Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes
Abstract
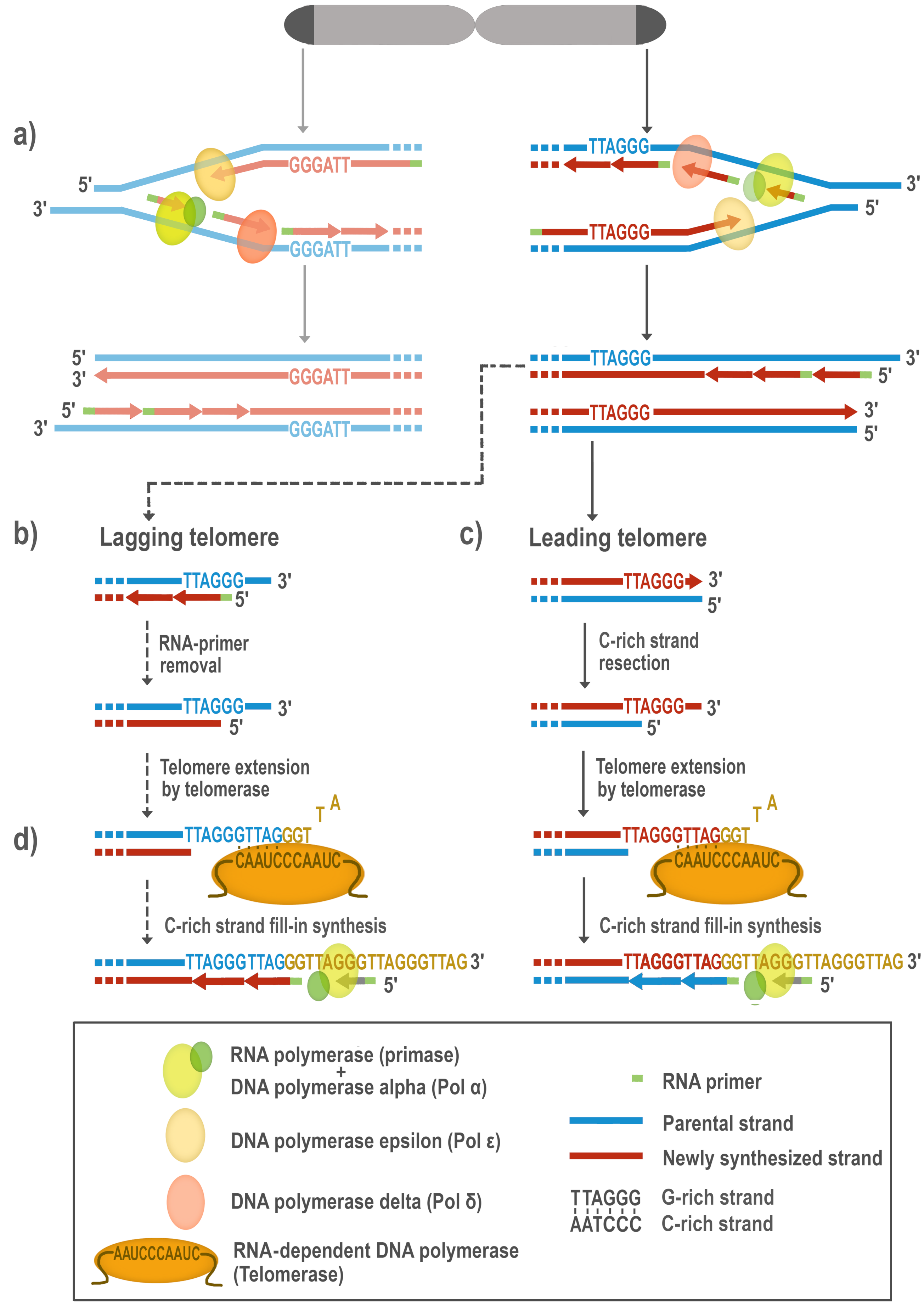
1. Telomerase Activity
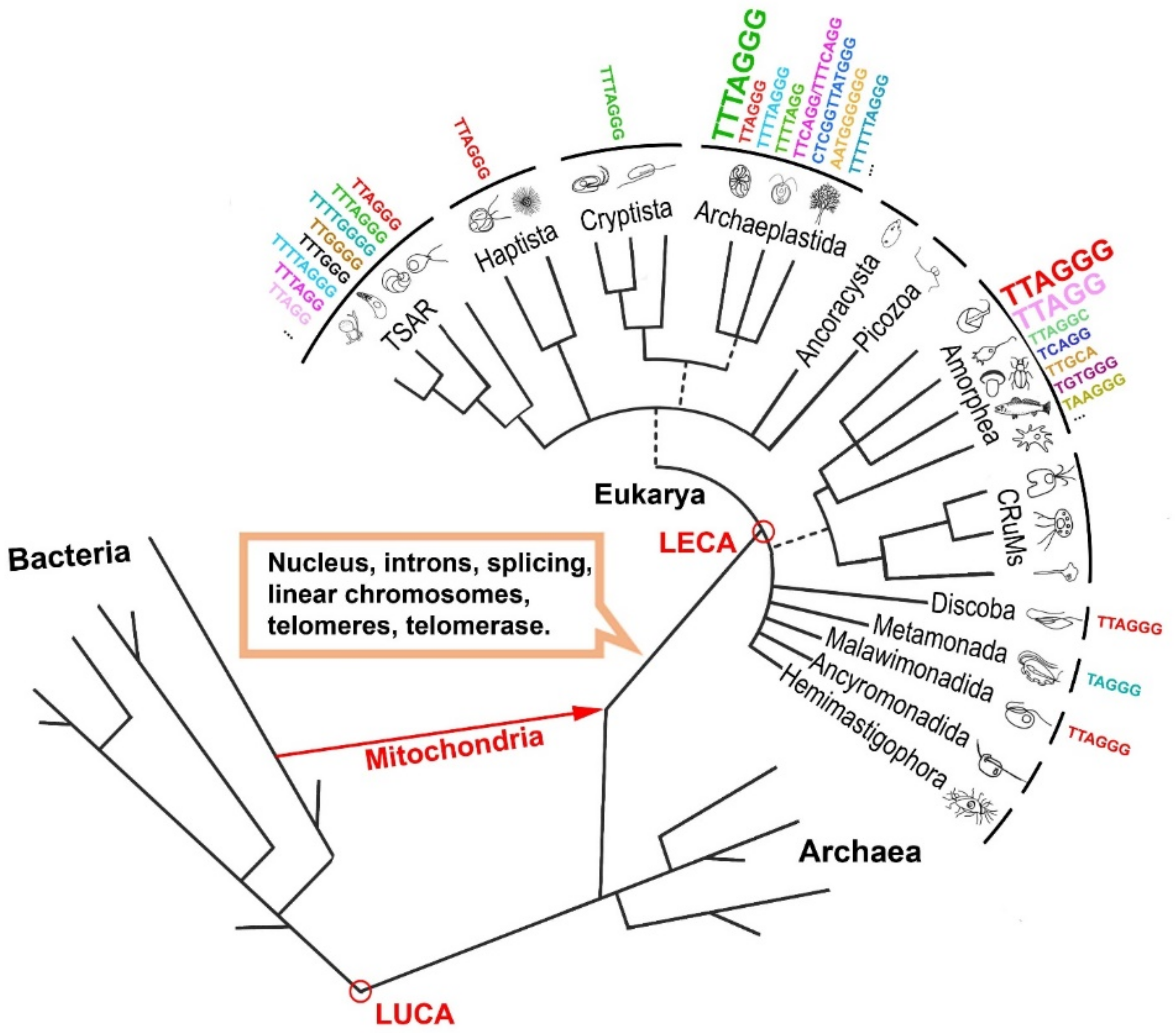
2. The Origin of Telomerase
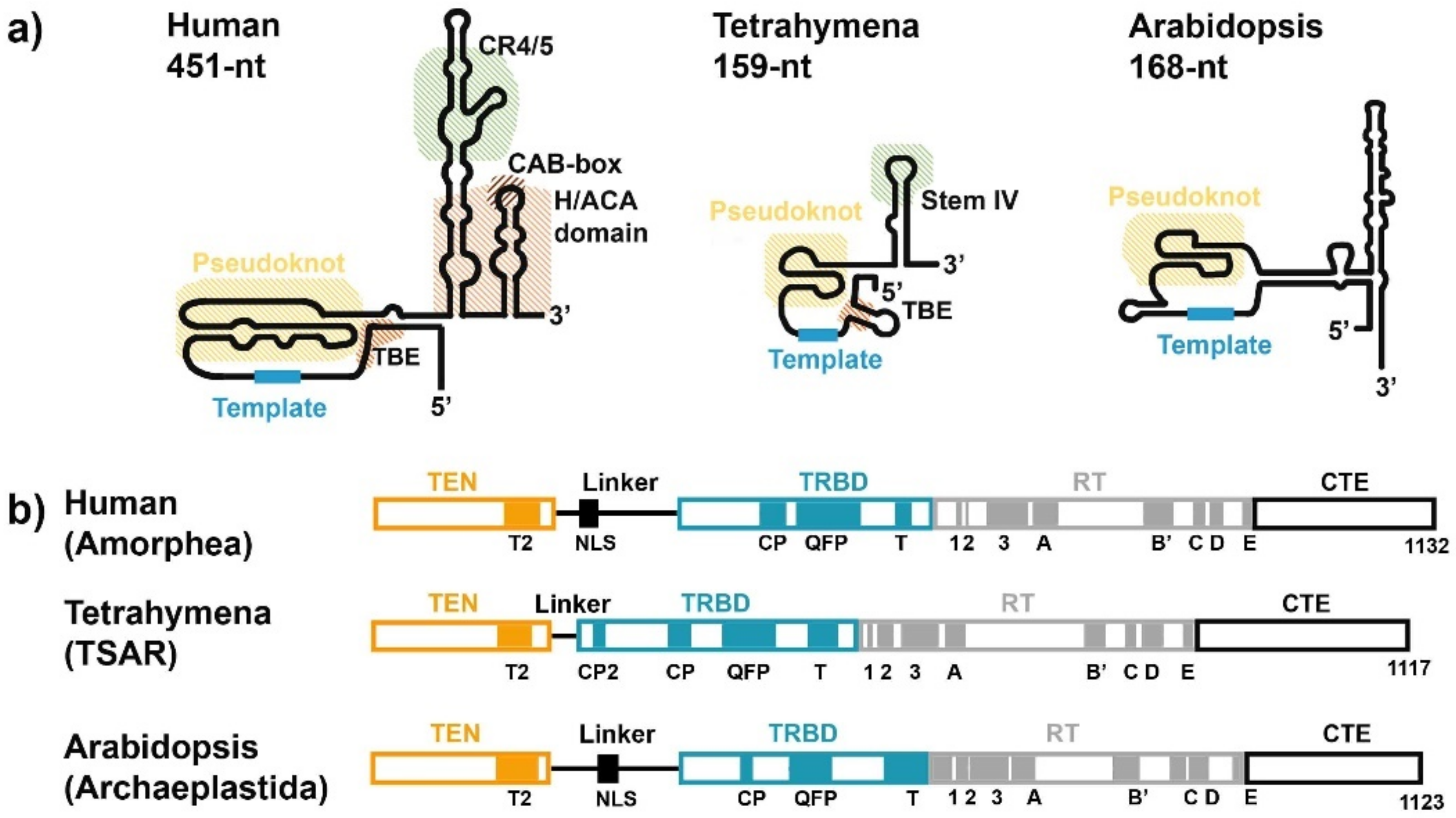
3. RNA Subunit of Telomerase
4. TERT Subunit of Telomerase
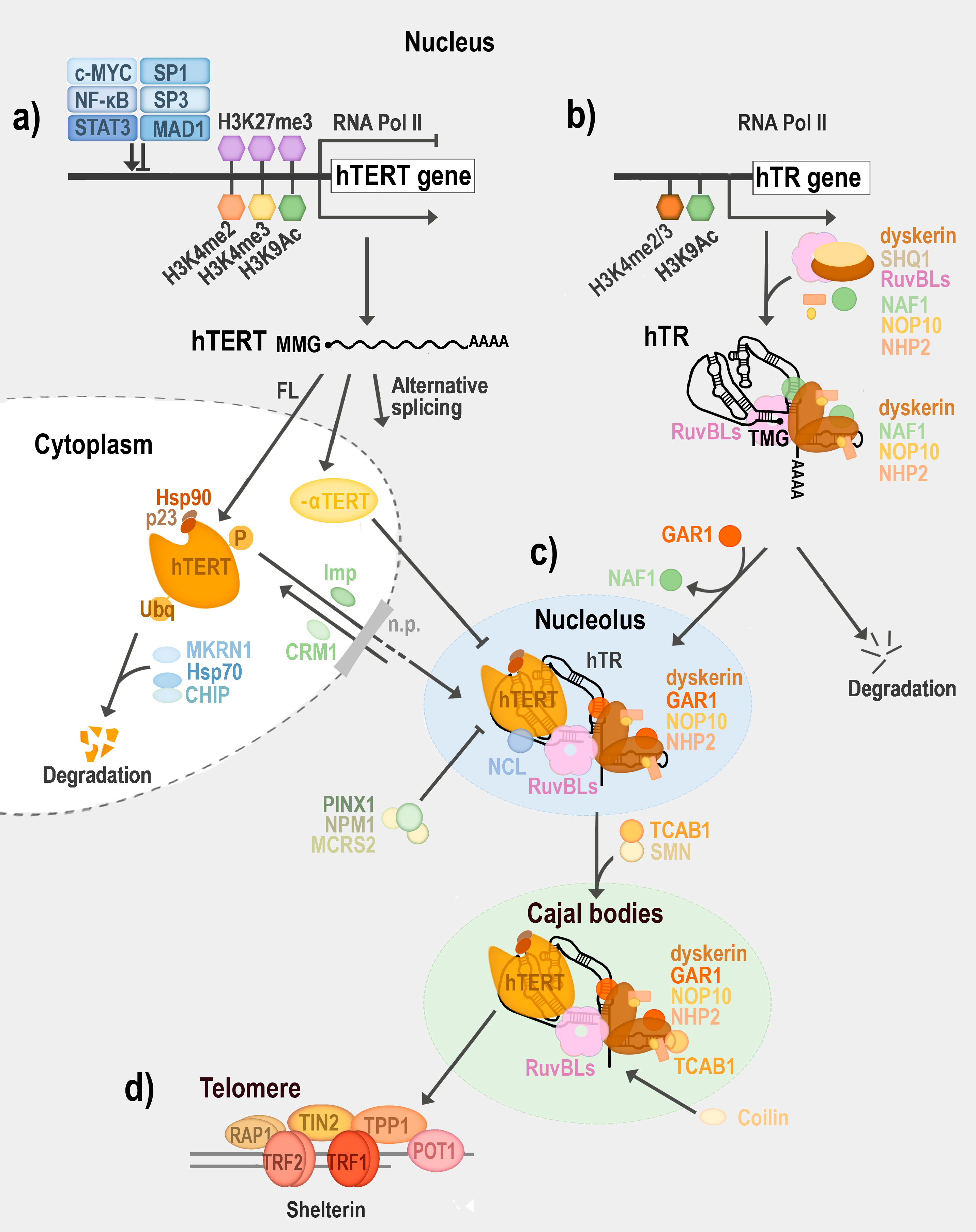
5. Telomerase Regulation
6. Composition of Enzymatically Active Telomerase
7. Conclusions
Abreviations
| h | human |
| AAA+ | ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities |
| ALT | alternative mechanisms of lengthening of telomeres |
| ARM | armadillo/β-catenin-like repeat-containing protein |
| At | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| CAB-box | Cajal body-box |
| CBF5 | centromere-binding factor |
| CR4/5 | conserved region 4/5 |
| CRM1 | chromosome region maintenance 1 protein homolog |
| CRuMs | collodictyonids, Rigifilida, Mantamonas |
| CTE | C-terminal extension |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| DNA Pol α | DNA polymerase alpha |
| DNA Pol δ | DNA polymerase delta |
| DNA Pol ε | DNA polymerase epsilon |
| eToL | Tree of Life |
| FHC | fetal human colon |
| FL | full-length |
| GAR1,2 | Glycine Arginine Rich 1, 2 |
| H/ACA | H/ACA (H-box (consensus ANANNA) and ACA-box (ACA)) |
| HR | homologous recombination |
| Hsp70 | heat shock protein 70 |
| Hsp90 | heat shock protein 90 |
| HT-29 | adenocarcinoma colon |
| CHIP | carboxyl-terminus of Hsp70 Interacting Protein |
| CHR19 | chromatin remodeling 19 |
| Imp | importin |
| LECA | last eukaryote common ancestor |
| LUCA | last universal common ancestor |
| MCRS2 | microspherule protein 2 |
| MKRN1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase makorin-1 |
| MMG | monomethylguanosine |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| mtDNA | mitochondrial DNA |
| n.p. | nuclear pores |
| NAF1 | nuclear assembly factor 1 |
| NCL | nucleolin |
| NF- κB | nuclear factor κB |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NHP2 | non-histone protein 2 |
| NLS | nucleus localization-like signal |
| non-LTR-retrotransposons | non-long-terminal-repeat retrotransposons |
| NOP10 | nucleolar protein 10 |
| NPM | nucleophosmin |
| NUC-L1 | nucleolin-like1 |
| P | phosphorylation |
| p23 | co-chaperone |
| PINX1 | PIN2/TERF1—interacting telomerase inhibitor 1 |
| poly (A) tail | polyadenylate tail |
| POT1 | protection of telomeres protein 1 |
| POT1a | protection of telomeres protein 1a |
| RAP1 | repressor/activator site binding protein |
| RID1 | RNA interaction domain 1 |
| RNA Pol II | RNA polymerase II |
| RNA Pol III | RNA polymerase III |
| RNPs | ribonucleoproteins |
| RT | reverse transcriptase |
| RT domain | reverse transcriptase motifs domain |
| RT-qPCR | reverse transcription-quantitative PCR |
| RuvBL1 | RuvB-like 1 AAA+ ATPases (pontin) |
| RuvBL2 | RuvB-like 2 AAA+ ATPases (reptin) |
| scaRNA | small Cajal body RNA |
| SHQ1 | snRNA of the box H/ACA family quantitative accumulation 1 |
| SMN | survival motor neuron protein |
| snoRNA | small nucleolar RNA |
| SP1/3 | specificity protein 1/3 |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of Transcription 3 |
| t/PK | template/pseudoknot |
| TAC1 | telomerase activator 1 |
| TBE | template boundary element |
| TCAB1 | telomere cajal body protein 1 |
| TEN | telomerase essential N-terminal domain |
| TERT | catalytic telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TIN2 | TRF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 |
| TMG | N2, 2, 7 trimethylguanosine |
| TPP1 | TIN2- and POT1-organizing protein |
| TR, TER, TERC | telomerase RNA component |
| TRBD | RNA-binding domain |
| TRF1/2 | telomeric-repeat binding factor 1/2 |
| TSAR | telonemids, stramenopiles, alveolates, and Rhizaria |
| Ubq | ubiquitin |
| USE | upstream sequence element |
| Wnt/β-catenin | wnt/beta-catenin |
| - α TERT | minus alpha TERT |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olovnikov, A.M. Principle of marginotomy in template synthesis of polynucleotides. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1971, 201, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greider, C.W. Telomeres and senescence: The history, the experiment, the future. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, R178–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, G.; Lansdorp, P.M. Telomeres and Aging. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leman, A.; Noguchi, E. The Replication Fork: Understanding the Eukaryotic Replication Machinery and the Challenges to Genome Duplication. Genes 2013, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, E.; Géli, V. How telomeres are replicated. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diede, S.J.; Gottschling, D.E. Telomerase-Mediated Telomere Addition In Vivo Requires DNA Primase and DNA Polymerases α and δ. Cell 1999, 99, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fojtová, M.; Fajkus, J. Telomeres in Plants and Humans: Not So Different, Not So Similar. Cells 2019, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Senescence and immortalization: Role of telomeres and telomerase. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Kovařík, A.; Královics, R. Telomerase activity in plant cells. FEBS Lett. 1996, 391, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurečková, J.F.; Sýkorová, E.; Hafidh, S.; Honys, D.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M. Tissue-specific expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase gene variants in Nicotiana tabacum. Planta 2017, 245, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrocká, A.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M. Developmental silencing of the AtTERT gene is associated with increased H3K27me3 loading and maintenance of its euchromatic environment. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riha, K.; Fajkus, J.; Siroky, J.; Vyskot, B. Developmental Control of Telomere Lengths and Telomerase Activity in Plants. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachová, D.; Fojtová, M.; Dvořáčková, M.; Mozgová, I.; Lermontova, I.; Peška, V.; Schubert, I.; Fajkus, J.; Sýkorová, E. Structure-function relationships during transgenic telomerase expression in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 149, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Telomeres and telomerase: Three decades of progress. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.-S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Human Telomerase and Its Regulation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilion, A.A.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Gupta, J.; Shay, J.W.; Bacchetti, S.; Greider, C.W. Human Telomerase RNA and Telomerase Activity in Immortal Cell Lines and Tumor Tissues. Cancer Res. 1996, 1996, 645–650. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Hodes, R.J.; Weng, N. Cutting Edge: Telomerase Activation in Human T Lymphocytes Does Not Require Increase in Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Protein but Is Associated with hTERT Phosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4826–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, N.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Hodes, R.J. Regulation of telomerase RNA template expression in human T lymphocyte development and activation. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3215–3220. [Google Scholar]
- Fajkus, P.; Peška, V.; Závodník, M.; Fojtová, M.; Fulnečková, J.; Dobias, Š.; Kilar, A.; Dvořáčková, M.; Zachová, D.; Nečasová, I.; et al. Telomerase RNAs in land plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 9842–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Okada, T.; Fukushima, T.; Tsudzuki, T.; Sugiura, M.; Yukawa, Y. A novel hypoxic stress-responsive long non-coding RNA transcribed by RNA polymerase III in Arabidopsis. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell 1987, 51, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J. Telomere- and Telomerase-Associated Proteins and Their Functions in the Plant Cell. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Parrinello, S.; Kim, J.; Campisi, J. Mus musculus and Mus spretus homologues of the human telomere-associated protein TIN2. Genomics 2003, 81, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, F.; Roger, A.J.; Brown, M.W.; Simpson, A.G.B. The New Tree of Eukaryotes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Mirkin, S.M. At the Beginning of the End and in the Middle of the Beginning: Structure and Maintenance of Telomeric DNA Repeats and Interstitial Telomeric Sequences. Genes 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepsiova, R.; Necasova, I.; Willcox, S.; Prochazkova, K.; Gorilak, P.; Nosek, J.; Hofr, C.; Griffith, J.D.; Tomaska, L. Evolution of Telomeres in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Its Possible Relationship to the Diversification of Telomere Binding Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, V.; Grozeva, S.; Gokhman, V. Telomere structure in insects: A review. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2020, 58, 127–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, M.; Král, J.; Traut, W.; Zrzavý, J.; Marec, F. The evolutionary origin of insect telomeric repeats, (TTAGG) N. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicky, C.; Villeneuve, A.M.; Lauper, N.; Codourey, L.; Tobler, H.; Muller, F. Telomeric repeats (TTAGGC)n are sufficient for chromosome capping function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8983–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenák, F.; Juríková, K.; Sepšiová, R.; Neboháčová, M.; Nosek, J.; Tomáška, L. Double-stranded telomeric DNA binding proteins: Diversity matters. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Osanai, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Kojima, K.K. Telomere-specific non-LTR retrotransposons and telomere maintenance in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casacuberta, E. Drosophila: Retrotransposons Making up Telomeres. Viruses 2017, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servant, G.; Deininger, P.L. Insertion of Retrotransposons at Chromosome Ends: Adaptive Response to Chromosome Maintenance. Front. Genet. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Fujiwara, H. Detection and distribution patterns of telomerase activity in insects: Telomerase activity in insects. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Okazaki, S.; Fujiwara, H. A New Family of Site-Specific Retrotransposons, SART1, Is Inserted into Telomeric Repeats of the Silkworm, Bombyx Mori. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.M.; Randall, T.A.; Capkova Frydrychova, R. Telomerase lost? Chromosoma 2016, 125, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V. The origin of introns and their role in eukaryogenesis: a compromise solution to the introns-early versus introns-late debate? Biol. Direct 2006, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulnečková, J.; Ševčíková, T.; Fajkus, J.; Lukešová, A.; Lukeš, M.; Vlček, Č.; Lang, B.F.; Kim, E.; Eliáš, M.; Sýkorová, E. A Broad Phylogenetic Survey Unveils the Diversity and Evolution of Telomeres in Eukaryotes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adl, S.M.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Bass, D.; Bowser, S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; Dunthorn, M.; Hampl, V.; et al. The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 429–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, E.J.; Ausubel, F.M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 1988, 53, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Kunická, Z.; Chase, M.W.; Bennett, M.D.