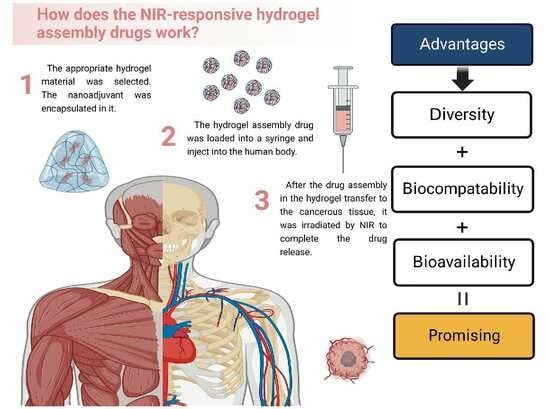
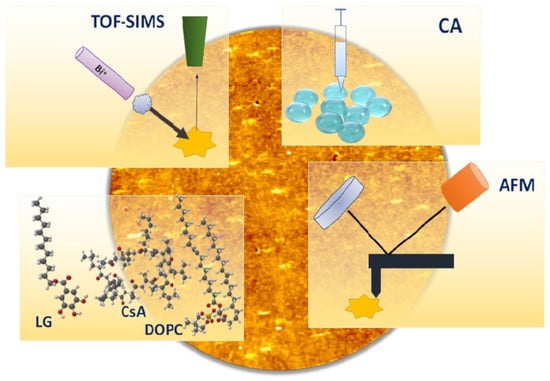
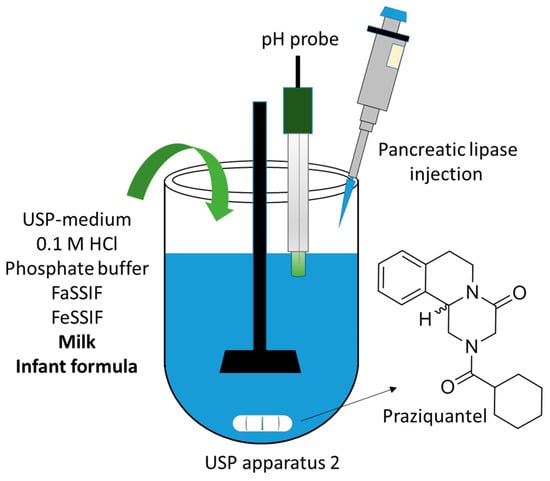
Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology
A topical collection in Pharmaceutics (ISSN 1999-4923).
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 13696Editor
Interests: freeze drying; fast disintegrating tablets; reformulation of medicines; microarray
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
With the aim of presenting advanced research and reviews in the field of science and technology of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics in various countries and territories all over the world, the journal has launched this collection, details of which can be found at the website links below.
We welcome scholars to collaborate with us on the future collections in this collection!
Pharmaceutics Editorial Office
pharmaceutics@mdpi.com
______
Your country/region is not included? Click here to propose.
Related Special Issues
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Japan in Pharmaceutics (11 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Korea in Pharmaceutics (27 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Switzerland in Pharmaceutics (5 articles)
- Pharmaceutics and Drug Delivery in Italy in Pharmaceutics (21 articles)
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism in Canada: The Current Landscape in Pharmaceutics (21 articles)
- Drug Delivery Technology Development in Canada in Pharmaceutics (18 articles)
- Drug Delivery in The Netherlands in Pharmaceutics (18 articles)
- Advanced Drug Delivery Systems and Technology in Hungary in Pharmaceutics (16 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Research in the Czech Republic in Pharmaceutics (16 articles)
- Design, Development, and Characterization of Drug and Gene Delivery Systems in the Russian Federation in Pharmaceutics (9 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Estonia in Pharmaceutics (3 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Portugal in Pharmaceutics (5 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Germany in Pharmaceutics (19 articles)
- Pharmaceutical Sciences in Canada in Pharmaceutics (43 articles)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Israel in Pharmaceutics (11 articles)