Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of the Compound
2.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
Computational Methodology for Michael Addition Feasibility
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Methodology
2.5. In Silico Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
2.6. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.7. Assessment of MepA and NorA Efflux Pump Inhibition via the Ethidium Bromide Assay
2.8. Evaluation of the Modulatory Activity of 4CpC on Antibiotic Resistance
2.9. Analysis of the Compound’s Effect on DNA
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Docking
Computational Analysis of Michael Addition Feasibility
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.3. In Silico Pharmacokinetic Predictions
3.4. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
3.5. Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps: Ethidium Bromide Assay Outcomes
3.6. Modulatory Effects of 4CpC on Antibiotic Resistance
3.7. Effects of the Compound on DNA Integrity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; 72p. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, A.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Potocki, L. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance-A Short Story of an Endless Arms Race. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdová, D.; Ruml, T.; Viktorová, J. Mechanism of Staphylococcal Resistance to Clinically Relevant Antibiotics. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 77, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Singh, D.V. Efflux Pumps: Gatekeepers of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Microb. Cell 2024, 11, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.S.; Victorelli, F.D.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. A Review of Analytical Methods for P-Coumaric Acid in Plant-Based Products, Beverages, and Biological Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, B.; Wicha, J.; Piechota, M.; Wolska, K.; Grużewska, A. Antibiofilm Activity of Trans-Cinnamaldehyde, p-Coumaric, and Ferulic Acids on Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Turkish J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Rao, S.; Sun, J.; Ma, C.; Li, J. P-Coumaric Acid Kills Bacteria through Dual Damage Mechanisms. Food Control 2012, 25, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, B.; Cheng, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, R. De Novo Biosynthesis of P-Coumaric Acid in E. Coli with a Trans-Cinnamic Acid 4-Hydroxylase from the Amaryllidaceae Plant Lycoris Aurea. Molecules 2018, 23, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribaudo, G. Natural Products Chemistry: Advances in Synthetic, Analytical and Bioactivity Studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Opportunities for Natural Products in 21st Century Antibiotic Discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokoane, T.L.; Kemboi, D.