Understanding the Heterogeneity of Obesity and the Relationship to the Brain-Gut Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. Anthropometrics Data
2.2.2. Diet Habits
2.2.3. Fecal Specimen
2.3. Microbiome Characterization: 16S Ribosomal RNA Sequencing
2.4. Fecal Amino Acids Characterization
2.5. Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.5.1. MRI Acquisition
2.5.2. Quality Control and Preprocessing of Images
2.5.3. Structural Image Parcellation
2.5.4. Brain Regions of Interest
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Participant Characteristics
3.2. Odds of Obesity
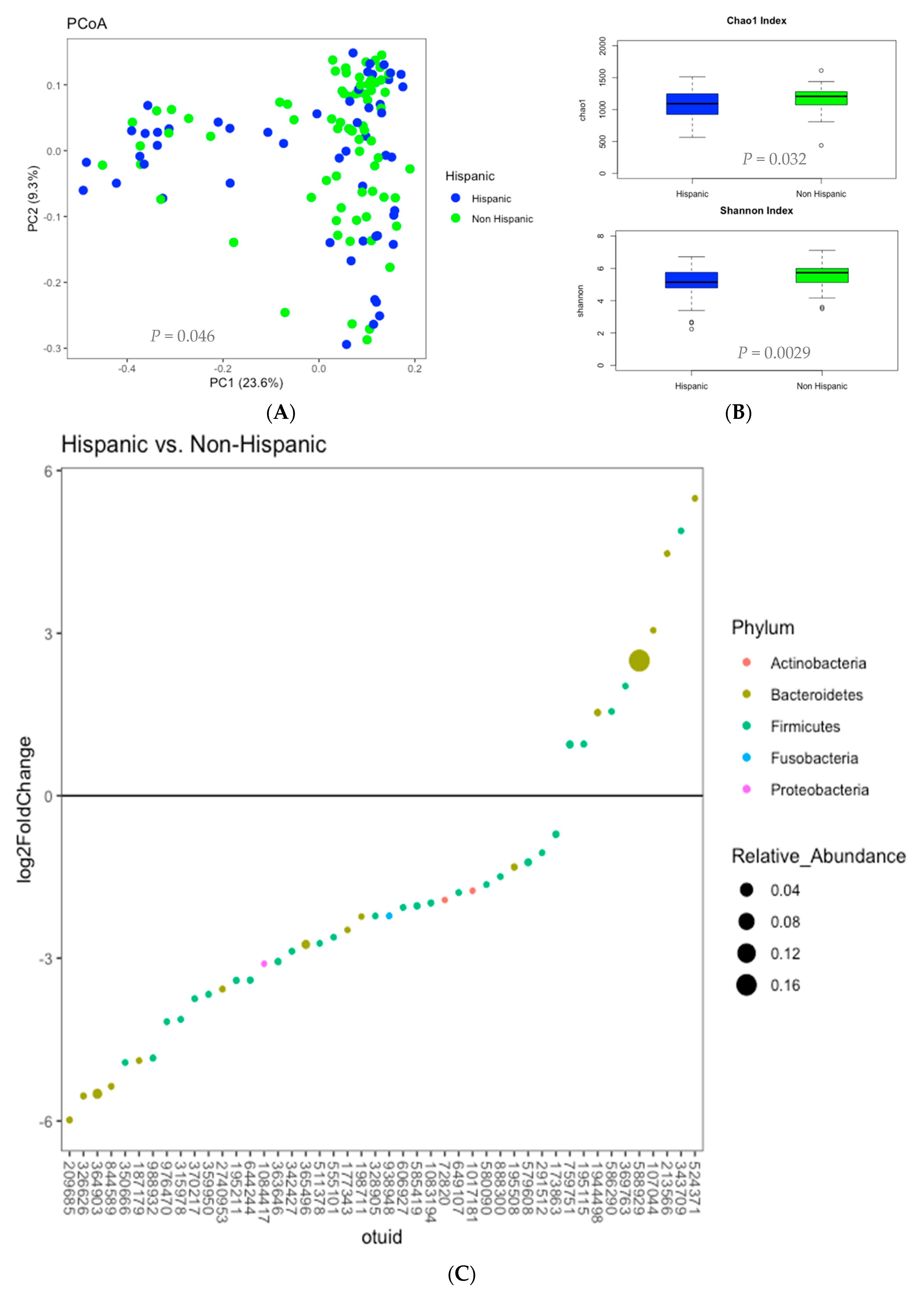
3.3. Microbiome Analysis
3.4. Amino Acid Metabolites
3.5. Brain Structural Volumes
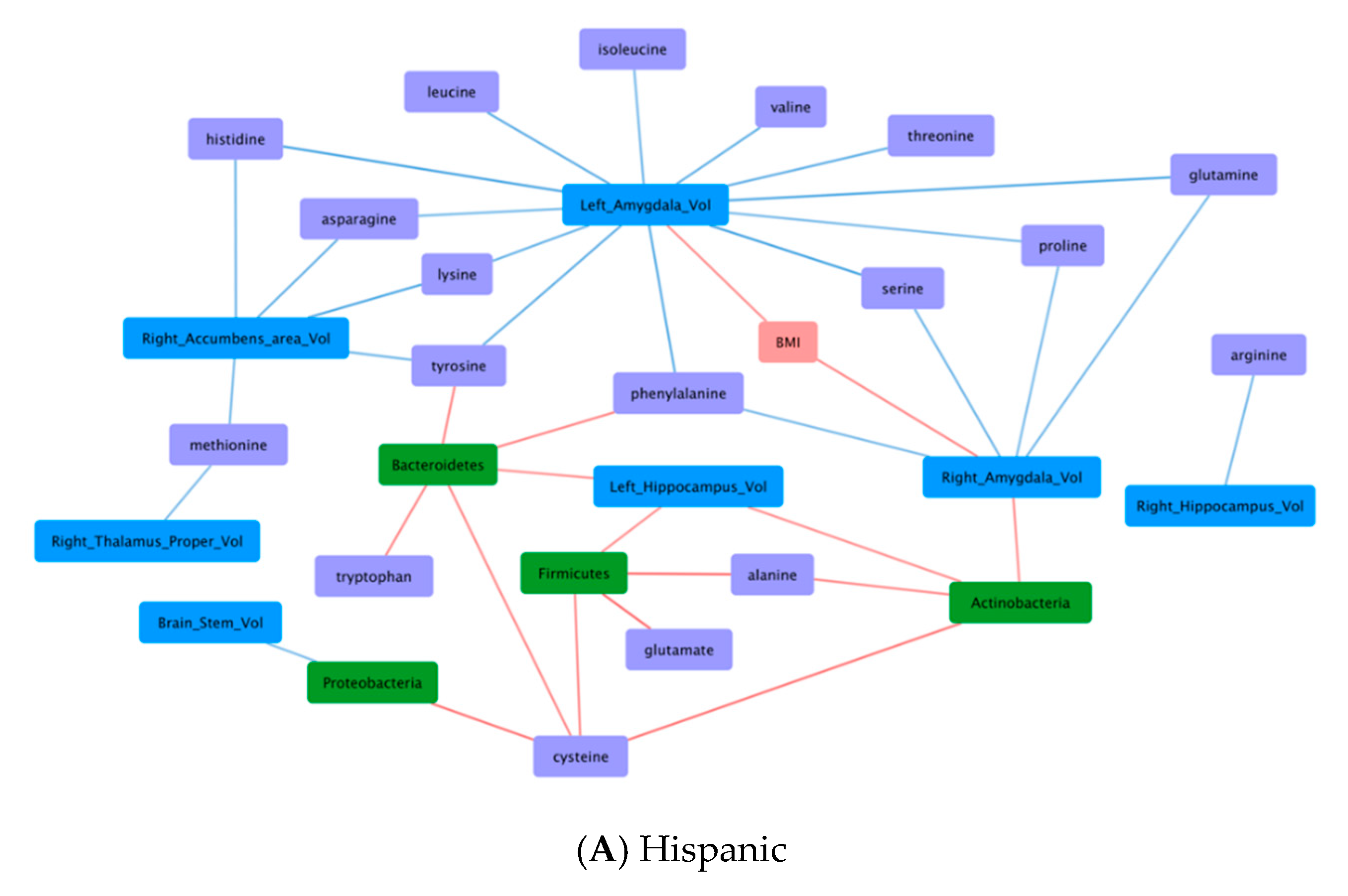
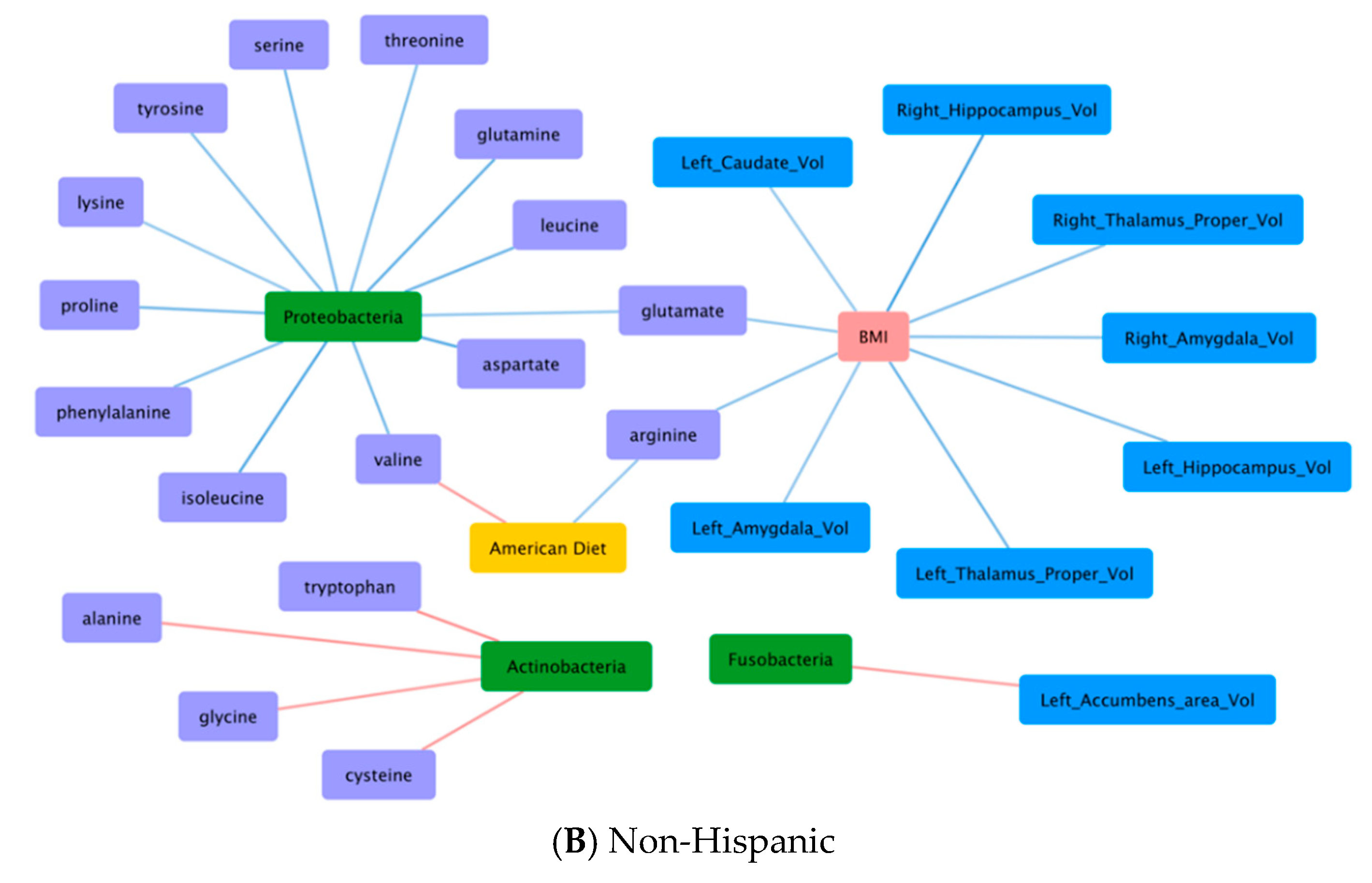
3.6. Correlations Demonstrating Brain-Gut Microbiome Interactions
3.6.1. BMI and Brain Structural Volumes (BMI-Brain)
3.6.2. BMI and Fecal Amino Acids (BMI-AA)
3.6.3. Gut Microbiome and Brain Structural Volumes (GM-Brain)
3.6.4. Gut Microbiome and Fecal Amino Acids (GM-AA)
3.6.5. Brain Structural Volumes and Fecal Amino Acids (Brain-AA)
3.6.6. Diet and Fecal Amino Acids (Diet-AA)
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, K.R.; Redden, D.T.; Wang, C.; Westfall, A.O.; Allison, D.B. Years of life lost due to obesity. JAMA 2003, 289, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Health Topics: Obesity. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/topics/obesity/en/ (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Bauer, U.E.; Briss, P.A.; Goodman, R.A.; Bowman, B.A. Prevention of chronic disease in the 21st century: Elimination of the leading preventable causes of premature death and disability in the USA. Lancet 2014, 384, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantalone, K.M.; Hobbs, T.M.; Chagin, K.M.; Kong, S.X.; Wells, B.J.; Kattan, M.W.; Bouchard, J.; Sakurada, B.; Milinovich, A.; Weng, W.; et al. Prevalence and recognition of obesity and its associated comorbidities: Cross-sectional analysis of electronic health record data from a large US integrated health system. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Global Health Observatory. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/theme-details/GHO/body-mass-index-(bmi)?introPage=intro_3.html (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- CDC 2019. Health United States. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus18.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office of Minority Health. Obesity and Hispanic Americans. 2020. Available online: https://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/omh/browse.aspx?lvl=4&lvlid=70 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Obesity Update 2017. OECD. 2017. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/els/health-systems/Obesity-Update-2017.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, C.A.; Slack, T.; Martin, C.K.; Broyles, S.T.; Heymsfield, S.B. Regional disparities in obesity prevalence in the United States: A spatial regime analysis. Obesity 2015, 23, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Cardel, M.; Donahoo, W.T.; Feingold, K.R.; Anawalt, B.; Boyce, A.; Chrousos, G.; de herder, W.W.; Dungan, K.; Grossman, A.; et al. Social and Environmental Factors Influencing Obesity. 2019. Available online: www.endotext.org (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Institute of Medicine (US). Committee on Assuring the Health of the Public in the 21st Century; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rohde, K.; Keller, M.; Poulsen, L.L.C.; Blüher, M.; Kovacs, P.; Böttcher, Y. Genetics and epigenetics in obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussaada, S.M.; Van Galen, K.A.; Cooiman, M.I.; Kleinendorst, L.; Hazebroek, E.J.; Van Haelst, M.M.; Ter Horst, K.W.; Serlie, M.J. The pathogenesis of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: The emerging biology of gut–brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustí, A.; García-Pardo, M.P.; López-Almela, I.; Campillo, I.; Maes, M.