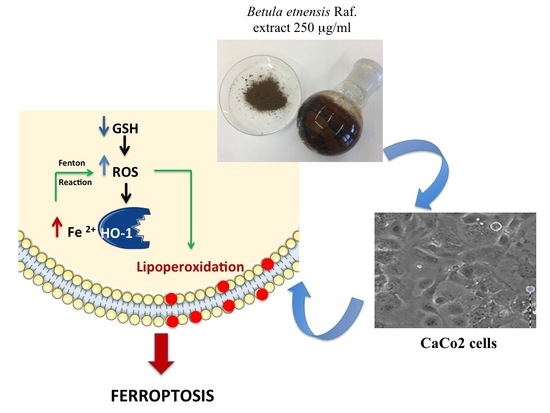
Betula etnensis Raf. (Betulaceae) Extract Induced HO-1 Expression and Ferroptosis Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
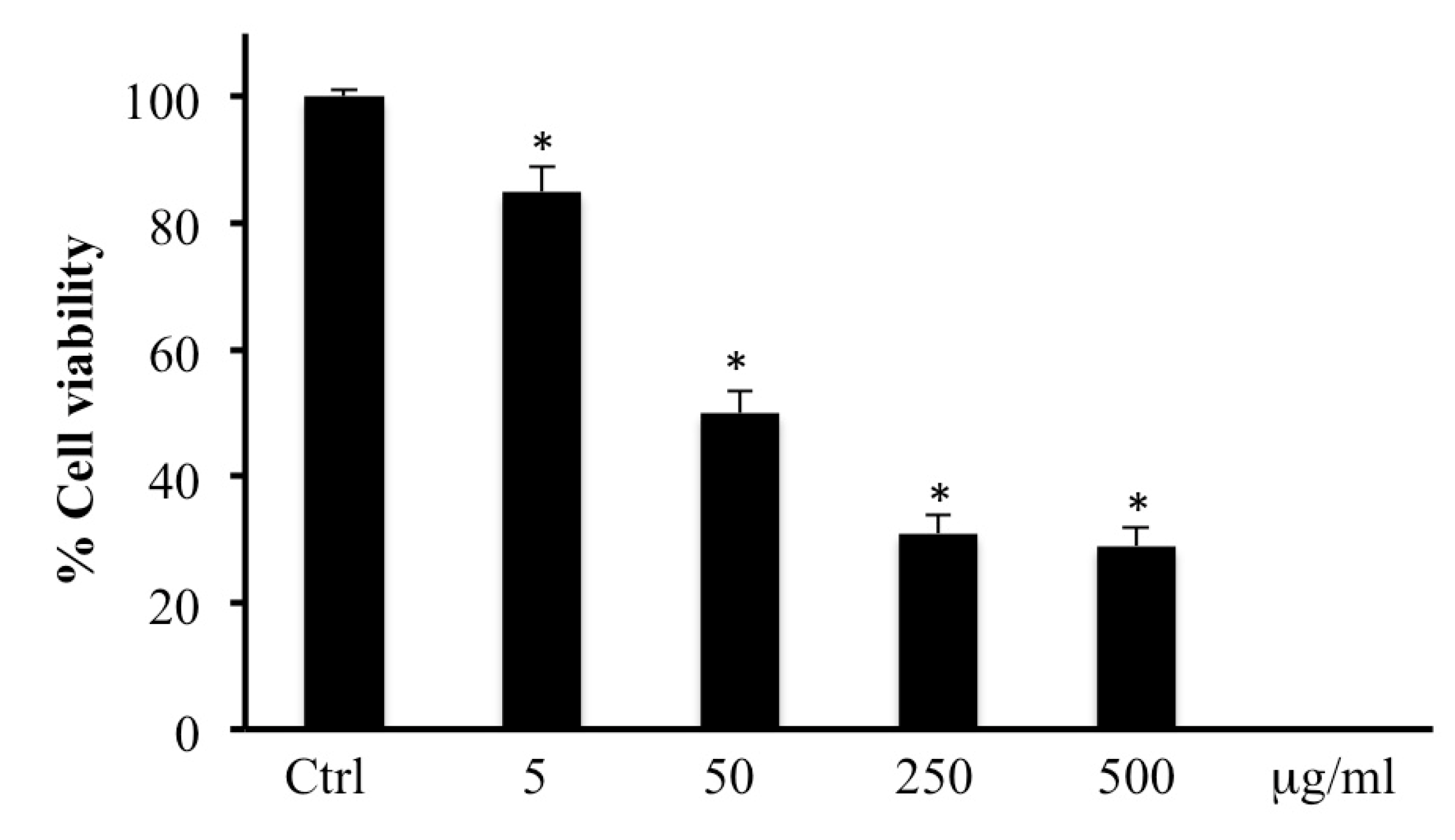
2.1. MTT Bioassay
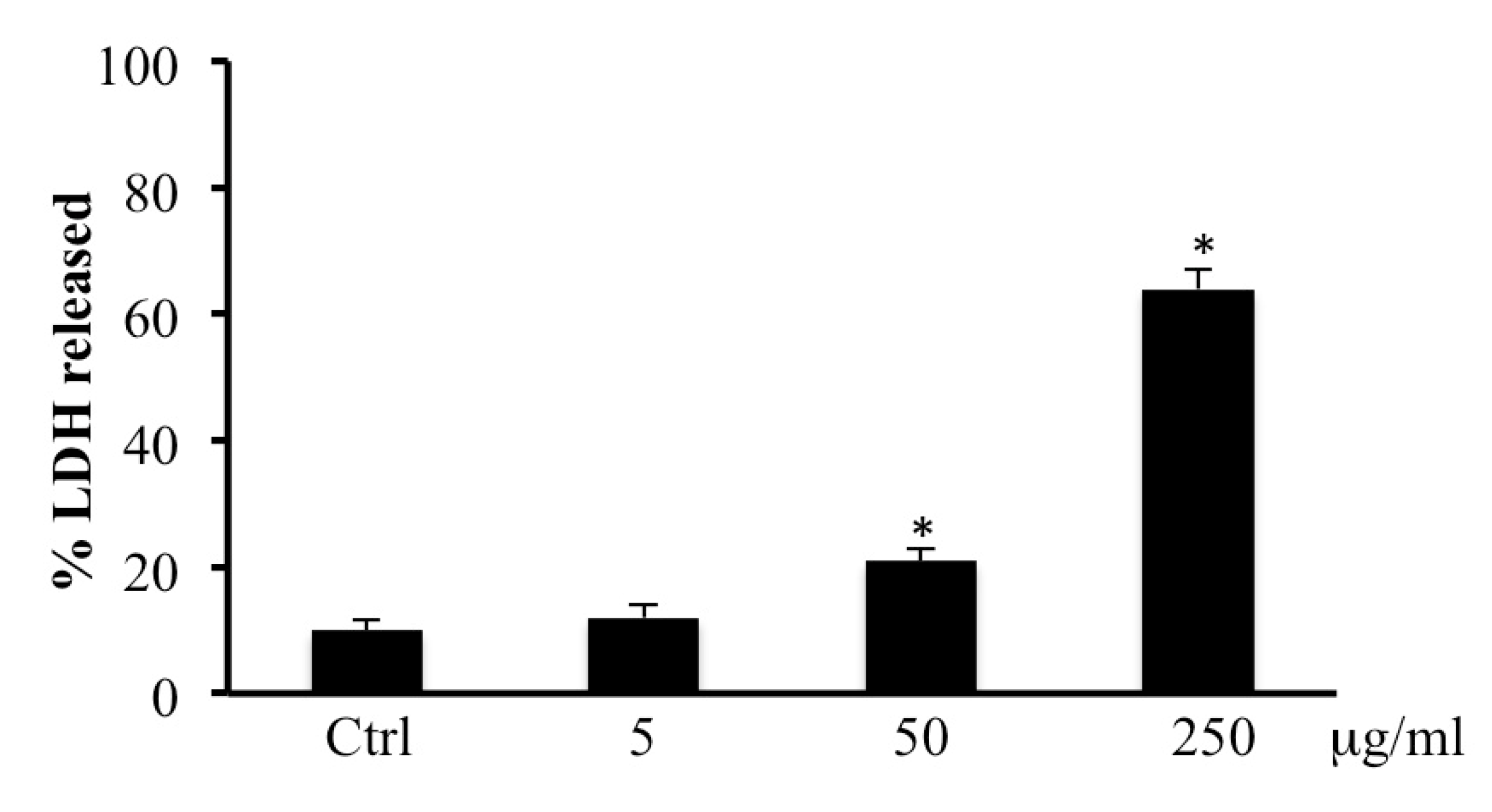
2.2. LDH Release
2.3. Annexin V and Dead Cell Evaluation
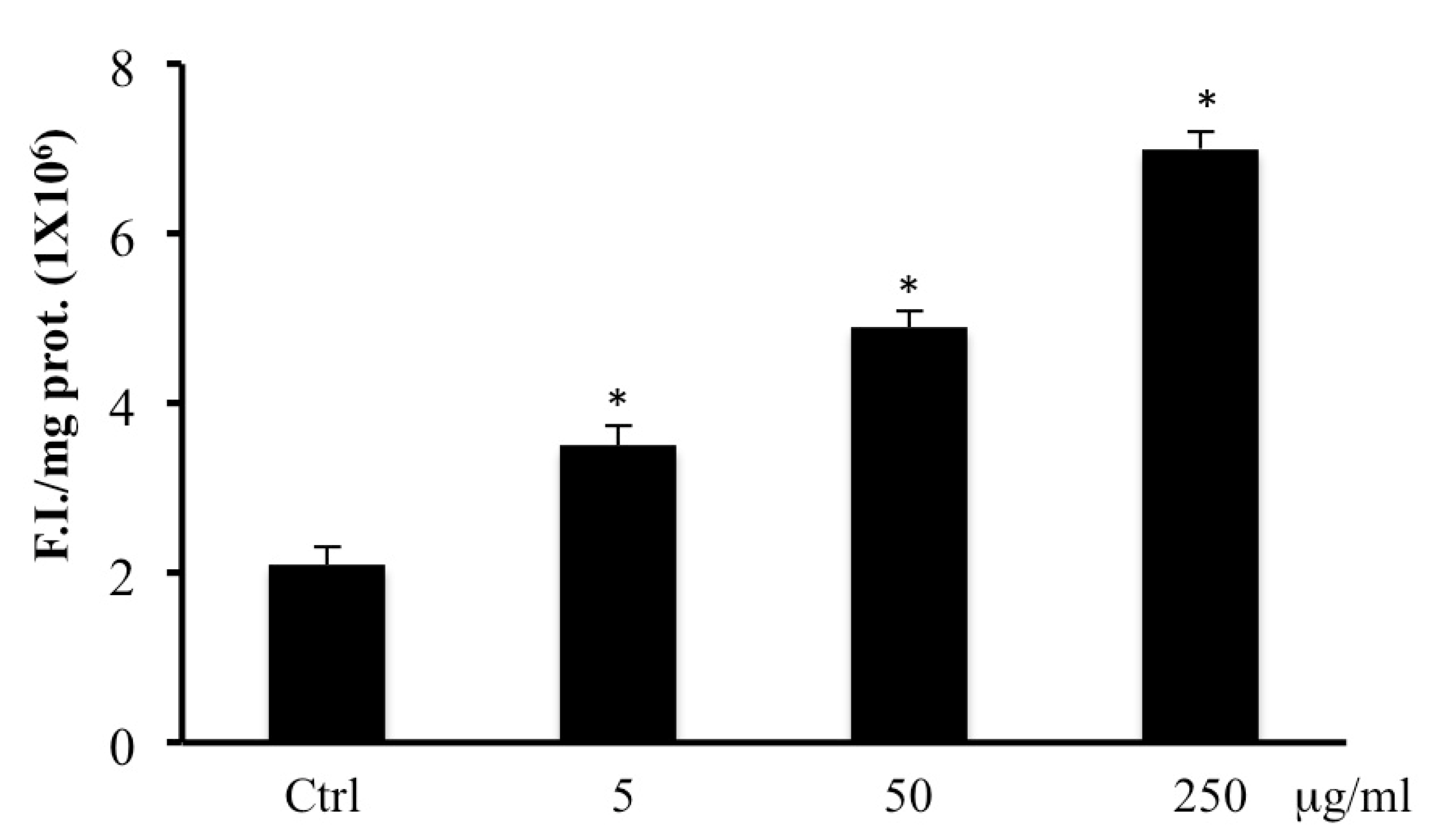
2.4. ROS Levels
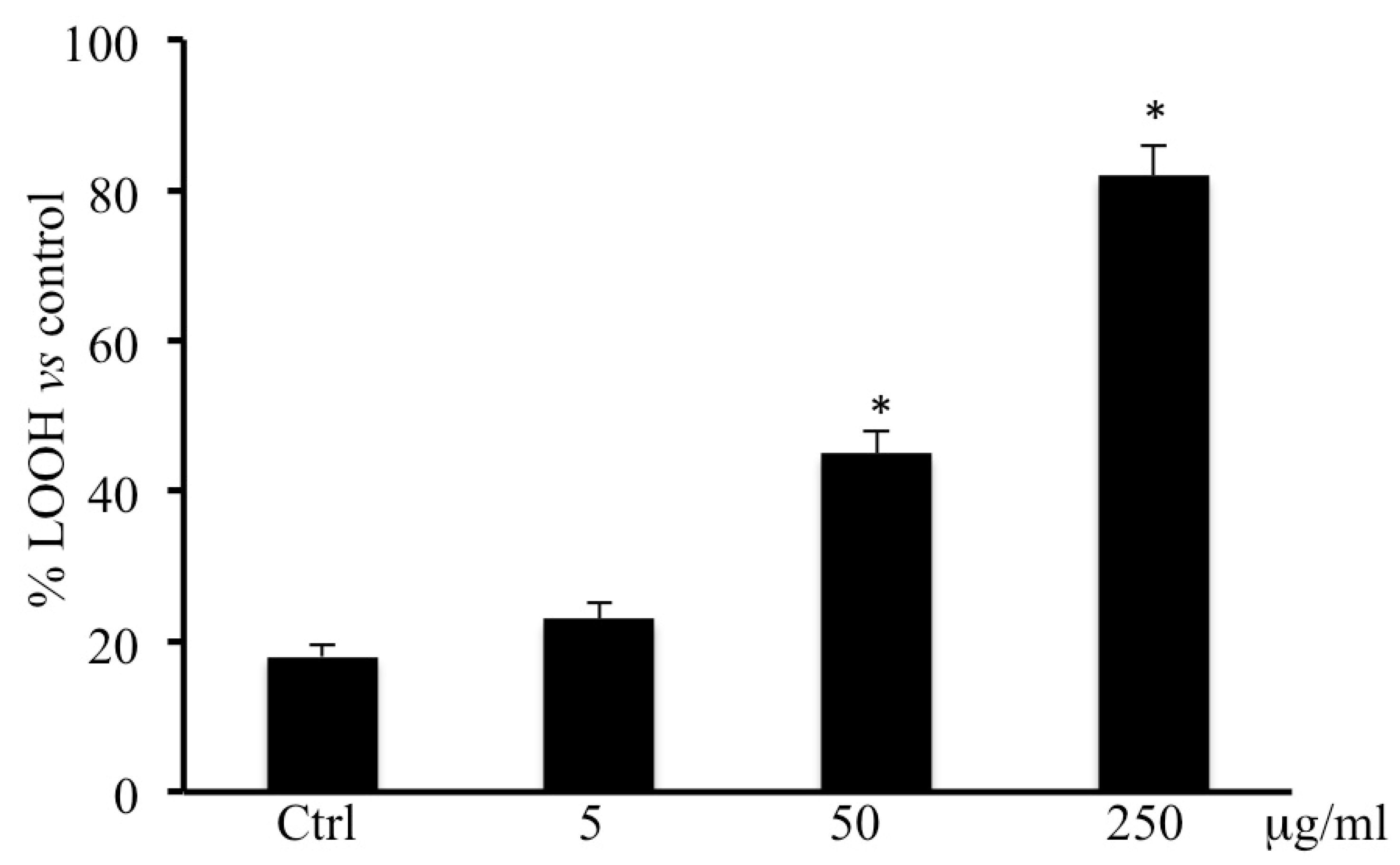
2.5. LOOH Levels
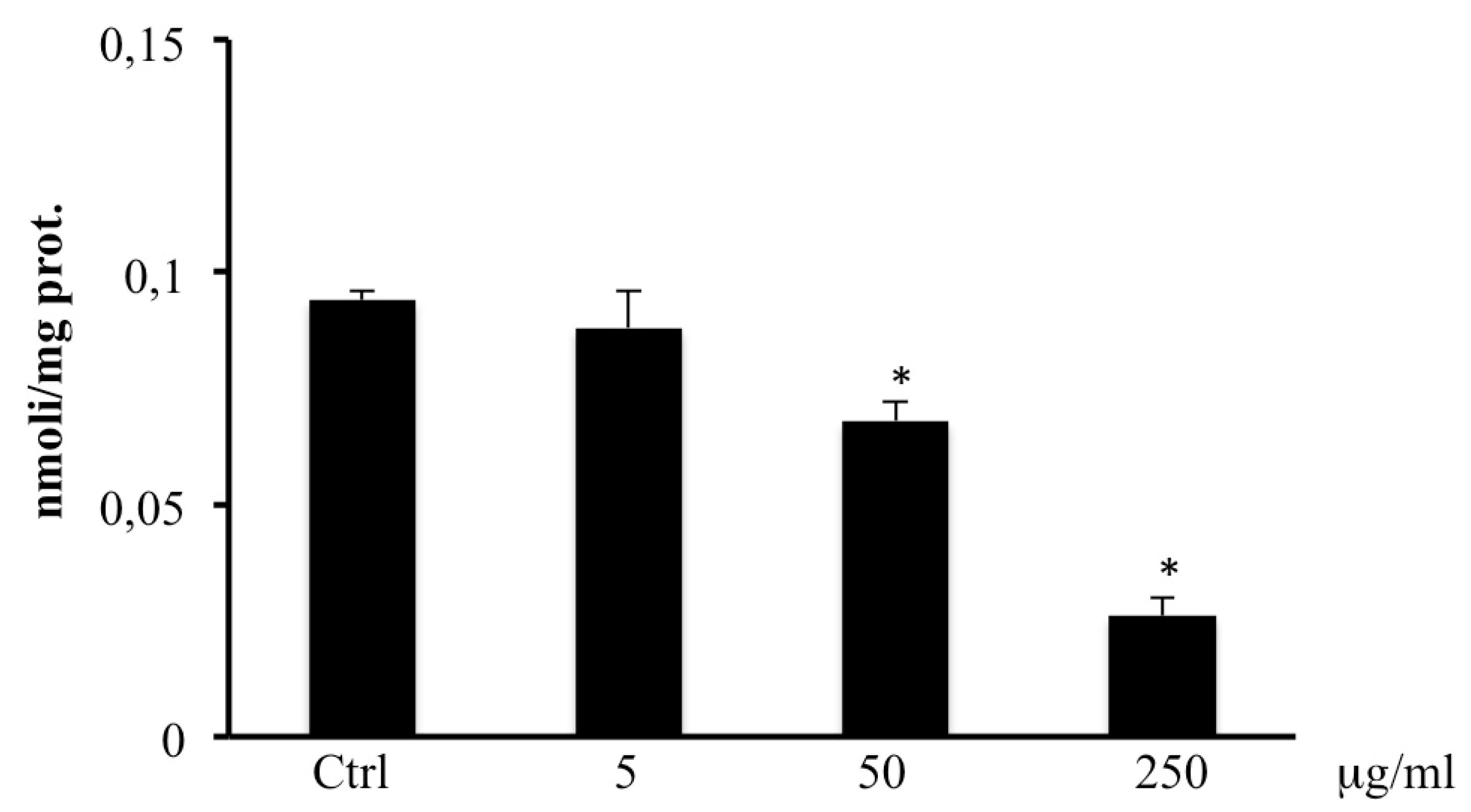
2.6. Total Thiol Groups
2.7. γ-GCS Determination
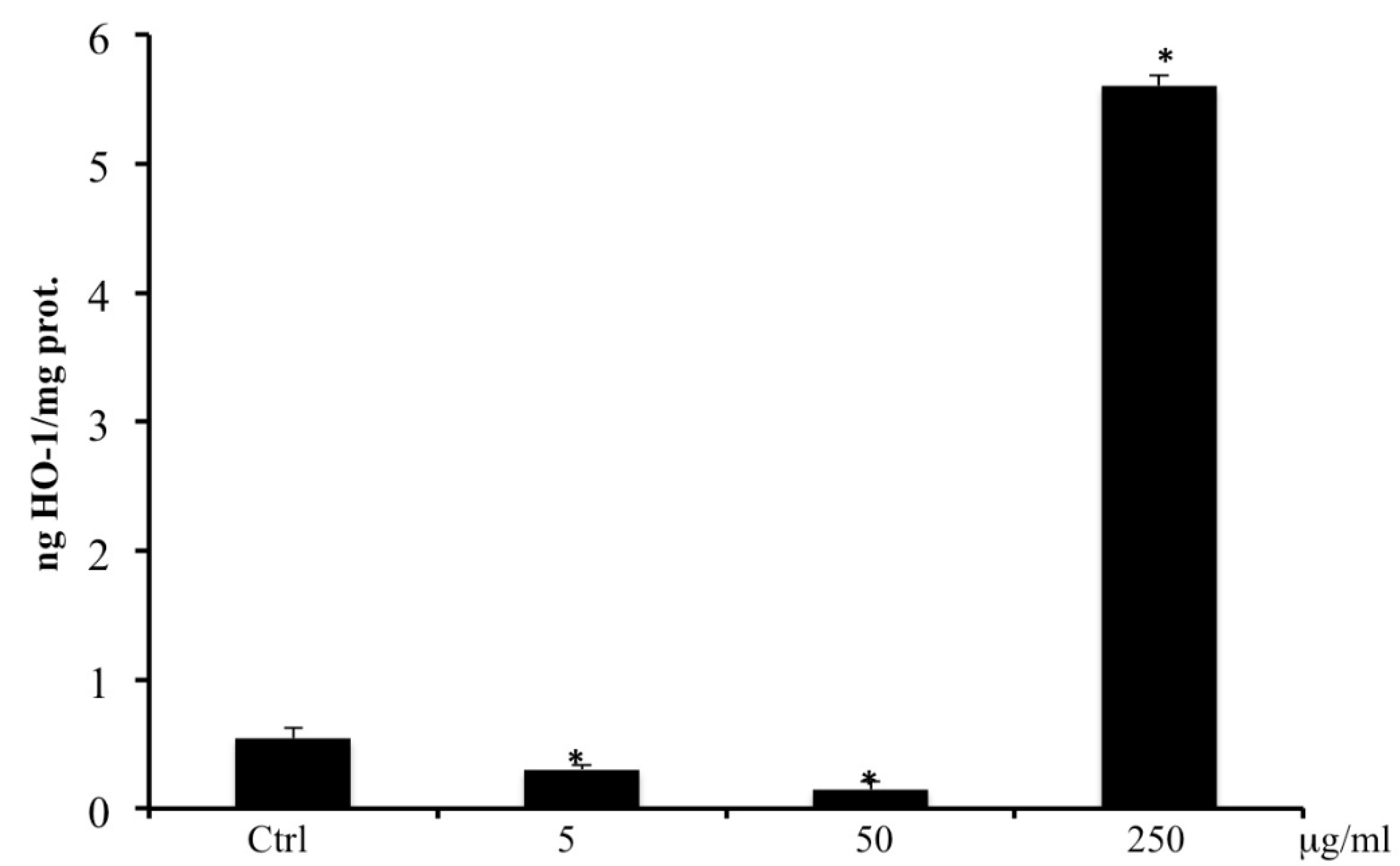
2.8. HO-1 by ELISA
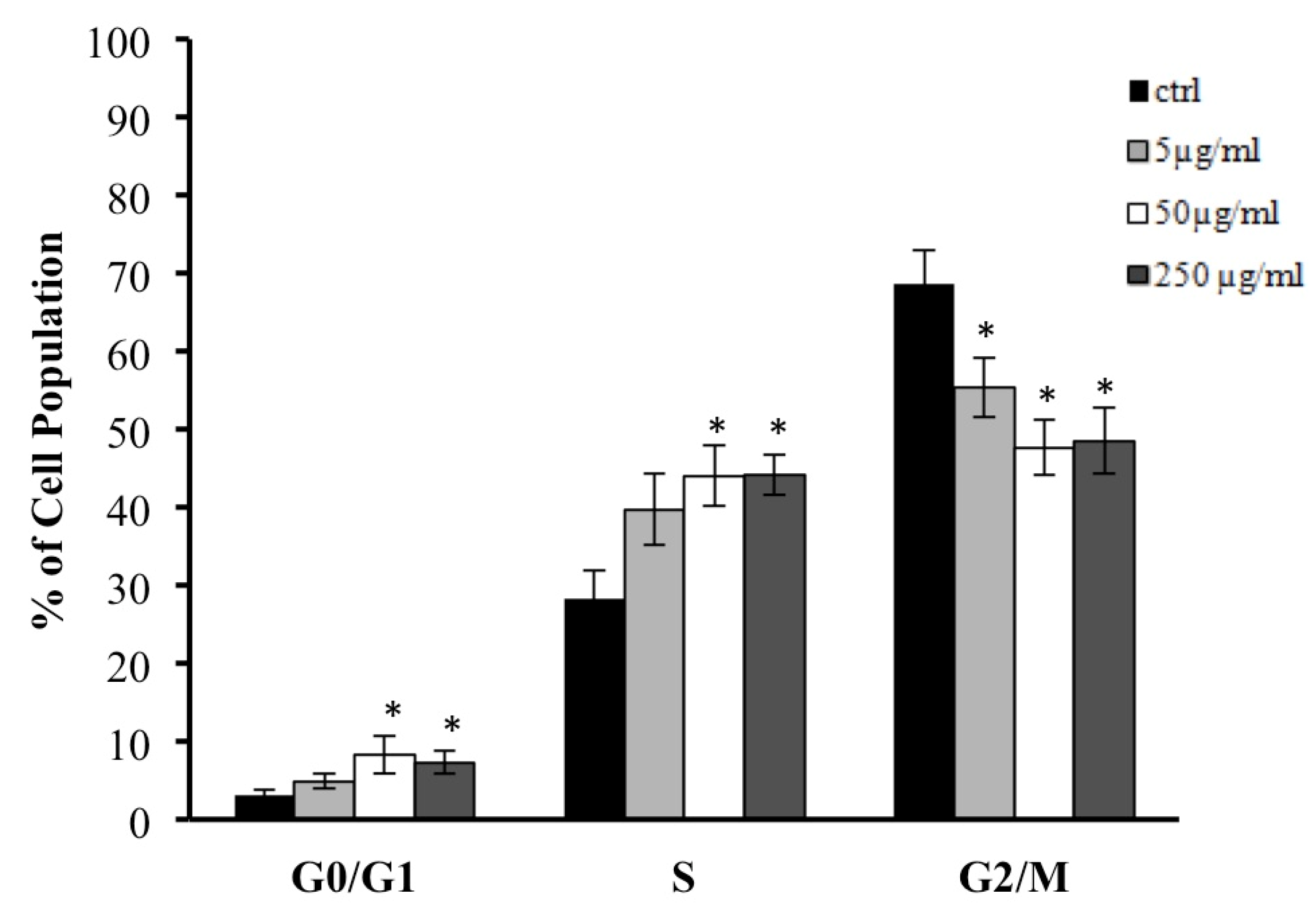
2.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plant Collection and Preparation of Extract
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.4. MTT Bioassay
4.5. Lactic Dehydrogenase Release
4.6. Annexin V and Dead Cell Evaluation
4.7. Reactive Oxygen Species Assay
4.8. Determination of Lipid Hydroperoxide Levels
4.9. Total Thiol Group Determination
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. HO-1 Protein Expression
4.12. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| LDH | Lactic dehydrogenase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| LOOH | Lipid hydroperoxide |
| RSH | Thiol groups |
| γ-GCS | γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase |
References