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. Telomere variability in the monocotyledonous plant order Asparagales. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sýkorová, E.; Leitch, A.R.; Fajkus, J. Asparagales Telomerases which Synthesize the Human Type of Telomeres. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, P.; Peška, V.; Sitová, Z.; Fulnečková, J.; Dvořáčková, M.; Gogela, R.; Sýkorová, E.; Hapala, J.; Fajkus, J. Allium telomeres unmasked: The unusual telomeric sequence (CTCGGTTATGGG) n is synthesized by telomerase. Plant J. 2016, 85, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peška, V.; Fajkus, P.; Fojtová, M.; Dvořáčková, M.; Hapala, J.; Dvořáček, V.; Polanská, P.; Leitch, A.R.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Characterisation of an unusual telomere motif (TTTTTTAGGG) n in the plant Cestrum elegans (Solanaceae), a species with a large genome. Plant J. 2015, 82, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.D.; Cao, H.X.; Jovtchev, G.; Neumann, P.; Novák, P.; Fojtová, M.; Vu, G.T.H.; Macas, J.; Fajkus, J.; Schubert, I.; et al. Centromere and telomere sequence alterations reflect the rapid genome evolution within the carnivorous plant genus Genlisea. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulnečková, J.; Ševčíková, T.; Lukešová, A.; Sýkorová, E. Transitions between the Arabidopsis-type and the human-type telomere sequence in green algae (clade Caudivolvoxa, Chlamydomonadales). Chromosoma 2016, 125, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peska, V.; Garcia, S. Origin, Diversity, and Evolution of Telomere Sequences in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, T. A loopy view of telomere evolution. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Group II Introns: Mobile Ribozymes that Invade DNA. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.M. Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Homologs from Fission Yeast and Human. Science 1997, 277, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingner, J. Reverse Transcriptase Motifs in the Catalytic Subunit of Telomerase. Science 1997, 276, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeke, J.D. The Unusual Phylogenetic Distribution of Retrotransposons: A Hypothesis. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreesen, O. Telomere structure and shortening in telomerase-deficient Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4536–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardini, M.A.; Lira, C.B.B.; Conte, F.F.; Camillo, L.R.; de Siqueira Neto, J.L.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Cano, M.I.N. The putative telomerase reverse transcriptase component of Leishmania amazonensis: Gene cloning and characterization. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 98, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlevsky, J.D.; Chen, J.J.-L. Evolutionary perspectives of telomerase RNA structure and function. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Chakrabarti, K. Current Perspectives of Telomerase Structure and Function in Eukaryotes with Emerging Views on Telomerase in Human Parasites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragnet, L.; Blasco, M.A.; Klapper, W.; Rasschaert, D. The RNA Subunit of Telomerase Is Encoded by Marek’s Disease Virus. JVI 2003, 77, 5985–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp-Fragnet, L.; Marie-Egyptienne, D.; Fakhoury, J.; Rasschaert, D.; Autexier, C. The human telomerase catalytic subunit and viral telomerase RNA reconstitute a functional telomerase complex in a cell-free system, but not in human cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; Gupta, J.; Bacchetti, S.; Reddel, R.R. Telomere elongation in immortal human cells without detectable telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, M.A.; Neumann, A.A.; Fasching, C.L.; Reddel, R.R. Telomere maintenance by recombination in human cells. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, V.; Blackburn, E.H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1− senescence. Cell 1993, 73, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Růčková, E.; Friml, J.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fajkus, J. Role of alternative telomere lengthening unmasked in telomerase knock-out mutant plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachouri-Lafond, R.; Dujon, B.; Gilson, E.; Westhof, E.; Fairhead, C.; Teixeira, M.T. Large telomerase RNA, telomere length heterogeneity and escape from senescence in Candida glabrata. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3605–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, E.D.; Collins, K. Biogenesis of telomerase ribonucleoproteins. RNA 2012, 18, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K. The biogenesis and regulation of telomerase holoenzymes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Funk, W.; Wang, S.; Weinrich, S.; Avilion, A.; Chiu, C.; Adams, R.; Chang, E.; Allsopp, R.; Yu, J.; et al. The RNA component of human telomerase. Science 1995, 269, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew-Budd, K.; Cheung, J.; Palos, K.; Forsythe, E.S.; Beilstein, M.A. Evolutionary and biochemical analyses reveal conservation of the Brassicaceae telomerase ribonucleoprotein complex. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0222687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Kannan, K.; Tseng, L.; Shippen, D.E. Two RNA subunits and POT1a are components of Arabidopsis telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Kannan, K.; Tseng, L.; Shippen, D.E. Retraction for Cifuentes-Rojas et al., Two RNA subunits and POT1a are components of Arabidopsis telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.A.; Upton, H.E.; Vogan, J.M.; Collins, K. Telomerase Mechanism of Telomere Synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Logeswaran, D.; Castillo-González, C.; Li, Y.; Bose, S.; Aklilu, B.B.; Ma, Z.; Polkhovskiy, A.