Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study (iBoneFIT Project)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Fitness
2.3. Physical Activity
2.4. Health-Related Quality of Life
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
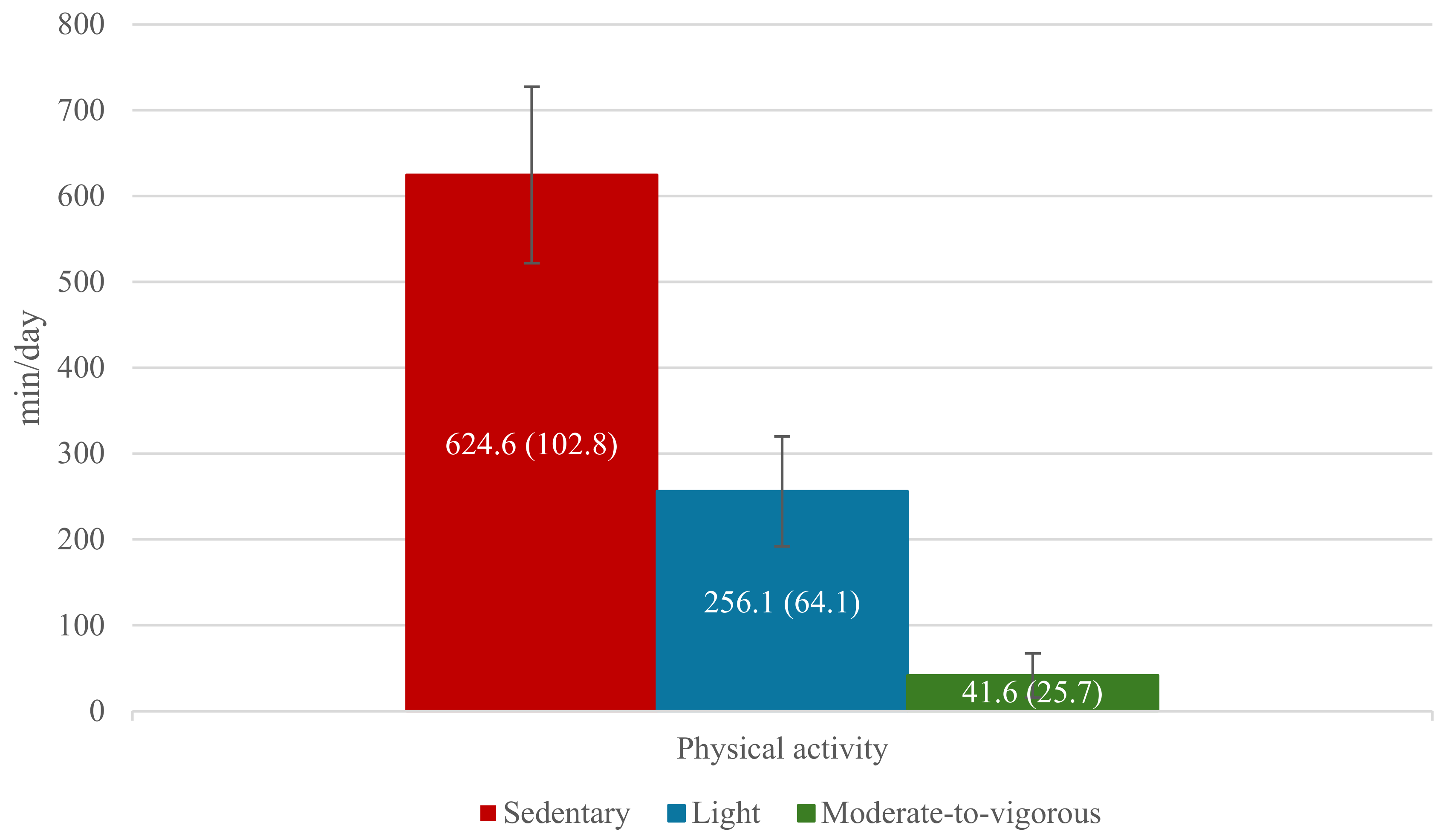
3.2. Physical Activity
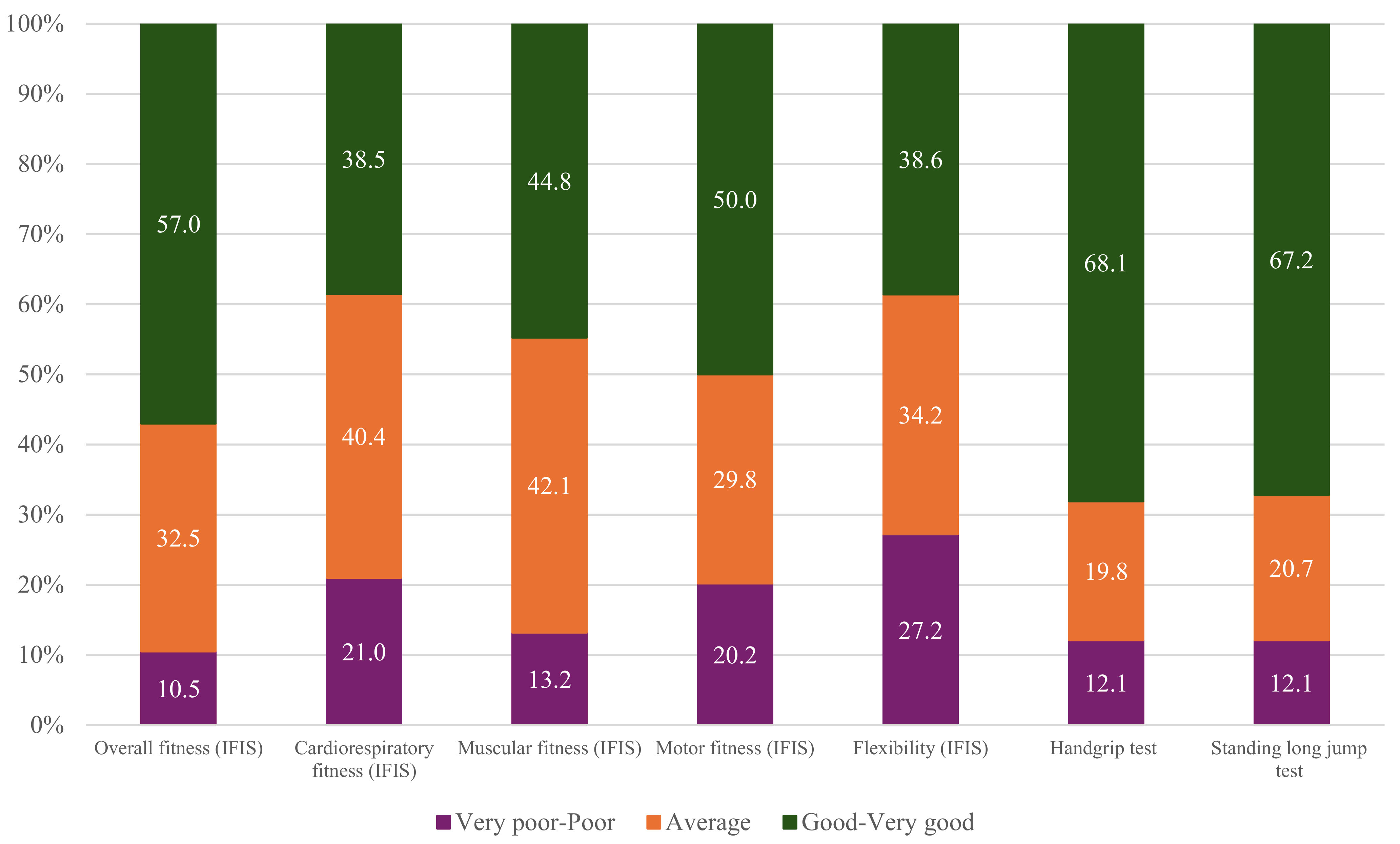
3.3. Fitness
3.4. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL)
3.5. Association Between Fitness and HRQoL
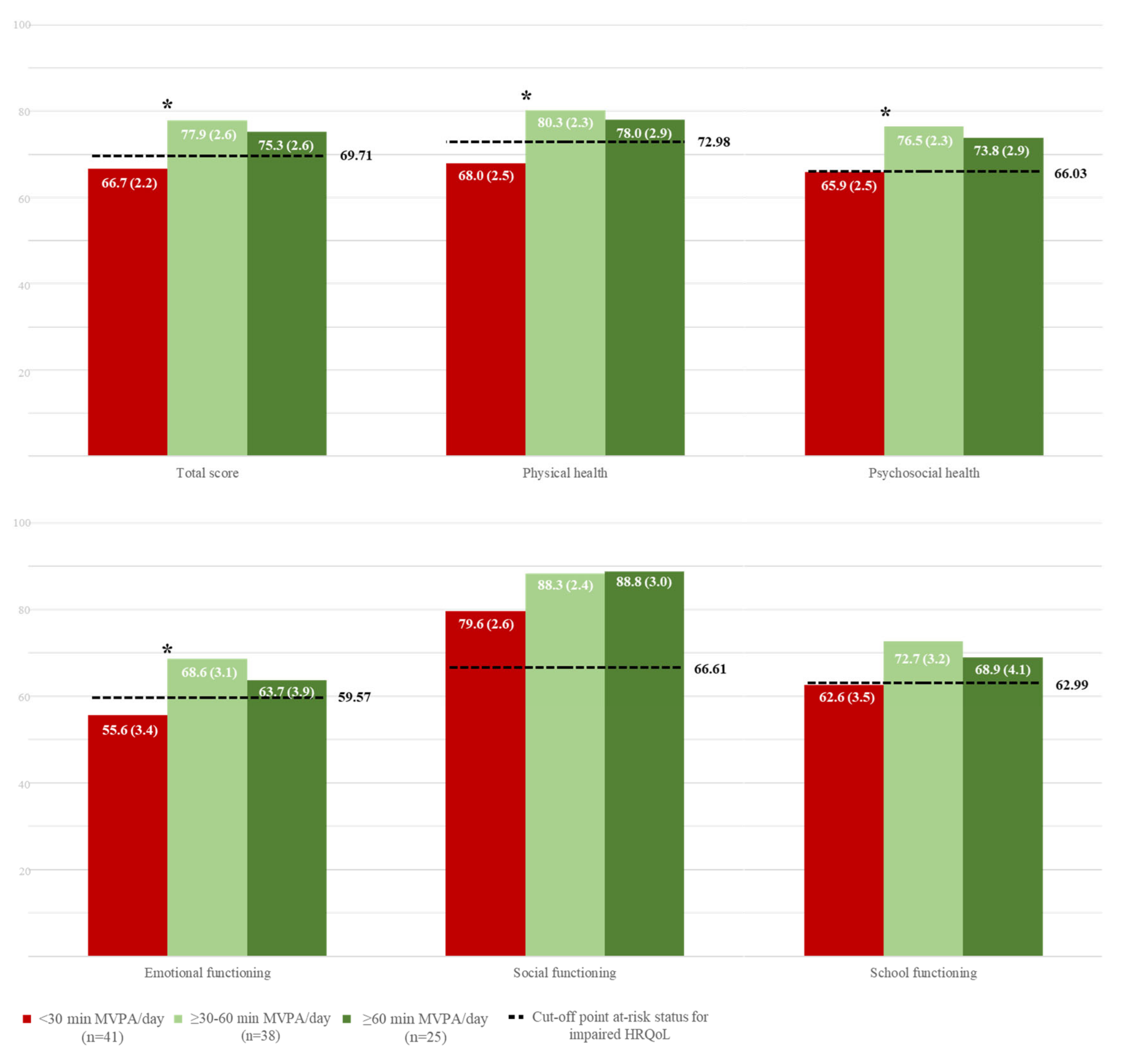
3.6. Associations Between Physical Activity and HRQoL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhakta, N.; Force, L.M.; Allemani, C.; Atun, R.; Bray, F.; Coleman, M.P.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Frazier, A.L.; Robison, L.L.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; et al. Childhood Cancer Burden: A Review of Global Estimates. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e42–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. In CureAll Framework: WHO Global Initiative for Childhood Cancer: Increasing Access, Advancing Quality, Saving Lives; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Colombet, M.; Ries, L.A.G.; Moreno, F.; Dolya, A.; Bray, F.; Hesseling, P.; Shin, H.Y.; Stiller, C.A.; Bouzbid, S.; et al. International Incidence of Childhood Cancer, 2001–2010: A Population-Based Registry Study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firkins, J.; Hansen, L.; Driessnack, M.; Dieckmann, N. Quality of Life in “Chronic” Cancer Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer Surviv. 2020, 14, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Juan, A.F.; Wolin, K.; Lucía, A. Physical Activity and Pediatric Cancer Survivorship. In Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 186, pp. 319–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neris, R.R.; Nascimento, L.C.; Leite, A.C.A.B.; Alvarenga, W.; Polita, N.B.; Zago, M.M.F. The Experience of Health-related Quality of Life in Extended and Permanent Cancer Survivors: A Qualitative Systematic Review. Psychooncology 2020, 29, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Treatment & Survivorship Facts & Figures 2019–2021; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wallander, J.L.; Koot, H.M. Quality of Life in Children: A Critical Examination of Concepts, Approaches, Issues, and Future Directions. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 45, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.; Waters, E.; Mackinnon, A.; Reddihough, D.; Graham, H.K.; Mehmet-Radji, O.; Boyd, R. Paediatric Quality of Life Instruments: A Review of the Impact of the Conceptual Framework on Outcomes. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2006, 48, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayers, P.M.; Machin, D. Developing and Validating Instruments for Assessing Quality of Life and Patient-Reported Outcomes. In Quality of Life: The Assessment, Analysis and Reporting of Patient-Reported Outcomes; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3–32. ISBN 1444337955. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; He, A.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, P. Research Trends and Hotspots of Health-Related Quality of Life: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2000 to 2019. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, G.O.; Jayawardene, W.; Lohrmann, D.K.; Mueller, E.L. Physical Activity and Fitness among Pediatric Cancer Survivors: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3183–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Martin, C.; Burton, M.; Walters, S.; Collins, K.; Wyld, L. Quality of Life versus Length of Life Considerations in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Literature Review. Psychooncology 2019, 28, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, K.K.; Mertens, A.C.; Hudson, M.M.; Wall, M.M.; Leisenring, W.M.