The Yin and Yang of IκB Kinases in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
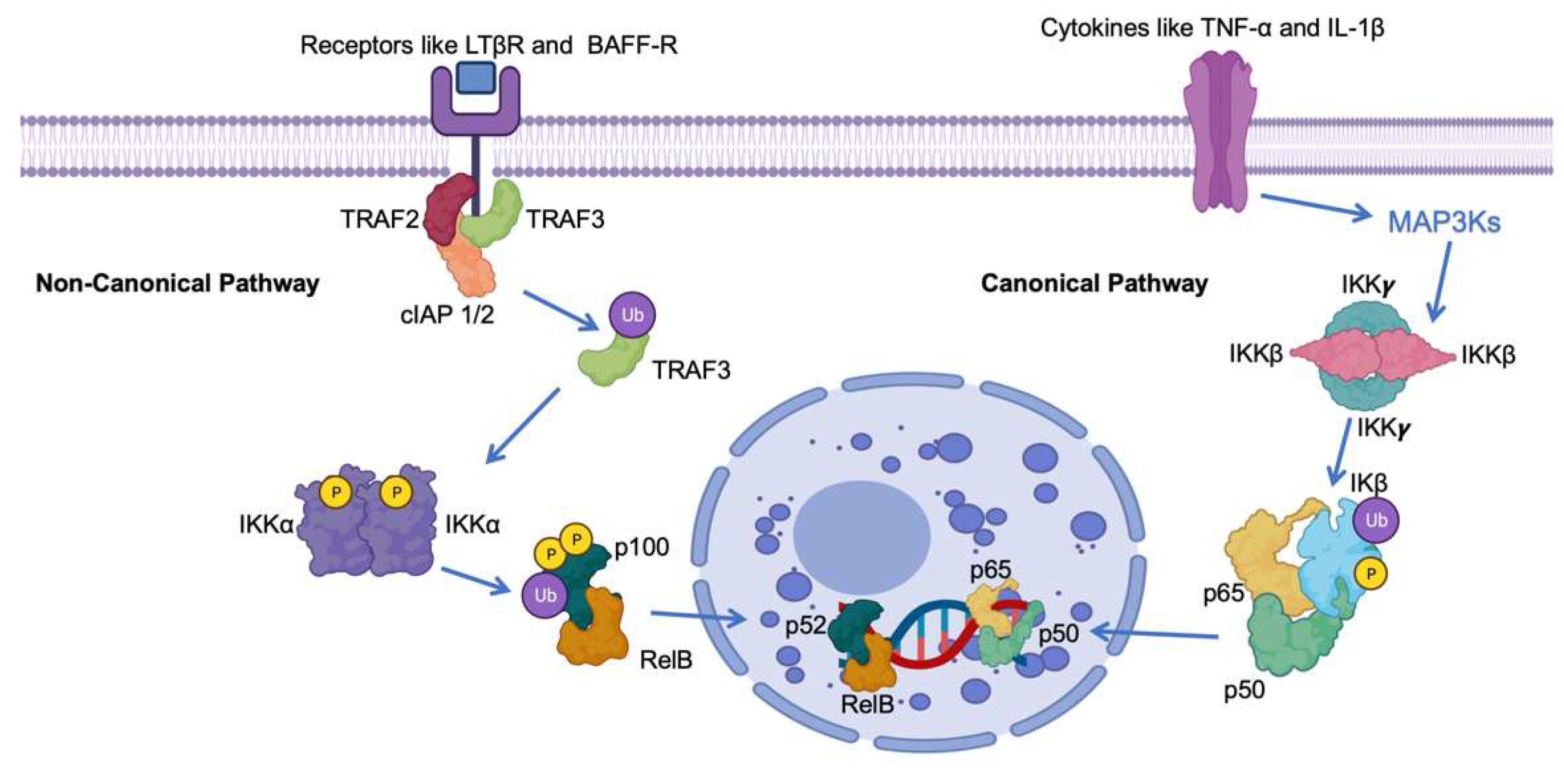
2. Canonical NF-κB Pathway
3. Non-Canonical NF-κB Pathway
4. The Dark Side: IκB Kinases as Tumor Promoters
4.1. IKKα (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Alpha)
4.2. IKKβ (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Beta)
5. The Bright Side: IKKs as Tumor Suppressors
5.1. IKKα in Tumor Suppression
5.2. IKKβ in Antitumor Immune Responses
6. Distinct Phosphorylation Events and Kinases
7. Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, S.; Vargas, J.; Hoffmann, A. Signaling via the NFκB system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, M.C.; Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. NF-κB, IκB, and IKK: Integral Components of Immune System Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1172, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xia, Y.; Parker, A.S.; Verma, I.M. IKK biology. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, J.K.; Baldwin, A.S. Targeting IKK and NF-κB for Therapy. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2017, 107, 77–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, R.J.; Hagan, R.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Expanding the View of IKK: New Substrates and New Biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senegas, A.; Gautheron, J.; Maurin, A.G.; Courtois, G. IKK-related genetic diseases: Probing NF-κB functions in humans and other matters. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1275–1287, Erratum in Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Hung, M.C. Beyond NF-κB activation: Nuclear functions of IκB kinase α. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, X.; Lu, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, Q.; Prochownik, E.V.; Li, Y. The IKKβ-USP30-ACLY Axis Controls Lipogenesis and Tumorigenesis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hamrashdi, M.; Brady, G. Regulation of IRF3 activation in human antiviral signaling pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 200, 115026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M.; Maniatis, T. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, M.; Dubois, N.; Musumeci, L.; Bours, V.; Robe, P.A. IκBζ: An emerging player in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66310–66322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Y.; Wei, W.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, M.; Tian, X.; et al. Characterization of a small-molecule inhibitor targeting NEMO/IKKβ to suppress colorectal cancer growth. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 71, Erratum in Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, Y. Integrity of IKK/NF-κB Shields Thymic Stroma That Suppresses Susceptibility to Autoimmunity, Fungal Infection, and Carcinogenesis. Bioessays 2018, 40, e1700131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, G.; Israël, A. IKK regulation and human genetics. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 349, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, M.J.; Ghosh, S. Signal transduction through NF-κB. Immunol. Today 1998, 19, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellweg, C.E. The Nuclear Factor κB pathway: A link to the immune system in the radiation response. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, P. NF-κB and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Edwards, J.; Pepper, C.; Mackay, S. Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets. Cells. 2018, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, S.; Saghari, S.; Bassiri, F.; Raesi, R.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: A focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 2770–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; West, A.P.; Ghosh, S. SnapShot: NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Cell 2006, 127, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibisana, J.N.; Okada, M. Encoding and decoding NF-κB nuclear dynamics. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2022, 77, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D.; Wolenski, F.S. NF-κB: Where did it come from and why? Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.M.; Gilmore, T.D. Looking Down on NF-κB. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 40, e00104-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, R.; Hunte, R.; Khan, W.N.; Shembade, N. A20-mediated negative regulation of canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunol. Res. 2013, 57, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.M.; TenOever, B.R. The IKK Kinases: Operators of Antiviral Signaling. Viruses 2010, 2, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinatizadeh, M.R.; Schock, B.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Zarandi, P.K.; Jalali, S.A.; Miri, S.R. The Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) signaling in cancer development and immune diseases. Genes Dis. 2020, 8, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Liang, H.; Rao, E.; Zheng, W.; Huang, X.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, M.; Mauceri, H.; et al. Non-canonical NF-κB Antagonizes STING Sensor-Mediated DNA Sensing in Radiotherapy. Immunity 2018, 49, 490–503.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-kappaB: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struzik, J.