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Shippen, D.E. The conserved structure of plant telomerase RNA provides the missing link for an evolutionary pathway from ciliates to humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24542–24550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chan, H.; Cash, D.D.; Miracco, E.J.; Ogorzalek Loo, R.R.; Upton, H.E.; Cascio, D.; O’Brien Johnson, R.; Collins, K.; Loo, J.A.; et al. Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase reveals previously unknown subunits, functions, and interactions. Science 2015, 350, aab4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Qi, X.; Bley, C.J.; Chen, J.J.-L. A novel motif in telomerase reverse transcriptase regulates telomere repeat addition rate and processivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1982–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.; Wang, Y.; Feigon, J. Progress in Human and Tetrahymena Telomerase Structure Determination. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 46, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Structure-function relationships in telomerase genes. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowiak, A.A.; Narayanan, A.; Li, Z.H.; Terns, R.M.; Terns, M.P. The snoRNA domain of vertebrate telomerase RNA functions to localize the RNA within the nucleus. RNA 2001, 7, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Tomlinson, R.L.; Lukowiak, A.A.; Terns, R.M.; Terns, M.P. Telomerase RNA Accumulates in Cajal Bodies in Human Cancer Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.; Funk, W.; Villeponteau, B.; Greider, C. Functional characterization and developmental regulation of mouse telomerase RNA. Science 1995, 269, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Filipowicz, W. Exonucleolytic processing of small nucleolar RNAs from pre-mRNA introns. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Fayet-Lebaron, E.; Jády, B.E. Box H/ACA Small Ribonucleoproteins. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, A.; Cowling, V.H. mRNA cap regulation in mammalian cell function and fate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta -Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Roake, C.M.; Galati, A.; Bavasso, F.; Micheli, E.; Saggio, I.; Schoeftner, S.; Cacchione, S.; Gatti, M.; Artandi, S.E.; et al. Loss of Human TGS1 Hypermethylase Promotes Increased Telomerase RNA and Telomere Elongation. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jády, B.E.; Bertrand, E.; Kiss, T. Human telomerase RNA and box H/ACA scaRNAs share a common Cajal body–specific localization signal. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, D.; Bensoussan, H.; Autexier, C. Telomerase Regulation from Beginning to the End. Genes 2016, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubtsova, M.; Dontsova, O. Human Telomerase RNA: Telomerase Component or More? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robart, A.R.; Collins, K. Investigation of Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Assembly, Activity, and Processivity Using Disease-linked Subunit Variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4375–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Brown, A.F.; Wu, J.; Xue, J.; Bley, C.J.; Rand, D.P.; Wu, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Lei, M. Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Logeswaran, D.; Chen, J.J. A single nucleotide incorporation step limits human telomerase repeat addition activity. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.; Greider, C.W. Tetrahymena telomerase catalyzes nucleolytic cleavage and nonprocessive elongation. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, N.F. A Physical and Functional Constituent of Telomerase Anchor Site. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26586–26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, B.M.; Parks, J.W.; Stone, M.D. The telomerase essential N-terminal domain promotes DNA synthesis by stabilizing short RNA-DNA hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5537–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, E.M.; Slivka, J.D.; Payne, B.; Comstock, M.J.; Schmidt, J.C. Observation of processive telomerase catalysis using high-resolution optical tweezers. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, T.J.; Marie-Egyptienne, D.T.; Autexier, C. Functional Organization of Repeat Addition Processivity and DNA Synthesis Determinants in the Human Telomerase Multimer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 3720–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sauerwald, A.; Sandin, S.; Cristofari, G.; Scheres, S.H.W.; Lingner, J.; Rhodes, D. Structure of active dimeric human telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, S.; Rhodes, D. Telomerase structure. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 25, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Tam, J.; Wu, R.A.; Greber, B.J.; Toso, D.; Nogales, E.; Collins, K. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2018, 557, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Miracco, E.J.; Hong, K.; Eckert, B.; Chan, H.; Cash, D.D.; Min, B.; Zhou, Z.H.; Collins, K.; Feigon, J. The architecture of Tetrahymena telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2013, 496, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerská, J.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Dokládal, L.; Schořová, Š.; Stejskal, K.; Obořil, M.; Honys, D.; Kozáková, L.; Polanská, P.S.; Sýkorová, E. Tandem affinity purification of AtTERT reveals putative interaction partners of plant telomerase in vivo. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergai, O.; Hernandez, N. How to Recruit the Correct RNA Polymerase? Lessons from snRNA Genes. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.D.; Collins, K. Biological and Biochemical Functions of RNA in the Tetrahymena Telomerase Holoenzyme. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4442–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roake, C.M.; Artandi, S.E. Regulation of human telomerase in homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, H.S.; Burke, W.D.; Eickbush, T.H. Putative telomerase catalytic subunits from Giardia lamblia and Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 2000, 251, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.G.; Pouchkina-Stantcheva, N.; Di Donfrancesco, A.; Kildisiute, G.; Sahu, S.; Aboobaker, A.A. The protein subunit of telomerase displays patterns of dynamic evolution and conservation across different metazoan taxa. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Khadka, P.; Chung, I.K. Nuclear import of hTERT requires a bipartite nuclear localization signal and Akt-mediated phosphorylation. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2684–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.; Rice, C.; Skordalakes, E. Structural Analysis Reveals the Deleterious Effects of Telomerase Mutations in Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4593–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autexier, C.; Lue, N.F. The Structure and Function of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 493–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, A.; Bowtell, D.D.L.; Abud, H.E.; Hime, G.R.; Venter, D.J.; Keese, P.K.; Duncan, E.L.; Reddel, R.R.; Jefferson, R.A. Isolation of a Candidate Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Gene, Which Reveals Complex Splicing Patterns in Different Cell Types. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, L.; Zhou, W.; McPhail, T.; Oulton, R.; Yeung, D.S.K.; Mar, V.; Bass, M.B.; Robinson, M.O. Human telomerase contains evolutionarily conserved catalytic and structural subunits. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3109–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerson, M.; Counter, C.M.; Eaton, E.N.; Ellisen, L.W.; Steiner, P.; Caddle, S.D.; Ziaugra, L.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Davidoff, M.J.; Liu, Q.; et al. hEST2, the Putative Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Gene, Is Up-Regulated in Tumor Cells and during Immortalization. Cell 1997, 90, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, E.; Fulnečková, J.; Mokroš, P.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M.; Peška, V. Three TERT genes in Nicotiana tabacum. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, E.; Tergaonkar, V. Transcriptional Regulation of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) by MYC. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, M.-M.; Chang, X.; Zeng, S.; Liu, C.; Liao, G.-B.; Wu, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, C.-J.; Yang, S.-M.; Li, X.-Z. Diverse regulatory manners of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlee, M.; Wang, J.; Toh, W.; Li, S. Transcription Regulation of the Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Gene. Genes 2016, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavin, P.; Redmond, A.; McBryan, J.; Cocchiglia, S.; Tibbitts, P.; Fahy-Browne, P.; Kay, E.; Treumann, A.; Perrem, K.; McIlroy, M.; et al. RuvBl2 cooperates with Ets2 to transcriptionally regulate hTERT in colon cancer. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, M.; Kyo, S.; Kanaya, T.; Hirano, H.; Takeda, J.; Yutsudo, M.; Inoue, M. Cloning of Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit (hTERT) Gene Promoter and Identification of Proximal Core Promoter Sequences Essential for Transcriptional Activation in Immortalized and Cancer Cells. Cancer Research 1999, 59, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horikawa, I.; Cable, P.L.; Afshari, C.; Barrett, J.C. Cloning and Characterization of the Promoter Region of Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crhák, T.; Zachová, D.; Fojtová, M.; Sýkorová, E. The region upstream of the telomerase reverse transcriptase gene is essential for in planta telomerase complementation. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.L.; Theodorescu, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Cech, T.R. Mutation of the TERT promoter, switch to active chromatin, and monoallelic TERT expression in multiple cancers. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akıncılar, S.C.; Khattar, E.; Boon, P.L.S.; Unal, B.; Fullwood, M.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Long-Range Chromatin Interactions Drive Mutant TERT Promoter Activation. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Fulnečková, J.; Hulánová, M.; Berková, K.; Říha, K.; Matyášek, R. Plant cells express telomerase activity upon transfer to callus culture, without extensively changing telomere lengths. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 260, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Wen, J.; Bacchetti, S. The human telomerase catalytic subunit hTERT: Organization of the gene and characterization of the promoter. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosz, W.; Pfab, A.; Ehrnsberger, H.F.; Holzinger, P.; Köllen, K.; Mortensen, S.A.; Bruckmann, A.; Schubert, T.; Längst, G.; Griesenbeck, J.; et al. The Composition of the Arabidopsis RNA Polymerase II Transcript Elongation Complex Reveals the Interplay between Elongation and mRNA Processing Factors. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 854–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.L.; Paucek, R.D.; Huang, F.W.; Ghandi, M.; Nwumeh, R.; Costello, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Allele-Specific DNA Methylation and Its Interplay with Repressive Histone Marks at Promoter-Mutant TERT Genes. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3700–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodnar, A.G. Extension of Life-Span by Introduction of Telomerase into Normal Human Cells. Science 1998, 279, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdlickova, R.; Nehyba, J.; Bose, H.R. Alternatively Spliced Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Variants Lacking Telomerase Activity Stimulate Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4283–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Kwon, T.; Kwon, D.Y.; Do, S.I. Akt Protein Kinase Enhances Human Telomerase Activity through Phosphorylation of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13085–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. Ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 modulates telomere length homeostasis through a proteolysis of hTERT. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, K.; Tamura, K.; Takahashi, H. Characterization of Oryza sativa telomerase reverse transcriptase and possible role of its phosphorylation in the control of telomerase activity. Gene 2004, 342, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Jin, E.; Chung, I.K.; Kim, W.T. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of telomerase activity by auxin, abscisic acid and protein phosphorylation in tobacco BY-2 suspension culture cells. Plant J. 2002, 29, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.A.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, J.S.; Khadka, P.; Cho, H.-S.; Chung, I.K. Akt-mediated phosphorylation increases the binding affinity of hTERT for importin to promote nuclear translocation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.S.; Riha, K.; Gao, F.; Ren, S.; McKnight, T.D.; Shippen, D.E. Disruption of the telomerase catalytic subunit gene from Arabidopsis inactivates telomerase and leads to a slow loss of telomeric DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14813–14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.P.; Hoare, S.F.; Glasspool, R.M.; Keith, W.N. Lack of Telomerase Gene Expression in Alternative Lengthening of Telomere Cells Is Associated with Chromatin Remodeling of the hTR and hTERT Gene Promoters. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7585–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, C.J.; Hoare, S.F.; Daidone, M.-G.; Zaffaroni, N.; Keith, W.N. High level of telomerase RNA gene expression is associated with chromatin modification, the ALT phenotype and poor prognosis in liposarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J.; Záveská Drábková, L.; Honys, D.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P. The plant Pontin and Reptin homologues, Ruv BL 1 and Ruv BL 2a, colocalize with TERT and TRB proteins in vivo, and participate in telomerase biogenesis. Plant J. 2019, 98, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendle, A.F.; Clark, G.P.; Boon, R.; Lewandowska, D.; Lam, Y.W.; Andersen, J.; Mann, M.; Lamond, A.I.; Brown, J.W.S.; Shaw, P.J. Proteomic Analysis of the Arabidopsis Nucleolus Suggests Novel Nucleolar Functions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lermontova, I.; Schubert, V.; Börnke, F.; Macas, J.; Schubert, I. Arabidopsis CBF5 interacts with the H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor NAF1. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurts, S.; Masutomi, K.; Delgermaa, L.; Arai, K.; Oishi, N.; Mizuno, H.; Hayashi, N.; Hahn, W.C.; Murakami, S. Nucleolin Interacts with Telomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51508–51515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontvianne, F.; Carpentier, M.-C.; Durut, N.; Pavlištová, V.; Jaške, K.; Schořová, Š.; Parrinello, H.; Rohmer, M.; Pikaard, C.S.; Fojtová, M.; et al. Identification of Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains Reveals a Role for the Nucleolus in 3D Organization of the A. thaliana Genome. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontvianne, F.; Abou-Ellail, M.; Douet, J.; Comella, P.; Matia, I.; Chandrasekhara, C.; DeBures, A.; Blevins, T.; Cooke, R.; Medina, F.J.; et al. Nucleolin Is Required for DNA Methylation State and the Expression of rRNA Gene Variants in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Meng, Z.; Mason, P.J.; Veenstra, T.D.; Artandi, S.E. Identification of ATPases Pontin and Reptin as Telomerase Components Essential for Holoenzyme Assembly. Cell 2008, 132, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.R.; Hebert, M.D. SMN and coilin negatively regulate dyskerin association with telomerase RNA. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, M.D.; Shpargel, K.B.; Ospina, J.K.; Tucker, K.E.; Matera, A.G. Coilin Methylation Regulates Nuclear Body Formation. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorackova, M. Analysis of Arabidopsis Telomere-Associated Proteins in Vivo. Ph.D. Thesis, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, F.L.; Batista, L.F.Z.; Freund, A.; Pech, M.F.; Venteicher, A.S.; Artandi, S.E. TPP1 OB-Fold Domain Controls Telomere Maintenance by Recruiting Telomerase to Chromosome Ends. Cell 2012, 150, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Vychodilová, I.; Dvořáčková, M.; Majerská, J.; Dokládal, L.; Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J. Telomere repeat binding proteins are functional components of Arabidopsis telomeres and interact with telomerase. Plant J. 2014, 77, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Telomerase Activity in Human Development Is Regulated by Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Transcription and by Alternate Splicing of hTERT Transcripts. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar]
