Functional Goat Milk Yogurt Dessert Enriched with Antioxidant Extract from Spent Coffee Grounds: Sensory and Consumer Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spent Coffee Extraction
2.2. Yoghurt Dessert Production
2.3. Sensory Evaluation
- A 5-point hedonic scale (1 = “Dislike extremely” to 5 = “Like extremely”) for sensory attributes;
- A 5-point Likert scale for overall satisfaction (1 = “Dissatisfied” to 5 = “Very satisfied”);
- A 5-point Likert scale for purchase intention (1 = “Would never buy” to 5 = “Would definitely buy”).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Demographics
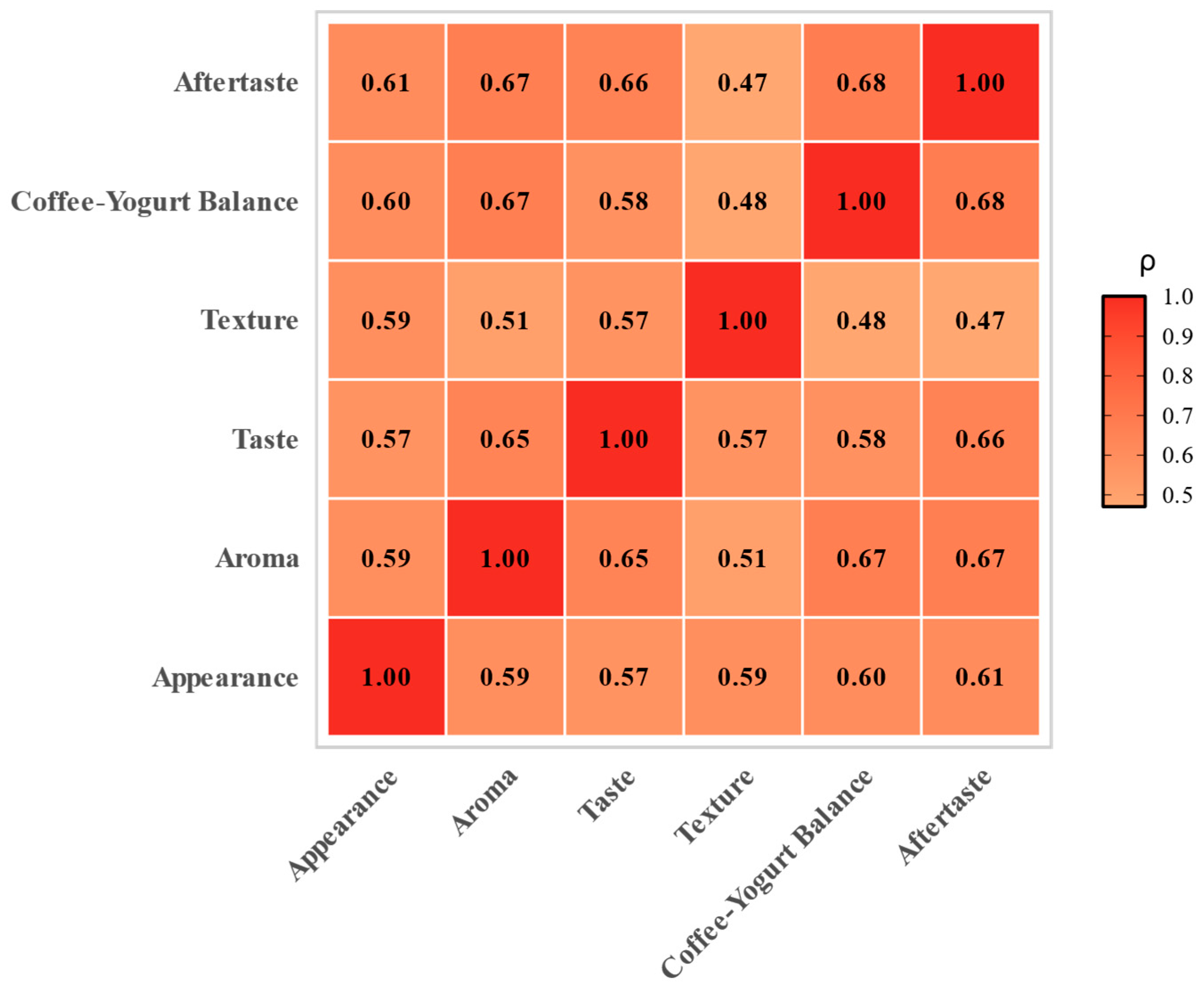
3.2. Sensory Analysis
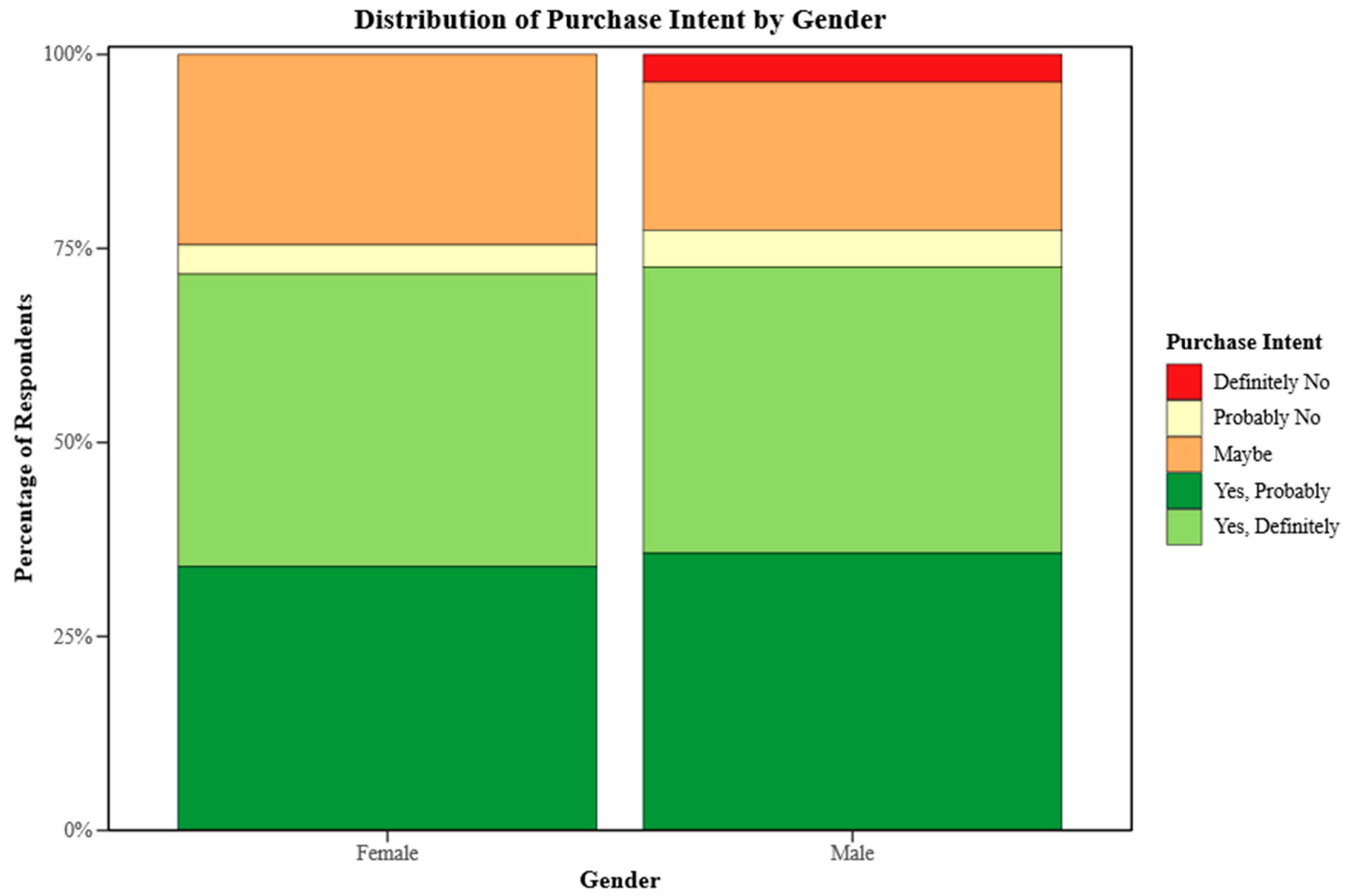
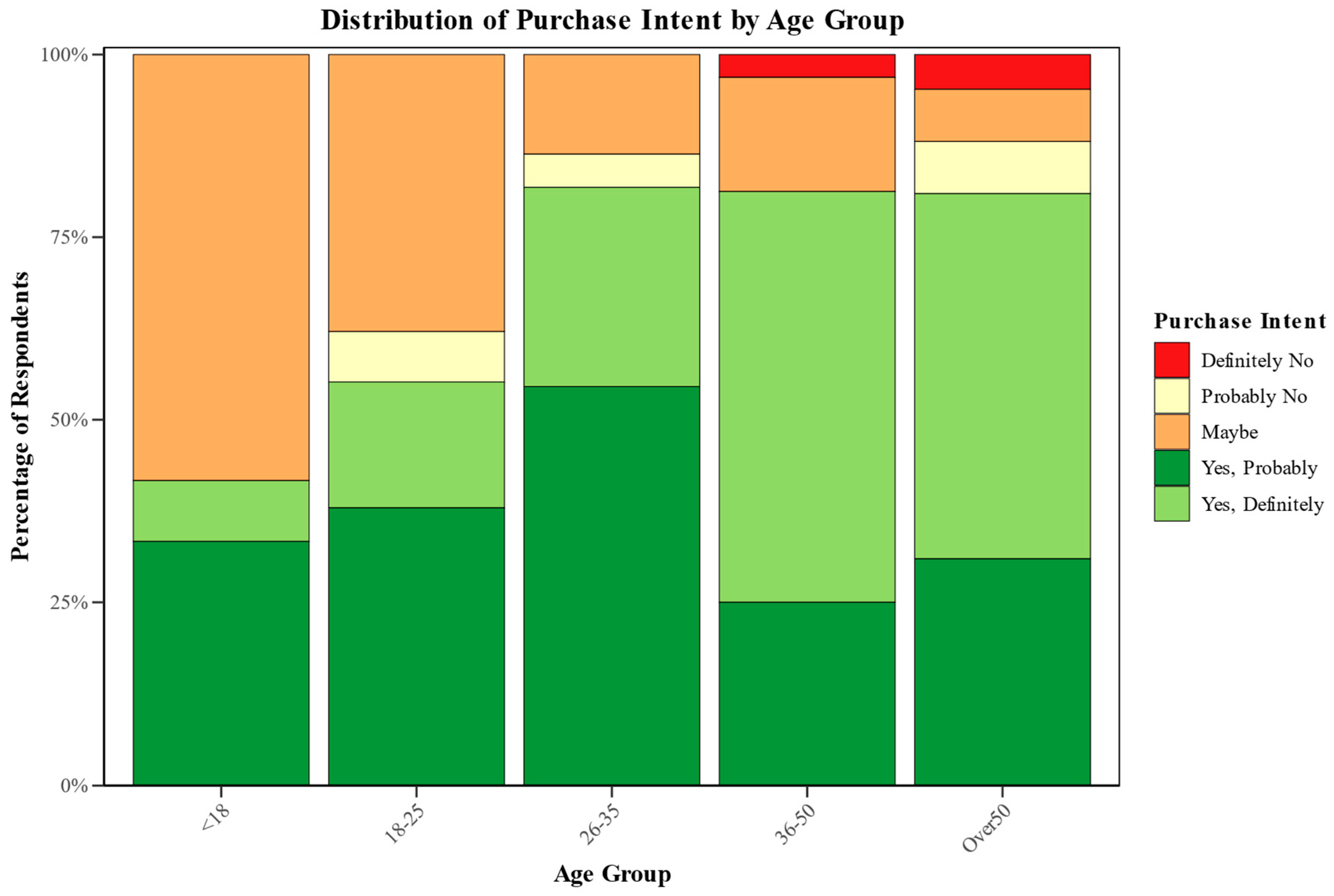
3.3. Consumer Acceptance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCGs | Spent coffee grounds |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Pamungkaningtyas, F.H.; Mariyatun, M.; Kamil, R.Z.; Setyawan, R.H.; Hasan, P.N.; Wiryohanjoyo, D.V.; Nurfiani, S.; Zulaichah, E.; Utami, I.S.; Utami, T.; et al. Sensory Evaluation of Yogurt-like Set and Yogurt-like Drink Produced by Indigenous Probiotic Strains for Market Test. Indones. Food Nutr. Prog. 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghvanidze, S.; Velikova, N.; Dodd, T.H.; Oldewage-Theron, W. Consumers’ environmental and ethical consciousness and the use of the related food products information: The role of perceived consumer effectiveness. Appetite 2016, 107, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Song, M.W.; Kim, K.-T.; Hong, W.-S.; Paik, H.-D. Antioxidant Effect and Sensory Evaluation of Yogurt Supplemented with Hydroponic Ginseng Root Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Garcia, H.S.; Beristain, C.I. Sensory evaluation of dairy products supplemented with microencapsulated conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderoni, S.; Perito, M.A. Sustainable consumption in the circular economy. An analysis of consumers’ purchase intentions for waste-to-value food. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, T.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Xie, T. Peanut sprout yogurt: Increased antioxidant activity and nutritional content and sensory evaluation by fuzzy mathematics. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, D.; Giacinti, G.; Chemello, G.; Frangipane, M.T. Improvement of the Sensory Characteristics of Goat Milk Yogurt. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Hyeonbin, O.; Lee, P.; Kim, Y.-S. The quality characteristics, antioxidant activity, and sensory evaluation of reduced-fat yogurt and nonfat yogurt supplemented with basil seed gum as a fat substitute. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.G.; Beltrão Filho, E.M.; de Sousa, S.; da Cruz, G.R.B.; de Cássia Ramos do Egypto Queiroga, R.; da Cruz, E.N. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of yoghurts made from goat and cow milk. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Esters, O.; Mc Namara, P.; Savaiano, D. Dietary and biological factors influencing lactose intolerance. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 22, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joon, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Brar, G.S.; Singh, P.K.; Panwar, H. Instrumental texture and syneresis analysis of yoghurt prepared from goat and cow milk. Pharma Innov. J. 2017, 6, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- Haenlein, G.F.W. Goat milk in human nutrition. Small Rumin. Res. 2004, 51, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep Prasanna, P.H.; Charalampopoulos, D. Encapsulation in an alginate–goats’ milk–inulin matrix improves survival of probiotic Bifidobacterium in simulated gastrointestinal conditions and goats’ milk yoghurt. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Juárez, M.; Ramos, M.; Haenlein, G.F.W. Physico-chemical characteristics of goat and sheep milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 68, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.K.; Jackman, J.A.; Valle-González, E.R.; Cho, N.-J. Antibacterial Free Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides: Biological Activities, Experimental Testing, and Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, É.M.D.; Macedo, L.M.D.; Tundisi, L.L.; Ataide, J.A.; Camargo, G.A.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mazzola, P.G. Coffee by-products in topical formulations: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffee Development Report|International Coffee Organization. Available online: https://ico.org/coffee-development-report-2/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Heeger, A.; Kosińska-Cagnazzo, A.; Cantergiani, E.; Andlauer, W. Bioactives of coffee cherry pulp and its utilisation for production of Cascara beverage. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monente, C.; Bravo, J.; Vitas, A.I.; Arbillaga, L.; De Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Coffee and spent coffee extracts protect against cell mutagens and inhibit growth of food-borne pathogen microorganisms. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Casal, S.; Alves, M.R.; Oliveira, M.B. Discrimination between arabica and robusta coffee species on the basis of their tocopherol profiles. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashin, A.; Yashin, Y.; Wang, J.; Nemzer, B. Antioxidant and Antiradical Activity of Coffee. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarharum, W.B.; Williams, D.J.; Smyth, H.E. Complexity of coffee flavor: A compositional and sensory perspective. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriot, I.; Le Quéré, J.-L.; Guichard, E. Interactions between coffee melanoidins and flavour compounds: Impact of freeze-drying (method and time) and roasting degree of coffee on melanoidins retention capacity. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.; Mussatto, S.; Teixeira, J.; Vilanova, M.; Oliveira, J. Increasing the Sustainability of the Coffee Agro-Industry: Spent Coffee Grounds as a Source of New Beverages. Beverages 2018, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondam, A.F.; Diolinda Da Silveira, D.; Pozzada Dos Santos, J.; Hoffmann, J.F. Phenolic compounds from coffee by-products: Extraction and application in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.; Juániz, I.; Monente, C.; Caemmerer, B.; Kroh, L.W.; De Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Evaluation of Spent Coffee Obtained from the Most Common Coffeemakers as a Source of Hydrophilic Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12565–12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalakshmi, K.; Rao, L.J.M.; Takano-Ishikawa, Y.; Goto, M. Bioactivities of low-grade green coffee and spent coffee in different in vitro model systems. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, J.; Estevinho, B.N.; Santos, L. Microencapsulation of natural antioxidants for food application—The specific case of coffee antioxidants—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldaiem, A.M.; Ali, A.H.; Shah, N.; Ayyash, M.; Mousa, A.H. Physicochemical analysis, rheological properties, and sensory evaluation of yogurt drink supplemented with roasted barley powder. LWT 2023, 173, 114319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, M.