Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
Methodology
2. Advanced Observational Instruments and Radiative Modeling
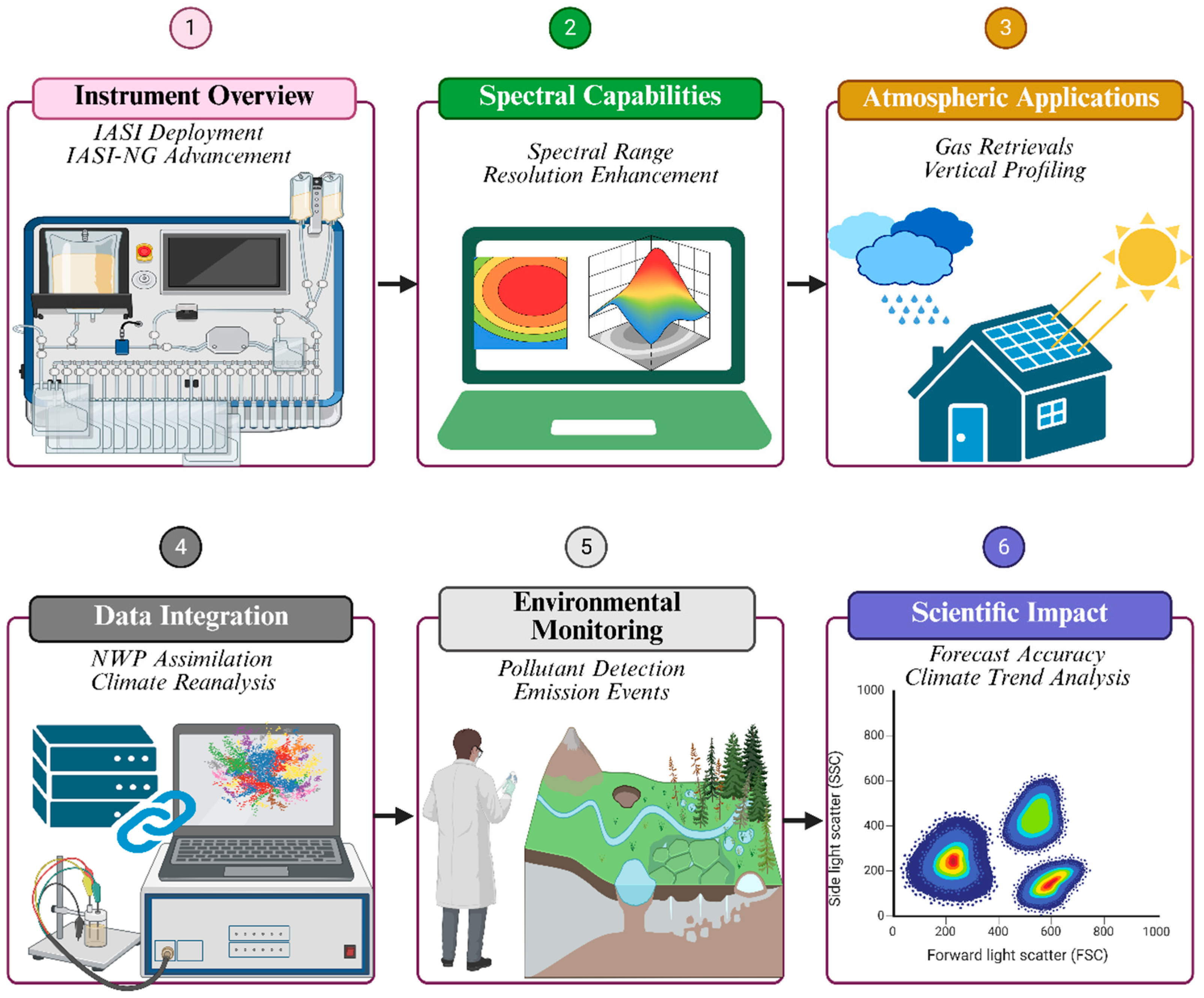
2.1. The Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI) and IASI-NG
2.2. Role of Radiative Transfer Models in Satellite Remote Sensing
- Model 1: Fundamentals of Radiative Transfer Models for Satellite Remote Sensing [39].
- Model 2: Calculation Framework for Atmospheric Retrievals from Hyperspectral Radiances Using RTMs.
3. Theoretical Foundations of Radiative Transfer
3.1. The Radiative Transfer Equation (RTE): From Schwarzschild to Deep Learning
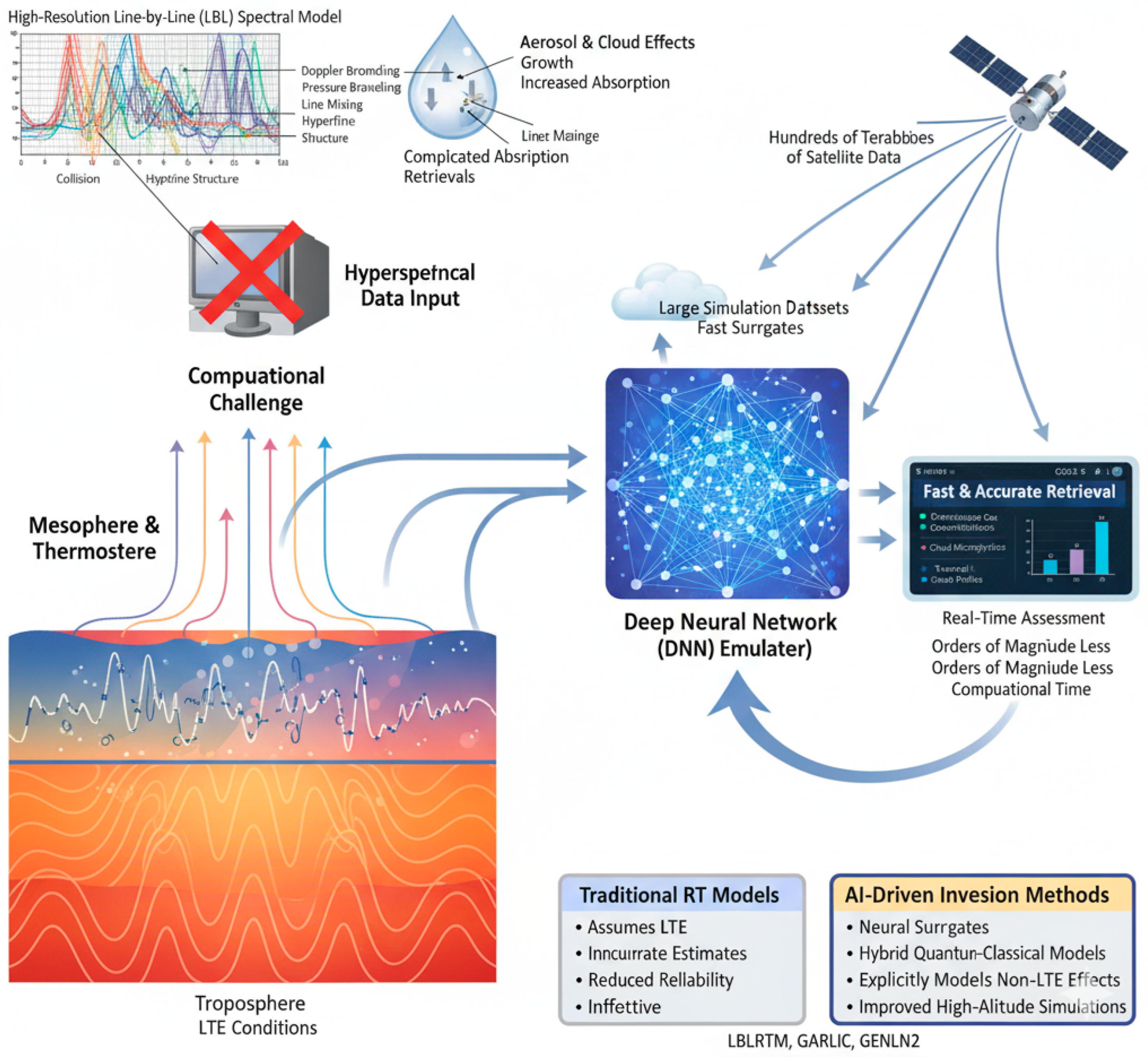
3.2. Computational Bottlenecks in Modern RT Solvers
3.3. Non-LTE and Spectral Complexity
- Model 3: Non-LTE Radiative Transfer and AI-Enhanced Atmospheric Retrievals.
4. Quantum Information Theory and Tensor Networks for Atmospheric Modelling
Quantum Machine Learning for Atmospheric Data Processing
5. Quantum-Inspired Machine Learning for Radiative Transfer
5.1. Fourier Neural Operators (FNOs): Spectral Learning in Radiative Physics
- Model 4: Fourier Neural Operators for Quantum-Inspired Radiative Transfer.
Quantum-Inspired Advances in Radiative Transfer Surrogates
5.2. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) vs. Quantum-Informed Models
5.3. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Learning Architectures
6. Neuromorphic Radiative Transfer and Edge AI for Atmospheric Modeling
6.1. Neuromorphic Computing for Atmospheric Radiative Models
6.2. Spike-Based Atmospheric Prediction
6.3. Edge Deployment in Satellites, UAVs, and IoT Networks
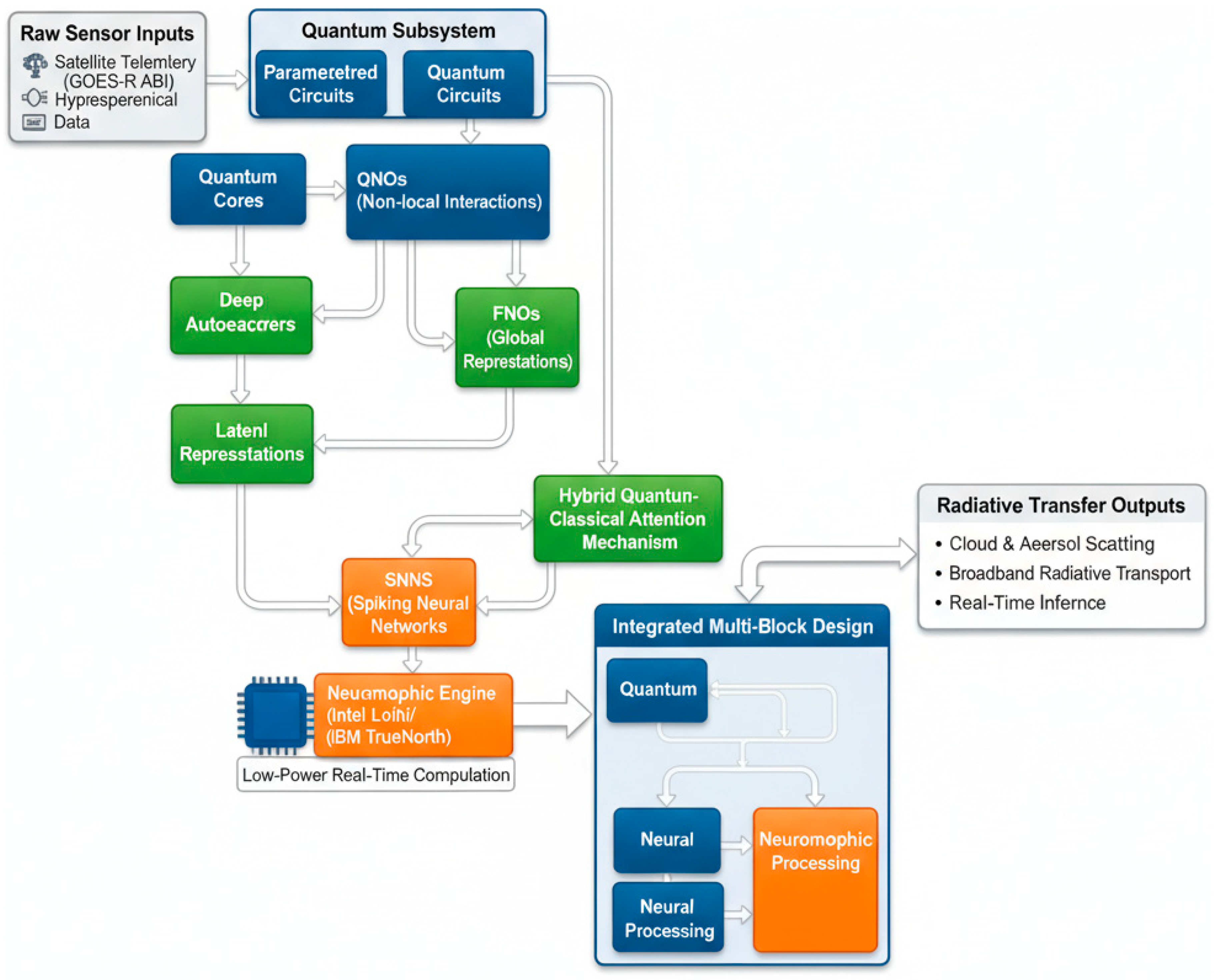
7. QINRT Framework
7.1. System Architecture: Integrating Quantum, Neural, and Neuromorphic Components
7.2. Dynamic Data Assimilation and Radiance Field Prediction
7.3. Benchmark Results and Cross-Dataset Validation
7.4. Disadvantages and Limitations of QINRT
8. Applications Across Earth and Planetary Sciences
8.1. Quantum-Augmented Climate Forecasting
8.2. Quantum Remote Sensing and Sensor Fusion
8.3. Biosignature Detection in Exoplanet Atmospheres
8.4. Interplanetary Radiative Transfer and Quantum Lidar
9. Securing Climate AI in the Quantum Era
9.1. Emerging Cyber Threats to Autonomous RT Models
9.2. Post-Quantum Cryptography for Data Integrity
9.3. Quantum Reservoir Computing for Extreme Climate Events
10. Limitations
11. Future Work
12. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor |
| DVS | Dynamic Vision Sensor |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| ERA5 | ECMWF Reanalysis v5 |
| FNO | Fourier Neural Operator |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| IASI | Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer |
| IASI-NG | Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer—Next Generation |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| PEPS | Projected Entangled Pair States |
| QAE | Quantum Autoencoder |
| QINRT | Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer |
| QML | Quantum Machine Learning |
| QNO | Quantum Neural Operator |
| RRTMG | Rapid Radiative Transfer Model for GCMs |
| RT | Radiative Transfer |
| SNN | Spiking Neural Network |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
References
- Johnson, B.T.; Dang, C.; Stegmann, P.; Liu, Q.; Moradi, I.; Auligne, T. The Community Radiative Transfer Model (CRTM): Community-focused collaborative model development accelerating research to operations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 104, E1817–E1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.P.; Johnson, M.S. EigenFlux: A Radiative Transfer Model for Systems with High Asymmetries. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Pitaval, R.-A.; Popović, B.M.; Qin, Y. Direct Satellite Access Using Multi-Dimensional Constellations. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 35th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Valencia, Spain, 2–5 September 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mellit, A. Artificial Intelligence technique for modelling and forecasting of solar radiation data: A review. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. 2008, 1, 52–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiano, M.; Cimini, D.; De Natale, M.P.; Di Paola, F.; Gallucci, D.; Larosa, S.; Marro, D.; Nilo, S.T.; Romano, F. Combining Passive Infrared and Microwave Satellite Observations to Investigate Cloud Microphysical Properties: A Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-W.; Lu, C.-H.; Liu, Q.; Collard, A.; Zhu, T.; Grogan, D.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Grumbine, R.; Bhattacharjee, P.S. The impact of aerosols on satellite radiance data assimilation using NCEP global data assimilation system. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Yazdani, M.H.; Azad, M.M.; Elahi, M.U.; Raouf, I.; Kim, H.S. Advancements in Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Laminated Composites: A Comprehensive Review. Mathematics 2024, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.O. Beyond the Equilibrium Assumption: Towards Non-LTE Analysis of Exoplanet Atmospheres. Ph.D. Thesis, UCL (University College London), London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Decin, L. Evolution and mass loss of cool aging stars: A daedalean story. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 59, 337–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collura, M.; Lami, G.; Ranabhat, N.; Santini, A. Tensor Network Techniques for Quantum Computation; SISSA Medialab Srl: Trieste, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, N. High-Dimensional Molecular Quantum Dynamics with Tensor-Trains and Quantum Computation. Ph.D. Thesis, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Bian, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, H.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Xiao, L. Single-pixel imaging based on deep learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.16869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, S.Y.