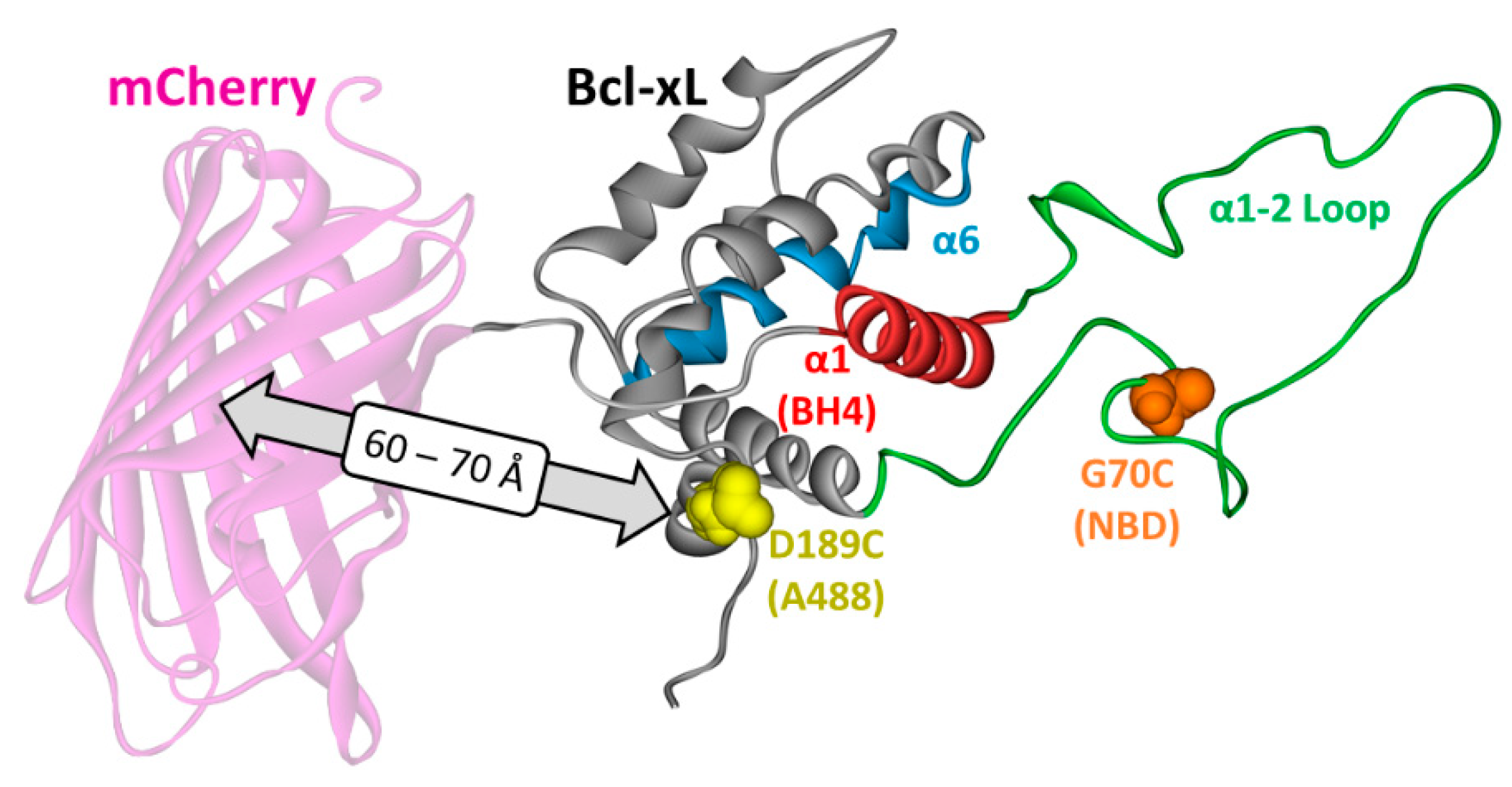
2. Materials and Methods
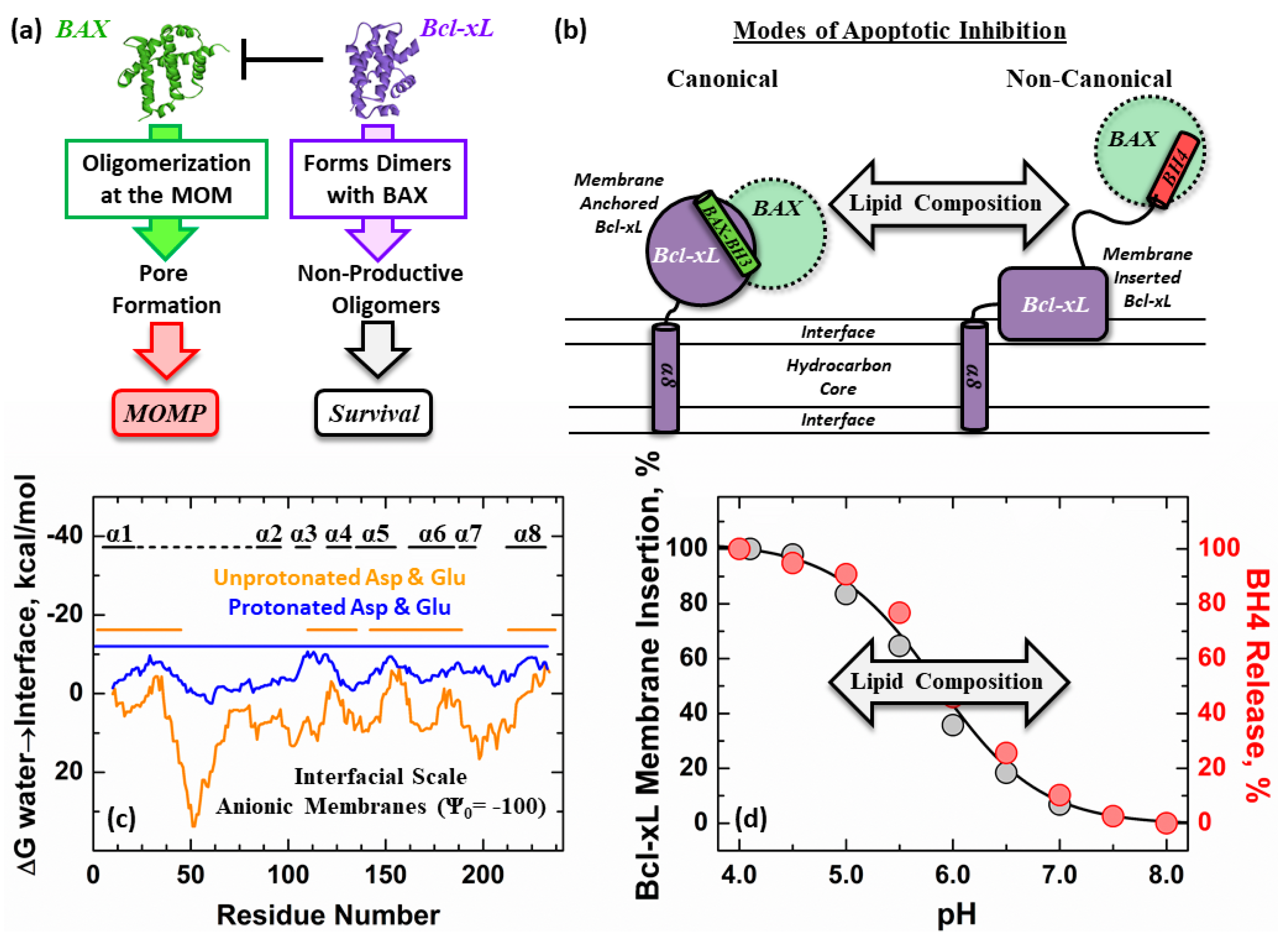
3. Results
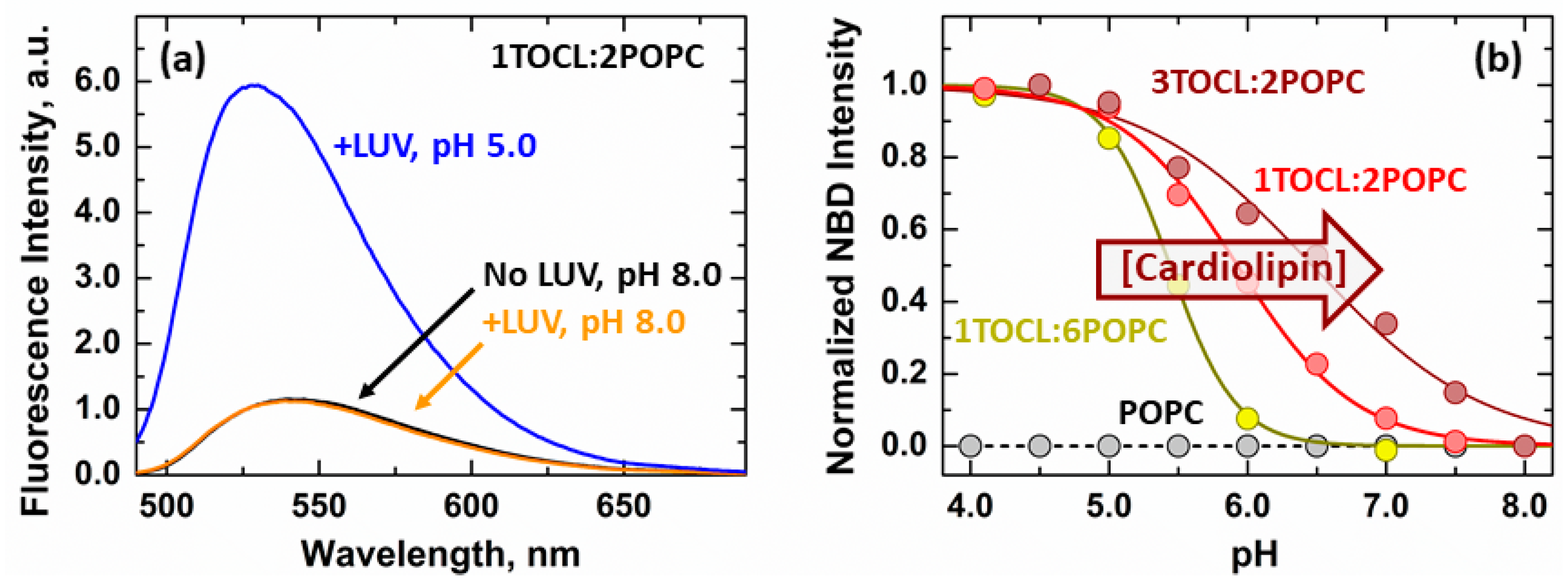
3.1. Membrane Interactions of the Loop between α1 and α2 Helices
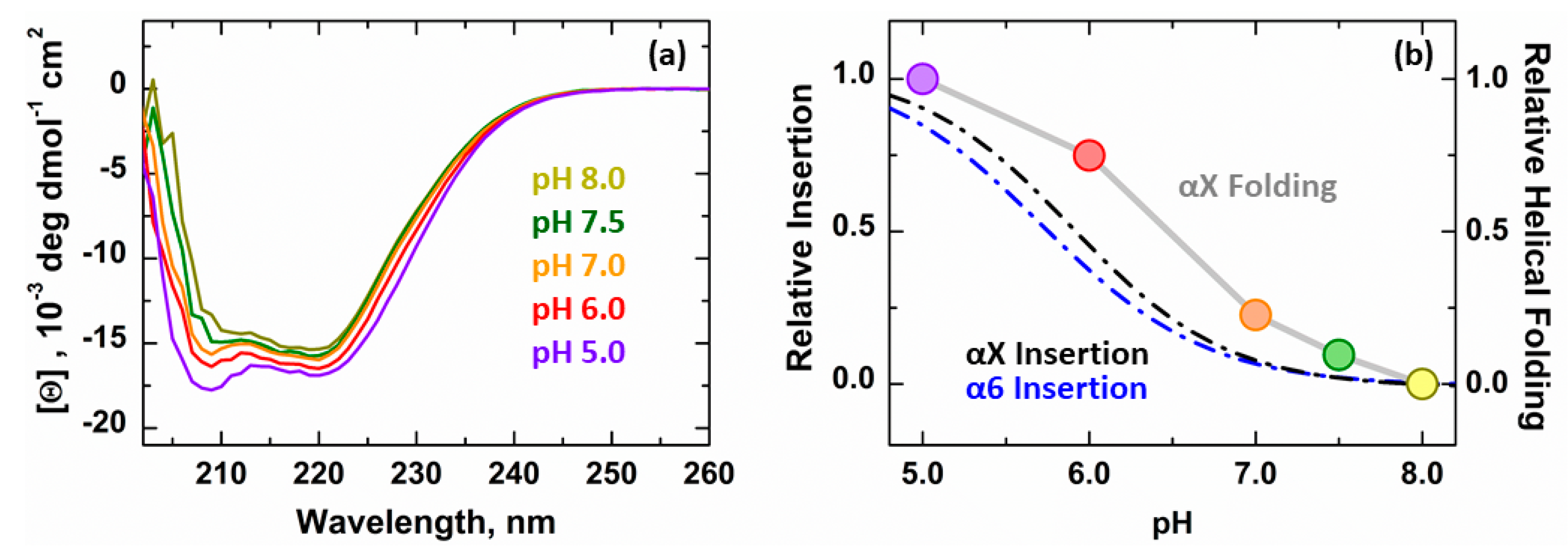
3.2. Secondary Structure Changes of Membrane-inserted Bcl-xL
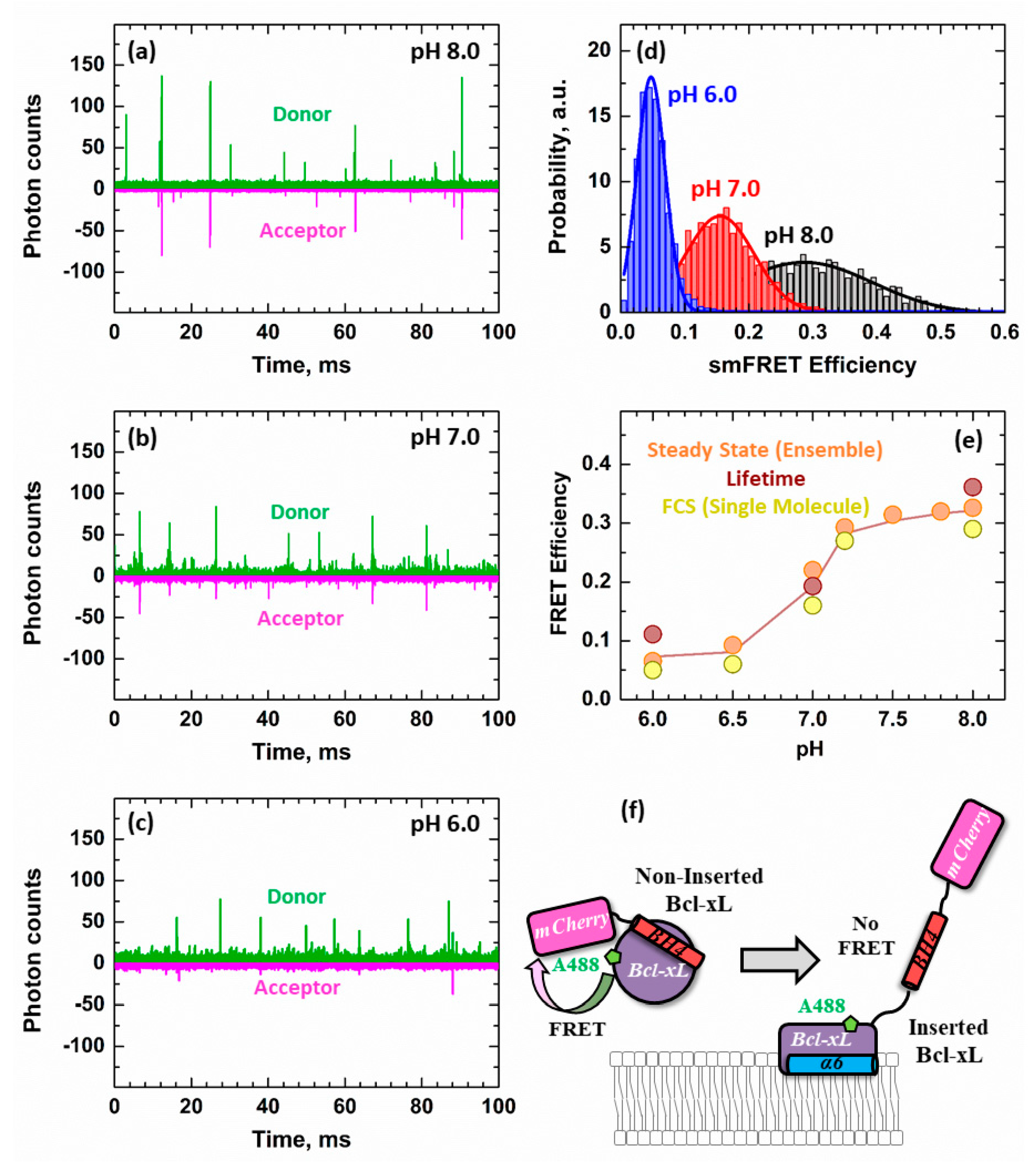
3.3. Ensemble and Single-Molecule FRET Measurements of the BH4 Domain Release in Membrane-Inserted Bcl-xL
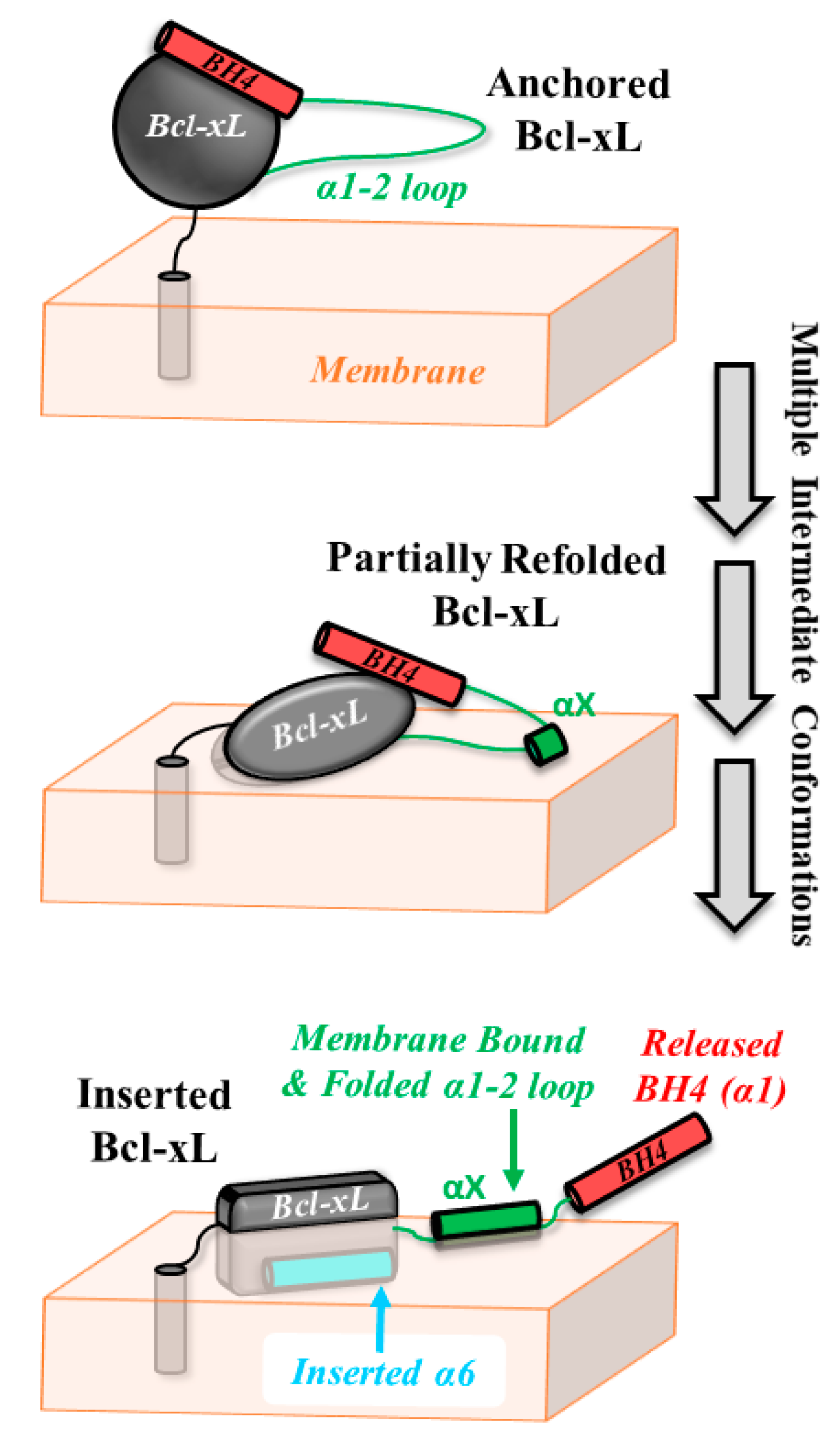
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hardwick, J.M.; Youle, R.J. SnapShot: BCL-2 proteins. Cell 2009, 138, 404–404e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, C.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Apoptosis: Embedded in membranes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, J.; Osterlund, E.J.; Andrews, D.W. BCL-2 family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billen, L.P.; Kokoski, C.L.; Lovell, J.F.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Bcl-XL inhibits membrane permeabilization by competing with Bax. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, T.; Follis, A.V.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Green, D.R. Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, B.; Lin, J.; Andrews, D.W. Embedded together: The life and death consequences of interaction of the Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Mooers, B.H.; Zhang, Z.; Kale, J.; Falcone, D.; McNichol, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Xing, C.; Andrews, D.W. After embedding in membranes antiapoptotic Bcl-XL protein binds both Bcl-2 homology region 3 and helix 1 of proapoptotic Bax protein to inhibit apoptotic mitochondrial permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11873–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subburaj, Y.; Cosentino, K.; Axmann, M.; Pedrueza-Villalmanzo, E.; Hermann, E.; Bleicken, S.; Spatz, J.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Bax monomers form dimer units in the membrane that further self-Assemble into multiple oligomeric species. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; O’Neill, K.L.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Han, N.; Pang, X.; Wu, W.; Struble, L.; Borgstahl, G.; Liu, Z.; et al. BH3-Only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M. BAX and BAK become killers without a BH3 trigger. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 967–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, C.; Jayasinghe, S.; Hristova, K.; White, S.H. MPEx: A tool for exploring membrane proteins. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posokhov, Y.O.; Rodnin, M.V.; Lu, L.; Ladokhin, A.S. Membrane insertion pathway of annexin B12: Thermodynamic and kinetic characterization by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence quenching. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5078–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez-Montes, V.; Vargas-Uribe, M.; Pandey, N.K.; Rodnin, M.V.; Langen, R.; Ladokhin, A.S. Lipid-Modulation of membrane insertion and refolding of the apoptotic inhibitor Bcl-xL. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchmore, S.W.; Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Nettesheim, D.; Chang, B.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Wong, S.L.; et al. X-Ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 1996, 381, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Vargas, M.P.; Chipuk, J.E. The deadly landscape of pro-Apoptotic BCL-2 proteins in the outer mitochondrial membrane. FEBS J. 2015, 283, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Fujimoto, L.M.; Hirshman, N.; Bobkov, A.A.; Antignani, A.; Youle, R.J.; Marassi, F.M. Conformation of BCL-XL upon membrane-Integration. J. Mol. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.L.; Oltersdorf, T.; Horne, W.; McConnell, M.; Wilson, G.; Weeks, S.; Garcia, T.; Fritz, L.C. A common binding site mediates heterodimerization and homodimerization of Bcl-2 family members. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 11350–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Nettesheim, D.