Abstract
We explored the intricate interplay of biological, social, and psychological factors contributing to substance use disorder (SUD) and co-occurring psychiatric symptoms. Drug misuse is a global concern, with increasing prevalence rates affecting mental well-being and safety. The spectrum of SUD includes polysubstance users, posing challenges for treatment and associated health outcomes. Various psychoactive substances like cannabis, hallucinogens, opioids, and stimulants impact addiction vulnerability, with marijuana being widely used globally. Gender differences in SUD prevalence have narrowed, with women escalating drug consumption rapidly once initiated. Age disparities in substance use highlight regional variations among adolescents. Comorbidities with psychiatric symptoms are common, with mood and anxiety disorders frequently observed. This study aimed to analyze factors influencing SUD development and maintenance to inform prevention strategies and treatment recommendations. By conducting a systematic search of databases, sixty articles were reviewed, revealing diverse methodologies and geographic locations. Biological factors, including neurotransmitter systems like endocannabinoid and dopaminergic systems, play a significant role in addiction. Genetic and neurobiological factors contribute to cannabis addiction susceptibility. Social factors such as childhood experiences and parenting styles influence substance use behaviors. Psychological factors like personality traits and mental health conditions interact with SUD development. Understanding these multifaceted interactions is crucial for designing effective interventions to address the complexities of SUD and co-occurring psychiatric symptoms.
1. Introduction
Drug misuse is a significant global issue. Statistics indicate that in 2021, approximately 5.8% of individuals aged 15–64 had engaged in drug use within the preceding 12 months. This number increased from 240 million in 2011 to 296 million in 2021, affecting health, particularly mental well-being and safety. Furthermore, stigma and discrimination often hinder individuals with drug-related challenges from seeking help, with less than 20% receiving treatment, and access to treatment varies greatly [1].
The substance use disorder spectrum includes both people who use one particular drug and individuals who use and/or abuse more than one, that is, “polysubstance users”. Polysubstance use disorders are more difficult to treat than single SUDs and are associated with more serious substance use, mental health, and physical health outcomes [2]. People with wide-ranging polysubstance use are more likely to experience additional clinical complexities than single substance users, including psychosis [2].
1.1. Psychoactive Substances and Addiction
According to the DSM substance use disorder definition, a “substance” has the main characteristic of activating the brain’s reward system, leading people to neglect normal activities in favor of taking the said substance [3]. This category, therefore, includes such substances as alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, hallucinogens, inhalants, opioids, sedatives, hypnotics or anxiolytics, stimulants (including amphetamine-type substances, cocaine, and other stimulants), and tobacco.
For the purpose of this review, we are taking into consideration only the substances that are culturally and most commonly referred to as “drugs”, which are natural or chemical substances known to have significant effects on human consciousness, decision-making processes, quality of life, as well as craving, tolerance, hazardous use, social and interpersonal problems, physical and psychological problems. In this perspective, the term “drugs” includes cannabis, hallucinogens (MDMA), opioids (heroin), hypnotics, and stimulants (cocaine and amphetamines).
These substances can also lead to addiction, especially in younger people. It was proved that those who start smoking, drinking, and taking drugs before the age of 18 are more likely to develop addictive behaviors toward these and other substances [4].
Marijuana is among the most often used illegal psychotropic substances internationally. According to the World Drug Report 2023, led by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, cannabis continues to be the most used drug, with an estimated 219 million users (4.3 percent of the global adult population) in 2021. According to current trends, there is a noticeable increase in both the use of marijuana and hospitalizations linked to marijuana, particularly among young people [1].
Hallucinogens can be divided into three groups: classical hallucinogens, which include substances like D-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), psilocybin, mescaline, DMT, and 251-NBOMe; dissociative hallucinogens, such as Phencyclidine (PCP), ketamine, dextromethorphan, and Salvia divinorum; other hallucinogens, such as MDMA, ibogaine, and salvia [5]. These substances are predominantly used for recreational purposes. In fact, data from 2020 indicates that 7.5% of adolescents have used hallucinogens at least once in their lives [6].
Opioids are used both medically and recreationally. In 2021, an estimated 60 million individuals engaged in non-medical opioid use, with 31.5 million using opiates, primarily heroin. Additionally, opioids continue to be the leading cause of fatal overdoses, accounting for nearly 70% of the 128,000 deaths attributed to drug use disorders in 2019 [1]. In Europe, heroin is the substance most closely related to crime. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), in its annual report based on information provided by the EU law enforcement agencies, points out that five percent of seizures involve heroin [7].
Stimulants such as cocaine are powerfully addictive stimulant drugs derived from the leaves of the coca plant exported from South America [8]. In 2020, 0.4% of the global population aged 15–64 used cocaine. The highest prevalence was in North America (2.5%), Oceania (1.9%), and Western and Central Europe (1.5%). The U.S. had the most users (6.5 million), but Colombia had the highest prevalence rate (3.4%) [9].
1.2. Gender Differences
Although substance use disorder is most frequently reported by males, evidence can be found that drug abuse is a widespread issue involving both men and women, with some peculiar differences [10]. Previous research indicated a notable gender disparity in SUDs, with a higher prevalence observed among men. However, recent studies suggest that this gender gap has significantly narrowed. Interestingly, women tend to escalate their drug consumption more rapidly than men once they initiate use, leading to more pronounced negative health and social consequences [11]. According to the World Drug Report 2023, in 2021, the majority of women were found to use amphetamine-type stimulants (45% of users) and engage in non-medical use of pharmaceuticals (with 45–49% of users being women), whereas men comprised the highest percentage of users in opiates (75%) and cocaine (73%) [1].
1.3. Age Differences
The use of cannabis among 15–16-year-olds varies by region, from less than 3 percent in Asia to over 17 percent in Oceania, but in most regions, the proportion of adolescents using the drug is higher than in the general population aged 15–64 [1].
Younger patients were more likely to report using cocaine and cannabis, violating lockdown rules, experiencing deteriorated family relationships, and facing reduced incomes. In contrast, older patients more frequently reported maintaining abstinence [12].
1.4. Comorbidity with Psychiatric Symptoms
SUDs frequently co-occur with other mental health conditions, especially among polysubstance users. Comorbidities observed during treatment are varied, with mood, anxiety, eating, and post-traumatic stress disorders (PTSDs) being the most common. Additionally, there is a notable prevalence of positive psychotic symptoms and schizophrenia. The connection between mental health and SUDs works both ways, with various mental health symptoms being linked to the use of different clusters of substances to achieve desired effects, such as intoxication, energy, or relief from distress [2].
Psychiatric symptoms and/or psychopathological behaviors are not only related to the development of a SUD; in fact, authors have found significant correlations between some psychiatric symptoms and various phases of drug addiction, e.g., abstinence [13] or craving [14].
1.5. Aim of this Study
This review aims to analyze the main factors contributing to the development and maintenance of SUD and its co-occurring psychiatric symptoms. We believe that, especially in cases of dual diagnosis, it is important to understand what factors can lead to a concerning phenomenon such as drug abuse. The purpose is multiple: on the one hand, we aim to provide scientific data to help project and implement effective prevention plans; on the other hand, we aim to understand what role psychiatric symptoms play in a substance abuse disorder. That is, whether the presence of psychiatric symptoms can be a cause of the disorder or whether it is a direct consequence of it and, in either case, to what extent it is possible to understand which case one is facing. In doing so, we will first analyze biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to developing a SUD; then, we will study both progression patterns and characteristics that represent potential risk or protection factors in relation to this disorder; last, attention will be given to the interaction between the various factors emerged in the previous paragraphs to give a better overview on the prodromal stages of SUD.