- Thanikachalam, K.; Khan, G. Colorectal Cancer and Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggar, F.A.; Boushey, R.P. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin. Colon Rectal. Surg. 2009, 22, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.; Thun, M.J.; Connell, C.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Jacobs, E.J.; Flanders, W.D.; Rodriguez, C.; Sinha, R.; Calle, E.E. Meat consumption and risk of colorectal cancer. JAMA 2005, 293, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bultman, S.J. Interplay between diet, gut microbiota, epigenetic events, and colorectal cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquaviva, R.; Sorrenti, V.; Santangelo, R.; Cardile, V.; Tomasello, B.; Malfa, G.; Vanella, L.; Amodeo, A.; Mastrojeni, S.; Pugliese, M.; et al. Effects of extract of Celtis aetnensis (Tornab.) Strobl twigs in human colon cancer cell cultures. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburger, J.H. Nutritional approach to cancer prevention with emphasis on vitamins, antioxidants, and carotenoids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, S226–S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Torikai, K.; Ohto, Y.; Murakami, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ohigashi, H. A simple phenolic antioxidant protocatechuic acid enhances tumor promotion and oxidative stress in female ICR mouse skin: Dose-and timing-dependent enhancement and involvement of bioactivation by tyrosinase. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chang, L.C. A dual role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, R.; Menichini, F.; Ragusa, S.; Genovese, C.; Amodeo, A.; Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.R.; Iauk, L. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of Betula aetnensis Rafin. (Betulaceae) leaves extract. Nat. Prod. Res 2013, 27, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Pandey, M.M.; Kumar Singh Rawat, A. Medicinal plants of the genus Betula-traditional uses and a phytochemical-pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, O.A.; Pashinskii, V.G.; Chuchalin, V.S. Comparative study of pharmacological activity of birch bark ethanol extracts. Pharm. Chem. J. 1999, 33, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, E.M.; Popa, G.; Gill, C.I.; McCann, M.J.; McDougall, G.J.; Stewart, D.; Rowland, I. Colon-available raspberry polyphenols exhibit anti-cancer effects on in vitro models of colon cancer. J. Carcinog. 2007, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshvildadze, V.; Legault, J.; Lavoie, S.; Gauthier, C.; Pichette, A. Anticancer diarylheptanoid glycosides from the inner bark of Betula papyrifera. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatti, S. Flora d’Italia, EFIZIO, Edagricole, New Business Media Italia, 2017, Vol. II, pp. 676–677. Available online: https://books.google.it/books?id=AqFexQEACAAJ&hl=it&source=gbs_book_other_versions (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Johnson, I. New approaches to the role of diet in the prevention of cancers of the alimentary tract. Mutat. Res. 2004, 551, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, W.R.; Giacca, A.; Medline, A. Possible mechanisms relating diet and risk of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, A.