Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection of Cathelicidin Proteins in the Milk of Goats After Intramammary Inoculation of Staphylococcus simulans
2.1.1. Outline of the Experimental Study
2.1.2. Animal Examinations and Samplings
2.1.3. Conventional Laboratory Examinations
2.2. Evaluation of the Presence of Cathelicidin Proteins in the Bulk-Tank Milk from Goat and Sheep Farms
2.2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2.2. Conventional Laboratory Examinations
2.3. Proteomics Analysis
2.4. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Individual Animal Study
3.1.1. Conventional Examinations
3.1.2. Proteomics Examinations
3.1.3. Detection of Cathelicidin Biomolecules for the Diagnosis of Mastitis
3.2. Farm Study
3.2.1. Characteristics of Farms
3.2.2. Conventional and Proteomics Examinations
4. Discussion
4.1. Individual Animal Study
4.2. Farm Study
4.3. Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, T.L.; Larson, M.A.; Mack, D.R.; Weber, A. Elevated extrahepatic expression and secretion of mammary-associated serum amyloid A 3 (M-SAA3) into colostrum. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 83, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.F.; Pisanu, S.; Marogna, G.; Cubeddu, T.; Pagnozzi, D.; Cacciotto, C.; Campesi, F.; Schianchi, G.; Rocca, S.; Uzzau, S. Production and release of antimicrobial and immune defense proteins by mammary epithelial cells following Streptococcus uberis infection of sheep. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3182–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.F.; Tedde, V.; Dore, S.; Pisanu, S.; Puggioni, G.M.G.; Roggio, A.M.; Pagnozzi, D.; Lollai, S.; Cannas, E.A.; Uzzau, S. Evaluation of milk cathelicidin for detection of dairy sheep mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 6446–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsafadou, A.I.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Billinis, C.; Barbagianni, M.S.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Spanos, S.A.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Fthenakis, G.C. Differential quantitative proteomics study of experimental Mannheimia haemolytica mastitis in sheep. J. Proteom. 2019, 205, 103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubeddu, T.; Cacciotto, C.; Pisanu, S.; Tedde, V.; Alberti, A.; Pittau, M.; Dore, S.; Cannas, A.; Uzzau, S.; Rocca, S.; et al. Cathelicidin production and release by mammary epithelial cells during infectious mastitis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 189, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogianni, V.S.; Menzies, P.I.; Fragkou, I.A.; Fthenakis, G.C. Principles of mastitis treatment in sheep and goats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsafadou, A.I.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Billinis, C.; Fragkou, I.A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Michael, C.K.; et al. Detection of Cathelicidin-1 in the Milk as an Early Indicator of Mastitis in Ewes. Pathogens 2019, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olumee-Shabon, Z.; Swain, T.; Smith, E.A.; Tall, E.; Boehmer, J.L. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in caprine milk during experimentally induced endotoxin mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reczyńska, D.; Witek, B.; Jarczak, J.; Czopowicz, M.; Mickiewicz, M.; Kaba, J.; Zwierzchowski, L.; Bagnicka, E. The impact of organic vs. inorganic selenium on dairy goat productivity and expression of selected genes in milk somatic cells. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedde, V.; Bronzo, V.; Puggioni, G.M.G.; Pollera, C.; Casula, A.; Curone, G.; Moroni, P.; Uzzau, S.; Addis, M.F. Milk cathelicidin and somatic cell counts in dairy goats along the course of lactation. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugami, Y.; Nii, T.; Isobe, N. Valine treatment enhances antimicrobial component production in mammary epithelial cells and the milk of lactating goats without influencing the tight junction barrier. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2023, 28, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.K.; Liang, Z.L.; Nii, T.; Suzuki, N.; Isobe, N. Antimicrobial component concentrations in the milk of peripartum goats. Anim. Sci. J. 2025, 96, e70029. [Google Scholar]
