Abstract
Processed cheese (PC) is a widely consumed dairy product and has undergone significant evolution over time, leading to various formulations aimed at enhancing texture and functionality. This review addresses the role of starch addition on PC, focusing on starch interactions with milk proteins and understanding its influence on the rheological properties, microstructure, and overall quality of PC. Our key findings indicate that starch serves as a cost-effective ingredient that can replace or supplement dairy components, improving texture and water-binding capacity while reducing formulation costs. Generally, starches containing a higher amylose content are associated with the increased hardness and decreased meltability of PC. The insights provided in this review underscore the importance of understanding starch–milk component interactions to optimize PC formulations, paving the way for future research and innovation.
1. Introduction
Processed cheese (PC) was first manufactured in the early 20th century, and since then, many different varieties of PC have been developed around the world. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) distinguishes three different categories of PC based on the type of ingredients used, i.e., pasteurized PC, pasteurized PC food, and pasteurized PC spread. The standards of identity for pasteurized PC, pasteurized PC food, and pasteurized PC spread according to the CFR for moisture, fat, and pH are less than or equal to 40% (w/w), 44% (w/w), and 44 to 60% (w/w); more than or equal to 30% (w/w), 23% (w/w), and 20% (w/w); and more than or equal to 5.3, 5.0, and 4.0, respectively [1]. There is also a further, less-defined category termed pasteurized PC products. This category of PC products has a composition similar to the various categories of PC; however, in contrast to pasteurized PC, pasteurized PC food, and pasteurized PC spread, PC product formulations may contain ingredients such as milk protein concentrate, milk protein isolates, and casein-based ingredients [1]. The CFR does not list starch as an optional ingredient for pasteurized PC, PC food, and PC spread. However, a draft for a standard for PC was started by the Codex Committee on Milk and Milk Products, which included the use of starch as an optional ingredient [2]. The use of starch in PC products is allowed in various countries, including the United Kingdom, Germany, and France, with French legislation stating a limit for starch addition up to 20 g kg−1 of PC [2]. PC analogues can also be manufactured by using both dairy and non-dairy ingredients to reduce the amount of natural cheese in the product [3]. Dairy-based PC analogues can be prepared by replacing milk fat with vegetable oils, such as soy bean oil, peanut oil, palm kernel oil, corn oil, or coconut oil [4]. On the other hand, non-dairy-based PC analogues are prepared by replacing both milk fat and milk protein with vegetable oils and plant protein, respectively [4].
The process of making PC includes the selection of natural cheeses and other dairy and non-dairy ingredients such as salt, water, emulsifying salts, and acidulants, followed by grinding and blending the ingredients and heating the mixture to a specified time–temperature combination before packaging, cooling, and storage [1,5]. PC is often used in foods like pizzas, burgers, and toasted sandwiches, and the characteristics of PC, such as firmness, viscosity, and meltability, play an important role in their functionality in these applications [6].
Starch is used in several dairy products, often to improve texture and rheological properties, and it is a readily available and low-cost polysaccharide [7]. Starch can also be used in PC as an additional ingredient, as well as in the form of a direct replacement for protein or fat since these dairy ingredients contribute most to the cost of PC products [3]. The efficacy of starch in PC products depends on several factors, including its origin, concentration, proportion of amylose to amylopectin, and processing variables, including temperature, pH, and shear [7,8]. When starch is used in dairy matrices, the swelling and gelatinization of the starch can be affected by the presence of milk components, especially milk proteins, because milk proteins can also form a gel upon heating. This can also lead to competition between the starch and milk proteins for water binding and gelation when heated together [9]. Therefore, the interactions during the heating of starch in the presence of milk components are important to understand the effect on the final properties of PC.
Previous studies have investigated the use of starch in dairy systems [7] as well as milk protein–starch interactions, along with their application in extrusion-based products [10] and the influence of starch on the rheology of model dairy systems [11]. However, there is no review focusing on the interactions of starches with individual milk components and emphasizing the role of starch in shaping the texture, rheology, and microstructure of PC products. Hence, this review focuses on the interactions of milk components with starch and its impact on the properties of PC products. For this purpose, we will start in Section 2 on starch and its gelatinization. Subsequently, Section 3 will focus on the interactions between milk proteins and starch, and Section 4 will focus on how other constituents of milk, such as salts and lactose, affect starch gelatinization. The insights of these sections are subsequently applied in the application of starch in PC, which is covered in Section 5.
2. Starch: An Overview
Starch is arranged in discrete particles referred to as starch granules, which vary in size, shape, morphology, and chemical composition, depending on the source of the starch [12]. Starch granules contain two different glucopyranose polymers, i.e., amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is composed of linear α-D-(1–4) glucose linkages, whereas the branched polymer chain of amylopectin contains both linear α-D-(1–4) glucose linkages and branched α-D-(1–6) linkages [12]. Amylose and amylopectin molecules are arranged as semi-crystalline aggregates in starch granules. Branched chains of amylopectin can form double helix structures, contributing to the crystallinity of starch, whereas amylose is amorphous and interspersed within amylopectin molecules [13]. The amylose and amylopectin contents of starch vary as a function of the source of the starch, as is highlighted in Table 1. The diameter of starch granules can range from 1 to 100 μm, and the shape of starch granules can be spherical, oval, discoid, polygonal, angular, or irregular, depending on the starch source [13].
The gelatinization of starch is a process that occurs upon heating the starch in the presence of water, resulting in an increase in viscosity due to the swelling and bursting of starch granules. In the presence of excess water and heating above the gelatinization temperature, the starch granules first swell and then eventually lose their native structure, resulting in a leaching out of amylose, followed by the disruption of the granules [9]. The swelling of the starch granules arises from the process of water uptake by the starch granules. During the cooking/heating of starch, hydrogen bonds within the starch chains are disrupted, allowing water molecules to combine with free hydroxyl groups, resulting in the swelling of the starch [14]. Swelling tends to make starch granules soft and fragile, ultimately affecting the texture and rheology of starch-based foods [14]. The first stages of this process are reversible below the gelatinization temperature, but above the gelatinization temperature, irreversible changes result in the loss of the crystallinity of the starch and the disruption of the starch granules. Upon its subsequent cooling, the starch is rearranged in an ordered and stable structure in a process called starch retrogradation [12,15].
