Abstract
This review provides insight on potential host-specific factors that increase individual susceptibility to infection and transmission of bovine digital dermatitis. Digital dermatitis is increasing in prevalence within herds worldwide and yields economic losses for producers and welfare issues for animals. A total of 34 relevant studies were reviewed based on the inclusion criteria. A decrease in susceptibility to disease was found in animals with specific genomic and hoof characteristics, thus citing the importance of sire selection when designing a breeding program. Animals with superior health status that lacked co-morbidities and mounted immune responses to infection were less likely to develop disease. Primiparous cattle and those in peak production were more likely to develop lesions, as were over-or-under-conditioned Holstein–Friesian breeds. Cattle with superior hoof conformation and gait were poor hosts for bacteria and therefore less likely to develop and spread infection. The lowest risk of transmission of digital dermatitis occurred during the dry period and post peak lactation and cattle with advanced lesions contributed to the persistence of the disease within a herd. It is hoped that this review will help producers design breeding and management programs for their herds, and help veterinarians advise clients on the subject.
1. Introduction
Digital dermatitis (DD) is an infectious disease of bovine claws that was discovered in the 1970s in Europe and originally called Mortellaro’s disease [1]. The disease causes painful, necrotizing wart-like lesions, often between the heel bulbs of the hindfeet, that can cause lameness [2]. Digital dermatitis is present internationally and once a herd is infected, the disease often becomes endemic as it is highly contagious, difficult to eradicate and displays varying response to treatment [1]. The prevalence of disease worldwide and within herds is continuously increasing, with DD reported as the most prevalent hoof disorder treated by hoof trimmers in the United States [3]. It is also reported by the same hoof trimmers as the most costly hoof disorder to producers due to direct and indirect costs: the cost of treatment, labor costs and decreased milk production and reproductive performance [3]. The secondary effects of DD infections have been extensively reported in the literature and include reproductive losses, decreased milk yield and the overall decreased welfare of cattle, leading to further economic losses for producers [4]. Spirochete bacteria, specifically Treponema spp., are responsible for the infection and several species of treponemes have been identified in lesions and implicated in the disease [1]. Other bacteria such as Dichelobacter have been isolated from lesions, but research suggests the disease is polytreponemal in origin rather than polymicrobial [1].
Digital dermatitis lesions are a significant cause of lameness in cattle; however, not all infections result in lameness [5]. For example, Yang et al. reported that the disease rarely yields clinical lameness in cattle housed in the New Zealand pastoral dairy systems [6]. The variations in clinical manifestations can make the detection of disease difficult and treatment practices variable, as individual animals are rarely treated due to the associated costs and labor required [7]. The infection is divided into stages using M scores (M0–M4.1) based on the macroscopic appearance, chronicity of lesions and response to treatment, and the evaluation is often made based on the visualization of lesions during milking [6,8]. The disease is dynamic in nature and the stage of present lesion may influence the persistence of the disease within a herd and the subsequent transmission to other cattle [6].
The epidemiological triad explaining the infection and spread of the disease consists of host, environmental and agent factors. Environmental factors that increase the susceptibility to infection include differences in the housing system and land access, flooring type, nutrition, foot hygiene and contact with environmental and fecal slurries, regular foot bathing and season [1,9,10]. Tissue invasion by multiple Treponema spp. and their virulence factors with a secondary infection from other bacteria contribute to developing lesions. However, this review will focus on the host factors that influence the development and spread of DD. Host factors consist of cow-specific characteristics that may foster a suitable environment for bacterial proliferation, increase susceptibility to infection, decrease immunity, etc. These host factors, combined with an appropriate environment and the presence of bacteria, promote the development of the disease. The aim of this review is to investigate specific host factors that promote the development and transmission of bovine digital dermatitis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
Two separate searches were performed in accordance with the 2020 preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [11]. The search terms and results from these are described in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
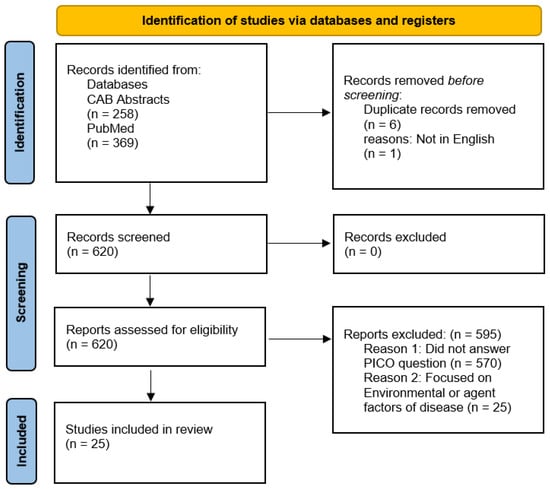
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram for articles sourced from CAB Abstracts and PubMed databases using the terms: TOPIC: (host) AND TOPIC: (transmission OR spread) AND TOPIC: (cattle OR bovine) AND TOPIC: (digital dermatitis).
