Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge
Definition
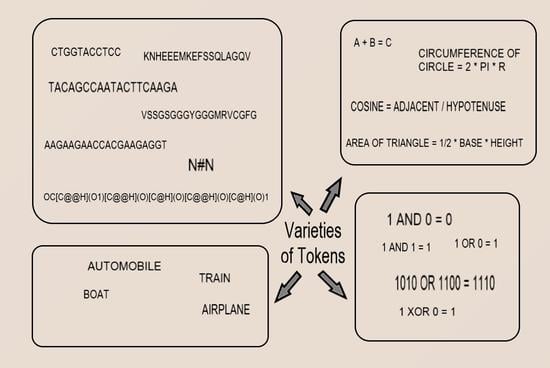
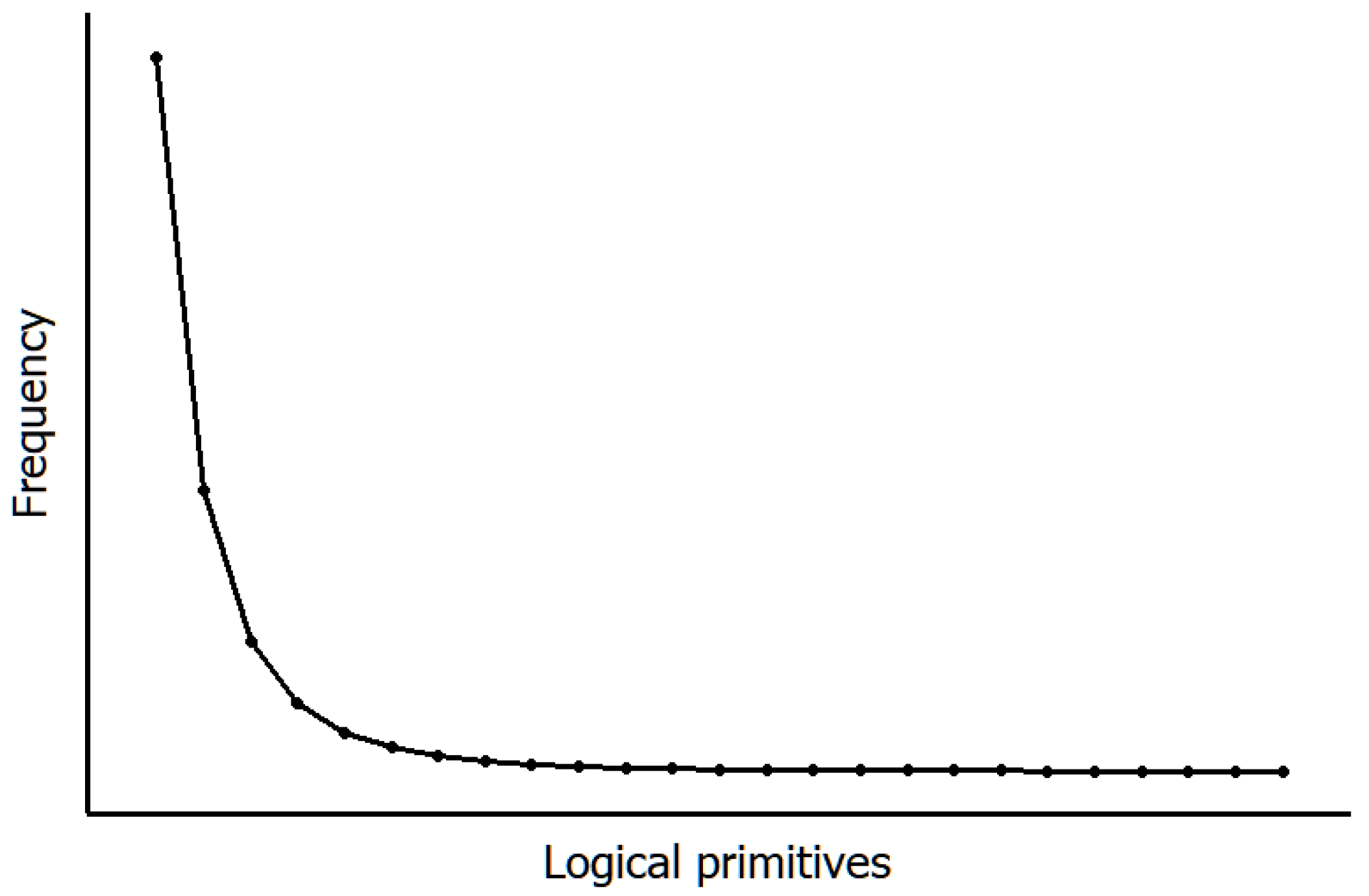
1. Tokens and Their Properties
2. Tokens as Elements of Nature
3. Tokens as Scientific Data
4. Tokens as Elements of Logic
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirth, N. Compiler Construction; Addison Wesley Longman Publishing, Co.: Harlow, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E. Connectionist learning procedures. Artif. Intell. 1989, 40, 185–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, H.; Jones, D. A Phonetic Dictionary of the English Language; Collins, B., Mees, I.M., Eds.; Daniel Jones: Selected Works; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Zand, J.; Roberts, S. Mixture Density Conditional Generative Adversarial Network Models (MD-CGAN). Signals 2021, 2, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, F.; Olivares, P.; Bugueño, M.; Molina, G.; Araya, M. On the Quality of Deep Representations for Kepler Light Curves Using Variational Auto-Encoders. Signals 2021, 2, 706–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Anwar, A.; Anwar, S.; Petersson, L.; Sharma, N.; Blumenstein, M. COVID-19 Detection from Radiographs: Is Deep Learning Able to Handle the Crisis? Signals 2022, 3, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, G.S.; Raven, J.E. The Presocratic Philosophers; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA. Available online: https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2016/entries/democritus; https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2016/entries/leucippus (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- Friedman, R. A Perspective on Information Optimality in a Neural Circuit and Other Biological Systems. Signals 2022, 3, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godel, K. Kurt Godel: Collected Works: Volume I: Publications 1929–1936; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Sci. Am. 1979, 241, 98–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models Are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. Available online: https://d4mucfpksywv.cloudfront.net/better-language-models/language_models_are_unsupervised_multitask_learners.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary; An Encyclopedia Britannica Company: Chicago, IL, USA. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/cognition (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Cambridge Dictionary; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK. Available online: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/cognition (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 138, 9–37. [Google Scholar]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bort, W.; Baskin, I.I.; Gimadiev, T.; Mukanov, A.; Nugmanov, R.; Sidorov, P.; Marcou, G.; Horvath, D.; Klimchuk, O.; Madzhidov, T.; et al. Discovery of novel chemical reactions by deep generative recurrent neural network. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, M.; Grazulis, S.; Girdzijauskaite, S.; Merkys, A.; Vaitkus, A. Using SMILES strings for the description of chemical connectivity in the Crystallography Open Database. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaller, P.; Hoover, B.; Reymond, J.L.; Strobelt, H.; Laino, T. Extraction of organic chemistry grammar from unsupervised learning of chemical reactions. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. A deep-learning system bridging molecule structure and biomedical text with comprehension comparable to human professionals. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R. A Hierarchy of Interactions between Pathogenic Virus and Vertebrate Host. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruz, N.; Schmidt, S.; Hocker, B. ProtGPT2 is a deep unsupervised language model for protein design. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.; Kardas, M.; Cucurull, G.; Scialom, T.; Hartshorn, A.; Saravia, E.; Poulton, A.; Kerkez, V.; Stojnic, R. Galactica: A Large Language Model for Science. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.09085. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, K.; Zídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Shmueli, Y.; et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic level protein structure with a language model. Science 2023, 379, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Ding, F.; Wang, R.; Shen, R.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Su, C.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Berger, B.; et al. High-resolution de novo structure prediction from primary sequence. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzi, A.; Balog, M.; Huang, A.; Hubert, T.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Barekatain, M.; Novikov, A.; Ruiz, F.J.R.; Schrittwieser, J.; Swirszcz, G.; et al. Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning. Nature 2022, 610, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, K.; Rajeswaran, A.; Lee, K.; Grover, A.; Laskin, M.; Abbeel, P.; Srinivas, A.; Mordatch, I. Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 15084–15097. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Waddell, W.W. The Parmenides of Plato; James Maclehose and Sons: Glasgow, UK, 1894. [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann, W. Public Opinion; Harcourt, Brace and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1922. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig, W. Grundzüge einer Theorie der Phylogenetischen Systematik; Deutscher Zentralverlag: Berlin, Germany, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig, W. Phylogenetic Systematics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1965, 10, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhat, W.; Hassan, A.; Korashy, H. Sentiment analysis algorithms and applications: A survey. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014, 5, 1093–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R. All Is Perception. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B. The Philosophy of Logical Atomism: Lectures 7–8. Monist 1919, 29, 345–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1937, s2–42, 230–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D.; et al. Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.07682. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokens in general | A token can be considered the elementary unit of a text document, speech, computer code, or another form of sequence information. |
| Tokens in Nature | In natural processes, a token can represent the elemental forms that matter are composed of, such as a chemical compound or the genetic material of a living organism. |
| Tokens as scientific data | In scientific data, a token can represent the smallest unit of information in a machine readable description of a chemical compound or a genetic sequence. |
| Tokens in math & logic | In the structured and precise languages of math and logic, a token can represent the elementary instructions that are read and processed, as in the case of an arithmetical expression, a keyword in a computer language, or a logical operator that connects logical statements. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friedman, R. Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 380-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010024
Friedman R. Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge. Encyclopedia. 2023; 3(1):380-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriedman, Robert. 2023. "Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge" Encyclopedia 3, no. 1: 380-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010024
APA StyleFriedman, R. (2023). Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge. Encyclopedia, 3(1), 380-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010024