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L. Manipulation of Non-canonical NF-κB Signaling by Non-oncogenic Viruses. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerovich, K.; Ortis, F.; Cardozo, A.K. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway and its contribution to β-cell failure in diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, F1–F6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Interplay Between Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling and Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 29, 730684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, A.R.; Tak, P.P.; Tas, S.W. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.; Garg, M.; Tergaonkar, V.; Tan, S.Y.; Sethi, G. Pharmacological significance of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trares, K.; Ackermann, J.; Koch, I. The canonical and non-canonical NF-κB pathways and their crosstalk: A comparative study based on Petri nets. Biosystems 2022, 211, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Ren, X.; Zhai, W.; Chen, Z. Progress and Prospects of Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Regulation of Liver Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, A.; Pepper, C.; Mitchell, S.; Pepper, A. NF-kB and the CLL microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1169397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.R.; Hahn, W.C. Emerging roles for the non-canonical IKKs in cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflug, K.M.; Sitcheran, R. Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase (NIK) in Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhou, X.; Sohn, J.H.; Zhu, L.; Jie, Z.; Yang, J.Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; et al. NF-κB-inducing kinase maintains T cell metabolic fitness in antitumor immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 193–204, Erratum in Nat Immunol. 2021 Feb 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Takiishi, T.; Violato, N.M.; Licata, G.; Dotta, F.; Sebastiani, G.; Marselli, L.; Singh, S.P.; Sze, M.; Van Loo, G.; et al. NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) is activated in pancreatic β-cells but does not contribute to the development of diabetes. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yang, J.M.; Zhao, Y. Pharmacological inhibition of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) with small molecules for the treatment of human diseases. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shen, J. NF-κB Inducing Kinase Regulates Intestinal Immunity and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 27, 895636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhong, X.; Shen, H.; Sheng, L.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Lok, A.S.; Omary, M.B.; Wang, S.; Rui, L. Biliary NIK promotes ductular reaction and liver injury and fibrosis in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Sinha, S.; Zhao, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Sathyanarayana, P.; Shahani, S.; Sherman, V.; Tilton, R.G.; Bajaj, M. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) mediates skeletal muscle insulin resistance: Blockade by adiponectin. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3622–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, Y.M.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Splittgerber, R.; Na, S.; Boyd, A.; Mosse, C.; Simons, C.; Richmond, A. NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK) modulates melanoma tumorigenesis by regulating expression of pro-survival factors through the β-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, C.S.; Nayeem, S.Z.; Dillon, E.L.; Sarkar, P.S.; Tumurbaatar, B.; Urban, R.J.; Wright, T.J.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Tilton, R.G.; Choudhary, S. Glucocorticoids increase skeletal muscle NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK): Links to muscle atrophy. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.; Macht, A.; Waisman, A.; Hövelmeyer, N. NF-κB-inducing kinase is essential for B-cell maintenance in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Sundar, I.K.; Hwang, J.W.; Yull, F.E.; Blackwell, T.S.; Kinnula, V.L.; Bulger, M.; Yao, H.; Rahman, I. NF-κB inducing kinase, NIK mediates cigarette smoke/TNFα-induced histone acetylation and inflammation through differential activation of IKKs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ito, T.; Shimizu, T.; Ishida, T.; Semba, K.; Watanabe, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Inoue, J. Epigenetic alteration of the NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) gene is involved in enhanced NIK expression in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Thaler, R.; Cox, L.; Ricci, B.; Zannit, H.M.; Wan, F.; Faccio, R.; Dudakovic, A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Veis, D.J. Constitutive activation of NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK) in the mesenchymal lineage using Osterix (Sp7)- or Fibroblast-specific protein 1 (S100a4)-Cre drives spontaneous soft tissue sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Torsoni, A.S.; Wu, F.; Shen, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Canet, M.J.; Shah, Y.M.; Omary, M.B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Hepatic NF-kB-inducing kinase (NIK) suppresses mouse liver regeneration in acute and chronic liver diseases. Elife 2018, 2, e34152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzawa, M.; Konno, H.; Qin, J.; Akiyama, N.; Miyauchi, M.; Ohashi, H.; Miyamoto-Sato, E.; Yanagawa, H.; Akiyama, T.; Inoue, J. Catalytic subunits of the phosphatase calcineurin interact with NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) and attenuate NIK-dependent gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2015, 1, 10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Santillan, K.