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Ghirardello, D.; Botta, C.; Rolle, L.; Guglielmetti, A.; Borotto Dalla Vecchia, S.; Zeppa, G. Coffee silverskin as nutraceutical ingredient in yogurt: Its effect on functional properties and its bioaccessibility. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4267–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Arias, J.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Vega-Castro, O.; Martínez-Monteagudo, S.I. Rheological, texture, structural, and functional properties of Greek-style yogurt fortified with cheese whey-spent coffee ground powder. LWT 2020, 129, 109523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, D.D.; Fuentes, S.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Ashman, H.; Dunshea, F.R. Cross-cultural effects of food product familiarity on sensory acceptability and non-invasive physiological responses of consumers. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elera, D.J.A.; Montes Villanueva, N.D.; Chunga Trelles, W.N. Whipped yogurt with organic panela and coffee: An innovation for the dairy industry. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2025, 28, e2024115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbae, J.; Koskei, R.; Mugendi, B. Effect of Addition of Coffee Extract on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Yoghurt. Eur. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2023, 5, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Ganguly, S.; Sarkar, U.; Das, S. Evaluation of rheological, physicochemical and sensory properties of low calorie coffee yogurt. Pharma Innov. J. 2017, 6, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, L. Textural characteristics and sensory evaluation of yogurt fortified with pectin extracted from steeped hawthorn wine pomace. Int. J. Food Eng. 2021, 17, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, P.; Ares, G. Sensory profiling, the blurred line between sensory and consumer science. A review of novel methods for product characterization. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.A. Invited Review: Sensory Analysis of Dairy Foods. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4925–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.; Sidel, J.L. Sensory Evaluation Practice; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; 408p. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices; Food Science Text Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-6487-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, M.C. Texture, Viscosity, and Food. In Food Texture and Viscosity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-0-12-119062-0. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, G.; Adjei, M.Y.B.; Agbenorhevi, J.K.; De-Souza, L.D.K.; Kpodo, F.M.; Pawar, G. Physical analysis and sensory properties of okra pectin chocolate during storage. JSFA Rep. 2025, 5, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, Z.; Erkaya-Kotan, T.; Şengül, M. Evaluation of physicochemical, microbiological, texture and microstructure characteristics of set-style yoghurt supplemented with quince seed mucilage powder as a novel natural stabiliser. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 114, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogendi, J.B.; De Steur, H.; Gellynck, X.; Makokha, A. Consumer evaluation of food with nutritional benefits: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.T.; Lu, P.; Parrella, J.A.; Leggette, H.R. Consumer Acceptance toward Functional Foods: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogue, J.; Coleman, T.; Sorenson, D. Determinants of consumers’ dietary behaviour for health-enhancing foods. Br. Food J. 2005, 107, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, Z.; Cherian, G.; Pasha, T.N.; Khattak, F.M.; Jabbar, M.A. Sensory evaluation and consumer acceptance of eggs from hens fed flax seed and 2 different antioxidants. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, A.; Annunziata, A.; Vecchio, R. Sociodemographic Factors Differentiating the Consumer and the Motivations for Functional Food Consumption. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, K. Environmental Consciousness, Purchase Intention, and Actual Purchase Behavior of Eco-Friendly Products: The Moderating Impact of Situational Context. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Category | Count | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 53 | 38.7% |
| Male | 84 | 61.3% | |
| Age Group | <18 | 12 | 8.8% |
| 18–25 | 29 | 21.2% | |
| 26–35 | 22 | 16.1% | |
| 36–50 | 32 | 23.4% | |
| Over 50 | 42 | 30.7% | |
| Yogurt Consumption | Never | 1 | 0.7% |
| Rarely | 20 | 14.6% | |
| Once per week | 26 | 19.0% | |
| 2–3 times per week | 59 | 43.1% | |
| Daily | 31 | 22.6% | |