- Nehyba, J.; Hrdlickova, R.; Bose, H.R. The Regulation of Telomerase by Alternative Splicing of TERT. In Reviews on Selected Topics of Telomere Biology; Li, B., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0849-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Tissue-specific alternate splicing of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) influences telomere lengths during human development. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, C.A.; Wolny, Y.M.; Adler, R.R.; Cohen, J. Alternative splicing of the telomerase catalytic subunit in human oocytes and embryos. MHR Basic Sci. Reprod. Med. 1999, 5, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, R.; Esumi, S.; Yagi, T.; Hirabayashi, T. Predominant Expression of rTERTb, an Inactive TERT Variant, in the Adult Rat Brain. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, A.T.; Slusher, A.L.; Sayed, M.E. Insights into Telomerase/hTERT Alternative Splicing Regulation Using Bioinformatics and Network Analysis in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Alternative splicing regulation of telomerase: A new paradigm? Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colgin, L.M.; Wilkinso, C.; Englezou, A.; Kilian, A.; Robinson, M.O.; Reddel, R.R. The hTERTα Splice Variant is a Dominant Negative Inhibitor of Telomerase Activity. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunická, Z.; Mucha, I.; Fajkus, J. Telomerase activity in head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3125–3129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Listerman, I.; Sun, J.; Gazzaniga, F.S.; Lukas, J.L.; Blackburn, E.H. The Major Reverse Transcriptase-Incompetent Splice Variant of the Human Telomerase Protein Inhibits Telomerase Activity but Protects from Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2817–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignol, P.; Collier, S.; Bush, M.; Shaw, P.; Doonan, J.H. Arabidopsis POT1A interacts with TERT-V(I8), an N-terminal splicing variant of telomerase. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotková, G.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Protect and regulate: Recent findings on plant POT1-like proteins. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Liu, H.; Takahashi, H. Auxin Induction of Cell Cycle Regulated Activity of Tobacco Telomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20997–21002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Johnston, J.S.; Shippen, D.E.; McKnight, T.D. TELOMERASE ACTIVATOR1 Induces Telomerase Activity and Potentiates Responses to Auxin in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2910–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Mandadi, K.K.; Boedeker, A.L.; Rathore, K.S.; McKnight, T.D. Regulation of Telomerase in Arabidopsis by BT2, an Apparent Target of TELOMERASE ACTIVATOR1. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Grenier St-Sauveur, V.; Bergeron, D.; Dupuis-Sandoval, F.; Scott, M.S.; Bachand, F. A Polyadenylation-Dependent 3′ End Maturation Pathway Is Required for the Synthesis of the Human Telomerase RNA. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-K.; Wang, H.-F.; Burns, A.M.; Schroeder, M.R.; Gaspari, M.; Baumann, P. Human Telomerase RNA Processing and Quality Control. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerská, J.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Non-telomeric activities of telomerase. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, M.A.; Rizen, M.; Greider, C.W.; Hanahan, D. Differential regulation of telomerase activity and telomerase RNA during multi-stage tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedde, M.; le Sage, C.; Duursma, A.; Zlotorynski, E.; van Leeuwen, B.; Nijkamp, W.; Beijersbergen, R.; Agami, R. Telomerase-independent Regulation of ATR by Human Telomerase RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 40503–40514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ségal-Bendirdjian, E.; Geli, V. Non-canonical Roles of Telomerase: Unraveling the Imbroglio. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokládal, L.; Benková, E.; Honys, D.; Dupľáková, N.; Lee, L.-Y.; Gelvin, S.B.; Sýkorová, E. An armadillo-domain protein participates in a telomerase interaction network. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-I.; Venteicher, A.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Jun, S.; Shkreli, M.; Chang, W.; Meng, Z.; Cheung, P.; Ji, H.; et al. Telomerase modulates Wnt signalling by association with target gene chromatin. Nature 2009, 460, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-T.; Meier, U.T. RNA-guided isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine—Pseudouridylation. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, S.A.; Khadka, P.; Roth, J.; Chung, I.K. Catalytically active telomerase holoenzyme is assembled in the dense fibrillar component of the nucleolus during S phase. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 141, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.H.-C.; Ho, S.-T.; Lau, K.-F.; Jin, R.; Wang, Y.-N.; Kung, H.-F.; Huang, J.-J.; Shaw, P.-C. Nucleophosmin Interacts with PIN2/TERF1-interacting Telomerase Inhibitor 1 (PinX1) and Attenuates the PinX1 Inhibition on Telomerase Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.T.T.; Wong, J.M.Y. Telomerase Biogenesis and Activities from the Perspective of Its Direct Interacting Partners. Cancers 2020, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, H.J.; Carrero, Z.I.; Douglas, H.E.; Hebert, M.D. Phosphorylation regulates coilin activity and RNA association. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Broome, H.J.; Hebert, M.D. Coilin Displays Differential Affinity for Specific RNAs In Vivo and Is Linked to Telomerase RNA Biogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Henriksson, S.; Weibrecht, I.; Smith, S.; Söderberg, O.; Strömblad, S.; Wiman, K.G.; Farnebo, M. WRAP53 Is Essential for Cajal Body Formation and for Targeting the Survival of Motor Neuron Complex to Cajal Bodies. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Abreu, E.B.; Meng, Z.; McCann, K.E.; Terns, R.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Terns, M.P.; Artandi, S.E. A Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Protein Required for Cajal Body Localization and Telomere Synthesis. Science 2009, 323, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweetlove, L.; Gutierrez, C. The journey to the end of the chromosome: Delivering active telomerase to telomeres in plants. Plant J. 2019, 98, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, A.J.; Yu, C.; Petukhova, N.V.; Kalinina, N.O.; Chen, J.; Taliansky, M.E. Cajal bodies and their role in plant stress and disease responses. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrumpfová, P.; Kuchař, M.; Miková, G.; Skříovská, L.; Kubičárová, T.; Fajkus, J. Characterization of two Arabidopsis thaliana myb-like proteins showing affinity to telomeric DNA sequence. Genome 2004, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgová, I.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Hofr, C.; Fajkus, J. Functional characterization of domains in AtTRB1, a putative telomere-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peska, V.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fajkus, J. Using the Telobox to Search for Plant Telomere Binding Proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mammals (Human) | Reference(s) | Plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) | Reference(s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) TERT | Minimal promoter | 330 bp upstream of the translation start site to 228 bp downstream. | [115,116,121] | 336 bp long promoter region of the translation start site with plausible regulatory intron 1. | [13,117] |
| RNA Polymerase | RNA Pol II | [115] | RNA Pol II | [122] | |
| Histone modifications of promoter | Telomerase-negative tissues: H3K27me3; telomerase-positive tissues (mutated TERT allele): H3K4me2, H3K4me3 and H3K9ac. | [118,119,123] | Telomerase-negative tissues: H3K27me3, H3K4me3, H3K9Ac; telomerase-positive tissues: H3K4me3, H3K9Ac. | [11] | |
| TERT expression in organism | TERT expression is strictly controlled at the transcript level. | [15,124] | The dynamics of TERT transcripts correlates with telomerase activity observed in plant tissues. | [7,11] | |
| Number of exons | 16 exons | [75,121] | 12 exons | [75] | |
| Alternative splicing of mRNA | TERT pre-mRNA can be spliced into at least 22 isoforms. | [125] | TERT pre-mRNA can be spliced into 3 isoforms. | [75] | |
| Post-translational modifications | Phosphorylation or ubiquitination. | [126,127] | No putative phosphorylation site in A. thaliana TERT (but predicted in rice or tabacum TERT ). | [128,129] | |
| Import to the cell nucleus | Importin α promotes nuclear import of the TERT. | [130] | Importin subunit alpha-4 is associated with TERT. | [98] | |
| Protein domains | TEN, TRBD, RT, CTE. | [75,108] | TEN, TRBD, RT, CTE. | [75] | |
| Protein length | 1132 aa | [108] | 1123 aa | [131] | |
| (b) TR | Histone modifications | TR expression in telomerase-positive cell lines is associated with H3K4me2/3, H3K9Ac and hyperacetylation of H4. | [132,133] | Not known yet. | |
| RNA Polymerase | RNA Pol II | [66] | RNA Pol III | [19,20] | |
| Modifications | 5′ end cap, internally modified, poly (A) tail | [83] | Not known yet. | ||
| Template region | 11 nt long template region (synthesizes 6 nt telomeric repeats GGTTAG). | [66,88] | 9 nt long template region (synthesizes 7 nt telomeric repeat GGTTAG). | [19] | |
| TR gene length | 451 nt long transcript | [66] | 268 nt long transcript | [19,20,71] | |
| TR expression in organism | In most tissues TR is ubiquitously expressed regardless of telomerase activity. | [16,17] | The dynamics of TR transcripts correlates with telomerase activity observed in plant tissues. | [7,11] | |
| (c) Nucleolus and CBs | TR scaffold proteins | Dyskerin, NOP10, NHP2, NAF1/GAR1. | [84,96] | Not known yet. Dyskerin (CBF5), NOP10, NHP2, NAF1, and GAR1 are localized in the nucleolus. Telomerase activity can be immunoprecipitated with dyskerin (CBF5) in plants. Dyskerin associates with TRB proteins. | [19,134,135,136] |
| Nucleolin | NCL involves nucleolar localization of TERT. | [137] | NUC-L1 has a role in telomere maintenance and telomere clustering. | [138,139] | |
| RuvBLs | RuvBLs (pontin and reptin) interact with TERT and dyskerin. | [140] | Interactions between TERT and RuvBL proteins are mediated by TRB proteins. | [134] | |
| coilin | Interacts with TR. | [141,142] | Colocalizes with TRB1 in the CBs adjacent to the nucleolus. | [143] | |
| (d) Association with telomere | The TPP1 protein interacts with TERT and facilitates the recruitment of the mature telomerase complex to the telomeres. | [144] | The TRB proteins interact with TERT and may help to recruit telomerase to the plant telomeres. | [145] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schrumpfová, P.P.; Fajkus, J. Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
Schrumpfová PP, Fajkus J. Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchrumpfová, Petra Procházková, and Jiří Fajkus. 2020. "Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
APA StyleSchrumpfová, P. P., & Fajkus, J. (2020). Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425





