Regulation of Signaling and Metabolism by Lipin-mediated Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
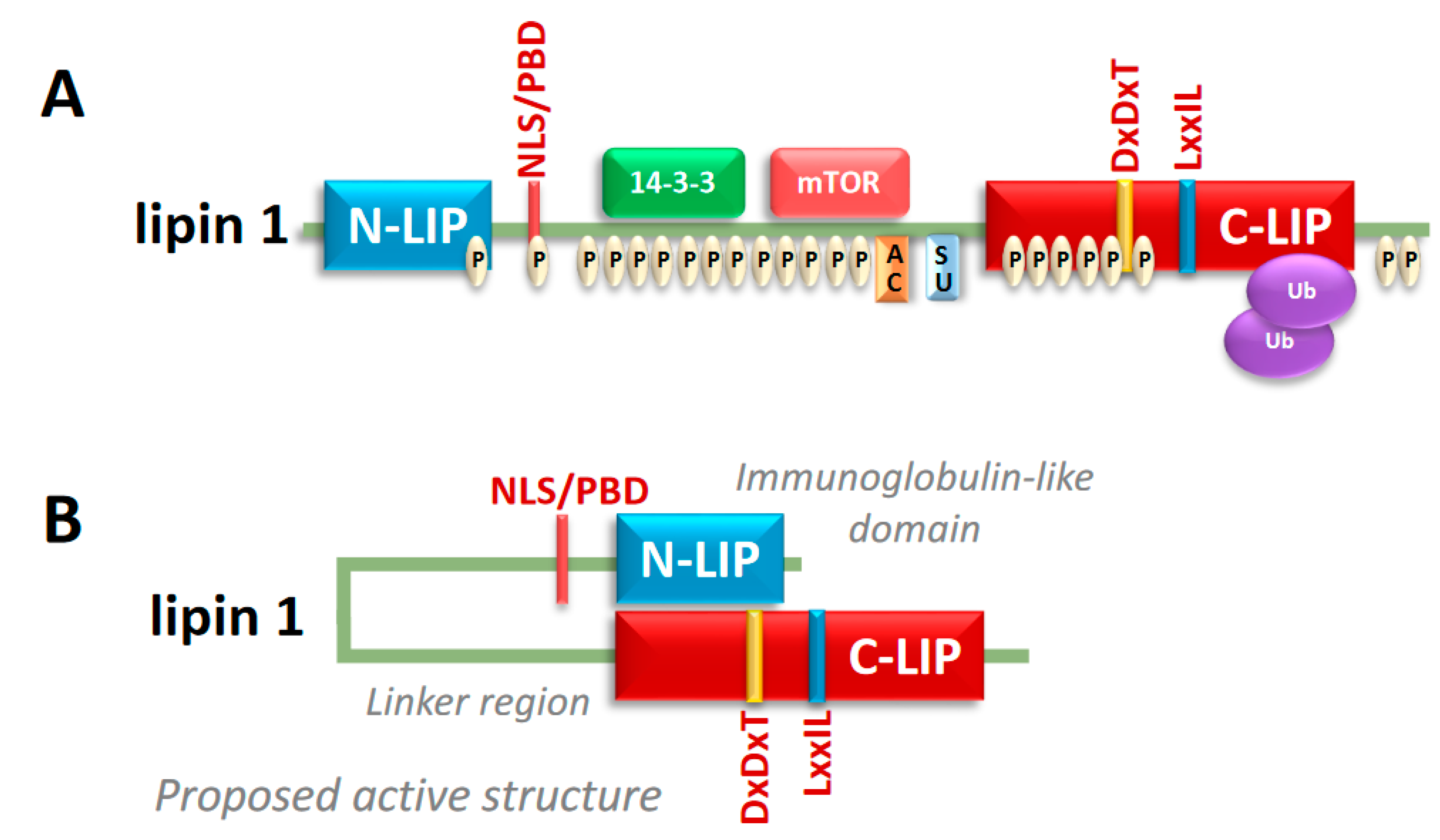
2. Lipin Protein Structure and Regulation
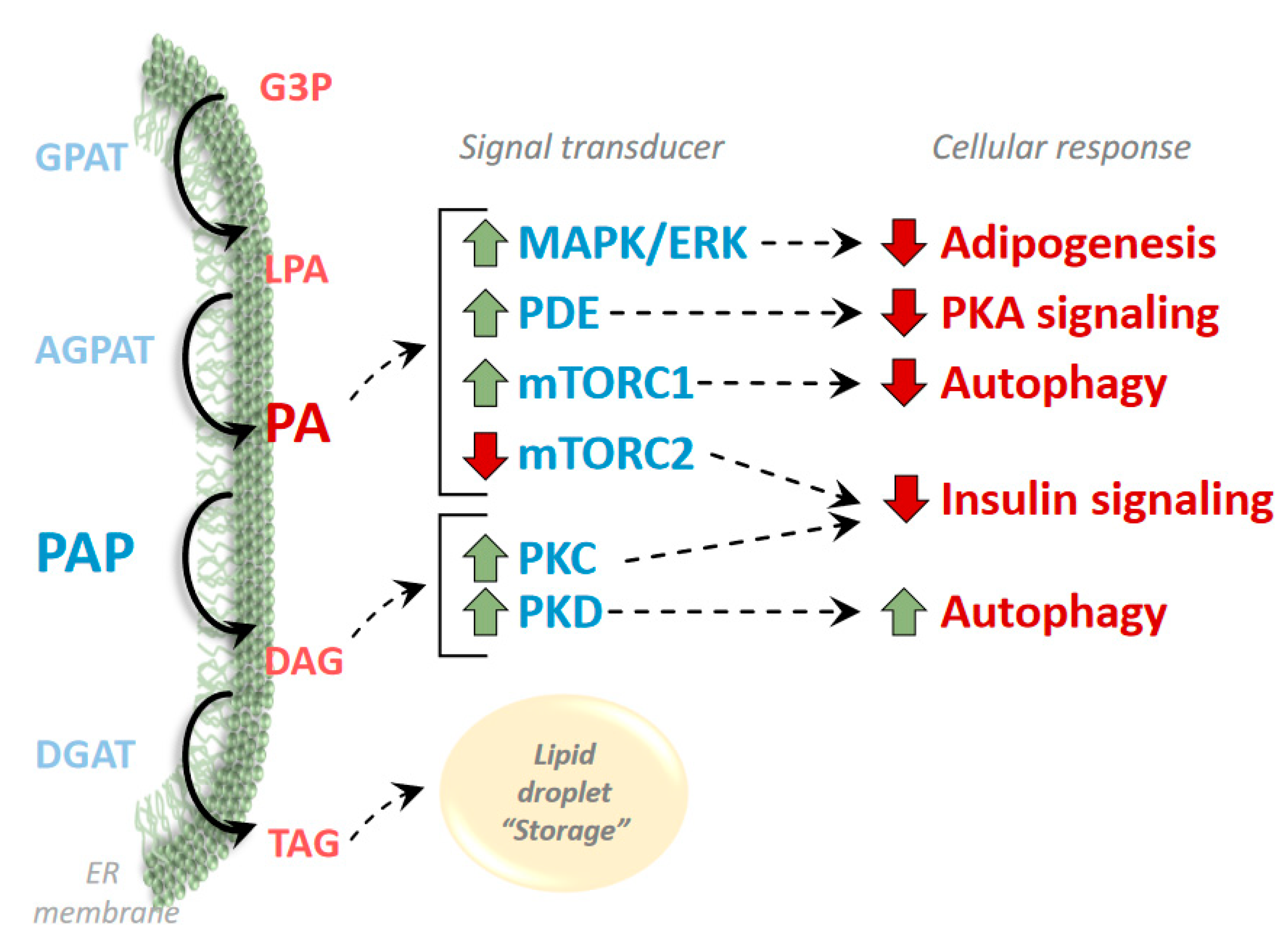
3. Phosphatidic Acid and Diacylglycerol as Regulators of Signaling Pathways
4. Adipose Tissue
5. Skeletal Muscle
6. Cardiac Muscle
7. Liver
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, S.B.; Kennedy, E.P.; Kiyasu, J.Y. The Enzymatic Synthesis of Triglycerides. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.W.; Weiss, S.B.; Kennedy, E.P. The Enzymatic Dephosphorylation of Phosphatidic Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 228, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, G.-S.; Wu, W.-I.; Carman, G.M. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Lipin homolog is a Mg2+-dependent phosphatidate phosphatase enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9210–9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péterfy, M.; Phan, J.; Xu, P.; Reue, K. Lipodystrophy in the fld mouse results from mutation of a new gene encoding a nuclear protein, lipin. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carman, G.M. Discoveries of the phosphatidate phosphatase genes in yeast published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, C.A.; Birkenmeier, E.H.; Ben-Zeev, O.; Schotz, M.C.; Sweet, H.O.; Davisson, M.T.; Gordon, J.I. The fatty liver dystrophy (fld) mutation. A new mutant mouse with a developmental abnormality in triglyceride metabolism and associated tissue-specific defects in lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 7994–8003. [Google Scholar]
- Donkor, J.; Sariahmetoglu, M.; Dewald, J.; Brindley, D.N.; Reue, K. Three Mammalian Lipins Act as Phosphatidate Phosphatases with Distinct Tissue Expression Patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3450–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, M.S.; Schilling, J.D.; Wang, X.; Jay, P.Y.; Huss, J.M.; Su, X.; Finck, B.N. Cardiac lipin 1 expression is regulated by the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ coactivator 1α/estrogen related receptor axis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.E.; Huffman, T.A.; Chi, A.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Kumar, A.; Lawrence, J.C. Insulin Controls Subcellular Localization and Multisite Phosphorylation of the Phosphatidic Acid Phosphatase, Lipin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.R.; Donkor, J.; Zhang, P.; Csaki, L.S.; Vergnes, L.; Lee, J.M.; Dewald, J.; Brindley, D.N.; Atti, E.; Tetradis, S.; et al. Mouse lipin-1 and lipin-2 cooperate to maintain glycerolipid homeostasis in liver and aging cerebellum. PNAS 2012, 109, E2486–E2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, P.J.; Chen, S.; Tayeh, M.K.; Ochoa, L.; Leal, S.M.; Pelet, A.; Munnich, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Majeed, H.A.; El-Shanti, H. Homozygous mutations in LPIN2 are responsible for the syndrome of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis and congenital dyserythropoietic anaemia (Majeed syndrome). J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyo, V.I.; Hoffmann, R.M.; Wang, H.; Bell, J.A.; Burke, J.E.; Reue, K.; Airola, M.V.V. Crystal structure of a lipin/Pah phosphatidic acid phosphatase. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-H.; Qu, J.; Carmack, A.E.; Kim, H.B.; Chen, C.; Ren, H.; Morris, A.J.; Finck, B.N.; Harris, T.E. Lipin proteins form homo- and hetero-oligomers. Biochem J. 2010, 432, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutz, C.E.; Eaton, J.M.; Harris, T.E. Assembly of High Molecular Weight Complexes of Lipin on a Supported Lipid Bilayer Observed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5092–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boroda, S.; Takkellapati, S.; Lawrence, R.T.; Entwisle, S.W.; Pearson, J.M.; Granade, M.E.; Mullins, G.R.; Eaton, J.M.; Villén, J.; Harris, T.E. The phosphatidic acid-binding, polybasic domain is responsible for the differences in the phosphoregulation of lipins 1 and 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20481–20493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Federico, L.; Huang, H.; Sunkara, M.; Drennan, T.; Frohman, M.A.; Smyth, S.S.; Morris, A.J. A Phosphatidic Acid Binding/Nuclear Localization Motif Determines Lipin1 Function in Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis. MBoC 2010, 21, 3171–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finck, B.N.; Gropler, M.C.; Chen, Z.; Leone, T.C.; Croce, M.A.; Harris, T.E.; Lawrence, J.C.; Kelly, D.P. Lipin 1 is an inducible amplifier of the hepatic PGC-1alpha/PPARalpha regulatory pathway. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.B.; Kumar, A.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.-H.; Keller, S.R.; Lawrence, J.C.; Finck, B.N.; Harris, T.E. Lipin 1 Represses NFATc4 Transcriptional Activity in Adipocytes To Inhibit Secretion of Inflammatory Factors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 3126–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, T.A.; Mothe-Satney, I.; Lawrence, J.C. Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of lipin mediated by the mammalian target of rapamycin. PNAS 2002, 99, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.R.; Sengupta, S.S.; Harris, T.E.; Carmack, A.E.; Kang, S.A.; Balderas, E.; Guertin, D.A.; Madden, K.L.; Carpenter, A.E.; Finck, B.N.; et al. mTOR Complex 1 Regulates Lipin 1 Localization to Control the SREBP Pathway. Cell 2011, 146, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-H.; Gerace, L. Sumoylation regulates nuclear localization of lipin-1alpha in neuronal cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, T.Y.; Song, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Yi, C.; Lam, S.M.; Xu, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Tip60-mediated lipin 1 acetylation and ER translocation determine triacylglycerol synthesis rate. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Fukushima, H.; Ogura, K.; Lien, E.C.; Nihira, N.T.; Zhang, J.; North, B.J.; Guo, A.; Nagashima, K.