2. Materials and Methods
This review, while not a systematic review in the traditional sense, has implemented systematic search methods to ensure maximum transparency and rigor in the selection of included papers. The systematic search was conducted in January 2024, using Primo VE Discovery as a tool for aggregating results across several databases: PubMed; PubMed Central; Health & Medical Collection; ScienceDirect Freedom Collection; Wiley Online Library. Our selection of articles was obtained using four different search strings:
- (((substance use disorder) OR (addiction)) AND (psychiatric symptoms)) AND ((neurobiological factors) OR (genetic influences) OR (pharmacological factors));
- (((substance use disorder) OR (addiction)) AND (psychiatric symptoms)) AND ((mental health) OR (psychological factors) OR (cognitive processes));
- (((substance use disorder) OR (addiction)) AND (psychiatric symptoms)) AND ((family dynamics) OR (peer influence) Or (cultural norms));
- (((substance use disorder) OR (addiction)) AND (development) OR (progression patterns) OR (risk and protective factors)).
The choice of the search keywords was related to the main topics of our paper, that is to say, how biological, psychological, and social factors singularly contribute to the development and maintenance of substance use disorder (SUD), as well as how they interact with each other in individuals who show such disease; moreover, we intend to analyze which individual and social factors prevent or increase the possibility of developing a SUD and its co-occurring psychiatric symptoms.
This review includes the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 flow diagram [15] to describe the research methodology and selection of articles included.
While this review does not include certain features typically associated with systematic reviews, such as a meta-analysis or a risk of bias assessment, the systematic search methods employed ensure a comprehensive and transparent approach to the identification and selection of relevant studies. This approach enhances the reliability and validity of the findings presented in this review. It is important to note that the absence of these features does not undermine the value of the review but rather reflects the specific aims and scope of this particular piece of research.
Eligibility Criteria
We included articles that met the following criteria:
- All studies and reviews were published in indexed journals such as PubMed, PubMed Central, Health & Medical Collection, ScienceDirect Freedom Collection 2021, Wiley Online Library;
- Studies that included the keywords used and/or related to their topic;
- Studies that were published from the year 2022 on. The year 2022 was selected to provide sources as recent as possible that could include, but were not exclusively focused on, elements related to the COVID-19 pandemic lapse.
3. Results
Characteristics of Included Studies
This literature review examines sixty full-text articles to analyze the biological, psychological, and social factors influencing the development and persistence of SUD and its concurrent psychiatric symptoms (see flow diagram, Figure 1). Articles were selected based on their relevance to understanding the interaction among these factors, as well as identifying risk and protective factors useful for designing prevention strategies and treatment recommendations. The reviewed studies conducted between 2022 and 2024 were diverse in terms of geographic location, including Italy, India, Australia, Norway, Spain, Switzerland, and the United States. Methodologies employed varied, encompassing cross-sectional, longitudinal, and randomized controlled trial designs. Collectively, these studies offer comprehensive insights into contemporary SUD manifestations, their biological, psychological, and social etiology, the interplay among these factors, and the key determinants influencing treatment outcomes.
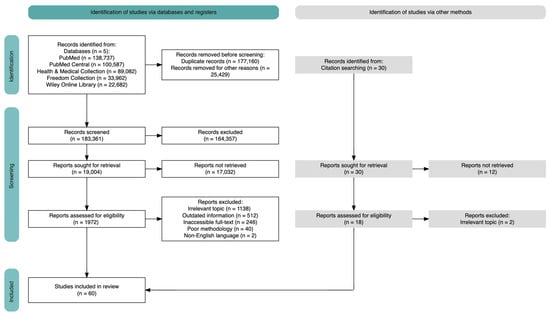
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews, which included searches of databases, registers, and other sources [15] generated using Haddaway and colleagues’ online generator [16].
4. Biological Factors
Throughout the years, several studies have been interested in investigating the biological factors that might underlie the development and maintenance of addictions to substances.
While a causal link between the presence of certain biological factors and the development of addiction has not yet been established with certainty, the results of some studies are interesting and promising in this regard, paving the way for subsequent insights that could deeply change the treatment perspectives of addiction and SUD [17].
A significant implication of neurotransmitter systems in substance addiction has been observed. A particularly relevant role seems to be played by the endocannabinoid and dopaminergic systems: substances bind to these systems and/or alter their neurotransmitter actions, leading to changes in a specific brain area activity. In these areas, there is a massive presence of receptors belonging to these two systems, such as the prefrontal cortex (PFC), the inferior cingulate gyrus (ICG) and anterior cingulate gyrus (ACG), the striatum, the thalamus, the nucleus accumbens (NAcc), the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) and the amygdala [17]. Activation of these brain areas is responsible for the feeling of gratification experienced by individuals with substance addictions, as they are brain regions responsible for regulating emotions, decision-making processes, and impulse control [17].
In the following sections, we will analyze which and how biological factors intervene for each class of drugs.
4.1. Cannabis Addiction
Genetic and Neurobiological Factors
Genetic variants of several elements of the endocannabinoid system have been suggested as possible risk factors for cannabis dependence [17]. Specifically, polymorphism of specific SNPs of the CNR1 gene, G allele, was associated with increased withdrawal and craving after brief cannabis abstinence and more significant responses in several brain areas, such as the OFC, the ICG, and the ACG [17]. In a study by Schacht et al., it was found that cannabis users carrying the G allele have a reduced hippocampal volume, and this could be due to the interaction of cannabis with the CB1 receptor altered by the polymorphism, which would act in a way that goes to alter the volume of the hippocampus [18]. Most recently, the CNR2 gene has been linked to an elevated risk of developing schizophrenia in patients with CUD (Cannabis Use Disorder) [19].
Studies have highlighted how alleles A and C are also strongly involved in cannabis addiction, as these alleles have been observed to correlate with increased activity and reactivity of specific brain areas closely related to gratification [17].
A recent study showed structural brain alterations in cannabis-dependent patients that appeared to be significantly associated with regional differences in the expression of MAGL, an enzyme responsible for the degradation of endocannabinoids [20].
Bhattacharyya et al. conducted a research study to evaluate the effect of THC on anxiety and amygdala response, from which they found that anxiety-induced THC intake modulated amygdala activation and increased CB1 cannabinoid receptor availability [21].
4.2. Opioid Addiction
Genetic and Neurobiological Factors
There is a lack of information about the polymorphism of the endocannabinoid system related to opioid addiction.
Similar to cannabis addiction, the involvement of specific genes and alleles, such as the C allele, can also be traced to opioid addiction. One study evaluated the association between CNR1 and the development of major depression and/or suicidal behaviors in opioid-dependent outpatients undergoing skilled methadone treatment. This work found that the C allele of CNR1 was closely correlated with a lower prevalence of lifelong major depression but not with suicidal behaviors [17]. There are numerous studies of the biological effects of opioids carried out using the animal model. In a significant study by Viganò et al., rats were chronically treated with morphine and CB1R binding, and levels of eCBs (endocannabinoids) were assessed. Morphine-tolerant rats showed reduced CB1R binding in the cerebellum and hippocampus and reduced CB1R functions in the NAcc [22].
4.3. Stimulant Addiction
Cocaine is a substance of abuse that destroys mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons, inhibiting dopamine uptake and leading to compulsive behavior and relapse.
