Establishing Experimental Conditions to Produce Lignin-Degrading Enzymes on Wheat Bran by Trametes versicolor CM13 Using Solid State Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Particle Analysis of Wheat Bran
2.2. Analysis of Growth of T. versicolor CM13 on Wheat Bran over Time
2.3. Effect of Enzyme Activities of T. versicolor CM13 at Two Different Moisture Contents
2.4. Analysis of Samples
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
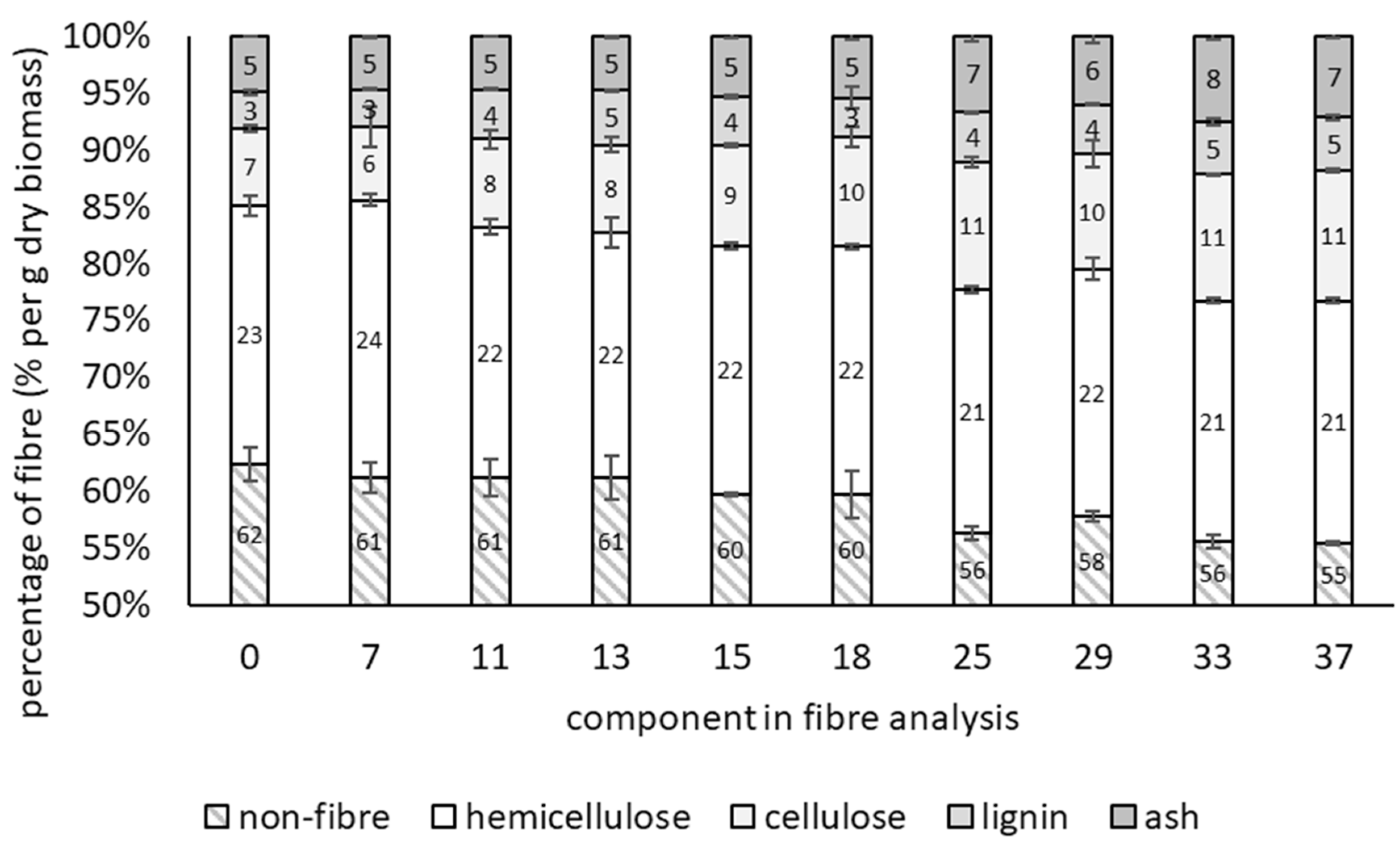
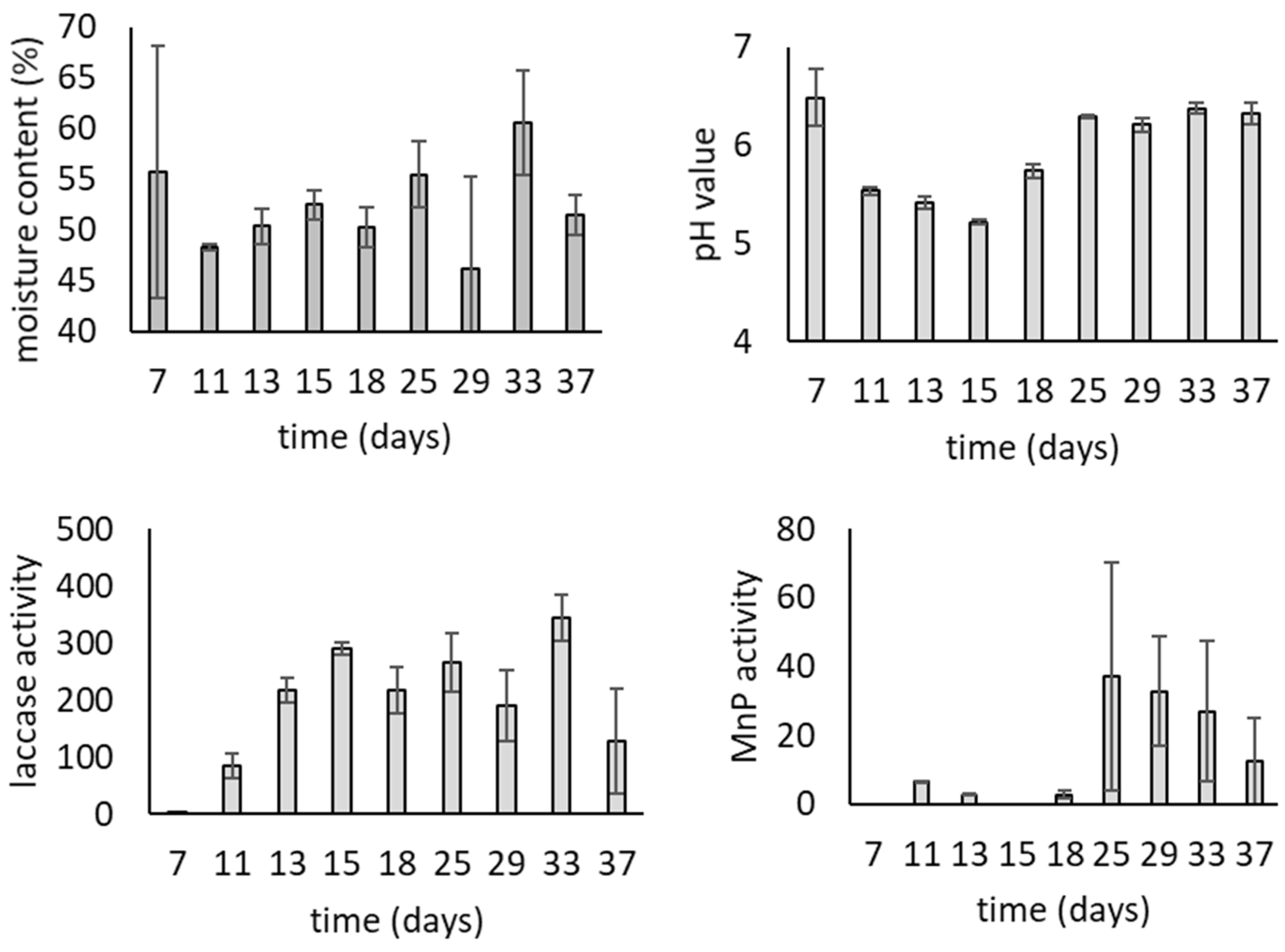
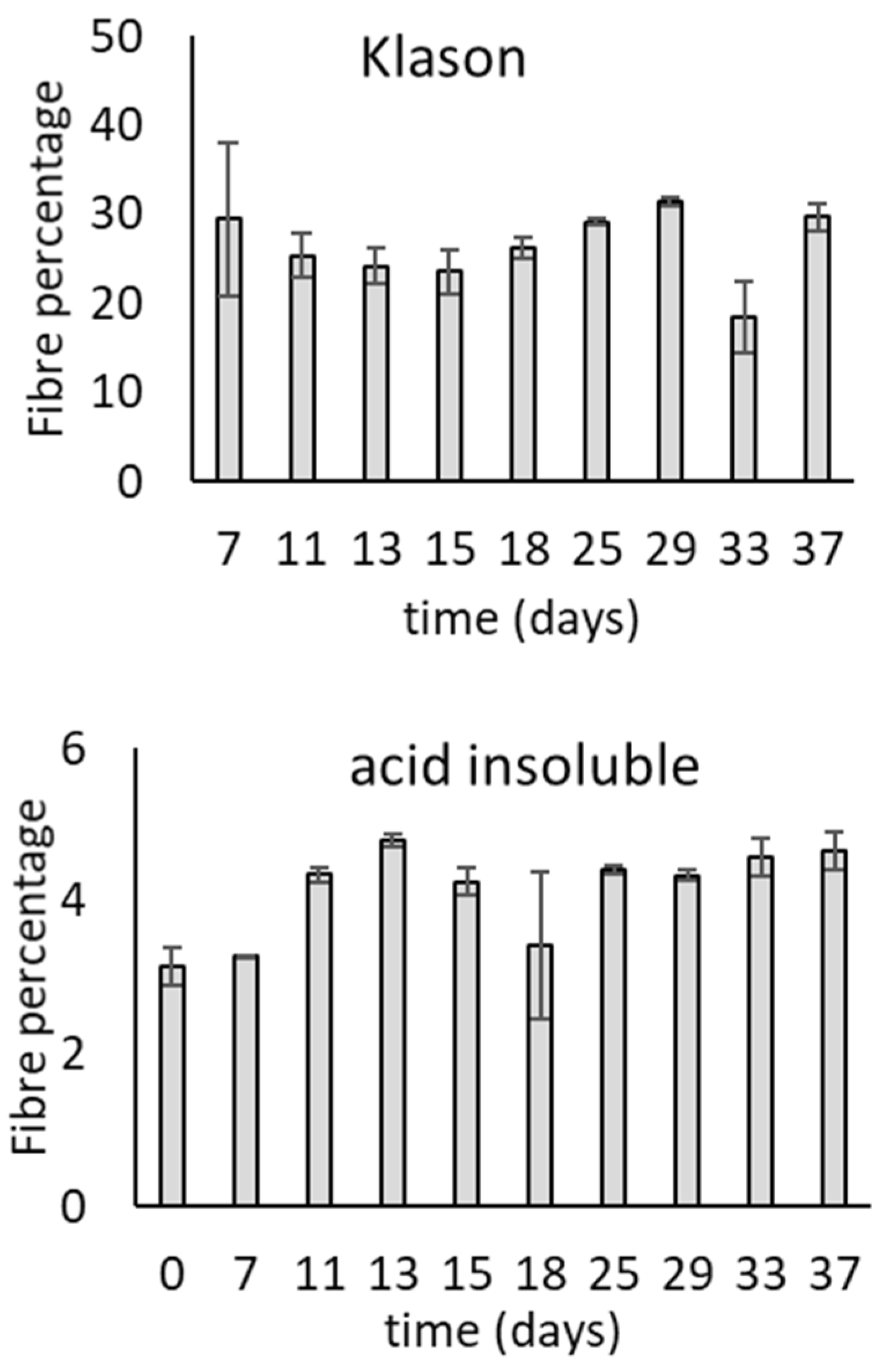
3.1. Growth of T. versicolor on Wheat Bran over Time
3.2. Growth of T. versicolor CM13 on Wheat Bran under Two Different Moisture Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Castro, R.J.S.; Sato, H.H. Enzyme production by solid state fermentation: General aspects and an analysis of the physicochemical characteristics of substrates for agro-industrial wastes valorization. Waste Biomass Valori. 2015, 6, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merali, Z.; Collins, S.R.; Elliston, A.; Wilson, D.R.; Käsper, A.; Waldron, K.W. Characterization of cell wall components of wheat bran following hydrothermal pretreatment and fractionation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsane, B.K.; Ghildyal, N.P.; Budiatman, S.; Ramakrishna, S.V. Engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1985, 7, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Bourgine, J.; Thomsen, M. Closing the loop of cereal waste and residues with sustainable technologies: An overview of enzyme production via fungal solid-state fermentation. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.A.; Arnaud, T.; Lu-Chau, T.A.; Fdz-Polanco, M.; Moreira, M.T.; Rivero, J.A.C. Review of solid state fermentation for lignocellulolytic enzyme production: Challenges for environmental applications. Rev. Environ. Sci. 2016, 15, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.W.; Charlton, A.; Hale, M.D.C. Fungal pre-treatment of forestry biomass with a focus on biorefining: A comparison of biomass degradation and enzyme activities by wood rot fungi across three tree species. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Liu, P.; Xie, S.; Sun, S. Recent Advancements and Challenges in Lignin Valorization: Green Routes towards Sustainable Bioproducts. Molecules 2022, 27, 6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, V.K.; Nguyen, D.D.; Dharmaraja, J.; Shobana, S.; Banu, J.R.; Saratale, R.G.; Chang, S.W.; Kumar, G. A review on lignin structure, pretreatments, fermentation reactions and biorefinery potential. Bioresourc. Technol. 2019, 271, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Duenas, F.J.; Lundell, T.; Floudas, D.; Nagy, L.G.; Barrasa, J.M.; Hibbett, D.S.; Martínez, A.T. Lignin-degrading peroxidases in Polyporales: An evolutionary survey based on 10 sequenced genomes. Mycologia 2013, 105, 1428–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.W.; Charlton, A.; Hale, M.D. Increased delignification by white rot fungi after pressure refining Miscanthus. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.A.; Bao, W.; Kawai, S.; Srebotnik, E.; Hammel, K.E. Manganese-dependent cleavage of nonphenolic lignin structures by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora in the absence of lignin peroxidase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3679–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.; Jeffries, T.W. Mineralization of 14C-ring-labeled synthetic lignin correlates with the production of lignin peroxidase, not of manganese peroxidase or laccase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.S.; Chander, M.; Gill, P.K. Involvement of lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase in degradation and selective ligninolysis of wheat straw. Int. Biodeterior Biodegrad 2002, 50, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofrichter, M. Review: Lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, R.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Y. Textile dye biodecolorization by manganese peroxidase: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, P.; Shukla, G.; Raj, G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bharagava, R.N. Microbial manganese peroxidase: A ligninolytic enzyme and its ample opportunities in research. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Yadav, M.; Hoque, R.A.; Yadav, H.S. Bioremediation mediated by manganese peroxidase—An overview. Biocatal. Biotransfor. 2022, 41, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessesse, A.; Mamo, G. High-level xylanase production by an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. by using solid-state fermentation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1999, 25, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.; Loguercio-Leite, C.; Esposito, E.; Reis, M.M. In vitro wood decay of Eucalyptus grandis by the basidiomycete fungus Phellinus flavomarginatus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2005, 55, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbonnais, R.; Paice, M.G.; Reid, D.; Lanthier, P.; Yaguchi, M. Lignin oxidation by laccase isozymes from Trametes versicolor and role of the mediator 2, 29-azinobis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonate) in kraft lignin depolymerization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1876–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichlerová, I.; Baldrian, P. Ligninolytic enzyme production and decolorization capacity of synthetic dyes by saprotrophic white rot, brown rot, and litter decomposing Basidiomycetes. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Oh, I.; Kim, C. Production and purification of remazol brilliant blue R decolorizing peroxidase from the culture filtrate of Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archibald, F.S. A new assay for lignin-type peroxidases employing the dye Azure B. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, C.; Peyron, S.; Mabille, F.; Lapierre, C.; Bouchet, B.; Abecassis, J.; Rouau, X. Individual contribution of grain outer layers and their cell wall structure to the mechanical properties of wheat bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, J.P.; Rinzema, A.; Tramper, J.; Van Sonsbeek, H.M.; Knol, W. Solid-state fermentation of wheat bran by Trichoderma reesei QM9414: Substrate composition changes, C balance, enzyme production, growth and kinetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 46, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.H.; Pham, T.A.; Kim, K. Improvement