Prevalence and Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Caeca
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design, Animals and Diet
2.2. Bird Performance
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Determination of Viable E. coli and Lactic Acid Bacteria Populations and Isolation of E. coli
2.5. Determination of Antimicrobial Resistance
2.6. Extraction of Genomic DNA
2.7. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Data Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
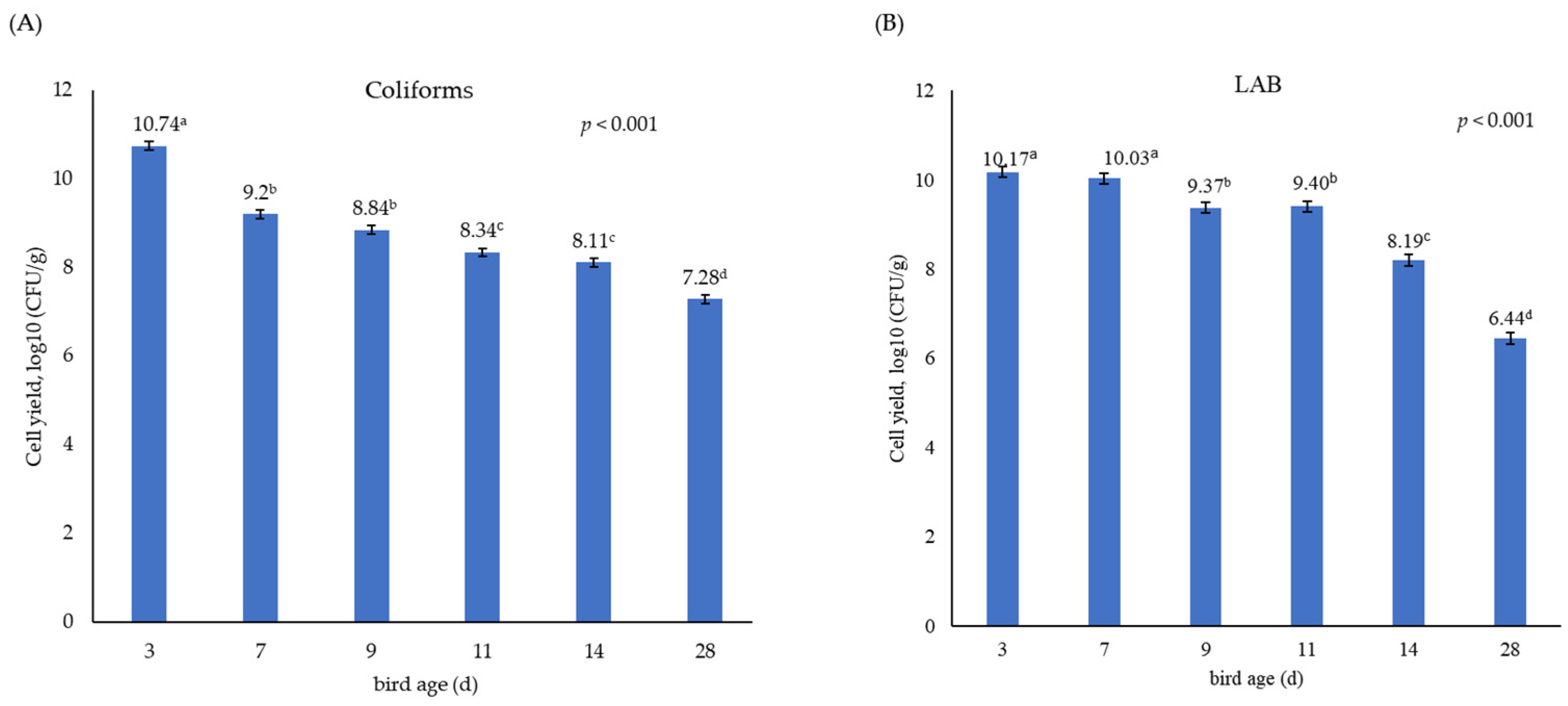
3.1. Growth Performance and Population Size of Coliforms and Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Caecum
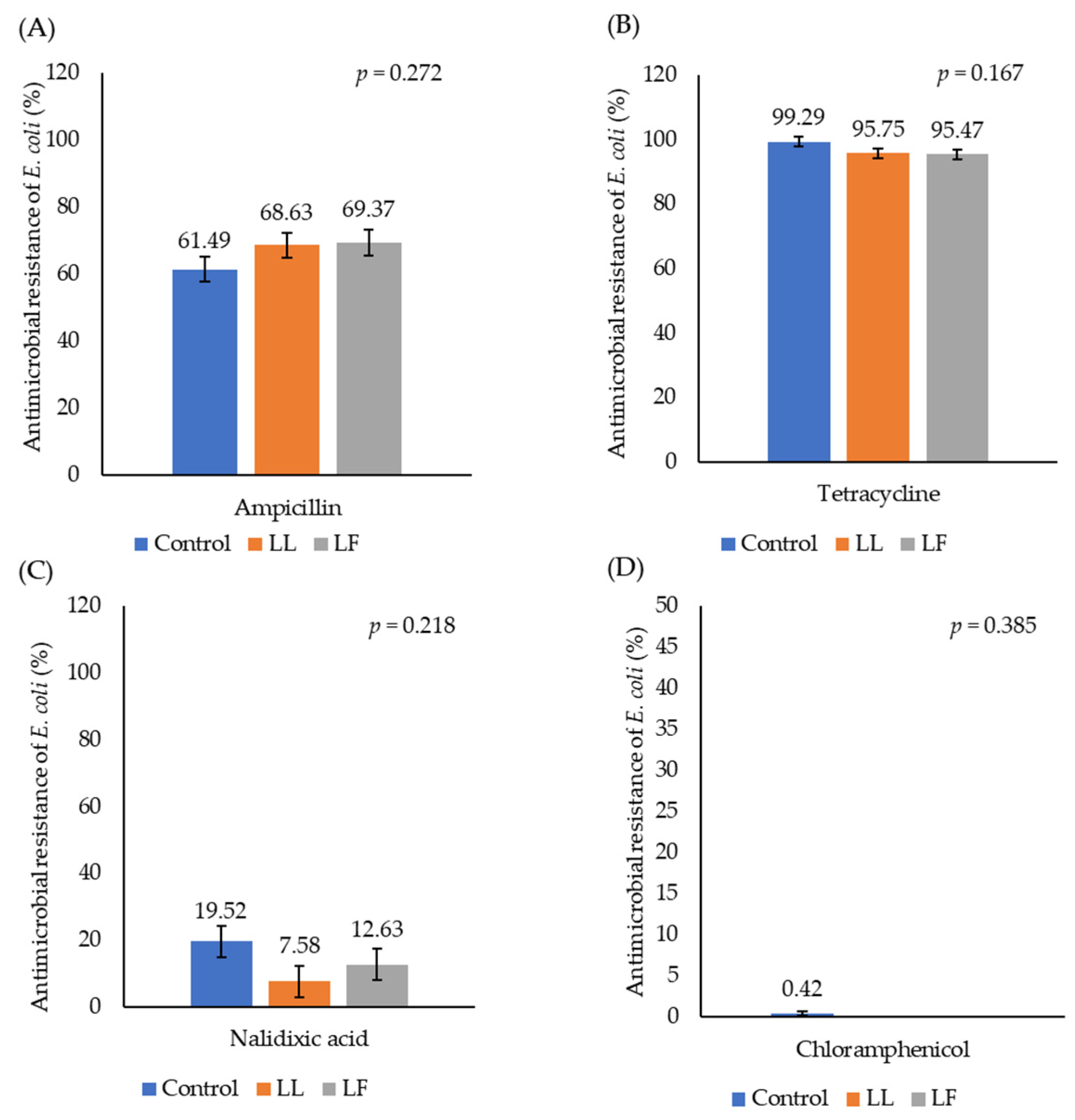
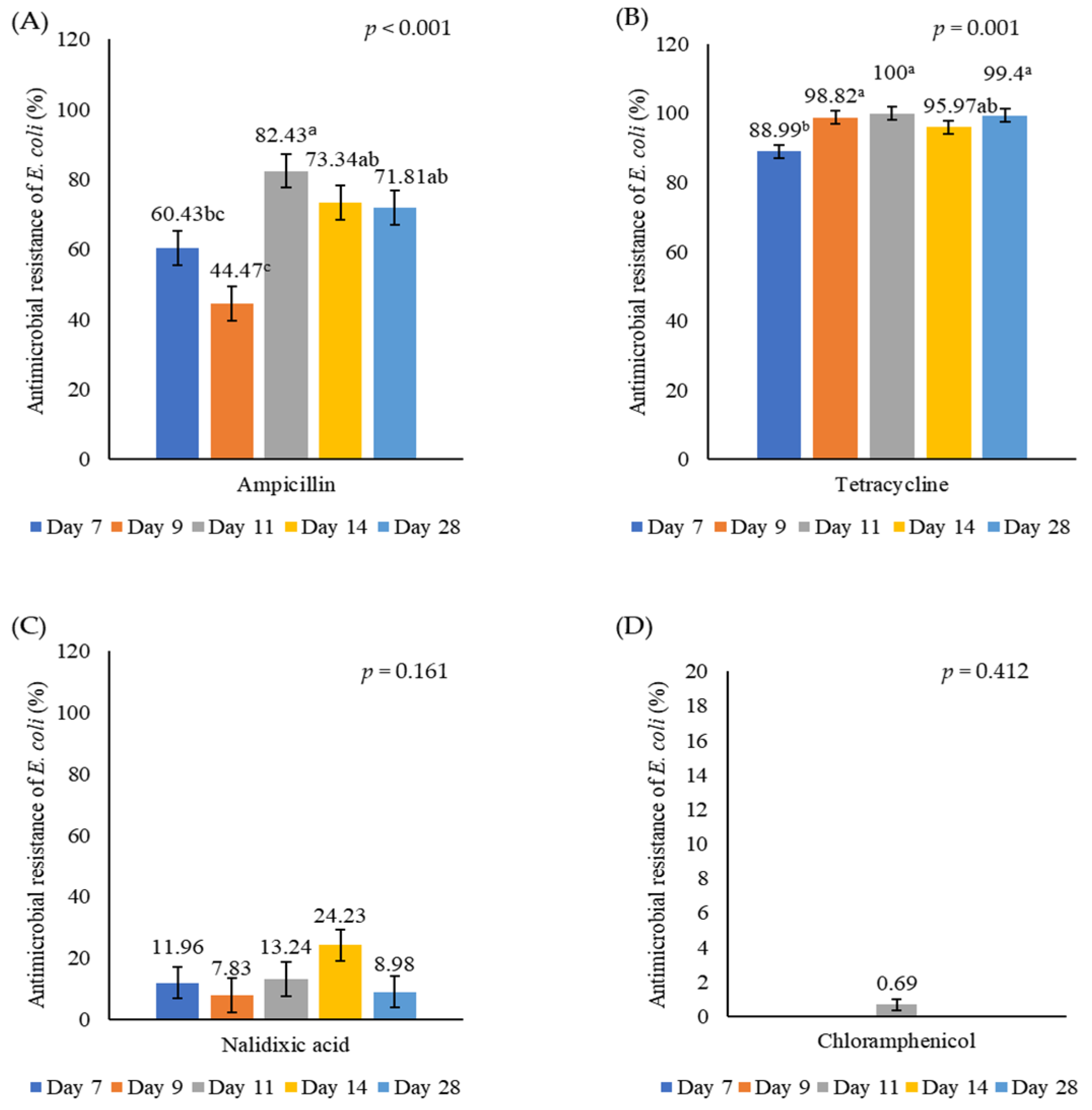
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance of E. coli in Caecal Digesta
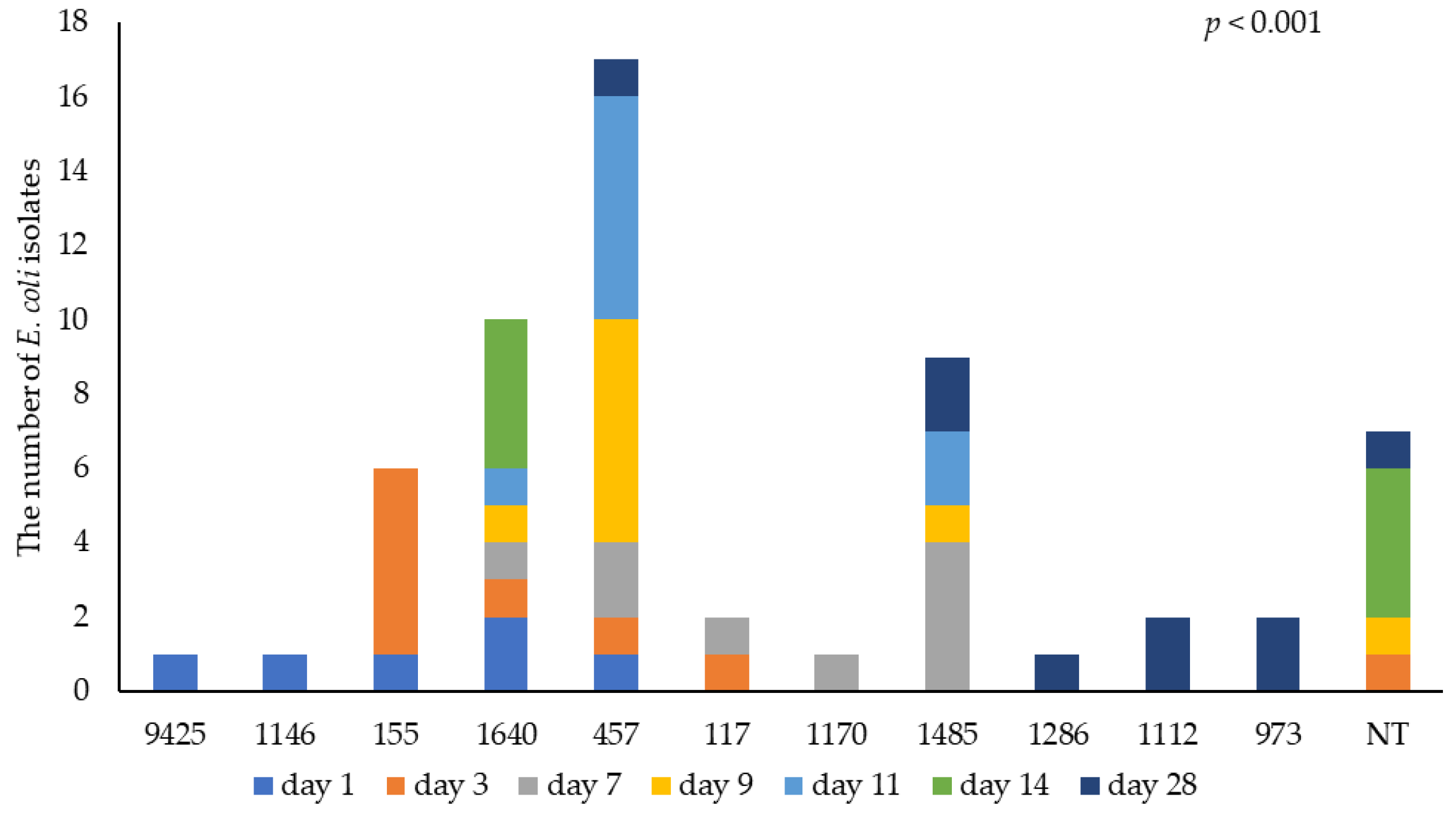
3.3. Identification of E. coli by WGS
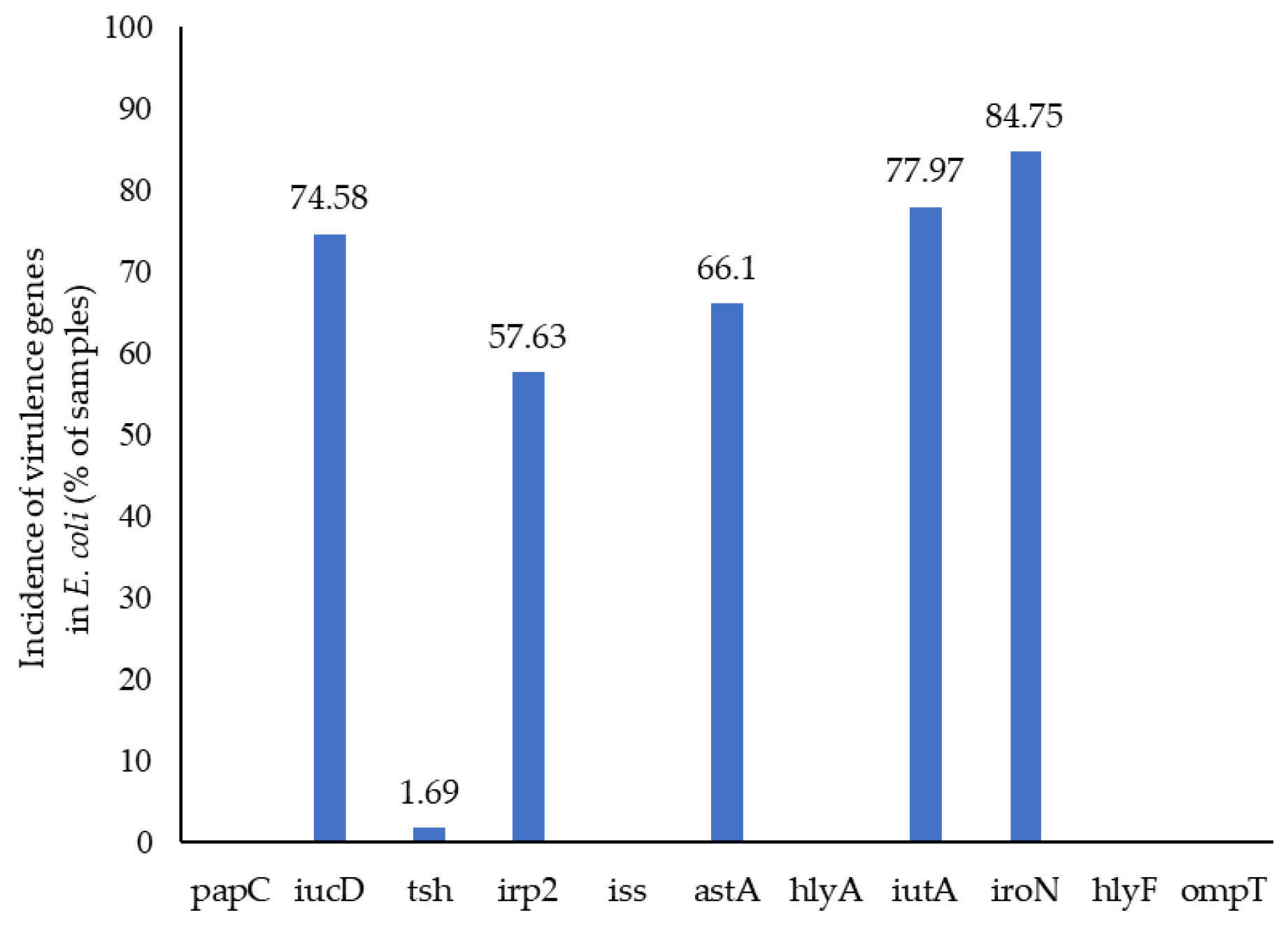
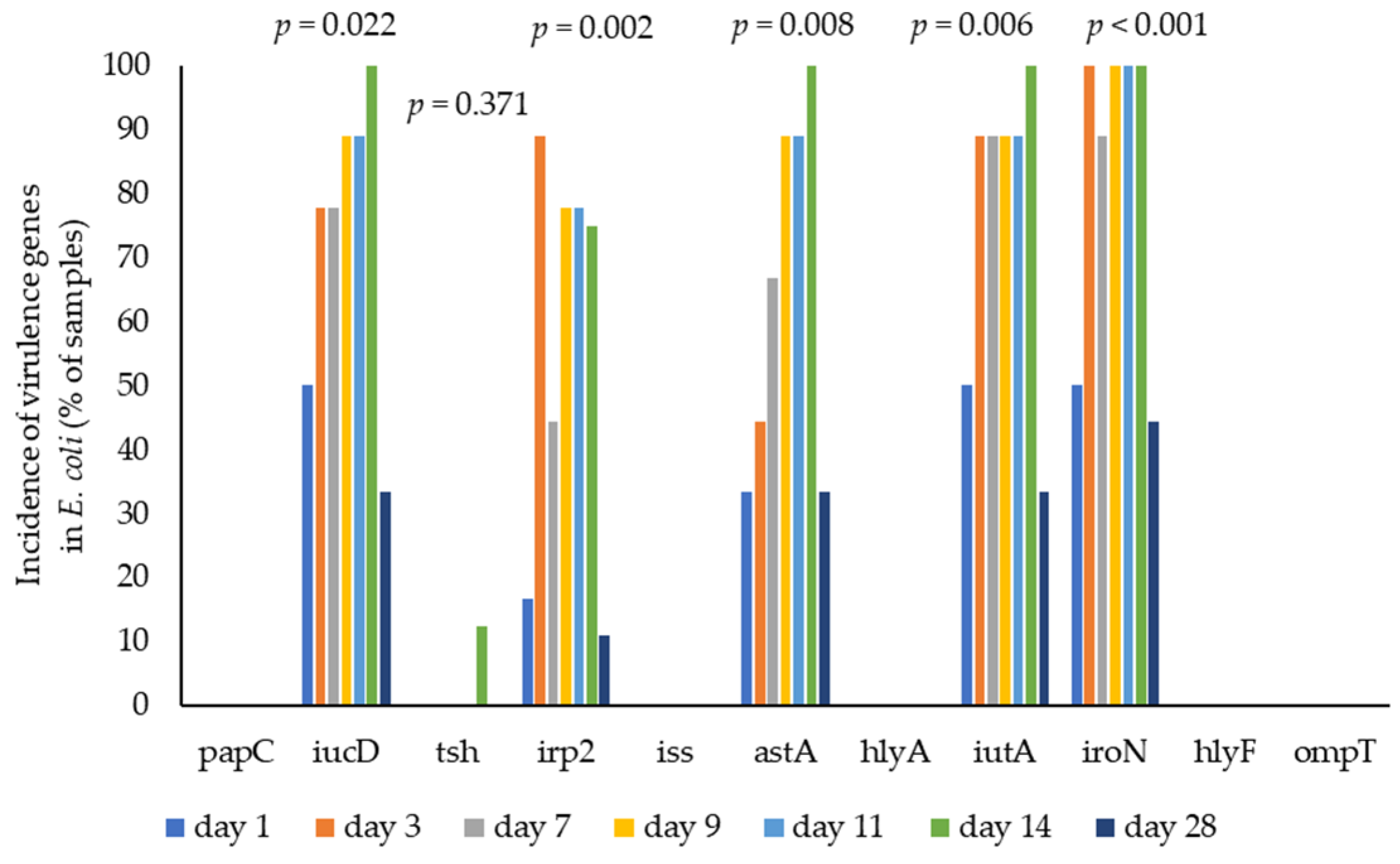
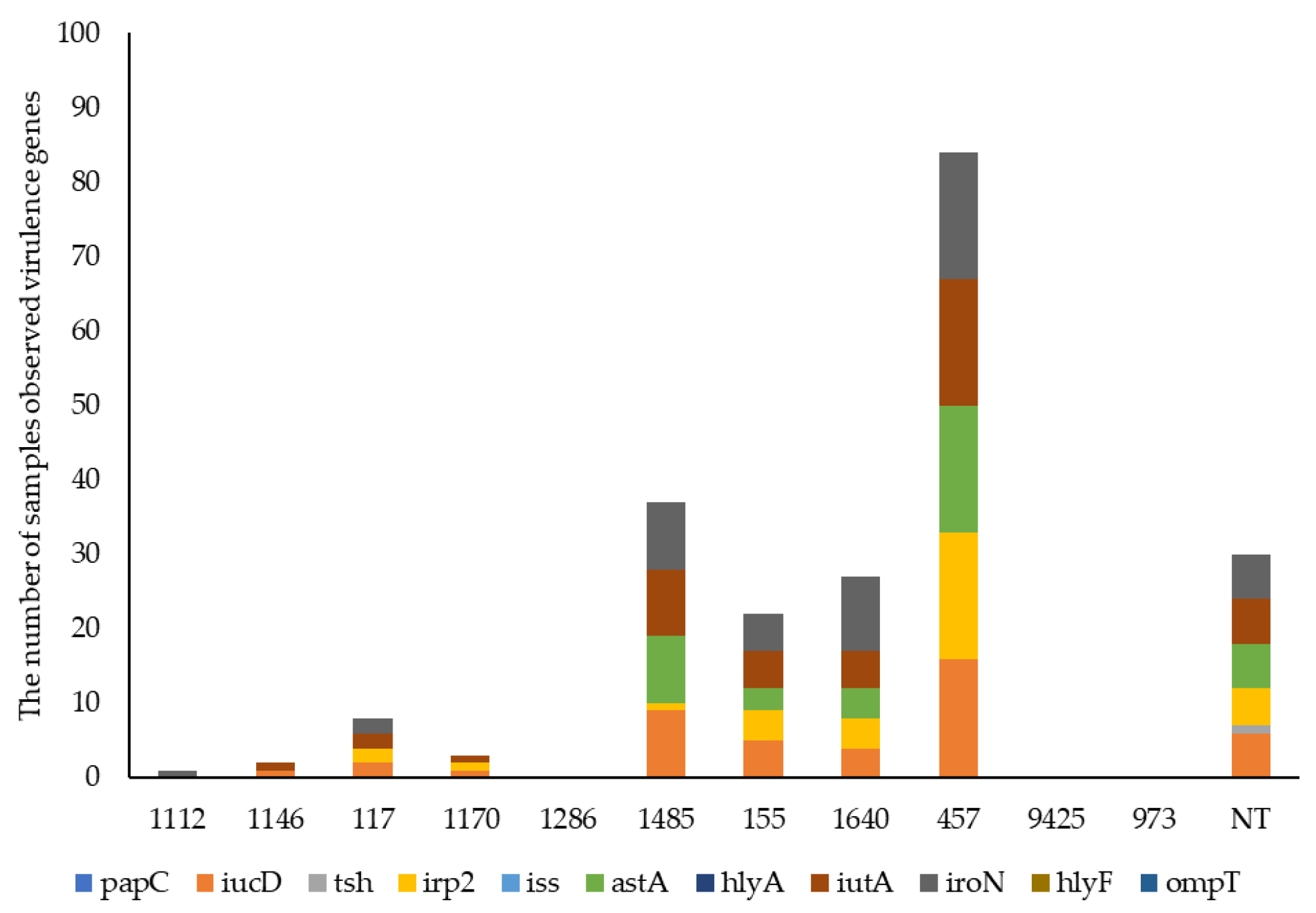
3.4. E. coli Virulence by WGS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hesp, A.; Veldman, K.; van der Goot, J.; Mevius, D.; van Schaik, G. Monitoring antimicrobial resistance trends in commensal Escherichia coli from livestock, the Netherlands, 1998 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1800438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, M.; Józefiak, A.; Kimsa-Furdzik, M.; Dziubdziela, L.; Hudak-Nowak, M.; Wilczyński, J.; Anusz, K. Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. conventionally sampled from factory-farmed chickens–clinical submissions. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 28, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrindt, U. (Patho-) genomics of Escherichia coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, G.; Campos, T.A.d.; Stehling, E.G.; Brocchi, M.; Silveira, W.D.d. Virulence factors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2009, 29, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M.; Dho-Moulin, M.; Dozois, C.M.; Curtiss III, R.; Brown, P.K.; Arné, P.; Brée, A.; Desautels, C.; Fairbrother, J.M. Role of virulence factors in resistance of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli to serum and in pathogenicity. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPeake, S.; Smyth, J.; Ball, H. Characterisation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) associated with colisepticaemia compared to faecal isolates from healthy birds. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 110, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, A.; Ferreira, A.; Fontes, M.; Themudo, P.; Albuquerque, T.; Soares, M.; Fevereiro, M.; Martins, L.; Corrêa de Sá, M. Detection of virulence-associated genes in pathogenic and commensal avian Escherichia coli isolates. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: A combination of virulence with antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Logue, C.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Sherwood, J.S.; Barnes, H.J.; DebRoy, C.; Wannemuehler, Y.M.; Obata-Yasuoka, M.; Spanjaard, L. Associations between multidrug resistance, plasmid content, and virulence potential among extraintestinal pathogenic and commensal Escherichia coli from humans and poultry. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capcarova, M.; Weiss, J.; Hrncar, C.; Kolesarova, A.; Pal, G. Effect of Lactobacillus fermentum and Enterococcus faecium strains on internal milieu, antioxidant status and body weight of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 94, e215–e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Wu, A.; Ding, X.; Lei, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, K.; Chio, J. Effects of probiotic-supplemented diets on growth performance and intestinal immune characteristics of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enan, G.; Abdel-Shafi, S.; Ouda, S.; Negm, S. Novel antibacterial activity of Lactococcus lactis subspecies lactis z11 isolated from zabady. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Aldeieg, M.; Woodward, M.; Juniper, D.; Rymer, C. The effect of Candida famata and Lactobacillus plantarum on the number of coliforms and the antibiotic resistance and virulence of Escherichia coli in the gut of broilers. Animal 2021, 15, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFRA. Code of Practice for the Welfare of Meat Chickens and Meat Breeding Chickens; Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aviagen. Ross 308 Broiler Managment Handbook. Available online: http://en.aviagen.com/brands/ross/products/ross-308 (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- Tonks, A.A. Exploring the Effects of Management Strategies on the Gut Microbiome and Metabolome of Growing Broiler Chickens: An Integrated Metagenomic and Metabolomic Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Reading, Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Musikasang, H.; Tani, A.; H-kittikun, A.; Maneerat, S. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from chicken gastrointestinal digestive tract. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Paula, A.; Casarotti, S.; Penna, A. Lactic acid bacteria antimicrobial compounds: Characteristics and applications. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, R.C.; Roy, P.C.; Sarkar, S.L.; Alam, R.-U.; Jahid, I.K. Isolation, characterization, and assessment of lactic acid bacteria toward their selection as poultry probiotics. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, S.M.L. The Role of Probiotics in the Poultry Industry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3531–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murry, A.; Hinton, A.; Buhr, R. Effect of botanical probiotic containing Lactobacilli on growth performance and populations of bacteria in the ceca, cloaca, and carcass rinse of broiler chickens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2006, 5, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olnood, C.G.; Beski, S.S.; Choct, M.; Iji, P.A. Novel probiotics: Their effects on growth performance, gut development, microbial community and activity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; El-Shall, N.A.; Khalil, D.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Swelum, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Ebaid, H.; Komany, A.; Sammour, R.H.; Sedeik, M.E. Incidence, pathotyping, and antibiotic susceptibility of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli among diseased broiler chicks. Pathogens 2020, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmett, K.; Williams, N.; Chaloner, G.; Humphrey, S.; Wigley, P.; Humphrey, T. The contribution of systemic Escherichia coli infection to the early mortalities of commercial broiler chickens. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnegowda, D.N.; Singh, B.R.; Mariappan, A.K.; Munuswamy, P.; Singh, K.P.; Saminathan, M.; Ramalingam, R.; Chellappa, M.M.; Singh, V.; Dhama, K. Molecular epidemiological studies on avian pathogenic Escherichia coli associated with septicemia in chickens in India. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.; Burkholder, K. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Yousaf, B.; Mian, A.A.; Rehman, A.; Farooq, M.S. Assessing the effect of administering different probiotics in drinking water supplement on broiler performance, blood biochemistry and immune response. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2011, 39, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Multidrug resistant commensal Escherichia coli in animals and its impact for public health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoušková, A.; Čížek, A. A complex approach to a complex problem: The use of whole-genome sequencing in monitoring avian-pathogenic Escherichia coli—A review. Acta Vet. Brno 2020, 89, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, R.; Christensen, H.; Ewers, C.; Bisgaard, M. Impact of Escherichia coli vaccine on parent stock mortality, first week mortality of broilers and population diversity of E. coli in vaccinated flocks. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Antão, E.-M.; Diehl, I.; Philipp, H.-C.; Wieler, L.H. Intestine and environment of the chicken as reservoirs for extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains with zoonotic potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires-dos-Santos, T.; Bisgaard, M.; Christensen, H. Genetic diversity and virulence profiles of Escherichia coli causing salpingitis and peritonitis in broiler breeders. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoudi, A.; Aggad, H. Antibioresistance of Escherichia coli strains isolated from chicken colibacillosis in Western Algeria. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2008, 32, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ngeleka, M.; Brereton, L.; Brown, G.; Fairbrother, J.M. Pathotypes of avian Escherichia coli as related to tsh-, pap-, pil-, and iuc-DNA sequences, and antibiotic sensitivity of isolates from internal tissues and the cloacae of broilers. Avian Dis. 2002, 46, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziva, F.; Stevens, M.P. Colibacillosis in poultry: Unravelling the molecular basis of virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli in their natural hosts. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, A.S. What is a virulence factor? Crit. Care 2008, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. The role of motility as a virulence factor in bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 291, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of minimal predictors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli virulence for use as a rapid diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Nakagawa, E.; Murase, T. Characteristics of Escherichia coli isolated from broiler chickens with colibacillosis in commercial farms from a common hatchery. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, C.-L.; Chang, S.-K.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Chou, C.-H. Characterization of Escherichia coli isolated from day-old chicken fluff in taiwanese hatcheries. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaili, C.; Messai, Y.; Bakour, R. Virulence gene profiles, antimicrobial resistance and phylogenetic groups of fecal Escherichia coli strains isolated from broiler chickens in Algeria. Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delicato, E.R.; de Brito, B.G.; Gaziri, L.C.J.; Vidotto, M.C. Virulence-associated genes in Escherichia coli isolates from poultry with colibacillosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbarpour, R.; Sami, M.; Salehi, M.; Ouromiei, M. Phylogenetic background and virulence genes of Escherichia coli isolates from colisepticemic and healthy broiler chickens in Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence factors, prevalence and potential transmission of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources: Recent reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Starter (0–14 d) | Grower/Finisher (15–28 d) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient composition (g/kg) | ||
| Barley | 40 | 40 |
| Wheat (12.5% CP) | 473 | 546 |
| Soya bean meal (48% CP) | 325 | 230 |
| Rapeseed meal | 42 | 40 |
| Soya bean oil | 50 | 55 |
| L-lysine HCl | 4 | 3 |
| DL-methionine | 3 | 2 |
| L-threonine | 2 | 2 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Salt | 2 | 2.5 |
| Limestone | 10 | 9 |
| Poultry vitamins/minerals 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Dicalcium phosphate (QPRDC) | 17.5 | 14 |
| Sunflower meal (expeller) | 20 | 45 |
| Titanium dioxide | 5 | 5 |
| Nutrient composition (g/kg) | ||
