Bone Marrow CD34+/lin− Cells of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CP-CML) After 12 Months of Nilotinib Treatment Exhibit a Different Gene Expression Signature Compared to the Diagnosis and the Corresponding Cells from Healthy Subjects
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Isolation of BM CD34+/lin− Cells Using Immunomagnetic Beads
2.3. Cell Cryopreservation and RNA Extraction
2.4. GEP Experiments
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses of GEP Data
- Pattern 1 with expression at diagnosis greater than expression at 12 months greater than expression in CTRLs;
- Pattern 2 with expression at diagnosis lower than expression at 12 months lower than expression in CTRLs;
- Pattern 3 with expression in CTRLs greater than expression at diagnosis greater than expression at 12 months;
- Pattern 4 with expression in CTRLs lower than expression at diagnosis lower than expression at 12 months;
- Other patterns not previously listed.
3. Results
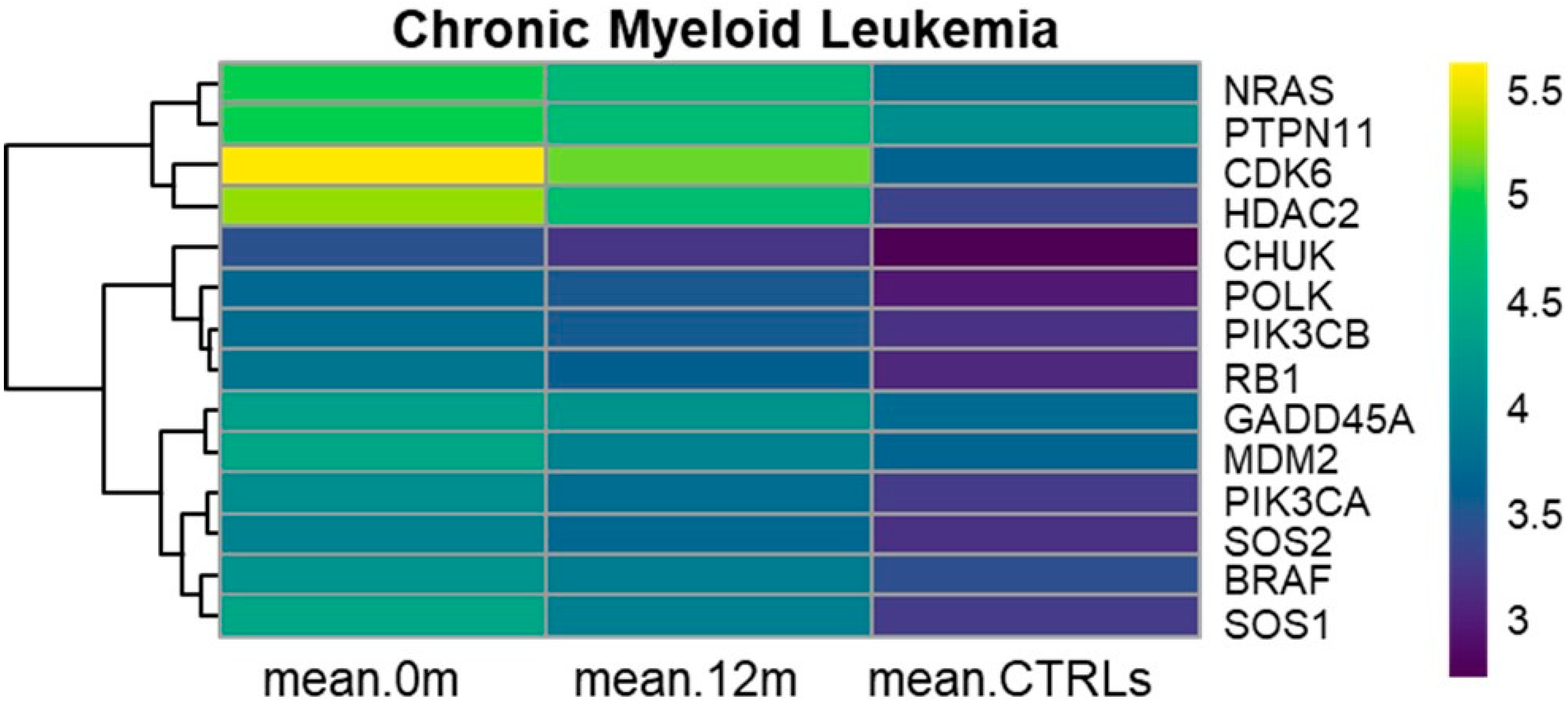
3.1. KEGG Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (hsa05220)
3.2. KEGG Cell Cycle (hsa04110)
3.3. KEGG PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway (hsa04151)
3.4. KEGG MAPK Signaling Pathway (hsa04010)
3.5. KEGG JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway (hsa04630)
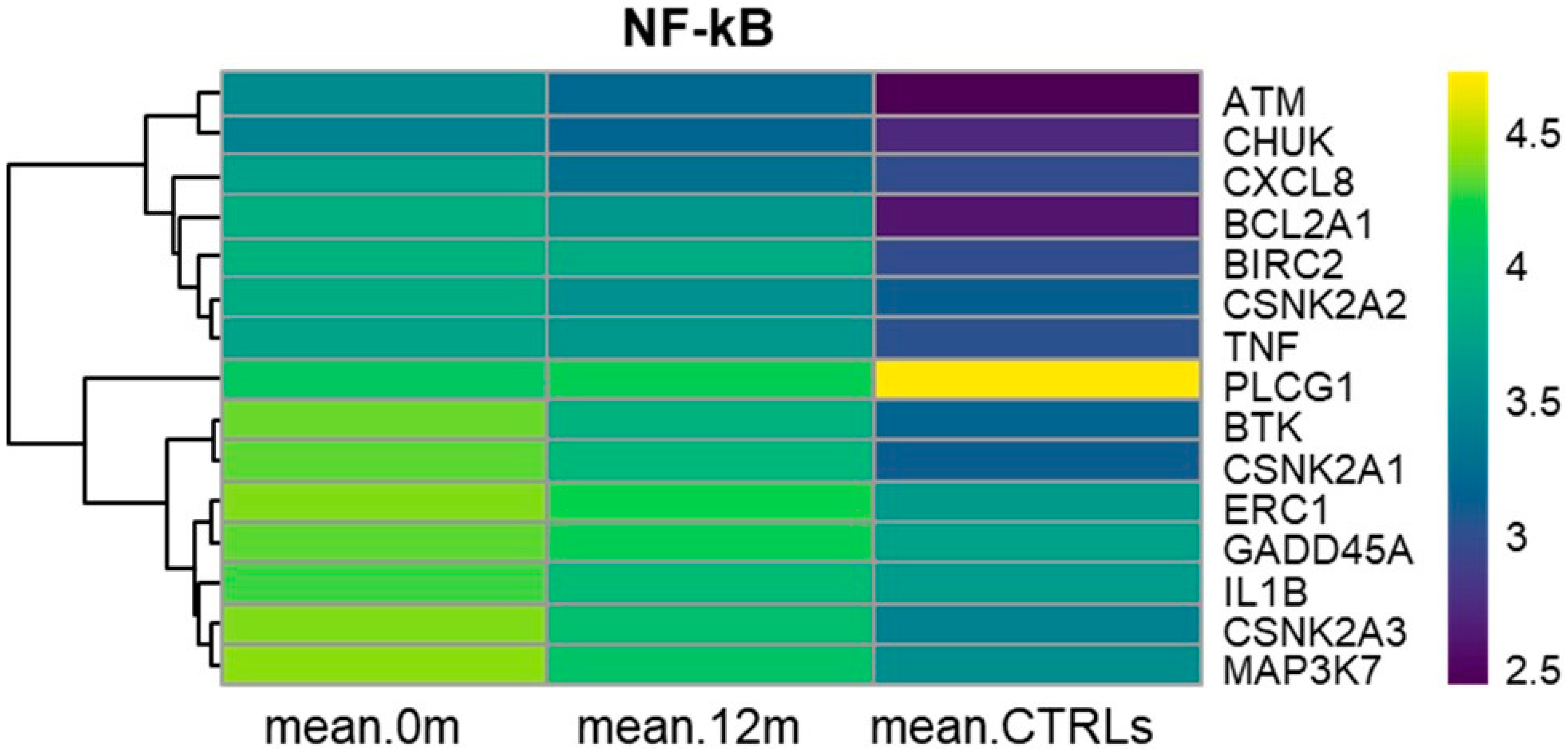
3.6. KEGG NF-kB Signaling Pathway (hsa04064)
3.7. KEGG Ras Signaling Pathway (hsa04014)
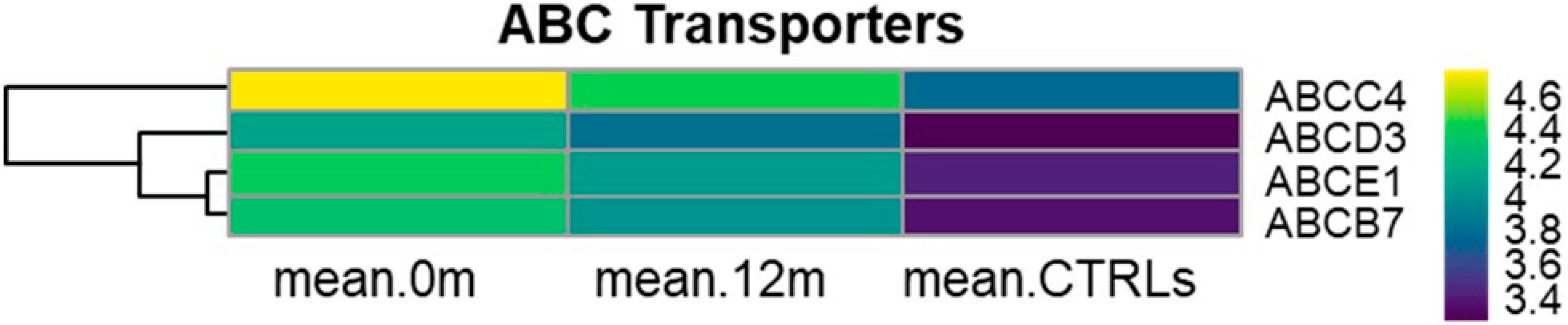
3.8. KEGG ABC Transporters (hsa02010)
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, X.; Jiang, X. Properties of Leukemic Stem Cells in Regulating Drug Resistance in Acute and Chronic Myeloid Leukemias. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, J.; Sasaki, K.; Issa, G.C.; Lipton, J.H.; Radich, J.P.; Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.M. Management of chronic myeloid leukemia in 2023-common ground and common sense. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, R.; Han, M.; Tan, Y.; Xie, M.; Gao, S.; Hu, J.F. Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Boquimpani, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-term outcomes with frontline nilotinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENESTnd 10-year analysis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2142–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojtahedi, H.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: Targeting therapeutic implications. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Rutella, S.; Almeida, A.M.; De Las Rivas, J.; Trougakos, I.P.; Sarmento Ribeiro, A.B. Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Relevance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muselli, F.; Peyron, J.F.; Mary, D. Druggable Biochemical Pathways and Potential Therapeutic Alternatives to Target Leukemic Stem Cells and Eliminate the Residual Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Ito, K. Leukemia Stem Cells as a Potential Target to Achieve Therapy-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungolino, E.; Rossi, G.; De Canal, G.; Trojani, A.; D’adda, M.; Perego, A.; Orlandi, E.M.; Lunghi, F.; Turrini, M.; Borin, L.; et al. Nilotinib induced bone marrow CD34+/lin−Ph+ cells early clearance in newly diagnosed CP-chronic myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, E162–E164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungolino, E.; D’adda, M.; De Canal, G.; Trojani, A.; Perego, A.; Elena, C.; Lunghi, F.; Turrini, M.; Borin, L.; Iurlo, A.; et al. Nilotinib-induced bone marrow CD34+/lin−Ph+ cells early clearance in newly diagnosed CP-Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Final report of the PhilosoPhi34 study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 107, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojani, A.; Pungolino, E.; Dal Molin, A.; Lodola, M.; Rossi, G.; D’Adda, M.; Perego, A.; Elena, C.; Turrini, M.; Borin, L.; et al. Nilotinib interferes with cell cycle, ABC transporters and JAK-STAT signaling pathway in CD34+/lin− cells of patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after 12 months of treatment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojani, A.; Pungolino, E.; Rossi, G.; D’Adda, M.; Lodola, M.; Camillo, B.D.; Perego, A.; Turrini, M.; Orlandi, E.; Borin, L.; et al. Wide-transcriptome analysis and cellularity of gene CD34+/lin− cells of patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia at diagnosis vs. 12 months of first-line nilotinib treatment. Cancer Biomark 2017, 21, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Bolstad, B.M.; Collin, F.; Cope, L.M.; Hobbs, B.; Speed, T.P. Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2003, 31, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.S.; Irizarry, R.A. A framework for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D. A direct approach to false Discovery Rate. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2002, 64, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.K.; Shi, C.J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.P.; Chen, Y.F.; Fu, L.W. Nilotinib enhances the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic drugs in CD34⁺CD38⁻ stem cells and ABC transporter overexpressing leukemia cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 3356–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Rana, A.; Datoguia, T.S.; Hamerschlak, N.; Brumatti, G. BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Complex Signaling Transduction: Challenges to Overcome Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wei, D.; Lu, T.; Ma, D.; Yu, K.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. CAY10683 and imatinib have synergistic effects in overcoming imatinib resistance via HDAC2 inhibition in chronic myeloid leukemia. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncker, B.P.; Chesnokov, I.N.; McConkey, B.J. The origin recognition complex protein family. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Strauss, A.C.; Chu, S.; Li, M.; Ho, Y.; Shiang, K.D.; Snyder, D.S.; Huettner, C.S.; Shultz, L.; Holyoake, T.; et al. Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs, M.C.; Kim, W.; Bariteau, M.; Davis, T.; Vempati, S.; Minehart, J.; Witkin, M.; Qi, J.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Bradner, J.E.; et al. Selective Inhibition of HDAC1 and HDAC2 as a Potential Therapeutic Option for B-ALL. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Schneeweiss-Gleixner, M.; Byrgazov, K.; Stefanzl, G.; Berger, D.; Eisenwort, G.; Lucini, C.B.; Herndlhofer, S.; Preuner, S.; Obrova, K.; Pusic, P.; et al. CDK4/CDK6 inhibition as a novel strategy to suppress the growth and survival of BCR-ABL1T315I+ clones in TKI-resistant CML. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiblecker, L.; Klampfl, T.; Doma, E.; Nebenfuehr, S.; Torres-Quesada, O.; Strich, S.; Heller, G.; Werdenich, D.; Tschulenk, W.; Zojer, M.; et al. CDK6 kinase inhibition unmasks metabolic dependencies in BCR::ABL1+ leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Toofan, P.; Busch, C.; Morrison, H.; O’Brien, S.; Jørgensen, H.; Copland, M.; Wheadon, H. Chronic myeloid leukaemia cells require the bone morphogenic protein pathway for cell cycle progression and self-renewal. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 927. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, V.; Gupta, S.K.; Kumari, G.; Verma, M. Combating TKI resistance in CML by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in combination with TKIs: A review. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makii, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Oda, K.; Uehara, Y.; Nishijima, A.; Koso, T.; Kawata, Y.; Kashiyama, T.; Miyasaka, A.; Sone, K.; et al. Anti-tumor activity of dual inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and MDM2 against clear cell ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 155, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.T.; Liu, W.; Mitchell, R.; Clarke, C.J.; Kinstrie, R.; Warren, F.; Almasoudi, H.; Stevens, T.; Dunn, K.; Pritchard, J.; et al. Activating p53 abolishes self-renewal of quiescent leukaemic stem cells in residual CML disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airiau, K.; Mahon, F.X.; Josselin, M.; Jeanneteau, M.; Belloc, F. PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors sensitize chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells to nilotinib and restore the response of progenitors to nilotinib in the presence of stem cell factor. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wan, Q.; Li, Z.; Chng, W.J. Janus Kinase Signaling: Oncogenic Criminal of Lymphoid Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Tolentino, J.H.; Argilagos, R.F.; Zhang, L.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Hazlehurst, L.A. Potentiation of Nilotinib-mediated cell death in the context of the bone marrow microenvironment requires a promiscuous JAK inhibitor in CML. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.P.; Song, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, M.S.; Petrus, M.N.; Thomas, C.J.; et al. A novel model of alternative NF-κB pathway activation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1976–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrà, G.; Torti, D.; Crivellaro, S.; Panuzzo, C.; Taulli, R.; Cilloni, D.; Guerrasio, A.; Saglio, G.; Morotti, A. The BCR-ABL/NF-κB signal transduction network: A long lasting relationship in Philadelphia positive Leukemias. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66287–66298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.G.; Lebecque, B.; Tassin, T.; Dannus, L.T.; Berger, J.; Soucal, M.; Guerci, A.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Johnson, H.; Etienne, G.; et al. Efficiency of nilotinib to target chronic phase-chronic myeloid leukaemia primary mature CD34− and immature CD34+ cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.M.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Allan, E.; Pearson, C.; Alcorn, M.J.; Richmond, L.; Holyoake, T.L. Primitive, quiescent, Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia are insensitive to STI571 in vitro. Blood 2002, 99, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.G.; Allan, E.K.; Jordanides, N.E.; Mountford, J.C.; Holyoake, T.L. Nilotinib exerts equipotent antiproliferative effects to imatinib and does not induce apoptosis in CD34+ CML cells. Blood 2007, 109, 4016–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in malignant tumors: Molecular mechanisms and future perspective. Signal Transduct Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuxiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, Q.; Zhou, H.; Hu, M.; Tao, S.