In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions
Definition
1. Introduction
2. Background and Overview
3. Principles of In Vivo Dosimetry
4. Techniques and Tools
5. Applications of IVD
5.1. EBRT
5.2. TBI
5.3. Brachytherapy
5.4. Pediatric Radiotherapy
6. Challenges and Limitations
6.1. Measurement Uncertainties
6.2. Technical Limitations
6.3. Clinical Integration
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Emerging Technologies
7.2. Advancements in Detector Materials and Nanotechnology
7.3. Integration with Adaptive Radiotherapy
7.4. Integration with FLASH Radiotherapy
7.5. Individualized Patient Dosimetry and Real-Time Feedback
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail, A.; Giraud, J.Y.; Lu, G.N.; Sihanath, R.; Pittet, P.; Galvan, J.M.; Balosso, J. Radiotherapy quality insurance by individualized in vivo dosimetry: State of the art. Cancer/Radiothér. 2009, 13, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leunens, G.; Van Dam, J.; Dutreix, A.; Van der Schueren, E. Quality assurance in radiotherapy by in vivo dosimetry. 2. Determination of the target absorbed dose. Radiother. Oncol. 1990, 19, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leunens, G.; Van Dam, J.; Dutreix, A.; Van der Schueren, E. Quality assurance in radiotherapy by in vivo dosimetry. 1. Entrance dose measurements, a reliable procedure. Radiother. Oncol. 1990, 17, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijnheer, B. State of the art of in vivo dosimetry. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 131, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Essers, M.; Mijnheer, B. In vivo dosimetry during external photon beam radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 43, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorino, C.; Corletto, D.; Mangili, P.; Broggi, S.; Bonini, A.; Cattaneo, G.M.; Parisi, R.; Rosso, A.; Signorotto, P.; Villa, E.; et al. Quality assurance by systematic in vivo dosimetry: Results on a large cohort of patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2000, 56, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rozendaal, R.A.; Mijnheer, B.J.; Hamming-Vrieze, O.; Mans, A.; Van Herk, M. Impact of daily anatomical changes on EPID-based in vivo dosimetry of VMAT treatments of head-and-neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, C.; Cherian, S.; Yousef, J.; Wang, K.; Mackley, H.B. Total body irradiation: A practical review. Appl. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Staffurth, J. A review of the clinical evidence for intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 22, 643–657. [Google Scholar]
- Hunte, S.O.; Clark, C.H.; Zyuzikov, N.; Nisbet, A. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT): A review of clinical outcomes—What is the clinical evidence for the most effective implementation? Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20201289. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.M. Physics and Dosimetric Principles of SRS and SBRT. Mathews J. Cancer Sci. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Healy, B.J.; Budanec, M.; Ourdane, B.; Peace, T.; Petrovic, B.; Sanz, D.E.; Scanderbeg, D.J.; Tuntipumiamorn, L. An IAEA survey of radiotherapy practice including quality assurance extent and depth. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, N.; Mijnheer, B.J.; Padgett, K.; Nalichowski, A.; Wu, C.; Nyflot, M.J.; Olch, A.J.; Papanikolaou, N.; Shi, J.; Holmes, S.M.; et al. Use of electronic portal imaging devices for pre-treatment and in vivo dosimetry patient-specific IMRT and VMAT QA: Report of AAPM Task Group 307. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, e865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaciregui-Ruiz, I.; Beddar, S.; Greer, P.; Jornet, N.; McCurdy, B.; Paiva-Fonseca, G.; Mijnheer, B.; Verhaegen, F. In vivo dosimetry in external beam photon radiotherapy: Requirements and future directions for research, development, and clinical practice. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Villaggi, E.; Bresciani, S.; Cilla, S.; Falco, M.D.; Garibaldi, C.; Russo, S.; Talamonti, C.; Stasi, M.; Mancosu, P. Estimating dose delivery accuracy in stereotactic body radiation therapy: A review of in-vivo measurement methods. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 149, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, O.A.; Workman, G.; Hounsell, A.R.; Prise, K.M.; Jain, S. In vivo dosimetry in pelvic brachytherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20220046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernli, C. A short history and critical review of individual monitoring. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 170, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, W.A. Evolution over the past century of quantities and units in radiation dosimetry. J. Radiol. Prot. 2007, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, S.A.; Pech-Canul, M.I. Development feasibility of TLD phosphors and thermoluminescent composite materials for potential applications in dosimetry: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A.B. Electronic dosimetry in radiation therapy. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, S134–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, L.J.; Carvajal, M.A.; Lopez-Villanueva, J.A.; Vilches, M.; Lallena, A.M.; Palma, A.J. Evaluation of a low-cost commercial mosfet as radiation dosimeter. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 125, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Elmpt, W.; McDermott, L.; Nijsten, S.; Wendling, M.; Lambin, P.; Mijnheer, B. A literature review of electronic portal imaging for radiotherapy dosimetry. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 88, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alecu, R.; Loomis, T.; Alecu, J.; Ochran, T. Guidelines on the implementation of diode in vivo dosimetry programs for photon and electron external beam therapy. Med. Dosim. 1999, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghzifene, A.; Followill, D.; Dewaraja, Y.K.; Allisy, P.J.; Kessler, C.; van der Merwe, D. International symposium on standards, applications and quality assurance in medical radiation dosimetry (IDOS 2019): Highlights of an IAEA meeting. Med. Phys. Int. 2019, 7, 342–360. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C. Depth dose enhancement on flattening-filter-free photon beam: A Monte Carlo study in nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Barest, G.; Brewster, L.J.; Chui, C.S.; Kutcher, G.J.; Laughlin, J.S.; Fuks, Z. A comprehensive three-dimensional radiation treatment planning system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1988, 15, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, T. Thermoluminescence in medical dosimetry. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 71, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.; Das, I.J.; Dempsey, J.F.; Lam, K.L.; LoSasso, T.J.; Olch, A.J.; Palta, J.R.; Reinstein, L.E.; Ritt, D.; Wilcox, E.E. TG-69: Radiographic film for megavoltage beam dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2007, 34, 2228–2258. [Google Scholar]