The gelatinization temperature of starch is defined as the temperature at which starch granules begin to swell and an increase in viscosity becomes notable [11]. With an increase in temperature above the gelatinization temperature, the disruption of the starch granules occurs, especially when combined with an increase in shear; this leads to the formation of a starch paste [11]. When the majority of the starch granules have been disrupted, the starch is said to be pasted. The pasting properties of starches, such as their viscosity, determine their functionality in food applications as thickening agents. The pasting properties can be determined using a Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA), which measures the viscosity profile of starch with changes in temperature [12].
In addition to their native form, starches can also be pre-gelatinized for several food applications. These pre-gelatinized starches, also called instant starches, are prepared by pre-cooking and drying native starches. This allows the formation of a stable and moderately viscous suspension when dispersed in cold water [16]. In some cases, native starch granules can exhibit several unfavourable characteristics such as low solubility and a low tolerance to processing conditions such as high shear, high pressure, and temperature, as well as strong acid and alkali conditions, making them less applicable to various applications [12,16,17]. To overcome some of these negatives, starches can be modified using physical (thermal treatment, osmotic pressure treatment, pulsed electric fields, ultrasound, and gamma irradiation), chemical (acid hydrolysis, alkali treatment, acetylation, cross-linking, and oxidation), enzymatic, and genetic methods to enhance their suitability for food applications [17]. Modified starches have gained popularity as additives in dairy beverages due to their cost-effectiveness, their wide availability, and their functional advantages [16]. More specific details about these modifications can be found elsewhere [12,13,16]; since the focus of this paper is on milk protein–starch interactions and their subsequent application in PC, we will not be delving into the modifications of starch.

Table 1.
Amylose and amylopectin content in different starches.
Table 1.
Amylose and amylopectin content in different starches.
| Starch Type | Amylose (%) | Amylopectin (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | 15–35 | 65–85 | [18] |
| Potato | 17–24 | 76–83 | [19] |
| Barley | 15–30 | 70–85 | [20] |
| Wheat | 20–25 | 75–80 | [19] |
| Corn | 17–25 | 75–83 | [19] |
| Maize | 24–28 | 72–76 | [21,22] |
| Oat | 19–34 | 66–81 | [23] |
| Tapioca | 15–26 | 74–85 | [24] |
3. Milk Protein–Starch Interactions
To date, there has been a vast amount of research conducted on the interactions between starch and milk proteins, and various effects have been observed [7,10,11]. The heat-induced milk protein–starch complexation depends on the type and concentration of starch, the type of milk protein used, and the physicochemical conditions used [25]. The interactions during the heating of starch–milk protein mixtures can be due to the adsorption of the milk protein onto the surface of the starch granules or due to the aggregation of the milk protein in the continuous phase [7,10].
Milk proteins can aggregate upon heating and in the presence of starch, and this can lead to microstructural phase separation. In a casein–starch mixture, caseins can form aggregates around the surface of starch granules. In a whey protein–starch mixture, whey proteins can form a gel upon heating, depending on the temperature, and can interfere with the gelatinization of starch. Milk proteins, especially whey proteins, can also compete with starch for water to form a gel [3,7,10]. The majority of starches are non-ionic and tend to show thermodynamic incompatibility or phase separation while interacting with milk proteins [7]. However, ionic starches, such as potato starch (with an anionic character due to the phosphate ester groups of amylopectin), and modified starches, such as phosphate starch (containing a charge on their surface), can interact with milk proteins via electrostatic interactions [7,26]. These interactions are also dependent on the pH of the system, as it affects the charge on the milk proteins and the starch. This section reviews the interactions of starch with caseins and with whey proteins. A summary is provided in Table 2, with a primary focus on the type of starch, amylose–amylopectin ratio (see Table 1), processing conditions, and concentration of starch and milk proteins.

Table 2.
Possible interaction between different starches and milk proteins (casein and whey proteins) based on the current literature.
3.1. Casein–Starch Interactions
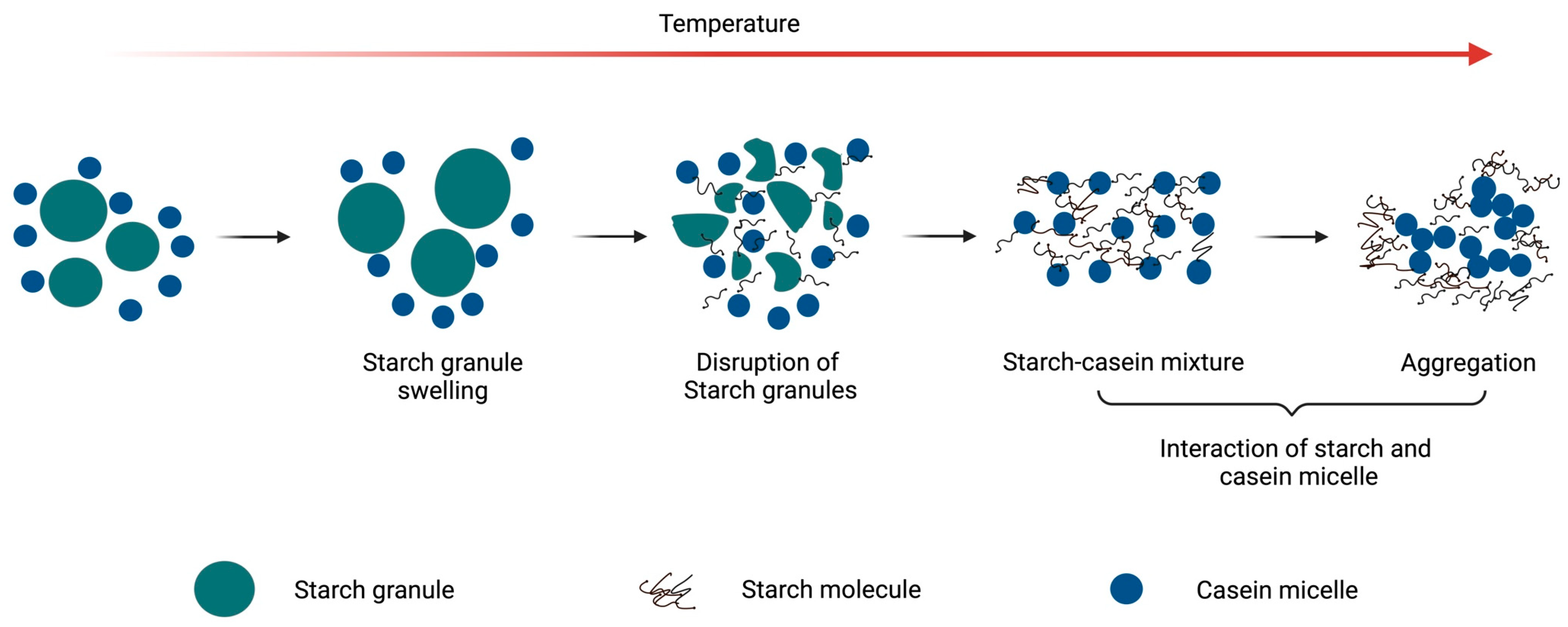