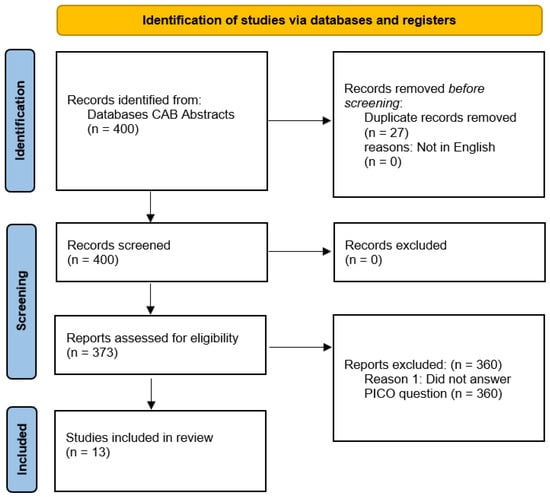
Figure 2.
PRISMA flow diagram for articles sourced from CAB Abstracts databases using the following terms: TOPIC: (production OR lactation OR fertility) AND TOPIC: (cattle OR bovine) AND TOPIC: (digital dermatitis).
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
Articles were not considered if they were not published between 2000 and 2021, if they were not in English, if they did not address the research question in terms of population, intervention, comparison and outcomes (PICO), or if they focused on environmental or agent factors of the disease.
3. Discussion
3.1. Development of Disease
Six host-specific factors were proposed by various authors that affect the susceptibility and development of the disease. Genetics, health status and the presence of co-morbidities, stage of production, age and parity, body-condition score and breed were discussed.
3.1.1. Genetics
Resistance to DD has a low heritability with studies recording breeding values ranging from 0.029–0.073 [12,13]. These low heritability values make breeding for resistance to DD difficult; however, research suggests specific aspects of an individual’s genome may alter the susceptibility to infection with DD. In a study conducted by El-Shafaey et al., the presence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on the IL8 and TLR4 genes associated with disease resistance and susceptibility were investigated via DNA sequencing [14]. It was found that animals resistant to DD had three repeated SNPs in the IL8 gene and one in the TLR4 gene. There were also two SNPs found in the TLR4 gene associated with increased disease susceptibility [14]. IL8 is a chemokine involved in the inflammatory process in the innate immune response and its expression is increased in the M2–M3 stages of DD [14]. TLR4 is a cell-surface membrane protein that binds and recognizes lipopolysaccharide pathogen-associated molecular patterns (LPS PAMPs) of invading bacteria. Therefore, individuals that expressed the specific SNPs had varying disease susceptibility based on which SNPs were present [14]. The data from this study is relevant as DNA screening can be a tool when designing breeding programs to potentially select for resistant animals and select against those with increased susceptibility based on the individual’s genome. These data reinforce that despite the inability to breed for resistance to DD based on heritability, a breeding program can still be designed, assuming it is based on the animal’s genome. A similar study produced by Scholey et al. uncovered an additional eight SNPs associated with increased susceptibility or resistance to DD, further supporting the ability to use DNA sequencing when designing a breeding program for desired traits [15]. Moreover, Onyiro suggests that breeding for genetic resistance to DD will also yield an increase in animal longevity and production as DD is negatively correlated with lifespan and milk fat [12]. This genetic information can be used in combination with improved environmental management to decrease the prevalence and severity of DD [16].
There were limitations to both studies as both used relatively small sample sizes. Herd owners identified susceptible and non-susceptible cattle in the study by Scholey et al.; therefore, animals may have been misclassified as this was a subjective measurement, rather than being based on quantitative measurements and lesions. Further, only specific gene markers were used in each study, therefore the results likely do not encompass all the possible SNPs associated with disease status [14].
Although resistance to DD has low heritability, other characteristics can be preferentially bred for in order to help reduce the susceptibility to DD via indirect means. Breeding from bulls with greater claw health has been shown to decrease the prevalence of DD and other claw disorders in their progeny [13]. Bulls with an Estimated Breeding value of >100 should be used as sires to improve the claw health of a herd [13]. Therefore, the genome of the sire’s progeny will contain characteristics that will yield enhanced claw health and thus decreased susceptibility to DD as damaged claws can foster the proliferation of treponemes.
