Biological, Biochemical and Elemental Traits of Clavelina oblonga, an Invasive Tunicate in the Adriatic Sea
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
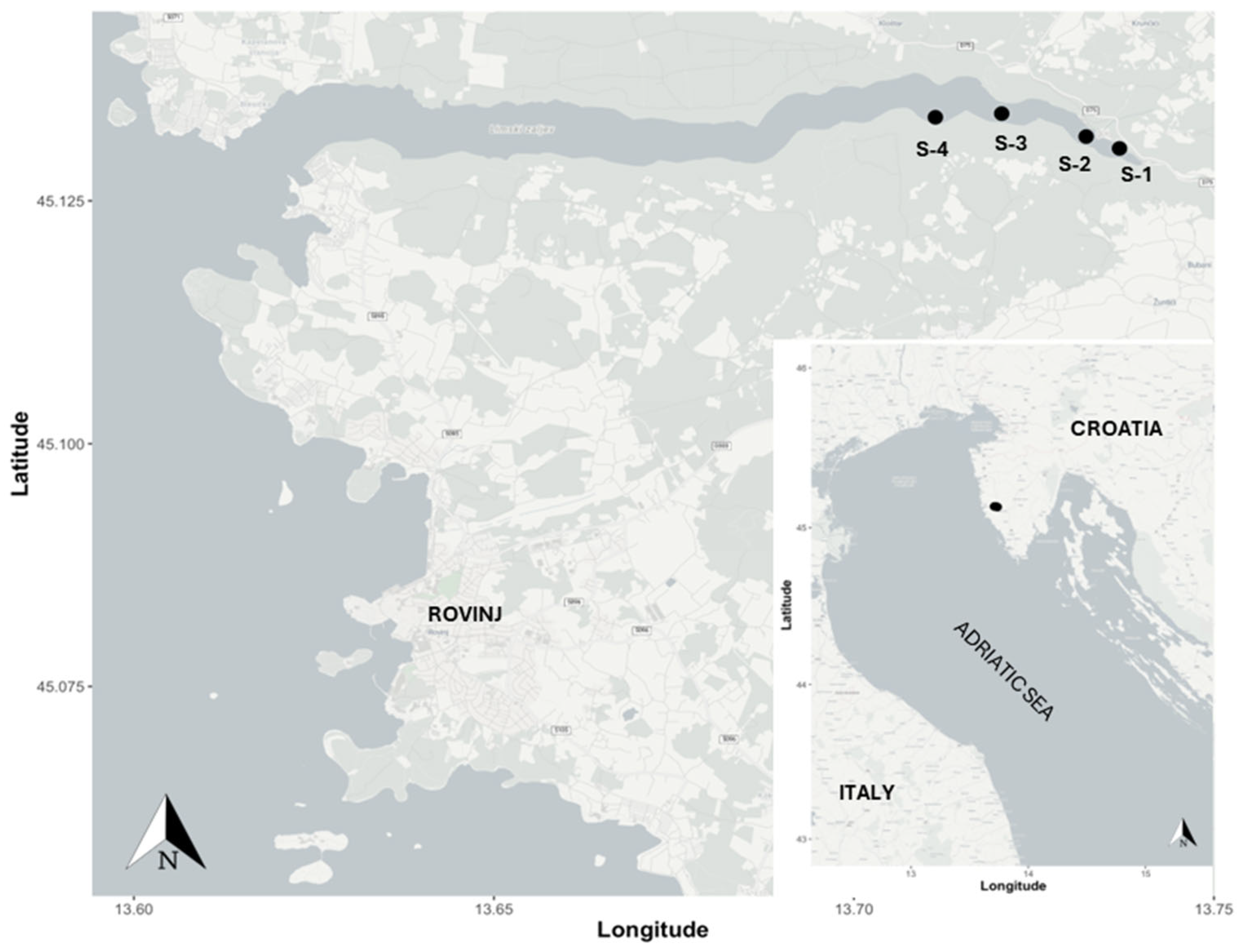
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Samples
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
2.5. Proximate Composition
2.6. Fatty Acid Composition
2.7. Trace and Macro Elements
3. Results
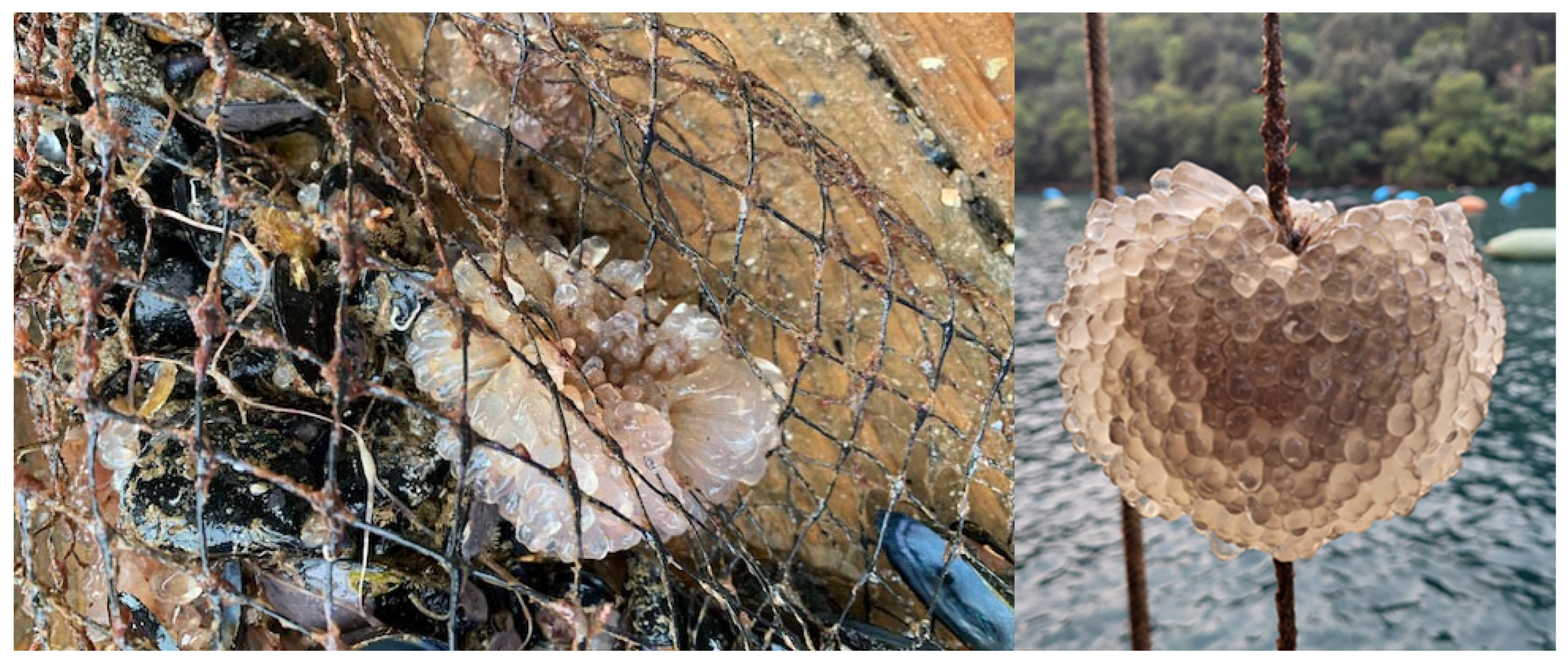
3.1. Temporal Dynamics and Biological Observations
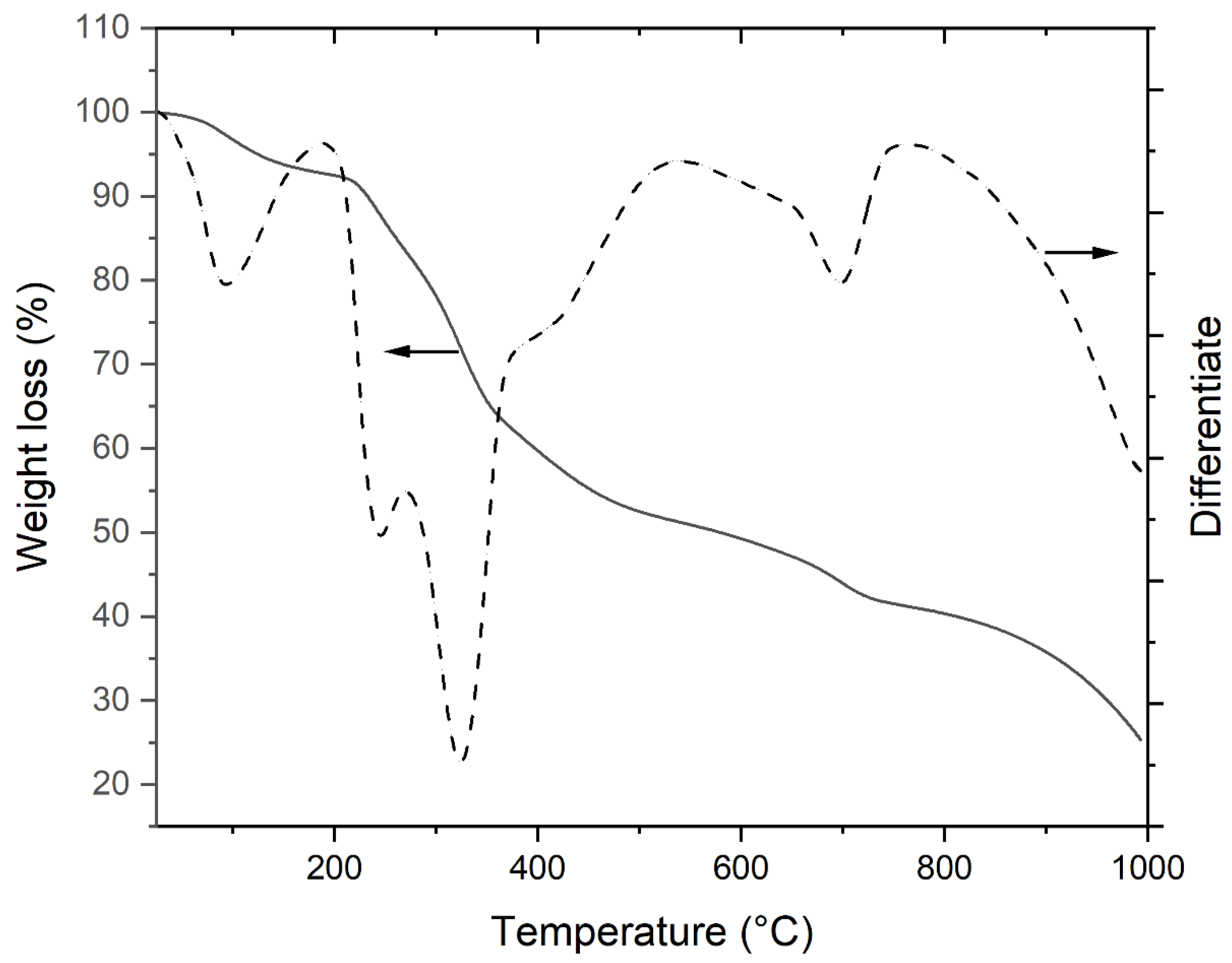
3.2. Thermal Properties
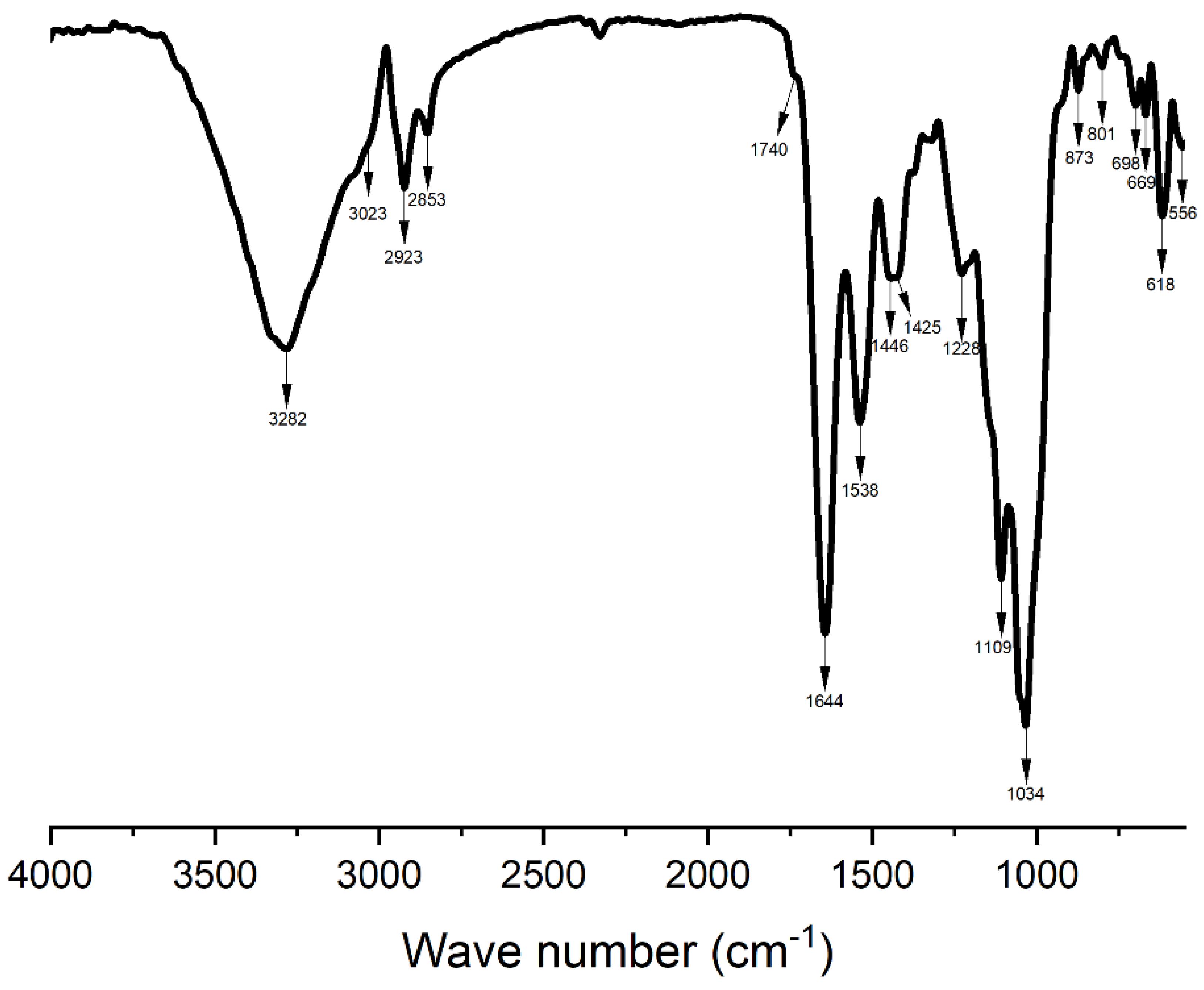
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
3.4. Proximate Composition
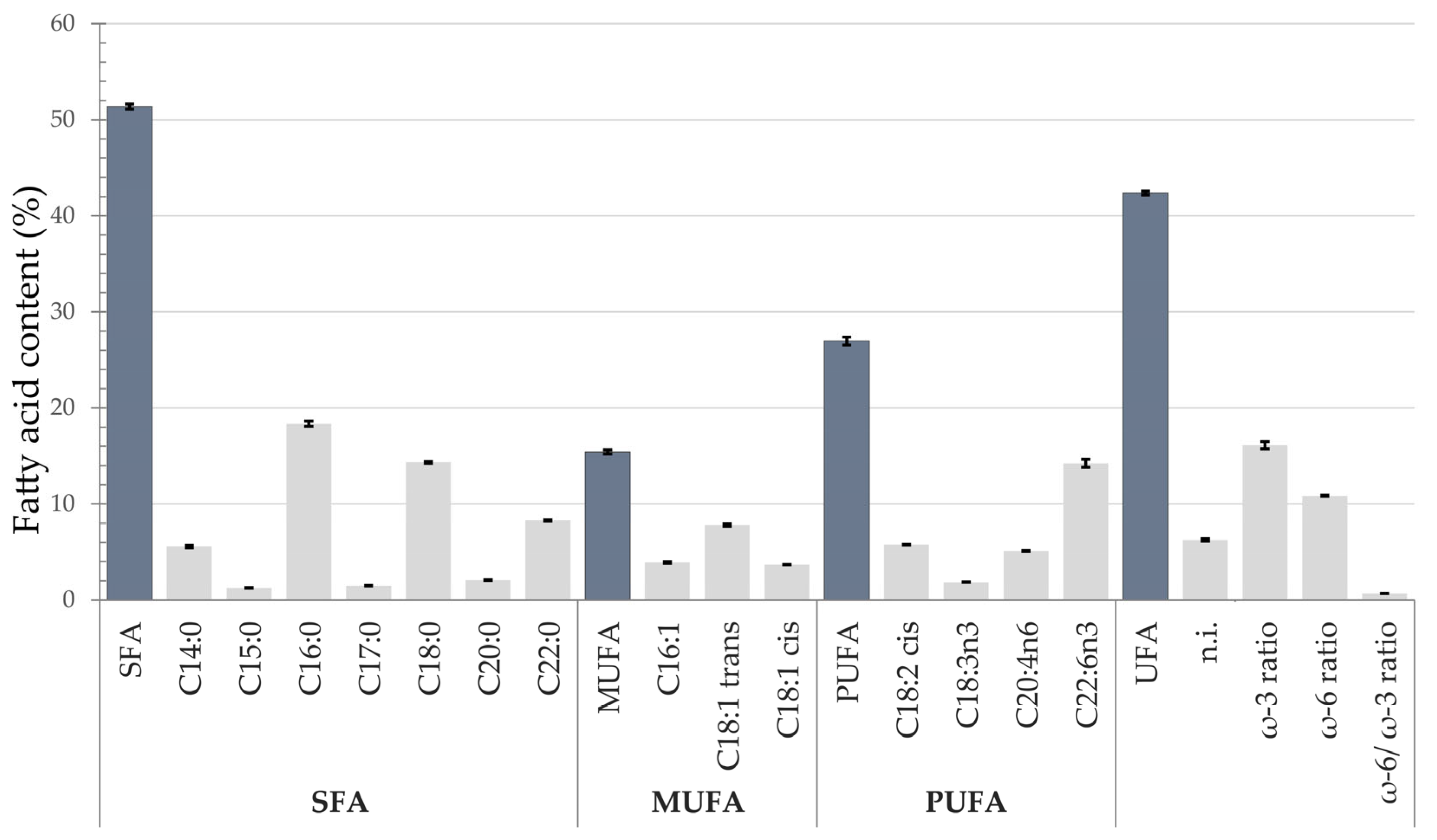
3.5. Fatty Acid Composition
3.6. Trace and Macroelements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, P.; Khong, H.Y.; Mao, W.; Chen, X.; Bao, L.; Wen, X.; Xu, Y. Tunicates as Sources of High-Quality Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds for Food/Feed and Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, J.; Luscombe, N.M.; Plessy, C. Widespread Use of the “Ascidian” Mitochondrial Genetic Code in Tunicates. F1000Research 2020, 8, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparini, F.; Manni, L.; Cima, F.; Zaniolo, G.; Burighel, P.; Caicci, F.; Franchi, N.; Schiavon, F.; Rigon, F.; Campagna, D.; et al. Sexual and Asexual Reproduction in the Colonial Ascidian Otryllus schlosseri. Genesis 2015, 53, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard-Dwyer, M.; López-Legentil, S.; Erwin, P.M. Microbiome Variability Across the Native and Invasive Ranges of the Ascidian Clavelina oblonga. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2021, 87, e02233-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colarusso, P.; Nelson, E.; Ayvazian, S.; Carman, M.; Chintala, M.; Grabbert, S.; Grunden, D. Quantifying the Ecological Impact of Invasive Tunicates to Shallow Coastal Water Systems. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2016, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, S.; Carman, M. Introduction to the Proceedings of the 5th International Invasive Sea Squirt Conference, 2014. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2016, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, D.M.; de Marco, P., Jr.; Andrade, A.F.A.; Rocha, R.M. Predicting Global Ascidian Invasions. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, V.; Pascual, M.