- Fthenakis, G.C.; Jones, J.E.T. The effect of inoculation of coagulase-negative staphylococci into the ovine mammary gland. J. Comp. Pathol. 1990, 102, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.A.; Misra, J.S. The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. J. Hyg. Camb. 1938, 38, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Cripps, P.J.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Chouzouris, T.M.; Lianou, D.T.; Calvo Gonzalez-Valerio, T.; Guix Vallverdu, R.; Argyros, S.; et al. Evaluation of efficacy of a biofilm-embedded bacteria-based vaccine against staphylococcal mastitis in sheep—A randomized, placebo-controlled field study. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9328–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, G.I.; Feltham, R.K.A. Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Euzeby, J.P. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: A folder available on the Internet. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalm, O.W.; Carroll, E.J.; Jain, N.C. Bovine Mastitis; Lea and Febiger: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on the welfare risks related to the farming of sheep for wool, meat and milk production. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3933–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, D.T.; Michael, C.K.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Petinaki, E.; Cripps, P.J.; Tsilipounidaki, K.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Politis, A.P.; Kordalis, N.G.; Ioannidi, K.S.; et al. Extensive countrywide field investigation of somatic cell counts and total bacterial counts in bulk-tank raw milk in goat herds in Greece. J. Dairy Res. 2021, 88, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Pierros, V.; Kontopodis, E.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Arsenos, G.; Karkabounas, S.C.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Tsangaris, G.T. Milk of Greek sheep and goat breeds; characterization by means of proteomics. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggans, G.R.; Shook, G.E. A lactation measure of somatic cell count. J. Dairy Sci. 1987, 70 (Suppl. S13), 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoi, M.; Manuelian, C.L.; Penasa, M.; De Marchi, M. Effects of somatic cell score on milk yield and mid-infrared predicted composition and technological traits of Brown Swiss, Holstein Friesian, and Simmental cattle breeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebu, A.; Teshome, Y.; Tamrat, H.; Bahiru, A. Mastitis in goat: A review of etiology, epidemiology, economic impact, and public health concerns. One Health 2025, 21, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.W.; Lai, S.J.; Yoshimura, Y.; Isobe, N. Expression of cathelicidins mRNA in the goat mammary gland and effect of the intramammary infusion of lipopolysaccharide on milk cathelicidin-2 concentration. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamova, O.; Orlov, D.; Stegemann, C.; Czihal, P.; Hoffmann, R.; Brogden, K.; Kolodkin, N.; Sakuta, G.; Tossi, A.; Sahl, H.G.; et al. ChBac3.4: A novel proline-rich antimicrobial peptide from goat leukocytes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2009, 15, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Nigam, R.; Pandey, V.; Singh, P. A minireview on antimicrobial peptides of goats and their role in host defense. Biosc. Biotech. Res. Comm. 2020, 13, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, H.; Fan, M.; Zhao, X.; Pan, M.; Ma, B.; Wei, Q. The relationship between mastitis and antimicrobial peptide S100A7 expression in dairy goats. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, P.; Page, K.L.; Hillerton, J.E. The effects of early antibiotic treatment following diagnosis of mastitis detected by a change in the electrical conductivity of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laven, R. Mastitis Part 4—Detecting and Treating Clinical Mastitis. NADIS Animal Health Skills. 2010. Available online: https://www.nadis.org.uk/disease-a-z/cattle/mastitis/mastitis-part-4-detecting-and-treating-clinical-mastitis/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Australian Code for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes, 8th ed.; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Festing, M.F.W. How to Reduce the Number of Animals Used in Research by Improving Experimental Design and Statistics. ANZCCART Fact Sheet T10. 2011. Available online: https://anzccart.adelaide.edu.au/ua/media/553/reduce-numbers-in-animals.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kosciuczuk, E.M.; Lisowski, P.; Jarczak, J.; Strzałkowska, N.; Jozwik, A.; Horbanczuk, J.; Krzyzewski, J.; Zwierzchowski, L.; Bagnicka, E. Cathelicidins: Family of antimicrobial peptides. A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 10957–10970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roby, K.D.; Nardo, A.D. Innate immunity and the role of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in inflammatory skin disease. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2013, 10, e79–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Harten, R.M.; van Woudenbergh, E.; van Dijk, A.; Haagsman, H.P. Cathelicidins: Immunomodulatory antimicrobials. Vaccines 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jin, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Differential abilities of mammalian cathelicidins to inhibit bacterial biofilm formation and promote multifaceted immune functions of neutrophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, M.E.S.; Vieira, B.; Calazans, A.P.C.T.; Destro, G.V.; Melo, K.; Rodrigues, E.; Waz, N.T.; Girardello, R.; Darrieux, M.; Converso, T.R. Recent advances in the therapeutic potential of cathelicidins. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1405760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.F.; Bronzo, V.; Puggioni, G.M.G.; Cacciotto, C.; Tedde, V.; Pagnozzi, D.; Locatelli, C.; Casula, A.; Curone, G.; Uzzau, S.; et al. Relationship between milk cathelicidin abundance and microbiologic culture in clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogridou-Vassiliadou, D. Mastitis-related pathogens in goat milk. Small Rumin. Res. 1991, 4, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Cripps, P.J.; Ioannidi, K.S.; Chatzopoulos, D.C.; Gougoulis, D.A.; Sarrou, S.; Orfanou, D.C.; Politis, A.; Calvo Gonzalez-Valerio, T.; Argyros, S.; et al. Extensive countrywide field investigation of subclinical mastitis in sheep in Greece. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7297–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J. Rapid coomassie blue staining of protein gels. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.F.; Tedde, V.; Puggioni, G.M.G.; Pisanu, S.; Casula, A.; Locatelli, C.; Rota, N.; Bronzo, V.; Moroni, P.; Uzzau, S. Evaluation of milk cathelicidin for detection of bovine mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8250–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puggioni, G.M.G.; Tedde, V.; Uzzau, S.; Guccione, J.; Ciaramella, P.; Pollera, C.; Moroni, P.; Bronzo, V.; Addis, M.F. Evaluation of a bovine cathelicidin ELISA for detecting mastitis in the dairy buffalo: Comparison with milk somatic cell count and bacteriological culture. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 128, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, R.J.; Patel, N.M.; Patel, Y.G.; Islam, M.M.; Nayak, J.B. Goat farming: A boon for economic upliftment. In Trends in Clinical Diseases, Production and Management of Goats; Rana, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 1, pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Calogero, A.; Montesano, D.; Naviglio, D. Relationships between food and diseases: What to know to ensure food safety. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyi, M.B. Review on goat mastitis and associated bacterial zoonoses in raw milk from mastitis infected dairy goat. Adv. Dairy Sci. Res. 2023, 1, 30–38. [Google Scholar]



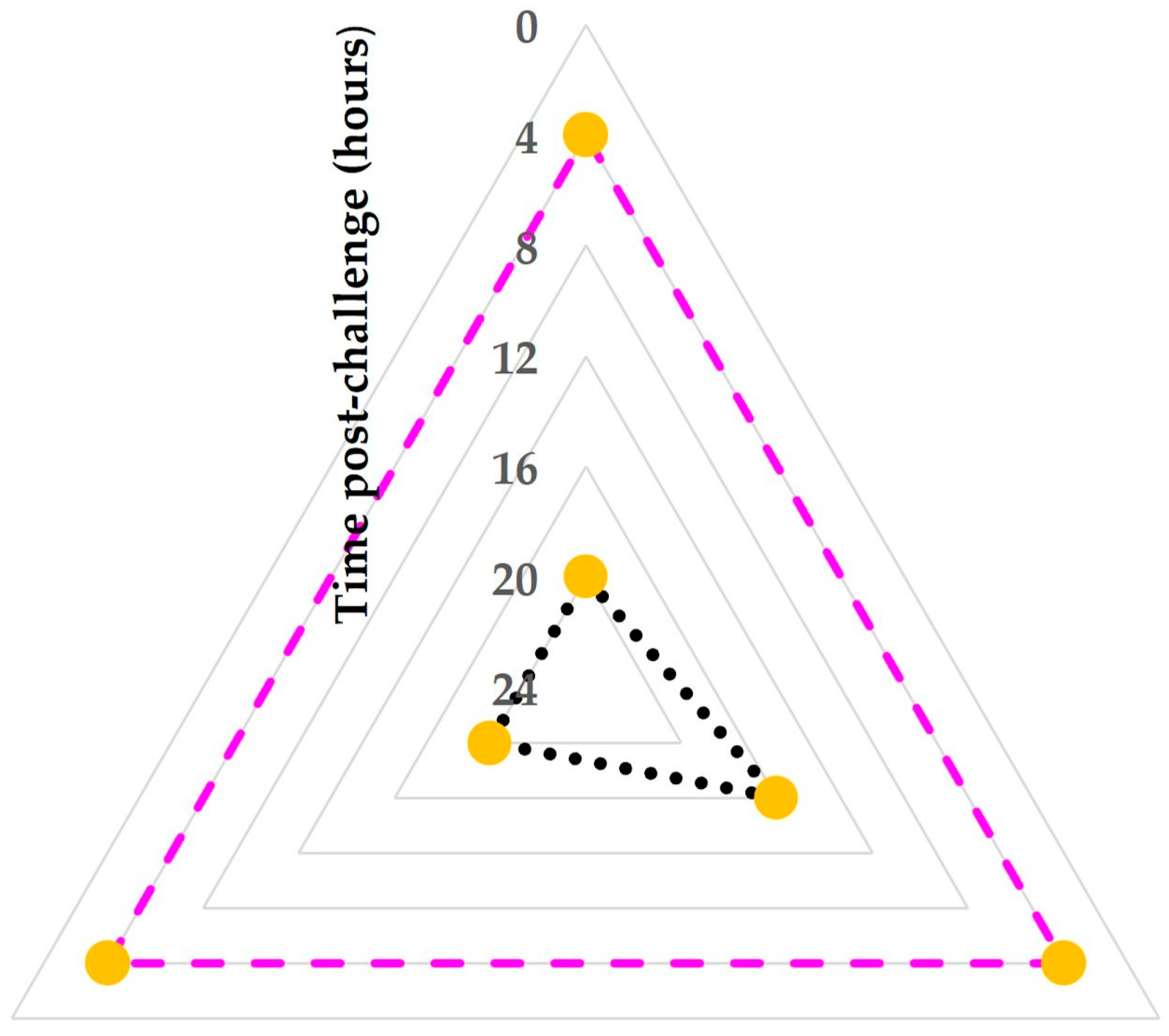
| Cathelicidin Proteins 1 | Mammary Gland 2 | Timepoint of the Study 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D(−1) | D(0) | D(0+ 4 h) | D(0+ 8 h) | D(0+ 12 h) | D(0+ 16 h) | D(0+ 20 h) | D(1) | D(1+ 8 h) | D(1+ 16 h) | D(2) | ||
| CHTL-1 | chall. | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 691.1 (379.0) | 1847.7 (1108.1) | 2594.5 (904.2) | 2421.5 (394.5) | 1344.4 (153.9) | 919.8 (36.4) | 613.3 (97.4) | 523.3 (154.3) | 452.4 (66.0) |
| contr. | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (10.7) | 15.0 (13.5) | 24.5 (15.1) | 24.1 (13.8) | 24.3 (13.3) | |
| CHTL-2 | chall. | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 304.8 (1237.1) | 4310.8 (3679.6) | 2123.8 (6352.5) | 3631.7 (2627.1) | 2249.7 (1245.0) | 1030.3 (1609.8) | 761.9 (1236.4) | 502.1 (612.5) | 436.3 (437.1) |
| contr. | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (4.7) | 0.0 (6.8) | 0.0 (12.8) | 0.0 (11.1) | |
| Presence of Mastitis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| + | – | ||
| Detection of Cathelicidin Proteins | + | 25 | 12 |
| – | 0 | 29 | |
| Goat Farms | Sheep Farms | |
|---|---|---|
| Somatic cell counts (cells mL−1) | 0.614 × 106 (0.467 × 106 –0.808 × 106) | 0.517 × 106 (0.415 × 106 –0.643 × 106) |
| Fat (%) | 4.70 ± 0.15 | 6.15 ± 0.10 |
| Total proteins (%) | 3.17 ± 0.02 | 4.50 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bourganou, M.V.; Liagka, D.V.; Vougas, K.; Lianou, D.T.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Dimoveli, K.S.; Politis, A.P.; Kordalis, N.G.; Petinaki, E.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; et al. Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis. Animals 2025, 15, 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152301
Bourganou MV, Liagka DV, Vougas K, Lianou DT, Vasileiou NGC, Dimoveli KS, Politis AP, Kordalis NG, Petinaki E, Mavrogianni VS, et al. Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis. Animals. 2025; 15(15):2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152301
Chicago/Turabian StyleBourganou, Maria V., Dimitra V. Liagka, Konstantinos Vougas, Daphne T. Lianou, Natalia G. C. Vasileiou, Konstantina S. Dimoveli, Antonis P. Politis, Nikos G. Kordalis, Efthymia Petinaki, Vasia S. Mavrogianni, and et al. 2025. "Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis" Animals 15, no. 15: 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152301
APA StyleBourganou, M. V., Liagka, D. V., Vougas, K., Lianou, D. T., Vasileiou, N. G. C., Dimoveli, K. S., Politis, A. P., Kordalis, N. G., Petinaki, E., Mavrogianni, V. S., Tsangaris, G. T., Fthenakis, G. C., & Katsafadou, A. I. (2025). Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis. Animals, 15(15), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15152301











