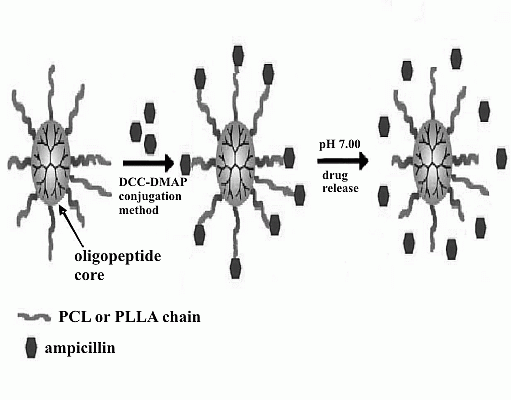
Ampicillin-Ester Bonded Branched Polymers: Characterization, Cyto-, Genotoxicity and Controlled Drug-Release Behaviour
Abstract
:1. Introduction
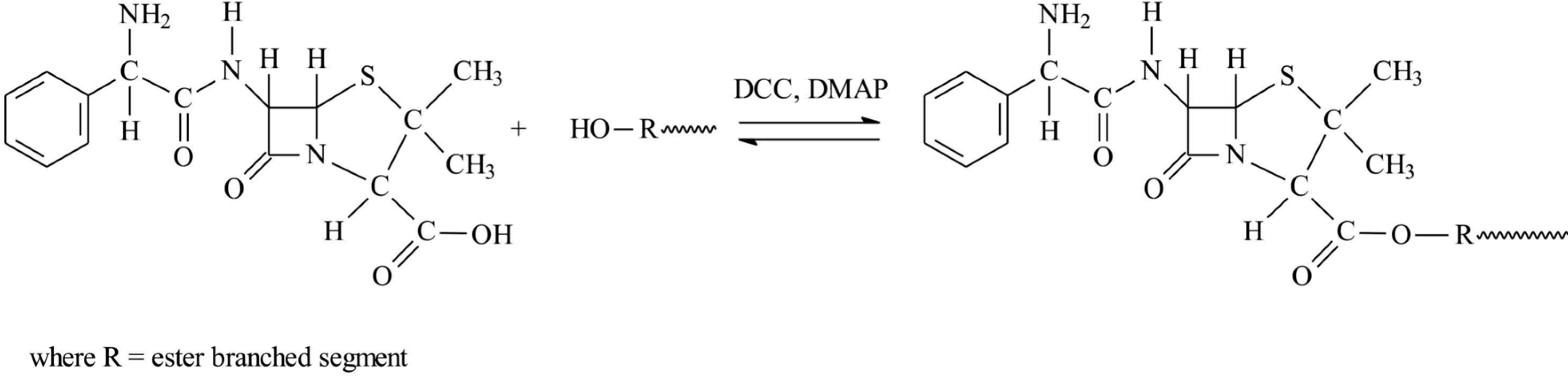
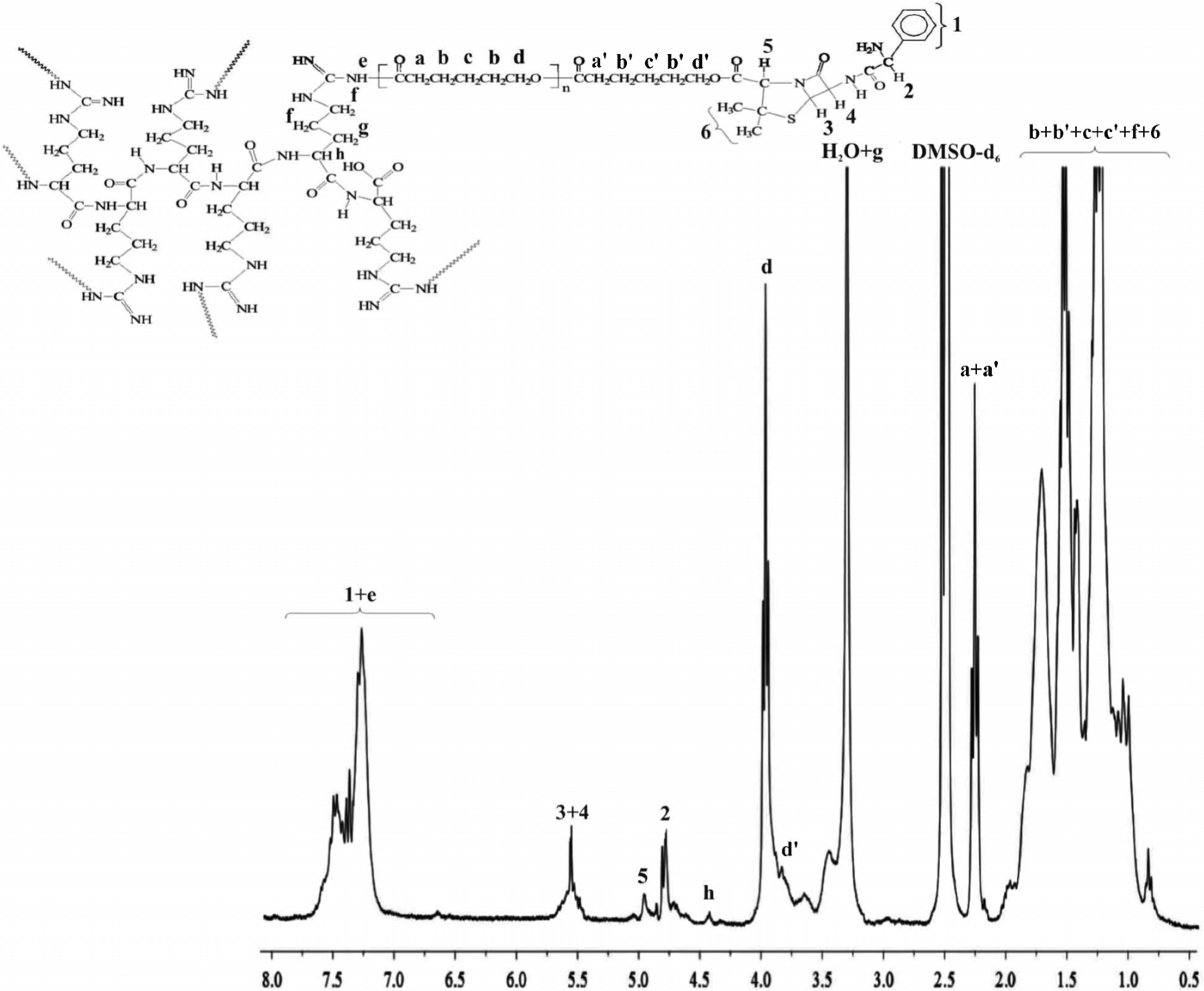
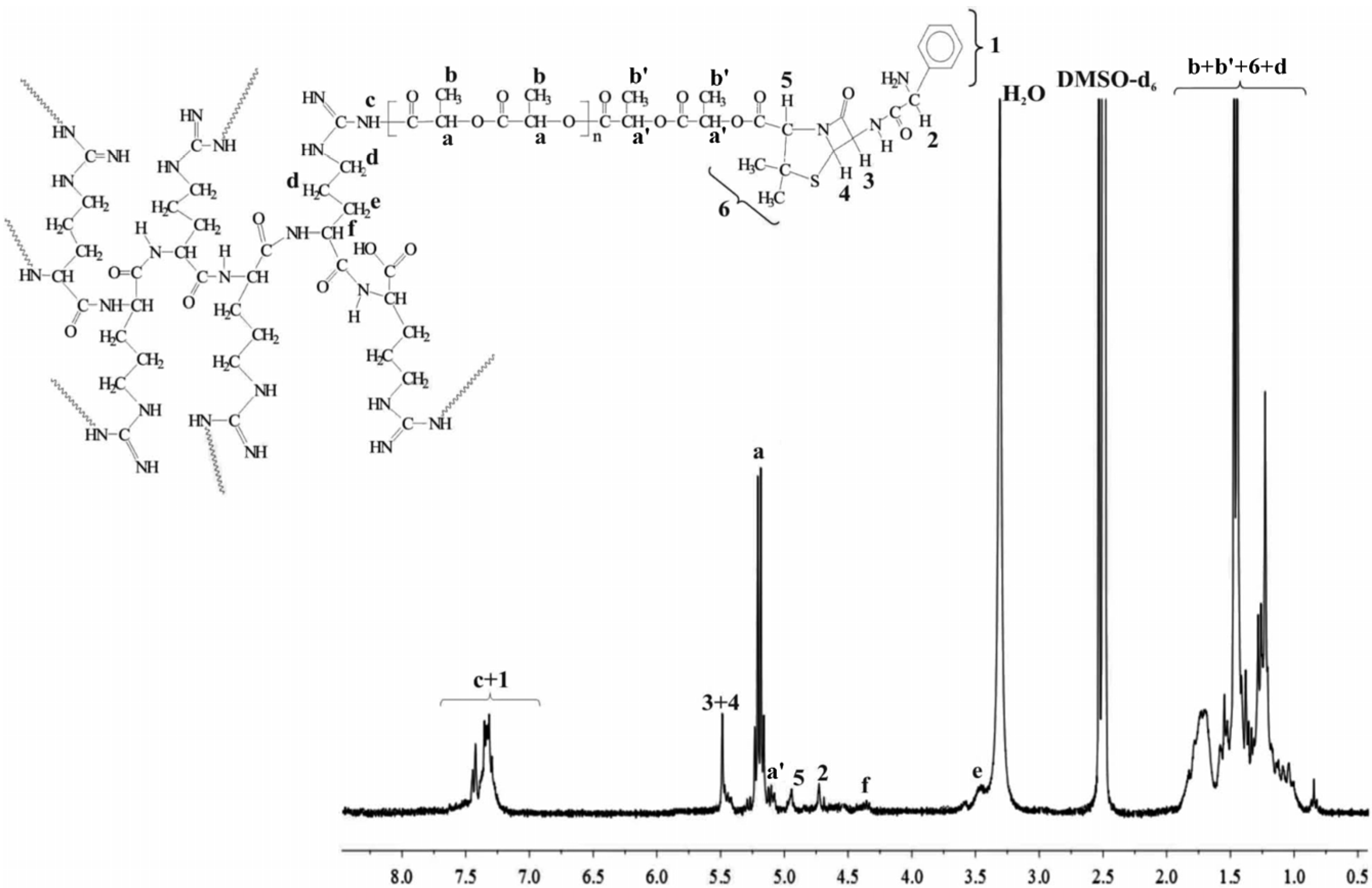
2. Results and Discussion
| Spirotox (24 h-PE a) | Microtox® (15 min-PE a) | Protoxkit F™ (24 h-PE a) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (1 mg/mL) | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 6AR/PCL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6AR/PLLA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Drug Release from the 6AR/PCL/Ampicillin and 6AR/PLLA/Ampicillin Conjugates
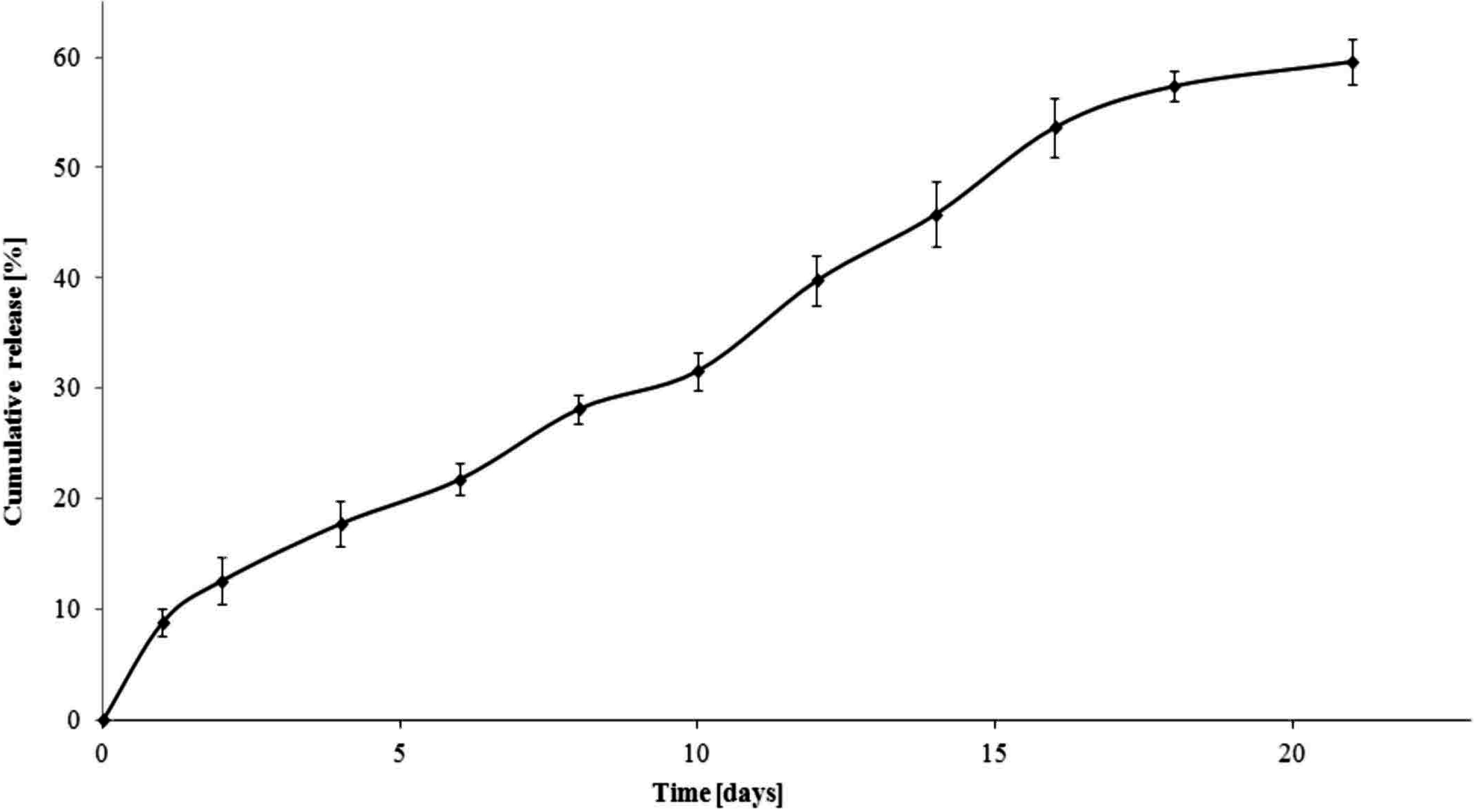
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Branched Macromolecular Conjugate Synthesis
3.2.2. Synthesis of Ampicillin Conjugated 6AR/PCL
3.2.3. Synthesis of Ampicillin Conjugated 6AR/PLLA
3.2.4. Toxicity Assays
3.2.5. The Umu-Test
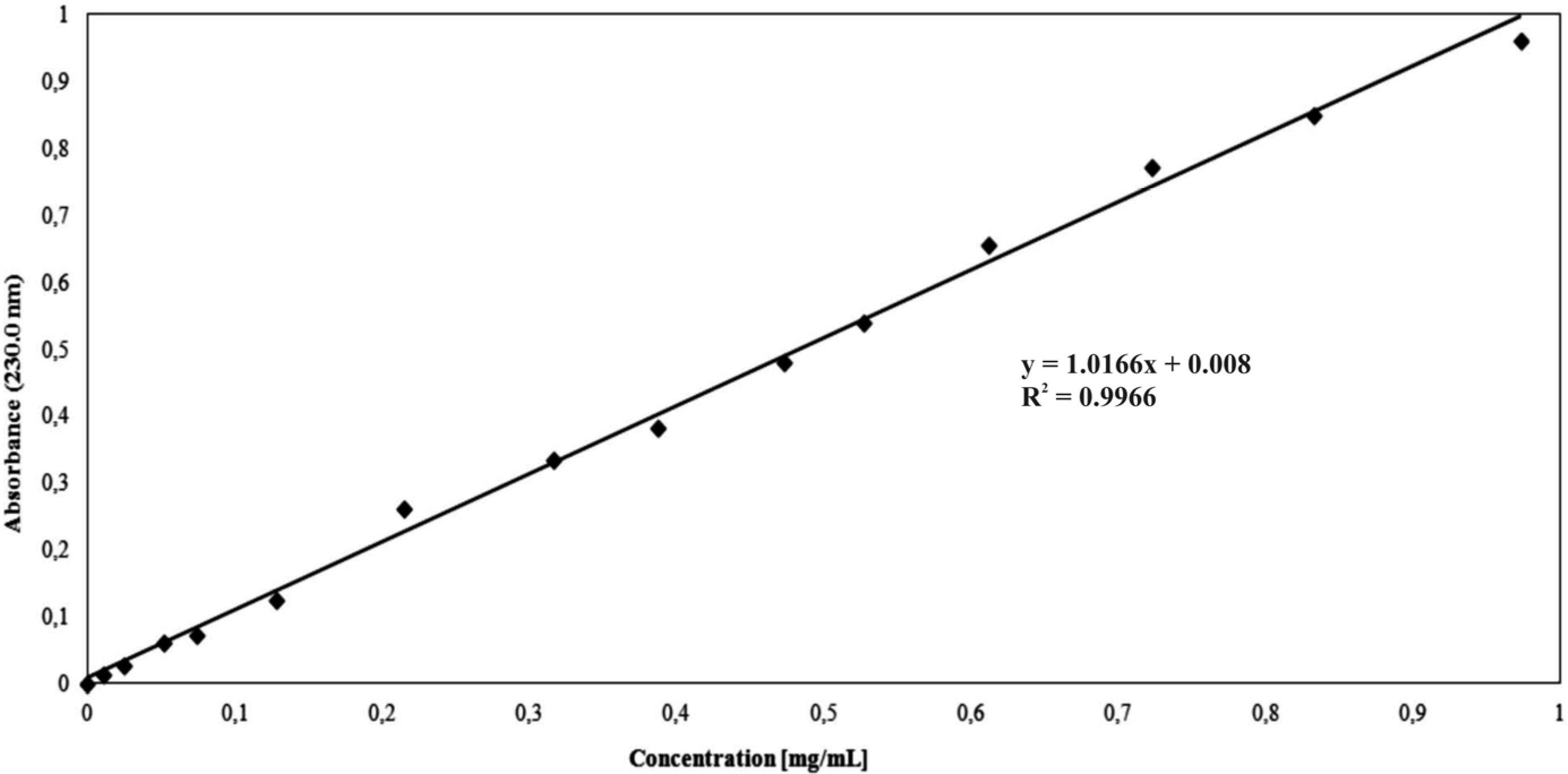
3.2.6. In Vitro Ampicillin Release Studies
3.2.7. Characterization Techniques
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishi, K.K.; Antony, M.; Jayakrishnan, A. Synthesis and evaluation of ampicillin-conjugated gum arabic microspheres for sustained release. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Yost, R.L.; Gotz, V.P. Effect of lactobacillus preparation on the oral absorption of ampicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 28, 727–729. [Google Scholar]
