The Molecular Mechanism by Which miR-129a-3p Targets the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Regulate Inflammatory Damage in 3D4/21 Cells Infected with Glaesserella parasuis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial and Cell Culture Conditions
2.3. Animals and Sample Collection
2.4. Cell Transfection and Processing
2.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.8. Dual-Luciferase Assay
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. G. parasuis Affects the Expression of miR-129a-3p in Piglets and PAM
3.2. miR-129a-3p Affects the Morphology of G. parasuis-Infected PAMs
3.3. miR-129a-3p Affects Lesion Characterization of G. parasuis-Infected PAMs
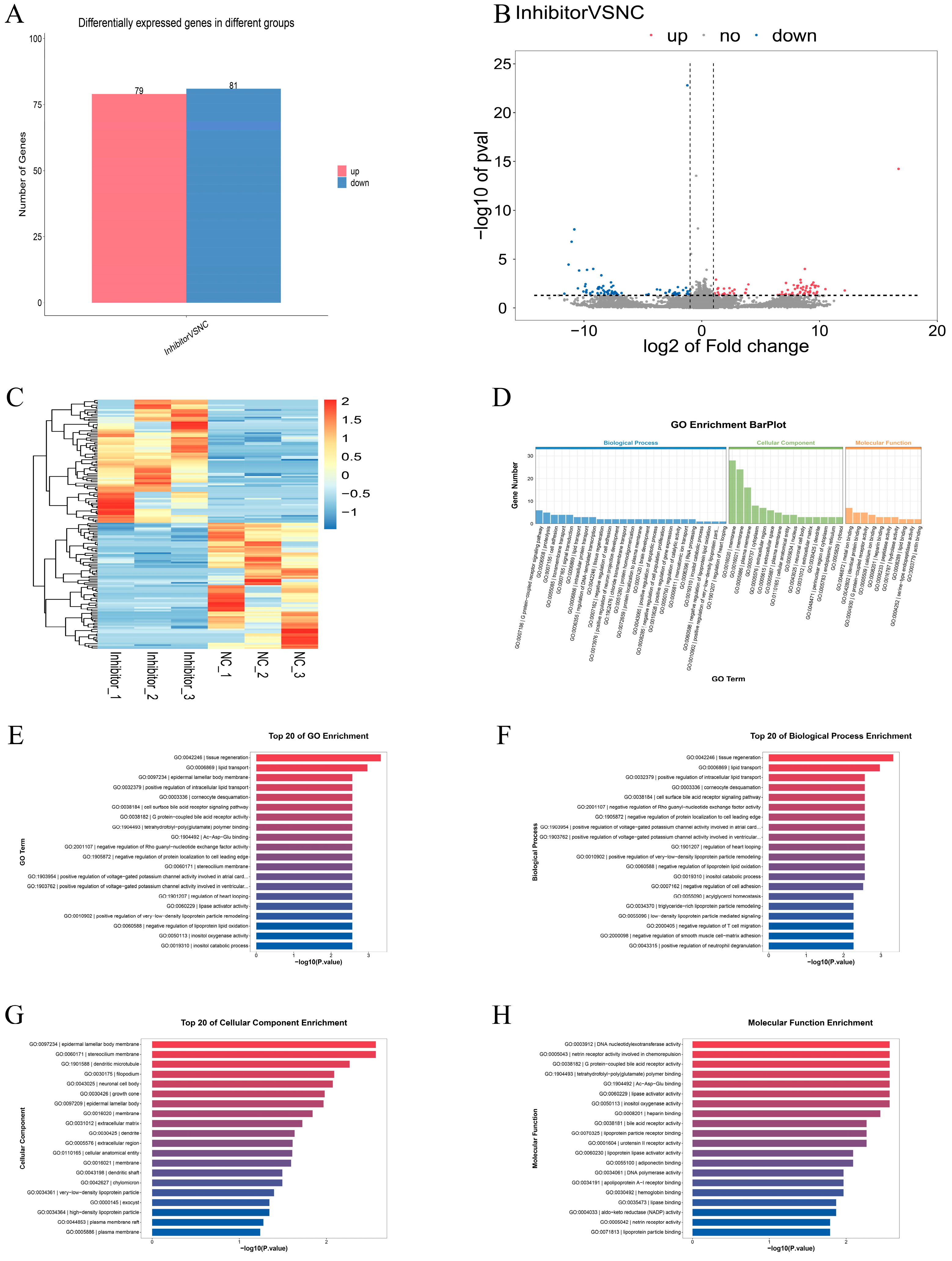
3.4. Differential Expression Analysis and Functional Annotation of mRNA After miR-129a-3p Inhibition
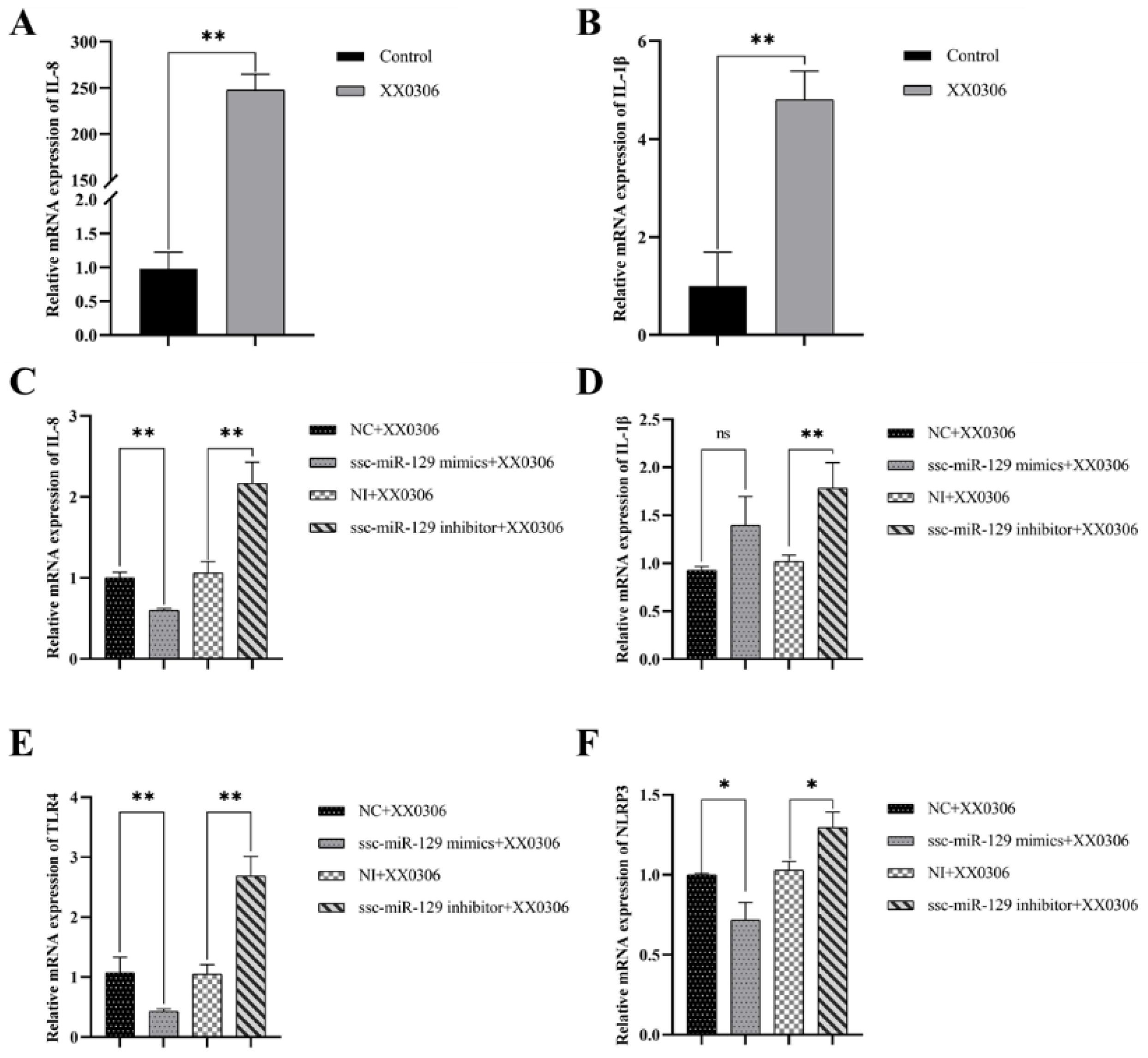
3.5. MiR-129a-3p Affects the Inflammatory Response to G. parasuis Infection in PAMs
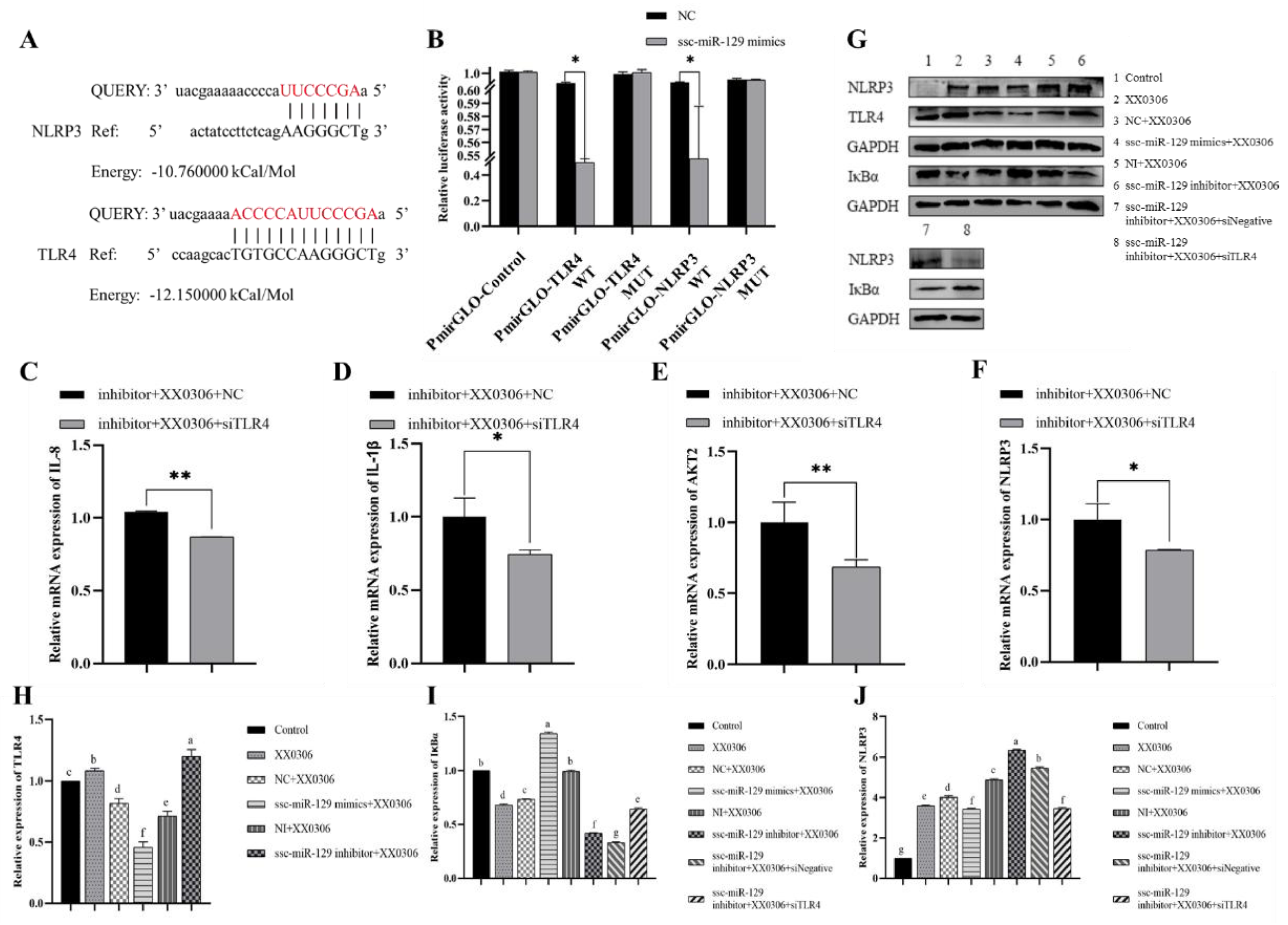
3.6. MiR-129a-3p Directly Targets the 3′-UTR of TLR4 and NLRP3
3.7. TLR4 siRNA Partially Reverses Changes in miR-129a-3p Inhibitor Associated with Inflammatory Factors and Inflammatory Signaling Pathway Molecules in G. parasuis-Infected PAMs
3.8. MiR-129a-3p Regulates Inflammation Through TLR4/NF-κB in G. parasuis-Infected PAM Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, X.; Chang, X.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Fan, H. Glaesserella parasuis induces inflammatory response in 3D4/21 cells through activation of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway via ROS. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 256, 109057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Wang, Z.; Wen, S.; Lin, Y.; Gu, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Cao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. LRRC8A promotes Glaesserella parasuis cytolethal distending toxin-induced p53-dependent apoptosis in NPTr cells. Virulence 2023, 14, 2287339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Song, X.; Cao, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yue, H.; Zhang, B. Glaesserella parasuis induces IL-17 production might through PKC-ERK/MAPK and IkappaB/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 273, 109521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Cao, H.; Zeng, W.; Li, Z.; He, Q. Deletion of the crp gene affects the virulence and the activation of the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in PK-15 and iPAM cells derived from G. parasuis serovar 5. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 261, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhuo, R.