Figure 1 schematically illustrates the interactions of starch with casein at increasing temperatures. Rice starch has been studied for its interactions with casein, particularly its behaviour during adsorption and thermal processing. The adsorption of caseins onto rice starch granules was highlighted by the formation of larger aggregates between the rice starch and sodium caseinate as compared to sodium caseinate alone [27]. Among the individual casein fractions, β-casein showed preferential adsorption in the starch granules over αs-casein when the sodium caseinate concentration increased from 0.25% to 10% (w/w) [27]. The gel structure of a rice starch–casein mixture containing 8% starch showed increased matrix continuity as the proportion of casein increased from 0.4 to 1.2% in a suspension [28]. The interactions between rice starch and casein were suggested to be driven primarily by hydrophobic interactions [28].
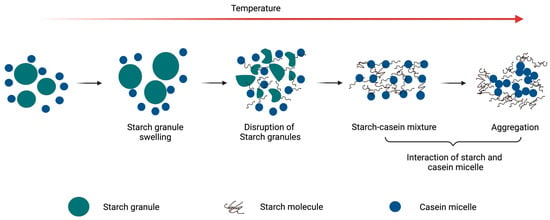
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of behaviour of casein–starch mixture with increase in temperature.
Potato starch hydrates quickly and forms a high-viscosity paste when heated and a clearer gel upon cooling; these properties make it ideal for achieving the desired texture and stability in various food products [32]. Caseins form an unevenly distributed network with potato starch, and aggregated protein particles were observed in the microstructure of this network [29]. This is attributed to the negative charge present on the surface of caseins, which causes repulsion from the negatively charged gelatinized potato starch [29]. Interactions between casein and potato starch were suggested to be primarily due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between the amino groups of the milk protein and the hydroxyl groups of the potato starch and oxidized potato starch [28].
Maize starch is widely used in food products for its influence on properties such as texture, viscosity, and stability. The properties of maize starch are significantly influenced by its structure, which consists of crystalline amylopectin and amorphous amylose regions [33]. The interaction of maize starch with milk proteins can affect the product’s overall quality [33,34]. The addition of pre-gelatinized and cross-linked maize starch has been shown to lead to the poor hydration of casein due to competition for water by the added starch and the adsorption of the caseins onto the starch granules [35,36].
The interactions of casein with modified starches have also been studied. The interaction of modified starches with casein largely depends on the type of modification and the environmental conditions. Modified starches such as phosphate starch, hydroxypropyl starch, and the starch ester of octenyl succinate were observed to interact with casein via the formation of hydrogen bonds, steric stabilization, and hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions [26].
3.2. Whey Protein–Starch Interactions
Whey proteins and starch can be thermodynamically incompatible since they compete for water. The interaction between starches, such as oat and rice starch, and whey proteins can influence the physicochemical and rheological properties of the starch–protein mixture. Recent studies [25,37] found that whey proteins affect the short-range crystalline order of oat and rice starches, which can restrict the starch chain’s reassembly into short-range helices and long-range crystallites during cooling [28]. Oat starch–whey protein gels were shown to have a denser and less porous microstructure compared to control oat starch gels, with larger pores suggesting the adsorption of whey proteins onto starch granules [25]. Similarly, whey proteins were shown to adsorb onto the surface of rice starch granules during dry heating, with no preferential adsorption between the major whey proteins α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin [37]. The interactions of rice starch with whey proteins during heating were reported to be predominantly due to increased exposure of hydrophobic regions of the proteins due to denaturation [28].
The rheological properties of heat-set whey protein–starch gels depend on the amylose content of the starch. For corn starch, which has a comparatively high amylose content (Table 1), the inclusion of whey protein weakens the gel by acting as an inactive filler, preventing amylose rearrangement. On the other hand, in gels from a starch with a low amylose content, whey protein acts as an active filler by increasing the elastic modulus [30]. Whey proteins have been shown to be surrounded by corn starch granules, whereas modifications in their orderly short-range structure were observed with increasing WPI concentrations [30]. Generally, changes in the short-range crystalline structure can be directly related to retrogradation, since this short-range crystalline structure defines the rate of crystallization during retrogradation [38]. The more prominent the short-range crystalline structure in the starch, the faster and more pronounced the retrogradation [38].
In the case of heat-set whey protein–wheat starch gels, a phase separation between the starch and the protein was observed [39]. Furthermore, studies on the addition of soluble potato starch to whey protein indicated the formation of a compatible complex between the whey protein and starch via hydrogen bonding, and this interaction became more pronounced at higher temperatures [31].
Overall, recent studies have shown that interactions between whey protein and starches are mainly driven by hydrogen bonds, and the interactions also modified the short-range crystalline order of the starches, affecting the crystallinity in the structures [7].
