Impact of Vegetal Protein on the Physicochemical and Microstructural Properties of Microencapsulated Mexican Red Pitaya (Stenocereus thurberi) Juice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemical Material
2.3. Juice Extraction
2.4. Protein Hydrolysis
2.5. Spray Drying Process
2.6. Proximal Characterization
2.7. Hygroscopicity (Hg)
2.8. Water Activity (aw)
2.9. Bulk Density
2.10. Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
2.11. Chemical Properties
2.11.1. Extract Preparation
2.11.2. Total Polyphenol Content
2.11.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.11.4. Total Betalain Content
2.12. Color Parameters
2.13. Stability of Powders During Storage
2.14. FTIR Analysis
2.15. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.16. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Materials and Encapsulated Materials
3.2. (Hg) and Water Activity (aw)
3.3. Water Absorption Indices (WAI) and Water Solubility Indices (WSI)
3.4. Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
3.5. Color
3.6. Chemical Properties
3.6.1. Total Betalain Content
3.6.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) and Antioxidant Activity (AA)
3.7. Stability of Encapsulated Materials During Storage
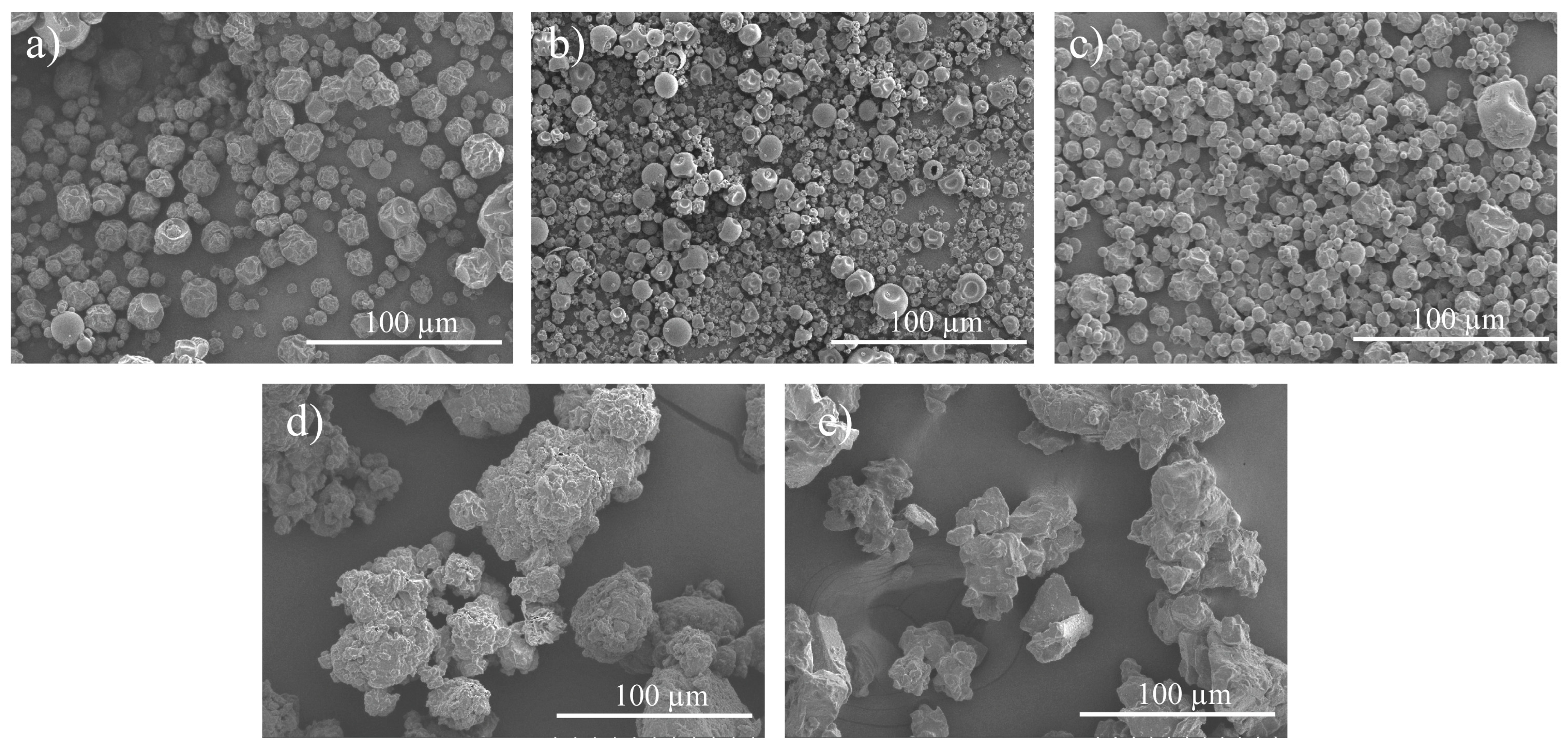
3.8. SEM
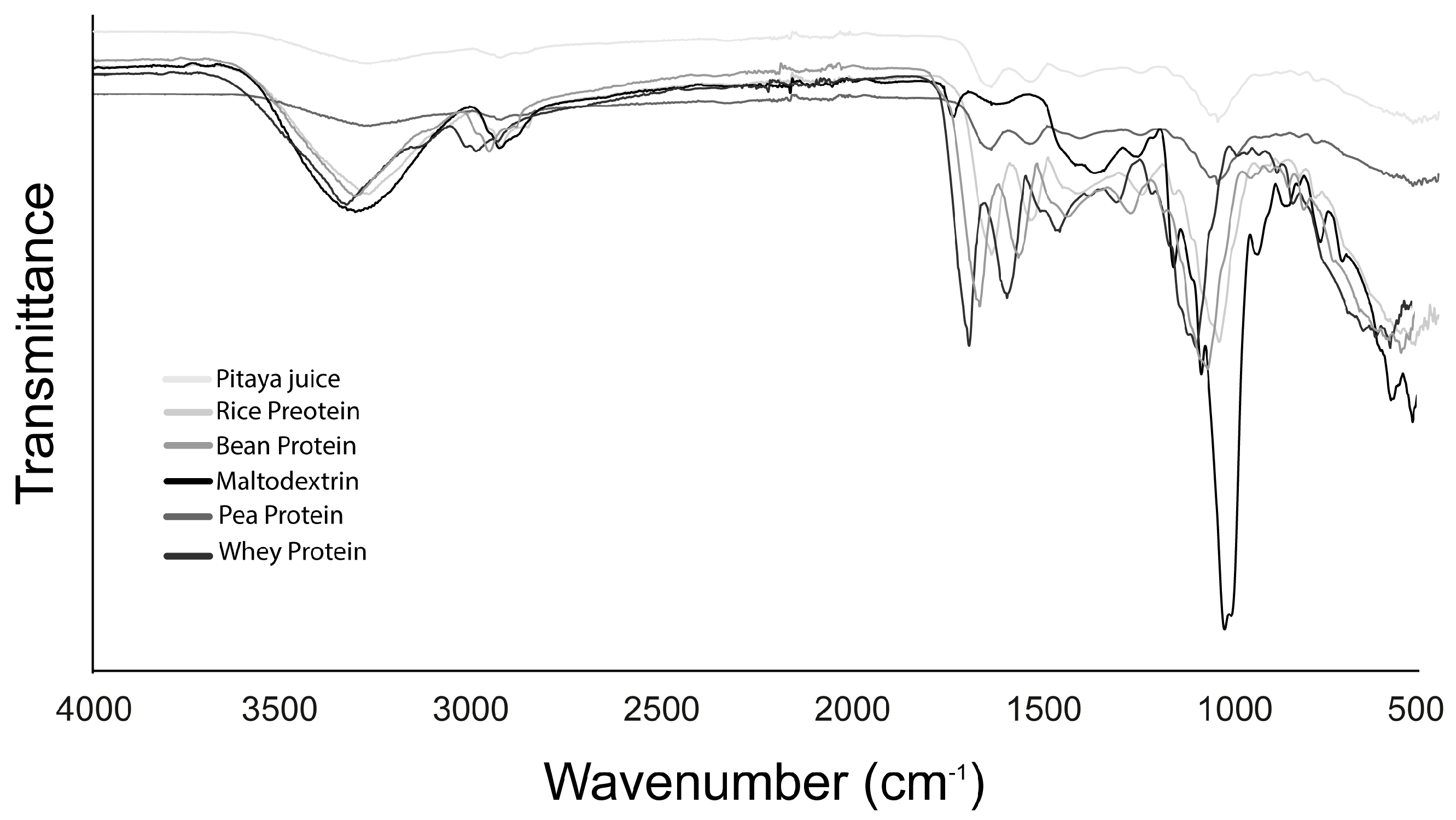
3.9. Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FT-IR) Spectrometry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- García-Cruz, L.; Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Valle-Guadarrama, S. Betalains, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in pitaya de mayo (Stenocereus griseus H.). Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2012, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Loredo, M.G.; García-Ochoa, F.; Barragán-Huerta, B.E. Comparative analysis of betalain content in Stenocereus stellatus fruits and other cactus fruits using principal component analysis. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delia, S.C.; Chávez, G.M.; Frank, M.L.M.; Araceli, S.G.P.; Irais, A.L.; Franco, A.A. Spray drying microencapsulation of betalain rich extracts from Escontria chiotilla and Stenocereus queretaroensis fruits using cactus mucilage. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Segovia, P.; Igual, M.; Martínez-Monzó, J. Beetroot microencapsulation with pea protein using spray drying: Physicochemical, structural and functional properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofinita, D.; Bindar, Y.; Samadhi, T.W.; Choliq, N.S.; Jaelawijaya, A.A. Increasing the Yield of Powder and Bioactive Materials during Extraction and Spray Drying of Dragon Fruit Skin Extracts. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2021, 53, 210612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.R.R.; Lima, A.B.; Ribeiro, C.M.C.M.; de Medeiros, P.V.Q.; Converti, A.; dos Santos Lima, M.; Maciel, M.I.S. Red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) as a source of betalains and phenolic compounds: Ultrasound extraction, microencapsulation, and evaluation of stability. Lwt 2024, 196, 115755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontul, I.; Topuz, A. Spray-drying of fruit and vegetable juices: Effect of drying conditions on the product yield and physical properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, L.P.; Karim, R.; Yusof, Y.A.; Wong, C.W.; Ghazali, H.M. Optimization of spray-drying parameters for the production of ‘Cempedak’ (Artocarpus integer) fruit powder. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 3238–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utpott, M.; Ramos de Araujo, R.; Galarza Vargas, C.; Nunes Paiva, A.R.; Tischer, B.; de Oliveira Rios, A.; Hickmann Flores, S. Characterization and application of red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) peel powder as a fat replacer in ice cream. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarbaglu, Z.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M. Spray drying encapsulation of bioactive compounds within protein-based carriers; different options and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, E.L.; Teodoro, R.A.R.; Félix, P.H.C.; de Barros Fernandes, R.V.; de Oliveira, É.R.; Veiga, T.R.L.A.; Botrel, D.A. Stability of spray-dried beetroot extract using oligosaccharides and whey proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazaria, B.; Kumar, P. Effect of whey protein concentrate as drying aid and drying parameters on physicochemical and functional properties of spray dried beetroot juice concentrate. Food Biosci. 2016, 14, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofinita, D.; Fawwaz, M.; Achmadi, A.B. Betalain extracts: Drying techniques, encapsulation, and application in food industry. Food Front. 2023, 4, 576–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ruan, S.; Azam, S.R.; Yang, N.O.; Ma, H. Effects of ultrasound-assisted sodium bisulfite pretreatment on the preparation of cholesterol-lowering peptide precursors from soybean protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria-Hernández, C.; Serna-Saldívar, S.; Chuck-Hernández, C. Physicochemical and functional properties of vegetable and cereal proteins as potential sources of novel food ingredients. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 53, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.H.G.; Kurozawa, L.E. Influence of rice protein hydrolysate on lipid oxidation stability and physico-chemical properties of linseed oil microparticles obtained through spray-drying. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Kimmel, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Improving the functionality of pea protein isolate through co-spray drying with emulsifying salt or disaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ibarra, C.; Ruiz-López, F.D.J.; Bautista-Villarreal, M.; Báez-González, J.G.; Rodríguez Romero, B.A.; González-Martínez, B.E.