Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)-Targeted Treatments—New Therapeutic Technologies for Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Acute Treatment
1.2. Preventive Treatment
2. CGRP and CGRP Receptor
3. Small Molecule CGRP Receptor Antagonists: Gepants
3.1. Mechanism of Action
3.2. Indications
3.3. Contraindications
3.4. Side Effects
| Gepants | Ubrogepant (MK-1602) | Rimegepant (BMS-927711) | Atogepant (MK-8031) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA indication | Acute treatment of migraine | Acute treatment of migraine | Preventive treatment of episodic migraine | Preventive treatment of episodic migraine |
| Route | Oral | Oral | Oral | Oral |
| Tmax | 1.5 h | 1.5 h | 1.5 h | 1–2 h |
| Half-life | 5–7 h | 11 h | 11 h | 11 h |
| Recommended dose | 50 or 100 mg | 75 mg | 75 mg every other day | 10 mg QD, 30 mg QD, 60 mg QD, 30 mg BID, 60 mg BID |
| Max dose | 200 mg/24 h | 75 mg/24 h | 75 mg/24 h | All to be taken QD |
| Contraindications | Concomitant administration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors; end-stage renal disease | History of hypersensitivity; severe hepatic impairment (Child–Pugh C); end-stage renal disease; concomitant administration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, P-glycoprotein | History of hypersensitivity; severe hepatic impairment (Child–Pugh C); severe renal impairment and end-stage renal disease | |
| Adverse effects | Nausea, somnolence, dry mouth, nasopharyngitis, head | Nausea, urinary tract infection, dizziness, increased AST and ALT, nasopharyngitis | Nausea, fatigue, constipation, upper respiratory infection, urinary tract infection, sleepiness | |
| Efficacy compared to placebo a | 20.8% of participants were pain-free at 2 h (vs. 12.6% with placebo). Reduction of migraine-associated symptoms in 37.3% (vs. 27.6% with placebo) [50,51,52,53] | 15.1–19.6% were pain-free at 2 h (vs. 6.4–12.0% with placebo) Reduction by 1.16 to 4.3 MMDs [36,38,39,49,54,55,56,57,58,59] | Reduction by 3.6–4.2 MMDs [60,61,62,63,64] | |
4. CGRP Monoclonal Autoantibodies
4.1. Mechanism of Action
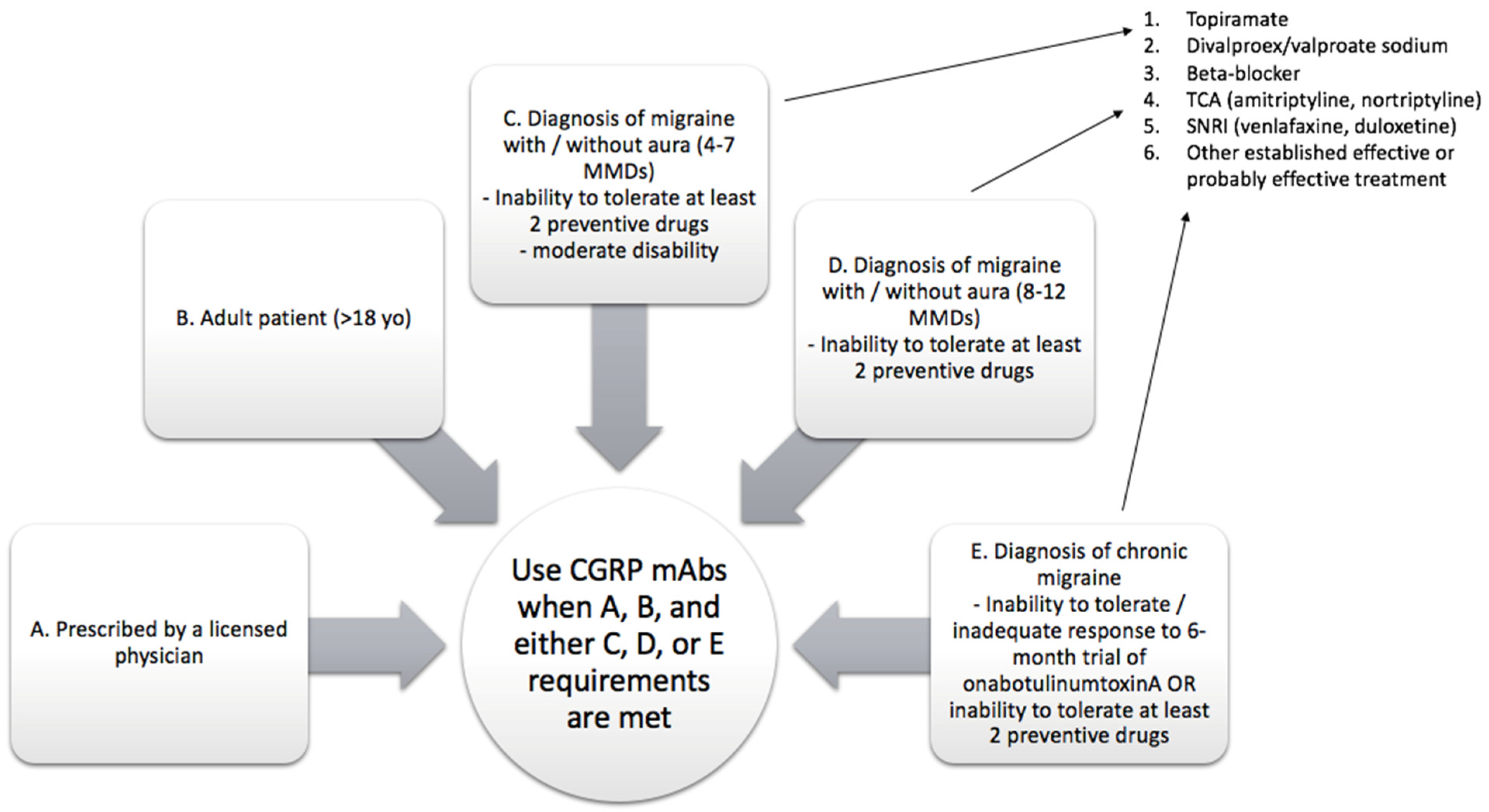
4.2. Indications
4.3. Contraindications
4.4. Side Effects
| CGRP mAbs | Erenumab (AMG334) | Fremanezumab (TEV-48125) | Galcanezumab (LY2951742) | Eptinezumab (ALD403) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA indication | Prevention of EM and CM | Prevention of EM and CM | Prevention of EM, CM and eCH | Prevention of EM and CM |
| Target | CLR/RAMP1 (receptor) | CGRP | CGRP | CGRP |
| Route of administration | SC | SC (IV load for cluster headache) | SC | IV |
| Frequency | Monthly | Monthly/quarterly | Monthly | Quarterly |
| Half-life | 28 days | 31 days | 28 days | 31 days |
| Recommended dose | 70 or 140 mg | 225 mg (monthly); 675 mg (quarterly) | 120 mg * | 100 to 300 mg |
| Starting dose | 70 or 140 mg | 225 mg or 675 mg | 240 mg as loading dose | |
| Contraindications | Hypersensitivity to drug, latex allergy, cardiovascular risk | Hypersensitivity to drug | Hypersensitivity to drug | Hypersensitivity to drug |
| Adverse reactions | Reaction at injection site, constipation, cramps, muscle spasms, elevated blood pressure, nervous system disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, vascular events, drug-induced liver injury, palpitation, arthralgia | Reaction at injection site (rash, pruritus, urticaria) up to one month after administration in 21.2% compared to 17.7% in placebo; headache, nasopharyngitis, gastroenteritis, back pain | Reaction at injection site | Infusion reaction |
| Efficacy compared to placebo a | −1.61 to −1.73 MMDs [69,73,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] | −2.19 to −2.38 MMDs [71,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] | −2.10 to −2.42 MMDs [70,89,103,104,105,106,107,108] | −1.43 MMDs [68,109,110,111] |
4.5. mAbs for Cluster Headache
5. Comparison between mAbs and Gepants, and Their Combination
6. Future Avenues of Research
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Birbeck, G.L. Migraine: The seventh disabler. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F. Migraine in the United States: A review of epidemiology and health care use. Neurology 1993, 43 (Suppl. 3), S6–S10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 17, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.J.; Birbeck, G.L.; Jensen, R.H.; Katsarava, Z.; Stovner, L.J.; Martelletti, P. Headache disorders are third cause of disability worldwide. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovner, L.J.; Hagen, K.; Jensen, R.; Katsarava, Z.; Lipton, R.; Scher, A.I.; Steiner, T.J.; Zwart, J.A. The global burden of headache: A documentation of headache prevalence and disability worldwide. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderPluym, J.H.; Charleston L 4th Stitzer, M.E.; Flippen, C.C., 2nd; Armand, C.E.; Kiarashi, J. A Review of Underserved and Vulnerable Populations in Headache Medicine in the United States: Challenges and Opportunities. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2022, 26, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Armand, C.E.; Charleston, L., IV; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Adams, A.M.; Lipton, R.B. Barriers to care in episodic and chronic migraine: Results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes Study. Headache 2021, 61, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleston, L., 4th; Royce, J.; Monteith, T.S.; Broner, S.W.; O’Brien, H.L.; Manrriquez, S.L.; Robbins, M.S. Underserved Populations in Headache Medicine Special Interest Section of the American Headache Society. Migraine Care Challenges and Strategies in US Uninsured and Underinsured Adults: A Narrative Review, Part 2. Headache 2018, 58, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleston, L., 4th; Royce, J.; Monteith, T.S.; Broner, S.W.; O’Brien, H.L.; Manrriquez, S.L.; Robbins, M.S. Migraine Care Challenges and Strategies in US Uninsured and Underinsured Adults: A Narrative Review, Part 1. Headache 2018, 58, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Bloudek, L.M.; Varon, S.F.; Oster, G. Adherence with migraine prophylaxis in clinical practice. Pain Pract. 2012, 12, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robblee, J.; Starling, A.J. SEEDS for success: Lifestyle management in migraine. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailani, J.; Burch, R.C.; Robbins, M.S.; Board of Directors of the American Headache Society. The American Headache Society Consensus Statement: Update on integrating new migraine treatments into clinical practice. Headache 2021, 61, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.S.; Victorio, M.C.; Bailey, M.; Cook, C.; Garza, I.; Huff, S.J.; Ready, D.; Schuster, N.M.; Seidenwurm, D.; Seng, E.; et al. Quality improvement in neurology: Headache quality measurement set. Neurology 2020, 95, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbussche, N.; Laterza, D.; Lisicki, M.; Lloyd, J.; Lupi, C.; Tischler, H.; Toom, K.; Vandervorst, F.; Quintana, S.; Paemeleire, K.; et al. Medication-overuse headache: A widely recognized entity amidst ongoing debate. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Dodick, D.; Evers, S.; Holle, D.; Jensen, R.H.; Lipton, R.B.; Porreca, F.; Silberstein, S.; Schwedt, T. Pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment of medication overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E.; Diamond, M.; Freitag, F.; Reed, M.L.; Stewart, W.F. Migraine prevalence, disease burden, and the need for preventive therapy. Neurology 2007, 68, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Holland, S.; Freitag, F.; Dodick, D.W.; Argoff, C.; Ashman, E. Evidence-based guideline update: Pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology 2012, 78, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, A.M.; Bloudek, L.M.; Becker, W.J.; Buse, D.C.; Varon, S.F.; Maglinte, G.A.; Wilcox, T.K.; Kawata, A.K.; Lipton, R.B. Patterns of use and reasons for discontinuation of prophylactic medications for episodic migraine and chronic migraine: Results from the second international burden of migraine study (IBMS-II). Headache 2013, 53, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, Z.; Dodick, D.W.; Varon, S.F.; Gillard, P.; Hansen, R.N.; Devine, E.B. Adherence to oral migraine-preventive medications among patients with chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A.; Warfvinge, K.; Krause, D.N. CGRP as the target of new migraine therapies—Successful translation from bench to clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, F.A.; King, R.; Smillie, S.J.; Kodji, X.; Brain, S.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1099–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Granstein, R.D. Roles of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the skin, and other physiological and pathophysiological functions. BrainBehav. Immun. 2021, 18, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.F. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP). A New Target for Migraine. Ann. Rev. Pharmac. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Johnson, K.W. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain 2017, 158, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, W.S.; Ashina, S.; Amin, F.M.; Goadsby, P.J.; Ashina, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, C.E.J.; Wilhour, D.A.; Silberstein, S.D. Novel Medications for the Treatment of Migraine. Headache 2019, 59, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, M.; Correnti, E.; Kamm, K.; Kelderman, T.; Papetti, L.; Rubio-Beltrán, E.; Vigneri, S.; Edvinsson, L.; Van Den Brink, A.M. Blocking CGRP in migraine patients—A review of pros and cons. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.W.; Conno, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Pearlman, E.; Koppenhaver, J.; Fan, X.; Lines, C.; Edvinsson, L.; Goadsby, P.J.; Michelson, D. Randomized controlled trial of the CGRP receptor antagonist telcagepant for migraine prevention. Neurology 2014, 83, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, I.M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonists: New therapeutic agents for migraine. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7838–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, N.M.; Rapoport, A.M. Calcitonin gene- related peptide-targeted therapies for migraine and cluster headache: A review. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 40, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, P.G.; Klein, B.C. Getting to the Heart of the Matter: Migraine, Triptans, DHE, Ditans, CGRP Antibodies, First/Second-Generation Gepants, and Cardiovascular Risk. Headache 2019, 59, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.B.R.; da Silva, M. Small molecule CGRP receptor antagonists for the preventive treatment of migraine: A review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 922, 174902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuteri, D.; Tarsitano, A.; Tonin, P.; Bagetta, G.; Corasaniti, M.T. Focus on zavegepant: The first intranasal third-generation gepant. Pain Manag. 2022, 12, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoff, E.; Johnston, K.; Croop, R.; Thiry, A.; Harris, L.; Powell, L.; Coric, V.; L’Italien, G.; Moren, J. Matching-adjusted indirect comparisons of oral rimegepant versus placebo, erenumab, and galcanezumab examining monthly migraine days and health-related quality of life in the treatment of migraine. Headache 2021, 61, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ajona, D.; Villar-Martinez, M.D.; Goadsby, P.J. New Generation Gepants: Migraine Acute and Preventive Medications. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croop, R.; Lipton, R.B.; Kudrow, D.; Stock, D.A.; Kamen, L.; Conway, C.M.; Stock, E.G.; Coric, V.; Goadsby, P.J. Oral rimegepant for preventive treatment of migraine: A phase 2/3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomski, A. Oral Rimegepant Safe, Effective for Migraine Prevention. JAMA 2021, 325, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallee, J.J.; Salvatore, C.A.; LeBourdelles, B.; Oliver, K.R.; Longmore, J.; Koblan, K.S.; Kane, S.A. Receptor activity-modifying protein 1 determines the species selectivity of non-peptide CGRP receptor antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14294–14298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, A.; Lionetto, L.; Simmaco, M.; Martelletti, P. CGRP receptor antagonists: An expanding drug class for acute migraine? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, A.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Villalon, C.M. Side effects associated with current and prospective antimigraine pharmacotherapies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvinsson, L. CGRP receptor antagonists and antibodies against CGRP and its receptor in migraine treatment. Br. Pharm. Soc. 2015, 80, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFalco, A.P.; Lazim, R.; Cope, N.E. Rimegepant Orally Disintegrating Tablet for Acute Migraine Treatment: A Review. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Castro, F.; Guerzoni, S.; Pellesi, L. Safety and Risk of Medication Overuse Headache in Lasmiditan and Second-Generation Gepants: A Rapid Review. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2021, 13, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.P.; Liang, C.S.; Chang, C.M.; Yang, C.C.; Shih, P.H.; Yau, Y.C.; Tang, K.T.; Wang, S.J. Comparison of New Pharmacologic Agents With Triptans for Treatment of Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2128544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Efficacy and Safety of Rimegepant for the Acute Treatment of Migraine: Evidence From Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navratilova, E.; Behravesh, S.; Oyarzo, J.; Dodick, D.W.; Banerjee, P.; Porreca, F. Ubrogepant does not induce latent sensitization in a preclinical model of medication overuse headache. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, J.S.; L’Italien, G.J.; Thiry, A.; Croop, R.; Coric, V.; Lipton, R.B. Rimegepant 75 mg results in reductions in monthly migraine days: Secondary analysis of a multicenter, open label long-term safety study of rimegepant for the acute treatment of migraine (1793). Neurology 2020, 94, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Dodick, D.W.; Lipton, R.B.; Ailani, J.; Lu, K.; Finnegan, M.; Trugman, J.M.; Szegedi, A. Ubrogepant for the treatment of migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Dodick, D.W.; Ailani, J.; Lu, K.; Finnegan, M.; Szegedi, A.; Trugman, J.M. Effect of ubrogepant vs placebo on pain and the most bothersome associated symptom in the acute treatment of migraine: The ACHIEVE II randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Lipton, R.B.; Ailani, J.; Singh, R.B.H.; Shewale, A.R.; Zhao, S.; Trugman, J.