- McKeever, S.W. Optically stimulated luminescence: A brief overview. Radiat. Meas. 2011, 46, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C.; Jiang, R.; Kiciak, A.; Markel, D. Dosimetric comparison between the prostate intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plans using the planning target volume (PTV) dose–volume factor. J. Radiother. Pract. 2016, 15, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C.; Owrangi, A.M. Dosimetric dependences of bone heterogeneity and beam angle on the unflattened and flattened photon beams: A Monte Carlo comparison. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 101, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C. Cone-beam CT dosimetry for the positional variation in isocenter: A Monte Carlo study. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butson, M.; Haque, M.; Smith, L.; Butson, E.; Odgers, D.; Pope, D.; Gorjiana, T.; Whitaker, M.; Morales, J.; Hong, A.; et al. Practical time considerations for optically stimulated luminescent dosimetry (OSLD) in total body irradiation. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2017, 40, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Doblado, F.; Terrón, J.A.; Sánchez-Nieto, B.; Arráns, R.; Errazquin, L.; Biggs, D.; Lee, C.; Núñez, L.; Delgado, A.; Muñiz, J.L. Verification of an on line in vivo semiconductor dosimetry system for TBI with two TLD procedures. Radiother. Oncol. 1995, 34, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nibhanupudy, J.R.; De Jesus, M.A.; Fujita, M.; Goldson, A.L. Radiation dose monitoring in a breast cancer patient with a pacemaker: A case report. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2001, 93, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Miften, M.; Mihailidis, D.; Kry, S.F.; Reft, C.; Esquivel, C.; Farr, J.; Followill, D.; Hurkmans, C.; Liu, A.; Gayou, O.; et al. Management of radiotherapy patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators: A report of the AAPM TG-203. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e757–e788. [Google Scholar]
- Dhivya, S.; Anuradha, C.; Murali, V.; Ramasubramanian, V. In-vivo dosimetry in total skin electron therapy: Literature review. J. Radiother. Pract. 2021, 20, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cortes, J.; Rivera-Montalvo, T.; Navarro, L.V.; Flores-López, O.; Roman, J.; Hernandez-Oviedo, J.O. Thermoluminescent dosimetry in total body irradiation. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 71, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kron, T. Applications of thermoluminescence dosimetry in medicine. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1999, 85, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzi, M. Novel silicon devices for radiation therapy monitoring. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2016, 809, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Colussi, V.C.; Beddar, A.S.; Kinsella, T.J.; Sibata, C.H. In vivo dosimetry using a single diode for megavoltage photon beam radiotherapy: Implementation and response characterization. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2001, 2, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Leung, M.K. Monte Carlo simulation of MOSFET dosimeter for electron backscatter using the GEANT4 code. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, W.L.; Ung, N.M.; Tiong, A.H.; Rosenfeld, A.B.; Wong, J.H. Characterisation of a MOSFET-based detector for dose measurement under megavoltage electron beam radiotherapy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, M.; Kumaraswamy, L.; Bailey, D.W.; De Boer, S.; Malhotra, H.K.; Podgorsak, M.B. Using an EPID for patient-specific VMAT quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, S.J.; McNamara, A.L.; Deshpande, S.; Holloway, L.; Greer, P.B.; Kuncic, Z.; Vial, P. Characterization of a novel EPID designed for simultaneous imaging and dose verification in radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 091902. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Senan, R.M.; Hatab, M.R. Characteristics of an OSLD in the diagnostic energy range. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.Y.; Chun, M.; Han, J.H.; Cho, J.D.; Kim, J.I. Prediction of midline dose from entrance and exit dose using OSLD measurements for Total body irradiation. J. Radiat. Prot. Res. 2017, 42, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jursinic, P.A. Characterization of optically stimulated luminescent dosimeters, OSLDs, for clinical dosimetric measurements. Med. Phys. 2007, 34, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar]
- Brodin, N.P.; Mehta, K.J.; Basavatia, A.; Goddard, L.C.; Fox, J.L.; Feldman, S.M.; McEvoy, M.P.; Tomé, W.A. A skin dose prediction model based on in vivo dosimetry and ultrasound skin bridge measurements during intraoperative breast radiation therapy. Brachytherapy 2019, 18, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butson, M.J.; Peter, K.N.; Cheung, T.; Metcalfe, P. Radiochromic film for medical radiation dosimetry. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2003, 41, 61–120. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keeffe, S.; McCarthy, D.; Woulfe, P.; Grattan, M.W.; Hounsell, A.R.; Sporea, D.; Mihai, L.; Vata, I.; Leen, G.A.; Lewis, E. A review of recent advances in optical fibre sensors for in vivo dosimetry during radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20140702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.; Yaosheng, H.; Yu, M.; Wenhui, Z.; Weimin, S.; Daxin, Z.; Ziyin, C.; Elfed, L. Embedded structure fiber-optic radiation dosimeter for radiotherapy applications. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 5172–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijnheer, B.; Olaciregui-Ruiz, I.; Rozendaal, R.; Sonke, J.J.; Spreeuw, H.; Tielenburg, R.; Van Herk, M.; Vijlbrief, R.; Mans, A. 3D EPID-based in vivo dosimetry for IMRT and VMAT. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 444, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.Y.; Deng, X.W.; Huang, S.M.; Shiu, A.; Lerch, M.; Metcalfe, P.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kron, T. Real-time in vivo dosimetry with MOSFET detectors in serial tomotherapy for head and neck cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, B.M.; McCowan, P.M. In vivo dosimetry for lung radiotherapy including SBRT. Phys. Med. 2017, 44, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Ghirelli, A.; Pini, S.; Alpi, P.; Barca, R.; Fondelli, S.; Leonulli, B.G.; Paoletti, L.; Rossi, F.; Bastiani, P.; et al. Clinical implementation of 3D in vivo dosimetry for abdominal and pelvic stereotactic treatments. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 154, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, S.C.; Wilks, R.; Kairn, T.; Crowe, S.B. Measuring dose from radiotherapy treatments in the vicinity of a cardiac pacemaker. Phys. Med. 2016, 32, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, G.; Schwegler, N. Low-dose testicular irradiation in seminoma patients. In-vivo dosimetry: In-vivo-dosimetrie. Strahlenther. Onkol. 