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, J.A. Protein concentrates on Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius Gray) as a functional ingredient: In silico docking of tepary bean lectin to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 661463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanovich, U.; Bernardes, G.J.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Protein micro-and nano-capsules for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Gao, L.; Geng, Q.; Li, T.; He, X.; Chen, J.; Dai, T. Effects of moderate enzymatic hydrolysis on structure and functional properties of pea protein. Foods 2022, 11, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting nitrogen into protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabio-García, D.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; Gutiérrez, D.L.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Meléndez-Pizarro, C.O.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.A.; Espinoza-Hicks, J.C. Effectiveness of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage as a carrier agent in microencapsulation of bioactive compounds of Amaranthus hypochondriacus var. Nutrisol. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tze, N.L.; Han, C.P.; Yusof, Y.A.; Ling, C.N.; Talib, R.A.; Taip, F.S.; Aziz, M.G. Physicochemical and nutritional properties of spray-dried pitaya fruit powder as natural colorant. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Dagnino, M.A.; Sánchez-Madrigal, M.Á.; Heredia-Olea, E.; Meléndez-Pizarro, C.O.; Ortiz-Basurto, R.I.; Lardizábal-Gutiérrez, D.; Quintero-Ramos, A. Microencapsulation of pitaya juice (Stenocereus stellatus) by spray drying using mixtures of fructans, whey protein, and modified starch as carrier agents. Biotecnia 2024, 26, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neder-Suárez, D.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Meléndez-Pizarro, C.O.; de Jesús Zazueta-Morales, J.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, M.G. Evaluation of the physicochemical properties of third-generation snacks made from blue corn, black beans, and sweet chard produced by extrusion. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paśko, P.; Galanty, A.; Zagrodzki, P.; Ku, Y.G.; Luksirikul, P.; Weisz, M.; Gorinstein, S. Bioactivity and cytotoxicity of different species of pitaya fruits–A comparative study with advanced chemometric analysis. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chiu, H.T.; Feng, Z.; Maes, E.; Serventi, L. Effect of spray-drying and freeze-drying on the composition, physical properties, and sensory quality of pea processing water (Liluva). Foods 2021, 10, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Z.; Shi, Q. Effect of carrier types on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of spray-dried black mulberry juice powders. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Peng, Q.; Zhong, J.Z.; Liu, W.; Zhong, Y.J.; Wang, F. Molecular and functional properties of protein fractions and isolate from cashew nut (Anacardium occidentale L.). Molecules 2018, 23, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlohi, M.; Manickavasagan, A.; Ali, A. The effect of protein drying aids on the quantity and quality of spray dried sugar-rich powders: A systematic review. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 1068–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora, M.C.; Carriazo, J.G.; Iturriaga, L.; Nazareno, M.A.; Osorio, C. Microencapsulation of betalains obtained from cactus fruit (Opuntia ficus-indica) by spray drying using cactus cladode mucilage and maltodextrin as encapsulating agents. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandate-Flores, L.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Velázquez, G.; Mayolo-Deloisa, K.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Torres, J.A.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Low-sugar content betaxanthins extracts from yellow pitaya (Stenocereus pruinosus). Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Reyes, E.; Castaño, J.; Carrillo-Navas, H.; Alvarez-Ramírez, J.; Gallardo-Rivera, R.; Pérez-Alonso, C.; Guadarrama-Lezama, A.Y. Thermodynamic sorption analysis and glass transition temperature of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) protein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Bhandari, B. Comparing the efficiency of protein and maltodextrin on spray drying of bayberry juice. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.A.; Pratap-Singh, A. Plant-based (hemp, pea and rice) protein–maltodextrin combinations as wall material for spray-drying microencapsulation of hempseed (Cannabis sativa) oil. Foods 2020, 9, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Labuza, T.P. Effect of water content on glass transition and protein aggregation of whey protein powders during short-term storage. Food Biophys. 2007, 2, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Giusti, M.M. The interactions between anthocyanin and whey protein: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5992–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Campos, L.; Valle-Guadarrama, S.; Martínez-Bustos, F.; Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Calvo-López, A.D. Encapsulation and pigmenting potential of betalains of pitaya (Stenocereus pruinosus) fruit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2436–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.N.D.; Tran, T.N.T.; Hoang, Q.B. Impact of maltodextrin and temperature on spray dried mixed flesh-peel matrix of red dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus) powder. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1155, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.T.; Nakamura, A.; Corredig, M. Pea soluble polysaccharide interactions with plant albumins. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.N.; Ishwarya, S.P.; Nisha, P. Nanoemulsion versus microemulsion systems for the encapsulation of beetroot extract: Comparison of physicochemical characteristics and betalain stability. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2021, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lucas, K.A.; Méndez-Lagunas, L.L.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, J.; Campanella, O.H.; Patel, B.K.; Barriada-Bernal, L.G. Physical properties of spray dryed Stenocereus griseus pitaya juice powder. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.H.; Hoskin, R.T.; Alghamdi, M.; Lila, M.A.; Chalova, V.I. Betalain–Chickpea Protein Particles Produced by Freeze Drying and Spray Drying: Physicochemical Aspects, Storage Stability, and In Vitro Digestion. Foods 2025, 14, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laokuldilok, T.; Kanha, N. Effects of processing conditions on powder properties of black glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.) bran anthocyanins produced by spray drying and freeze drying. Lwt 2015, 64, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Moisture Content (%) | Protein (%) | Ash (%) | Fat (%) | Crude Fiber (%) | Carbohydrates (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | 1.14 ± 0.08 b | 55.19 ± 0.25 a | 0.74 ± 0.15 b | 0.08 ± 0.02 d | 1.31 ± 0.18 ab | 38.7 |
| PP | 1.37 ± 0.16 b | 43.88 ± 0.69 c | 2.19 ± 0.13 a | 0.69 ± 0.11 b | 1.05 ± 0.12 b | 43.9 |
| BP | 1.29 ± 0.12 b | 40.06 ± 0.36 d | 2.14 ± 0.09 a | 3.81 ± 0.12 a | 1.52 ± 0.15 a | 43.8 |
| WP | 2.08 ± 0.14 a | 49.22 ± 0.87 b | 2.18 ± 0.11 a | 0.63 ± 0.09 b | ND | 46.9 |
| MT | 1.54 ± 0.22 ab | 0.11 ± 0.01 e | 1.77 ± 0.18 a | 0.34 ± 0.08 c | ND | 96.2 |
| Treatment | Aw | Hg | YE | WSI | WAI | BD | TG | TPC | AA | BT | BTC | BTX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | 0.171 ± 0.01 b | 12.17 ± 0.18 c | 52.85 ± 4.44 b | 22.87 ± 0.37 e | 3.16 ± 0.14 a | 0.277 ± 0.004 c | 59.56 ± 0.72 b | 218.60 ± 19.90 d | 2.95 ± 0.16 e | 0.665 ± 0.012 c | 0.247 ± 0.005 d | 0.417 ± 0.006 c |
| PP | 0.151 ± 0.01 c | 17.91 ± 0.18 b | 54.81 ± 2.56 b | 37.83 ± 0.31 c | 3.06 ± 0.11 a | 0.350 ± 0.008 b | 59.91 ± 0.90 b | 639.71 ± 8.94 b | 10.71 ± 0.25 b | 0.772 ± 0.093 b | 0.282 ± 0.010 c | 0.490 ± 0.004 b |
| BP | 0.125 ± 0.01 e | 18.01 ± 0.41 b | 44.52 ± 6.25 c | 28.74 ± 0.62 d | 3.07 ± 0.10 a | 0.345 ± 0.006 b | 58.13 ± 0.86 b | 327.52 ± 13.48 c | 7.75 ± 0.10 c | 0.673 ± 0.025 c | 0.268 ± 0.015 cd | 0.408 ± 0.010 c |
| WP | 0.251 ± 0.02 a | 20.84 ± 0.22 a | 60.45 ± 4.36 a | 94.58 ± 0.02 b | 0.42 ± 0.01 b | 0.271 ± 0.002 c | 47.21 ± 0.69 c | 680.09 ± 13.48 a | 13.53 ± 0.31 a | 1.229 ± 0.079 a | 0.439 ± 0.005 a | 0.792 ± 0.006 a |
| MT | 0.144 ± 0.01 d | 21.10 ± 0.06 a | 63.82 ± 5.89 a | 99.38 ± 0.83 a | 0.33 ± 0.02 b | 0.463 ± 0.002 a | 64.83 ± 0.53 a | 292.84 ± 16.29 c | 5.64 ± 0.21 d | 0.803 ± 0.013 b | 0.335 ± 0.013 b | 0.488 ± 0.026 b |
| Treatment | L* | a* | b* | °Hue | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | 56.97 ± 0.29 b | 30.17 ± 0.30 e | 29.89 ± 0.33 c | 44.73 ± 0.09 a | |
| PP | 44.31 ± 0.16 d | 37.32 ± 0.23 b | 30.52 ± 0.10 b | 39.27 ± 0.06 d | |