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Famuyide, I.M.; McGaw, L.J.; Tembu, V.J. Extractives from Artemisia Afra with Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Properties. Plants 2023, 12, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, N.; Xu, R.; Li, G.; Dong, H.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Fan, M.; Wei, X. Deciphering the Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of P-Coumaric Acid against Alicyclobacillus Acidoterrestris and Its Application in Apple Juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 378, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefo Kengne, N.; Wangso, H.; Silvère Gade, I.; Laya, A.; Paul Bayang, J.; Bargui Koubala, B.; Laurent, S.; Henoumont, C.; Talla, E. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of a New Phenolic Coumpound from the Roots Barks of Cassia Arereh Delile (Fabaceae). Results Chem. 2024, 11, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Cao, S.; Liu, J. Sesquiterpenes and Monoterpenes from the Leaves and Stems of Illicium Simonsii and Their Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iawsipo, P.; Sangnim, T.; Thalang, P.P.N.; Chernchom, R.; Bantao, R.; Luangpraditkun, K. Bioactivities and Promising Active Compounds of Etlingera Pavieana (Pierre Ex Gagnep) R.M.Sm. Rhizome Extract for Dermatological Applications. Nat. Resour. Hum. Heal. 2025, 5, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Melo, A.K.; da Nóbrega Alves, D.; Queiroga Gomes da Costa, P.C.; Pereira Lopes, S.; Pergentino de Sousa, D.; Queiroga Sarmento Guerra, F.; Vieira Sobral, M.; Gomes Moura, A.P.; Scotti, L.; Dias de Castro, R. Antifungal Activity, Mode of Action, and Cytotoxicity of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: A Promising New Molecule. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202400330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, É.P.; Alves, D.D.N.; Lopes, S.P.; Lazarini, J.G.; Rosalen, P.L.; de Sousa, D.P.; de Castro, R.D. Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity, and Toxicological Evaluation of a p-Coumaric Acid Derivative as a Potential New Antibacterial Agent. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, lxaf065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2025 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1516–D1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1263, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS Documentation, GROMACS 2024.1. Available online: https://manual.gromacs.org/documentation/2024.1/manual-2024.1.