1999, 175, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, N.; Nedaie, H.A.; Esmati, E.; Nosrati, H.; Jamali, M. Dose measurement outside of radiotherapy treatment field (Peripheral dose) using thermoluminesent dosimeters. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 12, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Carnicer, A.; Letellier, V.; Rucka, G.; Angellier, G.; Sauerwein, W.; Hérault, J. An indirect in vivo dosimetry system for ocular proton therapy. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 161, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Wolanski, M.; Zhao, Q.; Fanelli, L.; Gautam, A.; Pack, D.; Das, I.J. Dosimetric characteristics of a single use MOSFET dosimeter for in vivo dosimetry in proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 4266–4273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.P.; Warry, A.J.; Eaton, D.J.; Collis, C.H.; Rosenberg, I. In vivo dosimetry for total body irradiation: Five-year results and technique comparison. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2014, 15, 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, G.P.; Johansen, J.G.; Smith, R.L.; Beaulieu, L.; Beddar, S.; Kertzscher, G.; Verhaegen, F.; Tanderup, K. In vivo dosimetry in brachytherapy: Requirements and future directions for research, development, and clinical practice. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakody, M.; Jeyasugiththan, J.; Rajasooriyar, C.; Chougule, A. Dosimetry procedure to verify dose in High Dose Rate (HDR) brachytherapy treatment of cancer patients: A systematic review. Phys. Med. 2022, 96, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stathopoulos, I.; Ploussi, A.; Syrgiamiotis, V.; Makri, T.; Hatzigiorgi, C.; Carinou, E.; Sakellaropoulos, G.; Panayiotakis, G.S.; Efstathopoulos, E.P. In vivo dosimetry for head CT examinations in paediatric patients. Phys. Med. 2016, 32, 205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, C.C.; Dias, H.B.; Alves, M.D.; Duarte, L.O.; Dias, T.M.; Dalenogare, M.O.; Viegas, C.C.; Elnecave, R.H. In vivo dosimetry of thyroid doses from different irradiated sites in children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, C.E.; Ebert, M.A.; Joseph, D.J. Feasible measurement errors when undertaking in vivo dosimetry during external beam radiotherapy of the breast. Med. Dosim. 2003, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Noel, A.; Aletti, P.; Bey, P.; Malissard, L. Detection of errors in individual patients in radiotherapy by systematic in vivo dosimetry. Radiother. Oncol. 1995, 34, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mans, A.; Wendling, M.; McDermott, L.N.; Sonke, J.J.; Tielenburg, R.; Vijlbrief, R.; Mijnheer, B.; Van Herk, M.; Stroom, J.C. Catching errors with in vivo EPID dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 2638–2644. [Google Scholar]
- Ketabi, A.; Karbasi, S.; Faghihi, R.; Mosleh-Shirazi, M.A. A phantom-based experimental and Monte Carlo study of the suitability of in-vivo diodes and TLD for entrance in-vivo dosimetry in small-to-medium sized 6 MV photon fields. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 201, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Parsai, E.I.; McNeeley, S.W.; Ayyangar, K.M. Quantitative assessment of beam perturbations caused by silicon diodes used for in vivo dosimetry. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 36, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, T.H.; Hanson, W.F.; Johnston, D.A. Uncertainty analysis of absorbed dose calculations from thermoluminescence dosimeters. Med. Phys. 1992, 19, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.J.; Ackerly, T.; He, C.; Patterson, W.; Powell, C.E.; Qiao, G.; Solomon, D.H.; Meder, R.; Geso, M. Small field size dose-profile measurements using gel dosimeters, gafchromic films and micro-thermoluminescent dosimeters. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.D.; Gamboa-deBuen, I.; Avila, O.; Brandan, M.E. Dosimetry in a mammography phantom using TLD-300 dosimeters. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4287–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Park, B.; Kim, Y.; Park, B.; Park, S.H. Compact and Real-Time Radiation Dosimeter Using Silicon Photomultipliers for In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiation Therapy. Sensors 2025, 25, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh-Shirazi, M.A.; Ketabi, A.; Karbasi, S.; Faghihi, R. A Monte Carlo and experimental investigation of the dosimetric behavior of low- and medium-perturbation diodes used for entrance in vivo dosimetry in megavoltage photon beams. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2012, 13, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, E.; Nevens, D.; Weytjens, R.; Mokaddem, A.T.; Verellen, D. Assessing the impact of adaptations to the clinical workflow in radiotherapy using transit in vivo dosimetry. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 25, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.P.; Han-Oh, S.; Moore, J.; Huang, E.; McNutt, T.R.; Souranis, A.N.; Briner, V.; Halthore, A.; Alcorn, S.R.; Meyer, J.J.; et al. Selective de-implementation of routine in vivo dosimetry. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, M.D.; Giancaterino, S.; De Nicola, A.; Adorante, N.; De Lorenzo, R.G.; Di Tommaso, M.; Vinciguerra, A.; Trignani, M.; Perrotti, F.; Allajbej, A.; et al. A feasibility study for in vivo dosimetry procedure in routine clinical practice. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818779201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kry, S.F.; Alvarez, P.; Cygler, J.E.; DeWerd, L.A.; Howell, R.M.; Meeks, S.; O’Daniel, J.; Reft, C.; Sawakuchi, G.; Yukihara, E.G.; et al. AAPM TG 191: Clinical use of luminescent dosimeters: TLDs and OSLDs. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, e19–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Grigorov, G.N.; Barnett, R.B. Study on surface dose generated in prostate intensity-modulated radiation therapy treatment. Med. Dosim. 2006, 31, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Istisan Report 23/5. Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/6682486/23-5+web.pdf/05ce834b-d81a-9530-e156-45456b3b1406?t=1685451301943 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Bossuyt, E.; Weytjens, R.; Nevens, D.; De Vos, S.; Verellen, D. Evaluation of automated pre-treatment and transit in-vivo dosimetry in radiotherapy using empirically determined parameters. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 16, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C. Artificial intelligence in radiotherapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C. Artificial intelligence in radiotherapy and patient care. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.C. Quantum Computing and Machine Learning in Medical Decision-Making: A Comprehensive Review. Algorithms 2025, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Kong, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, M.; Huang, S.; Yan, H.; Xu, X. Preliminary application of EPID three-dimensional dose reconstruction in in vivo dose verification of breast cancer intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Phys. Med. 2025, 129, 104884. [Google Scholar]