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Hao, X. MicroRNA-145 promotes the apoptosis of leukemic stem cells and enhances drug-resistant K562/ADM cell sensitivity to adriamycin via the regulation of ABCE1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trojani, A.; Pungolino, E.; Di Camillo, B.; Bossi, L.E.; Palumbo, C.; D’adda, M.; Perego, A.; Turrini, M.; Elena, C.; Borin, L.M.; et al. Bone Marrow CD34+/lin− Cells of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CP-CML) After 12 Months of Nilotinib Treatment Exhibit a Different Gene Expression Signature Compared to the Diagnosis and the Corresponding Cells from Healthy Subjects. Cancers 2025, 17, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061022
Trojani A, Pungolino E, Di Camillo B, Bossi LE, Palumbo C, D’adda M, Perego A, Turrini M, Elena C, Borin LM, et al. Bone Marrow CD34+/lin− Cells of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CP-CML) After 12 Months of Nilotinib Treatment Exhibit a Different Gene Expression Signature Compared to the Diagnosis and the Corresponding Cells from Healthy Subjects. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061022
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrojani, Alessandra, Ester Pungolino, Barbara Di Camillo, Luca Emanuele Bossi, Cassandra Palumbo, Mariella D’adda, Alessandra Perego, Mauro Turrini, Chiara Elena, Lorenza Maria Borin, and et al. 2025. "Bone Marrow CD34+/lin− Cells of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CP-CML) After 12 Months of Nilotinib Treatment Exhibit a Different Gene Expression Signature Compared to the Diagnosis and the Corresponding Cells from Healthy Subjects" Cancers 17, no. 6: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061022
APA StyleTrojani, A., Pungolino, E., Di Camillo, B., Bossi, L. E., Palumbo, C., D’adda, M., Perego, A., Turrini, M., Elena, C., Borin, L. M., Iurlo, A., Malato, S., Spina, F., Latargia, M. L., Spedini, P., Artale, S., Anghilieri, M., Carraro, M. C., Bucelli, C., ... Cairoli, R. (2025). Bone Marrow CD34+/lin− Cells of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CP-CML) After 12 Months of Nilotinib Treatment Exhibit a Different Gene Expression Signature Compared to the Diagnosis and the Corresponding Cells from Healthy Subjects. Cancers, 17(6), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061022