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Turon, X. When Invasion Biology Meets Taxonomy: Clavelina oblonga (Ascidiacea) Is an Old Invader in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, K.A.; Eggleston, D.B. Testing Ecological Theories in the Anthropocene: Alteration of Succession by an Invasive Marine Species. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthan, G.; Murugan, R. Molecular Phylogeny of Four Ascidian Species Inferred from Mitochondrial Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I (COI) Sequence. Mitochondr. DNA 2018, 29, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragkousis, M.; Zenetos, A.; Ben Souissi, J.; Tsiamis, K.; Ferrario, J.; Marchini, A.; Edelist, D.; Crocetta, F.; Bariche, M.; Deidun, A.; et al. Unpublished Mediterranean and Black Sea Records of Marine Alien, Cryptogenic, and Neonative Species. BIR 2023, 12, 339–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Excellent Chemical and Material Cellulose from Tunicates: Diversity in Cellulose Production Yield and Chemical and Morphological Structures from Different Tunicate Species. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3427–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnarić, N.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Jaklin, A.; Hamer, B. Susceptibility of Invasive Tunicates Clavelina oblonga to Reduced Seawater Salinities. Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 27, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supić, N.; Kraus, R.; Kuzmić, M.; Paschini, E.; Precali, R.; Russo, A.; Vilibić, I. Predictability of Northern Adriatic Winter Conditions. J. Marine Syst. 2012, 90, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the Global Threat of Invasive Species to Marine Biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G. Invasive Sea Squirts: A Growing Global Problem. J. Exp. Mar. Bio Ecol. 2007, 342, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.M.; Guerra-Castro, E.; Lira, C.; Pauls, S.M.; Hernández, I.; Pérez, A.; Sardi, A.; Pérez, J.; Herrera, C.; Carbonini, A.K.; et al. Inventory of Ascidians (Tunicata, Ascidiacea) from the National Park La Restinga, Isla Margarita, Venezuela. Biota Neotrop. 2010, 10, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casso, M.; Navarro, M.; Ordóñez, V.