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Jin, H.; Hua, K. AMPK signaling pathway regulated the expression of the ApoA1 gene via the transcription factor Egr1 during G. parasuis stimulation. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 294, 110106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Dong, Q.; Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, R.; Tian, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, W.; Qiu, Y.; et al. PD-1/PD-L1 axis induced host immunosuppression via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in piglets infected by Glaesserella parasuis. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Li, F.; Chen, K.; Ding, W.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, K.; Zhao, Z. Comparison of the Glaesserella parasuis Virulence in Mice and Piglets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 659244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Cao, Q.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.; Lv, Y.; Tan, C.; Dai, M.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Sialylated Lipooligosaccharide Contributes to Glaesserella parasuis Penetration of Porcine Respiratory Epithelial Barrier. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Ma, Z.; Fan, H. Glaesserella parasuis serotype 4 exploits fibronectin via RlpA for tracheal colonization following porcine circovirus type 2 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yao, D. MiR-206 Suppresses Triacylglycerol Accumulation via Fatty Acid Elongase 6 in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals 2024, 14, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Sharma, N.; Prasad, M. Noncoding but Coding: Pri-miRNA into the Action. Trends Plant. Sci. 2021, 26, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, M.; Mohan, M. MicroRNAs: History, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D.; Schaefer, A. General principals of miRNA biogenesis and regulation in the brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Tran, N. Global miRNA to miRNA Interactions: Impacts for miR-21. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.; Mano, M.; Eulalio, A. MicroRNAs at the Host-Bacteria Interface: Host Defense or Bacterial Offense. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groven, R.V.M.; Greven, J.; Mert, U.; Horst, K.; Zhao, Q.; Blokhuis, T.J.; Huber-Lang, M.; Hildebrand, F.; van Griensven, M. Circulating miRNA expression in extracellular vesicles is associated with specific injuries after multiple trauma and surgical invasiveness. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1273612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Trials and Tribulations of MicroRNA Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.W.; Nemunaitis, J. Modulation of miRNA activity in human cancer: A new paradigm for cancer gene therapy? Cancer Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad-Kazan, H.; Bitar, N.; Najar, M.; Lewalle, P.; Fayyad-Kazan, M.; Badran, R.; Hamade, E.; Daher, A.; Hussein, N.; ElDirani, R.; et al. Circulating miR-150 and miR-342 in plasma are novel potential biomarkers for acute myeloid leukemia. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.W.; Tsai, K.N.; Chen, Y.S.; Chang, R.Y. Differential miRNA Expression Profiling Reveals Correlation of miR125b-5p with Persistent Infection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Elfenbein, S.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, M.; Qiu, C.; Ding, Y.; Lu, J. Characterization of the mammalian miRNA turnover landscape. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2326–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Du, M.; Luo, H.; Ran, F.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hao, J.; Li, D.; Li, J. Multifunctional mesoporous silica-cerium oxide nanozymes facilitate miR129 delivery for high-quality healing of radiation-induced skin injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Yim, R.L.; Kwong, Y.L.; Leung, C.Y.; Hui, P.K.; Cheung, F.; Liang, R.; Jin, D.Y.; Chim, C.S. Epigenetic inactivation of the MIR129-2 in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.W.; Pyun, J.M.; Bice, P.J.; Bennett, D.A.; Saykin, A.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, Y.H.; Nho, K. miR-129-5p as a biomarker for pathology and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Xu, L.; Jia, X.; Li, S.; Wei, L. MicroRNA-129 plays a protective role in sepsis-induced acute lung injury through the suppression of pulmonary inflammation via the modulation of the TAK1/NF-kappaB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, M.; Xiang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. Exosomal-miR-129-2-3p derived from Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected intestinal epithelial cells promotes experimental colitis through regulating TIMELESS-mediated cellular senescence pathway. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2240035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, D.; Zhu, R.; Cao, Y. Exosomal miR-155-5p drives widespread macrophage M1 polarization in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced acute lung injury via the MSK1/p38-MAPK axis. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Pu, F.; Zhou, F.; Dai, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Xia, P. Has-miR-30c-1-3p inhibits macrophage autophagy and promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival by targeting ATG4B and ATG9B. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, K.; Shi, M.; Gong, H.; Han, M.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. MicroRNAs in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric cancer: Function and clinical application. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 205, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipoor, S.D. Editorial: Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers in infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1239739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doghish, A.S.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Nassar, Y.A.; Nasr, S.M.; Mohammed, O.A.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Rizk, N.I.; Lutfy, R.H.; Abdel Mageed, S.S.; Ismail, M.A.; et al. Harnessing miRNAs: A Novel Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goekeri, C.; Pennitz, P.; Groenewald, W.; Behrendt, U.; Kirsten, H.; Zobel, C.M.; Berger, S.; Heinz, G.A.; Mashreghi, M.F.; Wienhold, S.M.; et al. MicroRNA-223 Dampens Pulmonary Inflammation during Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Cells 2023, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.C. G protein-coupled receptor connectivity to NF-kappaB in inflammation and cancer. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 27, 320–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H. PPAR-alpha Agonist WY-14643 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation in Synovial Fibroblasts via NF-kB Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 59, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, X.; Liu, M.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, M.; Lin, H.; Fan, H. Glaesserella parasuis serotype 4 HPS4-YC disrupts the integrity of the swine tracheal epithelial barrier and facilitates bacterial translocation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, X.; Xu, K.; Chen, H. Transcriptome Analysis of miRNA and mRNA in Porcine Skeletal Muscle following Glaesserella parasuis Challenge. Genes 2024, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Jia, Y.C.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.; Yin, R.L.; Yuan, J.; Wang, L.X.; Guo, Z.B.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. Virulence assessment of four Glaesserella parasuis strains isolated in Liaoning province of China. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 158, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Qi, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Su, J.; Yu, D.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. The G-Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor Gpbar1 (TGR5) Inhibits Gastric Inflammation Through Antagonizing NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Guo, P.; Su, T.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. G protein-coupled receptor kinase type 2 and beta-arrestin2: Key players in immune cell functions and inflammation. Cell Signal. 2022, 95, 110337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, P.O.; Kleb, S.S.; Noonepalle, S.K.; Amuso, V.M.; Varshney, R.; Rudolph, M.C.; Dhaliwal, T.K.; Nguyen, D.V.; Mazumder, M.F.; Babirye, N.S.; et al. G-protein-coupled receptor 84 regulates acute inflammation in normal and diabetic skin wounds. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, P.; Chang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. ER-localized Hrd1 ubiquitinates and inactivates Usp15 to promote TLR4-induced inflammation during bacterial infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2331–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimy, J.K.; Reeves, B.C.; Kahle, K.T. Targeting TLR4-dependent inflammation in post-hemorrhagic brain injury. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Masking of typical TLR4 and TLR5 ligands modulates inflammation and resolution by Helicobacter pylori. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, T.; Han, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Ni, X. Propofol Regulates the TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway Through miRNA-155 to Protect Colorectal Cancer Intestinal Barrier. Inflammation 2021, 44, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Shikonin improve sepsis-induced lung injury via regulation of miRNA-140-5p/TLR4-a vitro and vivo study. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Zheng, H.; Lv, J.; Fu, Z.; Mao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B. Mechanism of Zhenwu Decoction modulating TLR4/NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha loop through miR-451 to delay renal fibrosis in type 2 CRS. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Li, K.Y.; Lan, Y.; Zeng, H.Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Wang, H. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A key contributor to the inflammation formation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 174, 113683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Su, X.; Yan, S.; Su, W.; et al. A Novel Drug Combination of Mangiferin and Cinnamic Acid Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting TLR4/NFkappaB/NLRP3 Activation-Induced Pyroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Hua, F.; Zhang, Z. Beta-amyloid activates NLRP3 inflammasome via TLR4 in mouse microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 736, 135279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.J.; Ohta, S.; Sheu, K.M.; Spreafico, R.; Adelaja, A.; Taylor, B.; Hoffmann, A. NF-kappaB dynamics determine the stimulus specificity of epigenomic reprogramming in macrophages. Science 2021, 372, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Zou, J.; Cai, J.; Shi, R.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis polysaccharide ameliorates cholestatic liver injury by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inhibiting the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, S.M.; Ghosh, S.; Tantiwong, P.; Meka, C.S.; Eagan, P.; Jenkinson, C.P.; Cersosimo, E.; Defronzo, R.A.; Coletta, D.K.; Sriwijitkamol, A.; et al. Elevated toll-like receptor 4 expression and signaling in muscle from insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ); droplet (
); droplet ( ); phagosome (
); phagosome ( ); cytoplasmic lysis (
); cytoplasmic lysis ( ); medullary structure (
); medullary structure ( ); vacuole (
); vacuole ( ); crescent (
); crescent ( ); Cell membrane rupture lysis (
); Cell membrane rupture lysis ( ); mitochondria (
); mitochondria ( ); golgi apparatus (
); golgi apparatus ( ); rough endoplasmic reticulum (
); rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ); multivesicular body (
); multivesicular body ( ); scale (
); scale ( )). ns p > 0.05 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
)). ns p > 0.05 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
 ); droplet (
); droplet ( ); phagosome (
); phagosome ( ); cytoplasmic lysis (
); cytoplasmic lysis ( ); medullary structure (
); medullary structure ( ); vacuole (
); vacuole ( ); crescent (
); crescent ( ); Cell membrane rupture lysis (
); Cell membrane rupture lysis ( ); mitochondria (
); mitochondria ( ); golgi apparatus (
); golgi apparatus ( ); rough endoplasmic reticulum (
); rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ); multivesicular body (
); multivesicular body ( ); scale (
); scale ( )). ns p > 0.05 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
)). ns p > 0.05 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control.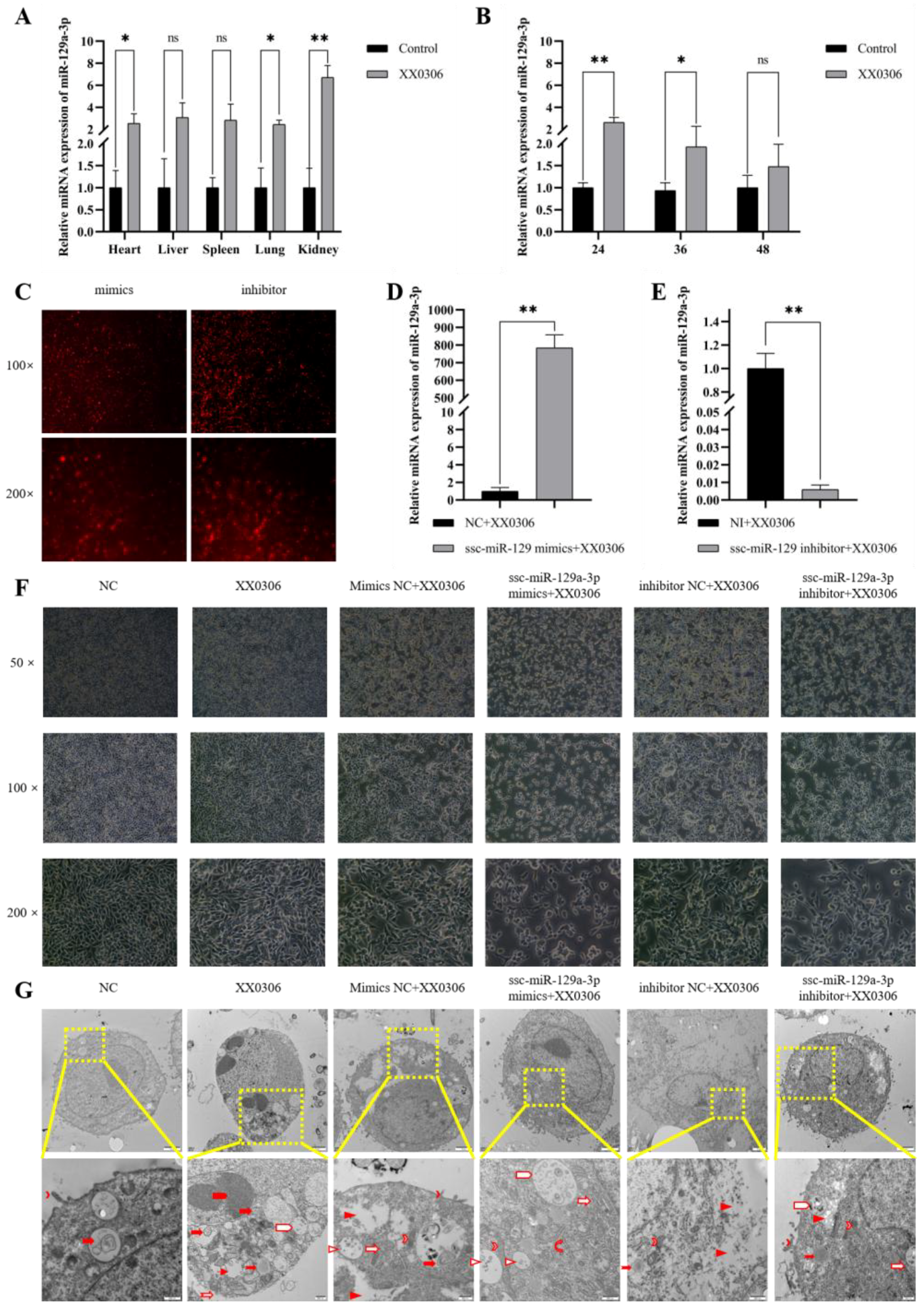
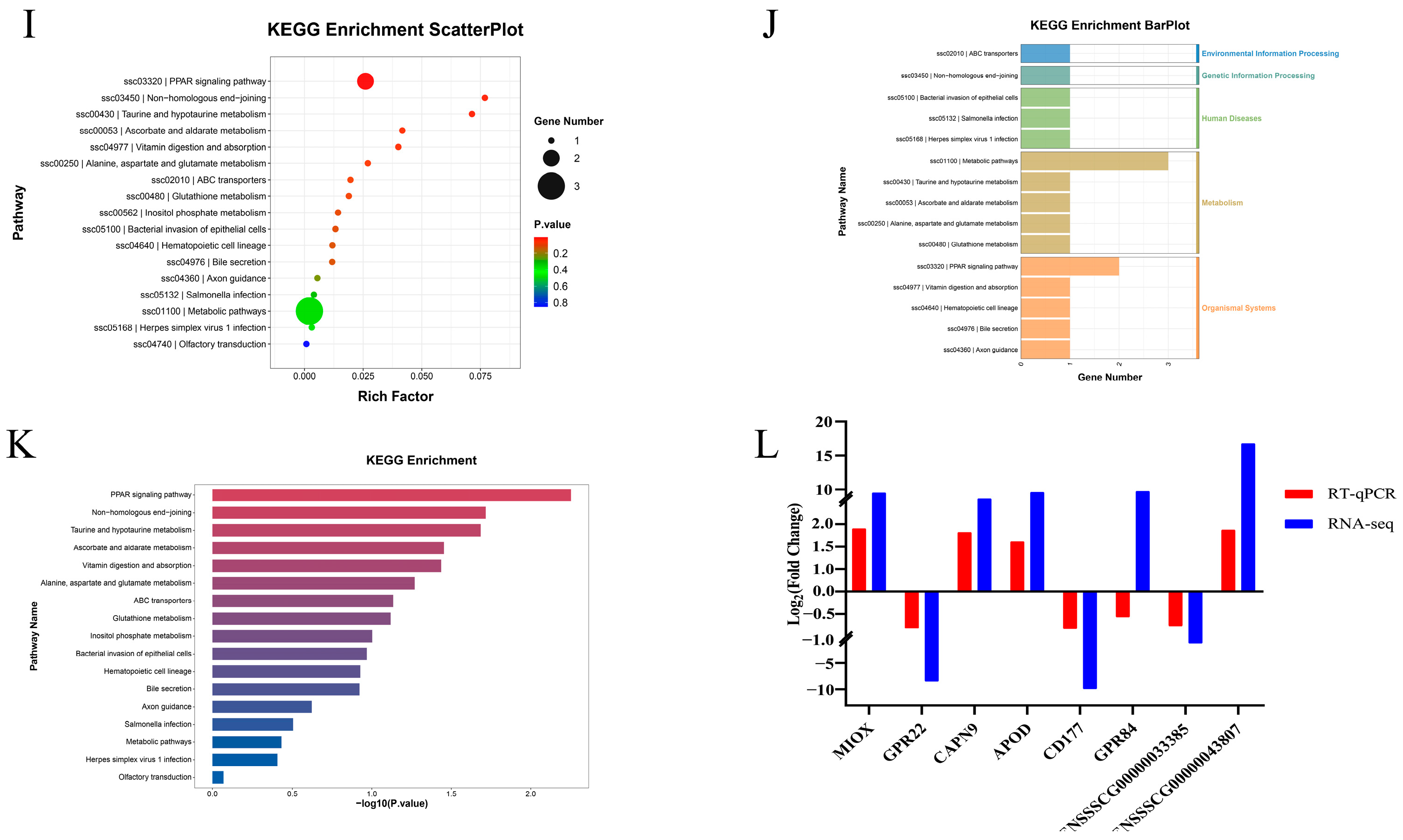