- Barza, M. Tissue directed antibiotic therapy: Antibiotics dynamics in cells and tissue. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkens, P.M. Intracellular distribution and activity of antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1991, 10, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, A.C.; Santos, J.D.; Monteiro, F.J.; Gibson, I.R.; Knowles, J.C. Adsorption and release studies of sodium ampicillin from hydroxyapatite and glass-reinforced hydroxyapatite composites. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, B.V.; Jariwala, U.; Jayachandran, P.; Vidyalakshmi, K.; Dudhani, R.V. Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy and release pattern of tetracycline and metronidazole using a local delivery system. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Friedman, M.; Soskolne, A.; Sela, M.N. A new degradable controlled release device for treatment of periodontal disease: In vitro release study. J. Periodontol. 1990, 61, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.A. Complications of external skeletal fixation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. R. 1983, 180, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlborg, H.G.; Josefsson, P.O. Pin-tract complications in external fixation of fractures of the distal radius. Acta Opthop. 1999, 70, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garberina, M.J.; Fitch, R.D.; Hoffmann, E.D.; Hardaker, W.T.; Vail, T.P.; Scully, S.P. Knee arthrodesis with circular external fixation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. R. 2001, 382, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollwitzer, H.; Ibrahim, K.; Meyer, H.; Mittelmeier, W.; Busch, R.; Stemberger, A. Antibacterial poly(d,l-lactic acid) coating of medical implants using a biodegradable drug delivery technology. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth. 2003, 51, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, D.; Dhawale, S.; Khandare, J.; Patil, M.; Khade, T.; Gavitre, B.; Bobe, K.; Kulkarni, V.; Gaikwad, U. Polymer-drug conjugates: Recent achievements. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.S.; Patel, S.V.; Talpada, N.P.; Patel, H.A. Bioactive polymers: Synthesis, release study and antimicrobial properties of polymer bound ampicillin. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1999, 271, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Bansal, K.; Kaushik, R.; Kumria, R.; Trehan, A. Poly-epsilon-caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatius, A.A.; Claes, L.E. In-vitro biocompatibility of bioresorbable polymers-poly(l,dl-lactide) and poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide). Biomaterials 1996, 17, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Leonas, K.K.; Zhao, Y. Antimicrobial properties and release profile of ampicillin from electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofiber yarns. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2010, 5, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Aumsuwan, N.; Danyus, R.C.; Heinhorst, S.; Urban, M.W. Attachment of ampicillin to expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene): Surface reactions leading to inhibition of microbial growth. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Raucci, M.G.; de Marco, D.; Ambrosio, L. Release kinetics of ampicillin, characterization and bioactivity of TiO2/PCL hybrid materials synthesized by sol-gel processing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 77, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Oledzka, E.; Sobczak, M.; Kolakowski, M.; Kraska, B.; Kamysz, W.; Kolodziejski, W. Development of creatine and arginine-6-oligomer for the ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Kelly, J.P.; Rajasekaran, S.K. An investigation of the value of the Tetrahymena. pyriformis as a test organism for assessing the acute toxicity of antidepressants. Biomed. Res. 2008, 19, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, C.; Dias, N.; Kapanen, A.; Malachova, K.; Vandrovcova, M.; Itavaara, M.; Lima, N. Comparative use of bacterial, algal and protozoan tests to study toxicity of azo- and antraquinone dyes. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptula, A.O.; Patlewicz, G.; Roberts, D.W.; Schultz, T.W. Non-enzymatic glutathione reactivity and in vitro toxicity: A non-animal approach to skin sensitization. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Hajdaniak, M.; Oledzka, E.; Goś, P.; Kołodziejski, W.L. Use of aliphatic poly(amide urethane)s for the controlled release of 5-fluorouracil. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 914–918. [Google Scholar]
- Oledzka, E.; Kaliszewska, D.; Sobczak, M.; Raczak, A.; Nikel, P.; Kołodziejski, W. Synthesis and properties of a star-shaped poly(ε-caprolactone)-ibuprofen conjugate. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczak, M. Synthesis and characterization of poliester conjugates of ciprofloxacin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3844–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Witkowska, E.; Oledzka, E.; Kolodziejski, W.L. Synthesis and structural analysis of polyester prodrugs of norfloxacin. Molecules 2008, 13, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Debek, C.; Oledzka, E.; Nałecz-Jawecki, G.; Kołodziejski, W.; Rajkiewicz, M. Segmented polyurethane elastomers derived from aliphatic polycarbonate and poly(ester-carbonate) soft segments for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 3904–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtoglu, Y.; Mishra, M.K.; Kannan, S.; Kannan, R.M. Drug release characteristics of PAMAM dendrimer–drug conjugates with different linkers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changerath, R.; Nair, P.D.; Mathew, S.; Nair, C.P. Poly(methyl methacrylate)-grafted chitosan microspheres for controlled release of ampicillin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 89, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalecz-Jawecki, G. Spirotox Test-Spirostomum Ambiguum Acute Toxicity Test. In Small-Scale Freshwater Toxicity Investigations; Blaise, C., Férard, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 299–322. [Google Scholar]
