Abstract
Background: Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), a neuroendocrine tumor originating from thyroid parafollicular C-cells, presents therapeutic challenges, particularly in advanced stages. While RET proto-oncogene mutations are known drivers, a comprehensive understanding of the broader somatic mutation landscape is needed to identify novel therapeutic targets and improve prognostication. This study leveraged the extensive AACR Project GENIE dataset to characterize MTC genomics. Methods: A retrospective analysis of MTC samples from GENIE examined recurrent somatic mutations, demographic/survival correlations, and copy number variations using targeted sequencing data (significance: p < 0.05). Results: Among 341 samples, RET mutations predominated (75.7%, mostly M918T), followed by HRAS (10.0%) and KRAS (5.6%), with mutual exclusivity between RET and RAS alterations. Recurrent mutations included KMT2D (5.3%), CDH11 (5.3%), ATM (5.0%), and TP53 (4.1%). NOTCH1 mutations were enriched in metastatic cases (p = 0.023). Preliminary associations included sex-linked mutations (BRAF/BRCA1/KIT in females, p = 0.028), and survival (ATM associated with longer survival, p = 0.016; BARD1/BLM/UBR5/MYH11 with shorter survival, p < 0.05), though limited subgroup sizes warrant caution. Conclusions: This large-scale genomic analysis confirms the centrality of RET and RAS pathway alterations in MTC and their mutual exclusivity. The association of NOTCH1 mutations with metastasis suggests a potential role in disease progression. While findings regarding demographic and survival correlations are preliminary, they generate hypotheses for future validation. This study enhances the genomic foundation for understanding MTC and underscores the need for integrated clinico-genomic datasets to refine therapeutic approaches.
1. Introduction
Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) is a neuroendocrine neoplasm arising from thyroid parafollicular C-cells [1,2], which produce calcitonin [3,4]. Representing 5–10% of thyroid malignancies globally [1,3], MTC is relatively rare, with an annual incidence of approximately 0.5–1.0 per 100,000 individuals [5]. The disease manifests in two primary forms: a sporadic variant accounting for 75–80% of cases, with peak incidence typically between ages 40 to 60, and a hereditary form comprising 20–25% [3,4], which is associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndromes (MEN2A, MEN2B, Familial MTC) and often presents earlier in young adulthood [1,4]. Prognostically, the overall 10-year survival rate for MTC ranges from 64% to 84%, largely dependent on the stage at diagnosis [5,6]. Common clinical presentations include a painless thyroid nodule or neck mass [1,4]; however, symptoms may also arise from excess calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) secretion (e.g., flushing, diarrhea) [3,4] or from local tissue invasion causing dysphagia and hoarseness [3,7,8,9].
The standard treatment for localized MTC involves total thyroidectomy with central lymph node dissection, aiming for complete tumor removal and biochemical cure, indicated by normalized calcitonin and CEA levels [10,11,12,13]. These biomarkers are crucial for monitoring treatment efficacy and detecting recurrence [12,13]. Management of recurrent or metastatic disease presents significant challenges [10,14], sometimes necessitating re-operation or palliative external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) [15]. Notably, MTC exhibits inherent resistance to radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy and traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy, distinguishing its treatment approach from that of differentiated thyroid cancers [10,14,15].
For progressive, metastatic MTC, several FDA-approved therapies are available, primarily multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs) or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) [10,14,15,16]. These agents, including Vandetanib [17,18] and Cabozantinib [18,19,20], target pathways involving the RET proto-oncogene and VEGFR, demonstrating clinical efficacy in advanced disease [10,15,16,19]. However, these systemic treatments are not curative, carry notable toxicities, and their long-term effectiveness can be limited by the development of resistance [10,16,18,19]. Consequently, there is a pressing need to enhance the biological understanding of MTC to identify novel therapeutic targets that can overcome these limitations and improve patient outcomes [10,11,19]. Ongoing research explores newer generation RET-selective inhibitors, immunotherapy options, and combination strategies [10,19,21].
At the molecular level, the RET proto-oncogene plays a central role in MTC pathogenesis [22,23,24]. Germline RET mutations are present in nearly all hereditary cases [22,24,25], while somatic RET mutations are found in approximately 40–60% of sporadic MTCs [23]. Mutations in RAS genes (primarily HRAS and KRAS) are also identified in roughly 20–30% of sporadic tumors, often occurring mutually exclusively with RET alterations [23]. These mutations drive oncogenesis by activating key signaling pathways such as MAPK and PI3K/AKT [26]. Importantly, RET and associated pathways are critical targets for the currently approved TKIs [23,27].
Despite these advances in targeted therapy, significant research gaps remain, particularly in characterizing the complete spectrum of genomic alterations beyond the well-known RET and RAS drivers. Secondary drivers contributing to disease progression or metastasis are also inadequately defined. This study aims to utilize a publicly accessible repository of patient-level data to comprehensively characterize the somatic mutational landscape of MTC. The goal is to enhance our understanding of its molecular mechanisms, suggest potential new therapeutic approaches, and ultimately improve disease modeling and treatment strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
This study utilized de-identified, publicly available data, thereby receiving an exemption from institutional review board review by Creighton University (Phoenix, AZ, USA). The data originate from the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Project Genomics Evidence Neoplasia Information Exchange (GENIE)® database, a large repository aggregating genomic sequencing information from 19 international cancer centers. Clinical and genomic records from this database were accessed, limited to data archived from 2017 onwards, on 15 April 2025, through the cBioPortal platform (v17.0-public).
