The Governance of Plastics
A topical collection in Social Sciences (ISSN 2076-0760).
Submission Status:
Closed
|
Viewed by 61301
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Rosalind Malcolm
Prof. Dr. Rosalind Malcolm
 Prof. Dr. Rosalind Malcolm
Prof. Dr. Rosalind Malcolm
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Environmental Regulatory Research Group, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, UK
Interests: governance of plastics waste; ecodesign laws; regulatory frameworks for environmental management, compliance and enforcement
 Dr. Katrien Steenmans
Dr. Katrien Steenmans
 Dr. Katrien Steenmans
Dr. Katrien Steenmans
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
School of Law, Coventry University, Coventry CV1 5FB, UK
Interests: EU environmental law; waste law; law and the circular economy; blockchain technology and governance; climate finance law; property rights in waste; property rights for promoting transitions towards circular economies; industrial symbiosis
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Despite the popular call towards a 'no-plastics' future, a world without plastics is unimaginable. The challenge is to find a way to prevent plastic waste from escaping into the environment, while enhancing a circular economy for plastics, that is, a closed-loop system where end-of-service-life plastic objects are not discarded but rather become a new resource. The increased use of plastics over the past 50–60 years is now presenting the world with what can only be described as a 'Wicked Problem', a problem combining technical and social aspects, for which traditional solutions cannot work. Simple regulatory solutions such as bans (as it can be seen in around 20 African countries where plastics bags have been banned) can be effective but may also cause disadvantages such as the loss of useful material. The danger from such a reactive regulatory approach is to displace the problems caused by our consumption and production patterns, while thinking that the problem of plastic waste in the environment has been solved. Bans on the importation of certain plastic waste by DAC-listed countries may control the problem in the interim but not solve it for the future. Implementing a circular economy for plastics requires sophisticated and imaginative thinking about the governance of plastics. This Special Issue will provide a vehicle to initiate and enhance such thinking.
This Special Issue aims to further explore governance issues in relation to the development of a circular plastics economy. There is currently very limited analysis of plastics production and disposal from a regulatory and governance perspective. There is also little scholarly consideration from a socio- or eco-legal perspective of the development of a circular economy for plastics. Much is written within other disciplines on both these topics, but there is a gap in the development of a legal analytical discourse. This Special Issue therefore seeks original research articles, case studies or systematic reviews focusing on, but not limited to, the following:
- Legal mechanisms governing plastics and plastic products, such as environmental taxation, extended producer responsibility, ecodesign, product impact assessment, etc.
- Regulatory opportunities and challenges for fostering circular plastics economies (in which plastic waste is prevented, and plastic is reused, recycled or recovered with the aim of sustainable development).
- Contractual and intellectual property implications of designing products for circular plastics economies.
- Consequences of COVID-19 on the regulation of plastics. COVID-19 has resulted in the increase of single-use plastics.
- Justice and equity issues related to the governance of plastics.
- Multidisciplinary approaches to the development of a circular plastics economy.
- Sustainability approaches in relation to plastics and corporate governance.
- Business models and corporate governance for a circular plastics economy.
- REACH, other legislation on chemicals and their impact on the governance of plastics.
- International approaches, especially in relation to the impact of plastics on global commons such as oceans.
- Property issues and liability for harm from waste plastics.
- Employment law issues relating to waste pickers.
Prof. Dr. Rosalind Malcolm
Dr. Katrien Steenmans
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a double-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Social Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plastics
- plastic waste
- circular economy
- waste law
- COVID-19
Published Papers (5 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Transforming the Global Plastics Economy: The Role of Economic Policies in the Global Governance of Plastic Pollution
by
Diana Barrowclough and Carolyn Deere Birkbeck
Cited by 59 | Viewed by 24608
Abstract
International policy discussions on plastic pollution are entering a new phase, with more than 100 governments calling for the launch of negotiations for a new global plastics agreement in 2022. This article aims to contribute to efforts to identify effective international policy levers
[...] Read more.