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Pascual, M.; Turon, X. Seasonal Patterns of Settlement and Growth of Introduced and Native Ascidians in Bivalve Cultures in the Ebro Delta (NE Iberian Peninsula). Reg. Stud. 2018, 23, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.M.; Venâncio, E.; Dionísio, M.A.; Heumüller, J.; Chainho, P.; Pombo, A. Comparison of the Efficiency of Different Eradication Treatments to Minimize the Impacts Caused by the Invasive Tunicate Styela plicata in Mussel Aquaculture. Animals 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, H.; Dukes, J.S. Impacts of Invasive Species on Ecosystem Services. In Biological Invasions; Nentwig, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar]
- Filgueira, R.; Strople, L.C.; Strohmeier, T.; Rastrick, S.; Strand, Ø. Mussels or Tunicates: That Is the Question. Evaluating Efficient and Sustainable Resource Use by Low-Trophic Species in Aquaculture Settings. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Kovačić, I.; Koščica, L.; Hamer, B. Physiological Indices of Maricultured Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 in Istria, Croatia: Seasonal and Transplantation Effect. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2016, 47, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucht, W.; Sidri, M.; Brummer, F.; Jaklin, A.; Hamer, B. Ecology and Distribution of the Sponge Aplysina aerophoba (Porifera, Demospongiae) in the Limski Kanal (Northern Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2008, 17, 890–901. [Google Scholar]
- Hamer, B.; Medaković, D.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Jakšić, Ž.; Štifanić, M.; Nerlović, V.; Travizi, A.; Precali, R.; Kanduč, T. Estimation of Freshwater Influx along the Eastern Adriatic Coast as a Possible Source of Stress for Marine Organisms. Acta Adriat. 2010, 51, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Klöppel, A.; Messal, C.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Matschullat, J.; Zucht, W.; Hamer, B.; Brümmer, F. Abiotic Sponge Ecology Conditions, Limski Kanal and Northern Adriatic Sea, Croatia. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 01, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, B.; Grozić, K.; Privileggio, L.; Balković, I.; Hamer, K.; Janči, T.; Maurić Maljković, M.; Jaklin, A.; Pavičić-Hamer, D. The Quality Indicators in Mussel Farming: Lim Bay Case Study. Meso 2025, 1, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; AOAC International: Arlington, WA, USA, 1995; Available online: https://www.lifewatch.be/imis?module=ref&refid=66388&printversion=1&dropIMIStitle=1 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Smedes, F. Determination of Total Lipid Using Non-Chlorinated Solvents. Analyst 1999, 124, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 12966-2:2017; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Preparation of Methyl Esters of Fatty Acids. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/11560.html (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. BBA-Bioenerg. 2006, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhamati, Z.; Marhamatizadeh, M.H.; Mohebbi, G. Evaluation of the physicochemical, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties of tunichrome released from Phallusia nigra Persian Gulf marine tunicate. J. Food Quality 2021, 2021, 5513717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Sugumaran, M.; Robinson, W.E. The crosslinking and antimicrobial properties of tunichrome. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; MacKenzie, A.D.; Jeffs, A.G. Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Likely Zooplankton Prey of Spiny Lobster (Jasus edwardsii) Phyllosomas. Aquacult. Nutr. 2015, 21, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, J.B.; Heine, J.; Slattery, M.; Weston, J. Biochemical and energetic composition, population biology, and chemical defense of the Antarctic ascidian Cnemidocarpa verrucosa Lesson. J. Exp. Mar. Bio Ecol. 1991, 147, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, M.; Putrone, V.; Brunetti, R. Morphometrics and energetic value of Adriatic ascidians. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1997, 38, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hamer, B.; Jakšić, Ž.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Perić, L.; Medaković, D.; Ivanković, D.; Pavičić, J.; Zilberberg, C.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G.; et al. Effect of Hypoosmotic Stress by Low Salinity Acclimation of Mediterranean Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis on Biological Parameters Used for Pollution Assessment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 89, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdows, J. The Effects of Fluctuating and Abrupt Changes in Salinity on the Performance of Mytilus edulis. In Marine Biology of Polar Regions and Effects of Stress on Marine Organisms; Gray, J.S., Christiansen, M.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Chichester, UK, 1985; pp. 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Dubischar, C.D.