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Jimenez-Hernandez, L.E.; Gaytan-Cervantes, J.; Muñoz-Galindo, L.; Piña-Sanchez, P.; Martinez-Ruiz, G.; Torres, J.; Garcia-Lopez, P.; Gonzalez-Torres, C.; et al. NF-kappaΒ-inducing kinase regulates stem cell phenotype in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 23, 37340, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2017, 23, 44971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Shen, H.; Chen, Z.; Yin, L.; Zan, L.; Rui, L. Carboxyl terminus of HSC70-interacting protein (CHIP) down-regulates NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) and suppresses NIK-induced liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11704–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflug, K.M.; Lee, D.W.; Keeney, J.N.; Sitcheran, R. NF-κB-inducing kinase maintains mitochondrial efficiency and systemic metabolic homeostasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Ji, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Kim, H.; Zhong, X.; Jin, M.G.; Shah, Y.M.; Omary, M.B.; Liu, Y.; Qi, L.; et al. Medullary thymic epithelial NF-kB-inducing kinase (NIK)/IKKα pathway shapes autoimmunity and liver and lung homeostasis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19090–19097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, Y.M.; Richmond, A. NF-κB inducing kinase: A key regulator in the immune system and in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2010, 21, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Sheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Su, H.; Yin, L.; Omary, M.B.; Rui, L. Mouse hepatocyte overexpression of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) triggers fatal macrophage-dependent liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ren, D.; Cho, K.W.; Jiang, L.; Shen, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Rui, L. NF-κB–inducing kinase (NIK) promotes hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance in obesity by augmenting glucagon action. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoberg, J.E.; Yeung, F.; Mayo, M.W. SMRT derepression by the IkappaB kinase alpha: A prerequisite to NF-kappaB transcription and survival. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoberg, J.E.; Popko, A.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Mayo, M.W. IkappaB kinase alpha-mediated derepression of SMRT potentiates acetylation of RelA/p65 by p300. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Majada, V.; Aguilera, C.; Villanueva, A.; Vilardell, F.; Robert-Moreno, A.; Aytés, A.; Real, F.X.; Capella, G.; Mayo, M.W.; Espinosa, L.; et al. Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 276–281, Erratum in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Majada, V.; Pujadas, J.; Vilardell, F.; Capella, G.; Mayo, M.W.; Bigas, A.; Espinosa, L. Aberrant cytoplasmic localization of N-CoR in colorectal tumors. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, P.; Fernández-Majada, V.; Villanueva, A.; Garcia-Carbonell, R.; Iglesias, M.; López, L.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Villà-Freixa, J.; Mulero, M.C.; Andreu, M.; et al. A truncated form of IKKα is responsible for specific nuclear IKK activity in colorectal cancer. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Liu, B.; Xia, X.; Zhu, F.; Jami, W.B.; Hu, Y. Role of IKKα in skin squamous cell carcinomas. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Xie, K.; Gou, Q.; Chen, N. IκB kinase α functions as a tumor suppressor in epithelial-derived tumors through an NF-κB-independent pathway (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, F.; Hu, Y. IκB kinase alpha and cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2012, 32, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Park, E.; Liu, B.; Xia, X.; Fischer, S.M.; Hu, Y. Critical role of IkappaB kinase alpha in embryonic skin development and skin carcinogenesis. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanese, K. Diagnosis and Management of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, S.C.; Grgic, M.; Ruzicka, T.; Herzinger, T. Silencing of the cell cycle checkpoint gene 14-3-3σ in basal cell carcinomas correlates with reduced expression of IKK-α. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, R.; Qin, B.; Cheng, K. Blocking IKKα expression inhibits prostate cancer invasiveness. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, M.; MacKenzie, L.; McAllister, M.J.; Roseweir, A.; McCall, P.; Hatziieremia, S.; Underwood, M.A.; Boyd, M.; Paul, A.; Plevin, R.; et al. Determining the prognostic significance of IKKα in prostate cancer. Prostate 2020, 80, 1188–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.P.; Li, J.; Yadav, S.S.; Tewari, A.K. Recent insights into NF-κB signalling pathways and the link between inflammation and prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2014, 114, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, J.; Zhang, X. CUEDC2: An emerging key player in inflammation and tumorigenesis. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, A.; Lau, R.; Cabrita, M.A.; Nolan, E.; Crooks, P.A.; Visvader, J.E.; Pratt, M.A. Persistent Activation of NF-κB in BRCA1-Deficient Mammary Progenitors Drives Aberrant Proliferation and Accumulation of DNA Damage. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Qin, Q.H.; Lv, F.Y.; Huang, Z.; Lian, B.; Wei, C.Y.; Mo, Q.G.; Tan, Q.X. IKKα inhibition re-sensitizes acquired adriamycin-resistant triple negative breast cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, M.G.; Karin, M. IKK{beta} as a target for treatment of inflammation induced bone loss. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64 (Suppl. S4), iv81–iv85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.; Navarro, M.; Suárez-Cabrera, C.; Bravo, A.; Ramirez, A. Context-Dependent Role of IKKβ in Cancer. Genes 2017, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, X.; Guo, M. Anti-inflammatory therapy of atherosclerosis: Focusing on IKKβ. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Purkayastha, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, G.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic programming of systemic ageing involving IKK-β, NF-κB and GnRH. Nature 2013, 497, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Hua, F.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.L. Therapeutic potential of IKK-β inhibitors from natural phenolics for inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyninck, K.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Van der Veken, P.; Haegeman, G.; Vanden Berghe, W. Withaferin a inhibits NK-kappaB activation by targeting cysteine 179 in IKKbeta. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe, W.; Sabbe, L.; Kaileh, M.; Haegeman, G.; Heyninck, K. Molecular insight in the multifunctional activities of withaferin a. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Roh, E.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, I.J.; Ahn, B.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, H.; Han, S.B.; Kim, Y. Benzoxathiole derivative blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation and nuclear fac-tor-kappaB-regulated gene transcription through inactivating inhibitory kappaB kinase beta. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Dian, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Cao, R.; Li, L.; Huang, N.; et al. Ainsliadimer a selectively inhibits IKKα/β by covalently binding a conserved cysteine. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, J.A.; Cook, S.J. Targeting IKKβ in Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities for the Therapeutic Utilisation of IKKβ Inhibitors. Cells 2018, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, S.; Pan, R.; Li, G.; Tang, H.; Jiang, M.; Xing, Y.; Jin, F.; Lin, L.; Dong, J. Curcumin Attenuates gp120-Induced Microglial Inflammation by Inhibiting Autophagy via the PI3K Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Pang, Q.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary resveratrol alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced ileitis through Nrf2 and NF-κB signalling pathways in ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lin, C.; Xie, F.; Jin, M.; Lin, F. Berberine Ameliorates Insulin Resistance by Inhibiting IKK/NF-κB, JNK, and IRS-1/AKT Signaling Pathway in Liver of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Rats. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2022, 20, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Catravas, J.D.; Odoms, K.; Denenberg, A.; Malhotra, V.; Wong, H.R. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green tea-derived polyphenol, inhibits IL-1 beta-dependent proinflammatory signal transduction in cultured respiratory epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerappan, K.; Natarajan, S.; Ethiraj, P.; Vetrivel, U.; Samuel, S. Inhibition of IKKβ by celastrol and its analogues—An in silico and in vitro approach. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauert-Wunderlich, H.; Siegmund, D.; Maier, E.; Giner, T.; Bargou, R.C.; Wajant, H.; Stühmer, T. The IKK inhibitor Bay 11-7082 induces cell death independent from inhibition of activation of NFκB transcription factors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, H.L.; Kan, R.; Chau, W.Y.; Man, O.Y.; Mak, N.K.; Fong, C.H.; Shuen, W.H.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.L. The anti-tumor function of the IKK inhibitor PS1145 and high levels of p65 and KLF4 are associated with the drug resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachse, F.; Becker, K.; Basel, T.J.; Weiss, D.; Rudack, C. IKK-2 inhibitor TPCA-1 represses nasal epithelial inflammation in vitro. Rhinology 2011, 49, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waga, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Miura, S.; Nishida, T.; Itai, A.; Nakanishi, R.; Kashiwakura, I. IKKβ Inhibitor IMD-0354 Attenuates Radiation Damage in Whole-body X-Irradiated Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 27, 5340290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.; Peggie, M.; Plater, L.; Sorcek, R.J.; Young, E.R.; Madwed, J.B.; Hough, J.; McIver, E.G.; Cohen, P. Novel cross-talk within the IKK family controls innate immunity. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.T.; Van Antwerp, D.; Mercurio, F.; Lee, K.F.; Verma, I.M. Severe liver degeneration in mice lacking the IkappaB kinase 2 gene. Science 1999, 284, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llona-Minguez, S.; Baiget, J.; Mackay, S.P. Small-molecule inhibitors of IκB kinase (IKK) and IKK-related kinases. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2013, 2, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamitsu, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakata, K.; Hibi, Y.; Victoriano, A.F.B.; Imai, K.; Onozaki, K.; Kitade, Y.; Okamoto, T. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by blocking IkappaB Kinase with noraristeromycin. J. Biochem. 2008, 144, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Malik, V.; Liu, Y.; Ryu, J.; Kaul, S.C.; Sundar, D.; Wadhwa, R. Molecular Insights Into Withaferin-A-Induced Senescence: Bioinformatics and Experimental Evidence to the Role of NFκB and CARF. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Ponomareva, L.; Veeranki, S.; Panchanathan, R.; Dickerson, E.; Choubey, D. Differential roles for the interferon-inducible IFI16 and AIM2 innate immune sensors for cytosolic DNA in cellular senescence of human fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafián-Labora, J.A.; O’Loghlen, A. NF-κB/IKK activation by small extracellular vesicles within the SASP. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yan, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Shan, L.; Wu, H.; Efferth, T. Onset of p53/NF-κB signaling crosstalk in human melanoma cells in response to anti-cancer theabrownin. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubey, D.; Panchanathan, R. IFI16, an amplifier of DNA-damage response: Role in cellular senescence and aging-associated inflammatory diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 28, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, J.; Zahlten, J.; Pollok, I.; Lippmann, J.; Scharf, S.; N’Guessan, P.D.; Opitz, B.; Flieger, A.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S.; et al. Legionella pneumophila-induced IκBζ-dependent expression of interleukin-6 in lung epithelium. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuollo, L.; Antonangeli, F.; Santoni, A.; Soriani, A. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) in the Challenging Future of Cancer Therapy and Age-Related Diseases. Biology 2020, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.G.; Faragher, R.G. Cellular senescence: From growth arrest to immunogenic conversion. Age. 2015, 37, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseeva, O.; Deschenes-Simard, X.; St-Germain, E.; Igelmann, S.; Huot, G.; Cadar, A.E.; Bourdeau, V.; Pollak, M.N.; Ferbeyre, G. Metformin inhibits the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by interfering with IKK/NF-kappaB activation. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576, PMID: 33262144; PMCID: PMC7706700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Robinson, A.R.; Wang, J.; Gregg, S.Q.; Clauson, C.L.; Reay, D.P.; Nasto, L.A.; St Croix, C.M.; Usas, A.; Vo, N.; et al. NF-kappaB inhibition delays DNA damage-induced senescence and aging in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, D.; Tao, L.; Luo, Q.; Chen, L. Solute carrier transporters: The metabolic gatekeepers of immune cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, C.; Gotot, J.; Piotrowski, E.C.; Philipp, M.S.; Courrèges, C.J.F.; Otte, M.S.; Guo, L.; Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Hornung, V.; Heine, A.; et al. Prolonged IKKβ Inhibition Improves Ongoing CTL Antitumor Responses by Incapacitating Regulatory T Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senftleben, U.; Li, Z.W.; Baud, V.; Karin, M. IKKbeta is essential for protecting T cells from TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Immunity 2001, 14, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Mao, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. IKK antagonizes activation-induced cell death of CD4+ T cells in aged mice via inhibition of JNK activation. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 48, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonska, M.; Joo, D.; Nurieva, R.I.; Zhao, X.; Chiao, P.; Sun, S.C.; Dong, C.; Lin, X. Activation of the transcription factor c-Maf in T cells is dependent on the CARMA1-IKKβ signaling cascade. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Xie, D.; Gorentla, B.; Shin, J.; Gao, J.; Zhong, X.P. Chronic activation of the kinase IKKβ impairs T cell function and survival. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.L.; Mashayekhi, M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.; Michelotti, M.; Tramontini Gunn, N.; Powers, S.; Zhu, X.; Evaristo, C.; et al. Basal NF-κB controls IL-7 responsiveness of quiescent naïve T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7397–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeucken, K.C.M.; van Rooijen, C.C.N.; Kan, Y.Y.; Kocken, L.A.; Jongejan, A.; van Steen, A.C.I.; van Buul, J.D.; Olsson, H.K.; van Hamburg, J.P.; Tas, S.W. Differential Contribution of NF-κB Signaling Pathways to CD4+ Memory T Cell Induced Activation of Endothelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 860327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Hsueh, C.H.; Tan, T.H. GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune disease. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, C.; Spranger, S.; Barnes, S.E.; Miller, M.L.; Molinero, L.L.; Locke, F.L.; Gajewski, T.F.; Alegre, M.L. Cutting Edge: Engineering Active IKKβ in T Cells Drives Tumor Rejection. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wagner, J.A.; Granstein, R.D. CGRP, PACAP, and VIP modulate Langerhans cell function by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, N.C.; Voll, R.E.; Voskens, C.J.; Gross, S.; Seliger, B.; Schuler, G.; Schaft, N.; Dörrie, J. NF-κB activation triggers NK-cell stimulation by monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919891622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Hawkins, O.E.; Barham, W.; Gilchuk, P.; Boothby, M.; Ayers, G.D.; Joyce, S.; Karin, M.; Yull, F.E.; Richmond, A. Myeloid IKKβ promotes antitumor immunity by modulating CCL11 and the innate immune response. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7274–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Pelaez, M.; Lamont, D.J.; Peggie, M.; Shpiro, N.; Gray, N.S.; Cohen, P. Protein kinase IKKβ-catalyzed phosphorylation of IRF5 at Ser462 induces its dimerization and nuclear translocation in myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17432–17437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratin, M.; Foray, C.; Demaria, O.; Habbeddine, M.; Pollet, E.; Maurizio, J.; Verthuy, C.; Davanture, S.; Azukizawa, H.; Flores-Langarica, A.; et al. Homeostatic NF-κB Signaling in Steady-State Migratory Dendritic Cells Regulates Immune Homeostasis and Tolerance. Immunity 2015, 42, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Xie, M.; Hopewell, E.L.; Albrecht, R.A.; Nogusa, S.; García-Sastre, A.; Balachandran, S.; Beg, A.A. Differential requirement for the IKKβ/NF-κB signaling module in regulating TLR- versus RLR-induced type 1 IFN expression in dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2538–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.T.; Wilkins, C.; Narita, M.; Green, R.; Knoll, M.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr. Differential and Overlapping Immune Programs Regulated by IRF3 and IRF5 in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3036–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NFkappa]B activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, A. IKK-mediated CYLD phosphorylation and cellular redox activity. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradère, J.P.; Hernandez, C.; Koppe, C.; Friedman, R.A.; Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. Negative regulation of NF-κB p65 activity by serine 536 phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Yu, C.; Bryant, C.L.N.; Wu, K.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, B.; Pan, Z.Q.; et al. IKK-Mediated Regulation of the COP9 Signalosome via Phosphorylation of CSN5. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchett, S.; Dondelinger, Y.; Barbarulo, A.; Bertrand, M.J.M.; Seddon, B. Phosphorylation of RIPK1 serine 25 mediates IKK dependent control of extrinsic cell death in T cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 1, 1067164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; He, J.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, J. IKKϵ negatively regulates RIG-I via direct phosphorylation. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Wong, K.I.; Sun, X.; Reilly, S.M.; Uhm, M.; Liao, Z.; Skorobogatko, Y.; Saltiel, A.R. TBK1 at the Crossroads of Inflammation and Energy Homeostasis in Adipose Tissue. Cell 2018, 172, 731–743.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remoli, A.L.; Sgarbanti, M.; Perrotti, E.; Acchioni, M.; Orsatti, R.; Acchioni, C.; Battistini, A.; Clarke, R.; Marsili, G. IκB kinase-ε-mediated phosphorylation triggers IRF-1 degradation in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, M.; Keck, F.; Bailey, C.; Narayanan, A. The role of the IKK complex in viral infections. Pathog Dis. 2014, 72, 32–44, Epub 2014 Aug 28. PMID: 25082354; PMCID: PMC7108545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, V.Y.; Li, Y.; Kim, D.; Zhong, X.; Du, Q.; Ghassemian, M.; Ghosh, G. Bcl3 Phosphorylation by Akt, Erk2, and IKK Is Required for Its Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 484–497.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Cao, Z.; Goeddel, D.V. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activates IKK-alpha by phosphorylation of Ser-176. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3792–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, R.J.; Baldwin, A.S. IKK promotes cytokine-induced and cancer-associated AMPK activity and attenuates phenformin-induced cell death in LKB1-deficient cells. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaan5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.F.; Hung, M.C. Advances in targeting IKK and IKK-related kinases for cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5656–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomer-Miller, B.; Higashimoto, T.; Lee, Y.K.; Zandi, E. Regulation of IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex by IKKgamma-dependent phosphorylation of the T-loop and C terminus of IKKbeta. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15268–15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehner, S.P.; Hofmann, T.G.; Ushmorov, A.; Dienz, O.; Wing-Lan Leung, I.; Lassam, N.; Scheidereit, C.; Dröge, W.; Schmitz, M.L. Mixed-lineage kinase 3 delivers CD3/CD28-derived signals into the IkappaB kinase complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 2556–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Banin, S.; Ouyang, H.; Li, G.C.; Courtois, G.; Shiloh, Y.; Karin, M.; Rotman, G. ATM is required for IkappaB kinase (IKKk) activation in response to DNA double strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8898–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menden, H.; Tate, E.; Hogg, N.; Sampath, V. LPS-mediated endothelial activation in pulmonary endothelial cells: Role of Nox2-dependent IKK-β phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L445–L455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wong, V.K.; Jiang, Z.H.; Jiang, S.P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Yao, X.J.; Su, X.H.; Yan, F.G.; Liu, J.; et al. Mutation of cysteine 46 in IKK-beta increases inflammatory responses. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31805–31819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, F.; Kawai, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Akira, S. NF-kappaB activation through IKK-i-dependent I-TRAF/TANK phosphorylation. Genes Cells 2000, 5, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motolani, A.; Martin, M.; Sun, M.; Lu, T. Phosphorylation of the Regulators, a Complex Facet of NF-κB Signaling in Cancer. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chariot, A. The NF-kappaB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesid, S.T.; Ernst, M.K.; LeBail, O.; Laurent-Winter, C.; Rice, N.; Israël, A. N- and C-terminal sequences control degradation of MAD3/I kappa B alpha in response to inducers of NF-kappa B activity. Mol. Cell Biol. 1995, 15, 5339–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkowitsch, L.; Leidner, J.; Ghosh, S.; Marienfeld, R.B. Phosphorylation of serine 68 in the IkappaB kinase (IKK)-binding domain of NEMO interferes with the structure of the IKK complex and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, E.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Karin, M. The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell 1997, 91, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbati, M.R.; Gilmore, T.D. Ser484 and Ser494 in REL are the major sites of IKK phosphorylation in vitro: Evidence that IKK does not directly enhance GAL4-REL transactivation. Gene Expr. 2008, 14, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitination in signaling to and activation of IKK. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napetschnig, J.; Wu, H. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Tong, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Major vault protein suppresses obesity and atherosclerosis through inhibiting IKK-NF-κB signaling mediated inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.C.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y. Tumor necrosis factor receptor- associated factor 6 (TRAF6) regulation of development, function, and homeostasis of the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanarek, N.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Regulation of NF-κB by ubiquitination and degradation of the IκBs. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Z.A.; Vemana, H.P.; Khasawneh, F.T. MALT1-ubiquitination triggers non-genomic NF-κB/IKK signaling upon platelet activation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Matsuzawa, A.; Zhang, W. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-κB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Deng, K.Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, P.X.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. The ubiquitin E3 ligase TRAF6 exacerbates pathological cardiac hypertrophy via TAK1-dependent signalling. Nat. Commun. 2016, 1, 11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, F.; Saeki, Y.; Ishido, S.; Kanno, J.; Tanaka, K. The K48–K63 Branched Ubiquitin Chain Regulates NF-κB Signaling. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Tu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Lin, X. K63-linked ubiquitination regulates RIPK1 kinase activity to prevent cell death during embryogenesis and inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, N.; Tinevez, J.Y.; Crowell, E.F.; Boisson, B.; Henriques, R.; Mhlanga, M.; Agou, F.; Israël, A.; Laplantine, E. TNF and IL-1 exhibit distinct ubiquitin requirements for inducing NEMO-IKK supramolecular structures. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, X.; Chellappa, V.; Donado, C.; Reyon, D.; Sekigami, Y.; Ataca, D.; Louissaint, A.; Mattoo, H.; Joung, J.K.; Pillai, S. IκB kinase β (IKBKB) mutations in lymphomas that constitutively activate canonical nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26960–26972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, V.; Rossi, D. NF-κB deregulation in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, B.G.; Gupta, V.A.; Vertino, P.M.; Boise, L.H. Cell of Origin and Genetic Alterations in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Front. Immunol. 2019, 21, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Calado, D.P.; Derudder, E.; Zhang, B.; Shimizu, Y.; Mackay, F.; Nishikawa, S.; Rajewsky, K.; Schmidt-Supprian, M. NIK overexpression amplifies, whereas ablation of its TRAF3-binding domain replaces BAFF:BAFF-R-mediated survival signals in B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10883–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatla, H.R.; Zou, Y.; Uddin, M.M.; Singha, B.; Bu, P.; Vancura, A.; Vancurova, I. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibition Induces IκB Kinase (IKK)-dependent Interleukin-8/CXCL8 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5043–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albensi, B.C.; Mattson, M.P. Evidence for the involvement of TNF and NF-kappaB in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Synapse 2000, 35, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, F.D.; Sweatt, J.D. The IkappaB kinase regulates chromatin structure during reconsolidation of conditioned fear memories. Neuron 2007, 55, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Fang, S.; Di, Y.; Ying, W.; Tan, Y.; Gu, W. Modulation of NF-κB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of IκB Kinase | Role in NF-κB Pathway | Function in NF-κB Regulation | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| IKKα (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Alpha) [7] | Non-Canonical NF-κB pathway | Phosphorylates p100, leading to partial proteasomal processing into p52. Initiates non-canonical gene transcription. Involved in cellular senescence. | p100 |
| IKKβ (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Beta) [8] | Canonical NF-κB pathway | Phosphorylates IκBα and IκBβ, marking them for degradation. Releases p50-RelA dimers for nuclear translocation. Associated with chronic inflammation and tumor promotion. | IκBα, IκBβ |
| IKKε (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Epsilon) [9] | Both canonical and non-canonical pathways | Regulates NF-κB activation, particularly in response to viral infections. Can promote cell survival. | - |
| TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) [10] | Non-Canonical NF-κB pathway | Activates IKKα and promotes non-canonical NF-κB signaling. Also involved in antiviral immune responses. | IKKα |
| IKKζ (Inhibitor of κB Kinase Zeta (MAIL)) [11] | Both canonical and non-canonical pathways | Modulates NF-κB signaling and immune responses. May play a role in inflammation and autoimmunity. | - |
| NEMO (NF-κB Essential Modulator) [12] | Central scaffold protein | Acts as an essential scaffold for IKKα and IKKβ, facilitating their activation. Essential for canonical NF-κB activation. | IKKα, IKKβ |
| Compound Name | Source or Synthesis | Cell Line/Organism | Concentration (μM) | Incubation Time (h) | Observed Effect on IKKβ/Target | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin [96] | Turmeric (Plant) | Various cancer cell lines (e.g., MCF-7, A549) | 10–50 | 12–48 | Inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation and NF-κB activation, leading to reduced pro-inflammatory and pro-survival gene expression. | 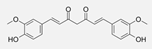 |
| Resveratrol [97] | Red grapes (plant) | Human prostate cancer cells (e.g., PC-3) | 50–100 | 24–72 | Suppression of IKKβ activity, resulting in reduced NF-κB-mediated transcription and anti-proliferative effects. |  |
| Berberine [98] | Berberis pant | Various cancer cell lines (e.g., HCT-116, MDA-MB-231) | 10–100 | 12–48 | Inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation, blocking NF-κB activation, and reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic genes. |  |
| EGCG (epigallocatechin-3-gallate) [99] | Green tea (plant) | Various cancer cell lines (e.g., A549, HCT-116) | 20–100 | 24–48 | Suppression of IKKβ phosphorylation, leading to decreased NF-κB activity and inhibition of pro-survival and pro-inflammatory pathways. |  |
| Celastrol [100] | Thunder of god vine (plant) | Human beast cancer cells (e.g., MDA-MB-231) | 0.5–1 | 6–24 | Inhibition of IKKβ activity, blocking NF-κB signaling, and promoting apoptosis in cancer cells. |  |
| BAY 11-7082 [101] | Synthetic compound | Multiple cancer cell lines (e.g., HeLa, U87) | 5–20 | 2–24 | Direct inhibition of IKKβ activity, leading to the suppression of NF-κB signaling and the downregulation of pro-survival and pro-inflammatory genes. |  |
| PS1145 [102] | Synthetic compound | Various cancer cell lines (e.g., A549, MDA-MB-231) | 1–10 | 4–24 | Selective inhibition of IKKβ, resulting in the attenuation of NF-κB signaling and the reduction in pro-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic gene expression. | 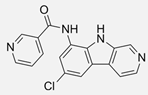 |
| TPCA-1 [103] | Synthetic compound | Human lung cancer cells (e.g., H1299) | 1–5 | 6–24 | Inhibition of IKKβ kinase activity, leading to the suppression of NF-κB-mediated transcription and anti-proliferative effects. |  |
| IMD-0354 [104] | Synthetic compound | Prostate cancer cells (e.g., PC-3) | 10–50 | 6–48 | Inhibition of IKKβ activity, resulting in reduced NF-κB signaling and the downregulation of genes associated with cell survival and inflammation. | 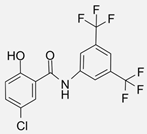 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdrabou, A.M. The Yin and Yang of IκB Kinases in Cancer. Kinases Phosphatases 2024, 2, 9-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2010002
Abdrabou AM. The Yin and Yang of IκB Kinases in Cancer. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2024; 2(1):9-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdrabou, Abdalla M. 2024. "The Yin and Yang of IκB Kinases in Cancer" Kinases and Phosphatases 2, no. 1: 9-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2010002
APA StyleAbdrabou, A. M. (2024). The Yin and Yang of IκB Kinases in Cancer. Kinases and Phosphatases, 2(1), 9-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2010002