The GENIE dataset reflects heterogeneity inherent in multi-center contributions. Genomic sequencing was performed using various platforms: targeted gene panels (covering 50 to 555 genes), whole-exome sequencing (WES), or whole-genome sequencing (WGS). Approximately 80% of the samples were analyzed via targeted panels, 15% via WES, and 5% via WGS. Correspondingly, sequencing depths varied, achieving over 500× for targeted panels, roughly 150× for WES, and approximately 30× for WGS. The dataset included both tumor-only sequencing specimens (65%) and matched tumor-normal pairs (35%), with the latter facilitating the filtration of germline variants.
While each contributing institution may employ unique bioinformatic pipelines for mutation calling and annotation, they all adhere to GENIE harmonization protocols, such as utilizing GATK for variant detection and ANNOVAR for annotation. It is acknowledged that variations in these pipelines might exist between, and even within, participating centers. Data on therapeutic response and clinical outcomes are present for certain cancer types in GENIE, but specific treatment regimens for the MTC cohort were not available.
This analysis queried patients within the GENIE dataset with a confirmed pathological diagnosis of MTC, selected from a broader cohort of thyroid malignancies. Samples were categorized based on origin: primary (from the initial tumor) or metastatic (from distant sites). We collected data encompassing somatic mutations, histological subtype, and clinical demographics (including race, sex, and age). Although the design of targeted sequencing panels differed across institutions, core cancer-related genes (e.g., RET, TP53, KMT2D) were typically included. Non-actionable genes were generally omitted from panels, and structural variants were excluded from this specific analysis.
Only nonsynonymous variants (missense, nonsense, frameshift, and splice-site mutations) with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of 5% or greater and sequencing coverage of at least 100× were retained for analysis. Synonymous mutations and variants of unknown significance were excluded. Mutation calls were sourced from the GENIE project’s harmonized Mutation Annotation Format (MAF) files, which provide standardized variant annotations (e.g., gene and protein alteration abbreviations) across all contributors. Copy number alterations (CNAs) were assessed, specifically focusing on homozygous deletions and high-level amplifications, and the frequencies of recurrent events were determined.
All statistical analyses were conducted using R/R Studio (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Boston, MA, USA) version 4.4.2. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were summarized as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages. Associations between categorical variables were examined using the chi-squared test. For comparisons of continuous variables between two groups, normality was assessed; a two-sided Student’s t-test was used for normally distributed data, and a Mann–Whitney U test was applied for non-normally distributed data. To account for multiple comparisons, the Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction was employed.
Differences in gene-specific mutation frequencies between primary and metastatic tumor groups were specifically evaluated using a chi-squared test comparing the proportion of mutated samples in each category. Samples with any missing data relevant to a specific analysis were excluded from that analysis.
The study cohort consisted of 304 patients with sufficient survival information to compute Kaplan–Meier curves, with overall survival time used for analysis. Two Kaplan–Meier curves were drawn for each gene in the database, with one curve representing all patients with a mutation in the given gene, and the other curve representing patients without a mutation in that gene. Log-rank tests between each curve were performed, with subsequent Benjamini–Hochberg multiple hypothesis test correction.
3. Results
Due to the limited sample size of MTC within genomic cohorts, the initial demographic analysis combined primary and metastatic tumor samples. This analysis included 341 samples obtained from 317 patients. Patient demographics and sample characteristics are detailed in Table 1. Of the patients, 183 (57.7%) were male and 129 (40.7%) were female. Regarding ethnicity, 185 (58.4%) were categorized as Non-Spanish/Non-Hispanic, 28 (8.8%) were Spanish/Hispanic, and the ethnicity for 104 (32.8%) patients was either unknown or not collected. By race, the cohort comprised 222 (70.0%) White, 23 (7.3%) Asian, and 23 (7.3%) Other. The race of 38 (12.0%) patients was unknown or not collected. The cohort included 3 pediatric patients (0.9%) and 314 adult patients (99.1%). Of the 341 samples analyzed, 136 (39.9%) were from primary tumors and 187 (54.8%) were from metastatic sites. The sample type was not collected for 13 (3.8%) samples.

Table 1.
MTC patient and sample demographics.
Figure 1 summarizes the most frequent somatic alterations identified in this MTC cohort. Across 341 profiled samples, the most commonly mutated genes included RET (n = 258; 75.7%), HRAS (n = 34; 10.0%), KRAS (n = 19; 5.6%), KMT2D (n = 18; 5.3%), CDH11 (n = 18; 5.3%), ATM (n = 17; 5.0%), TP53 (n = 14; 4.1%), SMARCA4 (n = 13; 3.8%), ARID1A (n = 13; 3.8%), FAT1 (n = 12; 3.5%), and KMT2A (n = 10; 2.9%). RET mutations were notably prevalent in this cohort. Structural variants were analyzed in 249 samples and were infrequent, with PRKN, EPB41, BRAF, and BCL6 each identified with structural variants in only two samples (0.8%). In addition, recurrent copy number alterations (CNAs) were assessed in 181 profiled samples. Homozygous deletions were most common in CDKN2A (n = 6; 3.3%) and CDKN2B (n = 4; 2.2%). Amplifications were observed in genes including RET (n = 3; 1.7%) and IKBKE (n = 2; 1.1%).
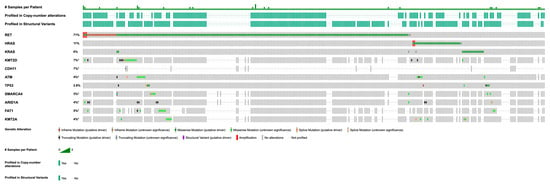
Figure 1.