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Sanz, Y. Interplay between the gut-brain axis, obesity and cognitive function. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.-R.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Blaming the brain for obesity: Integration of hedonic and homeostatic mechanisms. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.N. Obesity: Genes, brain, gut, and environment. Nutrition 2010, 26, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The brain-gut-microbiome axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhmann, H.; Le Roux, C.W.; Bueter, M. The gut–brain axis in obesity. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, E.P.J.G.; DeJong, C.H.C.; Rensen, S.S. The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrition 2015, 7, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision. 2010. Available online: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Hebebrand, J.; Holm, J.-C.; Woodward, E.; Baker, J.L.; Blaak, E.; Schutz, D.D.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; Frühbeck, G.; Halford, J.G.; Lissner, L.; et al. A proposal of the european association for the study of obesity to improve the ICD-11 diagnostic criteria for obesity based on the three dimensions etiology, degree of adiposity and health risk. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 284–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Modin, S.; Wahlström, R.; Hammarberg, S.A.W.; Krakau, I. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview is useful and well accepted as part of the clinical assessment for depression and anxiety in primary care: A mixed-methods study. BMC Fam. Pr. 2018, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Jacobs, J.P.; McHardy, I.H.; Braun, J. Sampling of intestinal microbiota and targeted amplification of bacte- rial 16S rRNA genes for microbial ecologic analysis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 107, 7.41.1–7.41.11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, K.; Aronov, P.A.; Hammock, B.D. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A.; Acosta, B.J.R.; Hamadani, B.K.; Torgerson, B.C.; Van Horn, J.D.; Chang, L.; Naliboff, B.; Tillisch, K.; Labus, J.S. Early adverse life events are associated with altered brain network architecture in a sex- dependent manner. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Species divergence and the measurement of microbial diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 557–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Di Rienzi, S.C.; Poole, A.C.; Koren, O.; Walters, W.A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E. Conducting a Microbiome Study. Cell 2014, 158, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste Not, Want Not: Why Rarefying Microbiome Data Is Inadmissible. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichaman, M.Z.; Garcia, G. Obesity in Hispanic Americans. Diabetes Care 1991, 14, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, K.Y.Z.; Leeds, M.J.; Ufelle, A.C. Epidemiology of obesity in the hispanic adult population in the United States. Fam. Community Heal. 2017, 40, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, C.A.; Slack, T.; Martin, C.K.; Broyles, S.T.; Heymsfield, S.B. Change in obesity prevalence across the united states is influenced by recreational and healthcare contexts, food environments, and hispanic populations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult Obesity Facts. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Curtin, L.R.; McDowell, M.A.; Tabak, C.J.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006, 295, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D. Prevalence and trends in overweight in Mexican-American adults and children. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62 Pt 2, S144–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayet, J.; Chapman, N.; Li, C.K.; Shahi, M.; Poulter, N.R.; Sever, P.S.; Foale, R.A.; Thom, S.A. Ethnic differences in the hypertensive heart and 24-hour blood pressure profile. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics: 2012 update: A report from the American Heart Association [published correction appears in Circulation. 2012, 125:e1002]. Circulation 2012, 125, e2–e220. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, L.K.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.A.; Gudzune, K.A.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Demerath, E.; Woodward, M.; Selvin, E.; Coresh, J. Changes in body mass index and obesity risk in married couples over 25 years. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.; on behalf of the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures for Hispanics/Latinos 2018–2020; American Cancer Society, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Creighton, M.J.; Goldman, N.; Pebley, A.R.; Chung, C.Y. Durational and generational differences in Mexican immigrant obesity: Is acculturation the explanation? Soc. Sci. Med. 2012, 75, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.S.; McCarthy, E.P.; Phillips, R.S.; Wee, C.C. Obesity among US immigrant subgroups by duration of residence. JAMA 2004, 292, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.S.; Huguet, N.; Newsom, J.T.; McFarland, B.H. The association between length of residence and obesity among Hispanic immigrants. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2004, 27, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelgreen, D.A.; Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Martinez, D.; Bretnall, A.; Eells, V.; Peng, Y.; Bermúdez, A. The longer you stay, the bigger you get: Length of time and language use in the U.S. are associated with obesity in Puerto Rican women. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2004, 125, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraído-Lanza, A.F.; Chao, M.T.; Flórez, K.R. Do healthy behaviors decline with greater acculturation? Implications for the Latino mortality paradox. Soc. Sci. Med. 2005, 61, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Larsen, P.; Harris, K.M.; Ward, D.S.; Popkin, B.M. Acculturation and overweight-related behaviors among Hispanic immigrants to the US: The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 57, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.W.; Williams, D.R.; Villamor, E. Very low food security predicts obesity predominantly in California Hispanic men and women. Public Heal. Nutr. 2012, 15, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wong, R.J.; Chou, C.; Ahmed, A. Long term trends and racial/ethnic disparities in the prevalence of obesity. J. Community Heal. 2014, 39, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, A.N.; McKenna, R.M.; Pintor, J.K.; Langellier, B.A.; Roby, D.H.; Pourat, N.; Bustamante, A.V.; Wallace, S.P. Health care access and physical and behavioral health among undocumented latinos in California. Med. Care 2018, 56, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone-Heinonen, J.; Howard, A.G.; Meyer, K.; Lewis, C.E.; Kiefe, C.I.; Laroche, H.H.; Gunderson, E.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Marriage and parenthood in relation to obesogenic neighborhood trajectories: The CARDIA study. Heal. Place 2015, 34, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bowie, J.; Juon, H.-S.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Cho, J. Factors associated with overweight and obesity among mexican americans and central americans: Results from the 2001 California health interview survey. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2006, 4, A10. [Google Scholar]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouter, K.E.; Van Raalte, D.H.; Groen, A.K.; Nieuwdorp, M. Role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of obesity and obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; Nilaweera, K.; Ross, P.R.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. The gut microbiota and its relationship to diet and obesity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, R.C.; Wang, Z.; Usyk, M.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Daviglus, M.L.; Schneiderman, N.; Talavera, G.A.; Gellman, M.D.; Thyagarajan, B.; Moon, J.-Y.; et al. Gut microbiome composition in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos is shaped by geographic relocation, environmental factors, and obesity. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.C.; Muzny, D.M.; McCormick, J.B.; Gibbs, R.A.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; Petrosino, J.F. 16S gut community of the Cameron County Hispanic Cohort. Microbiome 2015, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; O’Ryan, M.L.; Vidal, R.; Farfan, M. The human gut microbiome of Latin America populations. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, C.P.; Neut, C.; Desreumaux, P.; Colombel, J.F. Dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2004, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Sinha, R.; Pei, Z.; Dominianni, C.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Hayes, R.B.; Yang, L. Human gut microbiome and risk for colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-N.; Fang, J.-Y. Gut microbiota and colorectal cancer. Gastrointest. Tumors 2015, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Mainali, R.; Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.; Singh, R.; Kavanagh, K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kushugulova, A.; Marotta, F.; Yadav, H. Gut microbiome and aging: Physiological and mechanistic insights. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2018, 4, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriss, M.; Hazleton, K.Z.; Nusbacher, N.M.; Martin, C.G.; Lozupone, C.A. Low diversity gut microbiota dysbiosis: Drivers, functional implications and recovery. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indiani, C.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Castelo, P.M.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Darrieux, M.; Parisotto, T.M. Childhood obesity and firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.-J. Gut bacteria alteration in obese people and its relationship with gene polymorphism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Tkach, S.; et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittipo, P.; Lobionda, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Maynard, C.L. Intestinal microbiota and the immune system in metabolic diseases. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.A.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schaefer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in Lean and Overweight Healthy Subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.F.S.; Grześkowiak, Ł.; Franceschini, S.C.C.; Bressan, J.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F.; Peluzio, M.C.G. Higher level of faecal SCFA in women correlates with metabolic syndrome risk factors. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 109, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.T.H.; Hindlet, P.; Waligora-Dupriet, A.