3.1.2. Health Status and Co-Morbidities
A significant factor that contributes to developing the disease is the health of the animal. Cows that are immunocompromised or immunosuppressed are more susceptible to infection than those that are fit and healthy. Moen et al. found that animals positive for Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus were more likely to have DD lesions than those not immunocompromised by the virus [17]. Mastitis is another common infection of dairy cattle, and one would assume that an existing infection would increase the chance of developing concurrent DD. However, a study conducted by Motamedi et al. determined that infection with mastitis did have an overall influence on the development of DD and there was a decreased prevalence of DD in these cows [18]. Although these findings are counterintuitive, this study should be carefully evaluated for bias. It is unclear as to whether these results were yielded due to a genuine negative correlation between mastitis infection and DD or if using antibiotics in affected cows influenced the outcome [18]. DD results from bacterial infection; therefore, the use of antibiotics to treat mastitis potentially improved the immunity against treponeme invasion [18]. Nevertheless, the effect of concurrent diseases as common as mastitis on developing DD is an area for further research and evaluation.
Ischemic teat necrosis is an additional udder lesion of dairy cattle resulting from infectious agents. Clegg et al. found a relationship between the pathogens involved in this disease process and DD [19]. The treponemes isolated from the cases of ischemic teat necrosis were similar to those present in the DD lesions or in previous recorded cases of DD and other skin lesions [19]. These findings suggest that a concurrent infection with ischemic teat necrosis or other infectious skin diseases can predispose the host to DD lesions as these host tissues could be reservoirs for the culprit bacteria [19]. Therefore, producers must be conscious of the increased risks of developing DD if infectious udder diseases, specifically those caused by treponemes, are present in their herds.
Other co-morbidities that increase the risk of developing DD include several infectious claw disorders such as interdigital dermatitis/heel-horn erosion, interdigital hyperplasia and interdigital phlegmon [10]. The strongest correlation was found between interdigital dermatitis/heel erosion and DD as 32% of cattle with heel erosion also had evidence of DD [10]. This suggests that these infections may have a similar pathogenesis and cause [10]. Therefore, it is imperative for producers to effectively treat all forms of infectious claw disorders when diagnosed in order to prevent the development of additional diseases such as DD.
The health status of an animal is heavily influenced by the individual’s ability to mount an immune response against an invading pathogen. It has been shown that a stronger immune response aids in the prevention of an infectious hoof lesion [20]. There are two types of immune responses, antibody-mediated and cell-mediated, and the stronger of the two responses elicited may influence the susceptibility to infection with DD. An investigation by Cartwright et al. explored the relationship between the infection with DD and the strength of each type of mounted immune response to a patented test protocol. It was found that individuals who elicited a high antibody-mediated immune response to a standard antigenic stimulus had a lower prevalence of DD in comparison with those that exhibited an average or low response [20]. It was also observed that there was no significant difference in the prevalence of DD between those that elicited a high, average or low cell-mediated immune response [20]. Hence it was concluded that a high antibody-mediated immune response is the most effective host-immune defense against DD pathogens. The authors of this study also noted that their results are similar to those of a previous study in which cattle with a high antibody-mediated response had a decreased prevalence of mastitis in contrast to animals with an average or low response. These findings with the results from the Motamedi et al. raise the possibility that the antibody-mediated response elicited by the cattle with mastitis may have helped to defend the host against concurrent infection with DD. Further, the authors discussed that the offspring of sires with high immune responses had less incidence of disease than those of sires with unknown response levels. These results can be used in combination with other genetic information when designing a breeding program and selecting sires to produce more robust offspring with a decreased likelihood of developing DD.
A cow’s ability to mount an effective immune response can determine whether an infection can establish within host tissues. A varying expression of genes that code for immune cells and their reactions will determine the strength of the immune response displayed. Scholey et al. determined that DD lesions had an increased expression of mRNA that codes for proteins which encourage bacterial survival and immune evasion [2]. The invading bacteria stimulate the production of these proteins; therefore, cattle with an excessive immune response may perpetuate the infection and foster a beneficial environment for the treponemes to proliferate. There was also a decreased expression of specific major histocompatibility class II genes, which inhibit the local immune response and promote the establishment of disease, in DD lesions [2]. This reinforces the importance of an appropriate host-immune response in the defense against bacterial invasion.
3.1.3. Stage of Production
The stage of production affects the susceptibility of an animal to infection as their immune status, energy levels, feed intake, etc. vary throughout different stages, with several studies analyzing the susceptibility to DD infection based on the stage of lactation. There is conflicting evidence regarding the stage of lactation at which a cow is most at risk of developing DD lesions. In a study conducted by Nielsen et al., it was concluded that cattle in early lactation had a reduced risk of developing lesions in comparison with those in mid or late lactation, and the lesions that developed in late lactation were more likely to resolve [21]. The lesions present in late lactation also had a shorter duration than those present in early lactation [21]. A review by Vermeersch and Opsomer cited peak lactation and the first month after calving as the most susceptible timeframe for cattle to be infected [13]. The suggested explanation for these findings is that after calving, cows are in a negative energy balance which leads to less fat cushion and skin in the foot region [13]. This host environment is more vulnerable to invasion and breakdown of the skin barrier by bacteria. This conclusion agrees with the findings of Holzhauer et al. in which cattle in peak lactation had higher odds of developing DD than those past peak lactation (greater than 60 days on milk) [10]. Holzhauer et al. also found, coinciding with previous research, that dry cattle are the least at risk of developing DD [10]. A possible reasoning for this pattern is that dry cows are often fed a higher roughage feed, which results in more solid feces and thus less staining, moisture and fecal-matter buildup on the feet of cattle [10]. A similar study conducted on New Zealand dairy herds also found that lesions are more likely to resolve than develop during the late-lactation and dry periods compared to early and mid lactation [6].
The conflicting results in these studies may be due to variation in the climate and management factors such as the housing system (indoor vs. pastoral), foot-bathing protocol, hoof trimming, treatment provided, etc. and therefore the methods must be evaluated to ensure the results are comparable.
3.1.4. Age and Parity
Differences in the age and parity of cattle are a risk factor for developing DD. Lower parity and primiparous cows are more likely to develop DD lesions and persistent infections. An investigation conducted by Nielsen et al. compared DD lesions in parity 1, 2 and 3 lactating cattle. Parity 1 cattle had an increased risk of developing lesions compared to parity 3 cows; however, parity 2 cows had a risk greater than parity 1 animals [21]. Overall, the parity 3 cows had the least risk of developing DD lesions and were also more likely to recover from the lesions if infected, while parity 1 cattle were more likely to develop persistent lesions and the least likely to recover from them [21]. These findings agree with evidence from the study by Holzhauer et al. in which the risk of developing DD decreased with increasing parity [10]. These studies also reference that their findings coincide with earlier studies in which parity 1 cows were at a greater risk of DD than higher parity cows [10]. Parity 1 cows are often younger animals that are exposed to drastic alterations in diet, nutrition, and environment, which generates highly stressed and immunosuppressed animals [22]. Moreover, Relun et al. found that primiparous cattle with moderate DD lesions had a lower test-day milk yield than affected multiparous cattle, further supporting the notion that primiparous cattle are more vulnerable to acute infection [23].
Dolecheck et al. investigated the costs associated with DD infections of cattle in various production stages and parities. The case costs were the greatest at the beginning of lactation, therefore more animals were severely affected at this stage versus the dry period [24]. This supports the above statements that dry cows are less susceptible and more likely to recover from infection compared to those in peak production. The study also suggests there were greater costs with multiparous cases versus primiparous cases with the lowest costs associated with primiparous cows past peak lactation [24]. It is unclear if this results from decreased disease occurrence or fewer losses associated with decreased production in primiparous cattle. Due to this discrepancy, it is difficult to determine if these findings, which contradict the above-mentioned studies that state that primiparous cattle are more susceptible to DD, can be used as contrasting evidence. More studies seem to support the notion that multiparous cattle are less likely to develop DD lesions.
The age at first calving also had a relationship with susceptibility to DD [25]. In a herd of heifers calving over a four-month period, late calvers were more susceptible to being intermittently or consistently infected. Therefore, an increased age at calving was related to a higher risk of acquiring DD lesions [25]. This may have been because healthier calves typically have superior growth rates and achieve breeding weight sooner than their less-fit herd mates, therefore being inseminated and subsequently calving earlier. The authors also suggested that some cattle may have had varying types of epithelium and foot conformations, rendering some more susceptible to barrier breakdown than others [25]. Schöpke et al. uncovered similar findings and suggested that this may coincide with older heifers spending longer periods potentially exposed to treponemes and thus being more likely to succumb to disease [26].