| ME (MJ/kg) | 10.4 | 10.8 |
| Crude protein | 236.0 | 212.0 |
| Total starch | 287.0 | 312.0 |
| Oil A (ether extract) | 41.9 | 41.6 |
| Sugar as sucrose | 42.3 | 38.3 |
| Cystine | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| Methionine | 6.0 | 4.7 |
| Lysine | 13.4 | 12.4 |
| Iron (mg/kg) | 109 | 126 |
| Control | LL | LF | SEM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight gain (days 1–14, g/bird/d) | 22.51 | 20.06 | 21.26 | 1.23 | 0.39 |
| Weight gain (days 15–28, g/bird/day) | 63.8 | 58.3 | 58.2 | 1.79 | 0.061 |
| Feed intake (days 15–28, g/bird/day) | 101.7 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 3.12 | 0.623 |
| FCR (days 15–28, g/bird/day) | 1.60 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 0.049 | 0.421 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, A.-R.; Woodward, M.J.; Rymer, C. Prevalence and Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Caeca. Animals 2025, 15, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101353
Lee A-R, Woodward MJ, Rymer C. Prevalence and Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Caeca. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101353
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ah-Ran, Martin John Woodward, and Caroline Rymer. 2025. "Prevalence and Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Caeca" Animals 15, no. 10: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101353
APA StyleLee, A.-R., Woodward, M. J., & Rymer, C. (2025). Prevalence and Characterisation of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) of Escherichia coli Isolated from Broiler Caeca. Animals, 15(10), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101353