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Ross, R.K.; Henderson, B.E. Intake of vegetables, fruits, beta-carotene, vitamin C and vitamin supplements and cancer incidence among the elderly: A prospective study. Br. J. Cancer 1992, 66, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, J.B.; Saiful Yazan, L.; Tor, Y.S.; Wibowo, A.; Ismail, N.; How, C.W.; Armania, N.; Loh, S.P.; Ismail, I.S.; Cheah, Y.K.; et al. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by betulinic acid-rich fraction from Dillenia suffruticosa root in MCF-7 cells involved p53/p21 and mitochondrial signalling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 166, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.S.; Bicknell, R. Hypoxia and oxidative stress in breast cancer. Oxidative stress: Its effects on the growth, metastatic potential and response to therapy of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2001, 3, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Seo, M.S.; Baines, I.C.; Tekle, E.; Chock, P.B.; Rhee, S.G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role in EGF receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, J.S.; Sefton, B.M. The activated form of the lck tyrosine protein kinase in cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide is phosphorylated at both Tyr-394 and Tyr-505. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25429–25432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundersan, M.; Yu, Z.X.; Ferrans, V.J.; Irani, K.; Finkel, T. Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science 1995, 270, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devary, Y.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Smeal, T.; Karin, M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell 1992, 71, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanceta, L.; Li, C.; Choi, A.M.; Eaton, J.W. Heme oxygenase-1 overexpression alters intracellular iron distribution. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozkowicz, A.; Was, H.; Dulak, J. Heme Oxygenase-1 in tumors: Is it a false friend? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2099–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Piva, A.; Sorrenti, V.; Vanella, L.; Piva, G.; Casadei, G.; La Fauci, L.; Ritieni, A.; Bognanno, M.; et al. Protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside on ochratoxin A-mediated damage in the rat. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasa, K.; Kitayama, M.; Fukuda, H.; Kimura, K.; Yanagawa, T.; Ishii, T.; Nakashima, K.; Yamada, K. Oxidative stress-related proteins A170 and heme oxygense-1 are differently induced in the rat cerebellum under kainate-mediated excitotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 282, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busserolles, J.; Megias, J.; Terencio, M.C.; Alcaraz, M.J. Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits apoptosis in Caco-2 cells via activation of Akt pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2006, 38, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. HO-1/CO system in tumor growth, angiogenesis and metabolism-Targeting HO-1 as an anti-tumor therapy. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2015, 74, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Marinari, U.M.; Moretta, L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. HO-1 induction in cancer progression: A matter of cell adaptation. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.Y.; Park, E.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, S.W. Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates Erastin induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 2018, 416, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.C.; Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Yu, Y.L.; Chou, R.H.; Chang, W.C. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates BAY 11-7085 induced ferroptosis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassannia, B.; Wiernicki, B.; Ingold, I.; Qu, F.; Van Herck, S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayır, H.; Abhari, B.A.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Choi, S.M.; et al. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillemi, R.; Cardullo, N.; Greco, V.; Malfa, G.; Tomasello, B.; Sciuto, S. Synthesis of amphiphilic resveratrol lipoconjugates and evaluation of their anticancer activity towards neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfa, G.A.; Tomasello, B.; Sinatra, F.; Villaggio, G.; Amenta, F.; Avola, R.; Renis, M. Reactive response evaluation of primary human astrocytes after methylmercury exposure. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, R.; Di Giacomo, C.; Vanella, L.; Santangelo, R.; Sorrenti, V.; Barbagallo, I.; Genovese, C.; Mastrojeni, S.; Ragusa, S.; Iauk, L. Antioxidant activity of extracts of Momordica foetida Schumach. et Thonn. Molecules 2013, 18, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, R.; Di Giacomo, C.; Sorrenti, V.; Galvano, F.; Santangelo, R.; Cardile, V.; Gangia, S.; D’Orazio, N.; Abraham, N.G.; Vanella, L. Antiproliferative effect of oleuropein in prostate cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li Volti, G.; Galvano, F.; Frigiola, A.; Guccione, S.; Di Giacomo, C.; Forte, S.; Tringali, G.; Caruso, M.; Adekoya, O.A.; Gazzolo, D. Potential immunoregulatory role of heme oxygenase-1 in human milk: A combined biochemical and molecular modeling approach. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Live | Early Apoptosis | Late Apoptosis | Dead Cells | Total Apoptosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 96.0 ± 0.045% | 0% | 1.64 ± 0.09% | 2.36 ± 0.06% | 1.64 ± 0.05% |