- Negrete-Hernandez, I.M.; Lozano, I.B.; Roman-Lopez, J.; Guzman-Castañeda, J.I. Implementation of OSL nanoDot dosimetry in different treatment techniques for head and neck cancer. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2025, 201, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, B.N.; Van Dung, P.; Tinh, H.T.; Ha, N.T.; Duc, N.M. Photon energy estimation in diagnostic radiology using OSL dosimeters: Experimental validation and Monte Carlo simulations. Radiat. Meas. 2025, 180, 107342. [Google Scholar]
- de Andrade, E.M.; Paixão, L.; Mendes, B.M.; Fonseca, T.C. Monte Carlo modeling and simulation of a new 3D printed phantom for WBC calibration with ballistic gel as a tissue substitute. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2025, 215, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Owrangi, A.M. Mucosal dosimetry on unflattened photon beams: A Monte Carlo phantom study. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 5, 015007. [Google Scholar]
- Spina, A.; Chow, J.C. Dosimetric impact on the flattening filter and addition of gold nanoparticles in radiotherapy: A Monte Carlo study on depth dose using the 6 and 10 MV FFF photon beams. Materials 2022, 15, 7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Sahare, P.D. Dosimetry characteristics of NaLi2PO4: Tb3+ OSLD phosphor. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 330, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.M.; DeLoid, G.M.; Demokritou, P. A critical review of in vitro dosimetry for engineered nanomaterials. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 3015–3032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Gao, J.; Hei, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H. A highly sensitive γ-radiation dosimeter based on the CeO2 nanowires. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2009, 41, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.Q. CeO2 nanowires aqueous γ-radiation dosimeter for low dose sensitively detecting. Procedia Eng. 2013, 52, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikh, A.; Beuve, M.; Balosso, J. Nanotechnology in radiation oncology: The need for implantable nano dosimeters for in-vivo real time measurements. Int. J. Cancer Ther. Oncol. 2015, 3, 3217. [Google Scholar]
- Lim-Reinders, S.; Keller, B.M.; Al-Ward, S.; Sahgal, A.; Kim, A. Online adaptive radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, F.; Bradley, D.A.; Tarif, Z.H.; Khodaei, A.; Basaif, A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Abdul-Rashid, H.A. Time-resolved optical fiber measurements: A review of scintillator materials and applications. Radiat. Detect. Technol. Methods 2025, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ruda, H.E. Flash radiotherapy: Innovative cancer treatment. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 808–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ruda, H.E. Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Ruda, H.E.; Chow, J.C. FLASH radiotherapy and the use of radiation dosimeters. Cancers 2023, 15, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ruda, H.E. Impact of Scattering Foil Composition on Electron Energy Distribution in a Clinical Linear Accelerator Modified for FLASH Radiotherapy: A Monte Carlo Study. Materials 2024, 17, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, M.; Eberlein, U. The relevance of dosimetry in precision medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Yi, L.; Hu, D.; Luo, Z.