Methamphetamine, on the other hand, induces specific damage to the dopaminergic neurotransmitter system and is associated with cell death. A single intake of methamphetamine alters concentrations of certain endocannabinoids in the striatum of adult male mice, suggesting that the endocannabinoid system may be involved in brain responses to these drugs [17].
Alterations at central and peripheral levels have been found in individuals exposed to psychostimulants such as amphetamines and cocaine [17]. Specific polymorphisms of the CNR1 gene have been associated with the development of stimulant dependence. Furthermore, numerous changes in the targets of the endocannabinoid system have been traced mainly from cocaine studies, revealing the importance of this system in regulating different aspects of stimulant addiction, such as gratification, motivation, withdrawal, or relapse [17].
Genetic and Neurobiological Factors
Several studies highlight the functional importance of the endocannabinoid system in regulating the actions produced by psychostimulant substances, such as cocaine and amphetamine.
To this date, it has been confirmed that some genetic variant contributes to the vulnerability to relapse of stimulant-dependent individuals. Indeed, it has been found that two independent variants of CNR1, the G allele genotype and the T/T genotype, had a significant effect on the risk of cocaine addiction in Euro-Americans as well as in African-Americans with these genotypes [23].
The importance of the dopaminergic system should also not be underestimated. Indeed, D1 receptors are crucial in mediating the action of cocaine, the search for the substance leading to self-administration and cocaine-related effects in gene expression in the striatum [24]. D2 receptor levels, on the other hand, predict the “liking” effects of psychostimulants such as methylphenidate. Chronic cocaine use or abuse attenuates the availability of D2/D3 receptors in the striatum and abrupt dopaminergic responses to the administration of psychostimulants [24].
4.4. Hallucinogens Addiction
Genetic and Neurobiological Factors
Several studies have evaluated the effects of dissociative drugs on the cannabis and endogenous systems. Subchronic administration of ketamine in mice increased endocannabinoid concentrations in the CPU, amygdala, and hippocampus [25].
Although limited information is currently available on the subject, most authors support the potential usefulness of identifying changes in cannabinoid receptors, ligands, or enzymes as biomarkers to improve the diagnostic classification of patients with SUD and increase the success of their drug treatment [17].
4.5. Pharmacology and Treatment Insights on SUD
Despite extensive investigations, the field of pharmacotherapy for SUDs remains relatively uncharted. While significant progress has been made in understanding the neurobiology and behavioral aspects of addiction, the development of targeted medications has proven challenging. So far, there is no drug treatment approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or EMA (European Medicines Agency) for most substance use disorders, except for AUD (Alcohol Use Disorder), NUD (Nicotine Use Disorder), and OUD (Opioid Use Disorder) [26].
Since GABAergic system dysfunction is associated with substance use, a number of studies have also been conducted on the efficacy of antiepileptic drugs [27] and combination therapies [28]. Another treatment strategy is to target the endophenotypes associated with SUDs. For example, using cognitive enhancers to improve decision-making, planning, or impulse control may be a useful strategy [29]. Several pharmacological studies are currently underway [28].
In addition to new pharmacological perspectives, alternative therapies, such as psychotherapy (including drug-supported), mindfulness-based interventions (MBI), and the use of virtual reality (VR) techniques can be considered [28]. Table 1 presents an overview of biological factors associated with various types of substance addiction, including cannabis, opioids, stimulants, and hallucinogens.

Table 1.
Table showing biological factors associated with various types of substance addiction, including cannabis, opioids, stimulants, and hallucinogens. This table summarizes genetic variants, structural brain alterations, and involvement of neurotransmitter systems, highlighting key factors influencing addiction development and maintenance.
5. Psychological Factors
5.1. Complex Entanglement: Substance Use Disorder; Personality; and Psychopathology
Substance use disorder can be viewed as a complex intertwining of behavior, personality, and psychopathology. The co-occurrence of substance use and psychopathology (dual diagnosis) can be explained by shared risk factors such as socioeconomic status and personality traits [30,31,32]. Many people with SUDs show psychiatric comorbidity, personality, mood, and anxiety disorders [12,30,31,32,33], especially in cases of poly-drug use, where eating disorders, psychotic symptoms, schizophrenia [2], and PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) [4,34] can also be found; in some cases, the dual diagnosis of SUD and ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder) is also found [35].
According to several surveys, approximately 10–20% of the population suffers from an addiction-related problem [31], and half of the people with a substance use disorder experience other mental disorders during their lifetime, and vice versa [36], as the relationship between the two would appear to be bidirectional [2]. A positive association was found between anxiety, depression, and craving intensity. In addition, time of abstinence could influence the association between craving and psychiatric symptoms [13].
5.2. Mental Health Conditions
5.2.1. Personality Factors and Addiction
Temperament and personality traits represent crucial factors that contribute to the development and persistence of addiction-related behaviors [31,32]. Among these traits, disinhibition and lack of self-control, which are intended to be the ability to regulate one’s behavior, emotions, and cognition, represent key elements. Self-control is considered a transdiagnostic dimension; its absence can manifest in both externalized behaviors, as in substance-related disorders and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and internalizing behaviors, as in mood or anxiety disorders [31]. In addition, high levels of behavioral activation (BAS) and low levels of self-control (EC) have been associated with Cluster B of personality disorders, while high levels of behavioral inhibition (BIS) and low levels of self-control (EC) have been linked to Cluster C. As for Cluster A, a mixed pattern of BAS and BIS has been observed [31,32].
The development of clinical symptoms, especially anxiety and depression, and the manifestation of personality disorders both correlated with low levels of self-control (effortful control—EC) and high levels of behavioral inhibition (BIS) in people with SUD [31,32]. Hence, there is a greater inclination to neuroticism, which is considered an additional personality trait that represents a vulnerability factor for the development and persistence of SUD [30].
Several studies indicate that low self-esteem is frequently observed in patients with SUD. However, in contrast to this perspective, other studies that have examined the relationship between SUD and self-esteem have found high levels of self-esteem [37].
In the following section, we will briefly analyze the psychological factors that are most found in comorbidity with SUDs.
5.2.2. Anxiety and Addiction
Anxiety disorders are frequently found in patients diagnosed with substance use disorder (SUD) [31,36], and research also shows a strong correlation with craving intensity [13]. Anxiety symptoms reveal a strong association with substance use and addiction severity [30]. In addition, stress has been observed to have a positive correlation with craving intensity in opiate and methamphetamine use.
5.2.3. Mood Disorders and Addiction
Mood disorders are commonly found in comorbidity both with SUD [31,36] and craving intensity [13]. In particular, depression was proved to have a positive correlation with craving intensity for heroin in patients receiving methadone maintenance treatment [13]. Interestingly, although substance use may impair brain function and cause depressive or anxiety symptoms, people may use substances more frequently as a form of “self-medication” to manage such symptoms [30].
5.2.4. ADHD and SUD
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is found in around 25% of people with SUD [36]. ADHD is also considered an important risk factor for the development of SUD, as it promotes early use of illicit substance use, thus being an important predictor of the development of substance use disorder [38]. According to some data, the presence of an ADHD disorder would increase an individual’s vulnerability to developing a psychoactive substance abuse disorder by a factor of two [33]. Conversely, addiction exerts a negative impact on the course of ADHD by exacerbating cognitive and memory impairment. The course of SUD is found to be more severe in patients with comorbidity with ADHD than in those with SUD alone [33].
