Flash Radiotherapy: Innovative Cancer Treatment
Definition
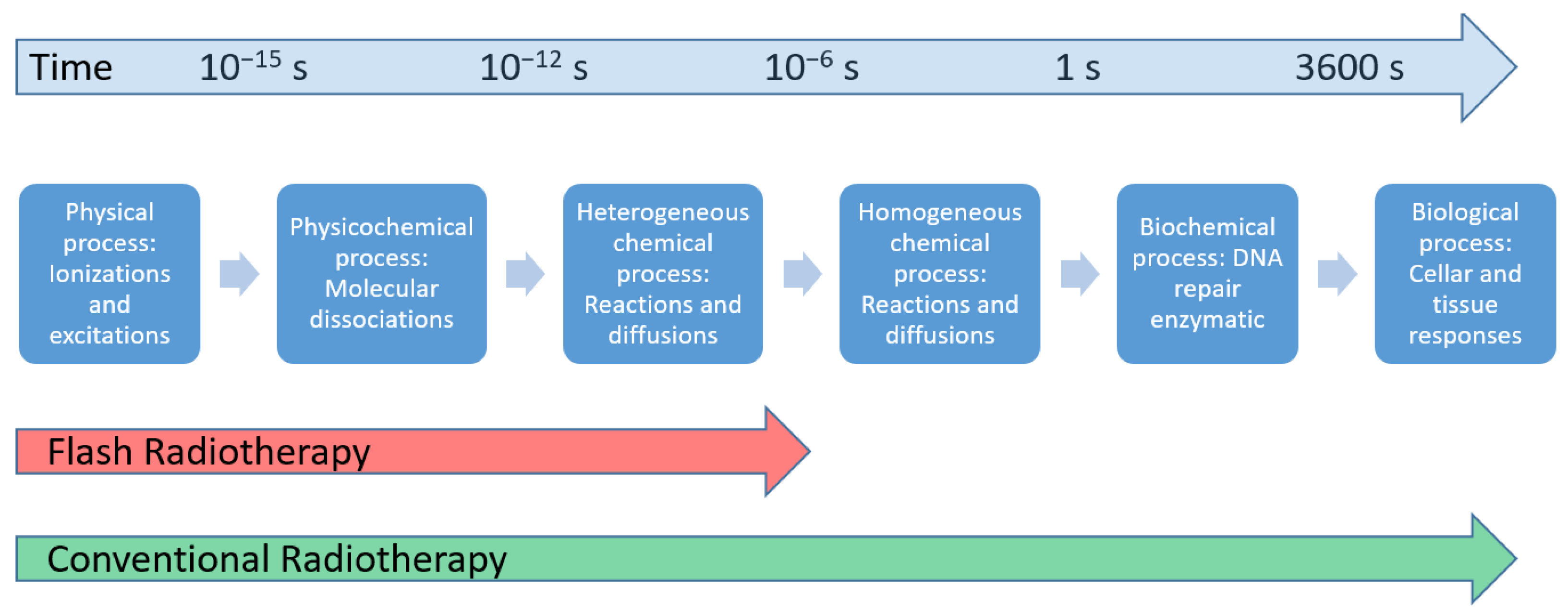
:1. Introduction
2. Background and History
3. Rationale and Mechanism
3.1. Oxygen Effect
3.2. ROS and Free Radicals
3.3. Immune and Inflammatory Response
4. Flash Radiation Beams and Dosimetry
4.1. Very High Energy Electron Beams
4.2. Photon Beams
4.3. Proton and Heavy-Ion Beams
5. Current Challenges and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandra, R.A.; Keane, F.K.; Voncken, F.E.; Thomas, C.R. Contemporary radiotherapy: Present and future. Lancet 2021, 398, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citrin, D.E. Recent developments in radiotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, M.E.; Folkes, L.K.; O’neill, P. Biological consequences of radiation-induced DNA damage: Relevance to radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groelly, F.J.; Fawkes, M.; Dagg, R.A.; Blackford, A.N.; Tarsounas, M. Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Rehman, S. An overview of cancer treatment modalities. Neoplasm 2018, 1, 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Barazzuol, L.; Coppes, R.P.; van Luijk, P. Prevention and treatment of radiotherapy-induced side effects. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.B.; Coleman, C.N.; Anscher, M.S.; McBride, W.H. Effects of radiation on normal tissue: Consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Kelsey, C.R.; Palta, M.; Cabrera, A.R.; Salama, J.K.; Patel, P.; Perez, B.A.; Lee, J.; Yin, F.F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy: A critical review for nonradiation oncologists. Cancer 2014, 120, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavassa, S.; Bessieres, I.; Edouard, M.; Mathot, M.; Moignier, A. Complexity metrics for IMRT and VMAT plans: A review of current literature and applications. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffurth, J. A review of the clinical evidence for intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 2, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.J.; Robinson, M.H. Radiotherapy: Technical aspects. Medicine 2016, 44, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.C.; Hendry, J.H.; Limoli, C.L. Biological benefits of UHDR FLASH radiotherapy: Sleeping beauty awoken. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszak, N.; Suchorska, W.M.; Milecki, P.; Kruszyna-Mochalska, M.; Misiarz, A.; Pracz, J.; Malicki, J. FLASH Radiotherapy: An emerging approach in radiation therapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2022, 27, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, A.; Vecoli, C.; Labate, L.; Panetta, D.; Andreassi, M.G.; Gizzi, L.A. FLASH UHDRs in radiotherapy: Preclinical and radiobiological evidence. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, L.G.; Bezak, E.; Peukert, D.D.; Wilson, P. Translational research in FLASH radiotherapy—From radiobiological mechanisms to in vivo results. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.A.; Moran, J.M.; Jaffray, D.A.; Buchsbaum, J.C. A roadmap to clinical trials for FLASH. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4099–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lan, T.; Feng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Ma, X.; Du, J.; Hou, G.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy: A promising new method for radiotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, G.; Dai, T.; Du, X. FLASH radiotherapy: History and future. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamperis, E.; Kodona, C.; Giannouzakos, V. A FLASH back to radiotherapy’s past and then fast forward to the future. J. Cancer Prev. Curr. Res. 2019, 10, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Huh, H.; Kim, S. History of radiation therapy technology. Prog. Med. Phys. 2020, 31, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, D.L.; Boag, J.W. Modification of the oxygen effect when bacteria are given large pulses of radiation. Nature 1959, 183, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Town, C.D. Effect of high dose rates on survival of mammalian cells. Nature 1967, 215, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.J.; Hall, E.J.; Forster, D.W.; Storr, T.H.; Goodman, M.J. Survival of mammalian cells exposed to x-rays at ultra-high dose-rates. Br. J. Radiol. 