International policy discussions on plastic pollution are entering a new phase, with more than 100 governments calling for the launch of negotiations for a new global plastics agreement in 2022. This article aims to contribute to efforts to identify effective international policy levers to address plastic pollution. It takes stock of the evolution of views and perceptions on this complex and multi-faceted topic—from concerns about marine pollution and waste management towards new strategic directions that involve the entire plastics life-cycle and include climate and health impacts associated with the proliferation of plastics. It also traces the progressive development of responses—from voluntary approaches involving multiple stakeholders to national and international approaches focused on regulation. The paper is informed by desk research, a literature review and participation by the authors in informal and formal global governance processes on plastic pollution, the environment and development in the United Nations and World Trade Organization between 2019 and 2021. It also draws on empirical findings from a novel and original database on the life-cycle of plastic trade created by the authors. The paper argues that the important focus on downstream dimensions of plastic pollution—and strategies to address them—needs to be complemented by a broad life-cycle and “upstream” perspective that addresses plastic pollution at its source. It highlights the political economy tensions and inconsistencies at hand, observing that while some countries are taking concerted efforts to reduce pollution (including through bans on certain kinds of plastic and plastic products); to promote more circular plastic economies; and to reduce the carbon footprint of plastics (as part of a wider effort to decarbonize their economies), trade and investment in the plastic industry continues to rise. The paper argues that to reduce plastic pollution, emerging global governance efforts must integrate international environmental law and cooperation with a complementary and enabling global framework that addresses the economic, financial, industrial and trade policies needed to drive the necessary transformation of the plastics sector.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Plastic ‘Highways’ to the Sea: The Problem of Litter in English Inland Waterways
by
Samantha Davey
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3936
Abstract
There is a conspicuous lacuna in the Environmental Protection Act (EPA) 1990 because it imposes no legal duty on statutory bodies to clear litter from aquatic environments (rivers, canals and lakes) in England and Wales. This paper identifies a significant gap in the
[...] Read more.
There is a conspicuous lacuna in the Environmental Protection Act (EPA) 1990 because it imposes no legal duty on statutory bodies to clear litter from aquatic environments (rivers, canals and lakes) in England and Wales. This paper identifies a significant gap in the law on aquatic environmental protection by undertaking doctrinal research, including contextual analysis of references to rivers in ‘soft’ law (e.g., policy documents such as the Conservative Government’s Litter Strategy) and ‘hard law’ (e.g., legislation including the EPA 1990); an examination of the problems with existing legal frameworks in this sphere and an exploration of legislative and practical measures which could protect our rivers and other inland waterways from litter. A legislative amendment to the EPA is proposed with discussion of whether imposing a duty on an existing body or a new, specialised body to clear litter from rivers will ameliorate these problems. The intention behind this paper is to initiate an informed debate on how to protect aquatic environments from the harmful effects of litter.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
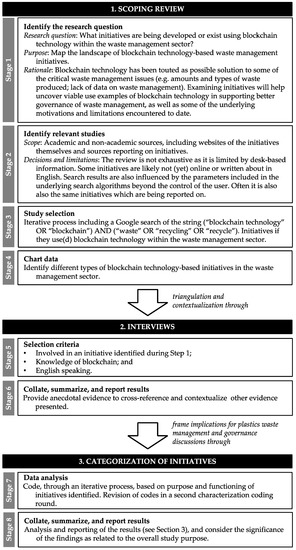
Blockchain Technology for Governance of Plastic Waste Management: Where Are We?
by
Katrien Steenmans, Phillip Taylor and Ine Steenmans
Cited by 47 | Viewed by 9284
Abstract
Blockchain technology is emerging as a plausible disruptor of waste management practices that influence the governance of plastics. The interest among the waste management community in the potential and fundamental changes to complex resource management associated with blockchain adoption parallels recent research in
[...] Read more.