5.2.5. Traumatic Events, PTSD, and SUD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is frequently found in comorbidity with SUD [2,34], and both disorders tend to occur commonly during adolescence. According to some theories, the experience of traumatic events in adolescence might promote the development of SUD, in turn facilitating the onset of PTSD. Other hypotheses state that the coexistence of the two disorders could result from the adoption of substance use as a coping strategy to mitigate the effects of symptoms associated with PTSD [34].
It appears that some substances are able to influence the immediate experience of PTSD symptoms, predisposing to a subsequent inclination to use such substances [34]. A history of trauma is a significant risk factor for violent and suicidal behavior in individuals with SUD. This suggests the need to carefully consider the psychological and trauma context in the assessment and treatment of patients with SUD.
An additional study examined the co-occurrence of Sexual Compulsive Behavior Disorder (CSBD) and tendencies for risky sexual actions among women with SUD [11]. The results indicate that women with SUD manifest more pronounced symptoms of CSBD and show a greater propensity for risky sexual behavior than controls. In this context, it appears that CSBD plays a mediating role in the association between substance use and risky sexual behaviors.
In addition, it was found that addictive behaviors were related to emotional abuse during childhood but were not associated with other types of abuse [11].
5.2.6. SUD and ASD
SUD and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are often found in comorbidity with each other, resulting in a dual diagnosis; in most of these cases, people use substances as a means to manage high levels of anxiety, stress, and social difficulties, including perceived social rejection [35]. The cause of this phenomenon seems mainly neurobiological, although its interaction with psychological aspects will be explored in depth in another paragraph.
5.2.7. Self-Harm and Suicide Risk in People with SUD
Individuals suffering from chronic pain or mood disorders often find themselves disproportionately prescribed opioid medications. This subgroup faces a greater risk of suicide. Numerous studies have explored the potential connections between suicidal symptoms and SUD. Some findings suggest that a diagnosis of any SUD amplifies the likelihood of suicide, and conversely, an increased suicide risk is associated with SUDs. In-depth research comparing the impact of specific substances has highlighted that opioids, in particular, exhibit a stronger correlation with suicidal ideation and attempts compared to substances like cocaine and cannabis. The intricate interplay between chronic pain, mood disorders, opioid use, and the heightened risk of suicide underscores the complexity of these issues and the need for comprehensive and multifaceted care approaches [39]. For research purposes, it is essential to consider comorbid disorders alongside substance use disorders (SUDs), which may include mood and personality disorders. Additionally, assessing anxiety and depression symptoms is crucial to providing personalized treatments to individuals at risk of suicidal ideation [40]. Table 2 presents a summary of psychological factors related to substance addiction, including complex entanglement with behavior, personality, and psychopathology, as well as specific psychological factors such as anxiety, mood disorders, ADHD, PTSD, ASD, and the risk of self-harm and suicide.

Table 2.
Table summarizing psychological factors associated with substance addiction, including complex entanglement with behavior, personality, and psychopathology, as well as specific psychological factors such as anxiety, mood disorders, ADHD, PTSD, ASD, and the risk of self-harm and suicide. References are provided for each factor.
6. Social Factors
SUD is a complex condition that is influenced by a multitude of factors, including social ones. Social factors play a significant role in both the development and maintenance of SUD. Social determinants of health (SDoH) are referred to as the conditions in which individuals are born, grow, live, work, and age [41]. These circumstances are influenced by the distribution of financial resources, power, and assets at global, national, and local scales [41]. In the following paragraph, we will analyze social factors that contribute to the development and maintenance of SUD.
6.1. Childhood
To understand how an addiction can seep into a person’s life, we need to start by examining the context in which the individual grew up, starting right from childhood. The parental style with which the child is raised and the resulting family dynamics play a very important role in both the development of the individual and the development of addiction. Children raised with an authoritarian parenting style characterized by demanding, strict, and firm parents who show little affection, warmth, and involvement will tend to be more likely to use alcohol and other substances. In contrast, an authoritative parenting style, characterized by high demands and responsiveness, has been found to have positive results, decreasing the likelihood of children’s use of alcohol, cigarettes, and cannabis. The neglectful parenting style with low demand and responsiveness is most likely to be associated with substance use; finally, although to a lesser extent, the permissive parenting style, with low demand and high responsiveness, was also found to be related to substance use [42].
In addition, traumas experienced in childhood (physical or emotional abuse, neglect), even occurring only once [43,44], lead to adverse physiological consequences and poor health outcomes, causing, for example, increased cortisol levels that subsequently increase the risk of substance use [42]. This could explain the relationship between the mechanisms involved in coping with trauma and those that lead to substance use, putting stress at the center of the relationship: while milder forms can result in positive behavioral effects, severe or chronic levels can cripple it, so that the individual will try to cope with it by taking substances that can quell perceived stress and anxiety, increasing the likelihood of developing an addiction [44].
6.2. Adolescence
As widely known, adolescence is a crucial period for biological, psychological, and social development, but it is also a sensitive time when one is particularly susceptible to substance use, its negative effects, and subsequent addictions [44,45]. Early encounters with substances increase the likelihood of future problems (physical, behavioral, social, and health) but also raise the risk of addiction if you start before age 18 [44]. Adolescents may start experimenting with substances out of simple curiosity, boredom, rebellion, societal pressure, relationship breakdown, or to improve concentration, physical endurance, learning difficulties, and gain a sense of identity. Students who use them are also the ones who commit more crimes, such as bullying or violent behavior, with insignificant psychological, behavioral, and sociocultural consequences [44].
In this scenario, studies have found that parental support is a protective factor against the onset of SUD: adolescents aged 9 to 18 years with positive parental relationships, characterized by emotional closeness and supervision, are less likely to try alcohol, marijuana, and cigarettes; conversely, lower levels of family functioning increase the likelihood of these behaviors being enacted [46]. This is a very interesting result when compared with peer support, as opposite effects are obtained: peer support is correlated with higher alcohol consumption. Both the subject’s perceived rejection of parents and peers and loneliness are associated with alcohol consumption [4,42,46]. Social support is the most effective tool used to aid in the disorder’s resolution; it encompasses a variety of behaviors ranging from simply being present, listening, and sharing problems to providing concrete help. Offering this support can be family, friends, and professionals, and it is important because addiction requires much more support than physical illness, as it is characterized by withdrawal and severing ties with toxic friendships [47].
The relationship between social conditions and drug use is two-way. In parallel with what has been said so far, SUD adversely affects social behavior, leading the individual to avoid social situations so that he or she has more time to spend on drug taking rather than on rewarding social situations, thus entering a vicious cycle in which the individual begins to take drugs more often, thus increasing his or her isolation. This phenomenon has increased in recent years due to the lockdown, which has forced young people to stay at home for long periods of time. In fact, it has been found that COVID-19 contributed to the increase in overdoses and social isolation [44].
6.3. Adulthood
As they age, individuals with AUD report having had a family characterized by less cohesion and expressiveness and more conflict: these are risk factors for alcohol use, disguised by the individual’s justifications for why they use (e.g., alcohol makes me worry less) [46]. Increasing levels of loneliness, also experienced during COVID-19, are related to increased alcohol use and anxiety [46]. Lack of social support, medical complications, and confrontation with bereavement are features of older age that could contribute to the onset of SUD or AUD [42]. This increases the likelihood of premature mortality, impacting healthy aging and increasing health risks: alcohol consumption impacts higher rates of dementia and vulnerability to negative withdrawal symptoms due to their frailty and the presence of comorbidities [42].