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Xing, B.; Wang, J.W.; Lee, C.N.; Zhang, R.; et al. A swallowable X-ray dosimeter for the real-time monitoring of radiotherapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanzo, M.; Pirrone, G.; Mileto, M.; Massarut, S.; Stancanello, J.; Baradaran-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Rink, A.; Barresi, L.; Vinante, L.; Piccoli, E.; et al. Prediction of skin dose in low-kV intraoperative radiotherapy using machine learning models trained on results of in vivo dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
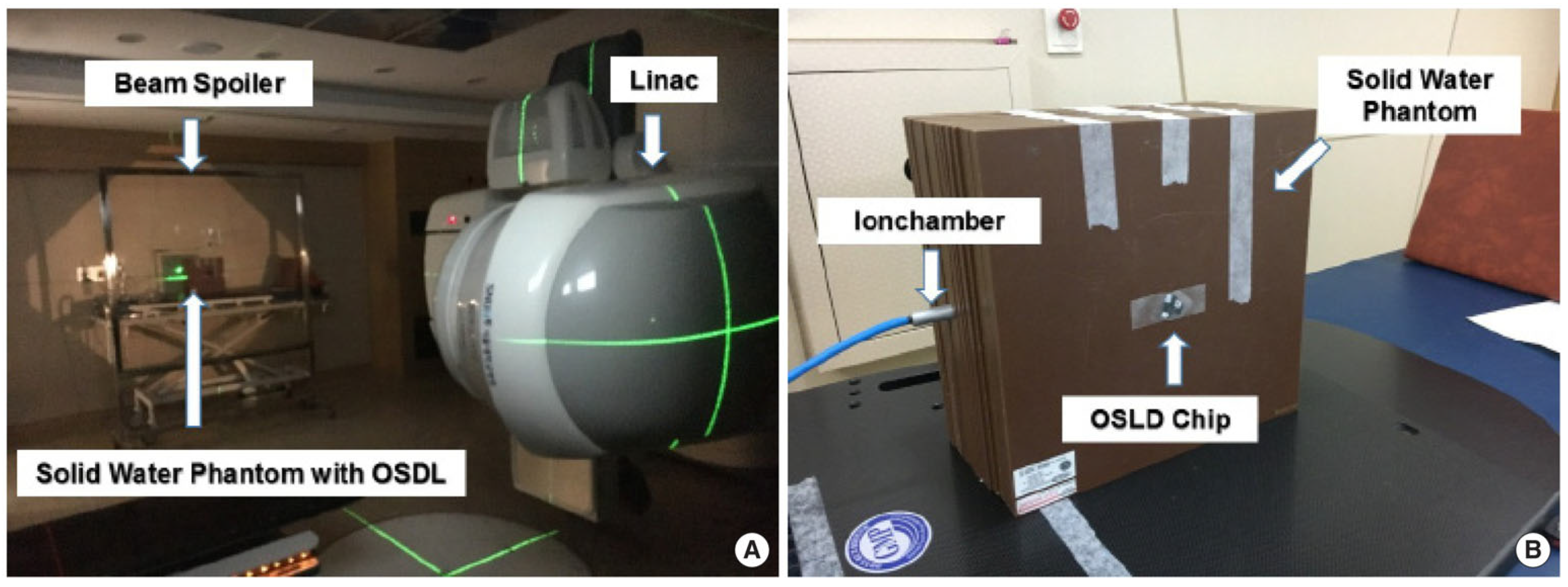

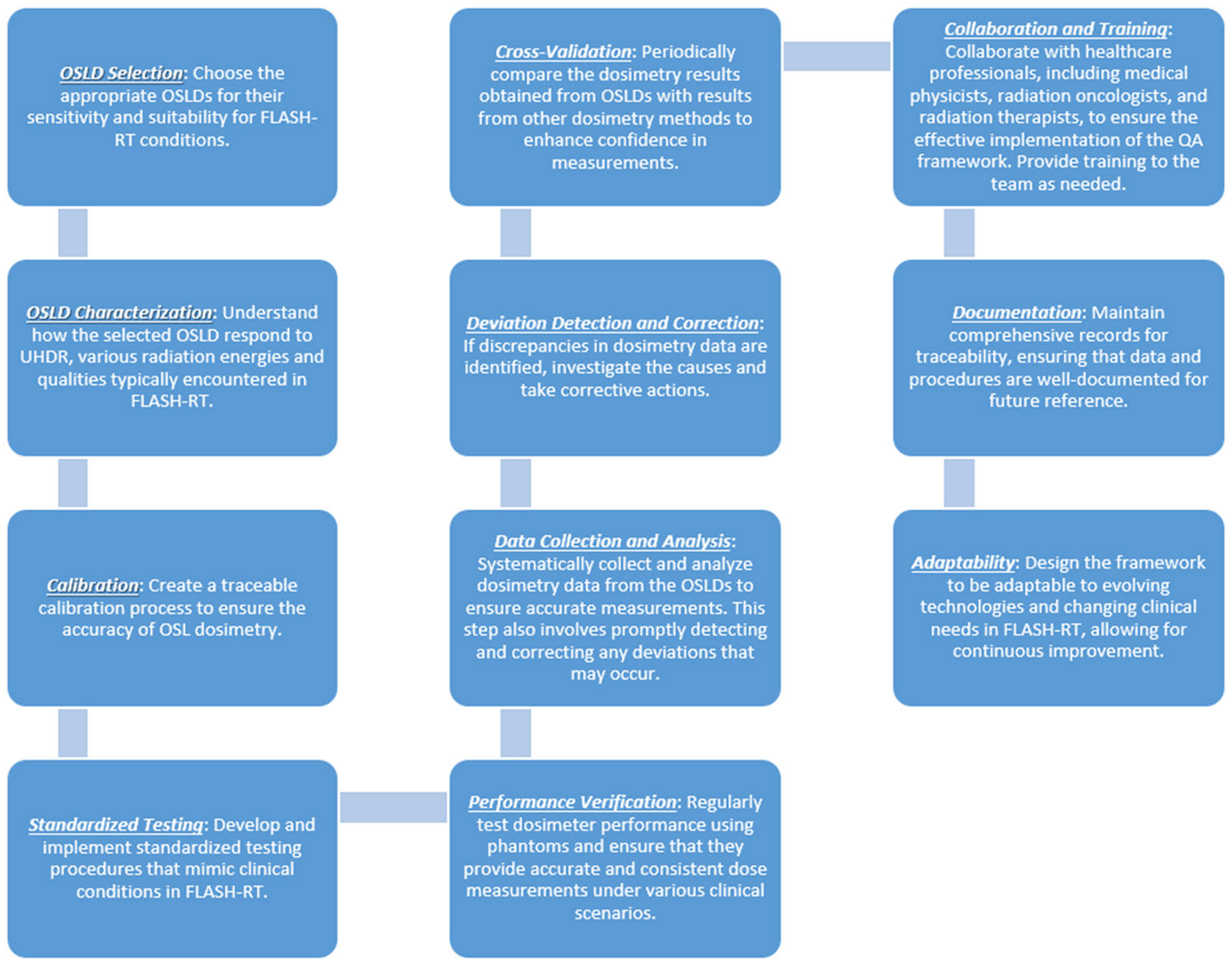
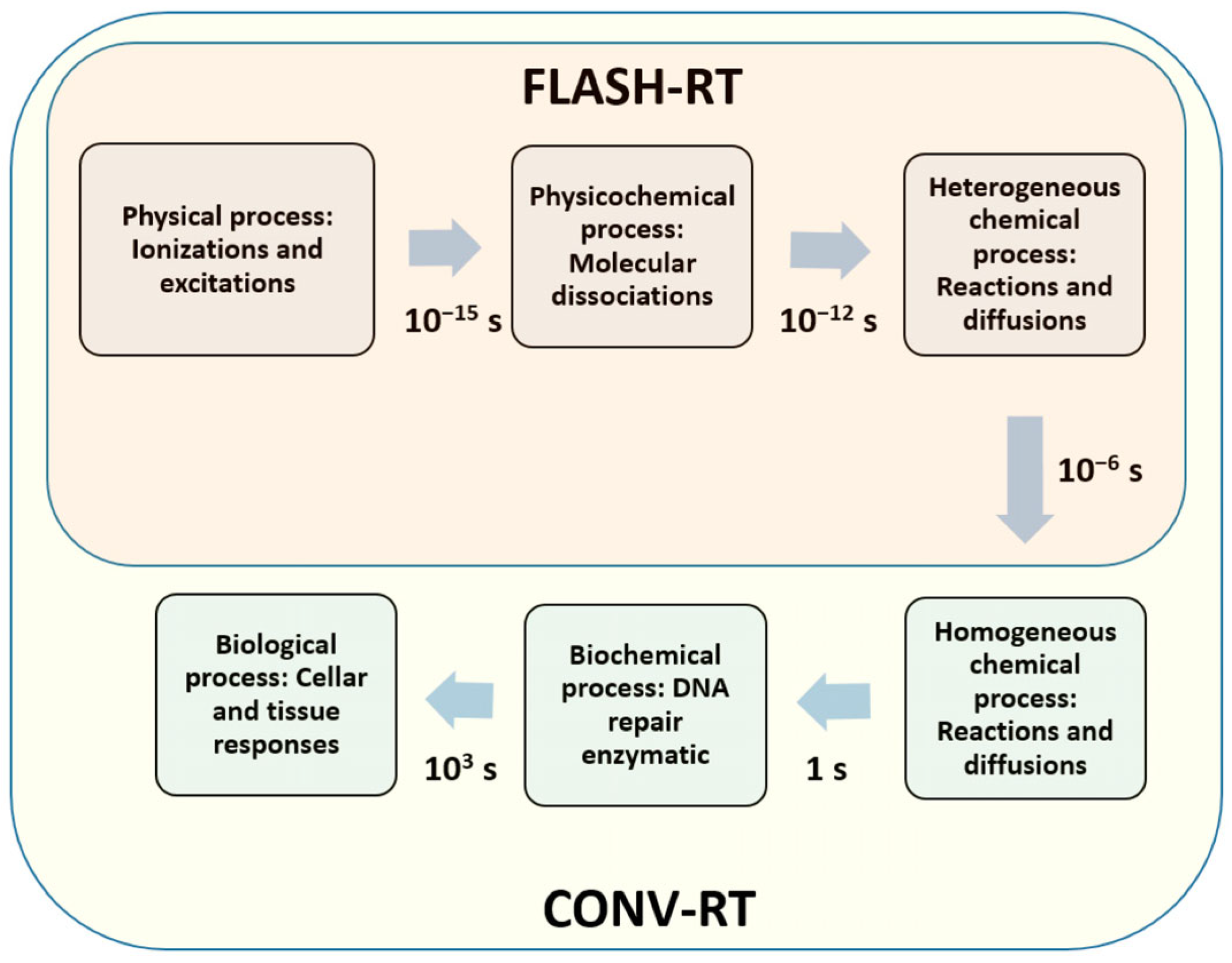
| Dosimeter Type | Characteristics | Applications | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoluminescent Dosimeters (TLDs) | Passive devices, measuring cumulative dose via light emitted during heating. | Point-dose verification, total-skin electron therapy, and TBI. | Compact size, reusability, high accuracy. | Requires specialized readout equipment, does not provide real-time feedback. | [37,38,39] |
| Diodes | Active semiconductor devices, providing real-time dose measurements. | Point-dose verification in IMRT. | Real-time data, high sensitivity. | Temperature and angular dependence. | [40,41] |
| MOSFETs | Active dosimeters, miniaturized and versatile. | Pediatric treatments, small-field dosimetry. | Small size, easy to use, real-time measurements. | Sensitive to cumulative radiation damage. | [42,43] |
| EPIDs | Originally designed for imaging, they have been adapted for dosimetry by analyzing exit-beam intensity profiles. | Dose distribution verification in VMAT. | Integrated imaging and dosimetry, seamless workflow. | Limited spatial resolution compared to other tools. | [44,45] |
| OSLDs | Measure dose via luminescence released upon light stimulation of radiation-sensitive material. | TBI monitoring, small-field radiotherapy, IORT. | High accuracy, reusability, excellent stability. | Requires specialized stimulation and readout equipment. | [46,47,48,49] |
| Radiochromic Films | Measure dose via color change proportional to radiation, analyzed using optical scanners. | Complex dose distributions, total-skin electron therapy. | High spatial resolution, ideal for complex measurements. | Single-use, requires careful handling. | [50] |
| Fiber-Optic Dosimeters | Real-time measurements using flexible fiber-optic sensors; they induce minimal perturbation of radiation field. | Challenging anatomical locations. | Resistant to electromagnetic interference, provide real-time data. | Specialized fabrication and calibration needed. | [51,52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, J.C.L.; Ruda, H.E. In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5010040
Chow JCL, Ruda HE. In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions. Encyclopedia. 2025; 5(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, James C. L., and Harry E. Ruda. 2025. "In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions" Encyclopedia 5, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5010040
APA StyleChow, J. C. L., & Ruda, H. E. (2025). In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions. Encyclopedia, 5(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5010040