-J.; Kapel, N.; Neveux, N.; Mignon, V.; Deloménie, C.; Farinotti, R.; Fève, B.; Buyse, M. Disturbed intestinal nitrogen homeostasis in a mouse model of high-fat diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2014, 306, E668–E680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. The Relationship between Branched-Chain Amino Acid Related Metabolomic Signature and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2794591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomkajło, M.; Rybka, J.; Mierzchała-Pasierb, M.; Gamian, A.; Stankiewicz-Olczyk, J.; Bolanowski, M.; Daroszewski, J. Specific plasma amino acid disturbances associated with metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology 2017, 58, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, D.A.; Luck, H.; Tsai, S.; Winer, S. The intestinal immune system in obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo-Buitrago, M.E.; Sabater-Masdeu, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Caballano-Infantes, E.; Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Coll, C.; Ramió, L.; Palomino-Schätzlein, M.; Gutiérrez-Carcedo, P.; Pérez-Brocal, V.; et al. Glutamate interactions with obesity, insulin resistance, cognition and gut microbiota composition. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besten, G.D.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, N.F.; Liu, Y.; Zakeri, I.F.; Mohney, R.P.; Mehta, N.R.; Voruganti, V.S.; Goring, H.H.H.; Cole, S.A.; Comuzzie, A.G. Global metabolomic profiling targeting childhood obesity in the Hispanic population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourino, M.C.; De Oliveira, E.M.; Bellé, L.P.; Olivo, F.; Albuquerque, R.C.; Dörr, F.A.; Okada, S.S.; Migliorini, S.; Soares, I.S.; Campa, A. Tryptamine and dimethyltryptamine inhibit indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase and increase the tumor-reactive effect of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Immunity Mediated by Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Ardiansyah; Hirahara, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Tomita, S.; Aso, H.; Komai, M.; et al. Dietary tryptophan alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 42, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Cheng-Qi, H. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portune, K.J.; Beaumont, M.; Davila, A.-M.; Tomé, D.; Blachier, F.; Sanz, Y. Gut microbiota role in dietary protein metabolism and health-related outcomes: The two sides of the coin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, D.R.; Foley, K.F.; McQuoid, C.; Simpson, J.; Sharkey, K.A.; Mawe, G.M. Serotonin transporter function and expression are reduced in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2005, 17, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyler, S.C.; Lord, C.C.; Lee, S.; Elmquist, J.K.; Liu, C. Serotonergic control of metabolic homeostasis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Djazayeri, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Qi, L.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Aslibekyan, S.; Chamari, M.; Hassani, H.; Koletzko, B.; Uhl, O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2019, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashina, C.; Tsujino, I.; Watanabe, T.; Sakaue, S.; Ikeda, D.; Yamada, A.; Sato, T.; Ohira, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Oyama-Manabe, N.; et al. Associations among the plasma amino acid profile, obesity, and glucose metabolism in Japanese adults with normal glucose tolerance. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheflin, A.M.; Melby, C.L.; Carbonero, F.; Weir, T.L. Linking dietary patterns with gut microbial composition and function. Gut Microbes 2016, 8, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Compher, C.; Chen, E.Z.; Smith, S.A.; Shah, R.D.; Bittinger, K.; Chehoud, C.; Albenberg, L.G.; Nessel, L.; Gilroy, E.; et al. Comparative metabolomics in vegans and omnivores reveal constraints on diet-dependent gut microbiota metabolite production. Gut 2016, 65, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirpuri, J.; Raetz, M.; Sturge, C.R.; Wilhelm, C.L.; Benson, A.; Savani, R.