of fungal cellulase production by mutation and optimization of solid state fermentation. Mycobiology 2011, 39, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.W.; Charlton, A.; Hale, M.D.C. Fibre degradation of wheat straw by Pleurotus erygnii under low moisture conditions during solid-state fermentation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijwani, K.; Oberoi, H.S.; Vadlani, P.V. Production of a cellulolytic enzyme system in mixed-culture solid-state fermentation of soybean hulls supplemented with wheat bran. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Sun, X.F.; Tomkinson, J. Hemicelluloses and their derivatives. In Hemicelluloses: Science and Technology; Gatenholm, P., Tenkanen, M., Eds.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 2–22. [Google Scholar]
- van Kuijk, S.J.; Del Río, J.C.; Rencoret, J.; Gutiérrez, A.; Sonnenberg, A.S.; Baars, J.J.; Hendriks, W.H.; Cone, J.W. Selective ligninolysis of wheat straw and wood chips by the white-rot fungus Lentinula edodes and its influence on in vitro rumen degradability. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Cone, J.W.; Hendriks, W.H.; Sonnenberg, A.S. Wheat bran addition improves Ceriporiopsis subvermispora and Lentinula edodes growth on wheat straw, but not delignification. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 259, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaud, N.; Giniés, C.; Navarro, D.; Fabre, N.; Crapart, S.; Gimbert, I.H.; Levasseur, A.; Raouche, S.; Sigoillot, J.C. Exploring fungal biodiversity: Organic acid production by 66 strains of filamentous fungi. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunzel, M.; Schußler, A.; Saha, G.T. Chemical characterization of Klason lignin preparations from plant-based foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12506–12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salame, T.M.; Knop, D.; Levinson, D.; Yarden, O.; Hadar, Y. Redundancy among manganese peroxidases in Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Lin, M.; Zang, Q.; Shi, S. Solid state bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues by Inonotus obliquus for production of cellulolytic enzymes and saccharification. Bioresourc. Technol. 