- Protoxkit F™ Freshwater Toxicity Test with a Ciliate Protozoan. In Standard Operational Procedure; Belgium: Creasel, Deinze, 1998; p. 18.
- Water Quality-Determination of the Genotoxicity of Water and Waste Water Using the Umu-Tes; International Standard ISO/FDIS 13829: 2000; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Sample Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Oledzka, E.; Sobczak, M.; Nalecz-Jawecki, G.; Skrzypczak, A.; Kolodziejski, W. Ampicillin-Ester Bonded Branched Polymers: Characterization, Cyto-, Genotoxicity and Controlled Drug-Release Behaviour. Molecules 2014, 19, 7543-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19067543
Oledzka E, Sobczak M, Nalecz-Jawecki G, Skrzypczak A, Kolodziejski W. Ampicillin-Ester Bonded Branched Polymers: Characterization, Cyto-, Genotoxicity and Controlled Drug-Release Behaviour. Molecules. 2014; 19(6):7543-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19067543
Chicago/Turabian StyleOledzka, Ewa, Marcin Sobczak, Grzegorz Nalecz-Jawecki, Agata Skrzypczak, and Waclaw Kolodziejski. 2014. "Ampicillin-Ester Bonded Branched Polymers: Characterization, Cyto-, Genotoxicity and Controlled Drug-Release Behaviour" Molecules 19, no. 6: 7543-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19067543
APA StyleOledzka, E., Sobczak, M., Nalecz-Jawecki, G., Skrzypczak, A., & Kolodziejski, W. (2014). Ampicillin-Ester Bonded Branched Polymers: Characterization, Cyto-, Genotoxicity and Controlled Drug-Release Behaviour. Molecules, 19(6), 7543-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19067543