Alterations in the MicroRNA of the Blood of Autism Spectrum Disorder Patients: Effects on Epigenetic Regulation and Potential Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
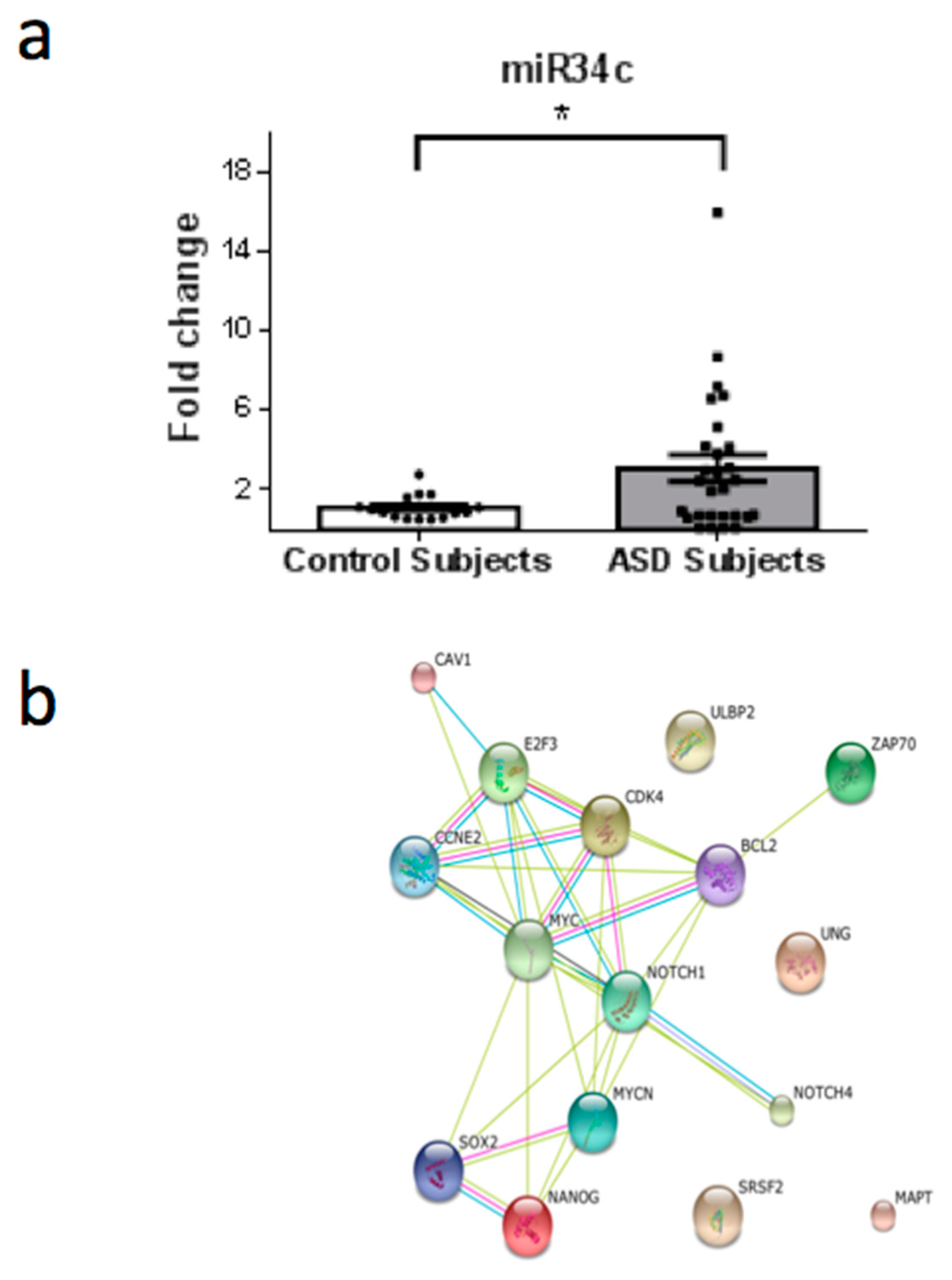
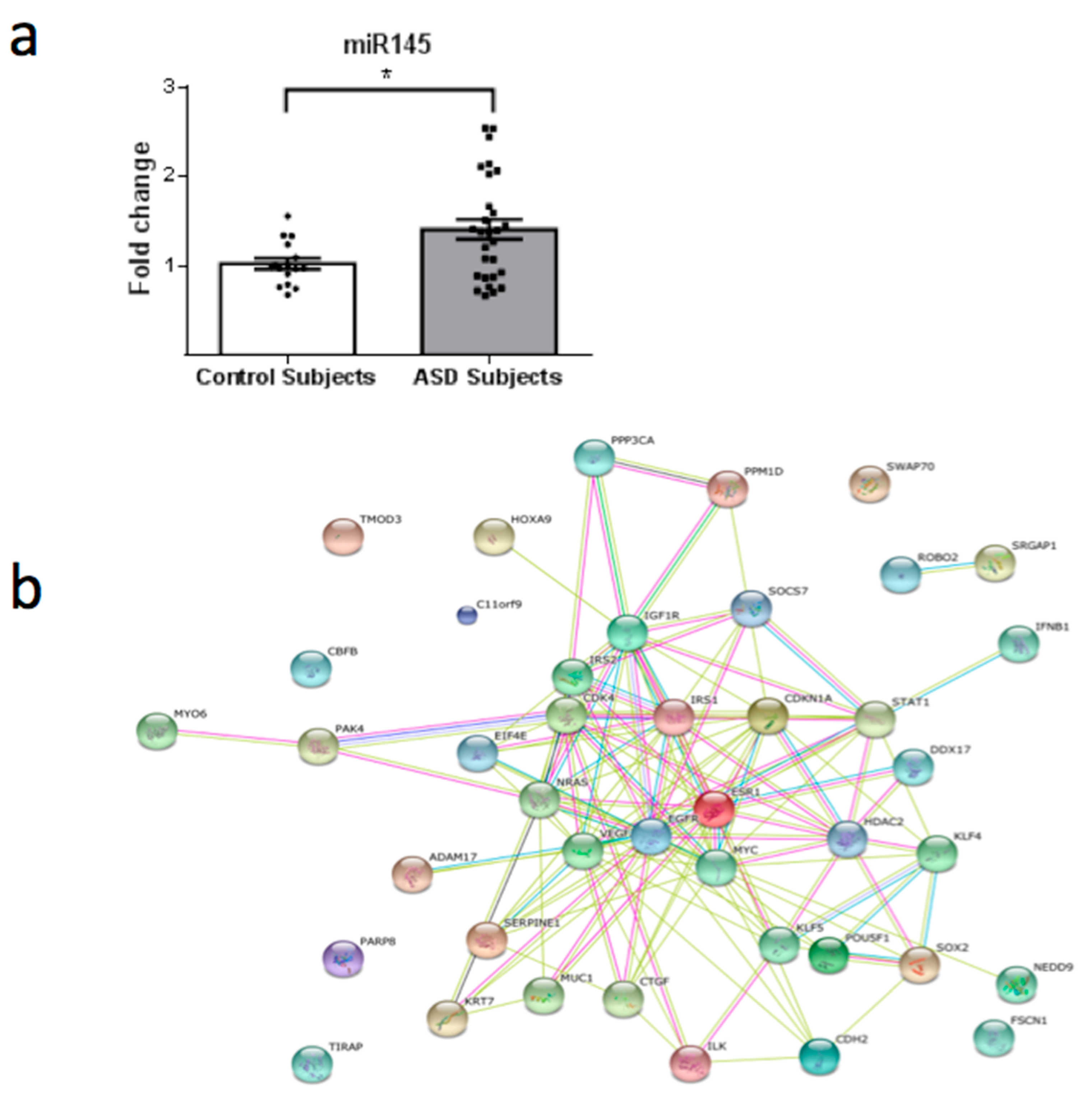
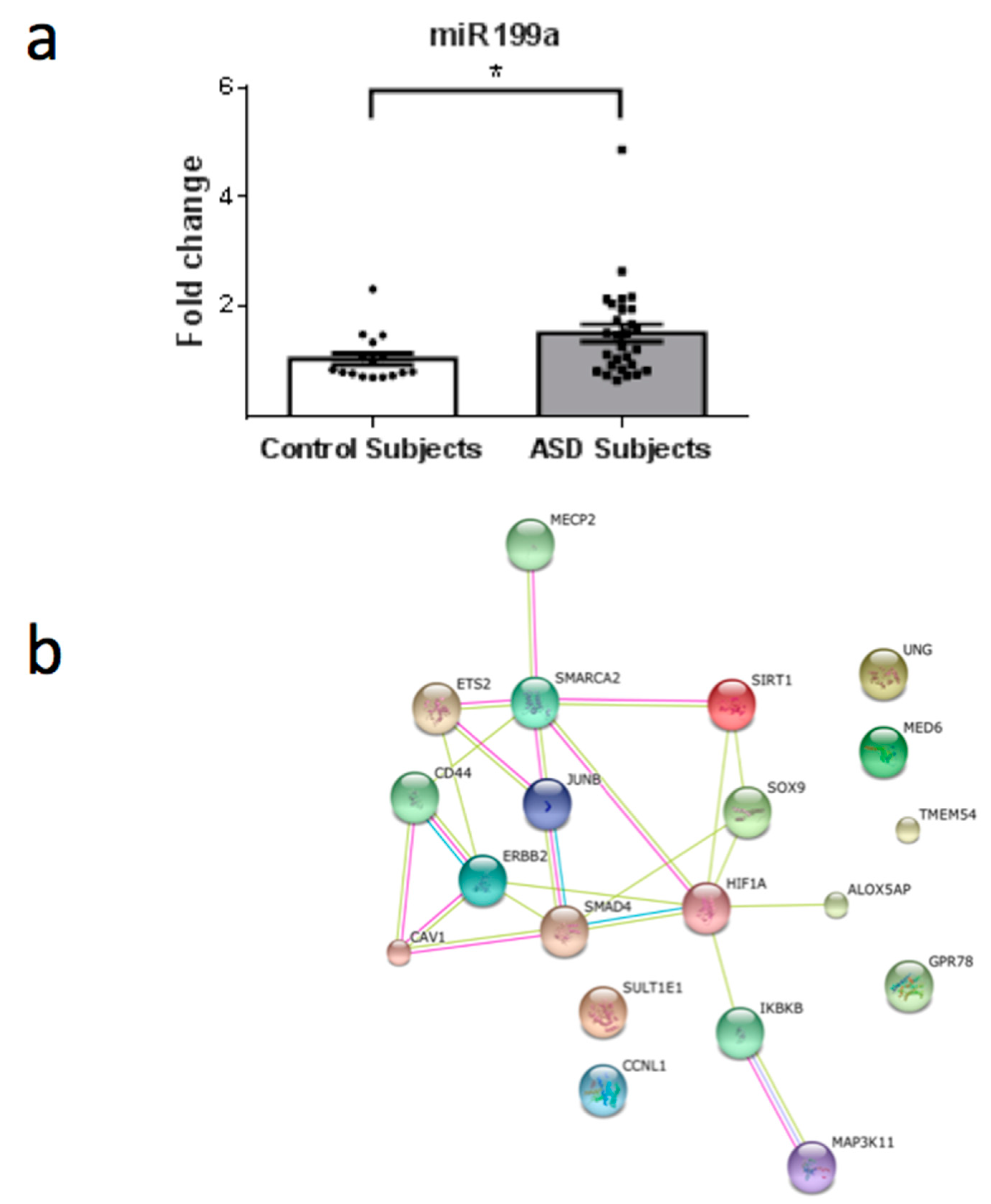
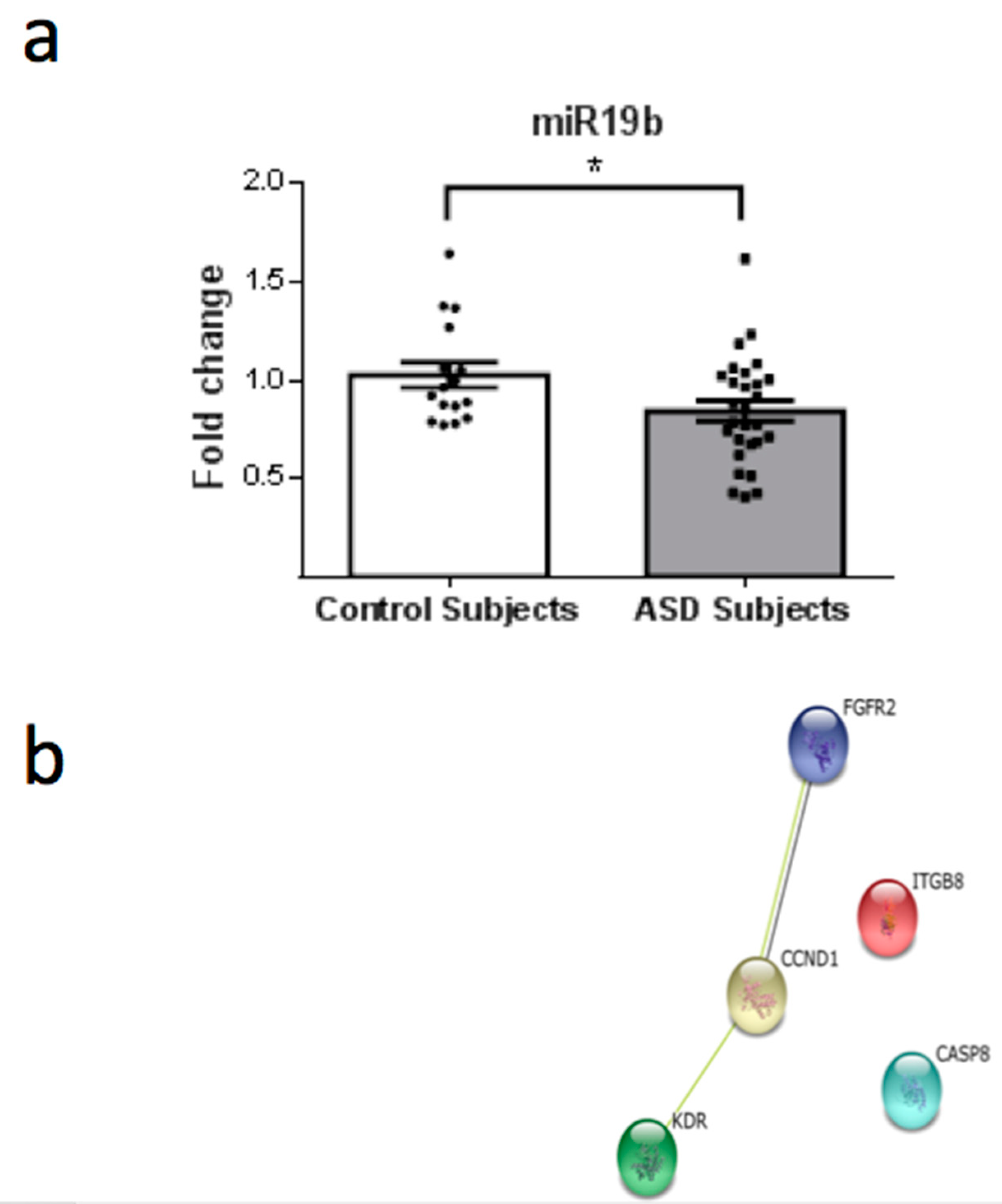
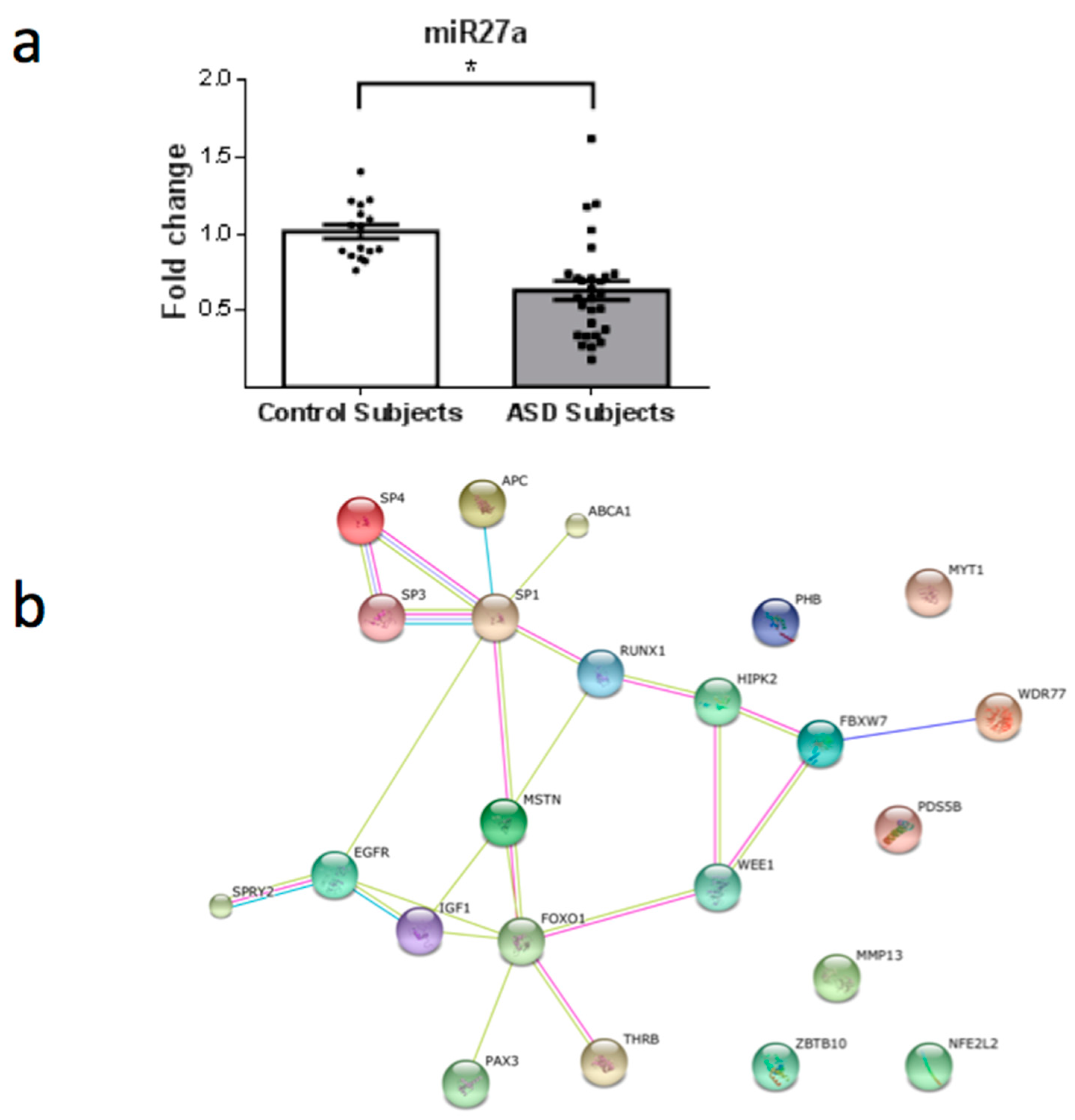
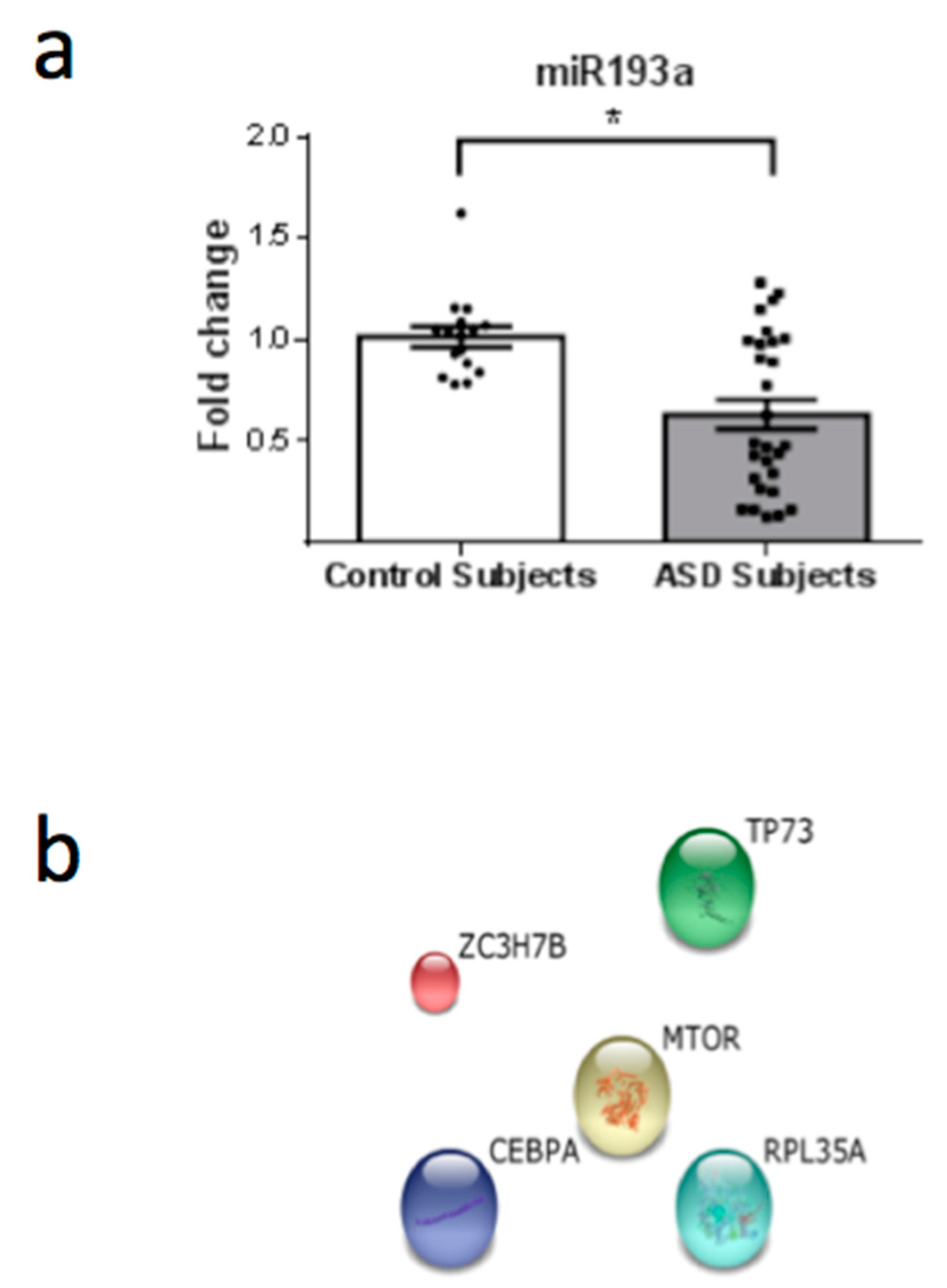
3. Results
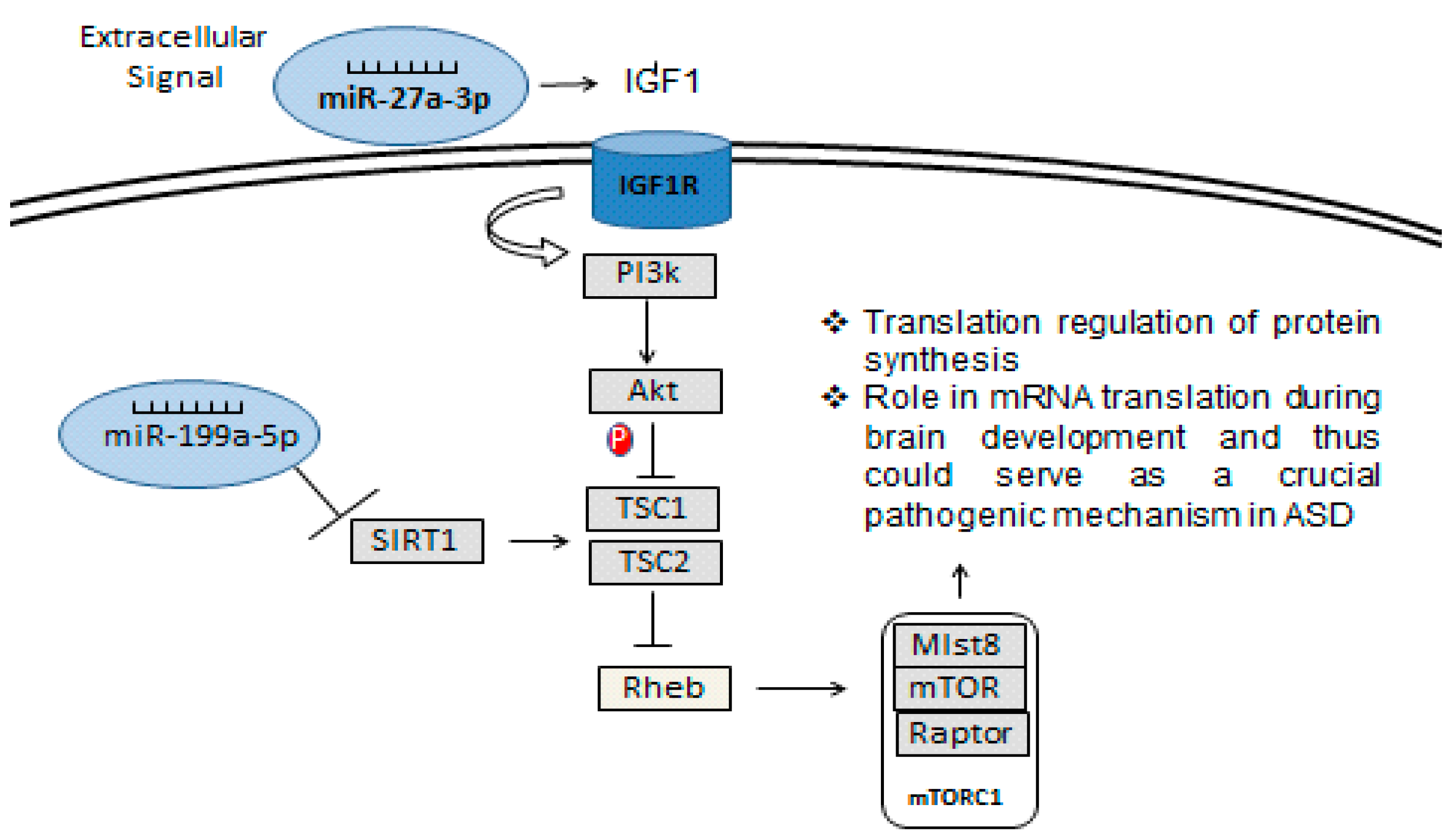
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baio, J.; Wiggins, L.; Christensen, D.L.; Maenner, M.J.; Daniels, J.; Warren, Z.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; Zahorodny, W.; Robinson Rosenberg, C.; White, T.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 67, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, A.M.; Napolioni, V. Autism Genetics. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 251, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristino, A.S.; Williams, S.M.; Hawi, Z.; An, J.Y.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Schwartz, C.E.; Costa Lda, F.; Claudianos, C. Neurodevelopmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders Represent an Interconnected Molecular System. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glessner, J.T.; Connolly, J.J.; Hakonarson, H. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Autism. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 1, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, S.E.; Lemery-Chalfant, K.; Jahromi, L.B.; Valiente, C. A Review of Gene-environment Correlations and Their Implications for Autism: A Conceptual Model. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 120, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafodatskaya, D.; Brian, C.; Szatmari, P.; Weksberg, R. Autism Spectrum Disorders and Epigenetics. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 49, 794–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siniscalco, D.; Cirillo, A.; Bradstreet, A.J.; Antonucci, A. Epigenetic Findings in Autism: New Perspectives for Therapy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4261–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Long, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Qiu, R.; Zhuang, W.; Tang, B.; Xia, K.; Jiang, H. Investigation of Gene Regulatory Networks Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder Based on MiRNA Expression in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcuve, G.P.; Mojgan, R.; Davie, J.R. Epigenetic Control. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul, Q.A.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Epigenetic modifications of gene expression by lifestyle and environment. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yongjuan, X.; Wenhao, Z.; Zilong, Q. The Epigenetic Switches for Neural Development and Psychiatric Disorders. J. Genet. Genom. 2013, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N. MicroRNA Biogenesis: Coordinated Cropping and Dicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsimali, M.; Kloosterman, W.P.; de Bruijn, E.; Rosa, F.; Plasterk, R.H.; Wilson, S.W. MicroRNAs Show a Wide Diversity of Expression Profiles in the Developing and Mature Central Nervous System. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.; Yu, S.L.; Hsieh, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Wen, C.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Hsiao, P.C.; Hsiao, C.K.; Liu, C.M.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Aberration as Potential Peripheral Blood Biomarkers for Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zovoilis, A.; Agbemenyah, H.Y.; Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Stilling, R.M.; Edbauer, D.; Rao, P.; Farinelli, L.; Delalle, I.; Schmitt, A.; Falkai, P.; et al. microRNA-34c is a novel target to treat dementias. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.; Shepherd, C. A Prevalence Study of Autism in Tuberous Sclerosis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1993, 23, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creemers, E.E.; Tijsen, A.J.; Pinto, Y.M. Circulating microRNAs: Novel Biomarkers and Extracellular Communicators in Cardiovascular Disease? Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, R.J.; DeVellis, R.F.; Daly, K. Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1980, 10, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Dilavore, P.; Risi, S. Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule; Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.J.; Bohnet, S.J.; Meyerson, J.M.; Krueger, J.M. Sleep loss changes microRNA levels in the brain: A possible mechanism for state-dependent translational regulation. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 422, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbato, C.; Ruberti, F.; Cogoni, C. Searching for MIND: microRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eacker, S.M.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Understanding microRNAs in neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-Time Quantification of microRNAs by Stem-Loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Rashanravan, B.; Lee, T. Th1- and Th2-like Cytokines in CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Autism. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998, 85, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalco, D.; Mijatovic, T.; Bosmans, E.; Cirillo, A.; Kruzliak, P.; Lombardi, V.C.; Meirleir, K.; Antonucci, N. Decreased Numbers of CD57+CD3− Cells Identify Potential Innate Immune Differences in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Vivo 2016, 30, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vojdani, A.; Mumper, E.; Granpeesheh, D.; Mielke, L.; Traver, D.; Bock, K.; Hirani, K.; Neubrander, J.; Woeller, K.N.; O’Hara, N.; et al. Low Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Activity in Autism: The Role of Glutathione, IL-2 and IL-15. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 205, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantomio, D.; Chana, G.; Laskaris, L.; Testa, R.; Everall, I.; Pantelis, C.; Skafidas, E. Convergent Evidence for mGluR5 in Synaptic and Neuroinflammatory Pathways Implicated in ASD. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 52, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Picard, C.; Chemin, K.; Dogniaux, S.; le Deist, F.; Hivroz, C. ZAP70: A Master Regulator of Adaptive Immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2010, 32, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, M.L.; Conti, C.M.; Kempuraj, D.J.; Salini, V.; Vecchiet, J.; Tete, S.; Ciampoli, C.; Conti, F.; Cerulli, G.; Caraffa, A.; et al. Autism and Immunity: Revisited Study. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enstrom, A.M.; Lit, L.; Onore, C.E.; Gregg, J.P.; Hansen, R.L.; Pessah, I.N.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Van de Water, J.A.; Sharp, F.R.; Ashwood, P. Altered Gene Expression and Function of Peripheral Blood Natural Killer Cells in Children with Autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, K.Y. Transcriptional Dysregulation of Neocortical Circuit Assembly in ASD. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2013, 113, 167–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caillet-Boudin, M.L.; Buée, L.; Sergeant, N.; Lefebvre, B. Regulation of Human MAPT Gene Expression. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iovino, M.; Agathou, S.; González-Rueda, A.; Del Castillo Velasco-Herrera, M.; Borroni, B.; Alberici, A.; Lynch, T.; O’Dowd, S.; Geti, I.; Gaffney, D.; et al. Early Maturation and Distinct Tau Pathology in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons from Patients with MAPT Mutations. Brain 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.H. The Physiology and Pathology of Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau. Essays Biochem. 2014, 56, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, O.H.; Zhu, P.; Ostendorff, H.P.; Golebiewski, M.; Tiefenbach, J.; Peters, M.A.; Brill, B.; Groner, B.; Bach, I.; Heinzel, T.; et al. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid Selectively Induces Proteasomal Degradation of HDAC2. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, H.; Spiegelman, D.; Buka, S.L. Prenatal Risk Factors for Autism: Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 195, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, H.S.; McBurney, M.; Robbins, P.D. SIRT1 Negatively Regulates the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, C.A.; Cheng, C.M. Signaling by Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 in Brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Bulleit, R.F. Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I) Is a Critical Trophic Factor for Developing Cerebellar Granule Cells. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 99, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, P.C.; D’Mello, S.R. Survival of Cultured Cerebellar Granule Neurons Can Be Maintained by Akt-Dependent and Akt-Independent Signaling Pathways. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 127, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeffer, C.A.; Sanchez, E.; Hagerman, R.J.; Mu, Y.; Nguyen, D.V.; Wong, H.; Whelan, A.M.; Zukin, R.S.; Klann, E.; Tassone, F. Altered mTOR Signaling and Enhanced CYFIP2 Expression Levels in Subjects with Fragile X Syndrome. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, S.; Boggio, E.M.; Grosso, S.; Lonetti, G.; Forlani, G.; Stefanelli, G.; Calcagno, E.; Morello, N.; Landsberger, N.; Biffo, S.; et al. Reduced AKT/mTOR Signaling and Protein Synthesis Dysregulation in a Rett Syndrome Animal Model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollizzi, K.; Malinowska-Kolodziej, I.; Stumm, M.; Lane, H.; Kwiatkowski, D. Equivalent Benefit of mTORC1 Blockade and Combined PI3K-mTOR Blockade in a Mouse Model of Tuberous Sclerosis. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropea, D.; Giacometti, E.; Wilson, N.R.; Beard, C.; McCurry, C.; Fu, D.D.; Flannery, R.; Jaenisch, R.; Sur, M. Partial Reversal of Rett Syndrome-like Symptoms in MeCP2 Mutant Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of posttranscriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz de León-Guerrero, S.; Pedraza-Alva, G.; Pérez-Martínez, L. In Sickness and in Health: The Role of Methyl-CpG Binding Protein 2 in the Central Nervous System. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.E.; Wu, H. The Ups and Downs of BDNF in Rett Syndrome. Neuron 2006, 49, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.L.; Zilong, Q. MeCP2: Multifaceted Roles in Gene Regulation and Neural Development. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ID | Chromosome | Accession miRBase | Mature Sequence | Forward Primer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-19b-1-5p | 13 | MI0000074 | AGUUUUGCAGGUUUGCAUCCAGC | AGTTTTGCAGGTTTGCATCCAGC |
| hsa-miR-24-2-5p | 19 | MI0000081 | UGCCUACUGAGCUGAAACACAG | TGCCTACTGAGCTGAAACACAG |