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Proteobacteria-specific IgA regulates maturation of the intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbies 2013, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulangé, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumas, M.-E. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, A.K.; Valdivia-Garcia, M.; Refsum, H.; Butte, N. The Association of cysteine with obesity, inflammatory cytokines and insulin resistance in hispanic children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbagy, A.K.; Kozich, V.; Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H. Cysteine and obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Mestre, Z.L.; Bischoff-Grethe, A.; Eichen, D.M.; Wierenga, C.E.; Strong, D.; Boutelle, K.N. Hippocampal atrophy and altered brain responses to pleasant tastes among obese compared with healthy weight children. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.A.; Carlsson, C.M.; Trivedi, M.A.; Sager, M.A.; Johnson, S.C. The effect of body mass index on global brain volume in middle-aged adults: A cross sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2005, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, I.A.; Jansen, P.R.; Lamb, H.J. Obesity, brain volume, and white matter microstructure at MRI: A cross-sectional UK biobank study. Radiology 2019, 291, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debette, S.; Seshadri, S.; Beiser, A.; Au, R.; Himali, J.J.; Palumbo, C.; Wolf, P.A.; DeCarli, C. Midlife vascular risk factor exposure accelerates structural brain aging and cognitive decline. Neurology 2011, 77, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, C.A.; Ho, A.J.; Parikshak, N.N.; Becker, J.T.; Lopez, O.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Hua, X.; Leow, A.D.; Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. Brain structure and obesity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F.; Matthews, P.M.; Ropele, S.; Schmidt, H.; Smith, S. Risk factors for progression of brain atrophy in aging: Six-year follow-up of normal subjects. Neurology 2005, 64, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannacciulli, N.; Del Parigi, A.; Chen, K.; Le, D.S.N.T.; Reiman, E.M.; Tataranni, P.A. Brain abnormalities in human obesity: A voxel-based morphometric study. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzenius, J.D.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Cabeen, R.P.; Conturo, T.E.; McMichael, A.R.; Lane, E.M.; Heaps, J.M.; Salminen, L.E.; Baker, L.M.; Gunstad, J.; et al. Impact of body mass index on neuronal fiber bundle lengths among healthy older adults. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013, 7, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, B.; Cheng, J.; Li, H. Brain structural differences between normal and obese adults and their links with lack of perseverance, negative urgency, and sensation seeking. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, D.H.; Melendez, R.I.; Zaborszky, L.; Napier, T.C. The ventral pallidum: Subregion-specific functional anatomy and roles in motivated behaviors. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 130, 29–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedernaes, J.; Bass, J. Decoding obesity in the brainstem. eLife 2016, 5, e16393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoschke, N.; Lorenzetti, V.; Caeyenberghs, K.; Verdejo-García, A. Impulsivity and body fat accumulation are linked to cortical and subcortical brain volumes among adolescents and adults. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlaki, G.; Molnar, D.; Smeets, P.A.M.; Ahrens, W.; Wolters, M.; Eiben, G.; Lissner, L.; Erhard, P.; Van Meer, F.