An interesting aspect emerging from research is the incidence of SUDs in young adults aged 18 to 25. Approximately 21% of young adults meet the diagnostic criteria for SUDs, a stark contrast to the 9% prevalence in 12–17-year-olds and 7% in individuals aged 26 and above [48]. These data could be explained by many factors. For instance, difficulties that people aged 18–25 face in successfully adapting to this transitional phase could lead them to turn to substance use as a coping mechanism. Furthermore, there is evidence indicating that early manifestations of delinquency or aggression are correlated with substance use in young adults [48].
6.4. Social Background
The social context in which an individual grows up and lives has a crucial role in the development of certain addictions. One research study found that most addicts ignore the idea of marriage so they can devote their time to addictive behaviors without having responsibility or being criticized by their spouse. More than half of the sample was male and came from urban areas, easily accessible for drug cultivation and dealing, with many security and surveillance problems [47]. Another study found that disorder in the neighborhood, such as the presence of graffiti, noise nuisance, and crime, was associated with alcohol use more prominently in women but not in men, for whom, instead, a risk factor was social cohesion, defined as feelings of attachment to the neighborhood, relationships and solidarity with neighbors, and the neighborhood in general [46]. Table 3 presents a summary of social factors related to substance addiction, including influences from childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and social background, with corresponding references.

Table 3.
Table summarizing social factors associated with substance addiction, including influences from childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and social background. Each factor is described along with relevant references.
7. Progression Patterns and Factors of Risk and Protection
Understanding how addictions develop and persist is crucial for adopting the most effective prevention and intervention strategies. This paragraph aims to examine both the patterns of progression in substance use and the related risk and protective factors in order to provide a comprehensive framework for the complexity of this phenomenon.
7.1. Risk and Protection Factors
7.1.1. Impaired Illness Awareness
Impaired illness awareness of addiction to recreational or pharmaceutical substances is an understudied construct that impacts intervention adoption, treatment-seeking behaviors, and retention in treatment [49]. In substance use disorder, the term illness awareness refers to one’s subjective recognition of having a problem with substance use. It also includes one’s acceptance of the need for treatment and the negative consequences that arise from substance use [49].
Individuals with impaired illness awareness in substance use disorder are less likely to utilize clinical services and more likely to drop out of treatment despite the severity of the use. On the other hand, higher levels of illness awareness in substance use disorder are associated with better treatment engagement and adherence and improved clinical outcomes [49].
7.1.2. Transitional Age Youth (TAY)
A narrative review shows a strong connection between mental disorders and SUD in TAY, the span period that encompasses adolescence and emerging adulthood, approximately between 15 and 25 years of age. Initiation of drug use peaks in adolescence, but in many cases, drug use gradually decreases after this period [50]. Most adolescents do not show problematic use patterns, and this spike can be considered experimental drug use [50].
All children entering adolescence are at risk for adverse health outcomes related to alcohol or other drug use. Substance misuse increases markedly from mid to late adolescence [51]. For adolescents, any level of SU is risky and can result in negative developmental outcomes, including disruption of brain development, educational underachievement, behavioral consequences (e.g., driving, sexual behavior), and injury, as well as the potential for inducing or exacerbating mental comorbidities and progression to SUD [6,51]. Furthermore, early-onset substance use is associated with increased psychosocial problems and problematic substance use later in life [52].
7.1.3. Preexisting Mental Disorders
It has been found that preexisting mental disorders represent risk factors for the emergence and progression of SUD [50]. A narrative review highlights a common comorbidity between mental disorders and SUD among adolescents and young adults [50]. According to the authors, the two issues negatively influence each other. A study of juvenile detainees [53] demonstrated that substance use, behavioral disorders, and internalizing disorders predict the development of SUD. This underlines the importance of treating childhood/adolescent disorders to reduce the emergence of secondary SUD [50].
7.1.4. Socioeconomic Position
Emerging evidence shows that low Socioeconomic Position (SEP) is an important determinant of many mental disorders, including substance use disorders [54,55,56]. In a cohort study involving 1.6 million individuals in the Stockholm region [54], alcohol and drug use disorders were more common among individuals with lower levels of education compared to those with higher levels of education, both in males and females.
7.1.5. Physical Activity and Peer Interactions
Peer interactions are often enmeshed within physical activities in adolescence, and physical activity is broadly (positively) related to mental health via psychosocial, behavioral, and physiological mechanisms [52]. Two studies that examined pairs of discordant twins on physical activity found that physical inactivity in adolescence was associated with increased consumption of alcohol, drugs, and smoking in young adulthood [52].
Peer interactions are often linked to physical activities during adolescence. Across adolescence, peer relationships become more important as friends increasingly become a source of social support and influence on developing adaptive and maladaptive behaviors [52]. In the context of substance use disorders, observational studies on adolescents have yielded conflicting results depending on the type of physical activity and substances under examination [52]. Factors such as rejection and loneliness may increase the risk of substance-related issues in adolescence and early adulthood. Social integration may lead to greater access to substances, as well as friendship with deviant peers. Conversely, friendship with peers who do not use substances may serve as a protective factor [52]. This study employed a co-twin control design to explore participation in sports, physical activity, and friendship quality as predictors of substance use. The results indicate that participation in sports and positive friendship quality were associated with the increased likelihood of substance use [52].
In a longitudinal study [57], participants (N = 2880) completed four annual surveys during late adolescence and the transition to young adulthood as part of an ongoing longitudinal study. Results highlight key individual and community-level protective factors that decrease the risk of opioid use [57].
7.1.6. Use Aimed at Increasing Sexual Performance
While long-term use of alcohol, opioids, or sedatives is often associated with impaired sexual function, the use of alcohol, cannabis, cocaine, amphetamines, or hallucinogens may increase sexual arousal in the short term [58]. This may lead to performance-enhancing use.
Several studies have investigated the association between prevalent SUD and hypersexuality. The targeted use of drugs to evoke specific physical and/or psychological effects during sexual activity (e.g., to increase sexual performance or achieve sexual disinhibition) is termed chemsex [58].
7.1.7. Media Representation of Drugs
Media representation about substances and alcohol (TV shows and movies that display people openly using drugs and/or alcohol) has a strong impact on the ideas children and adolescents will have about them. They are also more likely to start to use them and, therefore, develop SUDs [45]. The power of the media should be used to positively influence opinions and beliefs about drugs and alcohol, given its power in teens’ lives.
7.1.8. Correlation between Risk and Protection Factors
Risk factors often exhibit positive correlations with each other and negative associations with protective factors [59]. Essentially, individuals with certain risk factors are more likely to encounter additional risks, while protective factors tend to be less prevalent. Furthermore, the cumulative impact of these factors significantly influences the development or prevention of behavioral health issues. Young people with multiple risk factors face a higher likelihood of experiencing conditions affecting their physical or mental well-being, whereas those with multiple protective factors are at a reduced risk [59].
8. Interactions between Psychological, Social, and Biological Factors
In the previous paragraphs of this article, we analyzed the extent to which individual factors (biological, psychological, and social) contributed to the development and maintenance of substance use disorder. However, these factors rarely have a significant influence if taken individually; it is, therefore, important to acknowledge the co-presence of these factors and pay attention to how they interact with each other in a person’s life.
In this section, we will examine how, collectively, these factors interact with each other in individuals with SUD.