Recurrent genetic alterations in MTC, filtered for genes with ≥5 mutations, ≥100× coverage, and ≥5% variant allele frequency (VAF). Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete profiling data for this gene across all samples.
3.1. Genetic Differences by Race and Sex
Analysis of mutational profiles stratified by self-reported race/ethnicity revealed several statistically significant associations (Table 2), although many were based on observations in very small subgroups and require cautious interpretation. Mutations in ASXL1, JAK1, PIK3C2G, and FLT4 were significantly enriched in patients identifying as Native American (each p < 0.001); however, each association was driven by a mutation identified in the single Native American patient included in this specific analysis for whom race data were available and the gene was sequenced. Mutations in SMC3 (p < 0.001, based on 3 occurrences) and CRKL (p = 0.001, based on 2 occurrences) showed significant enrichment in the Asian patient subgroup (N = 23 total Asian patients). A distinct set of mutations, including ABL1, RAF1, SMAD4, and SRC, were significantly enriched in Black patients (each p < 0.001), although again, each association stemmed from a single observation within the Black patient subgroup (N = 9 total Black patients). Furthermore, alterations in PREX2 (p < 0.001), ZFHX3 (p < 0.001), FANCD2 (p < 0.001), PAX3 (p = 0.001), and BRIP1 (p = 0.002) were most prevalent in the ‘Other’ racial category (N = 23 total), driven by two or three occurrences for each gene.

Table 2.
Race/Ethnicity and Sex-Associated Mutations (p < 0.05).
When stratified by sex, some differences in mutation frequencies were also observed (Table 2). Mutations in BRAF, BRCA1, and KIT reached statistical significance for enrichment in female patients (p = 0.0277 for each), although this was based on observing mutations in four female samples (2.9%) versus zero male samples for each gene. The four BRAF mutations identified in female patients included one p.V600E variants and three non-V600E variants, specifically a EPB41-BRAF Fusion, p.L525R, and p.E24D. Alterations in FGFR3, AR, EXO1, and TET1 showed trends toward higher frequency in females (p = 0.068), but did not reach statistical significance. Conversely, no specific mutations reached statistical significance for enrichment in male patients based on the available data and applied thresholds. These preliminary demographic associations warrant validation in larger, more diverse cohorts.
3.2. Co-Occurrence and Mutual Exclusivity of Mutations
Significant mutual exclusivity patterns were observed among frequently mutated genes in this cohort. Mutations in RET were significantly mutually exclusive with mutations in HRAS (p < 0.001) and KRAS (p < 0.001), with zero or only one co-occurrence observed, respectively. A trend towards mutual exclusivity was also noted between RET and TP53 mutations (p = 0.015), with zero co-occurrences. Conversely, significant co-occurrence patterns were also identified. ATM mutations frequently co-occurred with ARID1A mutations (n = 3; p = 0.009) and showed a tendency to co-occur with SMARCA4 mutations (n = 2; p = 0.035). KMT2D mutations significantly co-occurred with FAT1 mutations (n = 2; p = 0.019), and KRAS mutations significantly co-occurred with KMT2A mutations (n = 2; p = 0.026).
3.3. Primary vs. Metastatic Mutations
The overall study cohort included 136 primary and 187 metastatic samples. For the comparative genomic analysis based on the available data, several differences were observed between these groups. NOTCH1 mutations were significantly enriched in and exclusively observed within metastatic samples (n = 7, 3.74%; p = 0.0229) compared to primary tumors where they were absent. RET mutations were also significantly more frequent in the metastatic cohort compared to the primary cohort (77.54% vs. 63.24%; p = 0.006). Conversely, mutations in AXL, BRAF, and MRE11 were observed only in primary samples (n = 3, 2.21% each), although this exclusivity did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.0737). Trends towards enrichment were observed for ARID1A in metastatic samples (p = 0.080) and for HRAS in primary samples (p = 0.093). While these specific gene-level differences, particularly the significant enrichment of NOTCH1 and higher frequency of RET mutations in metastases, were identified in this comparison, the analysis primarily focused on individual gene frequencies rather than a comprehensive assessment of shifts in the entire mutational landscape signature between primary and metastatic tumors.
3.4. Most Common Specific Mutations in RET
The most prevalent somatic mutations (Table 3, Figure 2) identified across the analyzed cohort include M918T (n = 82, 67.8%), a recurrent missense variant in the RET proto-oncogene (COSMIC ID: 295), characterized by constitutive kinase activation and strongly associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma. The C634R substitution (n = 12, 9.9%; COSMIC ID: 28), a cysteine-altering missense mutation in RET’s extracellular domain, disrupts disulfide bonding and is linked to multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. Third, E632_L633del (n = 9, 7.4%), an in-frame deletion (IF del) within RET’s intracellular juxtamembrane region, promotes dimerization-independent kinase activation. The C634Y variant (n = 2, 1.7%; COSMIC ID: 28) similarly alters cysteine residues, while S891A (n = 1, 0.8%), a missense mutation in RET’s kinase domain, confers resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.

Table 3.
Most common specific somatic mutations in the RET gene.
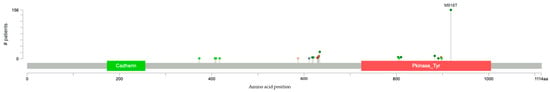
Figure 2.
Lollipop diagram of the most common specific mutations in RET-mutated MTC.
3.5. Mutations Associated with Differential Survival
The study cohort consisted of 304 patients (see Table 4) with sufficient survival information to compute Kaplan–Meier curves, with overall survival time used for analysis. BARD1, BLM, UBR5, and MYH11 were each found to be mutated in at least three samples, and mutations in these genes were associated with poorer overall survival compared to non-mutated cases, while mutations in ATM were associated with longer overall survival compared to non-mutated cases.