-C.; Huang, W.-H.; Huang, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-J. Quantum-Enhanced Parameter-Efficient Learning for Typhoon Trajectory Forecasting. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.09395. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, M.; Liu, Y.-X. Quantum-Classical Computing for Time-Dependent Ion-Atom Collision Dynamics: Applications to Charge Transfer Cross Section Simulations. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.19374. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gallo, M.; Khaddam-Aljameh, R.; Stanisavljevic, M.; Vasilopoulos, A.; Kersting, B.; Dazzi, M.; Karunaratne, G.; Brändli, M.; Singh, A.; Müller, S.M.; et al. A 64-core mixed-signal in-memory compute chip based on phase-change memory for deep neural network inference. Nat. Electron. 2023, 6, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nau, M.A.; Vija, A.H.; Gohn, W.; Reymann, M.P.; Maier, A.K. Exploring the limitations of hybrid adiabatic quantum computing for emission tomography reconstruction. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granet, E.; Ghanem, K.; Dreyer, H. Practicality of a quantum adiabatic algorithm for chemistry applications. Phys. Rev. A 2025, 111, 022428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-M. Denoising quantum mixed states using quantum autoencoders. Quantum Inf. Process. 2024, 23, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, W.S.; Kowalski, A.F.; Flagg, L.; MacGregor, M.A.; Lim, O.; Radica, M.; Piaulet, C.; Roy, P.-A.; Lafrenière, D.; Benneke, B.; et al. Characterizing the near-infrared spectra of flares from TRAPPIST-1 during JWST transit spectroscopy observations. Astrophys. J. 2023, 959, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Earth Science Technology Office. Toward Quantum Enhanced Sensing and Measurements for Earth Observation in 2040; Technical Interchange Meeting Report; NASA Ames Research Center: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://esto.nasa.gov/files/NASA-QuantumSensing-TM_Report-Final.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Shamoo, Y. Adversarial Attacks and Defense Mechanisms in the Age of Quantum Computing. In Leveraging Large Language Models for Quantum-Aware Cybersecurity; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 301–344. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.K.J.; Swaroop, A.S.; Prasad, A.H.; Nithin, D.; Singh, T. Artificial Neural Networks in Cryptography: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions for Secure Systems. Front. Collab. Res. 2024, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri, B. Spectroscopic techniques conceptualized with the remote sensing of atmospheric carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2024, 59, 1344–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, M.; Tirelli, C.; Ceccherini, S.; Belotti, C.; Cortesi, U.; Palchetti, L. Synergistic retrieval and complete data fusion methods applied to simulated FORUM and IASI-NG measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 6723–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- August, T. Operational Sounding of Thermodynamic Variables in the Atmosphere. In Satellites for Atmospheric Sciences 2: Meteorology, Climate and Atmospheric Composition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 9–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, B.; Thépaut, J.-N.; Eyre, J. The Assimilation of Satellite Data in Numerical Weather Prediction Systems. In Satellites for Atmospheric Sciences 2: Meteorology, Climate and Atmospheric Composition; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 69–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.; Modani, M.; Islam, S.; Khare, M.; Srivastava, R.K. Evolution of Weather and Climate Prediction Systems. In Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies Against Climate Change in Natural Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 243–265. [Google Scholar]
- Grzegorski, M.; Poli, G.; Cacciari, A.; Jafariserajehlou, S.; Holdak, A.; Lang, R.; Vazquez-Navarro, M.; Munro, R.; Fougnie, B. Multi-Sensor Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Properties for Near-Real-Time Applications Using the Metop Series of Satellites: Concept, Detailed Description, and First Validation. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeed, R. IASI Ammonia Observations to Study Land-Use Change, Soil-Atmosphere Exchange and the Effect of Meteorology. Ph.D. Thesis, Sorbonne Université, Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tsivlidou, M. Ozone and Carbon Monoxide in the Tropical Trosphere, as Seen by Aircraft and Satellite Data; as Seen by Aircraft (IAGOS) and Satellite (IASI) Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier-Toulouse III, Toulouse, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mermigkas, M. Remote Sensing of Greenhouse Gases with FTIR Spectroscopy and Estimate of Their Emissions. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Sciences, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUTH), Thessaloniki, Greece, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dumez, J.-N.; Giraudeau, P. Fast 2D Solution-State NMR: Concepts and Applications; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.; Weng, B.; Wang, C.; Bedle, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.-M.; Crowell, S.; Koch, J. Multi-Scale Integrated Monitoring System for Enhancing Methane Emission Detection, Quantification & Prediction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Tiwari, G.; Singh, A.; Samanta, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Routray, A.; Kumar, S.; Patel, S.S.; Lodh, A. Tropical Cyclones Across Global Basins: Dynamics, Tracking Algorithms, Forecasting, and Emerging Scientometric Research Trends. Meteorol. Appl. 2025, 32, e70067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.; Singh, R.; Thapliyal, P. Synergy Between Polar-Orbiting and Geostationary Sensors in Estimating Near Surface Winds Over the Oceanic Region: A Tropical Cyclone Case Study. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2025, 53, 2901–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Luo, T.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y. Variation and comparison of cloud cover in MODIS and four reanalysis datasets of ERA-interim, ERA5, MERRA-2 and NCEP. Atmos. Res. 2023, 281, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleist, D.; Carley, J.R.; Collard, A.; Liu, E.; Liu, S.; Martin, C.R.; Thomas, C.; Treadon, R.; Vernieres, G. Data Assimilation Strategy and Development Plan for NCEP’s Environmental Modeling Center; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.-F.; Bauwens, M.; Doumbia, T.; Elguindi, N.; Darras, S.; Granier, C.; De Smedt, I.; Lerot, C.; Van Roozendael, M.; et al. Atmospheric impacts of COVID-19 on NOx and VOC levels over China based on TROPOMI and IASI satellite data and modeling. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, G.; Zerubia, J.; Serpico, S.B.; Benediktsson, J.A. Mathematical models and methods for remote sensing image analysis: An introduction. In Mathematical Models for Remote Sensing Image Processing: Models and Methods for the Analysis of 2D Satellite and Aerial Images; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, Y. Prediction of atmospheric carbon dioxide radiative transfer model based on machine learning. Front. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 6, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-W.; Lu, C.-H.; Johnson, B.T.; Dang, C.; Stegmann, P.; Grogan, D.; Ge, G.; Hu, M. The influence of aerosols on satellite infrared radiance simulations and Jacobians: Numerical experiments of CRTM and GSI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Venteo, A.B.; Garcia, J.L.; Berger, K.; Estévez, J.; Vicent, J.; Pérez-Suay, A.; Van Wittenberghe, S.; Verrelst, J. Gaussian Process Regression Hybrid Models for the Top-of-Atmosphere Retrieval of Vegetation Traits Applied to PRISMA and EnMAP Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J. Global characteristics of cloud macro-physical properties from active satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Res. 2024, 302, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yi, B.; Bi, L. Sensitivity of mixed-phase cloud optical properties to cloud particle model and microphysical factors at wavelengths from 0.2 to 100 µm. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ștefănie, H.I.; Radovici, A.; Mereuță, A.; Arghiuș, V.; Cămărășan, H.; Costin, D.; Botezan, C.; Gînscă, C.; Ajtai, N. Variation of aerosol optical properties over Cluj-Napoca, Romania, based on 10 years of AERONET data and MODIS MAIAC AOD product. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labzovskii, L.D.; Kenea, S.T.; Lindqvist, H.; Kim, J.; Li, S.; Byun, Y.-H.; Goo, T.-Y. Towards robust calculation of interannual CO2 growth signal from TCCON (total carbon column observing network). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; Hong, H. Comparison of total column and surface mixing ratio of carbon monoxide derived from the TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 precursor with in-situ measurements from extensive ground-based network over South Korea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, X.; Lu, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D. Improving the data quality of CO2 continuous emissions monitoring systems: In the context of China’s emissions trading scheme. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 115, 108037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Z. Methods, Progress and Challenges in Global Monitoring of Carbon Emissions from Biomass Combustion. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Garrett, K.; Liu, Q.; Maddy, E.S.; Ide, K.; Boukabara, S. A deep-learning-based microwave radiative transfer emulator for data assimilation and remote sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8819–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, T.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Song, L.; Xu, Z.; et al. Improving regional climate simulations based on a hybrid data assimilation and machine learning method. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, F.; Janett, G.; Belluzzi, L.; Alemán, T.D.P.; Ballester, E.A.; Bueno, J.T.; Benedusi, P.; Riva, S.; Krause, R. A numerical approach for modelling the polarisation signals of strong resonance lines with partial frequency redistribution. Numerical applications to two-term atoms and plane-parallel atmospheres. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.20968. [Google Scholar]
- Temgoua, F.M.; Nguimdo, L.A.; Njomo, D. Two-Stream Approximation to the Radiative Transfer Equation: A New Improvement and Comparative Accuracy with Existing Methods. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 41, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S. Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Using early rejection Markov chain Monte Carlo and Gaussian processes to accelerate ABC methods. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2025, 34, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doicu, A.; Mishchenko, M.I.; Efremenko, D.S.; Trautmann, T. Spectral spherical harmonics discrete ordinate method. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2021, 258, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Rath, A.; Yazici, Ö.; Slusallek, P. MARS: Multi-sample Allocation through Russian roulette and Splitting. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Papers; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Loveridge, J.R. Advancing the Satellite Remote Sensing of Heterogeneous Clouds Through the Development of a Tomographic Technique That Uses 3D Radiative Transfer. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.; Palma, M.G.; Hattink, M.; Rubio-Noriega, R.; Orosa, L.; Mutlu, O.; Bergman, K.; Azevedo, R. Optically connected memory for disaggregated data centers. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2022, 163, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Matilainen, M.; Taskinen, S.; Nordhausen, K. A review of second-order blind identification methods. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2022, 14, e1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, B.; Penna, M.; Viazzo, M.; Caprio, E.; Casacci, L.P.; Barbero, F.; Stefanini, I. Yeasts, arthropods, and environmental matrix: A triad to disentangle the multi-level definition of biodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, G.L.; Fauchez, T.J.; Kofman, V.; Alei, E.; Lee, E.K.; Janin, E.; Himes, M.D.; Leconte, J.; Leung, M.; Faggi, S.; et al. Modeling Atmospheric Lines by the Exoplanet Community (MALBEC) version 1.0: A CUISINES radiative transfer intercomparison project. Planet. Sci. J. 2024, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Zhou, W.; Cui, W.; Qi, Z. Research progress on hygroscopic agents for atmospheric water harvesting systems. Materials 2024, 17, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Tamizharasan, P.; Rahul, C. Design possibilities and challenges of DNN models: A review on the perspective of end devices. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5109–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.K. Advanced Deep Learning Frameworks for Pollution Modeling: Applications in Numerical Solving, Model Emulation, and Uncertainty-Aware Air Quality Forecasting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chetry, M.; Feng, R.; Babar, S.; Sun, H.; Zafar, I.; Mohany, M.; Afridi, H.I.; Khan, N.U.; Ali, I.; Shafiq, M.; et al. Early detection and analysis of accurate breast cancer for improved diagnosis using deep supervised learning for enhanced patient outcomes. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2025, 11, e2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Arevalo, I.; Iftekhar, A.; Manjunath, B. Methanemapper: Spectral absorption aware hyperspectral transformer for methane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 17609–17618. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, B.; Gentile, A.A.; Ghosh, A.; Elfving, V.E.; Jones, C.; Vodola, D.; Manobianco, J.; Weiss, H. Potential of quantum scientific machine learning applied to weather modeling. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 110, 052423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A. Unraveling Sentinel-5P Data Patterns: Advanced Pipeline for Comprehensive Atmospheric Analysis. Bachelor’s Thesis, Independent University Bangladesh, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, A.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Pumera, M. Low-dimensional materials for ammonia synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 5021–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Hanif, M.F.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Hanif, M.F.; Petros, F.B. Analyzing boron oxide networks through Shannon entropy and Pearson correlation coefficient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Analysis of Complex Dynamical Systems by Combining Recurrent Neural Networks and Mechanistic Models. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Soucasse, L. Radiative Transfer Modelling: Radiative Properties, Numerical Simulation and Coupled Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Saclay-CentraleSupélec, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guillén Pérez, A. Contribution to Enhancing the Cognitive Capability of Intelligent Transportation Systems Using Artificial Intelligence. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena, Murcia, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rayan, R.A.; Zafar, I.; Tsagkaris, C. Deep learning for health and medicine. In Deep Learning for Personalized Healthcare Services; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rayan, R.A.; Zafar, I.; Rajab, H.; Zubair, M.A.M.; Maqbool, M.; Hussain, S. Impact of IoT in biomedical applications using machine and deep learning. In Machine Learning Algorithms for Signal and Image Processing; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 339–360. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lai, C.; Hu, X. Transfer learning Fourier neural operator for solving parametric frequency-domain wave equations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuma, P.; Bender, F.A.-M.; Schuddeboom, A.; McDonald, A.J.; Seland, Ø. Machine learning of cloud types in satellite observations and climate models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 523–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.; Javaid, S.; Afzal, H.; Zafar, I.; Fayyaz, K.; ul Ain, Q.; Sharma, R. Exploring the multifunctional roles of quantum dots for unlocking the future of biology and medicine. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Penny, S.G. A regional hybrid gain data assimilation system and preliminary evaluation based on Radio Occultation reflectivity assimilation. SOLA 2022, 18, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z. A physics-incorporated deep learning framework for parameterization of atmospheric radiative transfer. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2023, 15, e2022MS003445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, D.; Voullième, D.C.; Buiter, S.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Vereecken, H.; González-Nicolás, A.; Wellmann, F. Perspectives of physics-based machine learning strategies for geoscientific applications governed by partial differential equations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 7375–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Mansoor, B.; Patwary, M.N.; Khan, N.M. Non-coherent and backscatter communications: Enabling ultra-massive connectivity in 6G wireless networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 38144–38186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffers, F.A. Seeing Beyond Pixels: Holography’s Mission to Craft the Ultimate Visual Experience. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kashif, M.; Shafique, M. Hqnet: Harnessing quantum noise for effective training of quantum neural networks in nisq era. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.08475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Heng, J.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Wang, J. Laser-Ironing Induced Capping Layer on Co-ZIF-L Promoting In Situ Surface Modification to High-Spin Oxide–Carbon Hybrids on the “Real Catalyst” for High OER Activity and Stability. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Zafar, I.; Shafiq, S.; Sehar, L.; Khalil, H.; Matloob, N.; Hina, M.; Muntaha, S.T.; Khan, H.; Khan, N.U.; et al. Deep learning-based computational approach for predicting ncRNAs-disease associations in metaplastic breast cancer diagnosis. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, K.; Puram, V.; Johnson, S.; Thomas, J.P. A Comprehensive Review of Quantum Circuit Optimization: Current Trends and Future Directions. Quantum Rep. 2025, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim-Guisbert, G.; Holian, M.; Giardino, S.; Vittal, V.; Koenig, J. A review on the potential applications and limitations of hardware approaches to quantum computing. Int. J. Stud. Proj. Report. 2025, 2, 203–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, P.; Dou, M.; Zheng, H.; Gu, Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Guo, G.-P. Improving the trainability of VQE on NISQ computers for solving portfolio optimization using convex interpolation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.05589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, V.K.; Quy, N.M.; Hoai, T.T.; Shaon, S.; Uddin, M.R.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.C.; Kaushik, A.; Chatzimisios, P. From Federated Learning to Quantum Federated Learning for Space-Air-Ground Integrated Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), Belgrade, Serbia, 25–27 November 2024; pp. 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Z. Transitioning from federated learning to quantum federated learning in internet of things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 27, 509–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Rashid, M.; Al-Kuwari, S.; Shafique, M. Alleviating barren plateaus in parameterized quantum machine learning circuits: Investigating advanced parameter initialization strategies. In Proceedings of the 2024 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Valencia, Spain, 25–27 March 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Anjimoon, S.; Baswaraju, S.; Sobti, R.; Ajmera, S.; Rana, A.; Hameed, A.A. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Approaches to Optimize Signal Processing in Massive MIMO Arrays. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Communication, Computer Sciences and Engineering (IC3SE), Gautam Buddha Nagar, India, 9–11 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.; Wild, A.; Orchard, G.; Sandamirskaya, Y.; Guerra, G.A.F.; Joshi, P.; Plank, P.; Risbud, S.R. Advancing neuromorphic computing with loihi: A survey of results and outlook. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karima, A.; AlKholeifya, A.; Choia, J.; Dhalla, J.; Hudaa, T.; Ranjekara, A.; Yousfia, Y.; Wischerta, D. Spiking Neural Network Design for on-board detection of methane emissions through Neuromorphic Computing. In Proceedings of the 75th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), Milan, Italy, 14–18 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.-F.; Gryllias, K. Brain-inspired spiking neural networks for industrial fault diagnosis: A survey, challenges, and opportunities. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2401.02429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, K.; Spiller, D.; Sabatini, R.; Amici, S.; Sasidharan, S.T.; Fayek, H.; Marzocca, P. Autonomous satellite wildfire detection using hyperspectral imagery and neural networks: A case study on australian wildfire. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, D.; Bono, F. An Application-Driven Survey on Event-Based Neuromorphic Computer Vision. Information 2024, 15, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, S.; Sears, B.; Schlager, S.; Kinnison, M.; Sublette, J.; Henderson, A. Real-time vision-based control of swap-constrained flight system with intel loihi 2. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.-H.; Zhong, H.-S.; Pan, F.; Chen, Z.-H.; Fu, R.; Su, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, P.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Leapfrogging Sycamore: Harnessing 1432 GPUs for 7× faster quantum random circuit sampling. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2025, 12, nwae317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.C.; Kundu, I.; Sharma, A.; Shivhare, P.; Afzal, A.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Park, S.G. Internet of Things integrated with solar energy applications: A state-of-the-art review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 24597–24652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikx, N.; Barhmi, K.; Visser, L.; de Bruin, T.; Pó, M.; Salah, A.; van Sark, W. All sky imaging-based short-term solar irradiance forecasting with Long Short-Term Memory networks. Sol. Energy 2024, 272, 112463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.; Keuninckx, L.; Gielen, G.; Catthoor, F. Neuromorphic Solutions for Sensor Fusion and Continual Learning Systems: Applications in Drone Navigation and Radar Sensing; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kahali, S.; Dey, S.; Kadway, C.; Mukherjee, A.; Pal, A.; Suri, M. Low-power lossless image compression on small satellite edge using spiking neural network. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hadrovic, A. Architecture on the Water. ISRG J. Arts Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2023, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Diana, L.; Dini, P. Review on Hardware Devices and Software Techniques Enabling Neural Network Inference Onboard Satellites. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poravanthattil, J. Fault Mitigation for Spiking-Neural-Network Classification of Neuromorphic Event Streams with Radiation-Induced Noise. Master’s Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Alqwider, W. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Advanced Wireless Networks Enabling Service and Spectrum Coexistence. Ph.D. Thesis, Mississippi State University, Starkville, MS, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Delic, D.; Afshar, S. Neuromorphic computing for compact lidar systems. In More-than-Moore Devices and Integration for Semiconductors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 191–240. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, D.; Pourreza, A.; Chakraborty, M.; Khalsa, S.D.S.; Brown, P.H. 3D radiative transfer modeling of almond canopy for nitrogen estimation by hyperspectral imaging. Precis. Agric. 2025, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Feng, T. Malware Analysis and Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Ma, C. Inversion of Aerosol Optical Depth: Incorporating Multi-Model Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4104612. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.; Giovanini, E.; Befus, K.; Marshall, E.; Allison, C. The use of UAV-based visible and multispectral thermal infrared data for active volcano monitoring and analysis: Test of a low-cost solution applied to the 2022 Meradalir eruption. Volcanica 2025, 8, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tat, L.W.; Schaeffer, H. BelNet: Basis enhanced learning, a mesh-free neural operator. Proc. R. Soc. A 2023, 479, 20230043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.K.; Rautela, K.S. Aerosol Atmospheric Rivers: Detection and Spatio-Temporal Patterns. In Aerosol Atmospheric Rivers: Availability, Spatiotemporal Characterisation, Predictability, and Impacts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Feng, T. Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Malware Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.B.; Dang, K.N. Comprehensive Review of Neuromorphic Systems. In Neuromorphic Computing Principles and Organization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 275–303. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, J.; Alikhani, S.; Malhotra, A.; Hamidi-Rad, S.; Alkhateeb, A. A Dataset Similarity Evaluation Framework for Wireless Communications and Sensing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.05556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, S.; Shafin, A.A.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Amin, M.; Shahir, R.S. Quantum-Enhanced Attention Mechanism in NLP: A Hybrid Classical-Quantum Approach. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.15630. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, G.; Xing, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Shan, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. A remote sensing technique for CO2 column density. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4016514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, A.R.; Pichuka, S.; Tripathi, A. Applications of sentinel-5p tropomi satellite sensor: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 20312–20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramôa, A.; Santos, L.P. Bayesian Quantum Amplitude Estimation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.04394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuGhanem, M. IBM quantum computers: Evolution, performance, and future directions. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Patil, A.; Sarkar, M.; Moorthi, S.M.; Dhar, D. Advancements in Data Processing and Calibration for the Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite (HySIS). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08917. [Google Scholar]
- Clerbaux, C.; Boynard, A.; Clarisse, L.; George, M.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Herbin, H.; Hurtmans, D.; Turquety, S.; Wespes, C.; Coheur, P.-F. Monitoring of atmospheric composition using the thermal infrared IASI/MetOp sounder. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6041–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Fang, S.; Sankarasubramanian, A.; Rad, A.M.; Kindl da Cunha, L.; Jennings, K.S.; Clarke, K.C.; Mazrooei, A.; Yeghiazarian, L. Comprehensive analysis of the NOAA National Water Model: A call for heterogeneous formulations and diagnostic model selection. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2023JD038534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomyts, E.G. Advancing the methods of geo-ecological forests monitoring under global warming. Resour. Environ. Inf. Eng. 2023, 5, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, M.; Shan, Y.; Shi, Y. Improved dust representation and impacts on dust transport and radiative effect in CAM5. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2021MS002845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Tan, C.; Wu, L.; Li, S.Z. Cosp: Co-supervised pretraining of pocket and ligand. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.12241. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Sangondimath, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Efficient and flexible aggregation and distribution of MODIS atmospheric products based on climate analytics as a service framework. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, Y. Radiative sensitivity quantified by a new set of radiation flux kernels based on the ECMWF Reanalysis v5 (ERA5). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 3001–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, A.; Bender, F.A.-M. Persistence and variability of Earth’s interhemispheric albedo symmetry in 19 years of CERES EBAF observations. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X. Quadranet v2: Efficient and sustainable training of high-order neural networks with quadratic adaptation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Z.-M.; Moradi, M.; Panahi, S.; Wang, Z.-H.; Lai, Y.-C. Machine-learning nowcasting of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. APL Mach. Learn. 2024, 2, 036103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, U.; Eswaran, V.; Murali, K.; Eswaran, V. Quantum-Based Predictive Modeling for Extreme Weather Events. In The Rise of Quantum Computing in Industry 6.0 Towards Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Feng, T. Detection of Malware by Deep Learning as CNN-LSTM Machine Learning Techniques in Real Time. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieneke, S.; Pacheco-Labrador, J.; Mahecha, M.D.; Poblador, S.; Vicca, S.; Janssens, I.A. Comparing the quantum use efficiency of red and far-red sun-induced fluorescence at leaf and canopy under heat-drought stress. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 311, 114294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, J.; Tzortziou, M.; Turner, K.J.; Goes, J.; Grunert, B. Chlorophyll dynamics from Sentinel-3 using an optimized algorithm for enhanced ecological monitoring in complex urban estuarine waters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabbert, D.; Petruccione, F. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Feature Extraction approach for Image Classification using Autoencoders and Quantum SVMs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ying, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Jiang, X.; Shuai, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, J. UNet-Att: A self-supervised denoising and recovery model for two-photon microscopic image. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.R.; Hansen, C.; Alexia, B.; Shamee, B.; Lloyd, B.; Beasley, A.; Brisken, W.; Paganelli, F.; Watts, G.; O’Neil, K.; et al. A planetary radar system for detection and high-resolution imaging of nearby celestial bodies. Microw. J. 2022, 65, 22–42. [Google Scholar]
- Karmous, S.; Adem, N.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Samarakoon, S. How can optical communications shape the future of deep space communications? A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 27, 725–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.I.; Kurunathan, H.; Eldefrawy, M.H.; Gruian, F.; Jonsson, M. Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of Securing Internet of Autonomous Vehicles with Lightweight Authentication. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 24207–24222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Razzaq, A.; Tariq, W.; Hameed, A.; Rehman, A.; Razzaq, K.; Sarfraz, S.; Rajput, N.A.; Zaki, H.E.M.; Shahid, M.S.; et al. Spectral Intelligence: AI-Driven Hyperspectral Imaging for Agricultural and Ecosystem Applications. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, P.; Gao, D.; Wu, O. Data poisoning in deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.22759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.R.; Kumar, S.A.; Reddy, A.G.; Das, A.K. Quantum secure authentication and key agreement protocols for IoT-enabled applications: A comprehensive survey and open challenges. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024, 54, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui Dekkaki, K.; Tasic, I.; Cano, M.-D. Exploring Post-Quantum Cryptography: Review and Directions for the Transition Process. Technologies 2024, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, H.; Gupta, D.S. A survey on lattice-based security and authentication schemes for smart-grid networks in the post-quantum era. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 36, e8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, P.D.O.A. Blockchain Technology Adoption and Environmental Performance. SSRN 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govia, L.C.G.; Ribeill, G.J.; Rowlands, G.E.; Krovi, H.K.; Ohki, T.A. Quantum reservoir computing with a single nonlinear oscillator. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 013077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujal, P.; Martínez-Peña, R.; Nokkala, J.; García-Beni, J.; Giorgi, G.L.; Soriano, M.C.; Zambrini, R. Opportunities in quantum reservoir computing and extreme learning machines. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2021, 4, 2100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Gao, Q.; Pradel, K.C.; Yasuoka, K.; Yamamoto, N. Natural quantum reservoir computing for temporal information processing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Beni, J.; Giorgi, G.L.; Soriano, M.C.; Zambrini, R. Scalable photonic platform for real-time quantum reservoir computing. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 20, 014051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornjača, M.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhao, C.; Wurtz, J.; Weinberg, P.; Hamdan, M.; Wang, S.T. Large-scale quantum reservoir learning with an analog quantum computer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.02553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, V.; Sohoni, M.M.; Presutti, F.; Malia, B.K.; Ma, S.Y.; Yanagimoto, R.; McMahon, P.L. Large-scale quantum reservoir computing using a Gaussian Boson Sampler. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Alkhalaf, O.H.; Alam, M.S.; Tiwari, S.P.; Shafiullah, M.; Al-Judaibi, S.M.; Al-Ismail, F.S. Climate change through quantum lens: Computing and machine learning. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 8, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgillo, A.R.; Sacchi, M.F.; Macchiavello, C. Detecting Markovianity of Quantum Processes via Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Baroni, A.; Bennink, R.; Buchs, G.; Pérez, E.A.C.; Eisenbach, M.; da Silva, R.F.; Meena, M.G.; Gottiparthi, K.; Groszkowski, P.; et al. Integrating quantum computing resources into scientific HPC ecosystems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2024, 161, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, J.N.; Madry, S. Space systems, quantum computers, big data and sustainability: New tools for the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. In Artificial Intelligence for Space: AI4SPACE; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 53–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wei, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Highly Programmable Haptic Decoding and Self-Adaptive Spatiotemporal Feedback Toward Embodied Intelligence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2500633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Approach | Data | Physics Constraints | Spectral Range | Reported Error | Speed | Generalization | Novelty Highlight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DISORT | Classical RT datasets | Fully enforced | UV–IR | Baseline (low) | Slow | Mission-specific | Standard classical solver |
| RRTMG | Atmospheric GCM data | Partially enforced | IR | Moderate | Moderate | Limited | Widely used in climate models |
| ML Surrogates (state-compression) | AQuA, NOAA | Limited | UV–IR | 10–20% RMSE | 5–20× faster | Limited cross-mission | Compresses state only; operator not captured |
| Tensor-network/Quantum-inspired | Small-scale simulations | Partial | Narrow | 5–15% RMSE | Moderate | Limited | Early-stage high-dimensional compression; limited validation |
| QINRT | AQuA-2024, NOAA-QClim | Fully enforced via physics-aware networks | UV–IR | 37–39% RMSE reduction vs 6S | Up to 10× faster | Cross-mission validated | Operator-aware surrogate; preserves physical constraints and generalization |
| Platform/Project | Neuromorphic Hardware | Primary Application Domain | Operational Environment | Key Capabilities/Highlights | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpaceX CubeSat | Intel Loihi | Onboard cloud radiative forcing estimation | LEO Satellite | Demonstrates feasibility of real-time RT estimation and energy-efficient atmospheric inference at the satellite edge. | [107] |
| IoT Solar Nodes | IBM TrueNorth | Adaptive irradiance sensing and sampling | Terrestrial/Remote | Enables autonomous irradiance monitoring and energy-aware sampling for long-term IoT deployment. | [108] |
| UAV Radiation Tracker | Custom SNN ASIC (Zurich) | Autonomous flight path rerouting (RT-based) | UAV/Mid-Troposphere | Integrates neuromorphic control for adaptive flight navigation and radiative sensing. | [109] |
| NASA NeuroCube | SNN Core Array | Hyperspectral data compression (Earth observation) | LEO Satellite | Applies neuromorphic encoding to achieve efficient hyperspectral data management in orbit. | [107] |
| DARPA FastNRT | Neuromorphic FPGA | Modeling of aerosols and radiative scattering | Tactical/Defense | Employs event-driven computation for rapid, low-power RT modeling and atmospheric scattering analysis. | [110] |
| Agro-RT IoT Network | IBM TrueNorth | Crop canopy reflectance estimation (NDVI-based RT) | Agricultural Fields | Supports precision agriculture through adaptive neuromorphic sensing of vegetation indices. | [111] |
| Neuromorphic Air Balloon | Intel Loihi 2 | Atmospheric scattering and thermal IR estimation | High-Altitude Balloons | Facilitates onboard adaptive learning and real-time RT inference in stratospheric environments. | [112] |
| Smart Dust Sensor Grid | BrainScaleS-2 (Heidelberg) | Distributed aerosol optical depth (AOD) sensing | Urban IoT Network | Utilizes spiking networks for synchronized, low-power distributed RT inversion and atmospheric sensing. | [113] |
| Seismic RT UAV | SpiNNaker-2 (Manchester) | Radiative heat estimation in volcanic regions | UAV/Hazard Zones | Demonstrates neuromorphic onboard processing for real-time hazard mapping and thermal radiation tracking. | [114] |
| Arctic RT Monitoring | BrainChip Akida | Snow albedo RT estimation and data compression | Polar Station | Enables autonomous, ultra-low-power operation in extreme cold environments for prolonged atmospheric monitoring. | [37] |
| Dataset | RMSE (QINRT) | RMSE (6S) | Relative Improvement Trend | Visible Bias (nm) | IR Bias (nm) | Computational Efficiency | Convergence Behavior | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IASI/MetOp Hyperspectral Radiance | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [126] |
| NOAA-QClim | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [127,128] |
| CAM5-COSP | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [129,130] |
| MODIS-Atmosphere | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [131] |
| ERA5-Radiative Flux | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [132] |
| CERES-EBAF | ≈ Lower RMSE | ≈ Higher RMSE | Reported 30–40% accuracy gain | Reduced | Reduced | Faster | Earlier | [133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhtar, M.S. Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence. AppliedMath 2025, 5, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5040145
Akhtar MS. Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence. AppliedMath. 2025; 5(4):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5040145
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhtar, Muhammad Shoaib. 2025. "Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence" AppliedMath 5, no. 4: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5040145
APA StyleAkhtar, M. S. (2025). Quantum-Inspired Neural Radiative Transfer (QINRT): A Multi-Scale Computational Framework for Next-Generation Climate Intelligence. AppliedMath, 5(4), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath5040145