8.1. A Biopsychosocial Model for Understanding Addiction
Substance addiction is a bio-psychosocial phenomenon. Psychosocial factors are multidimensional constructs pertaining to two different domains: psychological, which include factors such as depression, anxiety, distress, self-esteem, and satisfaction; and social (related to socioeconomic status, employment, religion, physical attributes, family, relationship with others, locality). These factors contribute to the development of mental and physical disorders [3]. In fact, drug use is frequently correlated with negative outcomes in people’s lives in various aspects. On the one hand, SUDs can lead to adverse physical, mental, and social consequences, including addiction, substance-induced disorders, neurological complications, cognitive impairment, unemployment, incarceration, and suicidal behavior [2]. On the other hand, stigma and discrimination make it less likely that people who use drugs will receive the help they need. Fewer than 20 percent of people with drug use disorders are in treatment, and access is highly unequal. Out of the approximately 39.5 million individuals globally diagnosed with drug use disorders in 2021, only one in five received treatment [1].
The importance of considering a biopsychosocial model in examining influences on the development of substance dependence disorder was confirmed by a 2020 study conducted at the Department of Health and Environmental Engineering at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Multidisciplinary Center for Health Equity Research at Texas A&M University [60]. The biopsychosocial model of addiction, in understanding the development and progression of substance use problems, emphasizes biological factors such as genetic predisposition, psychological and cognitive factors such as self-efficacy, outcome expectations, and readiness to change, and social factors such as family, peer, and partner influence. Therefore, understanding the interconnectedness of these factors could be an effective strategy in substance use prevention programs [61].
Substance use disorder involves a variety of neurobiological processes, including the brain reward system. This system, also known as the dopaminergic system, is crucial in sending behavioral responses related to pleasure and gratification. Thus, a key role in understanding how an SUD develops is played by the interaction between social environment, individual functioning, and family history.
8.2. Family History, Role Models, and Psychological Factors
Starting with the family during childhood, young people become involved in multiple activities when they enter school; especially during middle school, peers become increasingly important and are a factor influencing the individual’s development [62]. In adolescence, and more so in the transition to adulthood, romantic relationships become additional agents of socialization and represent, along with the peer group, an element of the reward system [63].
Family members serve as role models for children, as shown in research conducted by the University of Washington and the University of Southern California [64] involving 808 participants of different ethnicities and genders and ages from 10 to 33. The results showed that positive social and family environments create a positive model for future interactions. In contrast, a family history of depression may negatively influence mental health functioning during adulthood: the family environment characterized by chronic stress, conflict, or other forms of dysfunction influences the reward system, increasing sensitivity to rewarding stimuli and leading to greater reliance on substances that provide temporary relief. In addition, if there are substance use behaviors in the family, children may perceive such behaviors as acceptable, and this may trigger an approach to a range of substance-focused social contexts as they grow up. The authors found that some psychological factors, such as the presence of generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder or the experience of childhood trauma, are related to substance use. Psychological factors such as childhood trauma may modulate social perceptions and adaptation to stressful life contexts, which may promote the approach to substance use [4].
Other social factors, frequently associated with the development of psychopathological symptoms, are also linked to the development of SUD. According to research conducted in Stockholm, a low level of education increases the risk of substance use disorders and self-harm; furthermore, an association between low educational attainment and various mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, ADHD, and behavioral disorders, is highlighted [54].
8.3. Neurological Factors, Genetic Predispositions, and Personality Traits
Genetic predisposition can affect the brain’s response to opioids and its ability to regulate the impulse for substance use on the one hand and affect an individual’s vulnerability to developing psychological disorders such as anxiety or depression, which, in turn, are strongly linked to the risk of addiction [35]. For example, some theories suggest that individuals with autism spectrum disorder may possess dopaminergic differences in the fronto-cortical cortex, making them susceptible to repetitive pleasurable sensation seeking, with the risk of easily translating into addictive behaviors. In addition, there appears to be a common dysregulation of the limbic system in individuals with SUD and ASD [35].
In a systematic review exploring the impact of both PTSD and SUDs on uncontrolled craving for substances, it was found that post-traumatic stress disorder was significantly associated with increased levels of craving among patients with alcohol, cannabis, cocaine, tobacco, and other substance use disorders [65]. Some studies have also observed a correlation between the severity of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms and craving intensity, as substance use is a means of alleviating traumatic symptoms. The underlying mechanisms refer to negative emotional states, and emotional dysregulation plays a role in eliciting craving after traumatic exposure. Psychological, social, and biological factors may interact synergistically in craving and substance use. PTSD symptoms can trigger emotions that, in turn, would increase craving for substances, and similarly, exposure to traumatic environments can act as a trigger for craving.
8.4. Psychological Factors and Treatment Success Expectations
Working on addiction, we must also consider factors such as self-efficacy (confidence in one’s ability to succeed without the substance) and motivation (desire to change one’s behavior), which are positively correlated with treatment success and in direct relation to each other: lower self-efficacy influences motivation to seek positive social supports, and fewer social supports decrease self-efficacy [44].
9. Discussion
The development and maintenance of substance use disorders involve a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors.
In the biological realm, the endocannabinoid and dopaminergic systems, along with genetic variants in CNR1 and CNR2, contribute to specific pathways in cannabis, opioid, and stimulant addiction [17]. Psychological aspects reveal the significance of personality traits, such as disinhibition and low self-esteem, in addiction vulnerability [30]. The coexistence of anxiety, mood disorders, and addiction, coupled with the strong correlation between traumatic events and substance use, further emphasizes the importance of considering psychological dimensions [34]. Social elements, encompassing family background, parental styles, neighborhood characteristics, and peer support, significantly shape addiction patterns, while addiction, in turn, disrupts social behaviors, leading the individual to isolation [44]. The intricate interconnection of these factors underscores the multifaceted nature of addiction and the importance of comprehensive approaches in prevention and treatment strategies.
9.1. Future Research
There are several avenues for future research that could enhance our understanding of SUD and its co-occurring psychiatric symptoms. Firstly, longitudinal studies tracking individuals from adolescence to adulthood could provide valuable insights into the long-term impact of early substance use on mental health outcomes and addiction trajectories. Understanding how factors, such as childhood trauma, parental styles, and peer influences, interact over time to shape substance use behaviors is crucial for developing targeted prevention and intervention strategies. Secondly, investigating the role of genetic influences and neurobiological factors in predisposing individuals to specific types of substance addictions could offer a more nuanced understanding of addiction vulnerability. By exploring the genetic markers associated with different substance use disorders and their interactions with environmental factors, researchers can identify potential biomarkers for early detection and personalized treatment approaches. Furthermore, exploring the impact of social determinants such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and community support on SUD outcomes is essential for addressing disparities in addiction treatment and recovery. Research focusing on how social factors influence treatment engagement, retention, and outcomes can inform the development of more effective and equitable interventions for individuals with SUD. Lastly, investigating the impact of emerging trends, such as the use of digital technologies and social media on substance use behaviors, could provide valuable insights into novel risk factors for addiction. Understanding how online platforms influence substance-related attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions among different age groups can inform targeted prevention efforts in the digital age.
By addressing these research gaps and exploring the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors influencing SUD, future studies can contribute to more effective prevention strategies, personalized treatment approaches, and improved outcomes for individuals struggling with addiction and co-occurring psychiatric symptoms.
