Caveolin-1 Endows Order in Cholesterol-Rich Detergent Resistant Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. DRM Extraction
2.4. Protein Determination
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Proteomic Analysis
2.7. Lipid Analysis
2.8. Cav-1 Insertion in Liposomes Derived from DRMs
2.9. Langmuir Measurements
2.10. X-Ray Scattering Experiments
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
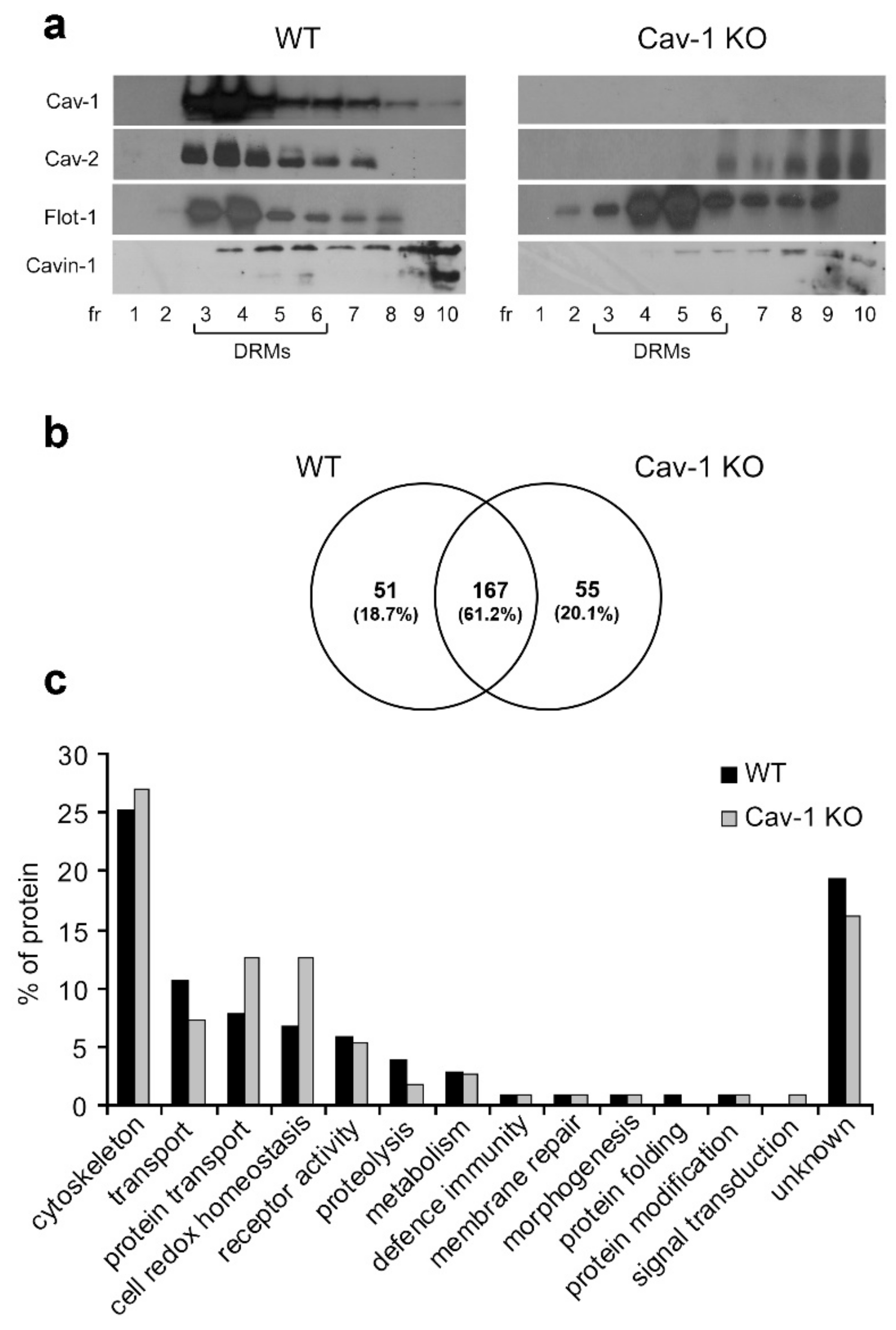
3.1. Characterization of DRMs from Lung Tissue of WT and Cav-1 KO Mice
3.2. Lipid Analysis
3.3. Langmuir Films
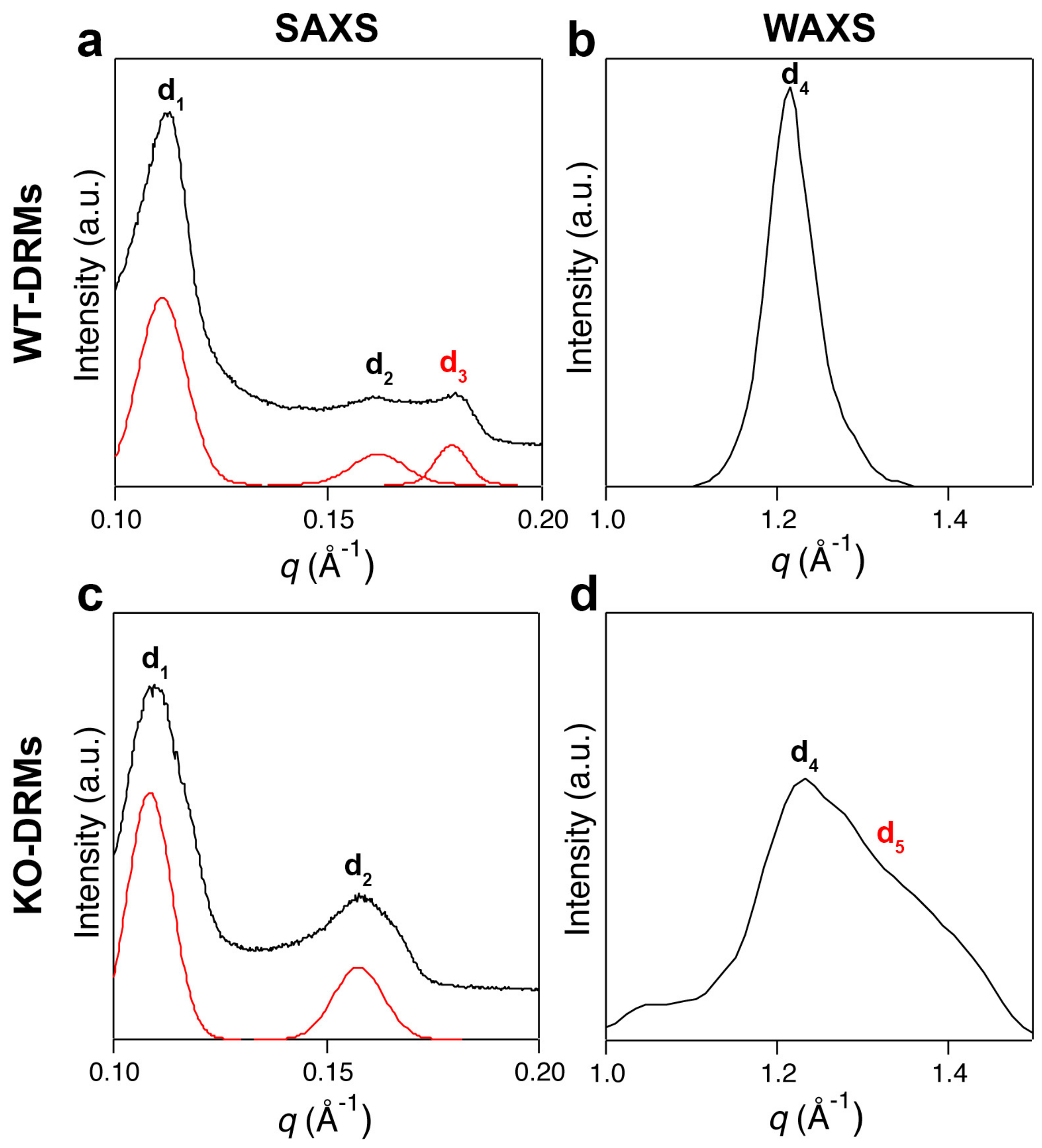
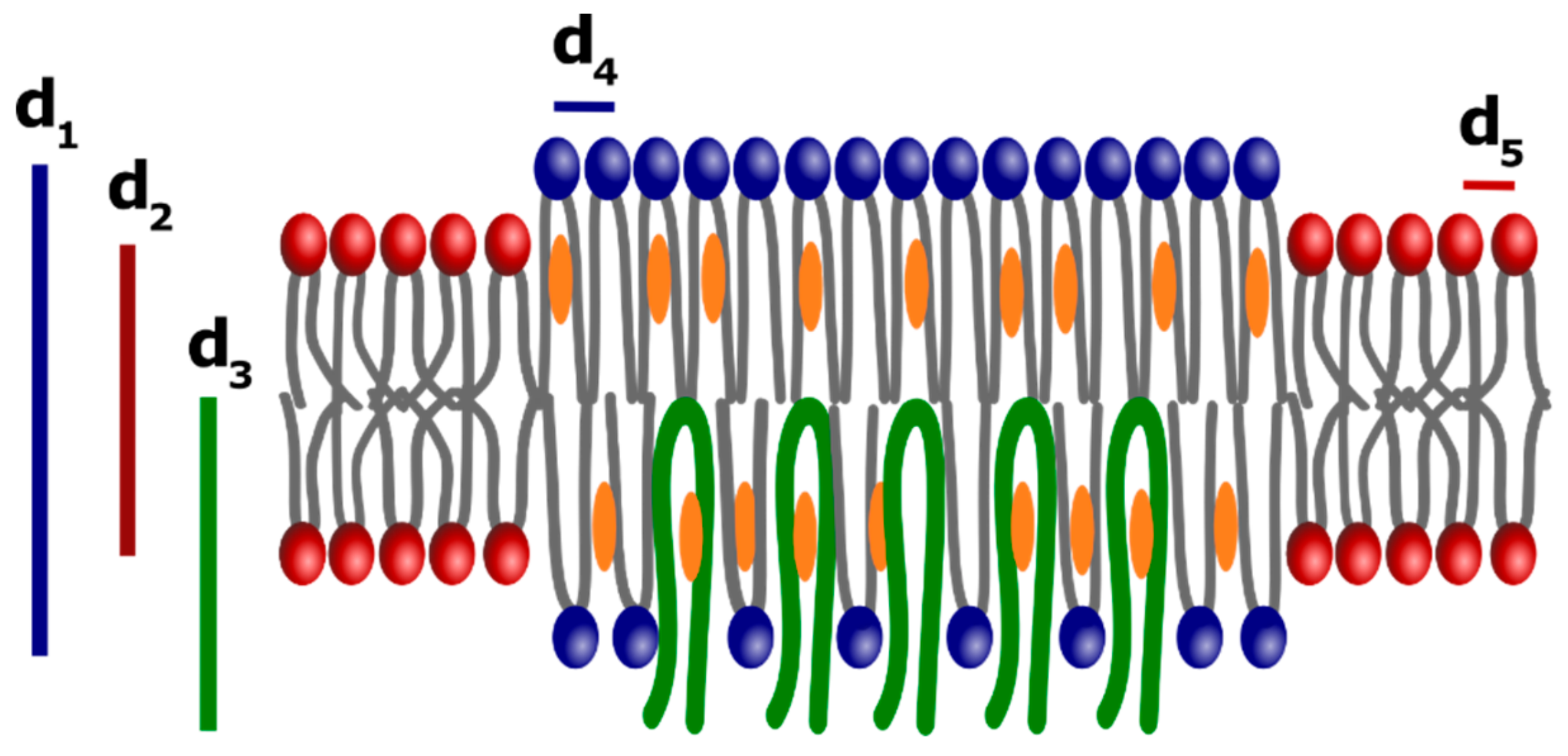
3.4. Small and Wide-Angle X-Ray Scattering
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sargiacomo, M.; Sudol, M.; Tang, Z.; Lisanti, M.P. Signal transducing molecules and glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked proteins form a caveolin-rich insoluble complex in MDCK cells. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.A.; Rose, J.K. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 1992, 68, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisanti, M.P.; Scherer, P.E.; Vidugiriene, J.; Tang, Z.; Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Tu, Y.H.; Cook, R.F.; Sargiacomo, M. Characterization of caveolin-rich membrane domains isolated from an endothelial-rich source: Implications for human disease. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 126, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisanti, M.P.; Tang, Z.L.; Sargiacomo, M. Caveolin forms a hetero-oligomeric protein complex that interacts with an apical GPI-linked protein: Implications for the biogenesis of caveolae. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.F. Lipid rafts: Contentious only from simplistic standpoints. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levental, I.; Veatch, S. The Continuing Mystery of Lipid Rafts. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4749–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Varma, R.; Sarasij, R.C.; Ira; Gousset, K.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Rao, M.; Mayor, S. Nanoscale organization of multiple GPI-anchored proteins in living cell membranes. Cell 2004, 116, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, K.S.; Lisanti, M.P. Expression and characterization of recombinant caveolin. Purification by polyhistidine tagging and cholesterol-dependent incorporation into defined lipid membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Peranen, J.; Schreiner, R.; Wieland, F.