| hsa-miR-25-3p | 7 | MI0000082 | CAUUGCACUUGUCUCGGUCUGA | CATTGCACTTGTCTCGGTCTGA |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 19 | MI0000085 | UUCACAGUGGCUAAGUUCCGC | TTCACAGTGGCTAAGTTCCGC |
| hsa-miR-29b-2-5p | 1 | MI0000107 | CUGGUUUCACAUGGUGGCUUAG | CTGGTTTCACATGGTGGCTTAG |
| hsa-miR-31-5p | 9 | MI0000089 | AGGCAAGAUGCUGGCAUAGCU | AGGCAAGATGCTGGCATAGCT |
| hsa-miR-34a-5p | 1 | MI0000268 | UGGCAGUGUCUUAGCUGGUUGU | TGGCAGTGTCTTAGCTGGTTGT |
| hsa-miR-34c-5p | 11 | MI0000743 | AGGCAGUGUAGUUAGCUGAUUGC | AGGCAGTGTAGTTAGCTGATTGC |
| hsa-miR-92a-2-5p | X | MI0000094 | GGGUGGGGAUUUGUUGCAUUAC | GGGTGGGGATTTGTTGCATTAC |
| hsa-miR-99a-5p | 21 | MI0000101 | AACCCGUAGAUCCGAUCUUGUG | AACCCGTAGATCCGATCTTGTG |
| hsa-miR-125a-5p | 19 | MI0000469 | UCCCUGAGACCCUUUAACCUGUGA | TCCCTGAGACCCTTTAACCTGTGA |
| hsa-miR-125b-1-3p | 11 | MI0000446 | ACGGGUUAGGCUCUUGGGAGCU | ACGGGTTAGGCTCTTGGGAGCT |
| hsa-miR-125b-2-3p | 21 | MI0000470 | UCACAAGUCAGGCUCUUGGGAC | TCACAAGTCAGGCTCTTGGGAC |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | 5 | MI0000461 | GUCCAGUUUUCCCAGGAAUCCCU | GTCCAGTTTTCCCAGGAATCCCT |
| hsa-miR-181b-5p | 1 | MI0000270 | AACAUUCAUUGCUGUCGGUGGGU | AACATTCAUUGCTGTCGGTGGGT |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | 3 | MI0000465 | CAACGGAAUCCCAAAAGCAGCUG | CAACGGAATCCCAAAAGCAGCTG |
| hsa-miR-193a-5p | 17 | MI0000487 | UGGGUCUUUGCGGGCGAGAUGA | TGGGTCTTTGCGGGCGAGATGA |
| hsa-miR-193b-3p | 16 | MI0003137 | AACUGGCCCUCAAAGUCCCGCU | AACTGGCCCTCAAAGTCCCGCT |
| hsa-miR-198 | 3 | MI0000240 | GGUCCAGAGGGGAGAUAGGUUC | GGTCCAGAGGGGAGATAGGTTC |
| hsa-miR-199a-5p | 19 | MI0000242 | CCCAGUGUUCAGACUACCUGUUC | CCCAGTGTTCAGACTACCTGTTC |
| hsa-miR-210-3p | 11 | MI0000286 | CUGUGCGUGUGACAGCGGCUGA | CTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGA |
| hsa-miR-214-3p | 1 | MI0000290 | ACAGCAGGCACAGACAGGCAGU | ACAGCAGGCACAGACAGGCAGT |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | X | MI0000298 | AGCUACAUUGUCUGCUGGGUUUC | AGCTACATTGTCTGCTGGGTTTC |
| hsa-miR-222-3p | X | MI0000299 | AGCUACAUCUGGCUACUGGGU | AGCTACATCTGGCTACTGGGT |
| hsa-miR-339-5p | 7 | MI0000815 | UCCCUGUCCUCCAGGAGCUCACG | TCCCTGTCCTCCAGGAGCTCACG |
| hsa-miR-370-3p | 14 | MI0000778 | GCCUGCUGGGGUGGAACCUGGU | GCCTGCTGGGGTGGAACCTGGT |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaccaro, T.D.S.; Sorrentino, J.M.; Salvador, S.; Veit, T.; Souza, D.O.; De Almeida, R.F. Alterations in the MicroRNA of the Blood of Autism Spectrum Disorder Patients: Effects on Epigenetic Regulation and Potential Biomarkers. Behav. Sci. 2018, 8, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8080075
Vaccaro TDS, Sorrentino JM, Salvador S, Veit T, Souza DO, De Almeida RF. Alterations in the MicroRNA of the Blood of Autism Spectrum Disorder Patients: Effects on Epigenetic Regulation and Potential Biomarkers. Behavioral Sciences. 2018; 8(8):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8080075
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaccaro, Tamara Da Silva, Julia Medeiros Sorrentino, Sócrates Salvador, Tiago Veit, Diogo Onofre Souza, and Roberto Farina De Almeida. 2018. "Alterations in the MicroRNA of the Blood of Autism Spectrum Disorder Patients: Effects on Epigenetic Regulation and Potential Biomarkers" Behavioral Sciences 8, no. 8: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8080075
APA StyleVaccaro, T. D. S., Sorrentino, J. M., Salvador, S., Veit, T., Souza, D. O., & De Almeida, R. F. (2018). Alterations in the MicroRNA of the Blood of Autism Spectrum Disorder Patients: Effects on Epigenetic Regulation and Potential Biomarkers. Behavioral Sciences, 8(8), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8080075