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. The SCFβ-TRCP E3 ubiquitin ligase complex targets Lipin1 for ubiquitination and degradation to promote hepatic lipogenesis. Sci Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropler, M.C.; Harris, T.E.; Hall, A.M.; Wolins, N.E.; Gross, R.W.; Han, X.; Chen, Z.; Finck, B.N. Lipin 2 Is a Liver-enriched Phosphatidate Phosphohydrolase Enzyme That Is Dynamically Regulated by Fasting and Obesity in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6763–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.M.; Mullins, G.R.; Brindley, D.N.; Harris, T.E. Phosphorylation of Lipin 1 and Charge on the Phosphatidic Acid Head Group Control Its Phosphatidic Acid Phosphatase Activity and Membrane Association. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9933–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarlinska, J.; Piaścik, M.; Sikorski, A.F.; Czogalla, A. Phosphatidic acid–a simple phospholipid with multiple faces. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, T.O.; Lass, A. DAG tales: The multiple faces of diacylglycerol--stereochemistry, metabolism, and signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3931–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, D.N.; Waggoner, D.W. Mammalian lipid phosphate phosphohydrolases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24281–24284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, D.N.; Pilquil, C. Lipid phosphate phosphatases and signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S225–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschi, A.; Lee, E.; Xu, L.; Garcia, A.; Gadir, N.; Foster, D.A. Regulation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Complex Assembly by Phosphatidic Acid: Competition with Rapamycin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.-S.; Sun, Y.; Arauz, E.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J. Phosphatidic Acid Activates Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (mTORC1) Kinase by Displacing FK506 Binding Protein 38 (FKBP38) and Exerting an Allosteric Effect. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29568–29574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Vilella-Bach, M.; Bachmann, R.; Flanigan, A.; Chen, J. Phosphatidic Acid-Mediated Mitogenic Activation of mTOR Signal. Science 2001, 294, 1942–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, T.K.; Duffy, L.R.; Frey, J.W.; Hornberger, T.A. The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phosphatidic acid in the regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin following eccentric contractions. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 2009, 587, 3691–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, J.; Peterfy, M.; Reue, K. Biphasic expression of lipin suggests dual roles in adipocyte development. Drug News Perspect. 2005, 18, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, B.P.C.; Kienesberger, P.C.; Dyck, J.R.B.; Brindley, D.N. Relationship of glucose and oleate metabolism to cardiac function in lipin-1 deficient (fld) mice. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.G.; Collier, S.L.; Chen, Z.; McCommis, K.S.; Pittman, S.K.; Yoshino, J.; Matkovich, S.J.; Hsu, F.-F.; Chrast, R.; Eaton, J.M.; et al. Loss of lipin 1–mediated phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase activity in muscle leads to skeletal myopathy in mice. Faseb J. 2018, 33, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Verity, M.A.; Reue, K. Lipin-1 Regulates Autophagy Clearance and Intersects with Statin Drug Effects in Skeletal Muscle. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wendel, A.A.; Keogh, M.R.; Harris, T.E.; Chen, J.; Coleman, R.A. Glycerolipid signals alter mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) to diminish insulin signaling. PNAS 2012, 109, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena, A.; Metz, C.; Jung, J.E.; Silva, A.; Otero, C.; Cancino, J.; Retamal, C.; Valenzuela, J.C.; Soza, A.; González, A. Phosphatidic Acid Induces Ligand-independent Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Endocytic Traffic through PDE4 Activation. MBoC 2010, 21, 2916–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaroff-Girard, A.; Bawab, S.E.; Némoz, G.; Lagarde, M.; Prigent, A.-F. Relationships between phosphatidic acid and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases in activated human blood mononuclear cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Némoz, G.; Sette, C.; Conti, M. Selective Activation of Rolipram-Sensitive, cAMP-Specific Phosphodiesterase Isoforms by Phosphatidic Acid. Mol Pharm. 1997, 51, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, M.S.; Chen, Z.; Ren, H.; Harris, T.E.; Chambers, K.T.; Hall, A.M.; Nadra, K.; Klein, S.; Chrast, R.; Su, X.; et al. Mice with an adipocyte-specific lipin 1 separation-of-function allele reveal unexpected roles for phosphatidic acid in metabolic regulation. PNAS 2013, 110, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, K.T.; Cooper, M.A.; Swearingen, A.R.; Schweitzer, G.G.; Weinheirmer, C.J.; Kovacs, A.; Finck, B.N. Myocardial Lipin 1 Knockout in Mice Approximates Cardiac Effects of Human LPIN1 Mutations. 2020; Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, T.; Esser, K.A.; Ren, H. Lipin1 Regulates Skeletal Muscle Differentiation through Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK) Activation and Cyclin D Complex-regulated Cell Cycle Withdrawal. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23646–23655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadra, K.; de Preux Charles, A.-S.; Médard, J.-J.; Hendriks, W.T.; Han, G.-S.; Grès, S.; Carman, G.M.; Saulnier-Blache, J.-S.; Verheijen, M.H.G.; Chrast, R. Phosphatidic acid mediates demyelination in Lpin1 mutant mice. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; O’Loughlin, L.; Brindley, D.N.; Reue, K. Regulation of lipin-1 gene expression by glucocorticoids during adipogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, T.; Hanazawa, S.; Murakami-Murofushi, K. Cyclic phosphatidic acid influences the expression and regulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Horst, K.W.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Versteeg, R.I.; Ackermans, M.T.; Nederveen, A.J.; la Fleur, S.E.; Romijn, J.A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Zhang, D.; Samuel, V.T.; et al. Hepatic Diacylglycerol-Associated Protein Kinase Cε Translocation Links Hepatic Steatosis to Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Humans. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Oh, K.-J.; Jo, H.-Y.; Hedrick, S.; Kim, Y.-N.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Park, T.