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Eberstadt, M.; Yoon, H.S.; Shuker, S.B.; Chang, B.S.; Minn, A.J.; et al. Structure of Bcl-xL-Bak peptide complex: Recognition between regulators of apoptosis. Science 1997, 275, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Westphal, D.; Dewson, G.; Ma, S.; Hockings, C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F.; Yao, S.; Robin, A.Y.; Smith, B.J.; et al. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell 2013, 152, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Uribe, M.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ladokhin, A.S. Comparison of membrane insertion pathways of the apoptotic regulator Bcl-xL and the diphtheria toxin translocation domain. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7901–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, L.A.; Wales, T.E.; Garner, T.P.; Wachter, F.; Lee, S.; Guerra, R.M.; Stewart, M.L.; Braun, C.R.; Bird, G.H.; Gavathiotis, E.; et al. Inhibition of Pro-Apoptotic BAX by a noncanonical interaction mechanism. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, M.J.; Bally, M.B.; Mayer, L.D.; Janoff, A.S.; Cullis, P.R. Generation of multilamellar and unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1986, 40, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.D.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 858, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugland, R.P. Handbook of Fluorescent Probes and Research Chemicals, 6th ed.; Molecular Probes, Inc.: Eugene, OR, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ladokhin, A.S. Fluorescence spectroscopy in thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of pH-dependent membrane protein insertion. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 466, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Posokhov, Y.O.; Ladokhin, A.S. Lifetime fluorescence method for determining membrane topology of proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 348, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–698. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrychenko, A.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ghatak, C.; Ladokhin, A.S. Joint refinement of FRET measurements using spectroscopic and computational tools. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 522, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, T.; Schlesinger, R.; Gabba, M.; Fitter, J. Native and unfolded states of phosphoglycerate kinase studied by single-molecule FRET. Chemphyschem 2011, 12, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yang, J.T.; Chau, K.H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 3350–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardail, D.; Privat, J.-P.; Egret-Charlier, M.; Levrat, C.; Lerme, F.; Louisot, P. Mitochondrial contact sites: Lipid composition and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 18797–18802. [Google Scholar]
- Daum, G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Biomembr. 1985, 822, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-Ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Cossman, J.; Jaffe, E.; Croce, C.M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science 1985, 228, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Youle, R.J. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis *. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, K.; García-Sáez, A.J. Mitochondrial alterations in apoptosis. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 181, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Regulating cell death at, on, and in membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2100–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimi, M.; Esposti, M.D. Apoptosis-Induced changes in mitochondrial lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; McStay, G.P.; Bharti, A.; Kuwana, T.; Clarke, C.J.; Siskind, L.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Green, D.R. Sphingolipid metabolism cooperates with BAK and BAX to promote the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Cell 2012, 148, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollville, E.; Martin, S.J. Greasing the path to BAX/BAK activation. Cell 2012, 148, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renault, T.T.; Chipuk, J.E. Death upon a kiss: Mitochondrial outer membrane composition and organelle communication govern sensitivity to BAK/BAX-dependent apoptosis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raemy, E.; Martinou, J.C. Involvement of cardiolipin in tBID-Induced activation of BAX during apoptosis. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 179, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladokhin, A.S.; White, S.H. Folding of amphipathic a-helices on membranes: Energetics of helix formation by melittin. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasquez-Montes, V.; Kyrychenko, A.; Vargas-Uribe, M.; Rodnin, M.V.; Ladokhin, A.S. Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells 2020, 9, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
Vasquez-Montes V, Kyrychenko A, Vargas-Uribe M, Rodnin MV, Ladokhin AS. Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells. 2020; 9(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasquez-Montes, Victor, Alexander Kyrychenko, Mauricio Vargas-Uribe, Mykola V. Rodnin, and Alexey S. Ladokhin. 2020. "Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions" Cells 9, no. 3: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539
APA StyleVasquez-Montes, V., Kyrychenko, A., Vargas-Uribe, M., Rodnin, M. V., & Ladokhin, A. S. (2020). Conformational Switching in Bcl-xL: Enabling Non-Canonic Inhibition of Apoptosis Involves Multiple Intermediates and Lipid Interactions. Cells, 9(3), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030539