1969, 42, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsey, S.; Bewley, D.K. Hypoxia in mouse intestine induced by electron irradiation at high dose-rates. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1971, 19, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, S.B.; Bewley, D.K. Effects of dose-rate on the radiation response of rat skin. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1974, 26, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gerweck, L.E.; Cascio, E.; Yang, Q.; Huang, P.; Niemierko, A.; Bertolet, A.; Nesteruk, K.P.; McNamara, A.; Schuemann, J. Proton FLASH effects on mouse skin at different oxygen tensions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaudon, V.; Labarbe, R.; Limoli, C.L. Model studies of the role of oxygen in the FLASH effect. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hageman, E.; Che, P.P.; Dahele, M.; Slotman, B.J.; Sminia, P. Radiobiological Aspects of FLASH Radiotherapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaudon, V.; Caplier, L.; Monceau, V.; Pouzoulet, F.; Sayarath, M.; Fouillade, C.; Poupon, M.F.; Brito, I.; Hupé, P.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Ultrahigh dose-rate FLASH irradiation increases the differential response between normal and tumour tissue in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 245ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.C.; De Fornel, P.; Petersson, K.; Favaudon, V.; Jaccard, M.; Germond, J.F.; Petit, B.; Burki, M.; Ferrand, G.; Patin, D.; et al. The Advantage of FLASH Radiotherapy Confirmed in Mini-pig and Cat-cancer Patients the Advantage of Flash Radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourhis, J.; Sozzi, W.J.; Jorge, P.G.; Gaide, O.; Bailat, C.; Duclos, F.; Patin, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Germond, J.F.; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, R.; Johnstone, C.; Boucher, S.; Esarey, E.; Geddes, C.G.; Kravchenko, M.; Kutsaev, S.; Loo, B.W., Jr.; Méot, F.; Mustapha, B.; et al. Transformative Technology for FLASH Radiation Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhang, R.; Schueler, E.; Taylor, P.A.; Mascia, A.E.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Zhao, T.; Ayan, A.S.; Sharma, M.; Yu, S.J.; et al. Framework for Quality Assurance of UHDR Clinical Trials Investigating FLASH Effects and Current Technology Gaps. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.C.; Bourhis, J.; Durante, M. Towards clinical translation of FLASH radiotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinganelli, W.; Weber, U.; Puspitasari, A.; Simoniello, P.; Abdollahi, A.; Oppermann, J.; Schuy, C.; Horst, F.; Helm, A.; Fournier, C.; et al. FLASH with carbon ions: Tumour control, normal tissue sparing, and distal metastasis in a mouse osteosarcoma model. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlen, T.T.; Germond, J.F.; Bourhis, J.; Vozenin, M.C.; Ozsahin, E.M.; Bochud, F.; Bailat, C.; Moeckli, R. Normal Tissue Sparing by FLASH as a Function of Single-Fraction Dose: A Quantitative Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Sitarz, M.K.; Ankjærgaard, C.; Johansen, J.; Andersen, C.E.; Kanouta, E.; Overgaard, C.; Grau, C.; Poulsen, P. In vivo validation and tissue sparing factor for acute damage of pencil beam scanning proton FLASH. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 167, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Acharya, M.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Loo, B.W., Jr.; Vozenin, M.C.; Maxim, P.G. Ultra-high dose rate electron beams and the FLASH effect: From preclinical evidence to a new radiotherapy paradigm. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2082–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenderfer, E.S.; Sørensen, B.S.; Mazal, A.; Carlson, D.J. The current status of preclinical proton FLASH radiation and future directions. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, G.; Ruan, J.L.; Paillas, S.; Cooper, C.R.; Petersson, K. In vitro assays for investigating the FLASH effect. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2022, 24, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer Bley, C.; Wolf, F.; Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Grilj, V.; Petridis, I.; Petit, B.; Böhlen, T.T.; Moeckli, R.; Limoli, C.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Dose-and volume-limiting late toxicity of FLASH radiotherapy in cats with squamous cell carcinoma of the nasal planum and in mini pigs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3814–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Hill, M. Faster and safer? FLASH UHDR in radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170628. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, S.; Owen, H.; Schippers, M.; Welsch, C. Technical challenges for FLASH proton therapy. Phys. Med. 2020, 78, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, J.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Jorge, P.G.; Bailat, C.; Petit, B.; Ollivier, J.; Jeanneret-Sozzi, W.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Moeckli, R.; et al. Clinical translation of FLASH radiotherapy: Why and how? Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Petersson, K.; Alikhani, L.; Yakkala, C.; Allen, B.D.; Ollivier, J.; Petit, B.; Jorge, P.G.; Syage, A.R.; et al. Long-term neurocognitive benefits of FLASH radiotherapy driven by reduced reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10943–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abolfath, R.; Grosshans, D.; Mohan, R. Oxygen depletion in FLASH ultra-high-dose-rate radiotherapy: A molecular dynamics simulation. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 6551–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, R.; Esipova, T.V.; Allu, S.R.; Ashraf, R.; Rahman, M.; Gunn, J.R.; Bruza, P.; Gladstone, D.J.; Williams, B.B.; et al. Quantification of oxygen depletion during FLASH irradiation in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perstin, A.; Poirier, Y.; Sawant, A.; Tambasco, M. Quantifying the DNA-damaging effects of FLASH irradiation with plasmid DNA. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, H.; Mein, S.; Dokic, I.; Haberer, T.; Debus, J.; Abdollahi, A.; Mairani, A. Deciphering time-dependent DNA damage complexity, repair, and oxygen tension: A mechanistic model for FLASH-dose-rate radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinganelli, W.; Sokol, O.; Quartieri, M.; Puspitasari, A.; Dokic, I.; Abdollahi, A.; Durante, M.; Haberer, T.; Debus, J.; Boscolo, D.; et al. UHDR (FLASH) carbon ion irradiation: Dosimetry and first cell experiments. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, G.; Konradsson, E.; Lempart, M.; Bäck, S.; Ceberg, C.; Petersson, K. The FLASH effect depends on oxygen concentration. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 92, 20190702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzer, R.; Poppinga, D.; Weidner, J.; Schüller, A.; Hackel, T.; Looe, H.K.; Poppe, B. Ion collection efficiency of ionization chambers in ultra-high dose-per-pulse electron beams. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.; Knoll, J.; Beyreuther, E.; Pawelke, J.; Skuza, R.; Hanley, R.; Brons, S.; Pagliari, F.; Seco, J. Does FLASH deplete oxygen? Experimental evaluation for photons, protons, and carbon ions. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, D.; Scifoni, E.; Durante, M.; Krämer, M.; Fuss, M.C. May oxygen depletion explain the FLASH effect? A chemical track structure analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 162, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarbe, R.; Hotoiu, L.; Barbier, J.; Favaudon, V. A physicochemical model of reaction kinetics supports peroxyl radical recombination as the main determinant of the FLASH effect. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 153, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G. Mechanisms underlying FLASH radiotherapy, a novel way to enlarge the differential responses to ionizing radiation between normal and tumour tissues. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2020, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyreuther, E.; Brand, M.; Hans, S.; Hideghéty, K.; Karsch, L.; Leßmann, E.; Schürer, M.; Szabó, E.R.; Pawelke, J. Feasibility of proton FLASH effect tested by zebrafish embryo irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, D.R.; Buettner, G.R.; Petronek, M.S.; St-Aubin, J.J.; Flynn, R.T.; Waldron, T.J.; Limoli, C.L. An integrated physico-chemical approach for explaining the differential impact of FLASH versus conventional dose rate irradiation on cancer and normal tissue responses. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xie, D.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Gao, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Xiao, D.; Wu, D.; et al. Radioprotective effect of X-ray abdominal FLASH irradiation: Adaptation to oxidative damage and inflammatory response may be benefiting factors. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4812–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velalopoulou, A.; Karagounis, I.V.; Cramer, G.M.; Kim, M.M.; Skoufos, G.; Goia, D.; Hagan, S.; Verginadis, I.I.; Shoniyozov, K.; Chiango, J.; et al. FLASH proton radiotherapy spares normal epithelial and mesenchymal tissues while preserving sarcoma response. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4808–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.J.; Petersson, K.; Olcina, M.M. The importance of hypoxia in radiotherapy for the immune response, metastatic potential and FLASH-RT. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.Y.; Gu, A.; Wang, W.; Oleinick, N.L.; Machtay, M. UHDR effect on circulating immune cells: A potential mechanism for FLASH effect? Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 149, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.R.; Parsons, J.L. FLASH radiotherapy: Current knowledge and future insights using proton-beam therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Mossahebi, S.; Miller, A.R. FLASH Radiotherapy. In Principles and Practice of Particle Therapy; Malouf TD and Trifiletti DM: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Chapter 8; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arina, A.; Beckett, M.; Fernandez, C.; Zheng, W.; Pitroda, S.; Chmura, S.J.; Luke, J.J.; Forde, M.; Hou, Y.; Burnette, B.; et al. Tumour-reprogrammed resident T cells resist radiation to control tumours. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmgaard, R.B.; Schaer, D.A.; Li, Y.; Castaneda, S.P.; Murphy, M.Y.; Xu, X.; Inigo, I.; Dobkin, J.; Manro, J.R.; Iversen, P.W.; et al. Targeting the TGFβ pathway with galunisertib, a TGFβRI small molecule inhibitor, promotes anti-tumour immunity leading to durable, complete responses, as monotherapy and in combination with checkpoint blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tauriello, D.V.; Sancho, E.; Batlle, E. Overcoming TGFβ-mediated immune evasion in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernet, V.; Ponette, E.; Deniaud-Alexandre, J.; Ménissier De-Murcia, G.; De Murcia, N.; Giocanti, F.; Megnin-Chanet, V.; Favaudon, M. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, a major determinant of early cell response to ionizing radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2000, 76, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Rama, N.; Saha, T.; Shukla, S.; Goda, C.; Milewski, D.; Mascia, A.E.; Vatner, R.E.; Sengupta, D.; Katsis, A.; Abel, E.; et al. Improved tumour control through t-cell infiltration modulated by UHDR proton FLASH using a clinical pencil beam scanning proton system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, S164–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Perentesis, J.P.; Khuntia, D.; Pfister, S.X.; Sharma, R.A. Can rational combination of UHDR FLASH radiotherapy with immunotherapy provide a novel approach to cancer treatment? Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, L.A.; Casey, K.M.; Wang, J.; Blaney, A.; Manjappa, R.; Breitkreutz, D.; Skinner, L.; Dutt, S.; Ko, R.B.; Bush, K.; et al. FLASH irradiation results in reduced severe skin toxicity compared to conventional-dose-rate irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.; McCauley, S.; Vairamani, K.; Speth, J.; Girdhani, S.; Abel, E.; Sharma, R.A.; Perentesis, J.P.; Wells, S.I.; Mascia, A.; et al. FLASH proton pencil beam scanning irradiation minimizes radiation-induced leg contracture and skin toxicity in mice. Cancers 2021, 13, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, M.; Grilj, V.; Brenner, D.J. Biological effects in normal cells exposed to FLASH dose rate protons. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobinskaya, O.; Siebenwirth, C.; Greubel, C.; Hable, V.; Hertenberger, R.; Humble, N.; Reinhardt, S.; Michalski, D.; Röper, B.; Multhoff, G.; et al. The effects of UHDR proton irradiation on growth delay in the treatment of human tumour xenografts in nude mice. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedl, A.A.; Prise, K.M.; Butterworth, K.T.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Favaudon, V. Radiobiology of the FLASH effect. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Yamada, S.; Ando, K.; Furusawa, Y.; Kawata, T.; Majima, H.; Nakano, T.; Tsujii, H. Measurements of the equivalent whole-body dose during radiation therapy by cytogenetic methods. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.A.; Lartey, F.M.; Schüler, E.; Rafat, M.; King, G.; Kim, A.; Ko, R.; Semaan, S.; Gonzalez, S.; Jenkins, M.; et al. Reduced cognitive deficits after FLASH irradiation of whole mouse brain are associated with less hippocampal dendritic spine loss and neuroinflammation. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, K.; Adrian, G.; Butterworth, K.; McMahon, S.J. A quantitative analysis of the role of oxygen tension in FLASH radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghband, Y.; Cheeks, S.N.; Allen, B.D.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Doan, N.L.; Petit, B.; Jorge, P.G.; Giedzinski, E.; Acharya, M.M.; Vozenin, M.C.; et al. Neuroprotection of radiosensitive juvenile mice by UHDR FLASH irradiation. Cancers 2020, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froidevaux, P.; Grilj, V.; Bailat, C.; Geyer, W.R.; Bochud, F.; Vozenin, M.C. FLASH irradiation does not induce lipid peroxidation in lipids micelles and liposomes. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 205, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.R.; Jones, D.J.; Jones, G.D.; Petersson, K. Comet Assay Profiling of FLASH-Induced Damage: Mechanistic Insights into the Effects of FLASH Irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Quan, H. Treatment planning consideration for very high-energy electron FLASH radiotherapy. Phys. Med. 2023, 107, 102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuensch, W. The CHUV-CERN Facility for FLASH Treatment of Large, Deep-Seated Tumours: The DEFT (Deep Electron FLASH Therapy) Facility. In Proceedings of the FLASH Radiotherapy & Particle Therapy Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 1–3 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maxim, P.G.; Tantawi, S.G.; Loo, B.W. PHASER: A platform for clinical translation of FLASH cancer radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, J.; Li, E.; Davis, J.; Cameron, M.; Rosenfeld, A.; Lerch, M. High spatial resolution scintillator dosimetry of synchrotron microbeams. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annabell, N.; Yagi, N.; Umetani, K.; Wong, C.; Geso, M. Evaluating the peak-to-valley dose ratio of synchrotron microbeams using PRESAGE fluorescence. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Krishnan, S.; Mclaughlin, W.E.; Lukaniec, B.; Baker, J.T.; Ailawadi, S.; Hirsch, K.N.; Cattell, R.F.; Roy, R.; Helfer, J. Merging orthovoltage x-ray minibeams spare the proximal tissues while producing a solid beam at the target. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezado, Y.; Martínez-Rovira, I.; Thengumpallil, S.; Deman, P. Dosimetry protocol for the preclinical trials in white-beam minibeam radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 5012–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyama, A.; Kondoh, T.; Nariyama, N.; Umetani, K.; Fukumoto, M.; Shinohara, K.; Kohmura, E. A narrow microbeam is more effective for tumour growth suppression than a wide microbeam: An in vivo study using implanted human glioma cells. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2011, 18, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Button, T.M.; Le Duc, G.; Zhong, N.; Peña, L.A.; Smith, J.A.; Martinez, S.R.; Bacarian, T.; Tammam, J.; Ren, B.; et al. Response of rat intracranial 9L gliosarcoma to microbeam radiation therapy. Neuro-Oncology 2002, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackwitz, T.; Debus, J. Clinical applications of proton and carbon ion therapy. In Seminars in Oncology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 46, pp. 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Jongen, Y. Radiotherapy systems using proton and carbon beams. Bull. Et Mémoires De L’académie R. De Médecine De Belg. 2008, 163, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Schippers, J.M. Beam delivery systems for particle radiation therapy: Current status and recent developments. Rev. Accel. Sci. Technol. 2009, 2, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, A.A.; Schulte, R.; Faddegon, B.; Blakely, E.A.; Roach, M., III. Clinical trials involving carbon-ion radiation therapy and the path forward. Cancer 2018, 124, 4467–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akakura, K.; Tsujii, H.; Morita, S.; Tsuji, H.; Yagishita, T.; Isaka, S.; Ito, H.; Akaza, H.; Hata, M.; Fujime, M.; et al. Phase I/II clinical trials of carbon ion therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate 2004, 58, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Tsujii, H.; Blakely, E.A.; Debus, J.; De Neve, W.; Durante, M.; Jäkel, O.; Mayer, R.; Orecchia, R.; Pötter, R.; et al. Carbon ion radiotherapy in Japan: An assessment of 20 years of clinical experience. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e93–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Favaudon, V.; Lentz, J.M.; Heinrich, S.; Patriarca, A.; de Marzi, L.; Fouillade, C.; Dutreix, M. Time-resolved dosimetry of pulsed electron beams in very high dose-rate, FLASH irradiation for radiotherapy preclinical studies. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2019, 944, 162537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Trovati, S.; King, G.; Lartey, F.; Rafat, M.; Villegas, M.; Praxel, A.J.; Loo, B.W., Jr.; Maxim, P.G. Experimental platform for UHDR FLASH irradiation of small animals using a clinical linear accelerator. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazalova-Carter, M.; Liu, M.; Palma, B.; Dunning, M.; McCormick, D.; Hemsing, E.; Nelson, J.; Jobe, K.; Colby, E.; Koong, A.C.; et al. Comparison of film measurements and Monte Carlo simulations of dose delivered with very high-energy electron beams in a polystyrene phantom. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, J.C.; Fournier, P.; Bartzsch, S.; Donzelli, M.; Cornelius, I.; Stevenson, A.W.; Requardt, H.; Bräuer-Krisch, E. Energy spectra considerations for synchrotron radiotherapy trials on the ID17 bio-medical beamline at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2015, 22, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darafsheh, A.; Hao, Y.; Zwart, T.; Wagner, M.; Catanzano, D.; Williamson, J.F.; Knutson, N.; Sun, B.; Mutic, S.; Zhao, T. Feasibility of proton FLASH irradiation using a synchrocyclotron for preclinical studies. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 4348–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, F.; Bailat, C.; Jorge, P.G.; Lerch, M.L.; Darafsheh, A. Ultra-high dose rate dosimetry: Challenges and opportunities for FLASH radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4912–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.R.; Rahman, M.; Zhang, R.; Williams, B.B.; Gladstone, D.J.; Pogue, B.W.; Bruza, P. Dosimetry for FLASH radiotherapy: A review of tools and the role of radioluminescence and Cherenkov emission. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Leung, M.K. Monte Carlo simulation of MOSFET dosimeter for electron backscatter using the GEANT4 code. Med. Phys. 2008, 35 6 Pt 1, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esplen, N.; Mendonca, M.S.; Bazalova-Carter, M. Physics and biology of ultrahigh dose-rate (FLASH) radiotherapy: A topical review. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 23TR03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.; Subiel, A.; Lee, N.; Flynn, S.; Cotterill, J.; Shipley, D.; Romano, F.; Speth, J.; Lee, E.