4. Interactions of Milk Fat and Lactose with Starch
Milk protein–starch interactions were discussed in the previous section. However, dairy matrices containing milk proteins often also contain other milk components, including lactose, salts, and milk fat, which can affect starch behaviour. This makes it important to understand the effects of these other milk components on the gelatinization characteristics of the starch [40]. Abu-Jdayil, et al. [41] found that increasing the concentration of sucrose, glucose, fructose, and milk fat in milk with added wheat starch increases the pasting viscosity of the system, indicating that these components affect starch gelatinization. Furthermore, sugar type was found to affect viscosity, with the maximum effect on viscosity observed in samples containing added fructose, followed by those containing added sucrose and glucose [41].
The effect of sugar type on starch gelatinization appears to be governed by the chemical groups present in the sugars; for instance, equatorial hydroxyl groups (e.g., ribose) prevent chain reordering and reduce paste viscosity, whereas sugars with axial hydroxyl groups (e.g., fructose) have the opposite effect, increasing viscosity [41]. Similar results were reported by other studies on the role of sugars (sucrose, fructose, maltose, ribose, and glucose) on sago starch [42] or cross-linked waxy maize starch [43]. No significant effect was observed on the particle size of heated starch granules with increasing sucrose concentrations [43].
The presence of sugar in a system with starch affects the gelatinization temperature of starch [44]. The replacement of sucrose by lactose in a 50:50 mixture with wheat starch increased the viscosity and storage modulus of mixtures as compared to sucrose and wheat starch mixtures as a result of a change in the gelatinization temperature. Since lactose contributes less to increasing the gelatinization temperature than sucrose, this led to an increase in the viscosity of samples with lactose when heated to the same temperature [44]. Similarly, a study revealed that gelatinization behaviour was affected by the presence of lactose and soluble minerals, either separately or in combination, with normal and waxy rice starch during pressure-induced gelation [40]. The presence of lactose and soluble minerals increased the gelatinization temperature of starch, thereby decreasing the swelling power [40]. The gelatinization of starch can also be affected due to a hindrance in water absorption as a result of the presence of lactose and soluble minerals. Hence, it can be concluded that the presence of sugars and milk fat affects starch gelatinization behaviour and thereby the rheology of mixtures.
5. Starch in Processed Cheese
Fat in PC enhances texture, imparts flavour, and creates a smooth mouthfeel [45]. However, consumer focus over the years has shifted towards reduced fat consumption [46]. Starches have emerged as an effective fat replacer in PC because of their macromolecular structure, ease of processing, affordability, and wide availability [47,48]. Starch-based fat replacers replicate (some of) the properties of fat in PC by increasing its water-holding capacity and thereby increasing its viscosity. A variety of starches, including potato, corn, wheat, maize, and tapioca starch, have been used as fat replacers in dairy products to maintain their melting properties and sensory properties despite this fat replacement [49]. Therefore, it is important to understand the starch-induced changes in PC’s microstructure, rheology, and textural attributes. A summary of the effects observed in PC products is provided in Table 3, and these are described further in the subsequent sections. An overview of the PC formulations in which starch addition has been tested is given in Table 4, from which it is clear that the inclusion of starch has both been the subject of studies for the purpose of fat replacement, as well as for the purpose of protein replacement.

Table 3.
Effect of using different starches on the rheological and textural properties of processed cheese and analogue cheese products.

Table 4.
Composition of processed/analogue cheeses made from different ingredients and various levels of different starches in the formulation.
5.1. Effect of Starch on the Microstructure of Processed Cheese
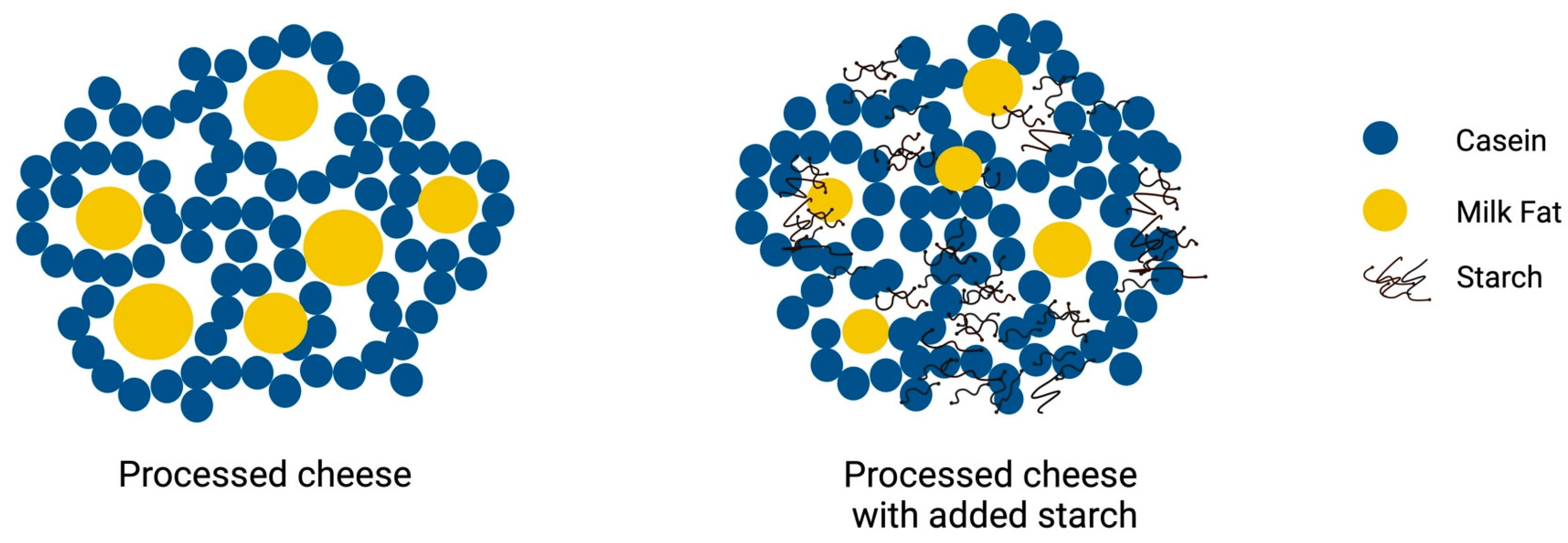
The microstructure of PC strongly affects its texture, meltability, and overall sensory properties. PC forms a complex matrix containing dispersed fat globules in a hydrated protein network stabilized by calcium-sequestering salts, usually sodium citrate, sodium phosphate, and polyphosphates [64]. These salts play a crucial role in creating a stable emulsion by interacting with proteins, especially casein, facilitating the even dispersion of fat within the cheese matrix. The emulsification process involves hydrating milk proteins to form a continuous protein matrix that traps the fat globules [5,64]. This, coupled with calcium-sequestering salts, imparts the characteristic smooth texture and uniform meltability of PC [65]. A schematic representation of the PC microstructure with and without the addition of starch is displayed in Figure 2.
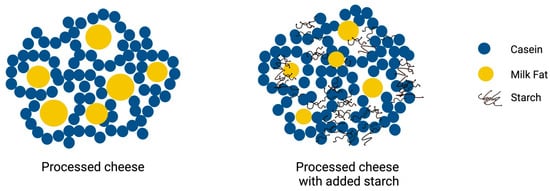
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of processed cheese microstructure without and with addition of starch.
Mounsey and O’Riordan [35,58] reported that PC prepared using rennet casein, vegetable fat, and potato starch, wheat starch, or maize starch contained evenly distributed fat globules in the protein matrix, whereas the fat droplets in PC made with waxy maize starch or rice starch were unevenly distributed and also larger (up to 65 µm). This was attributed to the fact that the ability of the protein to emulsify fat and form uniform droplets was diminished as a result of the pre-gelatinized starch and the rennet casein competing with one another for water [35,58]. Montesinos-Herrero, Cottell, O’Riordan and O’Sullivan [61] found that the use of native resistant starch in PC prepared with rennet casein, hydrogenated palm oil, and rapeseed oil led to an uneven distribution of fat droplets and that the droplets were clustered in the protein matrix, whereas an even distribution of fat was seen when retrograded resistant starch was used.
Ye and Hewitt [62] used confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) to examine the microstructure of imitation cheese prepared with rennet casein, soybean oil, and potato starch. They found that at a starch concentration of 3% (w/w), the fat was distributed unevenly and in large droplets. At a 7% starch concentration, the starch formed strands and clusters separated from the protein, and at an even higher concentration (10%), the starch formed its own continuous phase with one dispersed phase, i.e., the oil phase. Duggan, Noronha, O’riordan and O’sullivan [59] reported that cheeses containing different starches such as native corn starch, waxy corn starch, and pre-gelatinized starch had larger fat globules arranged in clusters within the cheese matrix, while resistance starch had smaller-sized fat globules with uniformly distributed starch granules. Overall, various types of starch affect the microstructure of PC differently, which ultimately leads to variations in PC’s textural and rheological properties such as viscosity, meltability, and hardness, as discussed further below.
5.2. Effect of Starch on Rheological Properties of Processed Cheese
The tendency of PC to spread and flow when fully melted depends on its viscosity [1]. PC viscosity is mainly governed by its proteins, primarily casein, along with its fat and emulsifying salts. The addition of starch to PC increases its viscosity by enhancing its water-binding capacity as a result of the gelatinization of starch upon heating. It has been reported that the size of the granules also affects the viscosity of PC, with larger granules contributing to a sharper increase in viscosity than smaller granules, due to the difference in water-binding capacity [66]. Starch distribution in PC is also affected by the amylose content of the starch used, and it was previously reported that cheese meltability decreases and viscosity increases with increasing amylose content in the starch [59,67]. It has been suggested that the linear chains of amylose in the starch make it easy for it to leach out from the starch granules into the cheese matrix, allowing protein–starch interactions, increasing viscosity, and decreasing meltability [54,59,67]. The highly branched amylopectin molecules do not have the ability to easily diffuse through a PC matrix; hence, amylopectin contributes less to the meltability and viscosity of PC [54,59].
Gampala and Brennan [54] reported a significant increase in the viscosity of PC prepared with cheddar cheese, skim milk powder, and butter when adding a large amount of maize starch, and this increase was attributed to the leaching of amylose from the starch granules, which aided gel formation and the binding of water; in contrast, amylopectin is highly branched and does not readily form gel. Gampala and Brennan [54] reported an increase in the viscosity of cheese containing pre-gelatinized rice and waxy maize starch. Talbot-Walsh, Kannar and Selomulya [52] studied the effect of different starches (5% w/w) such as potato, waxy maize, and corn starch on the viscosity of PC and found an increase in viscosity from 2.5 Pa·s in a control PC to 5–7 Pa·s in a PC with added starch. On the other hand, the 5% potato starch cheese had an inverse viscosity profile, with the lowest viscosity at the point where the cheese had a continuous starch matrix [52,63,66].
5.3. Effect of Starch on the Meltability of Processed Cheese
Meltability is an essential functional property, especially for cheeses used in hot food formulations [68], and the ease and extent to which cheese flows upon heating defines the meltability of PC. Cheese meltability is most commonly measured at 100 °C for 15 min in the Arnott method or 232 °C for 5 min in the Schreiber test [63]. The inclusion of pre-gelatinized starches in PC decreases its meltability by 30–50% [58]. The rapid immobilization of water by pre-gelatinized starches during the preparation of imitation cheese likely hinders protein hydration, resulting in an aggregated protein matrix [58]. Therefore, the product’s propensity to melt and flow at high temperatures is diminished by the increase in thermal energy needed to break up the aggregates [57].
Starch addition has been shown to significantly reduce the meltability of PC spreads [67,69]. Potato starch significantly reduces the meltability of PC prepared using natural cheese and butter; the higher the starch content, the slower the cheese melted [51]. This is because the starch becomes embedded in the protein network, and due to low water activity, it is harder for starch to separate from the binding sites of the cheese matrix [51]. The incorporation of wheat starch into imitation cheese has led to a notable decline in its meltability [66]. This was attributed to excessive fat emulsification, insufficient thermoplasticity in the starch granules, and the reduced moisture content of the product [56]. The possible reasons contributing to this reduced meltability could be the use of cross-linked and acetylated waxy starches [60], increases in viscosity, and decreases in the moisture content of the final product [70].
The phase behaviour of the protein–starch network is the main factor determining the properties of the added starch in PC. When added at low concentrations, the starch is confined to a dispersed phase and acts as a filler. This increases the gel strength without reducing the melting ability of the cheese. At high starch concentrations, the added starch forms a stranded network that separates from the protein phase, significantly reducing meltability [11]. Additionally, replacing fat with starch has a negative effect on the lubrication of the protein matrix, which resists flow during heating [50,67].
5.4. Effect of Starch on Textural Properties of Processed Cheese
Hardness can be defined as the force required to achieve a defined level of deformation [71]. The addition of different starches (waxy corn starch, potato starch, rice starch, wheat) increases the hardness of PC products [51,67]. Nevertheless, an increase in the moisture content of the product can counteract a rise in hardness by acting as a plasticizer [72]. Since starch and protein compete for water during heating, it was proposed by Mounsey and O'riordan [57] to add starch at the end of processing to make more water available for protein hydration and reduce hardness. This approach successfully maintained similar hardness values to the control cheese, confirming the anticipated reduction in cheese hardness [57]. The addition of potato starch as a replacement for fat caused a denser network because of the starch–protein interactions, leading to increased hardness [50]. The higher hardness of PC containing high-amylose-content starch is because of amylose leaching into the cheese matrix from the starch granules, strengthening the hydrogen bonds between the protein and carbohydrate molecules and ultimately contributing to the increased hardness of the cheese [3].
In contrast, the addition of pre-gelatinized starch reduces the hardness of the cheese, and the softest products are produced from lower-amylose starches, such as waxy maize or rice starch, indicating that the hydrogen-bonding association of leached amylose during the cooling process of the imitation cheeses likely has a greater structural influence than the association of amylopectin [58]. During the cooking/heating of starch, hydrogen bonds within the starch chains are disrupted, allowing water molecules to combine with free hydroxyl groups, resulting in the swelling of the starch [14]. Swelling softens the starch granules, ultimately affecting the texture and rheology of starch-based foods [14]. The hardness of cheese containing modified potato starch and maize starch increase linearly with an increase in starch content, which is correlated with increased viscosity [50,54]. The addition of modified potato starch as a fat replacer has led to an increase in hardness, owing to an increase in protein–protein interactions due to the absence of fat as well as the formation of a strong network by binding more water with starch addition [50].
The strength of the internal bonds that comprise the product’s body is known as cohesiveness [73]. A cheese with moderate cohesion is ideal for easy slicing or shredding with the least amount of matting. The adhesiveness of cheese reveals how the cheese and teeth interact, indicating the stickiness of the surface of the cheese. Due to the ability of starch to retain water, adding potato starch to PC increases casein matrix–moisture interactions and adhesiveness. Moreover, modified potato starch improves reduced-fat PC cohesiveness and adhesiveness as compared to a control [50]. Similarly, the cohesiveness of imitation cheese increases with increased concentrations of native resistant starch [61].
5.5. Role of pH in Starch Addition to Processed Cheese
Variations in pH will have a definite impact on the properties of PC since the change in pH influences the solubility/hydration of proteins along with the size of the fat globules in the microstructure. Talbot-Walsh, Kannar and Selomulya [52] reported that the effect of pH on starch in PC was dependent on the type of starch and governed by amylose content; the higher the amylose content, the more pronounced the effect on the microstructure and texture of PC within a particular range of pH. For example, 5% potato starch and corn starch were found to form a continuous network in the microstructure of PC within the pH ranges 4.8 to 5.35 and 4.9 to 5.05, respectively, and both samples had their highest hardness at pH 5.0. Beyond this range, the starch granules were present as discrete particles in the microstructure. Moreover, no impact of pH change was found on the distribution of waxy maize starch in the microstructure of PC, wherein starch granules were arranged as discrete granules, owing to the higher content of amylopectin in waxy maize starch, which does not leach out from granules easily [52]. In the aforementioned study, waxy maize starch had 2% amylose while the potato and corn starch had 19 and 17% starch, respectively. This correlated well with the findings of the authors that it is amylopectin that causes the difference in microstructure since it does not leach out easily into the cheese matrix while heating [52]. These findings state that the effect of pH on the microstructure of PC is more pronounced in native starches than in modified starches. Bravo-Núñez, et al. [74] found that the interaction between corn starch and whey protein was pH-dependent, with a decrease in pH to 4.5 enhancing the water-binding capacity due to protein denaturation near its isoelectric point (pI). Additionally, microscopical observations showed that the gel structure gradually disappeared with increasing pH, while the aggregation of proteins at a lower pH promoted gel formation.
Also, pH plays a major role in the meltability of PC; increasing the pH from 4.5 to 6.0 increased the meltability of the cheese. Cheese with 5% w/w potato and waxy starch demonstrated a similar meltability at pH 5.5–6 to control cheeses at pH 5, with no meltability observed in samples manufactured at a pH of 4.5 or below. These results suggest that the pH adjustment of cheese blends may be effective in mitigating the negative effects of the addition of starch on meltability [52].
6. Conclusions
The incorporation of starch into processed cheese (PC) enhances its textural and rheological attributes. Starch serves as an effective fat replacer and significantly influences the microstructure and functional properties of PC through complex interactions with milk proteins, particularly casein and whey. These interactions are affected by starch type, amylose content, and processing conditions, which in turn impact the viscosity, meltability, and textural attributes of PC. In PC, starches with a higher amylose content, such as maize and potato starches, generally lead to increased hardness and decreased meltability compared to PC with a lower amylose starch content due to amylose leaching out of the starch granules in the final product, causing increasing protein–carbohydrate bonding. Additionally, pH plays a significant role in modulating these interactions, highlighting the need for careful formulation strategies. This review underscores the potential of starch as a functional ingredient in PC, paving the way for meeting consumer preferences while maintaining product quality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.A., G.K.D. and T.H.; writing—original draft, F.A., V.P., R.K. and G.K.D.; writing—review and editing, F.A., G.K.D. and T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Gaurav Kr Deshwal is the recipient of a Walsh Scholarship from Teagasc, the Irish Agricultural and Food Development Authority (Ref. 2020213).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Figures in this manuscript were created using Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
T.H. is employed by FrieslandCampina. The research was conducted without any relationships with the company that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Kapoor, R.; Metzger, L.E. Process cheese: Scientific and technological aspects—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 194–214. [Google Scholar]
- Koca, N.; Erbay, Z.; Öztürk, M.U. Regulations and legislations on processed cheese. In Processed Cheese Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 449–490. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot-Walsh, G.; Kannar, D.; Selomulya, C. A review on technological parameters and recent advances in the fortification of processed cheese. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Mulsow, B.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Processed cheese and cheese analogues. In Structure of Dairy Products; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 210–235. [Google Scholar]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Akshit, F.; Altay, I.; Huppertz, T. A Review on the Production and Characteristics of Cheese Powders. Foods 2024, 13, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Hewitt, S.; Taylor, S. Characteristics of rennet–casein-based model processed cheese containing maize starch: Rheological properties, meltabilities and microstructures. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Sharafbafi, N.; Kristo, E. Polysaccharide–protein interactions in dairy matrices, control and design of structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Florczuk, A.; Dąbrowska, A.; Aljewicz, M. An evaluation of the effect of curdlan and scleroglucan on the functional properties of low-fat processed cheese spreads. LWT 2022, 163, 113564. [Google Scholar]
- Matignon, A.; Neveu, A.; Ducept, F.; Chantoiseau, E.; Barey, P.; Mauduit, S.; Michon, C. Influence of thermo-mechanical treatment and skim milk components on the swelling behavior and rheological properties of starch suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2015, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, L.; Brennan, M.A.; Mason, S.L.; Zheng, H.; Brennan, C.S. Rheological, pasting and microstructural studies of dairy protein–starch interactions and their application in extrusion-based products: A review. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600273. [Google Scholar]
- Considine, T.; Noisuwan, A.; Hemar, Y.; Wilkinson, B.; Bronlund, J.; Kasapis, S. Rheological investigations of the interactions between starch and milk proteins in model dairy systems: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, K.; Mir, N.A.; Yousuf, B.; Allai, F.M.; Sharma, S. Starch: An Overview. Food Biopolym. Struct. Funct. Nutraceutical Prop. 2021, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Compart, J.; Singh, A.; Fettke, J.; Apriyanto, A. Customizing starch properties: A review of starch modifications and their applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Cui, C.; Gao, L.; Qin, Y.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Shi, R.; Sun, Q. A review of starch swelling behavior: Its mechanism, determination methods, influencing factors, and influence on food quality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, J.A.; Bruneel, C.; Derde, L.J.; Gomand, S.V.; Pareyt, B.; Putseys, J.A.; Wilderjans, E.; Lamberts, L. Fate of starch in food processing: From raw materials to final food products. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia-Ud-Din; Xiong, H.; Fei, P. Physical and chemical modification of starches: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinhmar, A.; Pathera, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Nehra, M.; Thory, R.; Nain, V. Impact of various modification methods on physicochemical and functional properties of starch: A review. Starch-Stärke 2023, 75, 2200117. [Google Scholar]
- Bonto, A.P.; Tiozon Jr, R.N.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Camacho, D.H. Impact of ultrasonic treatment on rice starch and grain functional properties: A review. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 71, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, N.; Muhammad, N.; Abdullah, M. Potential of starch nanocomposites for biomedical applications. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; p. 012087. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, A.E.; Hristov, A.; Melgar, A.; Ropp, J.; Etter, R.; Zaman, S.; Hunt, C.; Huber, K.; Price, W. Effect of barley and its amylopectin content on ruminal fermentation and nitrogen utilization in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4321–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoud, O.A.E.; Nawaz, H.; Arêas, E.P. Chemistry and applications of polysaccharide solutions in strong electrolytes/dipolar aprotic solvents: An overview. Molecules 2013, 18, 1270–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatefov, E.B.; Goldstein, V.G.; Krivandin, A.V.; Wasserman, L.A. Main characteristics of processed grain starch products and physicochemical features of the starches from maize (Zea mays L.) with different genotypes. Polymers 2023, 15, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Kaur, K.; Basha, S.J.; Kennedy, J.F. Current trends in the preparation, characterization and applications of oat starch—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.-F.; Liu, W.; Whaley, J.K.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure, properties, and potential applications of waxy tapioca starches–A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Brennan, M.; Brennan, C.; Zheng, H. Influence of whey protein isolate on pasting, thermal, and structural characteristics of oat starch. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.-x.; Liang, Y.; Yu, B.; Tan, C.-p.; Cui, B. Interaction of starch and casein. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noisuwan, A.; Hemar, Y.; Wilkinson, B.; Bronlund, J. Adsorption of milk proteins onto rice starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Min, G.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Q. Starch-protein interplay varies the multi-scale structures of starch undergoing thermal processing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zhao, G.; Thaiudom, S. Evaluation of the physico-chemical properties of potato starch-based foods and their interactions with milk protein and soybean oil. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhong, F.; Goff, H.D.; Li, Y. Study on starch-protein interactions and their effects on physicochemical and digestible properties of the blends. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, R.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Liu, C. Soluble starch/whey protein isolate complex-stabilized high internal phase emulsion: Interaction and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Blecker, C. Physicochemical and structural characterization of potato starch with different degrees of gelatinization. Foods 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakelle, B.; Kian-Pour, N.; Toker, O.S.; Palabiyik, I. Effect of process conditions and amylose/amylopectin ratio on the pasting behavior of maize starch: A modeling approach. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 94, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Flores-Silva, P.C.; Sifuentes-Nieves, I.; Agama-Acevedo, E. Controlling starch digestibility and glycaemic response in maize-based foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103222. [Google Scholar]
- Mounsey, J.S.; O’Riordan, E.D. Influence of pre-gelatinised maize starch on the rheology, microstructure and processing of imitation cheese. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Azim, Z.; Alexander, M.; Koxholt, M.; Corredig, M. Influence of cross-linked waxy maize starch on the aggregation behavior of casein micelles during acid-induced gelation. Food Biophys. 2010, 5, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Du, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H. Morphological and physicochemical properties of rice starch dry heated with whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106091. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S. New insight into starch retrogradation: The effect of short-range molecular order in gelatinized starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106921. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Ashton, J.; Kasapis, S. The influence of chitosan on the structural properties of whey protein and wheat starch composite systems. Food Chem. 2015, 179, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.; Anema, S.; Pinder, D.; Wong, M. Effects of different components in skim milk on high-pressure-induced gelatinisation of waxy rice starch and normal rice starch. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Mohameed, H.A.; Eassa, A. Rheology of wheat starch–milk–sugar systems: Effect of starch concentration, sugar type and concentration, and milk fat content. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.B.; Williams, P.A. Effect of sugars on the thermal and rheological properties of sago starch. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1999, 50, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Acquarone, V.; Rao, M. Influence of sucrose on the rheology and granule size of cross-linked waxy maize starch dispersions heated at two temperatures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 51, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Irudayaraj, J.; Otgonchimeg, S.; Walsh, M. Rheological study of starch and dairy ingredient-based food systems. Food Chem. 2004, 86, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, T. The role of dairy ingredients in processed cheese products. In Dairy-Derived Ingredients; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 507–538. [Google Scholar]
- Diamantino, V.R.; Costa, M.S.; Taboga, S.R.; Vilamaior, P.S.; Franco, C.M.; Penna, A.L.B. Starch as a potential fat replacer for application in cheese: Behaviour of different starches in casein/starch mixtures and in the casein matrix. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 89, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, A.; Nasim, I.; ud Din, M.S.; Araki, T.; Khalid, N. Effects of different fat replacers on functional and rheological properties of low-fat mozzarella cheeses: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104136. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Yao, Y. Carbohydrates as fat replacers. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schädle, C.N.; Sanahuja, S.; Bader-Mittermaier, S. Influence of fat replacers on the rheological, tribological, and aroma release properties of reduced-fat emulsions. Foods 2022, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Tavakolipour, H.; Safaeian, S.; Nadushan, R.M. Exploring the potential of modified potato starch and seaweed salt as structuring agents to design processed cheeses with desirable properties. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 133, 105439. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, D.; Bennett, R.J.; Hemar, Y.; Reid, D.C.; Lee, S.K.; Illingworth, D. Effect of different starches on rheological and microstructural properties of (II) commercial processed cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot-Walsh, G.; Kannar, D.; Selomulya, C. pH effect on the physico-chemical, microstructural and sensorial properties of processed cheese manufactured with various starches. LWT 2019, 111, 414–422. [Google Scholar]
- Małecki, J.; Tomasevic, I.; Djekic, I.; Sołowiej, B.G. The effect of protein source on the physicochemical, nutritional properties and microstructure of high-protein bars intended for physically active people. Foods 2020, 9, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampala, P.; Brennan, C.S. Potential starch utilisation in a model processed cheese system. Starch-Stärke 2008, 60, 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Nakamura, T. Effects of starches on the mechanical properties and microstructure of processed cheeses with different types of casein network structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, J.S.; O’Riordan, E.D. Alteration of imitation cheese structure and melting behaviour with wheat starch. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, J.; O'riordan, E. Characteristics of imitation cheese containing native starches. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, J.S.; O’Riordan, E.D. Modification of imitation cheese structure and rheology using pre-gelatinised starches. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, E.; Noronha, N.; O’riordan, E.; O’sullivan, M. Effect of resistant starch on the water binding properties of imitation cheese. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, J.S.; O’riordan, E. Characteristics of imitation cheese containing native or modified rice starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Herrero, C.; Cottell, D.C.; O’Riordan, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Partial replacement of fat by functional fibre in imitation cheese: Effects on rheology and microstructure. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Hewitt, S. Phase structures impact the rheological properties of rennet-casein-based imitation cheese containing starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaouadj, F.; Ziane-Zafour, A.H.; Rebiha, M. Effects of modified starch and fat on the rheological characteristics of newly formulated processed cheese: Use of experimental design method. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 142, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Fenelon, M.; Huppertz, T. A review on the effect of calcium sequestering salts on casein micelles: From model milk protein systems to processed cheese. Molecules 2023, 28, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Bennett, R.; Hemar, Y.; Campanella, O. Rheological and microstructural characteristics of model processed cheese analogues. J. Texture Stud. 2001, 32, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.S.; Sharma, L.; Kaur, M. Effect of granule size on physicochemical, morphological, thermal and pasting properties of native and 2-octenyl-1-ylsuccinylated potato starch prepared by dry heating under different pH conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.; Abdeen, E.; El-Shafei, S.M.; Mohamed, A.H. Effect of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) Flour on the Production and Quality of Low-Fat Camel Milk Processed Cheese Spread. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2020, 23, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atik, D.S.; Huppertz, T. Melting of natural cheese: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, M.M.; Ali, M.A.; Shaaban, H.A.-G.; Mohamad, A.G.; Hasanain, A.M. Production of functional spreadable processed cheese using Chlorella vulgaris. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2018, 17, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, R.; Basak, S.; Gokhale, J. Recent trends in the development of healthy and functional cheese analogues-a review. LWT 2022, 155, 112991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, S.; Nateghi, L.; Eyvazzade, O.; Ebrahimi, M.T.A. The physicochemical, texture hardness and sensorial properties of ultrafiltrated low-fat cheese containing galactomannan and novagel gum. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2020, 19, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hennelly, P.; Dunne, P.; O’sullivan, M.; O’riordan, E. Textural, rheological and microstructural properties of imitation cheese containing inulin. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Ocampo, K.A.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Montejano-Gaitán, J.G.; Zárraga-Alcántar, R.; Cardador-Martínez, A. Evaluation of biological, textural, and physicochemical parameters of panela cheese added with probiotics. Foods 2020, 9, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Núñez, Á.; Garzón, R.; Rosell, C.M.; Gómez, M. Evaluation of starch–protein interactions as a function of pH. Foods 2019, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).