Table 4.
Mutations Correlated with Prolonged or Reduced Survival.
4. Discussion
This genomic analysis of 341 MTC samples from the AACR Project GENIE database confirmed the central role of the RET proto-oncogene, which was mutated in 75.7% of samples, with the M918T variant being the most prevalent specific alteration. Mutations in RAS pathway genes, primarily HRAS (10.0%) and KRAS (5.6%), represented the next most frequent category and demonstrated significant mutual exclusivity with RET alterations. Notably, RET mutations were significantly more frequent in metastatic samples compared to primary tumors (77.5% vs. 63.2%), and NOTCH1 mutations were observed exclusively in the metastatic cohort. While less common, recurrent mutations were also identified in genes involved in chromatin remodeling (KMT2D, SMARCA4, ARID1A) [28,29,30] and tumor suppression (TP53, ATM) [31,32]. Preliminary associations were observed between specific gene mutations and patient race/ethnicity and sex, though these require cautious interpretation.
4.1. Predominance of RET Alterations and Mutual Exclusivity with RAS Pathway Mutations
The high frequency of RET mutations (75.7%) in this large MTC cohort (Figure 1) strongly affirms its established role as the predominant oncogenic driver [22,23,24]. This observed rate is somewhat higher than the 40–60% somatic frequency often cited [23], a difference that could reflect the composition of the GENIE cohort, potentially including a higher proportion of advanced or hereditary cases (though distinguishing germline from somatic was not uniformly possible for all samples) where RET alterations are more prevalent [33,34]. Indeed, RET mutations were significantly more frequent in metastatic samples in our cohort (Section 3.3). The M918T variant’s striking prevalence, accounting for 67.8% of identified RET mutations (Table 3), highlights its particular significance in MTC pathogenesis, as it is known to confer constitutive kinase activation and is often associated with aggressive disease phenotypes [35]. This frequency of M918T among RET-mutated cases aligns well with the recent literature, which reports prevalence rates ranging from 57% to 80% in RET-mutated sporadic MTC cohorts [36]. Our findings, therefore, underscore the widespread importance of the M918T mutation as a key driver in MTC, particularly given its known association with more aggressive disease and higher risk of metastasis [35].
Other pathogenic RET alterations, such as C634R/Y and E632_L633del, further underscore the diversity of activating RET events driving MTC. Our finding of significant mutual exclusivity between RET mutations and those in HRAS (10.0%) or KRAS (5.6%) (p < 0.001 for both) aligns with previous reports [37] and the understanding that these genes often activate overlapping downstream pathways, primarily MAPK signaling [38,39]. Thus, an activating mutation in one gene may obviate the selective pressure for mutations in the others. While therapies targeting KRAS and HRAS exist for other cancers [40,41], the current FDA-approved targeted therapies for MTC predominantly focus on RET, such as the selective RET inhibitor Selpercatinib [42], reflecting the primary role of RET in this disease.
Our observation that RET mutations were more frequent in metastatic lesions (77.5%) compared to primary tumors (63.2%; Section 3.3) warrants careful interpretation. This finding does not imply an absence of driver mutations in primary MTCs; indeed, RET mutations still predominated in primary tumors in our cohort. Rather, this enrichment in metastases could suggest several non-mutually exclusive possibilities: RET mutations might be acquired or selected for during the process of metastatic progression, providing a survival or growth advantage in distant sites; alternatively, primary tumors harboring RET mutations may possess a greater intrinsic capacity to metastasize. Understanding the precise temporal relationship and clonal evolution between mutations in primary tumors and their corresponding metastases would require studies of paired samples, which were not available in this dataset.
4.2. Recurrent Somatic Mutations Beyond the RET/RAS Axis
Beyond the dominant RET/RAS alterations, our study identified recurrent mutations in genes involved in chromatin remodeling, such as KMT2D (5.3%), SMARCA4 (3.8%), and ARID1A (3.8%), and in tumor suppressors like TP53 (4.1%) and ATM (5.0%) (Figure 1). Mutations in KMT2D, ARID1A, and SMARCA4, key components of chromatin remodeling complexes, are increasingly recognized across various malignancies, including some neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), where they can contribute to oncogenesis by dysregulating gene expression programs essential for cellular homeostasis [28,29,30,43,44,45,46,47,48]. Similarly, TP53 and ATM are critical guardians of genomic integrity, and their inactivation through mutation is a common event in cancer progression, often associated with poorer prognosis or treatment resistance [31,32]. While their specific roles in RET-driven MTC are still being studied, alterations in these tumor suppressors could represent cooperating events in MTC development or progression, particularly in RET-negative tumors or those acquiring resistance. Further functional studies are needed to delineate their precise contribution to MTC biology and therapeutic response. Despite their known roles, none showed a significant association with survival in our preliminary analysis, possibly due to limited statistical power for these less frequent mutations.
4.3. Association of NOTCH1 Mutations with Metastatic Disease
NOTCH1 mutations (3.74%) were absent from primary tumors and found exclusively in metastatic samples in our cohort, reaching statistical significance (p = 0.0229). The NOTCH signaling pathway exhibits a complex, context-dependent dual role in cancer, functioning as an oncogene in certain malignancies (e.g., T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia) but as a tumor suppressor in others [49,50]. Our findings, consistent with previous reports suggesting that NOTCH1 may act as a tumor suppressor in MTC where its expression can inhibit growth [51,52], support a tumor-suppressive function in this specific context. Loss of NOTCH1 function might therefore facilitate metastatic dissemination or survival. This raises the possibility of therapeutic intervention, although no NOTCH-targeted therapies are currently FDA-approved for MTC. However, inhibitors of the NOTCH pathway, such as gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), have been investigated in other tumor types [53,54]. Future research could explore whether strategies to restore NOTCH1 function or target downstream effectors of NOTCH1 loss could hold therapeutic promise in NOTCH1-mutant metastatic MTC, or if pathway modulation is relevant in a broader MTC population.