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Viswanathan, H.N. Ubrogepant, an acute treatment for migraine, improved patient-reported functional disability and satisfaction in 2 single-attack phase 3 randomized trials, ACHIEVE I and II. Headache 2020, 60, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailani, J.; Lipton, R.B.; Hutchinson, S.; Knievel, K.; Lu, K.; Butler, M.; Yu, S.Y.; Finnegan, M.; Severt, L.; Trugman, J.M. Long-term safety evaluation of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine: Phase 3, randomized, 52-week extension trial. Headache 2020, 60, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Croop, R.; Stock, E.G.; Stock, D.A.; Morris, B.A.; Frost, M.; Dybowchik, G.M.; Conway, C.M.; Coric, V.; Goadsby, P.J. Rimegepant, an Oral Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor Antagonist, for Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croop, R.; Goadsby, P.J.; Stock, D.A.; Conway, C.M.; Forshaw, M.; Stock, M.D.; Coric, V.; Lipton, R.B. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of rimegepant orally disintegrating tablet for the acute treatment of migraine: A randomised, phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.; Goadsby, P.J.; Dodick, D.; Stock, D.; Manos, G.; Fischer, T.Z. BMS-927711 for the acute treatment of migraine: A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, dose-ranging trial. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, L.B.; Croop, C.; Stock, E.G.; Conway, C.M.; Forshaw, M.; Stock, E.; Coric, V.; Lipton, R.B. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of rimegepant 75 mg, an oral CGRP receptor antagonist, for the acute treatment of migraine: Results from a phase 3, double- blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, study 301 (PS123LB). Headache 2018, 58, 1287–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, G.; Croop, R.; Kudrow, D.; Halverson, P.; Lovegren, M.; Thiry, A.C.; Conway, C.M.; Coric, V.; Lipton, R.B. Safety of Rimegepant, an Oral CGRP Receptor Antagonist, Plus CGRP Monoclonal Antibodies for Migraine. Headache 2020, 60, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Italien, G.; Popoff, E.; Johnston, K.; McGrath, D.; Conway, C.M.; Powell, L.; Harris, L.; Kowalczyk, N.; Croop, R.; Coric, V. Rimegepant 75 mg for acute treatment of migraine is associated with significant reduction in monthly migraine days: Results from a long-term, open-label study. Cephalalgia Rep. 2022, 5, 25158163221075596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Dodick, D.W.; Ailani, J.; Trugman, J.M.; Finnegan, M.; Lu, K.; Szegedi, A. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of orally administered atogepant for the prevention of episodic migraine in adults: A double-blind, randomised phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailani, J.; Lipton, R.W.; Goadsby, P.J.; Guo, H.; Miceli, R.; Severt, L.; Finnegan, M.; Trugman, J.M. ADVANCE Study Group. Atogepant for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boinpally, R.; McNamee, B.; Yao, L.; Butler, M.; McGeeney, D.; Borbridge, L.; Periclou, A. A Single Supratherapeutic Dose of Atogepant Does Not Affect Cardiac Repolarization in Healthy Adults: Results From a Randomized, Single-Dose, Phase 1 Crossover Trial. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2021, 10, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boinpally, R.; Jakate, A.; Butler, M.; Borbridge, L.; Periclou, A. Single-Dose Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Atogepant in Adults With Hepatic Impairment: Results From an Open-Label, Phase 1 Trial. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2021, 10, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.C.; Kraft, W.; Bondiskey, P.; Colón-González, F.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Panebianco, D.; Mixon, L.; Dockendorf, M.F.; Matthews, C.Z.; et al. Atogepant Is Not Associated With Clinically Meaningful Alanine Aminotransferase Elevations in Healthy Adults. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasad, Y.W.; Asha, M.Z. Monoclonal antibodies as a preventive therapy for migraine: A meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 195, 105900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; You, C. Efficacy and Safety of Monoclonal Antibody Against Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide or Its Receptor for Migraine: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 649143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronna, E.; Gallardo, V.G.; Alpuente, A.; Torres-Ferrus, M.; Pozo-Rosich, P. Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies in chronic migraine with medication overuse: Real-life effectiveness and predictors of response at 6 months. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, M.; Saper, J.; Cady, R.; Schaeffler, B.A.; Biondi, D.M.; Hirman, J.; Pederson, S.; Allan, B.; Smith, J. Eptinezumab in episodic migraine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (PROMISE-1). Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, S.J.; Ashina, M.; Reuter, U.; Brandes, J.L.; Dolezil, D.; Silberstein, S.D.; Winner, P.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, S.; Mikol, D.D. Long-term safety and efficacy of erenumab in patients with chronic migraine: Results from a 52-week, open-label extension study. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporeale, A.; Kudrow, D.; Sides, R.; Wang, S.; Van Dycke, A.; Selzler, K.J.; Stauffer, V.L. A phase 3, long-term, open-label safety study of galcanezumab in patients with migraine. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Silbersten, S.D.; Yeung, P.P.; Cohen, J.M.; Ning, X.; Yang, R.; Dodick, D.W. Long-term safety, tolerability, and efficacy of fremanezumab in migraine: A randomized study. Neurology 2020, 95, e2487–e2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, B.; Neeb, L.; Reuter, U. Monoclonal antibodies for the prevention of migraine. Exp. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 12, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, S.; Hettie, G.; Loder, E.; Burch, R. Real-world effectiveness and tolerability of erenumab: A retrospective cohort study. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overeem, L.H.; Peikert, A.; Hofacker, M.D.; Kamm, K.; Ruscheweyh, R.; Gendolla, A.; Raffaelli, B.; Reuter, U.; Neeb, L. Effect of antibody switch in non-responders to a CGRP receptor antibody treatment in migraine: A multi-center retrospective cohort study. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnado, O.J.; Manjelievskaia, J.; Ye, W.; Perry, A.; Schuh, K.; Wenzel, R. Treatment Patterns for Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibodies Including Galcanezumab versus Conventional Preventive Treatments for Migraine: A Retrospective US Claims Study. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2022, 16, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restituto, D.F.; Fabo, E.; Bujanda, M.M. Salvage therapy for patients who do not respond to the first anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody: A new chance for patients with migraine? Sci. Lett. 2022, 2, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basedau, H.; Sturm, L.-M.; Mehnert, J.; Peng, K.P.; Schellong, M.; May, A. Migraine monoclonal antibodies against CGRP change brain activity depending on ligand or receptor target—An fMRI study. eLife 2022, 11, e77146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegeler, C.; May, A. Non-Responders to Treatment With Antibodies to the CGRP-Receptor May Profit From a Switch of Antibody Class. Headache 2019, 60, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, D.; Buciak, J.B.; Yang, J.; Pardridge, W.M. Blood-brain barrier transport of cationized immunoglobulin G: Enhanced delivery compared to native protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4761–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Erenumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseda, R.; Bedussi, F.; Gobbi, C.; Zecca, C.; Ceschi, A. Safety profile of erenumab, galcanezumab and fremanezumab in pregnancy and lactation: Analysis of the WHO pharmacovigilance database. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Xing, H.; Cai, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. The effect and safety of monoclonal antibodies to calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptor on migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.M.; Ning, X.; Kessler, Y.; Rasamoelisolo, M.; Ramirez Campos, V.; Seminerio, M.J.; Krasenbaum, L.J.; Shen, H.; Stratton, J. Immunogenicity of biologic therapies for migraine: A review of current evidence. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepper, S.; Ashina, M.; Reuter, U.; Brandes, J.L.; Dolezil, D.; Silberstein, S.; Winner, P.; Leonardi, D.; Mikol, D.; Lenz, R. Safety and efficacy of erenumab for preventive treatment of chronic migraine: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudrow, D.; Pascual, J.; Winner, P.K.; Dodick, D.W.; Tepper, S.J.; Reuter, U.; Hong, F.; Klatt, J.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, S.; et al. Vascular safety of erenumab for migraine prevention. Neurology 2020, 94, e497–e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Ashina, M.; Brandes, J.L.; Kudrow, D.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Osipova, V.; Palmer, K.; Picard, H.; Mikol, D.D.; Lenz, R.A. ARISE: A Phase 3 randomized trial of erenumab for episodic migraine. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Reuter, U.; Hallstrom, Y.; Broessner, G.; Bonner, J.H.; Zhang, F.; Sapra, S.; Picard, H.; Mikol, D.D.; Lenz, R.A. A controlled trial of erenumab for episodic migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, M.; Kudrow, D.; Reuter, U.; Dolezil, D.; Silberstein, S.; Tepper, S.J.; Xue, F.; Picard, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, A.; et al. Long-term tolerability and nonvascular safety of erenumab, a novel calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist for prevention of migraine: A pooled analysis of four placebo-controlled trials with long-term extensions. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, B.; Mussetto, V.; Israel, H.; Neeb, L.; Reuter, U. Erenumab and galcanezumab in chronic migraine prevention: Effects after treatment termination. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.E.; Younis, S.; Deen, M.; Khan, S.; Ghanizada, H.; Ashina, M. Migraine induction with calcitonin gene-related peptide in patients from erenumab trials. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 105–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B.; Hallström, Y.; Reuter, U.; Tepper, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Sapra, S.; Picard, H.; Mikol, D.D.; Lenz, R.A. Migraine-related disability, impact, and health-related quality of life among patients with episodic migraine receiving preventive treatment with erenumab. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoon, J.; Van Hecken, A.; Vandermeulen, C.; Yan, L.; Smith, B.; Chen, J.S.; Bautista, E.; Hamilton, L.; Waksman, J.; Vu, T.; et al. Phase I. Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Single-dose, and Multiple-dose Studies of Erenumab in Healthy Subjects and Patients With Migraine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Tepper, S.J.; Reuter, U.; Silberstein, S.; Stewart, W.F.; Nilsen, J.; Leonardi, D.K.; Desai, P.; Cheng, S.; Mikol, D.D.; et al. Erenumab in chronic migraine: Patient-reported outcomes in a randomized double-blind study. Neurology 2019, 92, e2250–e2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Dodick, D.W.; Silberstein, S.; Goadsby, P.J.; Reuter, U.; Ashina, M.; Saper, J.; Cady, R.; Chon, Y.; Dietrich, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of AMG 334 for prevention of episodic migraine: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, S.J.; Diener, H.C.; Ashina, M.; Brandes, J.L.; Friedman, D.I.; Reuter, U.; Cheng, S.; Nilsen, J.; Leonardi, D.K.; Lenz, R.A.; et al. Erenumab in chronic migraine with medication overuse: Subgroup analysis of a randomized trial. Neurology 2019, 92, e2309–e2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Fremanezumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; McAllister, P.; Jurgens, T.P.; Kessler, Y.; Ning, X.; Cohen, J.M.; Ramirez Campos, V.; Barash, S.; Silberstein, S.D. Safety and tolerability of fremanezumab in patients with episodic and chronic migraine: A pooled analysis of phase 3 studies. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.W.; Bigal, M.E.; Yeung, P.P.; Goadsby, P.J.; Blankenbiller, T.; Grozinki-Wolff, M.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.; Aycardi, E. Fremanezumab for the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine. N. Eng. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Silberstein, S.D.; Bigal, M.E.; Yeung, P.P.; Goadsby, P.J.; Blankenbiller, T.; Grozinki-Wolff, M.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.; Aycard, E. Effect of fremanezumab compared with placebo for prevention of episodic migraine: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, P.K.; Spierings, E.L.H.; Yeung, P.P.; Aycardi, E.; Blankenbiller, T.; Grozinski-Wolff, M.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y. Early Onset of Efficacy With Fremanezumab for the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine. Headache 2019, 59, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Diener, H.C.; Ning, X.; Galic, M.; Cohen, J.M.; Yang, R.; Mueller, M.; Ahn, A.H.; Carmeli Schwartz, Y.; Grozinski-Wolff, M.; et al. Fremanezumab versus placebo for migraine prevention in patients with documented failure to up to four migraine preventive medication classes (FOCUS): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3b trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, M.E.; Dodick, D.W.; Rapoport, A.M.; Silberstein, S.D.; Ma, Y.; Yang, R.; Loupe, P.S.; Burstein, R.; Newman, L.C.; Lipton, R.B. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of TEV-48125 for preventive treatment of high-frequency episodic migraine: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b study. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detke, H.C.; Goadsby, P.J.; Wang, S.; Friedman, D.I.; Selzler, K.J.; Aurora, S.K. Galcanezumab in chronic migraine: The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled REGAIN study. Neurology 2018, 91, e2211–e2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, V.L.; Wang, S.; Voulgaropoulos, M.; Skljarevski, V.; Kovacik, A.; Aurora, S.K. Effect of galcanezumab following treatment cessation in patients with migraine: Results from 2 randomized phase 3 trials. Headache 2019, 59, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Stauffer, V.L.; Day, K.A.; Lipsius, S.; Wilson, M.C. Galcanezumab in episodic migraine: Subgroup analyses of efficacy by high versus low frequency of migraine headaches in phase 3 studies (EVOLVE-1 & EVOLVE-2). J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Skljarevski, V.; Matharu, M.; Millen, B.A.; Ossipov, M.H.; Kim, B.K.; Yang, J.Y. Efficacy