| Names | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| mimic NC | sense: UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| antisense: ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT | |
| inhibitor NC | sense: CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA |
| ssc-miR-129a-3p mimics | sense: AAGCCCUUACCCCAAAAAGCAU |
| antisense: GCUUUUUGGGGUAAGGGCUUUU | |
| ssc-miR-129a-3p inhibitor | sense: AUGCUUUUUGGGGUAAGGGCUU |
| NC | sense: UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| siTLR4 | sense: CAGGAAUCCUGGUCUAUAATT |
| Gene Name | Accession No. | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ssc-miR-129a-3p | MIMAT0013959 | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAG GTATTCGCACTGGATACGACATGCTT |
| F: CGAAGCCCTTACCCCAAA | ||
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | ||
| U6 | XM_021101534.1 | RT: AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| F: CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA | ||
| R: AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| Gene Name | Accession No. | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | NM_001206359.1 | F: CACAGTCAAGGCGGAGAAC | 106 |
| R: CGTAGCACCAGCATCACC | |||
| IL-1β | XM_021085847.1 | F: TGATGCCAACGTGCAGTCTA | 92 |
| R: GGAGAGCCTTCAGCATGTGT | |||
| IL-8 | NM_213867.1 | F: TCCAAACTGGCTGTTGCCTTCTTG | 132 |
| R: GGGGTGGAAAGGTGTGGAATGC | |||
| AKT2 | XM_013988560.2 | F: AAAGTCATCCTGGTGCG | 137 |
| R: GGGTGCCTGGTGTTCTG | |||
| NLRP3 | NM_001256770.2 | F: GGAGGAGGAGGAAGAGGAGATA | 147 |
| R: AGGACTGAGAAGATGCCACTAC | |||
| TLR4 | NM_001113039.2 | F: CGTCAGTTCTCACCTTCCTCC | 165 |
| R: CATTCCTCACCCAGTCTTCGT |
| Gene Name | Accession No. | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ENSSSCG00000033385 | ENSSSCG00000033385 | F: GCACGCTTAGGGAGGAACAA |
| R: AGGACCTCTGGTCGGTAGTC | ||
| ENSSSCG00000043807 | ENSSSCG00000043807 | F: TGGGAATGTTTGGACCTTCGT |
| R: TTTTGCTCCAACAAGGGAACC | ||
| MIOX | ENSSSCG00000023749 | F: CTCTCAGGATGAAGGACCCAG |
| R: AGCTTGTAGGTGCGGAAGAC | ||
| GPR22 | ENSSSCG00000015442 | F: CTGAGTCTCTTCTCCCAGTCCT |
| R: ACTTGCCAGTTCAAAAGCAGC | ||
| CAPN9 | ENSSSCG00000010182 | F: AGAATGCGAGCCGGATGTTC |
| R: CAACCAAGACTCCTCGGGAC | ||
| APOD | ENSSSCG00000011831 | F: ATCTGAGCACGTTTGTCCCA |
| R: GCCTAAAAGCTGAGCTCGTG | ||
| GPR84 | ENSSSCG00000000291 | F: AAGGCCTAGATTTTGGAGTGGA |
| R: GCCATTCCCAGGCCTCTTTA | ||
| CD177 | ENSSSCG00000003051 | F: ATGGACCACAAGTGCGGAG |
| R: AGGAGTGATCTGTGTCCTGC |
| Gene Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TLR4 WT | CATGATACAACAGCCTTCACTTAAGGAGGGAAAACTCCCAACGTGTCCCTTGGTCAGCTGGATCCCGTGCTTGTTAACAAGTACTAAATCCTGCAACATGCCAAGCACTGTGCCAAGGGCTGGTGATTCAGTGATGCCCGAGATACACAGGACTGCCAGTCTCGTGGAGTTTACAATTTAGAGGGACTAAACACTGTTCTAAAATACAGAACTTCCAGGTGG | 222 |