2018, 247, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osma, J.F.; Moilanen, U.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Rodríguez-Couto, S. Morphology and laccase production of white-rot fungi grown on wheat bran flakes under semi-solid-state fermentation conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 318, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farani de Souza, D.; Kirst Tychanowicz, G.; Giatti Marques de Souza, C.; Peralta, R.M. Co-production of ligninolytic enzymes by Pleurotus pulmonarius on wheat bran solid state cultures. J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, F.; Leonowicz, A.; Higaki, M.; Fukuzumi, T. Laccase-less mutants induced by regeneration of protoplasts of Pleurotus basidiomycetes. J. Jpn. Wood Res. Soc. 1994, 40, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.H.; Cho, M.K.; Kim, M.; Jung, S.M.; Seo, J.H. Enhanced lignin biodegradation by a laccase-overexpressed white-rot fungus Polyporus brumalis in the pretreatment of wood chips. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Arora, P.K. Biotechnological applications of manganese peroxidases for sustainable management. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Induction, purification and characterization of a novel manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus CD2 and its application in the decolorization of different types of dye. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, H.; Jaouadi, N.Z.; Bouacem, K.; Zenati, B.; Kourdali, S.; Badis, A.; Annane, R.; Bouanane-Darenfed, A.; Bejar, S.; Jaouadi, B. Physical and enzymatic properties of a new manganese peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Trametes pubescens strain i8 for lignin biodegradation and textile-dyes biodecolorization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, V.; Shrivastava, R.; Shukla, D.; Modi, H.; Vyas, B.R.M. Mediator role of veratryl alcohol in the lignin peroxidase-catalyzed oxidative decolorization of Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, P.P.; Ramsay, J.A. Contribution of manganese peroxidase and laccase to dye decoloration by Trametes versicolor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locci, E.; Laconi, S.; Pompei, R.; Scano, P.; Lai, A.; Marincola, F.C. Wheat bran biodegradation by Pleurotus ostreatus: A solid-state Carbon-13 NMR study. Bioresourc. Technol. 