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Bathmann, U.V. The Tunicate Salpa thompsoni Ecology in the Southern Ocean. II. Proximate and Elemental Composition. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Ascidian Bioresources: Common and Variant Chemical Compositions and Exploitation Strategy–Examples of Halocynthia roretzi, Styela plicata, Ascidia sp. and Ciona intestinalis. Z. Naturforsch 2016, 71, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačić, I.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Kanduč, T.; Hamer, B. Adaptation of Cultured Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 from the Northern Adriatic Sea to Nearby Aquaculture Sites and Translocation. Acta Adriat. 2018, 58, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Khong, H.Y.; Wibowo, A.; Zhen, Y.; Peng, C.; Miao, W. Chemical compositions and nutritional profiles of two edible tunicate species (Halocynthia roretzi and Halocynthia aurantium). Heliyon 2024, 10, e32321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Chu, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-L.; Chang, J.-S. Thermal Degradation of Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids in Microalgae Analyzed by Evolutionary Computation. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2018, 160, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forfang, K.; Zimmermann, B.; Kosa, G.; Kohler, A.; Shapaval, V. FTIR Spectroscopy for Evaluation and Monitoring of Lipid Extraction Efficiency for Oleaginous Fungi. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurvell, H.F. Spectra– Structure Correlations in the Mid- and Far-Infrared. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; Chalmers, J.M., Griffiths, P.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 1783–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Pancake, S.J.; Karnovsky, M.L. The Isolation and Characterization of a Mucopolysaccharide Secreted by the Snail, Otella lactea. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Sugiyama, J.; Satoh, N. A Spectroscopic Assessment of Cellulose and the Molecular Mechanisms of Cellulose Biosynthesis in the Ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Mar. Genom. 2008, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mali, M.; Topić Popović, N.; Todisco, S.; Mastrorilli, P.; Nefedova, D.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Dell’Anna, M.M. Cellulose Recovery from Tunicates: A Circular Economy Approach for Aquaculture-Waste Management. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea: Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea 2024), Portorose, Slovenia, 14–16 October 2024; pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bauermeister, A.; Branco, P.C.; Furtado, L.C.; Jimenez, P.C.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; da Cruz Lotufo, T.M. Tunicates: A model organism to investigate the effects of associated-microbiota on the production of pharmaceuticals. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2018, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D. Caloric Variation in Crustacea and Other Animals. J. Anim. Ecol. 1977, 46, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, R.; Ivošević DeNardis, N. Tracking the Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Organic Particles to Predict Macroaggregation in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water 2023, 15, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Cheng, J.; Fu, R.; Zhan, A. Proteomic response to environmental stresses in the stolon of a highly invasive fouling ascidian. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 761628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, C.K.; Décima, M.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; Selph, K.E.; Yingling, N.; Stukel, M.R. Prey Size Spectra and Predator to Prey Size Ratios of Southern Ocean Salps. Mar. Biol. 2023, 170, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culkin, F.; Morris, R.J. The Fatty Acid Composition of Two Marine Filter-Feeders in Relation to a Phytoplankton Diet. Deep. Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1970, 17, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmai, C.; Jang, A.-Y.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, S.-M.; You, S.; Kang, S.; Park, W.J. Immunomodulatory Activities of Body Wall Fatty Acids Extracted from Halocynthia aurantium on RAW264.7 Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Rod-in, W.; Monmai, C.; Choi, G.S.; Park, W.J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Neutral Lipids, Glycolipids, Phospholipids from Halocynthia aurantium Tunic by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Echegaray, N.; Agregán, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Marine sources: Fish, shellfish, and algae. In Food Lipids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privileggio, L.; Grozić, K.; Maurić Maljković, M.