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Simons, K. VIP21/caveolin is a cholesterol-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10339–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, I.; Jasmin, J.F.; Pavlides, S.; Minetti, C.; Flomenberg, N.; Pestell, R.G.; Frank, P.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Clinical and translational implications of the caveolin gene family: Lessons from mouse models and human genetic disorders. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaus, K.; Le Lay, S.; Balasubramanian, N.; Schwartz, M.A. Integrin-mediated adhesion regulates membrane order. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, C.; Berking, A.; Agerer, F.; Buntru, A.; Neske, F.; Chhatwal, G.S.; Ohlsen, K.; Hauck, C.R. Caveolin limits membrane microdomain mobility and integrin-mediated uptake of fibronectin-binding pathogens. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4280–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariotti, N.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Hill, M.M.; Rodkey, T.L.; Inder, K.L.; Tanner, L.B.; Wenk, M.R.; Hancock, J.F.; Parton, R.G. Caveolae regulate the nanoscale organization of the plasma membrane to remotely control Ras signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parton, R.G.; Simons, K. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Veatch, S.L. Adhesion stabilizes robust lipid heterogeneity in supercritical membranes at physiological temperature. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.N.; Brown, D.A.; London, E. On the origin of sphingolipid/cholesterol-rich detergent-insoluble cell membranes: Physiological concentrations of cholesterol and sphingolipid induce formation of a detergent-insoluble, liquid-ordered lipid phase in model membranes. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 10944–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diociaiuti, M.; Bordi, F.; Motta, A.; Carosi, A.; Molinari, A.; Arancia, G.; Coluzza, C. Aggregation of gramicidin A in phospholipid Langmuir-Blodgett monolayers. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 3198–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diociaiuti, M.; Ruspantini, I.; Giordani, C.; Bordi, F.; Chistolini, P. Distribution of GD3 in DPPC monolayers: A thermodynamic and atomic force microscopy combined study. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, M.; Kubiak, J.; Lach, A.; Przybylo, M.; Sikorski, A.F. A raft-associated species of phosphatidylethanolamine interacts with cholesterol comparably to sphingomyelin. A Langmuir-Blodgett monolayer study. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz, J.P.; Sezgin, E.; Schwille, P.; Simons, K. Functional convergence of hopanoids and sterols in membrane ordering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14236–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, G.; Sciubba, F.; Caminiti, R. Effect of hydration on the structure of caveolae membranes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G. Langmuir-Blodgett Films; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Razani, B.; Engelman, J.A.; Wang, X.B.; Schubert, W.; Zhang, X.L.; Marks, C.B.; Macaluso, F.; Russell, R.G.; Li, M.; Pestell, R.G.; et al. Caveolin-1 null mice are viable but show evidence of hyperproliferative and vascular abnormalities. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38121–38138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fratini, F.; Raggi, C.; Sferra, G.; Birago, C.; Sansone, A.; Grasso, F.; Curra, C.; Olivieri, A.; Pace, T.; Mochi, S.; et al. An Integrated Approach to Explore Composition and Dynamics of Cholesterol-rich Membrane Microdomains in Sexual Stages of Malaria Parasite. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, E.; Carpinelli, G.; Proietti, E.; Belardelli, F.; Cantafora, A.; Podo, F. Alterations of lipid composition in Friend leukemia cell tumors in mice treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FEBS Lett. 1990, 260, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, W.W. The Preparation of Derivatives of Lipids, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Caracciolo, G.; Petruccetti, M.; Caminiti, R. A new experimental setup for the study of lipid hydration by energy dispersive X-ray diffraction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 414, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenitsch, H.; Rappolt, M.; Teixeira, C.V.; Majerowicz, M.; Laggner, P. In situ sensing of salinity in oriented lipid multilayers by surface X-ray scattering. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4621–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, I.; Sargiacomo, M.; Galbiati, F.; Rizzo, G.; Grignani, F.; Engelman, J.A.; Okamoto, T.; Ikezu, T.; Scherer, P.E.; Mora, R.; et al. Expression of caveolin-1 is required for the transport of caveolin-2 to the plasma membrane. Retention of caveolin-2 at the level of the golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25718–25725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.M.; Daud, N.H.; Aung, C.S.; Loo, D.; Martin, S.; Murphy, S.; Black, D.M.; Barry, R.; Simpson, F.; Liu, L.; et al. Co-regulation of cell polarization and migration by caveolar proteins PTRF/Cavin-1 and caveolin-1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Lay, S.; Li, Q.; Proschogo, N.; Rodriguez, M.; Gunaratnam, K.; Cartland, S.; Rentero, C.; Jessup, W.; Mitchell, T.; Gaus, K. Caveolin-1-dependent and -independent membrane domains. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortegren, U.; Aboulaich, N.; Ost, A.; Stralfors, P. A new role for caveolae as metabolic platforms. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maget-Dana, R. The monolayer technique: A potent tool for studying the interfacial properties of antimicrobial and membrane-lytic peptides and their interactions with lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1462, 109–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, J.H.; Karlstrom, G.; Mouritsen, O.G.; Wennerstrom, H.; Zuckermann, M.J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 905, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Lachataignerais, J.; Pons, R.; Amenitsch, H.; Rappolt, M.; Sartori, B.; Lopez, O. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate at different hydration conditions on dioleoyl phosphatidylcholine bilayers studied by grazing incidence X-ray diffraction. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5256–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappolt, M. The Biologically Relevant Lipid Mesophases as “seen” by X-rays. In Advances in Planar Lipid Bilayers and Liposomes; Leitmannova Liu, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 253–283. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, D.; Miller, I.R. Hydration of phospholipid bilayers in the presence and absence of cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1368, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, A.; Rappolt, M.; Amenitsch, H.; Laggner, P.; Pabst, G. Differential Modulation of Membrane Structure and Fluctuations by Plant Sterols and Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 3935–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargiacomo, M.; Scherer, P.E.; Tang, Z.; Kubler, E.; Song, K.S.; Sanders, M.C.; Lisanti, M.P. Oligomeric structure of caveolin: Implications for caveolae membrane organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9407–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Felger, T.A.; Larimore, W.L.; Mills, T.L., Jr. What every physician should know about the RUC. Fam. Pract. Manag. 2008, 15, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, D. Cholesterol modulates the structure, binding modes, and energetics of caveolin-membrane interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14556–14564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, E.; Nagiel, A.; Lin, A.J.; Golan, D.E.; Michel, T. Small interfering RNA-mediated down-regulation of caveolin-1 differentially modulates signaling pathways