| Coffee Consumption | Never | 19 | 13.9% |
| Rarely | 10 | 7.3% | |
| Once per week | 4 | 2.9% | |
| 2–3 times per week | 11 | 8.0% | |
| Daily | 93 | 67.9% | |
| Total respondents | 137 | 100% |
| Attribute | Series A | Series B | p-Value | p-Value (Adjusted) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aftertaste | 3.81 ± 1.20 | 3.99 ± 1.24 | 0.283 | 1.000 |
| Appearance | 3.97 ± 1.10 | 3.93 ± 1.12 | 0.848 | 1.000 |
| Aroma | 3.80 ± 1.05 | 3.97 ± 1.08 | 0.253 | 1.000 |
| Coffee–Yogurt Balance | 3.52 ± 1.08 | 3.66 ± 1.23 | 0.271 | 1.000 |
| Taste | 3.84 ± 1.04 | 3.99 ± 1.11 | 0.282 | 1.000 |
| Texture | 3.81 ± 1.30 | 4.19 ± 1.18 | 0.062 | 0.372 |
| Predictors | Odds Ratios | CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | 1.76 | 1.19–2.62 | 0.005 |
| Aroma | 1.73 | 1.19–2.51 | 0.005 |
| Taste | 2.24 | 1.41–3.57 | 0.001 |
| Coffee–Yogurt Balance | 1.63 | 1.14–2.34 | 0.008 |
| Aftertaste | 1.79 | 1.27–2.53 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maisoglou, I.; Koureas, M.; Dimitriou, L.; Meleti, E.; Alexandraki, M.; Kossyva, V.; Tzereme, A.; Vrontaki, M.; Manouras, V.; Manouras, A.; et al. Functional Goat Milk Yogurt Dessert Enriched with Antioxidant Extract from Spent Coffee Grounds: Sensory and Consumer Insights. Dietetics 2025, 4, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4030034
Maisoglou I, Koureas M, Dimitriou L, Meleti E, Alexandraki M, Kossyva V, Tzereme A, Vrontaki M, Manouras V, Manouras A, et al. Functional Goat Milk Yogurt Dessert Enriched with Antioxidant Extract from Spent Coffee Grounds: Sensory and Consumer Insights. Dietetics. 2025; 4(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaisoglou, Ioannis, Michalis Koureas, Lamprini Dimitriou, Ermioni Meleti, Maria Alexandraki, Vasiliki Kossyva, Anastasia Tzereme, Mariastela Vrontaki, Vasileios Manouras, Athanasios Manouras, and et al. 2025. "Functional Goat Milk Yogurt Dessert Enriched with Antioxidant Extract from Spent Coffee Grounds: Sensory and Consumer Insights" Dietetics 4, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4030034
APA StyleMaisoglou, I., Koureas, M., Dimitriou, L., Meleti, E., Alexandraki, M., Kossyva, V., Tzereme, A., Vrontaki, M., Manouras, V., Manouras, A., & Malisisova, E. (2025). Functional Goat Milk Yogurt Dessert Enriched with Antioxidant Extract from Spent Coffee Grounds: Sensory and Consumer Insights. Dietetics, 4(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4030034