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Volumetric gray matter measures of amygdala and accumbens in childhood overweight/obesity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, S.W.; Worhunsky, P.D.; Xu, J.; Morie, K.P.; Constable, R.T.; Malison, R.T.; Carroll, K.M.; Potenza, M.N. Gray-matter relationships to diagnostic and transdiagnostic features of drug and behavioral addictions. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; Stojek, M.K.; MacKillop, J. Interrelationships among impulsive personality traits, food addiction, and body mass index. Appetite 2014, 73, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dalaeen, A.; Ahram, M.; Al-Domi, H.A. Effects of obesity on hippocampus function: Synaptic plasticity hypothesis. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Romero, A.; Adam, T.C.; Hu, H.H.; Monterosso, J.; Page, K.A. Abdominal fat is associated with a greater brain reward response to high-calorie food cues in hispanic women. Obesity 2013, 21, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andolina, D.; Borreca, A. The Key Role of the Amygdala in Stress. The Amygdala-Where Emotions Shape Perception, Learning and Memories, Barbara Ferry, IntechOpen. 2017. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/the-amygdala-where-emotions-shape-perception-learning-and-memories/the-key-role-of-the-amygdala-in-stress (accessed on 1 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Valladolid-Acebes, I.; Merino, B.; Principato, A.; Fole, A.; Barbas, C.; Lorenzo, M.P.; García, A.; Del Olmo, N.; Ruiz-Gayo, M.; Cano, V. High-fat diets induce changes in hippocampal glutamate metabolism and neurotransmission. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2012, 302, E396–E402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamminga, C.A.; Southcott, S.; Sacco, C.; Wagner, A.D.; Ghose, S. Glutamate dysfunction in hippocampus: Relevance of dentate gyrus and CA3 signaling. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.R. Food addiction and obesity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, B.M. Precision obesity care on the horizon. Circulation 2018, 137, 1965–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall (n = 130) | Overweight (n = 62) | Obese (n = 68) | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | No | % | No | % | No | % | |
| Age | 0.17 | ||||||
| Less than 30 yo | 59 | 45.4% | 32 | 51.6% | 27 | 39.7% | |
| 30 yo or older | 71 | 54.6% | 30 | 48.4% | 41 | 60.3% | |
| Gender | 0.093 | ||||||
| Female | 87 | 66.9% | 37 | 59.7% | 50 | 73.5% | |
| Male | 43 | 33.1% | 25 | 40.3% | 18 | 26.5% | |
| Ethnicity | 0.014 * | ||||||
| Hispanic | 52 | 40.0% | 18 | 29.0% | 34 | 50.0% | |
| Non-Hispanic | 78 | 60.0% | 44 | 71.0% | 34 | 50.0% | |
| Education | 0.51 | ||||||
| College Graduate | 37 | 29.8% | 19 | 32.8% | 18 | 27.3% | |
| Non-College Graduate | 87 | 70.2% | 39 | 67.2% | 48 | 72.7% | |
| Annual Income | 0.88 | ||||||
| Less than $70 K | 64 | 55.7% | 31 | 56.4% | 33 | 55.0% | |
| $70 K or More | 51 | 44.3% | 24 | 43.6% | 27 | 45.0% | |
| Dietary Pattern | 0.031 * | ||||||
| American Diet | 99 | 76.2% | 42 | 67.7% | 57 | 83.8% | |
| Non-American Diet | 31 | 23.8% | 20 | 32.3% | 11 | 16.2% |
| . | Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analyses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Un-aOR | 95% CI | p Value | aOR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age | 0.79 | 0.55–1.12 | 0.17 | – | – | |
| Less than 30 yo | – | – | ||||
| 30 yo or older (reference) | ||||||
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 1.37 | 0.94–2.00 | 0.093 | – | – | |
| Male (reference) | – | – | ||||
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Hispanic | 1.56 | 1.08–2.26 | 0.014 * | 1.56 | 1.08–2.26 | 0.014 * |
| Non-Hispanic (reference) | – | – | – | – | ||
| Education | ||||||
| College Graduate | 0.88 | 0.59–1.30 | 0.51 | – | – | |
| Non-College Graduate (reference) | – | – | ||||
| Annual Income | ||||||
| Less than $70 K | 0.97 | 0.67–1.42 | 0.88 | – | – | |
| $70 K or More (reference) | – | – | ||||