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved Side-chain Torsion Potentials for the Amber Ff99SB Protein Force Field. Proteins 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R.G.; Sharanya, C.S.; Jayanandan, A.; Haridas, M.; Edwin Hillary, V.; Rajiv Gandhi, S.; Sridharan, G.; Sivasubramanian, R.; Silva Vasconcelos, A.B.; Montalvão, M.M.; et al. Multitargeted Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation Studies of Flavonoids and Volatile Components from the Peel of Citrus Sinensis L. (Osbeck) against Specific Tumor Protein Markers. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 3051–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, R.; Harvey, J.N.; Mulholland, A.J. A Practical Guide to Modelling Enzyme-Catalysed Reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3025–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. Gromacs: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A Message-Passing Parallel Molecular Dynamics Implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GROMACS. GROMACS 2023.1 Manual-Release Notes. Available online: https://manual.gromacs.org/documentation/current/release-notes/2023/2023.1.html (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Stroet, M.; Caron, B.; Visscher, K.M.; Geerke, D.P.; Malde, A.K.; Mark, A.E. Automated Topology Builder Version 3.0: Prediction of Solvation Free Enthalpies in Water and Hexane. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 5834–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Freitag, F.; Gattin, Z.; Haberkern, H.; Jaun, B.; Siwko, M.; Vyas, R.; Vangunsteren, W.F.; Dolenc, J. Validation of the GROMOS 54A7 Force Field Regarding Mixed α/β-Peptide Molecules. Helv. Chim. Acta 2012, 95, 2562–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and Testing of the GROMOS Force-Field Versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondi, A. Van Der Waals Volumes and Radii. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemkul, J. From Proteins to Perturbed Hamiltonians: A Suite of Tutorials for the GROMACS-2018 Molecular Simulation Package [Article v1.0]. Living J. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. PkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, P.R.; de Araújo, A.C.J.; Araújo, I.M.; de Almeida, R.S.; Borges, J.A.O.; Paulo, C.L.R.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.M.; Miranda, G.M.; Araújo-Neto, J.B.; Nascimento, I.J.S.; et al. Thiazine-Derived Compounds in Inhibiting Efflux Pump in Staphylococcus aureus K2068, MepA Gene Expression, and Membrane Permeability Alteration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, R.S.; Freitas, P.R.; de Araujo, A.C.J.; Tintino, S.R.