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Janči, T.; Relić, M.; Hamer, B. Effect of Mussel Meal Feed Supplement on Growth, Health Status, Proximate Composition and Fatty Acid Profile of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Fishes 2024, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depledge, M.H.; Rainbow, P.S. Models of Regulation and Accumulation of Trace Metals in Marine Invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 1990, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penezić, A.; Gašparović, B.; Cuculić, V.; Strmečki, S.; Djakovac, T.; Mlakar, M. Dissolved Trace Metals and Organic Matter Distribution in the Northern Adriatic, an Increasingly Oligotrophic Shallow Sea. Water 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žurga, P.; Dubrović, I.; Kapetanović, D.; Orlić, K.; Bolotin, J.; Kožul, V.; Nerlović, V.; Bobanović-Ćolić, S.; Burić, P.; Pohl, K.; et al. Performance of Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis under Variable Environmental Conditions and Anthropogenic Pressure: A Survey of Two Distinct Farming Sites in the Adriatic Sea. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilandžić, N.; Sedak, M.; Čalopek, B.; Zrnčić, S.; Oraić, D.; Benić, M.; Džafić, N.; Ostojić, D.M.; Bogdanović, T.; Petričević, S.; et al. Element Differences and Evaluation of the Dietary Intake from Farmed Oysters and Mussels Collected at Different Sites along the Croatian Coast of the Adriatic Sea. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2016, 45, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ščančar, J.; Zuliani, T.; Turk, T.; Milačič, R. Organotin Compounds and Selected Metals in the Marine Environment of Northern Adriatic Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzafriri-Milo, R.; Benaltabet, T.; Torfstein, A.; Shenkar, N. The Potential Use of Invasive Ascidians for Biomonitoring Heavy Metal Pollution. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, C.; Kanias, G.D. Tunicate Species as Marine Pollution Indicators. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1977, 8, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellante, A.; Piazzese, D.; Cataldo, S.; Parisi, M.G.; Cammarata, M. Evaluation and Comparison of Trace Metal Accumulation in Different Tissues of Potential Bioindicator Organisms: Macrobenthic Filter Feeders Styela plicata, Sabella spallanzanii, and Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, S.; Garcia-Risco, M.; Palacios, Ò.; Capdevila, M.; Cañestro, C.; Albalat, R. Tunicates