9.2. Limitations
While this review provides valuable insights into the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors contributing to SUD and co-occurring psychiatric symptoms, several limitations should be acknowledged. Firstly, the generalizability of the findings may be constrained by the geographic diversity of the included studies, which spanned various countries. This diversity could introduce cultural nuances that impacted the interpretation of results and the generalizability of the findings. The wide variation in cultural insights featured in this paper may result in a lack of overall consistency. Secondly, the methodologies employed in the reviewed studies varied, encompassing cross-sectional, longitudinal, and randomized controlled trial designs. Variability in study designs may affect the comparability and synthesis of results. Additionally, the reliance on published articles from indexed journals may introduce publication bias, potentially excluding valuable data from unpublished sources; therefore, we’ve incorporated the grey literature, including technical reports [5,6,8], organizational documents [1,9], blog posts [41], and theses [48], providing a more balanced and inclusive perspective. Finally, while efforts were made to include a comprehensive range of factors influencing SUD, there may exist additional variables not covered in this review that could contribute to a more holistic understanding of substance addiction.
10. Conclusions
The findings in the present review underscore the importance of considering a biopsychosocial model when understanding addiction, emphasizing the significant role played by neurotransmitter systems such as the endocannabinoid and dopaminergic systems in substance addiction. Moreover, this review highlights the impact of media representation on substance use behaviors among children and adolescents, emphasizing the need for positive messaging to counteract negative influences. Furthermore, awareness of the risks associated with substance use is particularly important from a prevention perspective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.I.B., A.L., D.C., I.T., V.D., V.G. and M.C.; methodology, C.I.B., M.C.; investigation, C.I.B., V.G. and M.C.; data curation, C.I.B.; writing—original draft preparation, C.I.B., A.L., D.C., I.T., V.D., V.G. and M.C.; writing—review and editing, C.I.B. and M.C.; visualization, M.C.; supervision, M.C.; project administration, C.I.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Drug Report 2023. Available online: www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/world-drug-report-2023.html (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Mefodeva, V.; Carlyle, M.; Walter, Z.; Chan, G.; Hides, L. Polysubstance Use in Young People Accessing Residential and Day-treatment Services for Substance Use: Substance Use Profiles, Psychiatric Comorbidity and Treatment Completion. Addiction 2022, 117, 3110–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5-TR, 5th ed.; Text Revision; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-0-89042-577-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, A.; Choudhari, S.G.; Dakhode, S.U.; Rannaware, A.; Gaidhane, A.M. Substance Abuse Amongst Adolescents: An Issue of Public Health Significance. Cureus 2022, 14, e31193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs|National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/psychedelic-dissociative-drugs (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. Monitoring the Future|National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/trends-statistics/monitoring-future (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Epidemia dei Nuovi Tossicodipendenti Endovena: Ritorno al Passato? Available online: https://www.readfiles.it/pages/Archivio/Epidemia-dei-nuovi-tossicodipendenti-endovena-ritorno-al-passato-idA5 (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. What Is Cocaine?|National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/cocaine/what-cocaine (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Global Report on Cocaine 2023; United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar, M.; Riaz, D.S. Psycho-Social and Morbidity of Substance Use Disorder in Women. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrati, Y.; Goldman, K.; Levin, K.; Rosca, P. Early-Life Trauma, Negative and Positive Life Events, Compulsive Sexual Behavior Disorder and Risky Sexual Action Tendencies among Young Women with Substance Use Disorder. Addict. Behav. 2022, 133, 107379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigre, C.; Grau-López, L.; Palma-Alvarez, R.F.; Perea-Ortueta, M.; Sorribes-Puertas, M.; Serrano-Pérez, P.; Quesada, M.; Segura, L.; Coronado, M.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; et al. A Multicenter Study on the Impact of Gender, Age, and Dual Diagnosis on Substance Consumption and Mental Health Status in Outpatients Treated for Substance Use Disorders During COVID-19 Lockdown. J. Dual Diagn. 2022, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.-H.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Y. Association Between Psychiatric Symptoms and Craving in Drug Withdrawal. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2023, 21, 3174–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Chen, C.-K.; Chen, C.-H.; Chang, H.-M.; Huang, M.-C.; Xu, K. Association of Craving and Depressive Symptoms in Ketamine-Dependent Patients Undergoing Withdrawal Treatment. Am. J. Addict. 2020, 29, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; García-Gutiérrez, M.; Gasparyan, A.; Navarro, D.; López-Picón, F.; Morcuende, Á.; Femenía, T.; Manzanares, J. Biomarkers of the Endocannabinoid System in Substance Use Disorders. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacht, J.P.; Hutchison, K.E.; Filbey, F.M. Associations between Cannabinoid Receptor-1 (CNR1) Variation and Hippocampus and Amygdala Volumes in Heavy Cannabis Users. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias Horcajadas, F.; Dávila Píriz, J.R.; Parra González, A.; Sánchez Romero, S.; Sánchez-Morla, E.; Ampuero Sánchez, I.; Ramos Atance, J.A. Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Gene is Associated with Comorbidity of Schizophrenia and Cannabis Dependence and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Gene is Associated with Cannabis Dependence in the Spanish Population.|Adicciones|EBSCOhost. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/contentitem/gcd:161894901?sid=ebsco:plink:crawler&id=ebsco:gcd:161894901 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Manza, P.; Yuan, K.; Shokri-Kojori, E.; Tomasi, D.; Volkow, N.D. Brain Structural Changes in Cannabis Dependence: Association with MAGL. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 3256–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Egerton, A.; Kim, E.; Rosso, L.; Riano Barros, D.; Hammers, A.; Brammer, M.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Howes, O.D.; McGuire, P. Acute Induction of Anxiety in Humans by Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Related to Amygdalar Cannabinoid-1 (CB1) Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viganò, D.; Grazia Cascio, M.; Rubino, T.; Fezza, F.; Vaccani, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Parolaro, D. Chronic Morphine Modulates the Contents of the Endocannabinoid, 2-Arachidonoyl Glycerol, in Rat Brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Kranzler, H.R.; Luo, X.; Yang, B.; Weiss, R.; Brady, K.; Poling, J.; Farrer, L.; Gelernter, J. Interaction between Two Independent CNR1 Variants Increases Risk for Cocaine Dependence in European Americans: A Replication Study in Family-Based Sample and Population-Based Sample. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, C.; Xi, Z. Identification of the Risk Genes Associated with Vulnerability to Addiction: Major Findings from Transgenic Animals. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 811192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Wan, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Fang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Endocannabinoid Signaling Regulates the Reinforcing and Psychostimulant Effects of Ketamine in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, O. Current Trends and Perspectives in the Immune Therapy for Substance Use Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 882491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, G.R.; Koob, G.F.; Cable, J. The Neurobiology of Addiction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1451, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, M. Neuroscientific Basis of Treatment for Substance Use Disorders. Noro Psikiyatri Arsivi 2022, 59 (Suppl. 1), 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Boyle, M. Neuroscience of Addiction: Relevance to Prevention and Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, J.Y.K.; Hu, H.; Lam, M.; Lui, S.S.Y.; Chan, R.C.K. The Interplay between Addictive Behaviour and Psychopathology and Personality in Substance Use Disorder: A Network Analysis in Treatment-Seeking Patients with Alcohol and Drug Use. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santens, E.; Dom, G.; Dierckx, E.; Claes, L. Reactive and Regulative Temperament in Relation to Clinical Symptomatology and Personality Disorders in Patients with a Substance Use Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santens, E.; Dom, G.; Dierckx, E.; Claes, L. The Role of Effortful Control in Substance Use Disorders. Eur. Psychiatry 2022, 65, S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buică, A.M.; Preda, D.M.; Andrei, L.E.; Stancu, M.; Gică, N.; Rad, F. Maladaptive Personality Traits in a Group of Patients with Substance Use Disorder and ADHD. Med. Kaunas Lith. 2022, 58, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basedow, L.A.; Wiedmann, M.F.; Roessner, V.; Golub, Y.; Kuitunen-Paul, S. Coping Motives Mediate the Relationship between PTSD and MDMA Use in Adolescents with Substance Use Disorders. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2022, 17, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKowen, J.; Woodward, D.; Yule, A.M.; DiSalvo, M.; Rao, V.; Greenbaum, J.; Joshi, G.; Wilens, T.E. Characterizing Autistic Traits in Treatment-seeking Young Adults with Substance Use Disorders. Am. J. Addict. 2022, 31, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Toro, E.; Wolf, C.J.H.; González, R.A.; van den Brink, W.; Schellekens, A.; Vélez-Pastrana, M.C.; AFP Working Collaborative Group. Network Analysis of DSM Symptoms of Substance Use Disorders and Frequently Co-Occurring Mental Disorders in Patients with Substance Use Disorder Who Seek Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, S.; Buzlu, S. The Relationships between Self-transcendence and Depressive Symptoms, Self-esteem, and Locus of Control in Individuals Diagnosed with Substance Addiction. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 2022, 58, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Scott, J.G.; Vuori, M.; Hurtig, T.; Halt, A.; Miettunen, J.; Alakokkare, A.; Niemelä, S. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity and Oppositional Defiant Disorder Symptoms in Adolescence and Risk of Substance Use Disorders—A General Population-based Birth Cohort Study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2023, 148, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekaria, V.; Patra, B.G.; Xi, W.; Murphy, S.M.; Avery, J.; Olfson, M.; Pathak, J. Association of Opioid or Other Substance Use Disorders with Health Care Use among Patients with Suicidal Symptoms. J. Subst. Use Addict. Treat. 2024, 156, 209177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, H.W.; Mosti, M.P.; Nordfjærn, T. Suicidal Ideation among Inpatients with Substance Use Disorders: Prevalence, Correlates and Gender Differences. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 317, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinspoon, P. Poverty, Homelessness, and Social Stigma Make Addiction More Deadly. Available online: https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/poverty-homelessness-and-social-stigma-make-addiction-more-deadly-202109282602 (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Stewart, S.; Copeland, A.; Cherry, K. Risk Factors for Substance Use across the Lifespan. J. Genet. Psychol. 2022, 184, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhern, J.P. Consideration of Social Determinants Risks in Substance Use Disorder Assessment and Treatment Plan Formulation. J. Addict. Nurs. 2022, 33, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomrenze, M.; Paliarin, F.; Maiya, R. Friend of the Devil: Negative Social Influences Driving Substance Use Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 836996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillman, M.A.; Daddis, S.T. Portrayal of Substance Use in Media and Its Effects on Substance Use Disorders among Youth. Addict. Subst. Abuse 2022, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.M.; Harrison, K.; Rawls, E.; Zilverstand, A. Gender Differences in the Psychosocial Determinants Underlying the Onset and Maintenance of Alcohol Use Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 808776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.; Abdelmonem, R.; Hassan, S. Relationship between Self-Efficacy, Social Support and Treatment Motivation among Addict Patients. Minia Sci. Nurs. J. 2022, 012, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K. Matching Treatment to Development: Emerging Adults and Substance-Use Disorder; Memorial University of Newfoundland: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kambari, Y.; Taggar, A.; Quilty, L.C.; Selby, P.; Caravaggio, F.; Ueno, F.; Torres, E.; Song, J.; Pollock, B.G.; et al. A Measure of Subjective Substance Use Disorder Awareness—Substance Use Awareness and Insight Scale (SAS). Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 231, 109129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, P.; Meyer, M.; Elsner, J.; Dürsteler, K.M.; Vogel, M.; Walter, M. Co-Occurring Mental Disorders in Transitional Aged Youth With Substance Use Disorders—A Narrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 827658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, P.A.; Ridenour, T.; Ialongo, N.; Spoth, R.; Prado, G.; Hammond, C.J.; Hawkins, J.D.; Adger, H. State of the Art in Substance Use Prevention and Early Intervention: Applications to Pediatric Primary Care Settings. Prev. Sci. 2022, 23, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, L.; Elam, K.K.; Quinn, P.D.; Adams, S.; Chirica, M.G.; Klonsky, E.D.; Pettersson, E.; Lundström, S.; Larsson, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; et al. Examining Protective Factors for Substance Use Problems and Self-Harm Behavior during Adolescence: A Longitudinal Co-Twin Control Study. Dev. Psychopathol. 2022, 34, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, K.M.; Zwecker, N.A.; Welty, L.J.; Hershfield, J.A.; Dulcan, M.K.; Teplin, L.A. Comorbidity and Continuity of Psychiatric Disorders in Youth After Detention: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Allebeck, P.; Burstöm, B.; Danielsson, A.-K.; Degenhardt, L.; Eikemo, T.A.; Ferrari, A.; Knudsen, A.K.; Lundin, A.; Manhica, H.; et al. Educational Level and the Risk of Mental Disorders, Substance Use Disorders and Self-Harm in Different Age-Groups: A Cohort Study Covering 1,6 Million Subjects in the Stockholm Region. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 32, e1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelpietra, G.; Knudsen, A.K.S.; Agardh, E.E.; Armocida, B.; Beghi, M.; Iburg, K.M.; Logroscino, G.; Starace, F.; Steel, N.; Addolorato, G.; et al. The Burden of Mental Disorders, Substance Use Disorders and Self-Harm among Young People in Europe, 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 16, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrank, M.; Nikendei, C.; Zehetmair, C.; Friederich, H.-C.; Nagy, E. The Burden of Substance Use and (Mental) Distress among Asylum Seekers: A Cross Sectional Study. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1258140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.P.; Tucker, J.S.; Dunbar, M.; Seelam, R.; D’Amico, E.J. Poly-Victimization and Opioid Use during Late Adolescence and Young Adulthood: Health Behavior Disparities and Protective Factors. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2022, 36, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, D.; Luck, T.; Bernard, M.; Moor, I.; Watzke, S. Study Protocol: Hypersexual and Hyposexual Behavior among Adults Diagnosed with Alcohol- and Substance Use Disorders-Associations between Traumatic Experiences and Problematic Sexual Behavior. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1088747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMHSA—Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Risk and Protective Factors 2019; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Montiel Ishino, F.A.; McNab, P.R.; Gilreath, T.; Salmeron, B.; Williams, F. A Comprehensive Multivariate Model of Biopsychosocial Factors Associated with Opioid Misuse and Use Disorder in a 2017–2018 United States National Survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skewes, M.C.; Gonzalez, V.M. The Biopsychosocial Model of Addiction. In Principles of Addiction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 61–70. ISBN 978-0-12-398336-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski, W.M.; Laursen, B.; Rubin, K.H. (Eds.) Handbook of Peer Interactions, Relationships, and Groups, 2nd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4625-2501-0. [Google Scholar]
- Furman, W.; Simon, V.A.; Shaffer, L.; Bouchey, H.A. Adolescents’ Working Models and Styles for Relationships with Parents, Friends, and Romantic Partners. Child Dev. 2002, 73, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.M.; Hill, K.G.; Epstein, M.; Lee, J.O.; Hawkins, J.D.; Catalano, R.F. Understanding the Interplay of Individual and Social–Developmental Factors in the Progression of Substance Use and Mental Health from Childhood to Adulthood. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 28, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, F.; Jakubiec, L.; Swendsen, J.; Fatseas, M. The Impact of Co-Occurring Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Substance Use Disorders on Craving: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 786664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).