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Absolute dosimetry for FLASH proton pencil beam scanning radiotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsch, L.; Beyreuther, E.; Burris-Mog, T.; Kraft, S.; Richter, C.; Zeil, K. Dose rate dependence for different dosimeters and detectors: TLD, OSL, EBT films, and diamond detectors. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Shrestha, N.; Ahmad, S.; Schnell, E.; Akselrod, M.S.; Yukihara, E.G. Demonstration of 2D dosimetry using Al2O3 optically stimulated luminescence films for therapeutic megavoltage x-ray and ion beams. Radiat. Meas. 2017, 106, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Trigilio, A.; Franciosini, G.; Moeckli, R.; Zhang, R.; Böhlen, T.T. FLASH radiotherapy treatment planning and models for electron beams. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marlen, P.; Dahele, M.; Folkerts, M.; Abel, E.; Slotman, B.J.; Verbakel, W.F. Bringing FLASH to the clinic: Treatment planning considerations for ultrahigh dose-rate proton beams. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; No, H.J.; Breitkreutz, D.Y.; Mascia, A.E.; Moeckli, R.; Bourhis, J.; Schüler, E.; Maxim, P.G.; Loo, B.W., Jr. Technological basis for clinical trials in FLASH radiation therapy: A review. Appl. Rad. Oncol. 2021, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Conventional Radiotherapy | Flash Radiotherapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation type | X-ray, gamma-ray, electron, proton, heavy-ion | X-ray, electron, proton, heavy-ion |
| Dose rate (Gy/s) | 0.001–0.4 | >40 |
| Irradiation time (s) | >120 | <1 |
| Tumour control | Efficient | Efficient |
| Normal tissue complication | High | Low |
| Mechanism | Repair, re-oxygenation, redistribution, repopulation, oxygen depletion, ROS | Oxygen depletion, ROS, immunoinflammatory response |
| References | Mechanism | Radiation | System | Dose (Gy) | Dose Rate (Gy/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petersson et al., 2020 [78] | Oxygen effect | Electrons | In vitro and in vivo | 0–30 | 0–100 |
| Labarbe et al., 2020 [27] | ROS | Electrons or photons | In vitro | 10 | 10−3–107 |
| Liew et al., 2021 [49] | Mechanistic radiobiological model | Electrons and photons | In vitro and in vivo | 2–32 | 10−2–104 |
| Cao et al., 2021 [47] | Oxygen effect | Electrons | In vitro and in vivo | 0–30 | 0–300 |
| Boscolo et al., 2021 [54] | Oxygen effect | Electrons | In vitro | 0–150 | 109 |
| Jansen et al., 2021 [53] | Oxygen effect | Photons, protons, and carbon ions | In vitro | 10 | 0–340 |
| Tinganelli et al., 2022 [35] | Oxygen effect | Ions | In vitro | 0–7.5 | 0–70 |
| Alaghband et al., 2023 [79] | Inflammatory response | Electrons | In vitro | 30 | 5.6 × 106 |
| Zhang et al., 2023 [26] | Oxygen effect | Protons | In vitro | 25–30 | 130 |
| Froidevaux et al., 2023 [80] | ROS | Electrons | In vivo | 5 | 107 |
| Cooper et al., 2023 [81] | Oxygen effect | Electrons | In vivo | 20 | 2 × 103 |
| Source | Radiation Type | Energy (MeV) | Mean Dose Rate (Gy/s) | Instantaneous Dose Rate (Gy/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetron [97] | Electrons | 4.5 | 1000 | 2 × 107 |
| Varian 21 EX [98] | Electrons | 9 | 900 | 1.7 × 106 |
| NLCTA [99] | VHEEs | 120 | 90 | 9 × 1012 |
| ESRF [100] | X-rays | 0.102 | 37 | 18 × 103 |
| HyperScan [101] | Protons | 230 | 200 | 13 × 103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, J.C.L.; Ruda, H.E. Flash Radiotherapy: Innovative Cancer Treatment. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 808-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3030058
Chow JCL, Ruda HE. Flash Radiotherapy: Innovative Cancer Treatment. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(3):808-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, James C. L., and Harry E. Ruda. 2023. "Flash Radiotherapy: Innovative Cancer Treatment" Encyclopedia 3, no. 3: 808-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3030058
APA StyleChow, J. C. L., & Ruda, H. E. (2023). Flash Radiotherapy: Innovative Cancer Treatment. Encyclopedia, 3(3), 808-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3030058