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Sklar, C.A.; Robison, L.L.; Gurney, J.G. Limitations on Physical Performance and Daily Activities among Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Ruiz, J.; Castillo, M.; Sjöström, M. Physical Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence: A Powerful Marker of Health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikkanen, E.; Gustafsson, S.; Ingelsson, E. Associations of Fitness, Physical Activity, Strength, and Genetic Risk With Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2018, 137, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braam, K.I.; van Dijk-Lokkart, E.M.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Takken, T.; Huisman, J.; Bierings, M.B.; Merks, J.H.M.; van de Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; van Dulmen–den Broeder, E.; Veening, M.A. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Physical Activity in Children with Cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götte, M.; Kesting, S.; Winter, C.; Rosenbaum, D.; Boos, J. Comparison of Self-Reported Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents before and during Cancer Treatment. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogksch, M.D.; Goodenough, C.G.; Finch, E.R.; Partin, R.E.; Ness, K.K. Physical Activity and Fitness in Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Scoping Review. Aging Cancer 2021, 2, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurz, A.; McLaughlin, E.; Lategan, C.; Chamorro Viña, C.; Grimshaw, S.L.; Hamari, L.; Götte, M.; Kesting, S.; Rossi, F.; van der Torre, P.; et al. The International Pediatric Oncology Exercise Guidelines (IPOEG). Transl. Behav. Med. 2021, 11, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götte, M.; Gauß, G.; Dirksen, U.; Driever, P.H.; Basu, O.; Baumann, F.T.; Wiskemann, J.; Boos, J.; Kesting, S.V. Multidisciplinary Network ActiveOncoKids Guidelines for Providing Movement and Exercise in Pediatric Oncology: Consensus-based Recommendations. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyu, C.; Halnon, N. Exercise Training in Cancer Survivors. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussenq, S.C.; Hintz, L.G.; Rafael, A.D.; Ramos, A.P.; Tapparello, D.; Dubón, A.P.; Dos Santos, R.Z.; Dias, M.; Benetti, M. Level of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 16, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M.C.; Mulrooney, D.A.; Steinberger, J.; Lee, J.; Baker, K.S.; Ness, K.K. Deficits in Physical Function Among Young Childhood Cancer Survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Sánchez, M.J.; Ortega-Acosta, M.J.; Mateos, M.E.; Benito-Bernal, A.I.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Labayen, I.; et al. The Effect of an Online Exercise Programme on Bone Health in Paediatric Cancer Survivors (IBoneFIT): Study Protocol of a Multi-Centre Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; España-Romero, V.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Martínez-Gómez, D.; Manios, Y.; Béghin, L.; Molnar, D.; Widhalm, K.; Moreno, L.A.; et al. The International Fitness Scale (IFIS): Usefulness of Self-Reported Fitness in Youth. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, M.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; García-Hermoso, A.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Ortega, F.B. Construct Validity and Test-Retest Reliability of the International Fitness Scale (IFIS) in Spanish Children Aged 9–12 Years. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.; España, V.; Castro, J.; Artero, E.; Ortega, F.; García, M.; Chillón, P.; Girela, M.; Mora, J.; Suni, J.; et al. Alpha-Fitness Test Battery: Health-Related Field-Based Fitness Tests Assessment in Children and Adolescents. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, A.V.; Mirkes, E.M.; Yates, T.; Clemes, S.; Davies, M.; Khunti, K.; Edwardson, C.L. Accelerometer-Assessed Physical Activity in Epidemiology. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migueles, J.H.; Rowlands, A.V.; Huber, F.; Sabia, S.; van Hees, V.T. GGIR: A Research Community–Driven Open Source R Package for Generating Physical Activity and Sleep Outcomes From Multi-Day Raw Accelerometer Data. J. Meas. Phys. Behav. 2019, 2, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, K.R.; Catellier, D.J.; Gill, K.; Ondrak, K.S.; McMurray, R.G. Calibration of Two Objective Measures of Physical Activity for Children. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Seid, M.; Kurtin, P.S. PedsQLTM 4.0: Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life InventoryTM Version 4.0 Generic Core Scales in Healthy and Patient Populations. Med. Care 2001, 39, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Seid, M.; Skarr, D. The PedsQLTM* 4.0 as a Pediatric Population Health Measure: Feasibility, Reliability, and Validity. Ambul. Pediatr. 2003, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.A.; Mckay, H.A.; Macdonald, H.; Nettlefold, L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Cameron, N.; Brasher, P.M.A. Enhancing a Somatic Maturity Prediction Model. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, P.R.; McMurray, I.; Brownlow, C. SPSS Explained, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, A.F.; Anthony, S.J.; Khan, A.; Sung, L.; Klaassen, R. Identifying Determinants of Quality of Life of Children with Cancer and Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Hillsdale, N., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.R.Y.B.; Yau, C.E.; Low, C.E.; Li, J.; Ho, R.C.M.; Ho, C.S.H. Severity and Longitudinal Course of Depression, Anxiety and Post-Traumatic Stress in Paediatric and Young Adult Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnasco, F.; Caruso, S.; Andreano, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Jankovic, M.; Biondi, A.; Miligi, L.; Casella, C.; Terenziani, M.; Massimino, M.; et al. Late Mortality and Causes of Death among 5-Year Survivors of Childhood Cancer Diagnosed in the Period 1960–1999 and Registered in the Italian Off-Therapy Registry. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 110, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, K.-S.; Koh, K.-N. Difficulties Faced by Long-Term Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Qualitative Study. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2018, 36, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, M.J.; Williams, A.M.; Liu, Q.; Hudson Scholle, S.; Bhakta, N.; Yasui, Y.; Robison, L.L.; Hudson, M.M. Cumulative Burden of Chronic Health Conditions among Adolescent and Young Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer: Identification of Vulnerable Groups at Key Medical Transitions. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer (PDQ®)—Health Professional Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/late-effects-hp-pdq#_4 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Gebauer, J.; Baust, K.; Bardi, E.; Grabow, D.; Stein, A.; van der Pal, H.J.; Calaminus, G.; Langer, T. Guidelines for Long-Term Follow-Up after Childhood Cancer: Practical Implications for the Daily Work. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.; Brähler, E.; Wild, P.S.; Jünger, C.; Faber, J.; Schneider, A.; Beutel, M.E. Risk Factors for Suicidal Ideation in a Large, Registry-Based Sample of Adult Long-Term Childhood Cancer Survivors. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka, A.; Chęcińska, A.; Zając-Spychała, O.; Więckowska, B.; Kramer, L.; Szymańska, P.; Adamczewska-Wawrzynowicz, K.; Barełkowska, M.; Wachowiak, J.; Derwich, K. Psychosocial Late Effects in Adolescent and Young Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer Diagnosed with Leukemia, Lymphoma, and Central Nervous System Tumor. J. Adolesc. Young Adult Oncol. 2021, 10, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, F.S.M.; Patton, M.; Alberts, N.M.; Kunin-Batson, A.; Olson-Bullis, B.A.; Forbes, C.; Russell, K.B.; Neville, A.; Heathcote, L.C.; Karlson, C.W.; et al. Pain in Long-term Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Current State of Knowledge and a Call to Action from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2021, 127, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wang, F.; Ni, Z.-H. Post-Traumatic Growth among Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2023, 63, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorp, M.; Erp, L.M.E.; Maas, A.; Kremer, L.C.M.; Dulmen-den Broeder, E.; Tissing, W.J.E.; Loonen, J.J.; Pal, H.J.H.; Vries, A.C.H.; Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; et al. Increased Health-related Quality of Life Impairments of Male and Female Survivors of Childhood Cancer: DCCSS LATER 2 Psycho-oncology Study. Cancer 2022, 128, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.-C.; Brinkman, T.M.; Kenzik, K.; Gurney, J.G.; Ness, K.K.; Lanctot, J.; Shenkman, E.; Robison, L.L.; Hudson, M.M.; Krull, K.R. Association Between the Prevalence of Symptoms and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Report From the St Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, D.A.; Wieder, M.S.; Steinberg, D.M. Social Isolation and Connection in Adolescents with Cancer and Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Adolesc. 2021, 87, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, J.; Tsonis, M. Quality of Life in Survivors of Childhood Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature (2001–2008). Support. Care Cancer 2009, 17, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhry, H.; Goldenberg, M.; Sayer, G.; Aye, S.S.; Bagot, K.; Pi, S.; Ghazzaoui, R.; Vo, N.; Gowrinathan, S.; Bolton, M.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life in Childhood Cancer. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2013, 34, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Xie, M.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, A.S.K. Effects of Exercise Intervention on Quality of Life in Adolescent and Young Adult Cancer Patients and Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419895590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Reina-Gutiérrez, S.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Bizzozero-Peroni, B.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Ubago-Guisado, E. Comparative Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Health-Related Quality of Life during and after Active Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Sport. Health Sci. 2023, 12, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.I.; Scherer, R.W.; Geigle, P.M.; Berlanstein, D.R.; Topaloglu, O.; Gotay, C.C.; Snyder, C. Exercise Interventions on Health-Related Quality of Life for Cancer Survivors. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 8, CD007566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braam, K.I.; van der Torre, P.; Takken, T.; Veening, M.A.; van Dulmen-den Broeder, E.; Kaspers, G.J.L. Physical Exercise Training Interventions for Children and Young Adults during and after Treatment for Childhood Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD008796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, D.; Wakefield, C.E.; Fardell, J.E.; Quinn, V.F.; Lim, Q.; Clifford, B.K.; Simar, D.; Ness, K.K.; Cohn, R.J. Distance-Delivered Physical Activity Interventions for Childhood Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 118, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffart, L.M.; Kalter, J.; Sweegers, M.G.; Courneya, K.S.; Newton, R.U.; Aaronson, N.K.; Jacobsen, P.B.; May, A.M.; Galvão, D.A.; Chinapaw, M.J.; et al. Effects and Moderators of Exercise on Quality of Life and Physical Function in Patients with Cancer: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of 34 RCTs. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Vincent, A.J.P.E. Exercise Improves Quality of Life in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wei, S.; Shi, Y.; Pang, S.; Qin, Q.; Yin, J.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wei, S.; Nie, S.; et al. The Dose–Response Effect of Physical Activity on Cancer Mortality: Findings from 71 Prospective Cohort Studies. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkhawaja, R.; Hänggi, J.; Schaffner, E.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Alkaiyat, A.; Dössegger, A.; Kayser, B.; Suggs, L.S.; Bringolf-Isler, B.; Probst-Hensch, N. Cross-Sectional but Not Prospective Association of Accelerometry-Derived Physical Activity With Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Public. Health 2024, 69, 1606737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikkel, J.; Götte, M.; Beckmann, M.; Kasper, S.; Hense, J.; Teufel, M.; Schuler, M.; Tewes, M. Fatigue, Barriers to Physical Activity and Predictors for Motivation to Exercise in Advanced Cancer Patients. BMC Palliat. Care 2020, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, C.E.; McLoone, J.; Goodenough, B.; Lenthen, K.; Cairns, D.R.; Cohn, R.J. The Psychosocial Impact of Completing Childhood Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2010, 35, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, L.J.R.; Cavers, D.G.; Rowa-Dewar, N. Parents’ perceptions and experiences of physical activity in childhood cancer survivors in Singapore: A qualitative study. Singap. Med. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeran, P.; Abraham, C.; Jones, K.; Villegas, M.E.; Avishai, A.; Symes, Y.R.; Ellinger, H.; Miles, E.; Gates, K.M.; Wright, C.E.; et al. Promoting Physical Activity among Cancer Survivors: Meta-Analysis and Meta-CART Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Health Psychol. 2019, 38, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsson, T.; Schmiegelow, K.; Thing, L.F.; Andersen, L.B.; Helms, A.S.; Ingersgaard, M.V.; Lindgren, L.H.; Larsen, H.B. Classmates Motivate Childhood Cancer Patients to Participate in Physical Activity during Treatment: A Qualitative Study. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2019, 28, e13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeschel, A.N.; Leach, C.R.; Shuval, K.; Stein, K.D.; Patel, A.V. Physical Activity in Cancer Survivors During “Re-Entry” Following Cancer Treatment. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2018, 15, 170277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health Benefits of Physical Activity. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söntgerath, R.; Eckert, K. Impairments of Lower Extremity Muscle Strength and Balance in Childhood Cancer Patients and Survivors: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 32, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz Kabak, V.; Calders, P.; Duger, T.; Mohammed, J.; van Breda, E. Short and Long-Term Impairments of Cardiopulmonary Fitness Level in Previous Childhood Cancer Cases: A Systematic Review. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.A.; Darling, T. V Childhood Cancer and Treatment Effects on Motor Performance. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 11, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquelo-Morales, P.; Sánchez-López, M.; Moya-Martínez, P.; García-Prieto, J.C.; Martínez-Andrés, M.; García, N.L.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Health-Related Quality of Life, Obesity, and Fitness in Schoolchildren: The Cuenca Study. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.R.; Natvig, G.K.; Aadland, E.; Moe, V.F.; Kolotkin, R.L.; Anderssen, S.A.; Resaland, G.K. Associations between Health-Related Quality of Life, Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Muscle Strength, Physical Activity and Waist Circumference in 10-Year-Old Children: The ASK Study. Qual. Life Res. 2017, 26, 3421–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Tébar, A.; Ruíz-Hermosa, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Cobo-Cuenca, A.I.; Bermejo-Cantarero, A.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Sánchez-López, M. Associations between Health-Related Quality of Life and Physical Fitness in 4–7-Year-Old Spanish Children: The MOVIKIDS Study. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras, P.A.; Vidal, J.; Ponseti, X.; Cantallops, J.; Palou, P. Predictors of Quality of Life in Children. J. Human. Sport. Exerc. 2011, 6, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, P.; Vidal, J.; Ponseti, X.; Cantallops, J.; Borràs, P.A. Relaciones Entre Calidad de Vida, Actividad Física, Sedentarismo y Fitness Cardiorrespiratorio En Niños. Rev. Psicol. Deporte 2012, 21, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, M.; Endes, K.; Brand, S.; Herrmann, C.; Colledge, F.; Donath, L.; Faude, O.; Hanssen, H.; Pühse, U.; Zahner, L. In 6- to 8-Year-Old Children, Cardiorespiratory Fitness Moderates the Relationship between Severity of Life Events and Health-Related Quality of Life. Qual. Life Res. 2017, 26, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lämmle, L.; Woll, A.; Mensink, G.; Bös, K. Distal and Proximal Factors of Health Behaviors and Their Associations with Health in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2944–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Moledo, C.; Castro-Pinero, J.; Ortega, F.B.; Mora, J.; Marquez, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Ruiz, J.R. Positive Health, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Fatness in Children and Adolescents. Eur. J. Public Health 2012, 22, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Mota, J.; Gaspar, T.; de Matos, M.G. Associations between Self-Reported Fitness and Self-Rated Health, Life-Satisfaction and Health-Related Quality of Life among Adolescents. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2017, 15, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, K.K.; Kaste, S.C.; Zhu, L.; Pui, C.-H.; Jeha, S.; Nathan, P.C.; Inaba, H.; Wasilewski-Masker, K.; Shah, D.; Wells, R.J.; et al. Skeletal, Neuromuscular and Fitness Impairments among Children with Newly Diagnosed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solana, A.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Marmol-Perez, A.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Moliner-Urdiales, D.; Ubago-Guisado, E. Is Higher Physical Fitness Associated with Better Psychological Health in Young Pediatric Cancer Survivors? A Cross-sectional Study from the iBoneFIT Project. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2023, 33, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, R.; Curry, S.; Hussey, J. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Health-Related Quality of Life in Survivors of Childhood Central Nervous System Tumours. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenroth, A.; Söntgerath, R.; Schuster, A.J.; von Busch, C.; Huber, G.; Eckert, K.; Kulozik, A.E.; Wiskemann, J. Muscle Strength and Quality of Life in Patients with Childhood Cancer at Early Phase of Primary Treatment. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 33, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batalik, L.; Winnige, P.; Dosbaba, F.; Vlazna, D.; Janikova, A. Home-Based Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Interventions in Cancer Patients and Survivors: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.S.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Rincón-Castanedo, C.; Takken, T.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Lucia, A. Exercise Training in Childhood Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 70, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, C.G.; Partin, R.E.; Ness, K.K. Skeletal Muscle and Childhood Cancer: Where Are We Now and Where We Go from Here. Aging Cancer 2021, 2, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years; SD) | 116 | 5.6 (3.4) |
| Infant (0–1 years) | 18 | 0.9 (0.5) |
| Toddler (2–4 years) | 26 | 3.2 (0.6) |
| Young child (5–7 years) | 42 | 5.7 (1.0) |
| Child (8–12 years) | 20 | 10.1 (1.1) |
| Adolescent (13–18 years) | 7 | 14.0 (0.6) |
| Time from diagnosis to testing (years; SD) | 110 | 06.4 (3.9) |
| Age at testing (years; SD) | 116 | 12.1 (3.3) |
| Young child (6–7 years) | 16 | 07.2 (0.5) |
| Child (8–12 years) | 49 | 10.4 (1.5) |
| Adolescent (13–18 years) | 51 | 15.3 (1.5) |
| Sex (n, %) | 116 | |
| Boys | 67; 57.8 | |
| Girls | 49; 42.2 | |
| Type of neoplasm (n, %) | 115 | |
| Soft tumors (hematologic) | 70; 60.9 | |
| Solid tumors | 45; 39.1 | |
| Distribution of cancer types (n, %) | 116 | |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 45; 38.8 | |
| Lymphoma | 14; 12.1 | |
| Central nervous system tumor | 11; 09.5 | |
| Renal tumor | 9; 07.8 | |
| Neuroblastoma | 8; 06.9 | |
| Malignant bone tumor | 8; 06.9 | |
| Histiocytosis | 6; 05.2 | |
| Soft tissue and other extraosseous sarcomas | 5; 04.3 | |
| Others (retinoblastoma, hepatic tumor, other malignant epithelial neoplasms, unknown) | 10; 08.6 | |
| Anthropometry | 116 | |
| Weight (kg; SD) | 46.6 (18.0) | |
| Height (cm; SD) | 147.5 (17.1) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2;SD) | 20.7 (4.7) | |
| Peak height velocity offset (years; SD) | −0.8 (2.7) |
| n | Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors | n | Normative Values | p-Value | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total score | 112 | 72.5 (12.2) | 5972 | 82.9 (13.2) | <0.001 | 0.79 |
| Physical health | 112 | 74.4 (13.9) | 5962 | 86.9 (13.9) | <0.001 | 0.90 |
| Psychosocial health | 112 | 71.5 (13.2) | 5963 | 80.7 (14.7) | <0.001 | 0.63 |
| Emotional functioning | 112 | 62.0 (18.0) | 5961 | 78.2 (18.6) | <0.001 | 0.87 |
| Social functioning | 112 | 84.9 (13.6) | 5948 | 84.0 (17.4) | 0.507 | - |
| School functioning | 112 | 67.7 (18.5) | 5908 | 79.9 (16.9) | <0.001 | 0.70 |
| n | Total Score | p-Value (ηp2) | Physical Health | p-Value (ηp2) | Psychosocial Health | p-Value (ηp2) | Emotional Functioning | p-Value (ηp2) | Social Functioning | p-Value (ηp2) | School Functioning | p-Value (ηp2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFIS-Overall fitness | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 12 | 63.8 (4.3) | 66.1 (4.9) | 62.6 (4.5) | 58.8 (6.3) | 73.4 (4.2) | 55.6 (6.6) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 63 | 74.4 (1.6) | 0.030 (0.07) | 76.0 (1.9) | 0.077 | 73.5 (1.7) | 0.035 (0.06) | 63.5 (2.4) | 0.515 | 88.1 (1.6) | 0.003 (0.12) | 69.0 (2.5) | 0.071 |