4.4. Preliminary Observations on Mutational Profiles Across Race and Sex
Our exploratory analysis of mutation frequencies stratified by self-reported race/ethnicity and sex revealed several associations that reached nominal statistical significance (Table 2). For example, mutations in BRAF, BRCA1, and KIT were observed exclusively in the female sub-cohort. However, it is crucial to interpret these findings with extreme caution. Many of these associations, particularly those within specific racial/ethnic subgroups (e.g., Native American N = 3, Black N = 9), were driven by mutations observed in three or fewer individuals. Such low event counts render these findings statistically fragile and highly susceptible to Type I errors, despite correction for multiple comparisons, and may reflect sampling bias within the database rather than true biological differences. Therefore, while multiple statistically significant associations were found, they currently lack statistical robustness. These results should be considered strictly hypothesis-generating. To robustly investigate potential demographic-specific mutational landscapes in MTC and discern true biological differences, larger, collaborative pooling efforts across international consortia are essential to create more diverse and demographically representative datasets with adequate statistical power.
4.5. Potential Associations Between Gene Mutations and Survival Outcomes
Our exploratory survival analysis suggested potential links between specific gene mutations and overall survival, though these require significant validation due to dataset limitations and small subgroup sizes. Mutations in BARD1, BLM, UBR5, and MYH11 were nominally associated with reduced survival (n = 3 cases each). These genes are involved in crucial pathways, including DNA repair (BARD1, BLM) [55], protein ubiquitination (UBR5) [56], and cytoskeletal function (MYH11) [57]. While statistically preliminary, the negative association for mutations in DNA repair genes like BARD1 and BLM is notable. Defects in DNA repair can lead to genomic instability but may also confer vulnerabilities; for instance, tumors with homologous recombination deficiencies (which can involve BARD1) may be sensitive to PARP inhibitors [58]. Although speculative for MTC at this stage, if these associations are validated, they could open avenues for precision medicine approaches in subsets of patients.
Conversely, ATM mutations (n = 16 cases) showed an association with potentially prolonged survival. This finding is intriguing given ATM’s critical role as a tumor suppressor in DNA damage response [31,55]. However, the prognostic impact of ATM mutations can be complex and context-dependent in different cancers [59]. If this association is confirmed in MTC, understanding the underlying mechanisms—perhaps related to specific mutation types or interactions with therapy—could provide novel prognostic insights.
It is essential to view these preliminary genomic associations cautiously, especially when compared to established clinical prognostic factors like the International Medullary Thyroid Cancer Grading System (IMTCGS) [60] and calcitonin/metastatic doubling times [61], which robustly stratify patient risk but were not available in our dataset. These clinical metrics remain the standard for prognostication.
Ultimately, the survival correlations observed here, particularly for low-frequency mutations, are hypothesis-generating at best. They underscore the critical need for validating potential genomic biomarkers in larger, prospective studies that integrate comprehensive genomic data with detailed clinical information, including standardized survival endpoints, tumor grade [62], and treatment history [56,63], to understand their true prognostic relevance in MTC. Crucially, such validation would require multivariate Cox proportional hazards models, adjusting for established clinical confounders such as age, stage, tumor grade, and treatment history, to ascertain any independent prognostic significance
4.6. Limitations
There are many limitations to consider in the context of this database study. Due to the lack of transcriptomic data in the AACR Project GENIE database, observed mutations cannot be directly correlated with changes in gene expression, thereby making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about downstream pathway effects [27]. The same applies to the lack of DNA methylation data; conclusions cannot be made about the epigenetic status of the tumor, despite identifying mutations in genes potentially involved in chromatin remodeling. Furthermore, without protein expression and miRNA data, conclusions regarding protein-level phenotypes or the regulatory influence of non-coding RNAs are precluded. In terms of sample size, although the overall GENIE database is large, the number of MTC samples (n = 341) remains relatively limited for detecting associations with lower-frequency mutations or conducting robust subgroup analyses, thereby reducing statistical power and potentially obscuring real associations. The small sample size is especially problematic when comparing across demographic groups, highlighting the need for more diverse data inclusion to better understand potential genetic differences in MTC across ethnicity and sex. Another important limitation is the general lack of specific treatment data for the MTC cohort within GENIE and the limitations of the available survival information, as discussed above. The gold standard for clinical correlation involves analyzing outcomes like progression-free or overall survival from diagnosis relative to specific treatments, demographics, and mutational status; such analyses are restricted with the current dataset. Similarly, detailed pathological subclassifications, such as the WHO recommended low-grade and high-grade MTC categories, were not uniformly available or extractable for this cohort from the aggregated GENIE data, precluding analyses stratified by these important prognostic indicators. The lack of serially collected samples also hinders the ability to distinguish potential driver mutations from passenger events acquired during tumor evolution or treatment. Furthermore, this study did not differentiate between truncal mutations, present in all tumor cells, and subclonal mutations, found only in a subset. Analyzing mutational clonality could offer deeper insights into tumor evolution, mechanisms of treatment resistance, and disease progression in MTC. Finally, the database contains occasional instances of multiple samples from the same patient, which could slightly skew the reported mutational frequencies if not accounted for in specific analyses.