Blockchain technology is emerging as a plausible disruptor of waste management practices that influence the governance of plastics. The interest among the waste management community in the potential and fundamental changes to complex resource management associated with blockchain adoption parallels recent research in other sectors, such as finance, health, public administration, etc. During any comparable period characterized by a step-change in positive coverage of an early-stage technology, it can be challenging for actors to access a grounded, evidence-based oversight of the current state of practice and make informed decisions about whether or how to adopt blockchain technology. The current absence of such a systematic overview of recent experiences with blockchain initiatives disrupting waste practices not only limits the visibility of these experimental efforts, but also limits the learning that can be shared across waste plastics researcher and practitioner communities. This paper contributes with a current overview of blockchain technology adoption in the waste management sector, giving particular attention to implications for the governance of plastics. Our study draws on both primary interview data and secondary documentation data to map the landscape of current blockchain initiatives in the global waste sector. We identify four areas of blockchain use that are beginning to change waste management practices (payment, recycling and reuse rewards, monitoring and tracking of waste, and smart contracts). We conclude by outlining five areas of significant blockchain uses, implications, and influences of relevance to the development of circular plastic waste governance in both research and practice.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Building Collective Ownership of Single-Use Plastic Waste in Youth Communities: A Jamaican Case Study
by
C. Andrea Bruce Clayton
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 6745
Abstract
Plastic pollution is a global environmental challenge with serious implications for human health. Most of the work on plastic waste to date has focused on assessing and mapping impacts and remedial activities, which are important but do not attempt to understand the attitude
[...] Read more.
Plastic pollution is a global environmental challenge with serious implications for human health. Most of the work on plastic waste to date has focused on assessing and mapping impacts and remedial activities, which are important but do not attempt to understand the attitude and behaviour of the consumer. The problem will only be resolved by changing behaviour to eliminate non-essential use of plastics and switch to less harmful alternatives, especially for Single-Use Plastic (SUP), which makes a disproportionate contribution to plastic waste. This study examines the attitudes and behaviour of teachers and parents/guardians in school communities as a step towards building collective ownership of SUP towards reducing the use of SUP. It establishes baseline data about attitudes and behaviour in four Jamaican primary schools. It examines the attitude of teachers and parents/guardians towards SUPs and uses cluster analysis to segment them based on attitude. The results identify the heterogeneous nature of groups within the same population and highlights the need for targeted interventions. This research can contribute towards the design of strategic interventions that will build a sense of collective ownership of the SUP problem and motivate effective changes in behaviour to minimise the use of SUPs in Jamaica.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
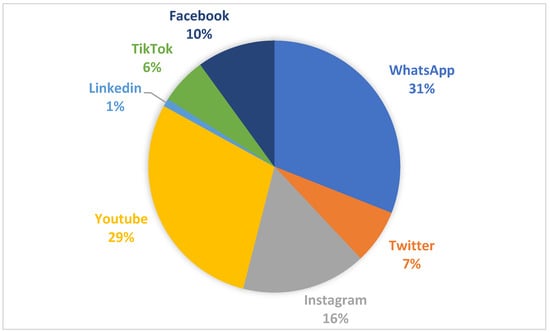
Investigating the Knowledge and Attitudes towards Plastic Pollution among the Youth in Nairobi, Kenya
by
Nicholas Oguge, Francis Oremo and Salome Adhiambo
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 13404
Abstract
Kenya has made many attempts to regulate the production of single-use plastics through partial bans and the imposition of hefty taxes. Whereas government initiatives are crucial to resolving single-use plastic pollution, commitments made by youths can be an important part of the solution.
[...] Read more.
Kenya has made many attempts to regulate the production of single-use plastics through partial bans and the imposition of hefty taxes. Whereas government initiatives are crucial to resolving single-use plastic pollution, commitments made by youths can be an important part of the solution. Yet, youths are habituated to using single-use plastics without understanding fully their negative impacts. Understanding the knowledge and attitudes of youths is of the utmost importance in the effort to turn the tide against plastic pollution. This study set out to investigate knowledge and attitudes towards single-use plastics among youths in Nairobi, Kenya. This was a mixed study approach, where both qualitative and quantitative data were derived. The results showed that youths perceive single-use plastics as a serious environmental and health issue. Most respondents expressed willingness to switch to reusable alternatives if provided with financial incentives. In addition, the results showed stronger support for enhanced awareness campaigns and plastic recycling infrastructure. Social media was the most preferred channel to disseminate plastic pollution messaging among the youth. These findings are important in policy development for intensifying awareness and targeting a range of communication and financial support to reduce single-use plastic pollution.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures