Semi-Active Vibration Control for High-Speed Elevator Using Magnetorheological Damper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
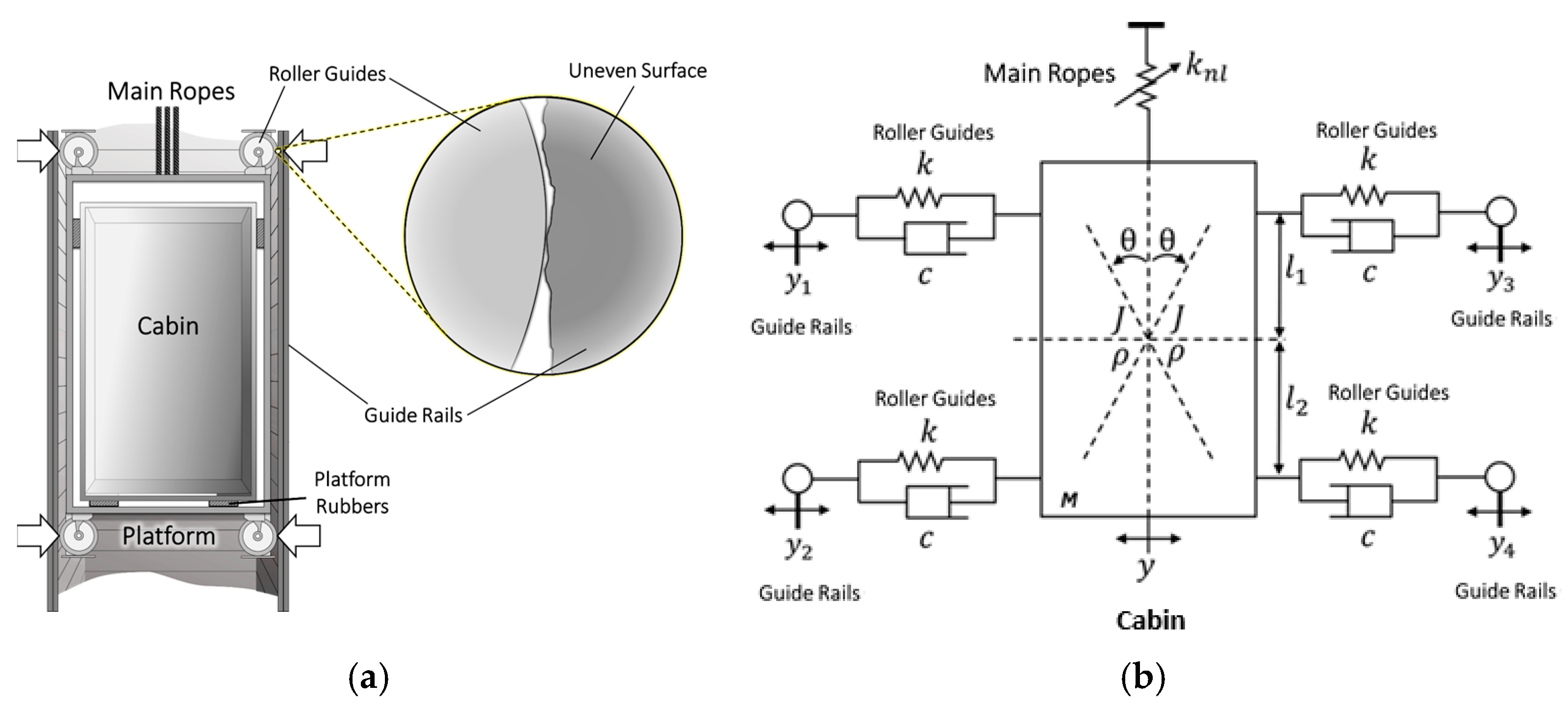
2.1. Mathematical Model of the Elevator
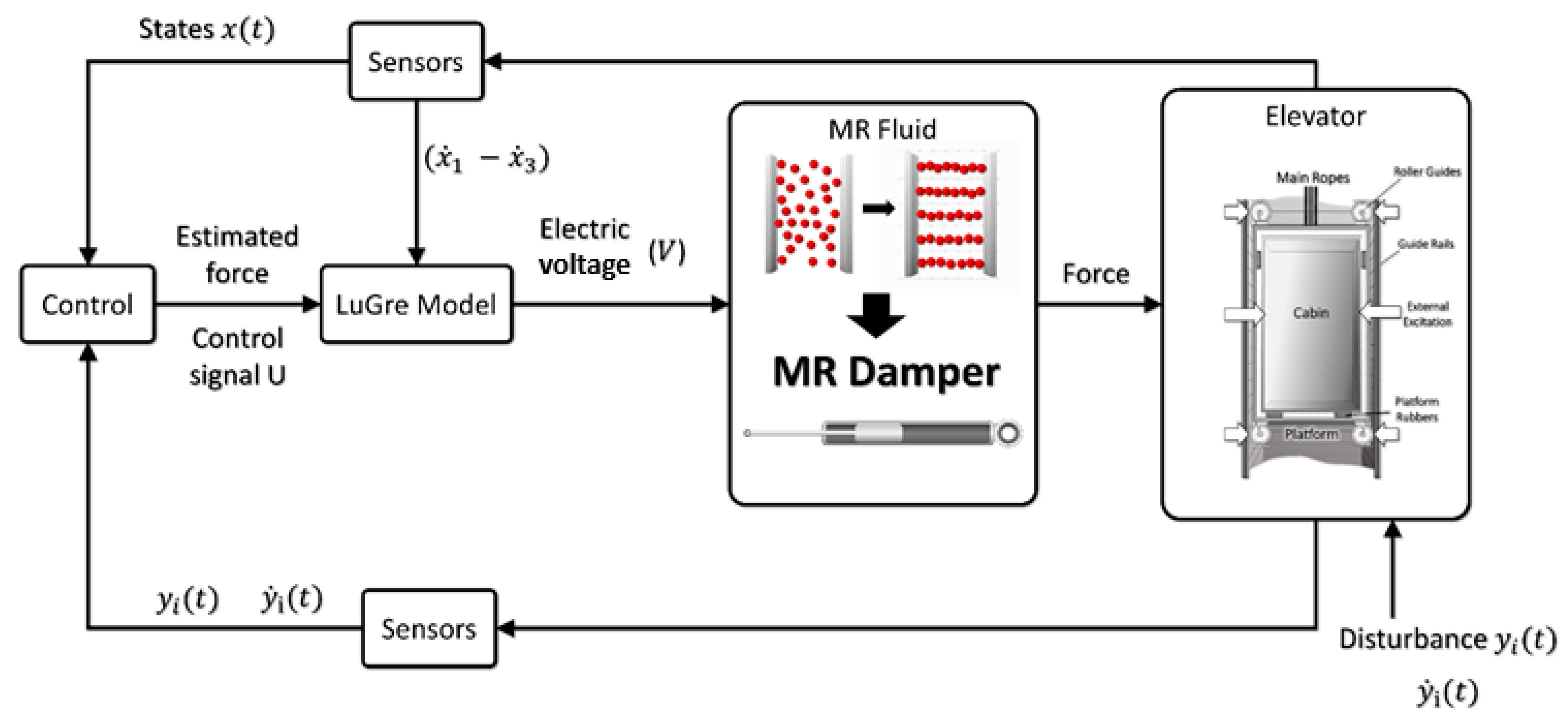
2.2. Proposed Elevator Vibration Control System
2.3. Mathematical Model for MR Damper
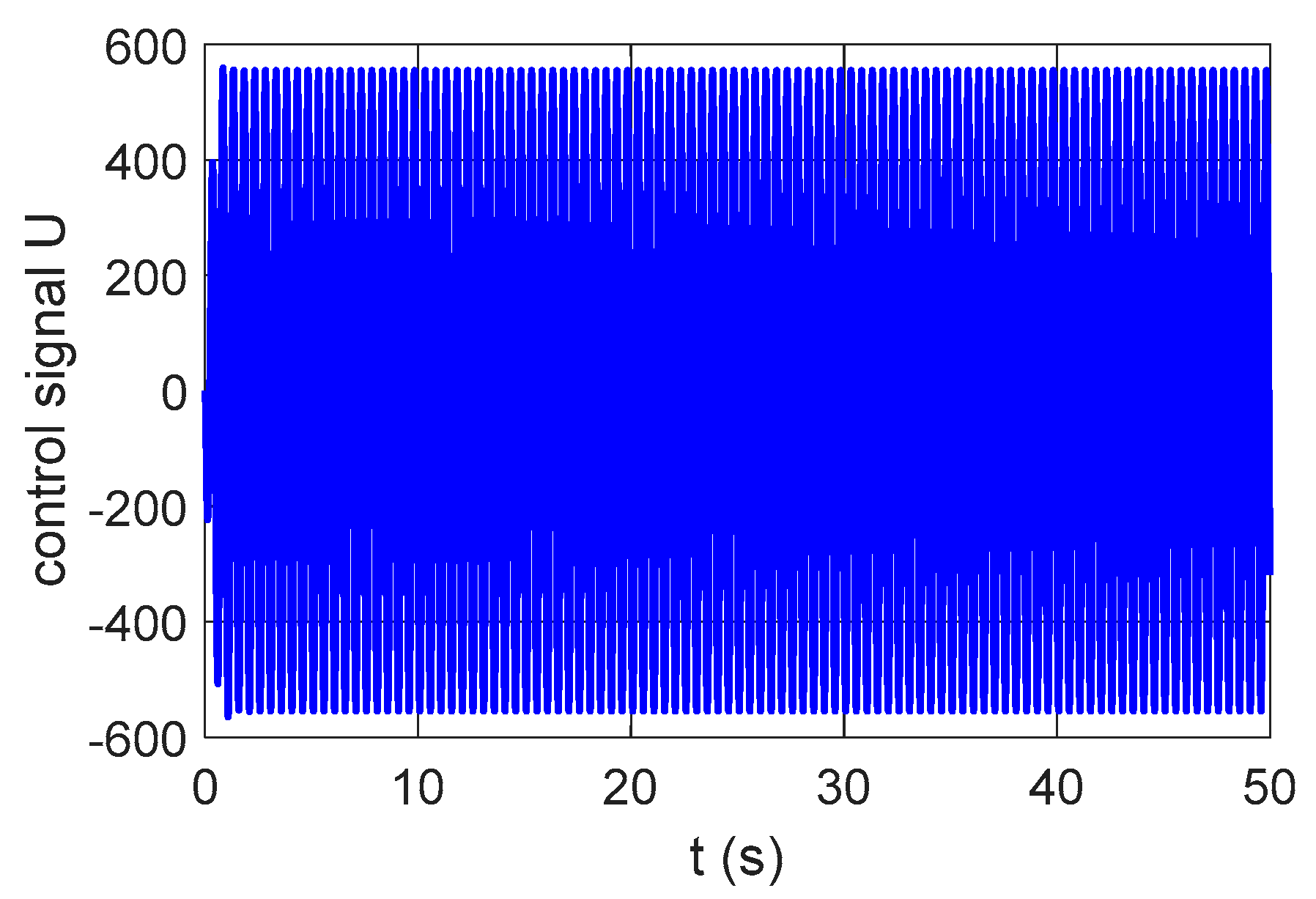
2.4. Electrical Voltage Control Project by SDRE Control
3. Results
3.1. Numerical Simulations for the Passive System
3.2. Numerical Simulations for the System with Active Control
3.3. Numerical Simulations for the System with Semi-Active Control by an MR Damper
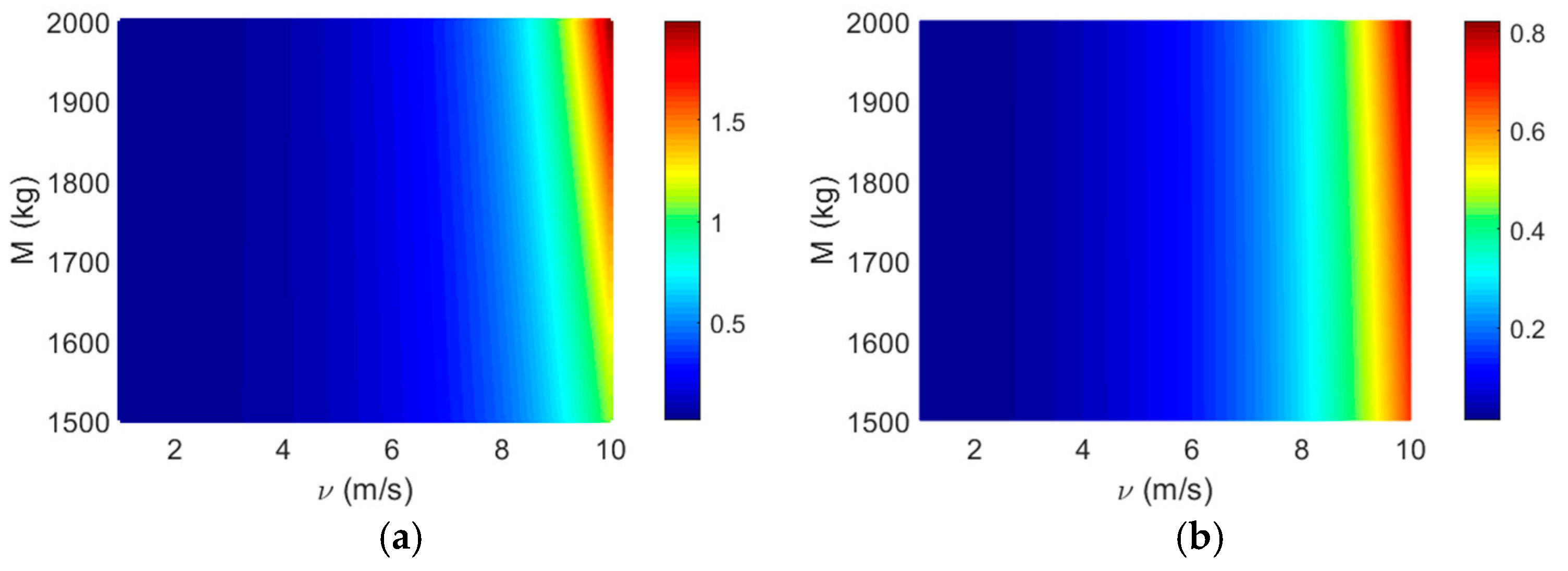
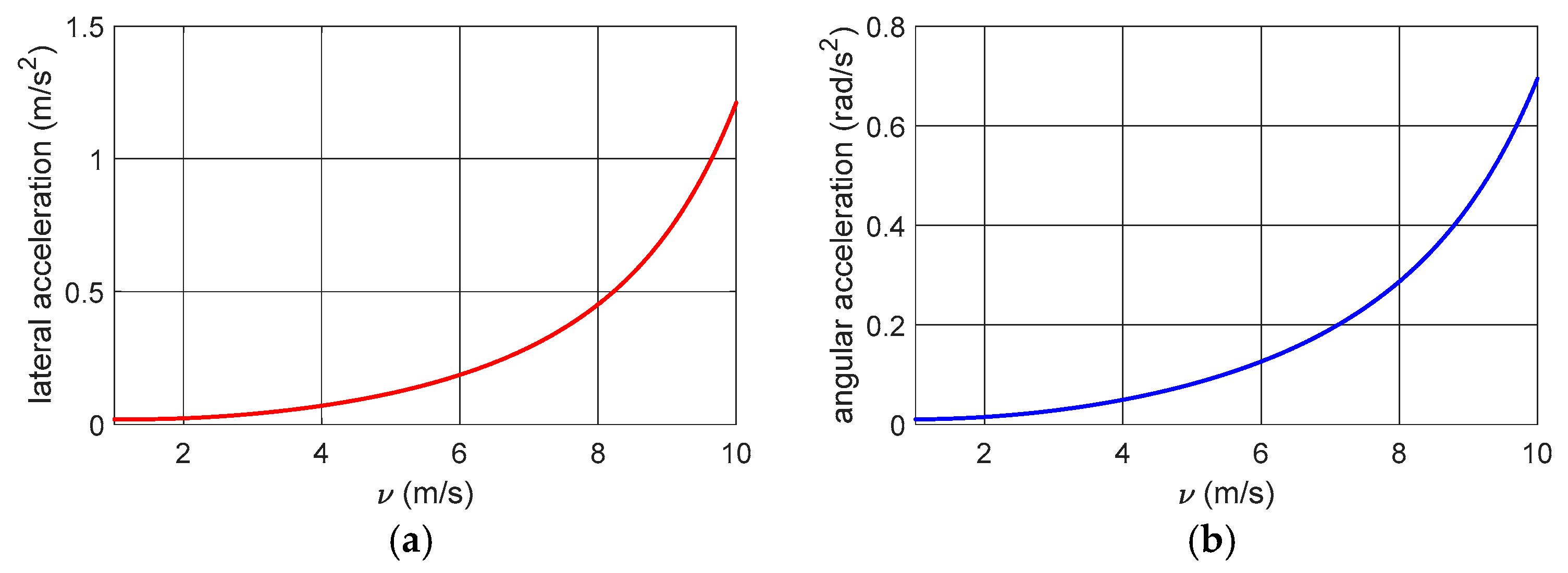
3.4. System Sensitivity in the Case of Parametric Variations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goncalves, M.; Balthazar, J.M.; Oliveira, C.; Fuziki, M.E.K.; Lenzi, G.G.; Tusset, A.M. Active Control System Applied to Vibration Level Control in High-Speed Elevators. Int. J. Robot. Control. Syst. 2022, 2, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. A Vibration-Related Design Parameter Optimization Method for High-Speed Elevator Horizontal Vibration Reduction. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusset, A.M.; Fuziki, M.E.K.; Lenzi, G.G.; Dos Santos, G.P.; Balthazar, J.M.; Brasil, R.M.L.R.F. Nonlinear Energy Sink Applied in the Vibration Suppression of a High-Speed Elevator System and Energy Harvesting. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Su, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. High-speed elevator car horizontal vibration fluid-solid interaction modeling method. J. Vib. Control 2021, 4, 2984–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, T.; Jing, H.; Zhang, R. Analysis of Longitudinal Vibration Acceleration Based on Continuous Time-Varying Model of High-Speed Elevator Lifting System with Random Parameters. Mech. Ind. 2021, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cao, G.; Yan, L.; Wang, L. Modelling and passive control of flexible guiding hoisting system with time-varying length. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2020, 26, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusset, A.M.; Santo, D.R.; Balthazar, J.M.; Piccirillo, V.; Dos Santos, L.C.C.; Brasil, R.M.L.R.F. Active Vibration Control of an Elevator System Using Magnetorheological Damper Actuator. Int. J. Nonlinear Dyn. Control. 2017, 1, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Jia, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L. Adaptive sliding mode control with fuzzy adjustment of switching term based on the Takagi-Sugeno model for horizontal vibration of the high-speed elevator cabin system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 4503–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Su, W.-C.; Huang, Y.-P. H∞ Direct Output Feedback Control of High-Speed Elevator Systems. Seismic Engineering. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–21 July 2011; Volume 8, pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L. Mixed H2/H∞ guaranteed cost control for high speed elevator active guide shoe with parametric uncertainties. Mech. Ind. 2020, 21, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, R.S.; Kaczmarczyk, S.; Picton, P.; Su, H. Modelling and simulation of a stationary high-rise elevator system to predict the dynamic interactions between its components. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 137, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.; Zhang, R. Dynamic analysis of high-speed traction elevator and traction car–rope time-varying system. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2019, 50, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusset, A.M.; Cruz, J.A.; Balthazar, J.M.; Fuziki, M.E.K.; Lenzi, G.G. Nonlinear Control and Numerical Analysis Applied in a Nonlinear Model of Cutting Process Subject to Non-Ideal Excitations. Modelling 2024, 5, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jeon, D. Vibration Suppression in an MR Fluid Damper Suspension System. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Ning, D.; Du, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, W. A New Generation of Magnetorheological Vehicle Suspension System with Tunable Stiffness and Damping Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2019, 15, 4696–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, W.G.; Salem, A.M. Semi-active control of tracked vehicle suspension incorporating magnetorheological dampers. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2017, 55, 626–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.L.; Nieto, A.J.; Chicharro, J.M.; Pintado, P. A semi-active vehicle suspension based on pneumatic springs and magnetorheological dampers. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterbee, D.C.; Sims, N.D.; Stanway, R.; Wolejsza, Z. Magnetorheological landing gear: 1. A design methodology. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, C.; Kim, B.; Choi, S. Design of a New Magnetorheological Damper Based on Passive Oleo-Pneumatic Landing Gear. J. Aircr. 2018, 55, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Kang, B.; Choi, S.; Tak, J.M.; Hwang, J. Control of Landing Efficiency of an Aircraft Landing Gear System with Magnetorheological Dampers. J. Aircr. 2019, 56, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Gong, X.; Zong, L.; Peng, C.; Xuan, S. Twin-tube and bypass-containing magnetorheological damper for use in railway vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. F J. Rapid 2015, 229, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Choi, S. Disturbance rejection and force-tracking controller of nonlinear lateral vibrations in passenger rail vehicle using magnetorheological fluid damper. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Saini, U.; Kumar, A. Semi-active Control to Reduce Lateral Vibration of Passenger Rail Vehicle Using Disturbance Rejection and Continuous State Damper Controllers. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2019, 7, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Liao, W. Optimal design of a magnetorheological damper used in smart prosthetic knees. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 35034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.D.; Sun, S.; Deng, L.; Ning, D.H.; Du, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, W.H. A variable resonance magnetorheological-fluid-based pendulum tuned mass damper for seismic vibration suppression. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2019, 116, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggumus, H.; Cetin, S. Vibration Control of Structures Using Magnetorheological Dampers with H∞ Method. Proc. Int. Struct. Eng. Constr. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Large-Scale Magnetorheological Fluid Damper for Vibration Mitigation: Modeling, Testing and Control; Department of Civil Engineering and Geological Sciences: Notre Dame, IN, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, J.; Klingenberg, D.J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Magnetorheological fluids: A review. Soft Matter. 2011, 7, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masa’id, A.; Lenggana, B.W.; Ubaidillah, U.; Susilo, D.D.; Choi, S.-B. A Review on Vibration Control Strategies Using Magnetorheological Materials Actuators: Application Perspective. Actuators 2023, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenggana, B.W.; Ubaidillah, U.; Imaduddin, F.; Choi, S.-B.; Purwana, Y.M.; Harjana, H. Review of Magnetorheological Damping Systems on a Seismic Building. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaroo, K.; Awan, A.W.; Islam, S. Semi-Active Suspension Design for an In-Wheel-Motor-Driven Electric Vehicle Using a Dynamic Vibration-Absorbing Structure and PID-Controlled Magnetorheological Damper. Machines 2025, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.T.; Wereley, N.M.; Hiemenz, G.J. Three-Axis Vibration Isolation of a Full-Scale Magnetorheological Seat Suspension. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yoo, S.; Yoon, D.; Jin, C.; Won, S.; Lee, J. Numerical Analysis of the Vehicle Damping Performance of a Magnetorheological Damper with an Additional Flow Energy Path. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Jiménez-Salas, M.; Boada, B.L. Robust Static Output Feedback Control of a Semi-Active Vehicle Suspension Based on Magnetorheological Dampers. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, J. An Improved Parameter Identification Algorithm for the Friction Model of Electro-Hydraulic Servo Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yao, H.; Nie, S. Parameter Identification of LuGre Friction Model Based on Interval Analysis. China Mech. Eng. 2013, 24, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, C.; Weber, F.; Guzella, L. Modeling of disc-type magnetorheological damper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 19, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, P.; Maślanka, M. Inverse LuGre model for a small-scale MR damper. In Proceedings of the 14th International Carpathian Control Conference (ICCC), Rytro, Poland, 26–29 May 2013; pp. 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, T. State-Dependent Riccati Equation (SDRE) Control: A Survey. IFAC Proceedings 2008, 41, 3761–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, C.; Li, S. Lateral Vibration Control Strategy of High-Speed Elevator Car Based on Sparrow Search Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.C.; Ohmori, H.; Sano, A. Modeling of MR damper with hysteresis for adaptive vibration control. In Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE International Conference on Decision and Control (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37475), Maui, HI, USA, 9–12 December 2003; Volume 4, pp. 3840–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


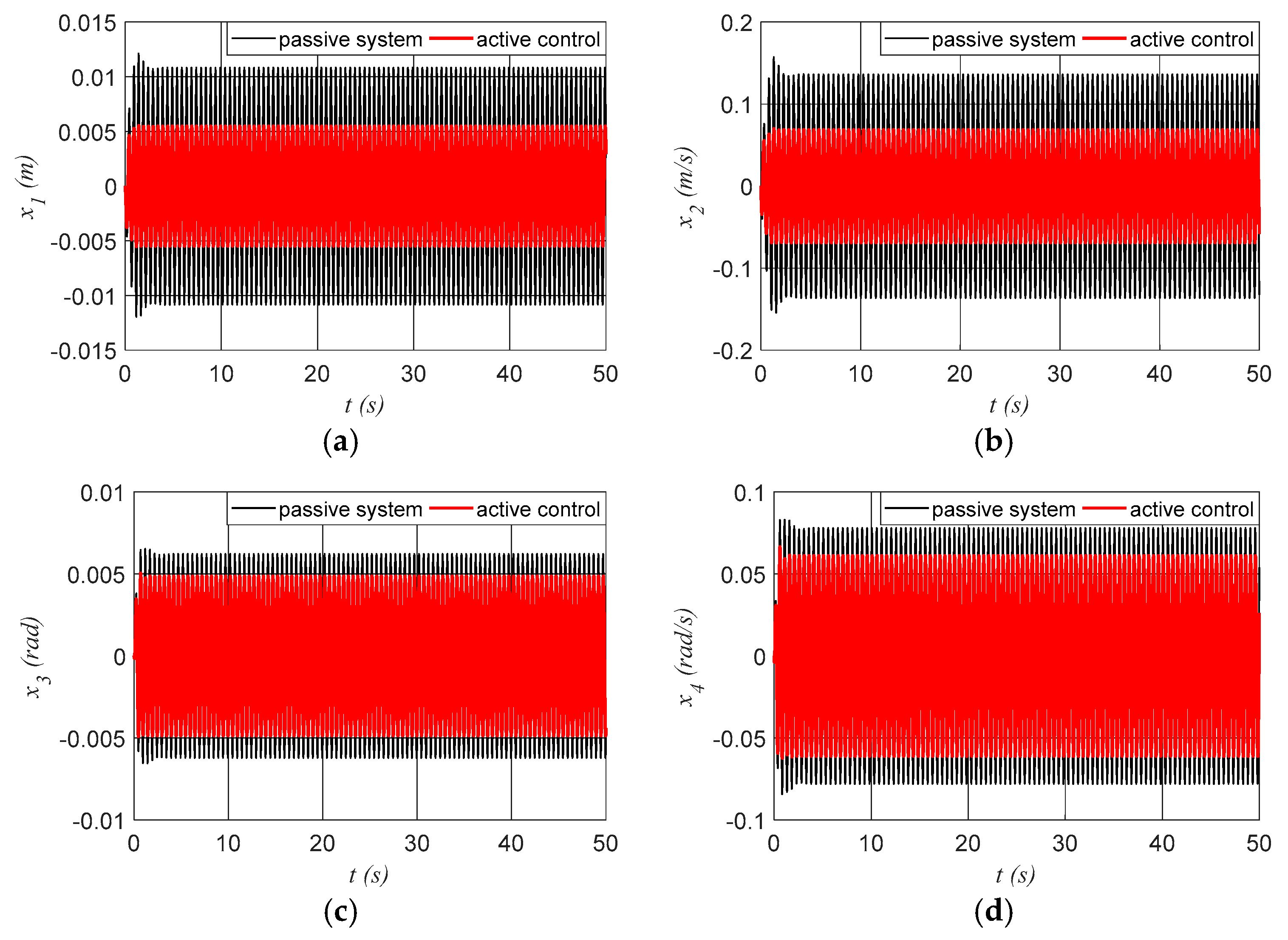
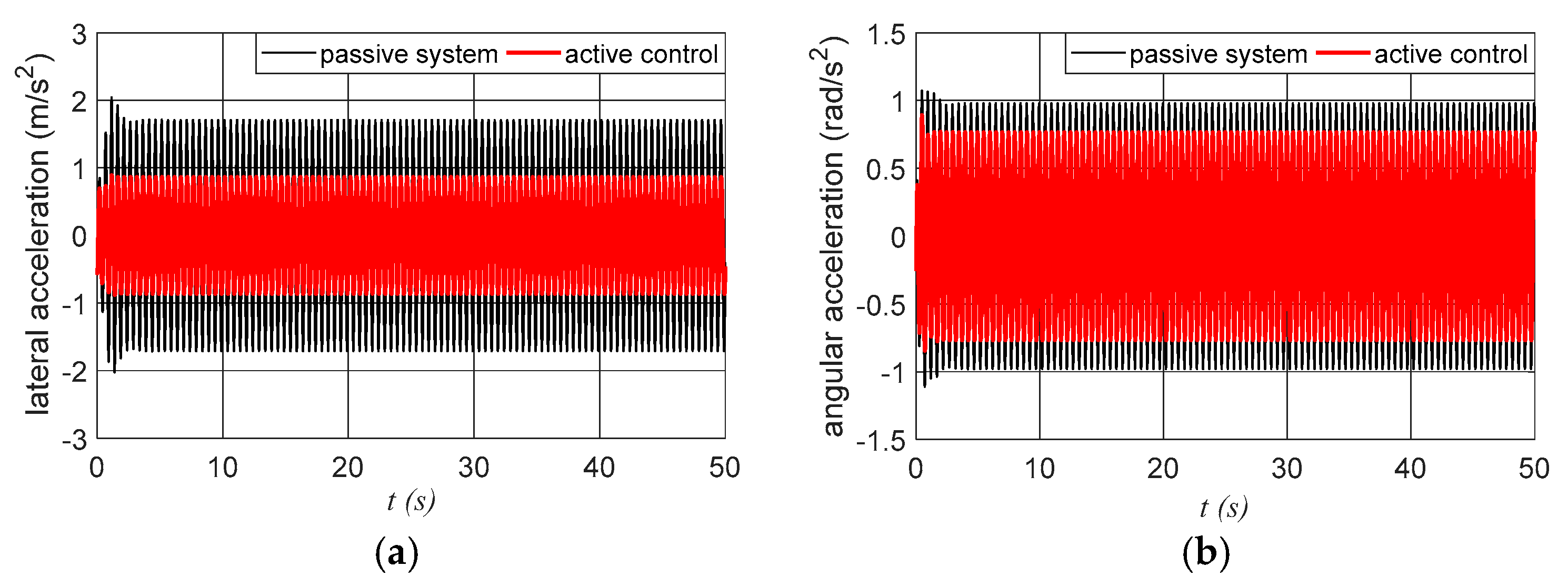
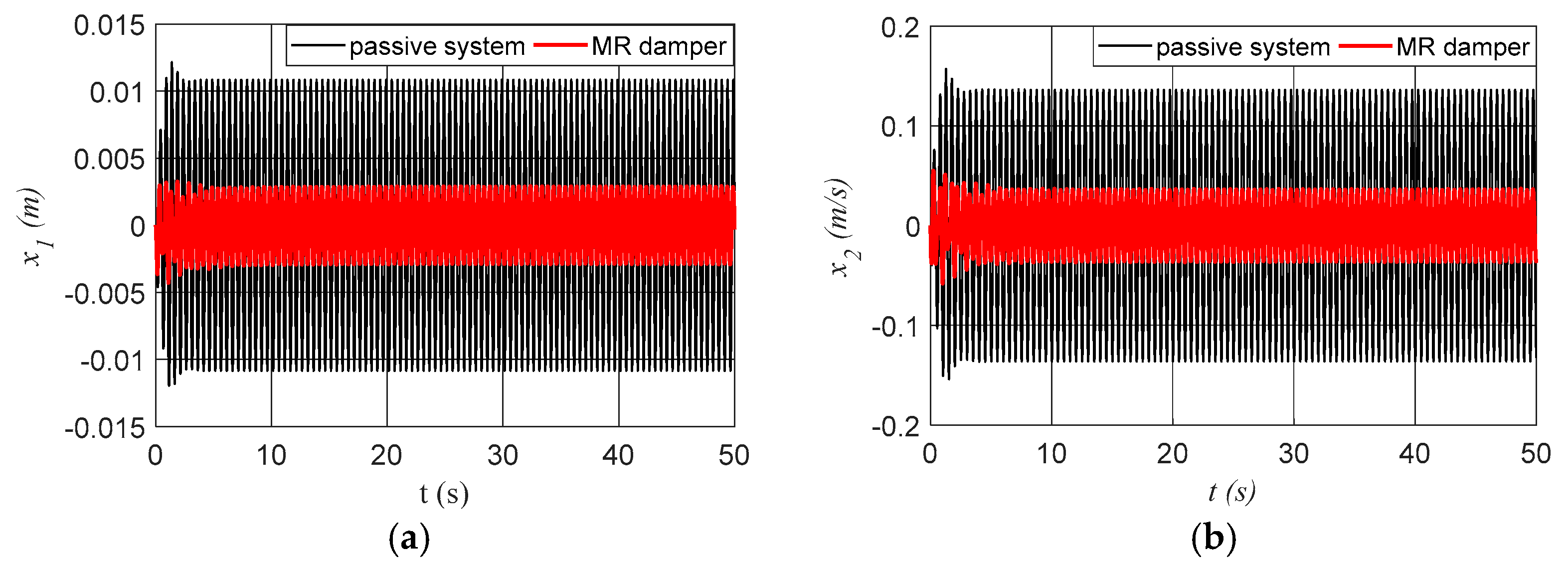
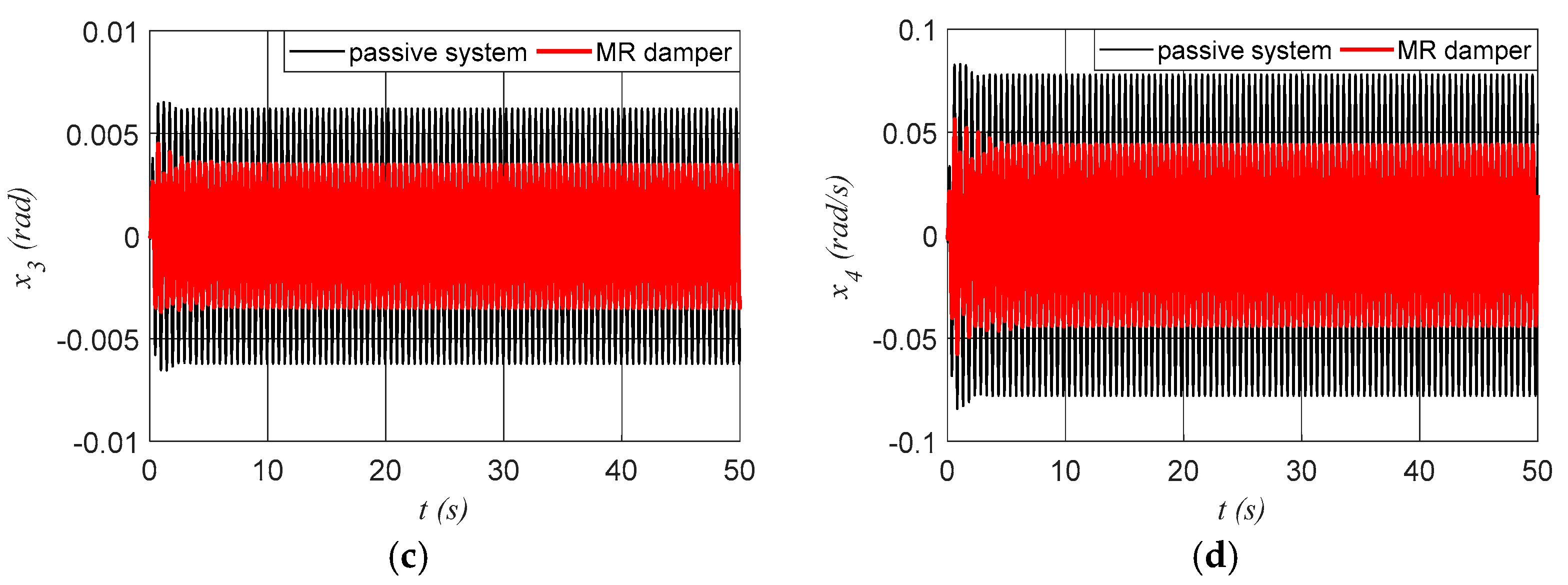
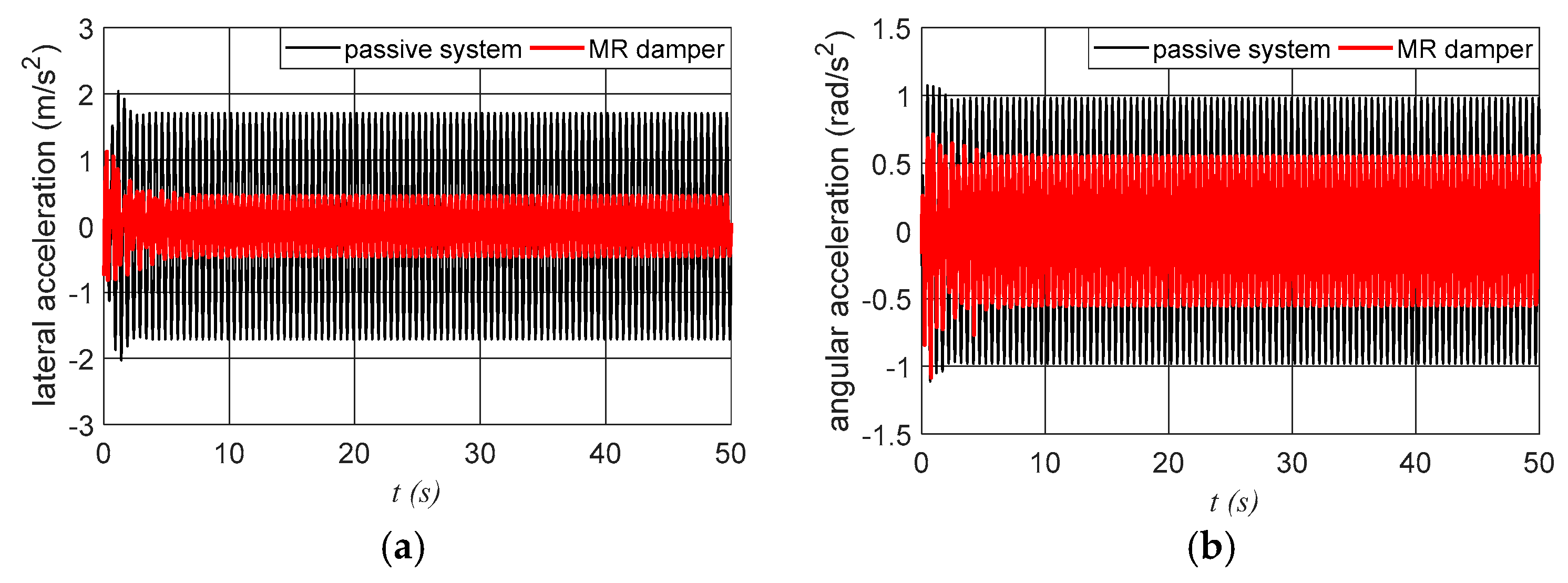

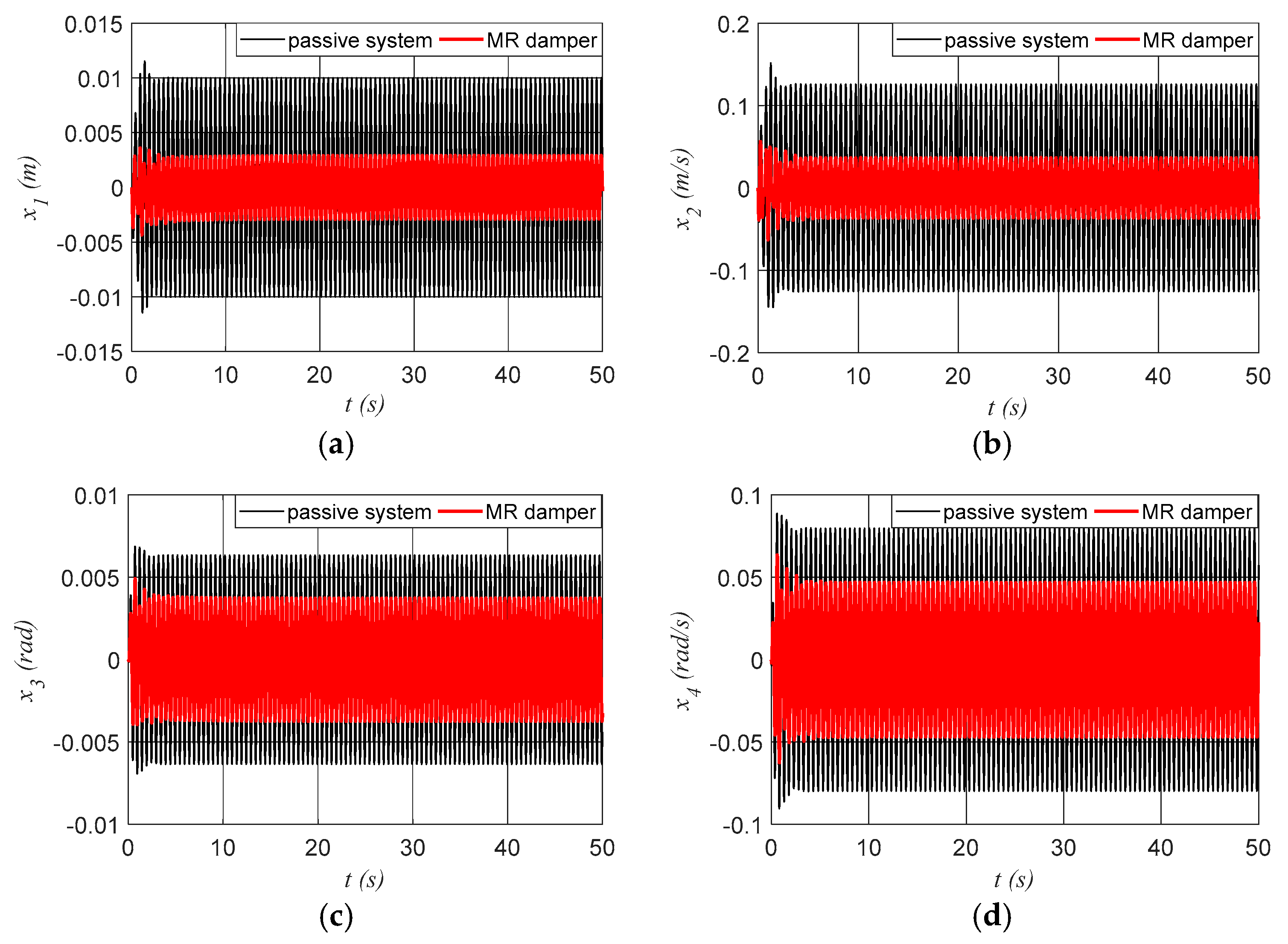
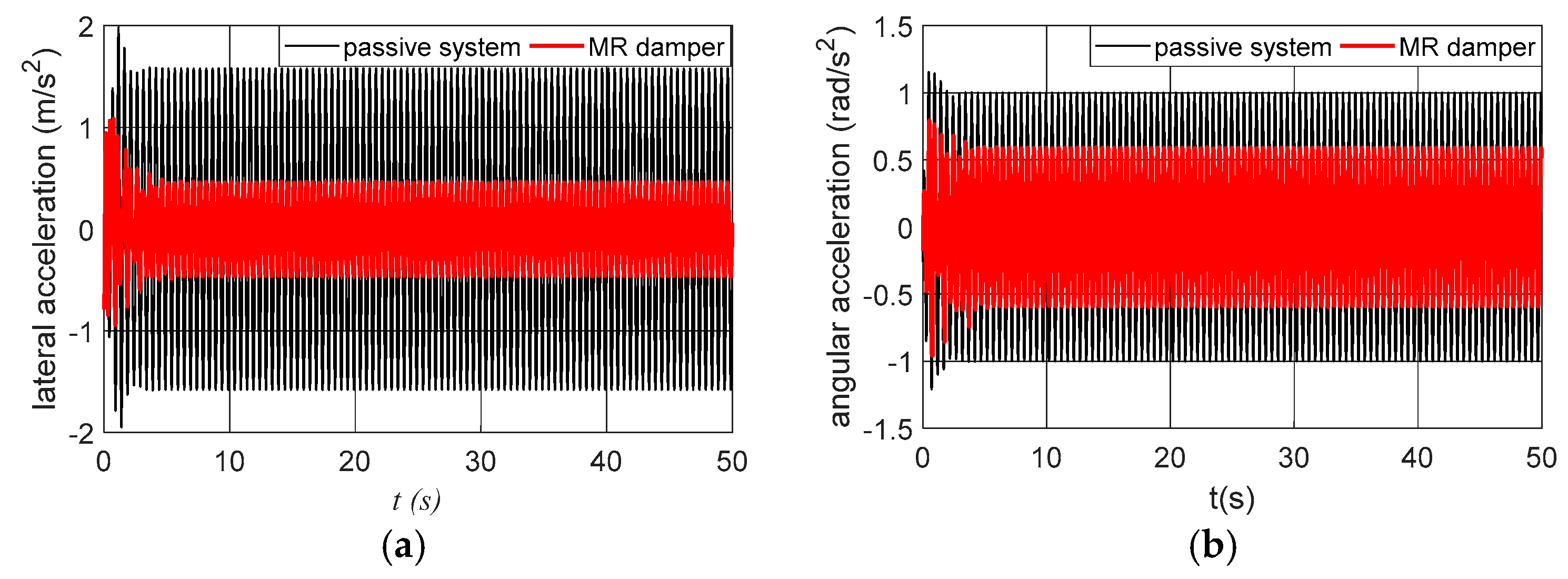
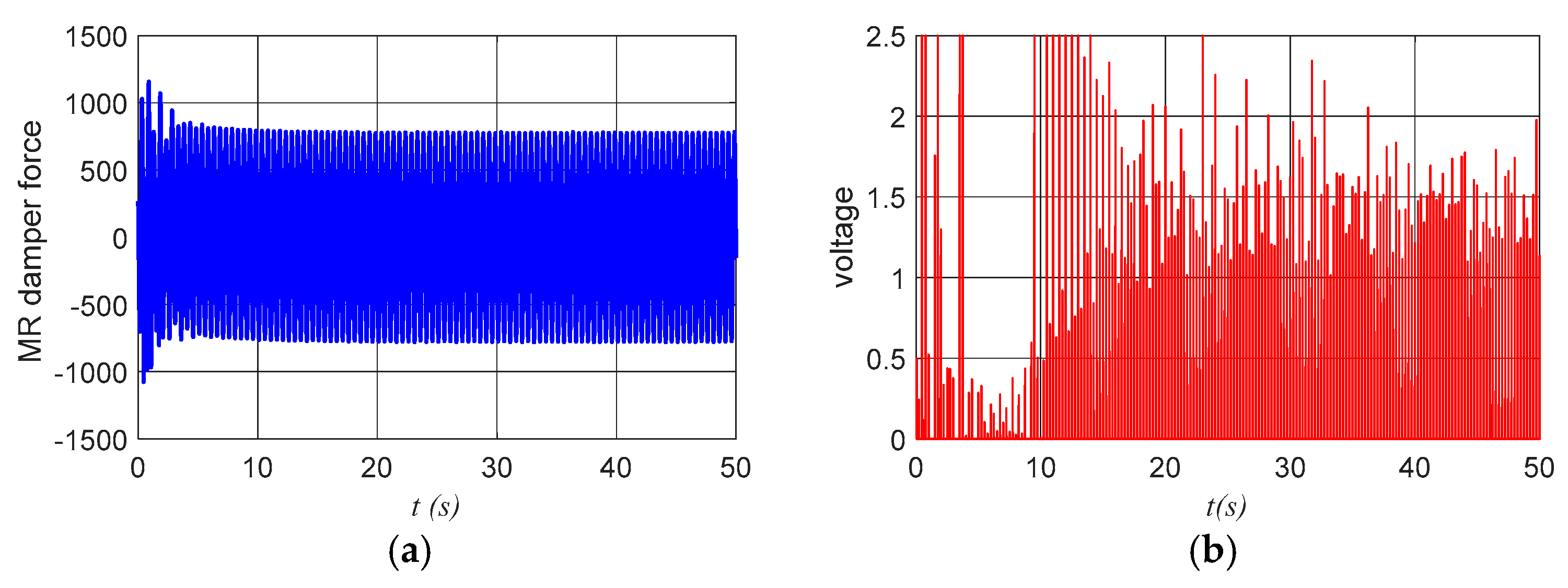
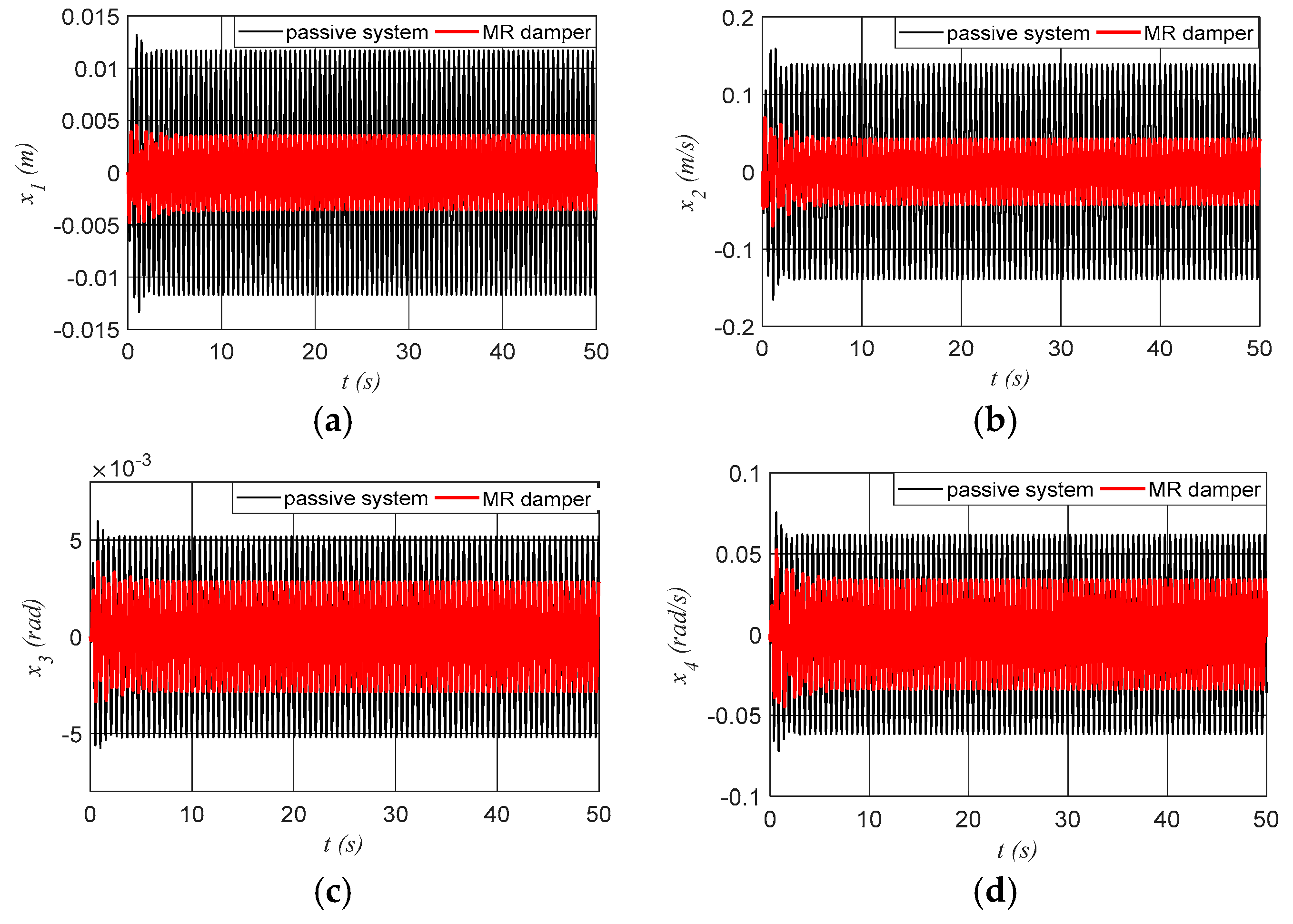
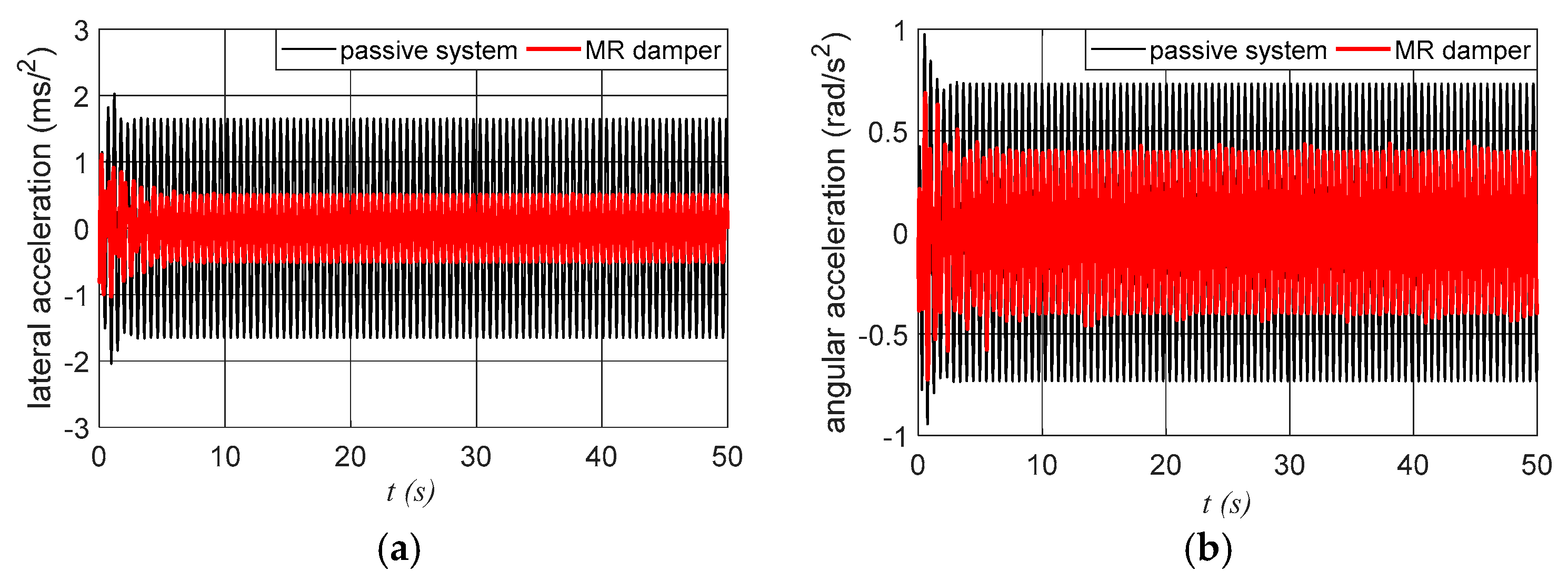

| x1 (m) | x2 (m/s) | x3 (rad) | x4 (rad/s) | al (m/s2) | aa (rad/s2) | |
| without parametric variations | 0.01084 | 0.1364 | 0.0062 | 0.07799 | 1.2106 | 0.603 |
| elevator parametric variations | 0.01 | 0.1257 | 0.0063 | 0.07973 | 1.1169 | 0.7098 |
| parametric variations in vibration source | 0.01171 | 0.139 | 0.005192 | 0.06163 | 1.1684 | 0.5201 |
| x1 (m) | x2 (m/s) | x3 (rad) | x4 (rad/s) | al (m/s2) | aa (rad/s2) | (N) | |
| without parametric variations | 0.0028 | 0.3569 | 0.0034 | 0.4375 | 0.3308 | 0.3919 | 763.1 |
| elevator parametric variations | 0.0029 | 0.03671 | 0.0037 | 0.04689 | 0.3347 | 0.4198 | 775.6 |
| parametric variations in vibration source | 0.003575 | 0.04202 | 0.002828 | 0.03339 | 0.3653 | 0.2860 | 945.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, M.; Fuziki, M.E.K.; Balthazar, J.M.; Lenzi, G.G.; Tusset, A.M. Semi-Active Vibration Control for High-Speed Elevator Using Magnetorheological Damper. Magnetism 2025, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020013
Gonçalves M, Fuziki MEK, Balthazar JM, Lenzi GG, Tusset AM. Semi-Active Vibration Control for High-Speed Elevator Using Magnetorheological Damper. Magnetism. 2025; 5(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Marcos, Maria E. K. Fuziki, Jose M. Balthazar, Giane G. Lenzi, and Angelo M. Tusset. 2025. "Semi-Active Vibration Control for High-Speed Elevator Using Magnetorheological Damper" Magnetism 5, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020013
APA StyleGonçalves, M., Fuziki, M. E. K., Balthazar, J. M., Lenzi, G. G., & Tusset, A. M. (2025). Semi-Active Vibration Control for High-Speed Elevator Using Magnetorheological Damper. Magnetism, 5(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020013