2008, 99, 4279–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A. Biobleaching: An eco-friendly approach to reduce chemical consumption and pollutants generation. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2020, 6, 20190044. [Google Scholar]

| Measured Parameter | Time | Saturation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microcosm size | 20 g | 20 g | 100 g |
| Prior homogenisation | no | no | yes |
| Moisture content | 7.90 | 15.1 | 2.25 |
| Biomass loss | ND | 19.8 | 7.53 |
| pH | 1.33 | 3.37 | 0.77 |
| Laccase | 32.7 | 36.1 | 6.13 |
| Manganese peroxidase | 34.7 | 98.4 | 36.0 |
| Remazol Brilliant Blue activity | ND | 144 | 14.8 |
| Day | Low | High | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content | 0 | 42.9 ± 0.18 a | 54.6 ± 0.80 b |
| 7 | 54.4 ± 3.87 b | 57.0 ± 1.73 bc | |
| 14 | 58.9 ± 1.61 b | 67.5 ± 1.61 d | |
| 21 | 62.6 ± 1.40 cd | 67.7 ± 0.95 d | |
| Biomass loss | 7 | 27.7 ± 6.06 a | 32.9 ± 5.28 a |
| 14 | 26.5 ± 2.79 a | 43.7 ± 3.29 b | |
| 21 | 45.1 ± 0.83 b | 46.7 ± 0.81 b | |
| pH | 0 | 6.22 ± 0.03 ab | 6.25 ± 0.01 b |
| 7 | 5.55 ± 0.11 a | 5.96 ± 0.09 b | |
| 14 | 5.80 ± 0.04 c | 6.10 ± 0.01 bc | |
| 21 | 6.22 ± 0.02 ab | 6.27 ± 0.04 a | |
| Laccase | 0 | 0.12 ± 0.00 a | 0.58 ± 0.59 a |
| 7 | 366 ± 25.6 b | 628 ± 27.7 c | |
| 14 | 529 ± 87.5 c | 777 ± 25.2 d | |
| 21 | 750 ± 30.5 d | 820 ± 30.8 d | |
| Manganese peroxidase | 7 | 1.69 ± 0.23 a | 1.23 ± 0.83 a |
| 14 | 3.41 ± 1.47 a | 6.85 ± 3.46 a | |
| 21 | 23.3 ± 6.45 b | 21.4 ± 2.54 b | |
| Lignin peroxidase | 7 | ND | ND |
| 14 | 0.47 ± 0.29 a | 0.55 ± 0.36 ab | |
| 21 | 0.00 ± 0.66 ab | 0.00 ± 4.16 ab | |
| Lignin-degrading activity | 7 | 0.00 ± 54.66 a | 107 ± 114 a |
| 14 | 632 ± 14.5 b | 792 ± 43.7 b | |
| 21 | 72.4 ± 39.1 b | 102 ± 10.1 b |
| Moisture Content | Time (Days) | Non-Fibre | Hemicellulose | Cellulose | Lignin | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43.9%, 54.6% | 0 | 62.4 ± 1.53 a | 22.7 ± 0.92 a | 6.82 ± 0.31 a | 3.23 ± 0.24 a | 5.01 ± 0.44 a |