-S.; Han, J.-S.; Choi, C.S.; Montminy, M.; et al. TORC2 Regulates Hepatic Insulin Signaling via a Mammalian Phosphatidic Acid Phosphatase, LIPIN1. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.; Jung, J.-Y.; Bae, I.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, T.R.; Shin, D.W. Lipin-1 expression is critical for keratinocyte differentiation. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Reue, K. Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E1195–E1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadra, K.; Médard, J.-J.; Mul, J.D.; Han, G.-S.; Grès, S.; Pende, M.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Cuppen, E.; Saulnier-Blache, J.-S.; et al. Cell Autonomous Lipin 1 Function Is Essential for Development and Maintenance of White and Brown Adipose Tissue. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4794–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, J.; Péterfy, M.; Reue, K. Lipin Expression Preceding Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-γ Is Critical for Adipogenesis in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29558–29564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sembongi, H.; Miranda, M.; Han, G.-S.; Fakas, S.; Grimsey, N.; Vendrell, J.; Carman, G.M.; Siniossoglou, S. Distinct Roles of the Phosphatidate Phosphatases Lipin 1 and 2 during Adipogenesis and Lipid Droplet Biogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34502–34513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Takeuchi, K.; Csaki, L.S.; Reue, K. Lipin-1 Phosphatidic Phosphatase Activity Modulates Phosphatidate Levels to Promote Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) Gene Expression during Adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3485–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.-K.; Lee, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, M.; Moon, J.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Kim, K.-S. Lipin1 Is a Key Factor for the Maturation and Maintenance of Adipocytes in the Regulatory Network with CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Protein α and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34896–34906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaki, L.S.; Reue, K. Lipins: Multifunctional Lipid Metabolism Proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topal, S.; Köse, M.D.; Ağın, H.; Sarı, F.; Çolak, M.; Atakul, G.; Karaarslan, U.; İşgüder, R. A neglected cause of recurrent rhabdomyolysis, LPIN1 gene defect: A rare case from Turkey. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2020, 62, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temprano, A.; Sembongi, H.; Han, G.-S.; Sebastián, D.; Capellades, J.; Moreno, C.; Guardiola, J.; Wabitsch, M.; Richart, C.; Yanes, O.; et al. Redundant roles of the phosphatidate phosphatase family in triacylglycerol synthesis in human adipocytes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaki, L.S.; Dwyer, J.R.; Li, X.; Nguyen, M.H.K.; Dewald, J.; Brindley, D.N.; Lusis, A.J.; Yoshinaga, Y.; de Jong, P.; Fong, L.; et al. Lipin-1 and lipin-3 together determine adiposity in vivo. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, M.A.; Eagon, J.C.; LaRiviere, L.L.; Korenblat, K.M.; Klein, S.; Finck, B.N. Hepatic Lipin 1β Expression Is Diminished in Insulin-Resistant Obese Subjects and Is Reactivated by Marked Weight Loss. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao-Borengasser, A.; Rasouli, N.; Varma, V.; Miles, L.M.; Phanavanh, B.; Starks, T.N.; Phan, J.; Spencer, H.J.; McGehee, R.E.; Reue, K.; et al. Lipin Expression Is Attenuated in Adipose Tissue of Insulin-Resistant Human Subjects and Increases With Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor γ Activation. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moller, F.; Wong, K.H.; Green, P. Control of fat cell phosphohydrolase by lipolytic agents. Can. J. Biochem. 1981, 59, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balboa, M.A.; de Pablo, N.; Meana, C.; Balsinde, J. The role of lipins in innate immunity and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2019, 1864, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michot, C.; Hubert, L.; Brivet, M.; Meirleir, L.D.; Valayannopoulos, V.; Müller-Felber, W.; Venkateswaran, R.; Ogier, H.; Desguerre, I.; Altuzarra, C.; et al. LPIN1 gene mutations: A major cause of severe rhabdomyolysis in early childhood. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, E1564–E1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, C.; Hubert, L.; Romero, N.B.; Gouda, A.; Mamoune, A.; Mathew, S.; Kirk, E.; Viollet, L.; Rahman, S.; Bekri, S.; et al. Study of LPIN1, LPIN2 and LPIN3 in rhabdomyolysis and exercise-induced myalgia. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2012, 35, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.G.; Collier, S.L.; Chen, Z.; Eaton, J.M.; Connolly, A.M.; Bucelli, R.C.; Pestronk, A.; Harris, T.E.; Finck, B.N. Rhabdomyolysis-Associated Mutations in Human LPIN1 Lead to Loss of Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity. Jimd Rep. 2015, 23, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Nemazanyy, I.; Paolini, C.; Tatsuta, T.; Crespin, P.; de Villeneuve, D.; Brodesser, S.; Benit, P.; Rustin, P.; Baraibar, M.A.; et al. Lipin1 deficiency causes sarcoplasmic reticulum stress and chaperone-responsive myopathy. Embo J. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jama, A.; Huang, D.; Alshudukhi, A.A.; Chrast, R.; Ren, H. Lipin1 is required for skeletal muscle development by regulating MEF2c and MyoD expression. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, A.; Khraiche, D.; Ou, P.; Mauvais, F.-X.; Madrange, M.; Guemann, A.-S.; Jais, J.-P.; Bonnet, D.; Hamel, Y.; de Lonlay, P. Cardiac function and exercise adaptation in 8 children with LPIN1 mutations. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, B.P.C.; Dyck, J.R.B.; Harris, T.E.; Brindley, D.N. Differential regulation of the expressions of the PGC-1α splice variants, lipins, and PPARα in heart compared to liver. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1662–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yin, H.; Mitra, M.S.; Liang, X.; Ajmo, J.M.; Nadra, K.; Chrast, R.; Finck, B.N.; You, M. Hepatic-specific lipin-1 deficiency exacerbates experimental alcohol-induced steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Liang, X.; Rogers, C.Q.; Rideout, D.; You, M. Involvement of adiponectin-SIRT1-AMPK signaling in the protective action of rosiglitazone against alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 298, G364–G374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindley, D.N. Some aspects of the physiological and pharmacological control of the synthesis of triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Int J. Obes 1978, 2, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Chen, Z.; Viswakarma, N.; Reddy, J.K.; Wolins, N.E.; Finck, B.N. Dynamic and differential regulation of proteins that coat lipid droplets in fatty liver dystrophic mice. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.G.; Chen, Z.; Gan, C.; McCommis, K.S.; Soufi, N.; Chrast, R.; Mitra, M.S.; Yang, K.; Gross, R.W.; Finck, B.N. Liver-specific loss of lipin-1-mediated phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity does not mitigate intrahepatic TG accumulation in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gropler, M.C.; Norris, J.; Lawrence, J.C.; Harris, T.E.; Finck, B.N. Alterations in Hepatic Metabolism in fld Mice Reveal a Role for Lipin 1 in Regulating VLDL-Triacylglyceride Secretion. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Seo, W.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-N.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, T.-S.; Choi, C.S.; Koo, S.-H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes LIPIN2-dependent hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, D.N.; Cooling, J.; Burditt, S.L.; Pritchard, P.H.; Pawson, S.; Sturton, R.G. The involvement of glucocorticoids in regulating the activity of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and the synthesis of triacylglycerols in the liver. Effects of feeding rats with glucose, sorbitol, fructose, glycerol and ethanol. Biochem. J. 1979, 180, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kim, C.; Jogasuria, A.; Han, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Shen, H.; Chrast, R.; Finck, B.N.; You, M. Myeloid Cell-Specific Lipin-1 Deficiency Stimulates Endocrine Adiponectin-FGF15 Axis and Ameliorates Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutkewitte, A.J.; Schweitzer, G.G.; Kennon-McGill, S.; Clemens, M.M.; James, L.P.; Jaeschke, H.; Finck, B.N.; McGill, M.R. Lipin deactivation after acetaminophen overdose causes phosphatidic acid accumulation in liver and plasma in mice and humans and enhances liver regeneration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lutkewitte, A.J.; Finck, B.N. Regulation of Signaling and Metabolism by Lipin-mediated Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101386
Lutkewitte AJ, Finck BN. Regulation of Signaling and Metabolism by Lipin-mediated Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLutkewitte, Andrew J., and Brian N. Finck. 2020. "Regulation of Signaling and Metabolism by Lipin-mediated Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101386
APA StyleLutkewitte, A. J., & Finck, B. N. (2020). Regulation of Signaling and Metabolism by Lipin-mediated Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase Activity. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101386