| BP | 39.82 ± 0.22 e | 37.16 ± 0.26 b | 26.56 ± 0.25 d | 35.55 ± 0.09 e | |
| WP | 55.74 ± 0.83 c | 35.42 ± 0.31 c | 31.21 ± 0.35 a | 41.38 ± 0.06 b | |
| MT | 59.29 ± 0.34 a | 34.89 ± 0.16 d | 30.33 ± 0.18 bc | 41.00 ± 0.10 c | |
| Pitaya juice | 29.45 ± 0.09 f | 45.93 ± 0.12 a | 10.03 ± 0.14 e | 12.34 ± 0.08 f |
| Treatment | Temperature | k (days−1) | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | Half-Life Period t1/2 (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | 30 | 0.0022 | 0.98 | 315.06 ± 32.67 bc |
| 45 | 0.0095 | 0.90 | 72.96 ± 15.40 e | |
| 60 | 0.0123 | 0.92 | 56.35 ± 4.55 e | |
| PP | 30 | 0.0035 | 0.98 | 198.04 ± 26.02 d |
| 45 | 0.0143 | 0.91 | 48.44 ± 3.58 e | |
| 60 | 0.0197 | 0.97 | 35.18 ± 4.64 e | |
| BP | 30 | 0.0037 | 0.94 | 187.33 ± 23.31 d |
| 45 | 0.0197 | 0.91 | 35.18 ± 6.35 e | |
| 60 | 0.0224 | 0.82 | 30.94 ± 10.90 e | |
| WP | 30 | 0.0031 | 0.97 | 223.59 ± 41.92 d |
| 45 | 0.0125 | 0.97 | 55.45 ± 4.56 e | |
| 60 | 0.0499 | 0.63 | 13.89 ± 0.77 e | |
| MT | 30 | 0.0008 | 0.92 | 818.28 ± 68.07 a |
| 45 | 0.0018 | 0.97 | 386.27 ± 30.34 b | |
| 60 | 0.0027 | 0.91 | 256.72 ± 41.25 cd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neder-Suárez, D.; Meléndez-Pizarro, C.O.; Pérez-Carrillo, E.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, J.A.; Valdez-Cárdenas, M.d.C.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, M.G.; Amaya-Guerra, C.A.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; Quintero-Ramos, A. Impact of Vegetal Protein on the Physicochemical and Microstructural Properties of Microencapsulated Mexican Red Pitaya (Stenocereus thurberi) Juice. AppliedChem 2025, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020012
Neder-Suárez D, Meléndez-Pizarro CO, Pérez-Carrillo E, Vázquez-Rodríguez JA, Valdez-Cárdenas MdC, Ruiz-Gutiérrez MG, Amaya-Guerra CA, Paraguay-Delgado F, Quintero-Ramos A. Impact of Vegetal Protein on the Physicochemical and Microstructural Properties of Microencapsulated Mexican Red Pitaya (Stenocereus thurberi) Juice. AppliedChem. 2025; 5(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeder-Suárez, David, Carmen Oralia Meléndez-Pizarro, Esther Pérez-Carrillo, Jesús Alberto Vázquez-Rodríguez, María del Cielo Valdez-Cárdenas, Martha Graciela Ruiz-Gutiérrez, Carlos Abel Amaya-Guerra, Francisco Paraguay-Delgado, and Armando Quintero-Ramos. 2025. "Impact of Vegetal Protein on the Physicochemical and Microstructural Properties of Microencapsulated Mexican Red Pitaya (Stenocereus thurberi) Juice" AppliedChem 5, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020012
APA StyleNeder-Suárez, D., Meléndez-Pizarro, C. O., Pérez-Carrillo, E., Vázquez-Rodríguez, J. A., Valdez-Cárdenas, M. d. C., Ruiz-Gutiérrez, M. G., Amaya-Guerra, C. A., Paraguay-Delgado, F., & Quintero-Ramos, A. (2025). Impact of Vegetal Protein on the Physicochemical and Microstructural Properties of Microencapsulated Mexican Red Pitaya (Stenocereus thurberi) Juice. AppliedChem, 5(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020012