and safety of galcanezumab for the prevention of episodic migraine: Results of the EVOLVE-2 Phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, V.L.; Dodick, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Carter, J.N.; Ailani, J.; Conley, R.R. Evaluation of Galcanezumab for the Prevention of Episodic Migraine: The EVOLVE- 1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Rosich, P.; Detke, H.C.; Wang, S.; Doležil, D.; Li, L.Q.; Aurora, S.K.; Reuter, U. Long-term treatment with galcanezumab in patients with chronic migraine: Results from the open-label extension of the REGAIN study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Lipton, R.B.; Silberstein, S.; Goadsby, P.J.; Biondi, D.; Hirman, J.; Cady, R.; Smith, J. Eptinezumab for prevention of chronic migraine: A randomized phase 2b clinical trial. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Goadsby, P.J.; Smith, J.; Schaeffler, B.A.; Biondi, D.M.; Hirman, J.; Pederson, S.; Allan, B.; Cady, R. Efficacy and safety of eptinezumab in patients with chronic migraine: PROMISE-2. Neurology 2020, 94, e1365–e1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, J.; Lipton, R.; Kudrow, D.; Hirman, J.; Dodick, D.; Silberstein, S.; Chakhava, G.; Smith, J. Primary Results of PROMISE-1 (Prevention Of Migraine via Intravenous eptinezumab Safety and Efficacy–1) Trial: A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Eptinezumab for Prevention of Frequent Episodic Migraines (S20.001). Neurology 2018, 90, S15. [Google Scholar]
- International Classification of Orofacial Pain, 1st edition (ICOP). Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 129–221. [CrossRef]
- Belin, A.C.; Ran, C.; Edvinsson, L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and cluster headache. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Edvinsson, L. Human in vivo evidence for trigeminovascular activation in cluster headache Neuropeptide changes and e ects of acute attacks therapies. Brain 1994, 117, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollesen, A.L.H.; Snoer, A.; Beske, R.P.; Guo, S.; Ho mann, J.; Jensen, R.H.; Ashina, M.E. Infusion of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide on Cluster Headache Attacks: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciullacci, M.; Alessandri, M.; Figini, M.; Geppetti, P.; Michelacci, S. Increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide from the extracerebral circulation during nitroglycerin-induced cluster headache attack. Pain 1995, 60, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellesi, L.; Chaudhry, B.A.; Vollesen, A.L.H.; Snoer, A.H.; Baumann, K.; Skov, P.R.; Jensen, R.H.; Ashina., M. PACAP38- and VIP-induced cluster headache attacks are not associated with changes of plasma CGRP or markers of mast cell activation. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Dodick, D.W.; Leone, M.; Bardos, J.N.; Oakes, T.M.; Millen, B.A.; Zhou, C.; Dowsett, S.A.; Aurora, S.K.; Ahn, A.H.; et al. Trial of Galcanezumab in Prevention of Episodic Cluster Headache. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Goadsby, P.J.; Lucas, C.; Jensen, R.; Bardos, J.N.; Martinez, J.M.; Zhou, C.; Aurora, S.K.; Yang, J.Y.; Conley, R.R.; et al. Phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled study of galcanezumab in patients with chronic cluster headache: Results from 3-month double-blind treatment. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscheweyh, R.; Broessner, G.; Gobrau, G.; Heinze-Kuhn, K.; Jurgens, T.P.; Kaltseis, K.; Kamm, K.; Peikert, A.; Raffaelli, B.; Rimmele, F.; et al. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide (-receptor) antibodies in chronic cluster headache: Results from a retrospective case series support individual treatment attempts. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Goasdby, P.J. CGRP pathway monoclonal antibodies for cluster headache. Expert Opin Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, K.; Kudrow, D.; Croop, R.; Lovegren, M.; Conway, C.M.; Coric, V.; Pilton, R.B. Potential for treatment benefit of small molecule CGRP receptor antagonist plus monoclonal antibody in migraine therapy. Neurology 2020, 94, e2121–e2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellesi, L. Combining two CGRP inhibitors to treat migraine. Exp. Opin. Drug Safety 2022, 21, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibler, R.C.; Knestrick, K.E.; Reidy, B.L.; Lax, D.N.; Powers, S.W. Management of Chronic Migraine in Children and Adolescents: Where are We in 2022? Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2022, 13, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangalli, L.; Gilbert, R.; Boggero, I. Pediatric Chronic Orofacial Pain: A Narrative Review of Biopsychosocial Associations and Treatment Approaches. Front. Pain Res. 2021, 2, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.W.