3.1.5. Body Condition
A cow’s ability to reach and maintain a target weight and body condition are essential benchmarks to achieve in order to increase successful mating, calving and productive seasons. An ideal body-condition score (BCS) ensures that cattle are receiving adequate nutrition to maintain their own health and that of their progeny. Poor or elevated body condition can predispose animals to a variety of metabolic and infectious diseases and decreased production. Cattle should ideally enter calving and peak lactation at a body-condition score of 3. Over-conditioned cows or cows with a BCS of less than 2.5 are at an increased risk of developing DD, amongst other disorders, as found by Schöpke et al. Cattle with a BCS of <2.5 had the highest prevalence of DD compared to cattle with BCSs of 2.5–3 and >3. Those in the ideal-BCS category (2.5–3) had the lowest prevalence of DD [27]. Cattle with an ideal BCS will have the most robust immune system, specifically when entering periods of great energy and metabolic demand, making them the least susceptible to disease.
3.1.6. Breed
Certain breeds of cattle are farmed in specific regions as they have been bred to adapt to that environment and climate. There are large varieties of breeds of beef cattle, however there are far fewer breeds of dairy cattle farmed internationally. Holzhauer et al. found that Holstein–Friesian (purebred and crossbred) cattle were at a greater risk of acquiring DD than Meuse–Rhine–Ijssel cattle, which are a dual-purpose breed [10]. Holstein–Friesian crossbreeds that are greater than 50% genetically Holstein–Friesian are also more likely to develop claw disorders [22]. The increased risk of Holstein–Friesian cattle acquiring DD compared to other breeds may be due to several confounding factors such as differences in foot conformation, body condition, housing system, and time spent walking [12]. An investigation conducted by Vlček et al. stated that DD was greater in Holsteins than Slovak Spotted cattle, which presents an additional example of Holsteins having a greater susceptibility to infection than other dairy breeds [28].
3.2. Transmission
Bovine DD is a highly contagious disease that, once established in a herd, is difficult to eradicate and prevent further spread. Estimates of the reproductive number (R, the average number of secondary cases per infectious case) for DD infection ranged from 0.5–3.3, meaning that the infection can likely spread within a population of nonimmunized animals [24]. The authors hypothesized that the hoof conformation, i.e., the tissues that act as reservoirs for bacteria, and the stage of production affect the transmission of DD within a herd.
3.2.1. Hoof Conformation
Variations in hoof conformation and gait influence cattle susceptibility to various lameness lesions. Onyiro et al. indicated that there are several physical and behavioral individual traits that promote the resistance or development of DD [12]. Cattle with improved bone quality, locomotion score and leg and feet composites had a decreased incidence of DD. Therefore, flatter bones, normal leg and foot positioning (absence of bowing, varus or valgus), and regular locomotion can decrease the risk of developing DD lesions [12]. A genetic correlation between these traits and DD was observed as animals with superior scores for these traits had a lower incidence of DD, suggesting that breeding from these animals can minimize the risk of DD infection in their progeny. A poor hoof conformation can predispose the development and subsequent transmission of DD. An infection with DD can lead to hoof-conformation changes that may promote the future development of disease and reinfection. The affected tissues become a reservoir for disease, thereby promoting the persistence of infection and the ability to spread the bacteria to other cattle [29]. Gomez et al. indicated that changes to the heel specifically foster a microenvironment for bacterial proliferation and transmission. Their results state that animals that developed deeper interdigital spaces because of DD infection were at a greater risk of reinfection and propagating the disease within the herd, in comparison with healthy cattle. These deep interdigital spaces allow for the collection of debris and waste buildup within the foot, facilitating a suitable environment for bacterial growth. Anaerobic environments readily establish within these spaces, possibly further maintaining the bacterial population. Dyskeratosis and increased skin proliferation was recorded in animals affected with M2 lesions and they had an increased risk of disease recurrence and spread [29]. Although the changes seen in these animals were recorded after infection with DD, these results can be extrapolated to hypothesize that animals born with deeper interdigital spaces, a type of dyskeratosis or readily reactive and proliferating skin may be more susceptible to DD infection and maintaining and spreading the bacteria to other cattle [30]. Biemans et al. found that cattle with M4 lesions contributed to a greater reproductive ratio of disease than those with lower class lesions, therefore emphasizing the importance of preventing lesions from progressing [31]. Moreover, producers can reference this information to promote the implementation of proper hoof trimming regulations and management to prevent conformation changes yielding more vulnerable and poor performing cattle [32].