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Miranda, G.M.; Sigueira, G.M.; Gonçalves, S.A.; Carvalho, D.T.; de Souza, T.B.; et al. Liposomal Formulation with Thiazolic Compounds against Bacterial Efflux Pumps. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misba, L.; Zaidi, S.; Khan, A.U. A Comparison of Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Phenothiazinium Dyes between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacterial Biofilm. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, W.; Shen, Q.; Ke, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bian, H. Natural Phenolics as Multitarget Antimicrobials for Food Preservation: Mechanisms of Action. Food Chem. X 2025, 31, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yao, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Z. The Phosphatidylglycerol Phosphate Synthase PgsA Utilizes a Trifurcated Amphipathic Cavity for Catalysis at the Membrane-Cytosol Interface. Curr. Res. Struct. Biol. 2021, 3, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luévano-Martínez, L.A.; Dunca, A.L. Origin and Diversification of the Cardiolipin Biosynthetic Pathway in the Eukarya Domain. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha Jyothi, R.S.; Sripathi, M.P.; Thirupathi, P. Recent Advances in Base-Assisted Michael Addition Reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2022, 26, 1264–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chang, J.S.; Griffor, M. Structure of the Adenylation Domain of NAD+-Dependent DNA Ligase from Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2009, 65, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.M.; D’Andréa, É.D.; Lee, C.W.; Soares, A.; Jakoncic, J.; Desbonnet, C.; Garcia-Solache, M.; Rice, L.B.; Page, R.; Peti, W. The Structures of Penicillin-Binding Protein 4 (PBP4) and PBP5 from Enterococci Provide Structural Insights into -Lactam Resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 18574–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, B.D.; Patel, D.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Mutagenesis and Modeling to Predict Structural and Functional Characteristics of the Staphylococcus aureus MepA Multidrug Efflux Pump. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolár, M.H.; Hobza, P. Computer Modeling of Halogen Bonds and Otherσ-Hole Interactions. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5155–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawley, D.N.; Sauer, D.B.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Koide, A.; Jedhe, G.S.; Suwatthee, T.