| 43.9% | 7 | 60.1 ± 1.23 a | 21.7 ± 0.79 b | 9.62 ± 0.45 ab | 3.84 ± 0.05 a | 3.28 ± 0.13 b |
| 14 | 60.1 ± 0.58 a | 20.5 ± 0.52 bc | 10.7 ± 0.49 ab | 3.79 ± 0.23 a | 3.51 ± 0.08 b | |
| 21 | 58.0 ± 0.69 a | 21.1 ± 0.06 bc | 11.5 ± 0.61 b | 4.31 ± 0.06 a | 3.61 ± 0.51 b | |
| 54.6% | 7 | 61.8 ± 0.54 a | 19.5 ± 0.39 c | 9.81 ± 0.24 ab | 3.65 ± 0.13 a | 3.65 ± 0.66 b |
| 14 | 62.6 ± 5.09 a | 20.7 ± 1.38 bc | 9.73 ± 3.43 ab | 1.96 ± 3.04 a | 3.53 ± 0.23 b | |
| 21 | 58.2 ± 0.74 a | 19.4 ± 0.51 c | 12.5 ± 0.42 b | 4.46 ± 0.17 a | 4.00 ± 0.17 ab | |
| 43.9% | 7 | 12.29 ± 4.39 a | 6.63 ± 0.80 a | 0.17 ± 0.55 a | 0.22 ± 0.20 a | |
| 14 | 15.46 ± 2.79 ab | 8.55 ± 1.40 ab | 0.00 ± 0.80 a | 0.47 ± 0.16 a | ||
| 21 | 23.95 ± 0.85 c | 10.72 ± 0.15 c | 0.80 ± 0.24 a | 0.64 ± 0.05 a | ||
| 54.6% | 7 | 10.32 ± 1.98 a | 7.95 ± 0.28 a | 0.00 ± 0.37 a | 0.26 ± 0.13 a | |
| 14 | 19.69 ± 1.12 bc | 10.36 ± 0.19 bc | 1.45 ± 2.26 a | 0.54 ± 0.20 a | ||
| 21 | 24.76 ± 0.87 c | 11.96 ± 0.16 c | 0.46 ± 0.20 a | 0.62 ± 0.07 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, P.W.; Charlton, A. Establishing Experimental Conditions to Produce Lignin-Degrading Enzymes on Wheat Bran by Trametes versicolor CM13 Using Solid State Fermentation. Waste 2023, 1, 711-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1030042
Baker PW, Charlton A. Establishing Experimental Conditions to Produce Lignin-Degrading Enzymes on Wheat Bran by Trametes versicolor CM13 Using Solid State Fermentation. Waste. 2023; 1(3):711-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Paul W., and Adam Charlton. 2023. "Establishing Experimental Conditions to Produce Lignin-Degrading Enzymes on Wheat Bran by Trametes versicolor CM13 Using Solid State Fermentation" Waste 1, no. 3: 711-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1030042
APA StyleBaker, P. W., & Charlton, A. (2023). Establishing Experimental Conditions to Produce Lignin-Degrading Enzymes on Wheat Bran by Trametes versicolor CM13 Using Solid State Fermentation. Waste, 1(3), 711-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1030042