| IFIS-Cardiorespiratory fitness | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 23 | 61.3 (2.4) | 61.1 (2.7) | 61.4 (2.6) | 54.1 (3.8) | 75.1 (3.1) | 54.9 (3.8) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 41 | 80.0 (1.7) | <0.001 (0.37) | 80.5 (1.9) | <0.001 (0.33) | 79.7 (1.8) | <0.001 (0.33) | 69.6 (2.7) | 0.003 (0.14) | 92.7 (2.2) | <0.001 (0.25) | 76.6 (2.7) | <0.001 (0.25) |
| IFIS-Muscular fitness | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 14 | 67.7 (3.4) | 70.2 (4.0) | 63.4 (3.6) | 53.9 (5.5) | 83.2 (3.3) | 62.2 (4.8) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 50 | 74.7 (1.7) | 0.083 | 76.7 (2.0) | 0.167 | 73.6 (1.8) | 0.090 | 64.7 (2.8) | 0.092 | 88.5 (1.7) | 0.170 | 67.6 (2.4) | 0.331 |
| IFIS-Motor fitness | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 23 | 65.8 (2.8) | 66.6 (3.0) | 65.4 (3.1) | 58.5 (4.5) | 77.5 (3.3) | 60.2 (4.2) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 54 | 77.2 (1.7) | 0.001 (0.13) | 79.5 (1.8) | <0.001 (0.15) | 76.0 (1.9) | 0.008 (0.09) | 66.2 (2.7) | 0.172 | 88.8 (2.0) | 0.008 (0.10) | 72.9 (2.6) | 0.018 (0.08) |
| IFIS-Flexibility | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 31 | 67.9 (2.3) | 69.3 (2.6) | 67.1 (2.6) | 59.4 (3.4) | 78.8 (2.4) | 63.0 (3.7) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 42 | 74.9 (2.0) | 0.029 (0.07) | 76.2 (2.2) | 0.055 | 74.2 (2.2) | 0.044 (0.06) | 64.6 (2.9) | 0.255 | 88.2 (2.0) | 0.005 (0.11) | 69.7 (3.1) | 0.185 |
| Handgrip test | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 13 | 67.1 (4.3) | 68.2 (4.6) | 66.5 (4.7) | 60.0 (6.0) | 78.5 (5.0) | 61.1 (6.9) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 74 | 73.2 (1.5) | 0.206 | 76.4 (1.6) | 0.122 | 71.5 (1.7) | 0.340 | 60.7 (2.1) | 0.915 | 84.9 (1.8) | 0.251 | 69.0 (2.4) | 0.302 |
| Standing long jump test | |||||||||||||
| Very poor to poor | 12 | 69.8 (3.5) | 69.8 (4.0) | 69.7 (3.8) | 68.1 (5.3) | 77.2 (4.3) | 63.8 (5.2) | ||||||
| Good to very good | 72 | 74.5 (1.4) | 0.221 | 77.3 (1.6) | 0.092 | 73.0 (1.5) | 0.431 | 63.2 (2.1) | 0.411 | 86.9 (1.7) | 0.051 | 69.0 (2.0) | 0.363 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redondo-Tébar, A.; Rodriguez-Solana, A.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Marmol-Perez, A.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; Pascual-Gázquez, J.F.; Herrada-Robles, M.; Sánchez-López, M.; et al. Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study (iBoneFIT Project). Cancers 2025, 17, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061030
Redondo-Tébar A, Rodriguez-Solana A, Gracia-Marco L, Marmol-Perez A, Gil-Cosano JJ, Cadenas-Sánchez C, Llorente-Cantarero FJ, Pascual-Gázquez JF, Herrada-Robles M, Sánchez-López M, et al. Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study (iBoneFIT Project). Cancers. 2025; 17(6):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061030
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedondo-Tébar, Andrés, Andrea Rodriguez-Solana, Luis Gracia-Marco, Andres Marmol-Perez, José J. Gil-Cosano, Cristina Cadenas-Sánchez, Francisco J. Llorente-Cantarero, Juan Francisco Pascual-Gázquez, María Herrada-Robles, Mairena Sánchez-López, and et al. 2025. "Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study (iBoneFIT Project)" Cancers 17, no. 6: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061030
APA StyleRedondo-Tébar, A., Rodriguez-Solana, A., Gracia-Marco, L., Marmol-Perez, A., Gil-Cosano, J. J., Cadenas-Sánchez, C., Llorente-Cantarero, F. J., Pascual-Gázquez, J. F., Herrada-Robles, M., Sánchez-López, M., & Ubago-Guisado, E. (2025). Physical Activity, Fitness, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study (iBoneFIT Project). Cancers, 17(6), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061030