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.M.; Allen, J.R.; LeCates, S.L.; Slater, S.K.; Zafar, M.; Kabbouche, M.A.; O’Brien, H.L.; Shenk, C.E.; Rausch, J.R.; et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy plus amitriptyline for chronic migraine in children and adolescents: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.W.; Coffey, C.S.; Chamberlin, L.A.; Ecklund, D.J.; Klingner, E.A.; Yankey, J.W.; Korbee, L.L.; Porter, L.L.; Hersey, A.D.; CHAMP Investigators. Trial of Amitriptyline, Topiramate, and Placebo for Pediatric Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szperka, C.L.; VanderPluym, J.; Orr, S.L.; Oakley, C.B.; Qubty, W.; Patniyot, I.; Lagman-Bartolome, A.M.; Morris, C.; Gautreaux, J.; Victorio, M.C.; et al. Recommendations on the Use of Anti-CGRP Monoclonal Antibodies in Children and Adolescents. Headache 2018, 58, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, K.A.; Gentile, C.P.; Szperka, C.L.; Yonker, M.; Gelfand, A.A.; Grimes, B.; Irzin, S.L. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Use for the Preventive Treatment of Refractory Headache Disorders in Adolescents. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 114, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Barak, O.; Radivojevic, A.; Jones, A.; Fiedler-Kelly, J.; Gillespie, M.; Brennan, M.; Gutman, D.; Rasamoelisolo, M.; Hallak, H.; Loupe, P.; et al. Dose selection for fremanezumab (AJOVY) phase 3 pediatric migraine studies using pharmacokinetic data from a pediatric phase 1 study and a population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation approach. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Cohen-Barak, O.; Radivojevic, A.; Fiedler-Kelly, J. Scaling Approaches for Pediatric Dose Selection: The Fremanezumab (AJOVY®) Journey to Select a Phase 3 Dose Using Pharmacokinetic Data from a Phase 1 Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannone, L.F.; De Cesaris, F.; Geppetti, P. Emerging Pharmacological Treatments for Migraine in the Pediatric Population. Life 2022, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, S. CGRP in Childhood and Adolescence Migraine: (Patho)physiological and Clinical Aspects. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2022, 26, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allergan. Study to Assess Adverse Events and Disease Activity of Oral Ubrogepant Tablets for the Acute Treatment of Migraine in Children and Adolescents (Ages 6–17). 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05125302 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Biohaven Pharmaceuticals Inc. Long-Term Safety Study of Rimegepant in Pediatric Subjects for the Acute Treatment of Migrain. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04743141 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Allergan. Long-Term Extension Study to Assess Safety and Tolerability of Oral Ubrogepant Tablets for the Acute Treatment of Migraine in Children and Adolescents (Ages 6–17). 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05127954 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Biohaven Pharmaceutical Holding Company Ltd. Randomized Study in Children and Adolescents with Migraine: Acute Treatment. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04649242 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Biohaven Pharmaceuticals LBAohCgsNaoO. Efficacy and Safety Study of Rimegepant for the Preventative Treatment of Migraine in Pediatric Subjects. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05156398 (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Al-Hassany, L.; Goadsby, P.J.; Danser, A.H.J.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-targeting drugs for migraine: How pharmacology might inform treatment decisions. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.P.; Al-Saoudi, A.; Ashina, M. Future prophylactic treatments in migraine: Beyond anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies and gepants. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sangalli, L.; Brazzoli, S. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)-Targeted Treatments—New Therapeutic Technologies for Migraine. Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3, 117-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3010008
Sangalli L, Brazzoli S. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)-Targeted Treatments—New Therapeutic Technologies for Migraine. Future Pharmacology. 2023; 3(1):117-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleSangalli, Linda, and Stefania Brazzoli. 2023. "Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)-Targeted Treatments—New Therapeutic Technologies for Migraine" Future Pharmacology 3, no. 1: 117-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3010008
APA StyleSangalli, L., & Brazzoli, S. (2023). Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)-Targeted Treatments—New Therapeutic Technologies for Migraine. Future Pharmacology, 3(1), 117-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol3010008