A limitation of the study conducted by Onyiro et al. is differentiating between an appropriate locomotion score and the changes in gait due to discomfort resulting from a co-morbidity. Pavlenko et al. found that cattle with DD lesions had increased activity times and vigilance and spent less time performing normal or desired behaviors such as laying down and ruminating [5]. Therefore, when selecting for sires with desired locomotion scores, it is important to note which cattle perform movements that optimize production and which changes in stride and gait are abnormal or associated with pain.
3.2.2. Tissues as Bacterial Reservoirs
An investigation by Evans et al. explored other tissues outside of the feet as potential reservoirs for treponeme bacteria and thus sources of shedding and transmission. Treponemes are present within DD lesions but typically absent in healthy feet, yielding the question of whether other healthy tissues in cattle can harbor the bacteria. Treponemes were isolated from the oral cavity of 14.3% of cattle and 14.8% of rectal tissues of tested cattle [9]. Treponemes were not identified in feces, therefore only minimal and sporadic shedding of bacteria from rectal tissues may be present and thus are not a significant source of transmission [9]. The bacteria isolated from the gingival tissue were only present in cattle symptomatic for DD; however, asymptomatic cattle harbored treponemes in the rectal cavity [9]. The presence of bacteria in several gastrointestinal tissues are alternative sources of infection and a potential concern for asymptomatic shedding from otherwise healthy animals. It may be possible for mucosal transmission of bacteria from the oral cavity, but additional research is required to determine the epidemiology. The authors also noted differences in bacterial reservoirs with variations in housing systems; therefore, environmental contribution must be considered when evaluating the host tissue’s ability to store bacteria. Further investigation is required to determine the contribution of oral and rectal harboring of bacteria to herd transmission of DD.
3.2.3. Stage of Production
Cattle have varying susceptibility to infection and ability to shed bacteria based on the stage of production. A study of New Zealand dairy cattle determined that late lactation and dry periods were associated with deceased transmission of DD in comparison with early and peak lactation [6]. This coincides with the above findings that late lactation is also when cattle are the least susceptible to infection. Cattle are stressed and likely immunocompromised during calving, therefore it is expected that the transmission rates of disease decreased after calving. Cattle were also more likely to be recovering from a previous lesion than acquiring a new infection [6]. The persistence of infection within a herd was heavily influenced by individuals with advanced lesions. These findings are relevant for producers as minimizing transmission rates in late-lactation and dry periods will decrease the number of novel infections acquired in subsequent lactations as there are fewer bacteria shed and circulating within the herd. Yang et al. emphasized the importance of preventing advanced lesions from developing as they predicted a significant increase in the prevalence of DD within future herds when advanced lesions are present [6]. Producers can use this information to ensure that optimal management and prophylaxis measures are implemented during times of elevated transmission. Additional screening checks for lesions and treatments such as foot bathing can be increased during this window to prevent the further spread of DD.
An alternative study conducted by Yang et al. indicated that heifers are a significant source of disease introduction and transmission to a herd [8]. It is thought that heifers are reservoirs for treponemes and are therefore a source of disease, particularly when introduced into a naïve herd [8]. The introduction of clinically affected animals into an immunologically naïve herd is a reported risk factor for the transmission of DD [33]. This reinforces the importance of proper heifer management to prevent them from becoming infectious and thus spreading the disease to the rest of the herd.
4. Conclusions
Digital dermatitis is an internationally emerging disease with consequences beyond lameness. Infection leads to poor performance in several production parameters including milk yield, fertility, reproduction, growth and increased economic costs due to treatment, culling and decreased performance [34]. This review emphasized host-specific factors that increase individual susceptibility to infection and transmission of the disease. Producers can use the information from this review to highlight characteristics in their herds that yield DD-susceptible cattle. Improvements to management can be implemented to improve future herd health and generate more robust cattle. The ability to breed for resistance to DD is limited; however, selecting for traits that minimize the risk of the development of lesions is possible [35]. The genetic testing of sires to identify those with SNPs present in their genome for increased susceptibility or resistance can be incorporated into breeding programs. Breeding from sires with improved claw health and hoof conformation can also bear progeny with greater protection from infection. Animals of superior health status lacking co-morbidities are less likely to acquire a DD infection, therefore again stressing the importance of proper management and disease prophylaxis to maintain a healthy herd. Ischemic teat necrosis, concurrent mastitis infections and claw diseases increased individual susceptibility to DD infection. The ability of a cow to mount an appropriate antibody-mediated immune response can also prevent the establishment of infection. Dry cattle and those past peak lactation are less likely to develop DD lesions compared to those at peak lactation and those in the first month post calving. Primiparous cattle are more likely to acquire DD and have persistent lesions as the risk of DD decreases with increasing parity. The breed and condition of cattle also influences the susceptibility to infection as Holstein-Friesians and over- or under-conditioned cows are at a greater risk of acquiring infection.