| Dietary Pattern | ||||||
| American Diet | 1.57 | 1.02–2.41 | 0.031 * | – | – | |
| Non-American Diet (reference) | – | – | ||||
| Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal Amino Acids | Hispanic | American Diet | Obesity |
| Glycine | 0.045 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Serine | 0.026 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Threonine | 0.030 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Alanine | 0.045 * | 0.30 | 0.85 |
| Aspartate | 0.030 * | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| Asparagine | 0.10 | 0.95 | 0.73 |
| Glutamate | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.73 |
| Glutamine | 0.033 * | 0.37 | 0.73 |
| Histidine | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| Lysine | 0.045 * | 0.89 | 0.73 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.026 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Tyrosine | 0.030 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Tryptophan | 0.030 * | 0.89 | 0.73 |
| Leucine | 0.030 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Isoleucine | 0.026 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Valine | 0.026 * | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Methionine | 0.026 * | 0.30 | 0.85 |
| Cysteine | 0.99 | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Arginine | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.73 |
| Proline | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.97 |
| Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Structures | Hispanic | American Diet | Obesity |
| Left Thalamus | 0.08 | 0.52 | 0.22 |
| Right Thalamus | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.24 |
| Left Caudate | 0.23 | 0.95 | 0.31 |
| Right Caudate | 0.23 | 0.95 | 0.31 |
| Left Putamen | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.77 |
| Right Putamen | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.84 |
| Left Pallidum | 0.036 * | 0.88 | 0.99 |
| Right Pallidum | 0.036 * | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| Left Hippocampus | 0.96 | 0.37 | 0.24 |
| Right Hippocampus | 0.96 | 0.74 | 0.16 |
| Left Amygdala | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.85 |
| Right Amygdala | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.85 |
| Left Nucleus Accumbens | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.48 |
| Right Nucleus Accumbens | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.48 |
| Brain Stem | 0.011 * | 0.043 * | 0.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, T.K.W.; Dong, T.S.; Chen, Z.; Elashoff, D.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Jacobs, J.P.; Lagishetty, V.; Vora, P.; Stains, J.; Mayer, E.A.; et al. Understanding the Heterogeneity of Obesity and the Relationship to the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123701
Hung TKW, Dong TS, Chen Z, Elashoff D, Sinsheimer JS, Jacobs JP, Lagishetty V, Vora P, Stains J, Mayer EA, et al. Understanding the Heterogeneity of Obesity and the Relationship to the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(12):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123701
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Tony K. W., Tien S. Dong, Zixi Chen, David Elashoff, Janet S. Sinsheimer, Jonathan P. Jacobs, Venu Lagishetty, Priten Vora, Jean Stains, Emeran A. Mayer, and et al. 2020. "Understanding the Heterogeneity of Obesity and the Relationship to the Brain-Gut Axis" Nutrients 12, no. 12: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123701
APA StyleHung, T. K. W., Dong, T. S., Chen, Z., Elashoff, D., Sinsheimer, J. S., Jacobs, J. P., Lagishetty, V., Vora, P., Stains, J., Mayer, E. A., & Gupta, A. (2020). Understanding the Heterogeneity of Obesity and the Relationship to the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients, 12(12), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123701