Despite these limitations, this study utilizes a large, multi-center genomic dataset to reinforce the established roles of key driver mutations in MTC pathogenesis, particularly RET, HRAS, and KRAS. It also highlights the potential significance of NOTCH1 alterations in metastatic disease and identifies other recurrently mutated genes warranting further investigation. While suggesting preliminary demographic associations, these require rigorous validation. Overall, this work contributes to the understanding of the MTC genomic landscape but underscores the need for integrated multi-omics studies and dedicated clinical cohorts with comprehensive annotations to fully elucidate MTC biology and improve patient outcomes.
5. Conclusions
This study, utilizing the AACR Project GENIE database, reinforces the dominant role of mutually exclusive RET and RAS mutations in MTC and highlights the significant association of NOTCH1 alterations with metastatic disease. While preliminary associations with race, sex, and survival were observed, these require cautious interpretation due to dataset limitations. Integrating comprehensive genomic data with detailed clinical and pathological features in future studies is crucial for improving risk stratification and therapeutic strategies in MTC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H.; methodology, B.H. and E.T.; software, E.T.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, B.H. and E.T.; investigation, B.H. and E.T.; data curation, B.H. and E.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.H., N.L. and E.T.; writing—review and editing, B.H., N.L., E.T. and P.T.S.; visualization, B.H. and N.L.; supervision, P.T.S.; project administration, B.H. and P.T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because the AACR Project GENIE is a publicly available cancer genomic database containing de-identified patient data, which minimizes potential risks to human subjects and eliminates the need for individual participant consent.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the nature of the study, which used only de-identified data from the publicly available AACR Project GENIE database, and this does not require individual informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the AACR GENIE Database at https://genie.cbioportal.org/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GENIE | AACR Project Genomics Evidence Neoplasia Information Exchange |
| AACR | American Association for Cancer Research |
| ABL1 | ABL proto-oncogene 1, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ARID1A | AT-Rich Interaction Domain 1A |
| ATM | ATM Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| ASXL1 | Additional Sex Combs Like Transcriptional Regulator 1 |
| BRAF | B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| BLM | BLM RecQ Like Helicase |
| BARD1 | BRCA1 Associated RING Domain 1 |
| BRCA1 | BRCA1 DNA Repair Associated |
| BRIP1 | BRCA1 interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 |
| CDH11 | Cadherin 11 |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen |
| COSMIC | Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer |
| CNAs | Copy Number Alterations |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A |
| CDKN2B | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2B |
| CRKL | CRK like proto-oncogene, adaptor protein (Crk-like protein) |
| EBRT | External beam radiation therapy |
| EXO1 | Exonuclease 1 |
| FANCD2 | Fanconi anemia complementation group D2 |
| FAT1 | FAT Atypical Cadherin 1 |
| FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FLT4 | Fms related receptor tyrosine kinase 4 |
| FMTC | Familial Medullary Thyroid Cancer |
| GATK | Genome Analysis Toolkit |
| HRAS | Harvey Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| HNSCC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| IF del | In-frame deletion |
| IMTCGS | International Medullary Thyroid Cancer Grading System |
| JAK1 | Janus Kinase 1 |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| KIT | KIT Proto-Oncogene, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| KMT2A | Lysine Methyltransferase 2A |
| KMT2D | Lysine Methyltransferase 2D |
| MTC | Medullary Thyroid Cancer |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MKIs | Multi-kinase inhibitors |
| MEN2A | Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2A |
| MEN2B | Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B |
| MAF | Mutation Annotation Format |
| MYH11 | Myosin Heavy Chain 11 |
| NOTCH1 | Notch Receptor 1 |
| PIK3C2G | Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 2 gamma |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Protein Kinase B |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PAX3 | Paired box 3 |
| PREX2 | Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 2 |
| RAI | Radioactive iodine |
| RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| RET | RET proto-oncogene |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SMAD4 | SMAD family member 4 |
| SMARCA4 | SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator Of Chromatin, Subfamily A, Member 4 |
| SMC3 | Structural maintenance of chromosome 3 |
| SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase SRC |
| TET1 | Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 1 |
| TP53 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| TKIs | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| UBR5 | Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase E3 Component N-Recognin 5 |
| VAF | Variant Allele Frequency |
| VEGFR | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| ZFHX3 | Zinc finger homeobox 3 |
References
- Segura, S.; Ramos-Rivera, G.; Suhrland, M. Educational Case: Endocrine Neoplasm: Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Acad. Pathol. 2018, 5, 2374289518775722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, A.; Chen, H.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M. In-Vivo Activation of Raf-1 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Development in a Xenograft Model of Human Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzweg, C.; Morris, J.C.; Bible, K.C. New Drugs for Medullary Thyroid Cancer: New Promises? Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R287–R297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Chen, H.; Sippel, R.S. Current Understanding and Management of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Oncologist 2013, 18, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, O.R.; Slipetsky, R.R.; Bojko, N.I. Principles of Medullary Thyroid Cancer Staging According to AJCC TNM 8th Edition. Acta Med. Leopoliensia 2021, 27, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, V.F.; Fuss, C.T.; Berr, C.M.; Frank-Raue, K.; Raue, F.; Hoster, E.; Hepprich, M.; Christ, E.; Pusl, T.; Reincke, M.; et al. Medullary Thyroid Cancer with Ectopic Cushing’s Syndrome: A Multicentre Case Series. Clin. Endocrinol. 2022, 96, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lin, C.; Yao, E.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Chuang, P.