Several host factors can influence the transmission of DD within a herd. Cattle with improved hoof conformation and gait characteristics are poor hosts for bacterial proliferation and reinfection, therefore decreasing their ability to spread the infection. Oral and rectal tissues are reservoirs for treponeme bacteria, therefore cattle with greater numbers of bacteria in these tissues may harbor and consequently shed infection at an increased rate. Cattle that develop advanced lesions have a greater contribution to the persistence of the disease within a herd than those with early-stage lesions. Cattle are least susceptible to infection in the dry period and post peak lactation, which coincides with the decreased transmission of disease during these periods.
Various aspects of DD infections require further research. Integrating desirable physical characteristics and genetic information into breeding programs requires additional research to emphasize which traits can be selected for and how they can aid in the prevention of infection. Producing robust progeny with improved immune systems and physical traits will provide optimal defense against introduction, establishment and reduce severity of infections. Further studies should also investigate host tissues as reservoirs for infection and if the gastrointestinal tract is a significant source of asymptomatic shedding of treponemes.
Studies that investigate several breeds should be launched to evaluate if Holstein-Friesians are truly the most susceptible to infection, or if those findings result from lack of diversity in sample populations.
Fostering cattle with ideal host defense mechanisms against infection in conjunction with proper management and control of environmental factors can work cohesively to prevent infection with DD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T.C. and D.S.B.; methodology, A.T.C. and D.S.B.; formal analysis, A.T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T.C.; writing—review and editing, D.S.B.; supervision, D.S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Evans, N.J.; Murray, R.D.; Carter, S.D. Bovine digital dermatitis: Current concepts from laboratory to farm. Vet. J. 2016, 211, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholey, R.A.; Evans, N.J.; Blowey, R.W.; Massey, J.P.; Murray, R.D.; Smith, R.F.; Ollier, W.E.; Carter, S.D. Identifying host pathogenic pathways in bovine digital dermatitis by RNA-Seq analysis. Vet. J. 2013, 3, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolecheck, K.; Dwyer, R.; Overton, M.; Bewley, J.M. A survey of United States dairy hoof care professionals on costs associated with treatment of foot disorders. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8313–8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omontese, B.; Bellet-Elias, R.; Molinero, A.; Catandi, G.D.; Casagrande, R.; Rodriguez, Z.; Bisinotto, R.S.; Cramer, G. Association between hoof lesions and fertility in lactating Jersey cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3401–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlenko, A.; Bergsten, C.; Ekesbo, I.; Kaart, T.; Aland, A.; Lidfors, L. Influence of digital dermatitis and sole ulcer on dairy cow behaviour and milk production. Animal 2011, 8, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.A.; Laven, R.A.; Müller, K.R.; Gates, M.C. Modelling the transmission dynamics of bovine digital dermatitis in New Zealand pastoral dairy production systems. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akin, I.; Akin, T. Economic impact of digital dermatitis treatment on a dairy farm: An application of the break-even analysis. Cienc. Rural 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.A.; Gates, M.C.; Müller, K.R.; Laven, R.A. Bayesian analysis of herd-level risk factors for bovine digital dermatitis in New Zealand dairy herds. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.J.; Timofte, D.; Isherwood, D.R.; Brown, J.M.; Williams, J.M.; Sherlock, K.; Lehane, M.J.; Murray, R.D.; Birtles, R.J.; Hart, C.A.; et al. Host and environmental reservoirs of infection for bovine digital dermatitis treponemes. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhauer, M.; Hardenberg, C.; Bartels, C.; Frankena, K. Herd-and cow-level prevalence of digital dermatitis in the Netherlands and associated risk factors. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyiro, O.; Andrews, L.; Brotherstone, S. Genetic parameters for digital dermatitis and correlations with locomotion, production, fertility traits, and longevity in Holstein-Friesian dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4037–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeersch, A.-S.; Opsomer, G. Digital dermatitis in cattle, part I: Factors contributing to the development of digital dermatitis. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 88, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shafaey, E.-S.; Ateya, A.; Ramadan, H.; Saleh, R.; Elseady, Y.; Fadl, E.A.E.; El-Khodery, S. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL8 and TLR4 genes as candidates for digital dermatitis resistance/susceptibility in Holstein cattle. Anim. Biotechnol. 