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Arora, P.S.; et al. Structural Basis for Inhibition of the Drug Efflux Pump NorA from Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjeddou, A.; Abbaz, T.; Gouasmia, A.K.; Villemin, D. Molecular Structure, HOMO-LUMO, MEP and Fukui Function Analysis of Some TTF-Donor Substituted Molecules Using DFT (B3LYP) Calculations. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, J.; Farnia, P.; Farnia, P.; Ghanavi, J.; Velayati, A.A. Molecular Dynamic Simulations and Molecular Docking as a Potential Way for Designed New Inhibitor Drug without Resistance. Tanaffos 2022, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fukutani, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Iwata, S.; Satoh, H. G-RMSD: Root Mean Square Deviation Based Method for Three-Dimensional Molecular Similarity Determination. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanov, M.Y.; Bogatyreva, N.S.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Radius of Gyration as an Indicator of Protein Structure Compactness. Mol. Biol. 2008, 42, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Tripathi, T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Protein and Protein–Ligand Complexes. In Computer-Aided Drug Design; Singh, D.B., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.A.; Levin, D.A. Electrospray Molecular Dynamics Simulations Using an Octree-Based Coulomb Interaction Method. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 033302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robalo, J.R.; Streacker, L.M.; Mendes de Oliveira, D.; Imhof, P.; Ben-Amotz, D.; Verde, A.V. Hydrophobic but Water-Friendly: Favorable Water-Perfluoromethyl Interactions Promote Hydration Shell Defects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tintino, S.R.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.M.; Campina, F.F.; Costa, M.S.; Cruz, R.P.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Andrade, J.C.; Sousa, E.O.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; et al. Cholesterol and Ergosterol Affect the Activity of Staphylococcus aureus Antibiotic Efflux Pumps. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 104, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, K.; Banerjee, A.; Jana, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Maiti, S.; Pati, B.R.; Mohapatra, P.K. Das Molecular Exposition of Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Efficacy by p-Coumaric Acid from an Edible Mushroom Termitomyces Heimii: In Vitro and in Silico Approach. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanufacturing 2023, 3, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijk, E.; Wittekoek, B.; Kuijper, E.J.; Smits, W.K. DNA Replication Proteins as Potential Targets for Antimicrobials in Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. PkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures (Theory-How to Enterpret PkCSM Result). Available online: https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/pkcsm/theory (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Mohamed, A.A.; El-Kadi, A. P-Glycoprotein Effects on Drugs Pharmacokinetics and Drug-Drug- Interactions and Their Clinical Implications. Libyan J. Pharm. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. In Silico Prediction of Human Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters with Improved Accuracy. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3968–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaretzki, J.; Matlock, M.; Swamidass, S.J. XenoSite: Accurately Predicting Cyp-Mediated Sites of Metabolism with Neural Networks. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 3373–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grime, K.H.; Barton, P.; McGinnity, D.F. Application of in Silico, in Vitro and Preclinical Pharmacokinetic Data for the Effective and Efficient Prediction of Human Pharmacokinetics. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, Z.d.S.; Macêdo, N.S.; Dantas, D.d.M.; Barbosa, C.R.d.S.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.d.M.; Tintino, S.R.; Alencar, G.G.; Silva, E.; Nunes, M.; Machado, M. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Inhibitory Activity of the NorA and TetK Efflux Pumps of Staphylococcus aureus by p -Coumaric Acid. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 200, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, J.N.; de Andrade Ferreira Barreto, J.; de Alcântara Oliveira, F.A.; Haydée Lima Ferreira, J.; Dias Rufino Arcanjo, D.; Emidio Sampaio Nogueira, C.; Machado Marinho, M.; dos Santos, H.S.; Maria Lins Rolim, H.; de Siqueira-Júnior, J.P.; et al. ADMET Study and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Efflux Pumps by a Synthetic P-Aminochalcone. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Misra, A.; Banerjee, S.; Dam, B. Adaptation of Ethidium Bromide Fluorescence Assay to Monitor Activity of Efflux Pumps in Bacterial Pure Cultures or Mixed Population from Environmental Samples. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Coopoosamy, R.M.; Gumede, N.J.; Sabiu, S. Computational Insights and In Vitro Validation of Antibacterial Potential of Shikimate Pathway-Derived Phenolic Acids as NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alegría, A.M.; Anduro-Corona, I.; Pérez-Martínez, C.J.; Corella-Madueño, M.A.G.; Rascón-Durán, M.L.