-T. Selective Ablation of Tumor Suppressors in Parafollicular C Cells Elicits Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3888–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Hauptmann, S.; Dralle, H. Increased Risk of Lymph Node Metastasis in Multifocal Hereditary and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.; Morris, L.G.; Haymart, M.; Chen, A.Y.; Goldenberg, D.; Morris, J.; Ogilvie, J.B.; Terris, D.J.; Netterville, J.; Wong, R.J.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Disease State Clinical Review: The Increasing Incidence of Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, M.A.; Castroneves, L.A. Overview of Management and Therapeutic Advances in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Oncol. 2025, 5, e240077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezkallah, E.; Elsaify, A.; Elsaify, W.M. Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Case Series Reports and Literature Review. J. Cancer Tumor Int. 2021, 11, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, F.; He, X. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma With Elevated Serum CEA and Normal Serum Calcitonin After Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 526716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siironen, P.; Hagström, J.; Mäenpää, H.O.; Louhimo, J.; Arola, J.; Haglund, C. Lymph Node Metastases and Elevated Postoperative Calcitonin: Predictors of Poor Survival in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Kim, I.J. Recent Updates on the Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzab, B.; Krajewska, J. Multikinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Progressive, Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer—An Evolving Paradigm. Eur. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kelil, T.; Keraliya, A.R.; Howard, S.A.; Krajewski, K.M.; Braschi-Amirfarzan, M.; Hornick, J.L.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Tirumani, S.H. Current Concepts in the Molecular Genetics and Management of Thyroid Cancer: An Update for Radiologists. Radiographics 2016, 36, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimboli, P.; Castellana, M.; Virili, C.; Giorgino, F.; Giovanella, L. Efficacy of Vandetanib in Treating Locally Advanced or Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma According to RECIST Criteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Gaudenzi, G.; Circelli, L.; Manzoni, M.F.; Bassi, A.; Fioritti, N.; Faggiano, A.; Colao, A.; NIKE Group. Animal Models of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: State of the Art and View to the Future. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R1–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, M.; Iacovelli, R.; Colonna, V.; Klinz, S.; Mauri, G.; Nuti, M. Antitumor Effects of the Multi-Target Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cabozantinib: A Comprehensive Review of the Preclinical Evidence. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 1029–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Elisei, R.; Müller, S.; Schöffski, P.; Brose, M.; Shah, M.; Licitra, L.; Krajewska, J.; Kreissl, M.; Niederle, B.; et al. Overall Survival Analysis of EXAM, a Phase III Trial of Cabozantinib in Patients with Radiographically Progressive Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirocchi, F.; Napoletano, C.; Pace, A.; Rahimi Koshkaki, H.; Di Filippo, A.; Zizzari, I.G.; Nuti, M.; Rughetti, A. Immunogenic Cell Death and Immunomodulatory Effects of Cabozantinib. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 755433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouz Salehian, R.S. RET Gene Abnormalities and Thyroid Disease: Who Should be Screened and When. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, C.; Hogan, J.; Raygada, M.; Thomas, B.J.; Akshintala, S.; Glod, J.W.; Del Rivero, J. Update on Targeted Therapy in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 708949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitze, G. Management of Patients with Hereditary Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 14, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisei, R.; Tacito, A.; Ramone, T.; Ciampi, R.; Bottici, V.; Cappagli, V.; Viola, D.; Matrone, A.; Lorusso, L.; Valerio, L.; et al. Twenty-Five Years Experience on RET Genetic Screening on Hereditary MTC: An Update on The Prevalence of Germline RET Mutations. Genes 2019, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Kumarasamy, V.; Camacho, D.; Sun, D. Involvement of G-Quadruplex Structures in Regulation of Human RET Gene Expression by Small Molecules in Human Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma TT Cells. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, L.M.Z.; Magalhães, P.K.R. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma—Adverse Events during Systemic Treatment: Risk-Benefit Ratio. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 61, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhar, S.S.; Lee, M.G. Cancer-Epigenetic Function of the Histone Methyltransferase KMT2D and Therapeutic Opportunities for the Treatment of KMT2D-Deficient Tumors. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinian, K.; Adashek, J.J.; Botta, G.P.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. SMARCA4: Implications of an Altered Chromatin-Remodeling Gene for Cancer Development and Therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartha, N.; Shen, L.; Maskin, C.; Wallace, M.; Schimenti, J.C. The Chromatin Remodeling Component Arid1a Is a Suppressor of Spontaneous Mammary Tumors in Mice. Genetics 2016, 203, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.M.; Rezaeian, A.-H. ATM: Main Features, Signaling Pathways, and Its Diverse Roles in DNA Damage Response, Tumor Suppression, and Cancer Development. Genes 2021, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting P53 Pathways: Mechanisms, Structures and Advances in Therapy. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binter, T.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Schernthaner-Reiter, M.H.; Arikan, M.; Hargitai, L.; Niederle, M.B.; Niederle, B.; Scheuba, C.; Riss, P. Does Genotype-Specific Phenotype in Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 Occur as Current Guidelines Predict? Cancers 2024, 16, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, N.; Navarro, E.; Mesa, J.; Casterás, A.; Alcázar, V.; Lamas, C.; Tébar, J.; Castaño, L.; Gaztambide, S.; Forga, L. RET Cys634Arg Mutation Confers a More Aggressive Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A Phenotype than Cys634Tyr Mutation. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 172, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Lorenz, K.; Weber, F.; Dralle, H. Dissection of RET p.M918T-Driven Progression of Hereditary vs. Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 109549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romei, C.; Ciampi, R.; Casella, F.; Tacito, A.; Torregrossa, L.; Ugolini, C.; Basolo, F.; Materazzi, G.; Vitti, P.; Elisei, R. RET Mutation Heterogeneity in Primary Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancers and Their Metastases. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9875–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Jiao, Y.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.; Bettegowda, C.; Roberts, N.J.; Bhan, S.; Ho, A.S.; Khan, Z.; Bishop, J.; et al. Exomic Sequencing of Medullary Thyroid Cancer Reveals Dominant and Mutually Exclusive Oncogenic Mutations in RET and RAS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E364–E369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-J.; Pan, W.-W.; Liu, S.-B.; Shen, Z.-F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.-L. ERK/MAPK Signalling Pathway and Tumorigenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regua, A.T.; Najjar, M.; Lo, H.-W. RET Signaling Pathway and RET Inhibitors in Human Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 932353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Grants Breakthrough Therapy Designation to Tipifarnib in HRAS + HNSCC. Targeted Oncology. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-grants-breakthrough-therapy-designation-to-tipifarnib-in-hras-hnscc (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Sotorasib with Panitumumab for KRAS G12C-Mutated Colorectal Cancer; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- FDA Approves Selpercatinib for Medullary Thyroid Cancer with an RET Variant|Oncology Nursing Society. Available online: https://www.ons.org/publications-research/voice/news-views/09-2024/fda-approves-selpercatinib-medullary-thyroid-cancer (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Nemtsova, M.V.; Kalinkin, A.I.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Bure, I.V.; Alekseeva, E.A.; Bykov, I.I.; Khorobrykh, T.V.; Mikhaylenko, D.S.; Tanas, A.S.; Strelnikov, V.V. Mutations in Epigenetic Regulation Genes in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, F.; Luo, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, D.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.; et al. Enhancer Reprogramming: Critical Roles in Cancer and Promising Therapeutic Strategies. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Chhangawala, S.; Cocco, E.; Razavi, P.; Cai, Y.; E Otto, J.; Ferrando, L.; Selenica, P.; Ladewig, E.; Chan, C.; et al. ARID1A Determines Luminal Identity and Therapeutic Response in Estrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Chen, L.H.; Huang, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, P.; Pirozzi, C.J.; Qin, X.; Bao, X.; Greer, P.K.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. KMT2D Maintains Neoplastic Cell Proliferation and Global Histone H3 Lysine 4 Monomethylation. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ying, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, X.; Fan, Y.; Tan, J.; Cao, Y.; Tsao, S.W.; Srivastava, G.; et al. The Human Cadherin 11 Is a Pro-Apoptotic Tumor Suppressor Modulating Cell Stemness through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Silenced in Common Carcinomas. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3901–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Du, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Current Insights into the Regulation of Programmed Cell Death by TP53 Mutation in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1023427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusewicz, D.; Orzechowska, M.; Bednarek, A.K. Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer-Review with Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobry, C.; Oh, P.; Mansour, M.R.; Look, A.T.; Aifantis, I. Notch Signaling: Switching an Oncogene to a Tumor Suppressor. Blood 2014, 123, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenter, R.; Patel, Z.; Chen, H. Notch Signaling in Thyroid Cancer. In Notch Signaling in Embryology and Cancer: Notch Signaling in Cancer; Reichrath, J., Reichrath, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Pisarnturakit, P.; Landowski, M.; Chen, H.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M. Expression of the Active Notch1 Decreases MTC Tumor Growth In Vivo. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaw, T.R.; Inga, E.; Chen, H.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Dudeja, V.; Bibb, J.A.; Ren, B.; Rose, J.B. Gamma Secretase Inhibitors in Cancer: A Current Perspective on Clinical Performance. Oncologist 2021, 26, e608–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipo, C.; Zlobin, A.; Kuprys, O. Gamma Secretase Inhibitors of Notch Signaling. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, K.; Jones, S.E.; Bannister, J.; Durin, M.-A.; Vendrell, I.; Fawkes, M.; Fischer, R.; Kessler, B.M.; Chapman, J.R.; Blackford, A.N. BLM and BRCA1-BARD1 coordinate complementary mechanisms of joint DNA molecule resolution. Molecular Cell 2024, 84, 640–658.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, S.; Saez, I.; Lee, H.J.; Gutierrez-Garcia, R.; Pokrzywa, W.; Fatima, A.; Hoppe, T.; Vilchez, D. The ubiquitin ligase UBR5 suppresses proteostasis collapse in pluripotent stem cells from Huntington’s disease patients. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MYH11—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics [WWW Document], n.d. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/myh11 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Dillon, K.M.; Bekele, R.T.; Sztupinszki, Z.; Hanlon, T.; Rafiei, S.; Szallasi, Z.; Choudhury, A.D.; Mouw, K.W. PALB2 or BARD1 Loss Confers Homologous Recombination Deficiency and PARP Inhibitor Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer. NPJ Precis. Onc. 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H. Targeting the ATM Pathway in Cancer: Opportunities, Challenges and Personalized Therapeutic Strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 129, 102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Fuchs, T.L.; Ahmadi, S.; Alghamdi, M.; Alzumaili, B.; Bani, M.-A.; Baudin, E.; Chou, A.; De Leo, A.; Fagin, J.A.; et al. International Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Grading System: A Validated Grading System for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.; Yeung, M.; Sherman, E.J.; Tuttle, R.M.; Sabra, M.M. Structural Doubling Time Predicts Overall Survival in Patients with Medullary Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Rapidly Progressive Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer Treated with Molecular Targeted Therapies. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.; Untch, B.R.; Shaha, A.R. Tumor Grade as a Novel Predictor of Outcomes in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. J. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 3, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gild, M.L.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Wirth, L.J.; Robinson, B.G. Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Updates and Challenges. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).