2017, 28, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, R.; Blowey, R.; Murray, R.; Smith, R.F.; Cameron, J.; Massey, J.P.; Ollier, W.E.; Carter, S.D. Investigating host genetic factors in bovine digital dermatitis. Vet. Rec. 2012, 171, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.; Danner, A.L.; Famula, T.R.; Oberbauer, A.M. Genome-wide association studies reveal susceptibility loci for digital dermatitis in holstein cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, A.; Holzhauer, M.; Berends, I. The effect of BVDV on various claw disorders: A case control pilot study. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference, American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 September 2007; p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Motamedi, N.; Mohamadnia, A.; Khoramian, B.; Azizzadeh, M. Evaluation of Mastitis Impact on Lameness and Digital Lesions in Dairy Cows. Iran. J. Vet. Surg. 2018, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, S.; Carter, S.; Stewart, J.; Amin, D.M.; Blowey, R.W.; Evans, N.J. Bovine ischaemic teat necrosis: A further potential role for digital dermatitis treponemes. Vet. Rec. 2016, 178, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, S.L.; Malchiodi, F.; Thompson-Crispi, K.; Miglior, F.; Mallard, B.A. Prevalence of digital dermatitis in Canadian dairy cattle classified as high, average, or low antibody-and cell-mediated immune responders. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8409–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, B.; Thomsen, P.; Green, L.E.; Kaler, J. A study of the dynamics of digital dermatitis in 742 lactating dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 104, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Refaai, W.; Van Aert, M.; El-Aal, A.A.; Behery, A.; Opsomer, G. Infectious diseases causing lameness in cattle with a main emphasis on digital dermatitis (Mortellaro disease). Livest. Sci. 2013, 156, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relun, A.; Lehebel, A.; Chesnin, A.; Guatteo, R.; Bareille, N. Association between digital dermatitis lesions and test-day milk yield of Holstein cows from 41 French dairy farms. J. Diary Sci. 2013, 96, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolecheck, K.; Overton, M.; Mark, T.; Bewley, J. Use of a stochastic simulation model to estimate the cost per case of digital dermatitis, sole ulcer, and white line disease by parity group and incidence timing. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capion, N.; Boye, M.; Ekstrøm, C.T.; Jensen, T.K. Infection dynamics of digital dermatitis in first-lactation Holstein cows in an infected herd. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6457–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpke, K.; Gomez, A.; Dunbar, K.; Swalve, H.; Döpfer, D. Investigating the genetic background of bovine digital dermatitis using improved definitions of clinical status. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 8164–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schöpke, K.; Weidling, S.; Pijl, R.; Swalve, H.J. Relationships between bovine hoof disorders, body condition traits, and test-day yields. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlček, M.; Ofúkaný, M.; Kanka, T.; Kadlečík, O.; Kasarda, R. Influence of claw disorders on production and reproduction performance in observed herds of dairy cows. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2016, 19, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, A.; Cook, N.; Rieman, J.; Dunbar, K.A.; Cooley, K.E.; Socha, M.T.; Döpfer, D. The effect of digital dermatitis on hoof conformation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, A.; Anklam, K.; Cook, N.; Rieman, J.; Dunbar, K.A.; Cooley, K.E.; Socha, M.T.; Döpfer, D. Immune response against Treponema spp. and ELISA detection of digital dermatitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4864–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemans, F.; Bijma, P.; Boots, N.M.; de Jong, M. Digital dermatitis in dairy cattle: The contribution of different disease classes to transmission. Epidemics 2018, 23, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogstad, Å.; Østerås, O.; Fjeldaas, T.; Refsdal, A. Bovine claw and limb disorders at claw trimming related to milk yield. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Döpfer, D.; Holzhauer, M.; van Boven, M. The dynamics of digital dermatitis in populations of dairy cattle: Model-based estimates of transition rates and implications for control. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, M.; Saavedra, E.; Gaytán, L.; Velizb, F.G.; Macías-Cruzc, U.; Avendaño-Reyesc, L.; García, E. The effect of lameness-causing lesions on milk yield and fertility of primiparous Holstein cows in a hot environment. Livest. Sci. 2018, 217, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemans, F.; De Jong, M.C.; Bijma, P. Genetic parameters and genomic breeding values for digital dermatitis in Holstein Friesian dairy cattle: Host susceptibility, infectivity and the basic reproduction ratio. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2019, 51, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).