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H. Quantification of DNA through the Nanodrop Spectrophotometer: Methodological Validation Using Standard Reference Material and Sprague Dawley Rat and Human DNA. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8896738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Analysis of DNA by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019, 2019, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



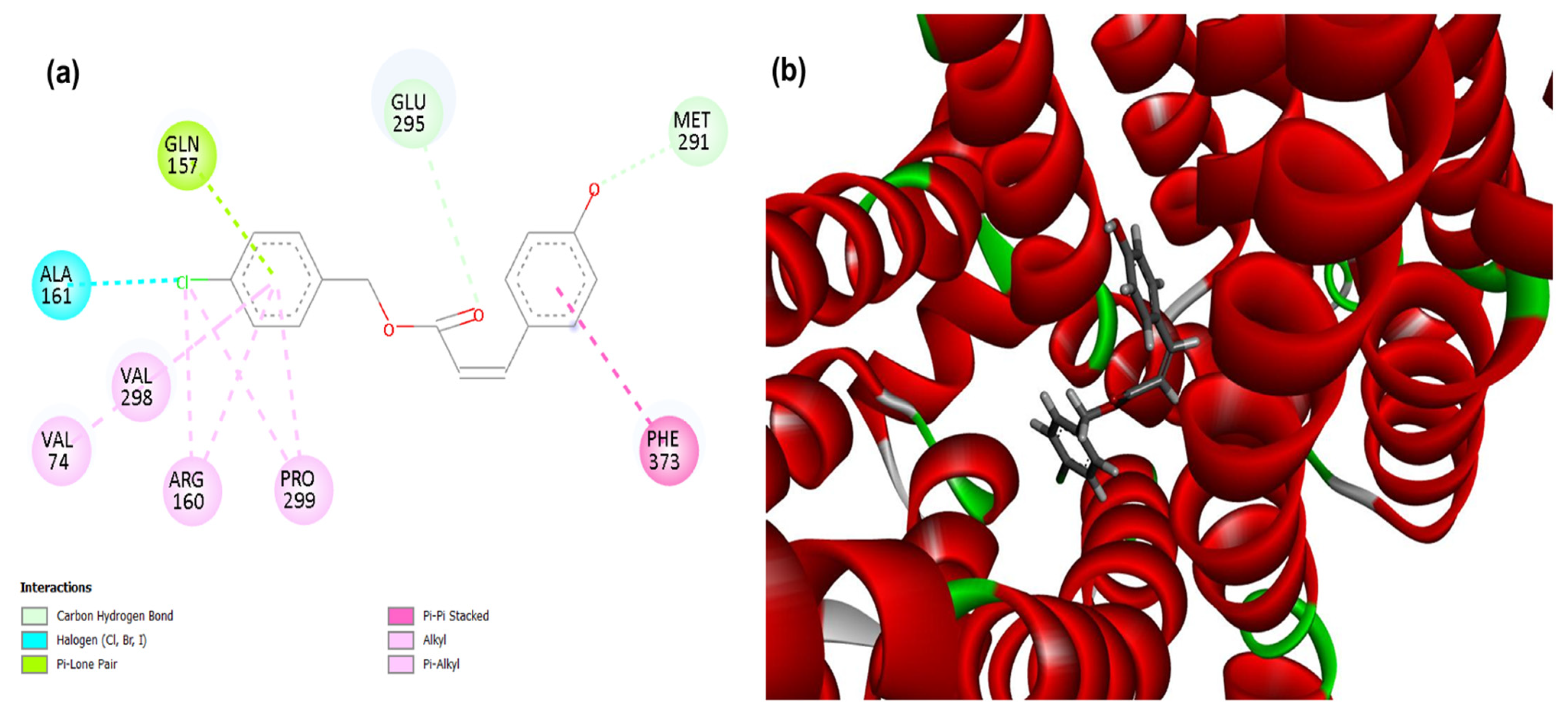
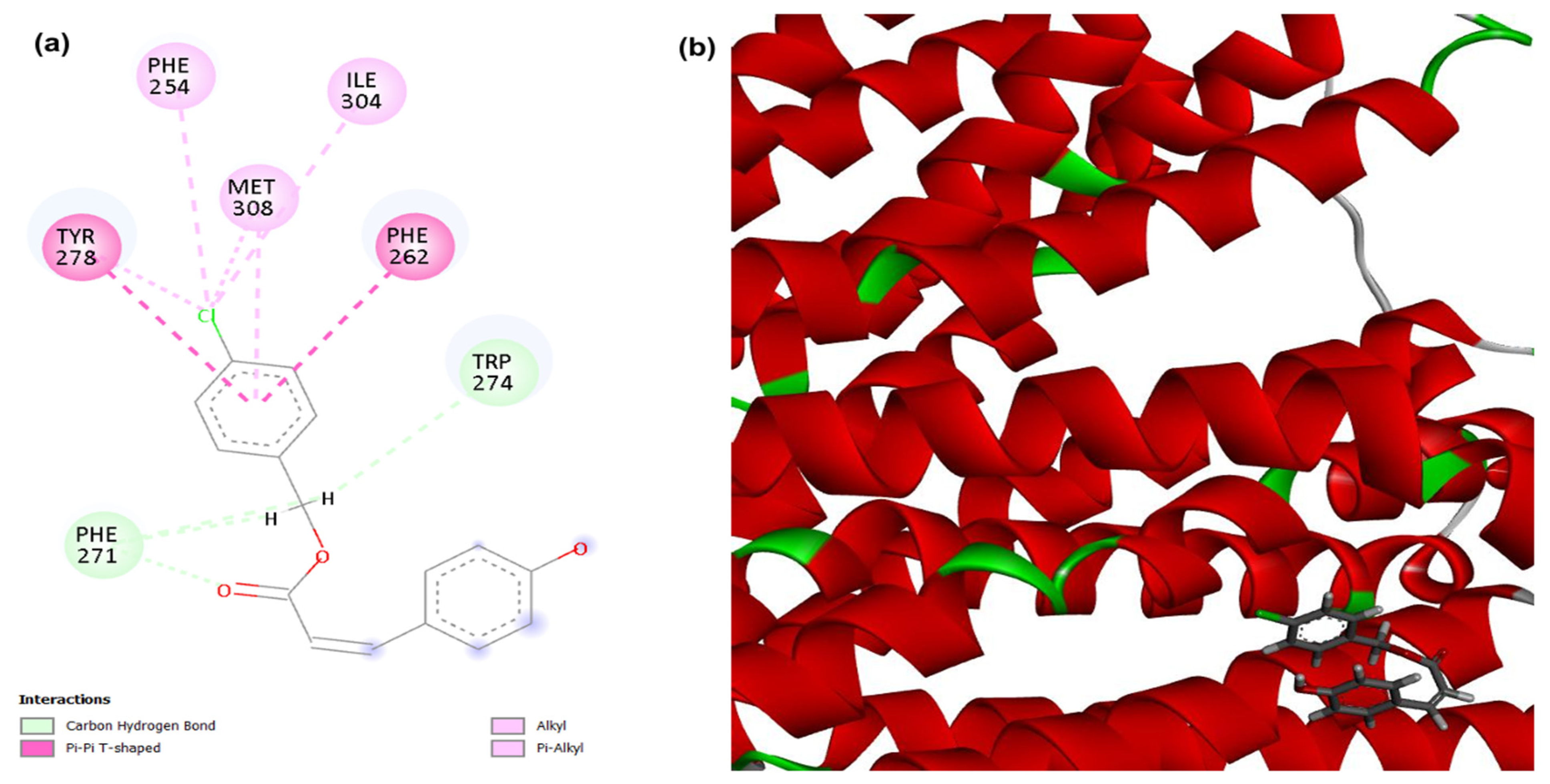



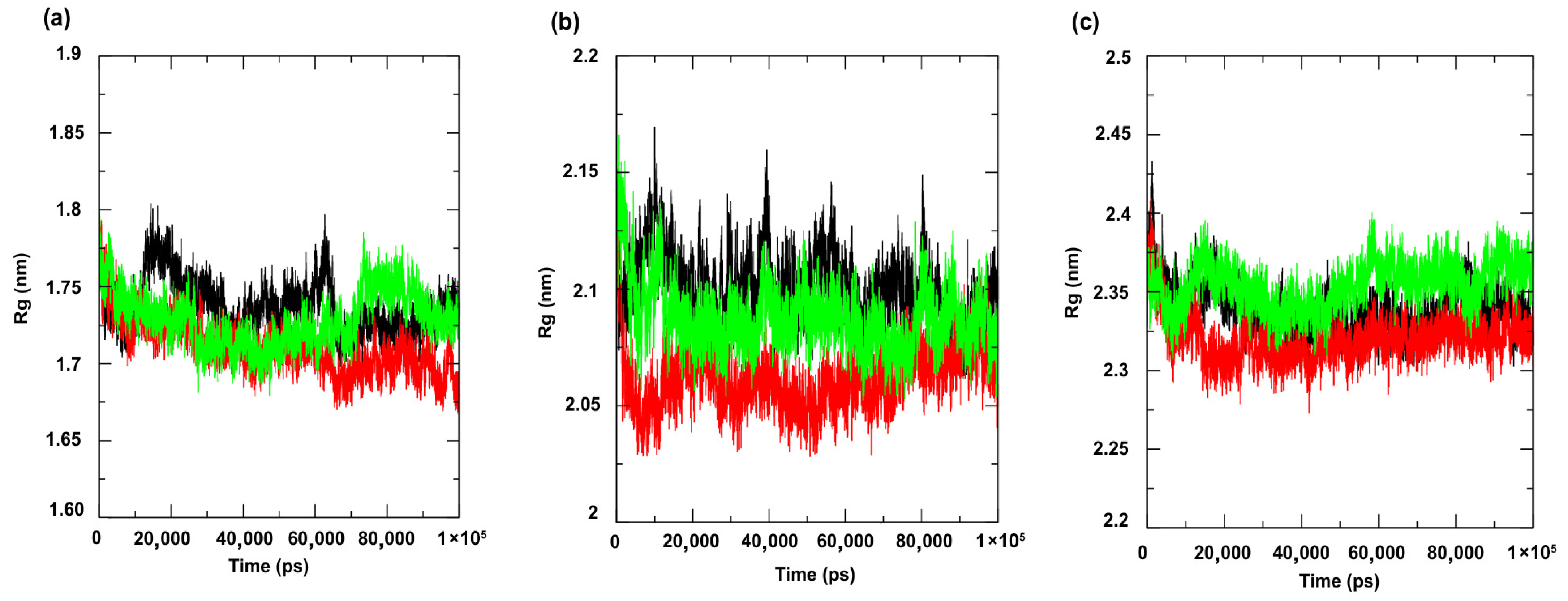
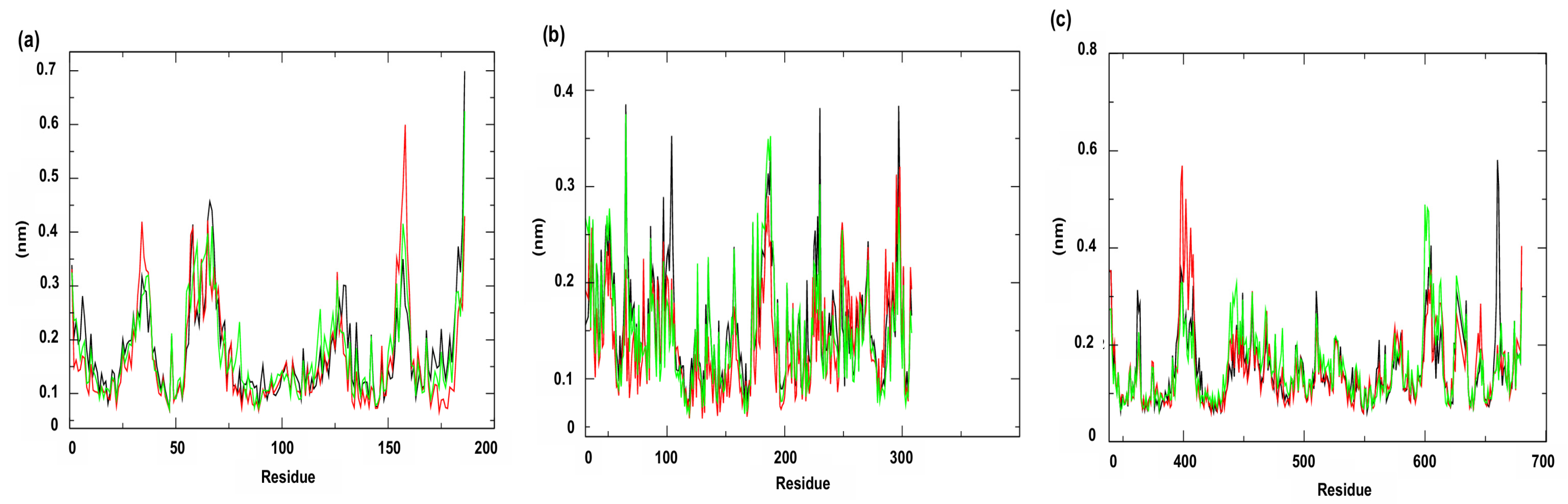




| Compounds | PgsA | DNA Ligase | PBP4 | MepA | NorA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4CpC | −113.343 | −105.397 | −70.920 | −123.85 | −108.877 |
| Control | −102.591 | −101.643 | −108.045 | −86.926 | −93.487 |
| Enzyme | Compound | Coulomb Energy (kJ·mol−1) | Lennard-Jones Energy (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PgsA | 4CpC | −241.229 | −96.147 * |
| Control | −102.851 | −97.673 | |
| DNA ligase | 4CpC | −258.000 | −113.223 |
| Control | −26.676 | −190.275 | |
| PBP4 | 4CpC | −301.038 | −98.6339 |
| Control | −124.426 | −105.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falcão, É.P.; Emídio, J.J.; de Sousa, N.F.; Marques, K.K.G.; Rocha, J.E.; Sobrinho, W.L.d.S.; Bezerra, J.F.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; Gonçalves, J.C.R.; et al. Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps. Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040071
Falcão ÉP, Emídio JJ, de Sousa NF, Marques KKG, Rocha JE, Sobrinho WLdS, Bezerra JF, Scotti L, Scotti MT, Gonçalves JCR, et al. Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps. Future Pharmacology. 2025; 5(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalcão, Éverton Paredes, Jeremias Justo Emídio, Natália Ferreira de Sousa, Karinne Kelly Gadelha Marques, Janaina Esmeraldo Rocha, Wellington Lima da Silva Sobrinho, João Felipe Bezerra, Luciana Scotti, Marcus Tullius Scotti, Juan Carlos Ramos Gonçalves, and et al. 2025. "Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps" Future Pharmacology 5, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040071
APA StyleFalcão, É. P., Emídio, J. J., de Sousa, N. F., Marques, K. K. G., Rocha, J. E., Sobrinho, W. L. d. S., Bezerra, J. F., Scotti, L., Scotti, M. T., Gonçalves, J. C. R., Coutinho, H. D. M., de Sousa, D. P., & de Castro, R. D. (2025). Antibacterial Mechanisms of 4-Chlorobenzyl p-Coumarate: Inhibition of MepA and NorA Efflux Pumps. Future Pharmacology, 5(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040071