illuminate the enigmatic evolution of chordate metallothioneins by gene gains and losses, independent modular expansions, and functional convergences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4435–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte (%) | Clavelina oblonga | Cnemidocarpa verrucosa | Polycitor adriaticus | Aplidium conicum | Aplidium elegans | Styela plicata | Botryllus schlosseri | Botrylloides violaceus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 95.440 ± 0.003 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ash | 29.1 ± 1.7 | 38.8 ± 1.7 | 44.1 ± 2.4 | 65.6 ± 5.7 | 52.7 ± 1.8 | 46.2 ± 8.6 | 55.4 ± 8.1 | 52.9 ± 0.6 |
| Proteins | 39.2 ± 0.7 | 55.3 ± 1.4 | 41.9 ± 4.0 | 26.0 ± 2.9 | 37.3 ± 4.3 | 40.9 ± 13.1 | 38.2 ± 7.4 | 41.5 ± 2.4 |
| Lipids | 8.6 ± 0.5 | 4.9 ± 0.9 | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.3 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topić Popović, N.; Hamer, B.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Janči, T.; Fiket, Ž.; Mali, M.; Privileggio, L.; Grozić, K.; Pavičić-Hamer, D.; Vranjković, L.; et al. Biological, Biochemical and Elemental Traits of Clavelina oblonga, an Invasive Tunicate in the Adriatic Sea. Animals 2025, 15, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101371
Topić Popović N, Hamer B, Strunjak-Perović I, Janči T, Fiket Ž, Mali M, Privileggio L, Grozić K, Pavičić-Hamer D, Vranjković L, et al. Biological, Biochemical and Elemental Traits of Clavelina oblonga, an Invasive Tunicate in the Adriatic Sea. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101371
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopić Popović, Natalija, Bojan Hamer, Ivančica Strunjak-Perović, Tibor Janči, Željka Fiket, Matilda Mali, Luca Privileggio, Kristina Grozić, Dijana Pavičić-Hamer, Lucija Vranjković, and et al. 2025. "Biological, Biochemical and Elemental Traits of Clavelina oblonga, an Invasive Tunicate in the Adriatic Sea" Animals 15, no. 10: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101371
APA StyleTopić Popović, N., Hamer, B., Strunjak-Perović, I., Janči, T., Fiket, Ž., Mali, M., Privileggio, L., Grozić, K., Pavičić-Hamer, D., Vranjković, L., Vujović, T., Miloš, M., Dell’Anna, M. M., Nefedova, D., & Čož-Rakovac, R. (2025). Biological, Biochemical and Elemental Traits of Clavelina oblonga, an Invasive Tunicate in the Adriatic Sea. Animals, 15(10), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101371