in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40659–40669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goni, F.M.; Alonso, A.; Bagatolli, L.A.; Brown, R.E.; Marsh, D.; Prieto, M.; Thewalt, J.L. Phase diagrams of lipid mixtures relevant to the study of membrane rafts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, R.F.; Loura, L.M.; Fedorov, A.; Prieto, M. Lipid rafts have different sizes depending on membrane composition: A time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer study. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, J.H.; Mouritsen, O.G.; Bloom, M. Relationships between lipid membrane area, hydrophobic thickness, and acyl-chain orientational order. The effects of cholesterol. Biophys. J. 1990, 57, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.R.; Whitehead, J.P.; Lu, D. Chain-length dependence of lipid bilayer properties near the liquid crystal to gel phase transition. Biophys. J. 1992, 63, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, T.T.; Toombes, G.E.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Smilgies, D.M.; Feigenson, G.W.; Nagle, J.F. Order parameters and areas in fluid-phase oriented lipid membranes using wide angle X-ray scattering. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, H. Probing the structure and dynamics of caveolin-1 in a caveolae-mimicking asymmetric lipid bilayer model. Eur. Biophys. J. EBJ 2016, 45, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raggi, C.; Diociaiuti, M.; Caracciolo, G.; Fratini, F.; Fantozzi, L.; Piccaro, G.; Fecchi, K.; Pizzi, E.; Marano, G.; Ciaffoni, F.; et al. Caveolin-1 Endows Order in Cholesterol-Rich Detergent Resistant Membranes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070287
Raggi C, Diociaiuti M, Caracciolo G, Fratini F, Fantozzi L, Piccaro G, Fecchi K, Pizzi E, Marano G, Ciaffoni F, et al. Caveolin-1 Endows Order in Cholesterol-Rich Detergent Resistant Membranes. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(7):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070287
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaggi, Carla, Marco Diociaiuti, Giulio Caracciolo, Federica Fratini, Luca Fantozzi, Giovanni Piccaro, Katia Fecchi, Elisabetta Pizzi, Giuseppe Marano, Fiorella Ciaffoni, and et al. 2019. "Caveolin-1 Endows Order in Cholesterol-Rich Detergent Resistant Membranes" Biomolecules 9, no. 7: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070287
APA StyleRaggi, C., Diociaiuti, M., Caracciolo, G., Fratini, F., Fantozzi, L., Piccaro, G., Fecchi, K., Pizzi, E., Marano, G., Ciaffoni, F., Bravo, E., Fiani, M. L., & Sargiacomo, M. (2019). Caveolin-1 Endows Order in Cholesterol-Rich Detergent Resistant Membranes. Biomolecules, 9(7), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070287