| TLR4 MUT | CATGATACAACAGCCTTCACTTAAGGAGGGAAAACTCCCAACGTGTCCCTTGGTCAGCTGGATCCCGTGCTTGTTAACAAGTACTAAATCCTGCAACATGCCAAGCACACTCCCTTCCCGAGGTGATTCAGTGATGCCCGAGATACACAGGACTGCCAGTCTCGTGGAGTTTACAATTTAGAGGGACTAAACACTGTTCTAAAATACAGAACTTCCAGGTGG | 222 |
| NLRP3 WT | GCAAGCTAAAGAAGCTCTGGTTGGTCAGTTGCTGTCTCACATCAGCGTGTTGTGAGGATCTTGCGTCCGTCCTGAGCAGCAATCATTCCCTGACCAGACTATAGACCCCAAGTTAAGGGCTCATGCCCTGGGAGACTCAGGAGTTGGAATTTTATGTGAAAAAGCAAAGCATCCACAATGTAACCTGCAAAAACTGGGGTTGGTGAATTCTGGCCTTACATC | 222 |
| NLRP3 MUT | GCAAGCTAAAGAAGCTCTGGTTGGTCAGTTGCTGTCTCACATCAGCGTGTTGTGAGGATCTTGCGTCCGTCCTGAGCAGCAATCATTCCCTGACCAGACTATAGACCCCAACTATTCCCGACATGCCCTGGGAGACTCAGGAGTTGGAATTTTATGTGAAAAAGCAAAGCATCCACAATGTAACCTGCAAAAACTGGGGTTGGTGAATTCTGGCCTTACATC | 222 |
| Names | Dilution Rate | Manufacturer | Product Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 1:10,000 | Proteintech, Wuhan, China | 10494-1-AP |
| IkB Alpha | 1:2000 | Proteintech, Wuhan, China | 10268-1-AP |
| NLRP3 | 1:300 | Proteintech, Wuhan, China | 19771-1-AP |
| TLR4 | 1:1000 | ABclonal, Wuhan, China | A5258 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N.; Shen, A.; Jia, Y.; Yin, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Yin, R. The Molecular Mechanism by Which miR-129a-3p Targets the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Regulate Inflammatory Damage in 3D4/21 Cells Infected with Glaesserella parasuis. Animals 2025, 15, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101355
Guo Z, Zhou Y, Li N, Shen A, Jia Y, Yin R, Yang J, Yuan J, Yin R. The Molecular Mechanism by Which miR-129a-3p Targets the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Regulate Inflammatory Damage in 3D4/21 Cells Infected with Glaesserella parasuis. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101355
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhongbo, Yuanyuan Zhou, Na Li, Aobo Shen, Yongchao Jia, Ronglan Yin, Junjie Yang, Jing Yuan, and Ronghuan Yin. 2025. "The Molecular Mechanism by Which miR-129a-3p Targets the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Regulate Inflammatory Damage in 3D4/21 Cells Infected with Glaesserella parasuis" Animals 15, no. 10: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101355
APA StyleGuo, Z., Zhou, Y., Li, N., Shen, A., Jia, Y., Yin, R., Yang, J., Yuan, J., & Yin, R. (2025). The Molecular Mechanism by Which miR-129a-3p Targets the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Regulate Inflammatory Damage in 3D4/21 Cells Infected with Glaesserella parasuis. Animals, 15(10), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101355