| 5 µg/mL | 92.30 ± 0.055% | 0% | 2.1 ± 0.035% | 4.9 ± 0.065% | 2.1 ± 0.08% |
| 50 µg/mL | 84.70 ± 0.08% * | 0% | 9.20 ± 0.09% | 6.10 ± 0.1% | 9.20 ± 1.25% |
| 250 µg/mL | 4.0 ± 0.084% * | 1.10 ± 0.085% | 10.65 ± 0.075% | 84.25 ± 0.5% | 11.75 ± 0.40% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malfa, G.A.; Tomasello, B.; Acquaviva, R.; Genovese, C.; La Mantia, A.; Cammarata, F.P.; Ragusa, M.; Renis, M.; Di Giacomo, C. Betula etnensis Raf. (Betulaceae) Extract Induced HO-1 Expression and Ferroptosis Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112723
Malfa GA, Tomasello B, Acquaviva R, Genovese C, La Mantia A, Cammarata FP, Ragusa M, Renis M, Di Giacomo C. Betula etnensis Raf. (Betulaceae) Extract Induced HO-1 Expression and Ferroptosis Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112723
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalfa, Giuseppe Antonio, Barbara Tomasello, Rosaria Acquaviva, Carlo Genovese, Alfonsina La Mantia, Francesco Paolo Cammarata, Monica Ragusa, Marcella Renis, and Claudia Di Giacomo. 2019. "Betula etnensis Raf. (Betulaceae) Extract Induced HO-1 Expression and Ferroptosis Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112723
APA StyleMalfa, G. A., Tomasello, B., Acquaviva, R., Genovese, C., La Mantia, A., Cammarata, F. P., Ragusa, M., Renis, M., & Di Giacomo, C. (2019). Betula etnensis Raf. (Betulaceae) Extract Induced HO-1 Expression and Ferroptosis Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112723