Revisiting an Indentation Method for Measuring Low Wear Rates Using 3D Interferometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
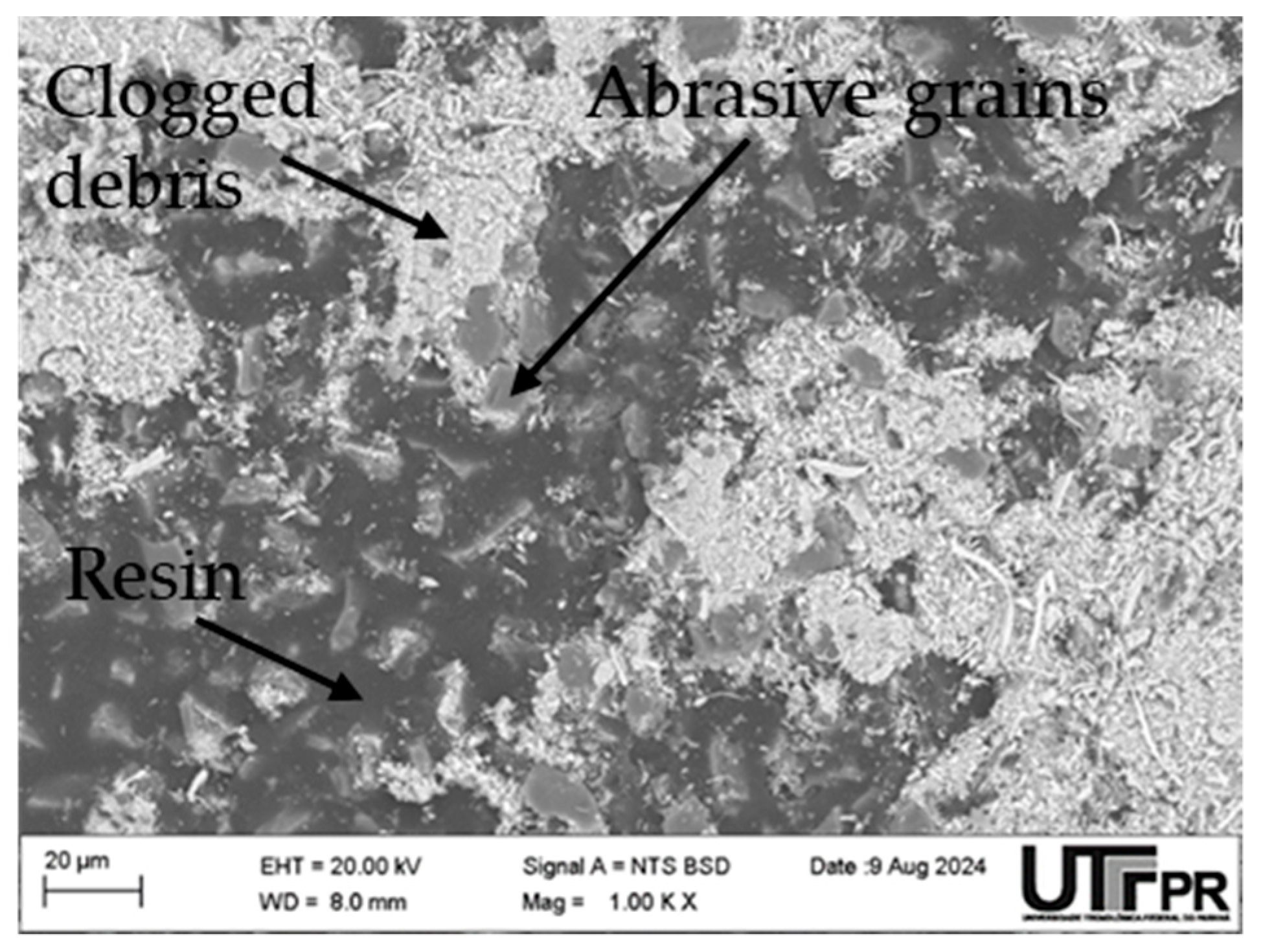
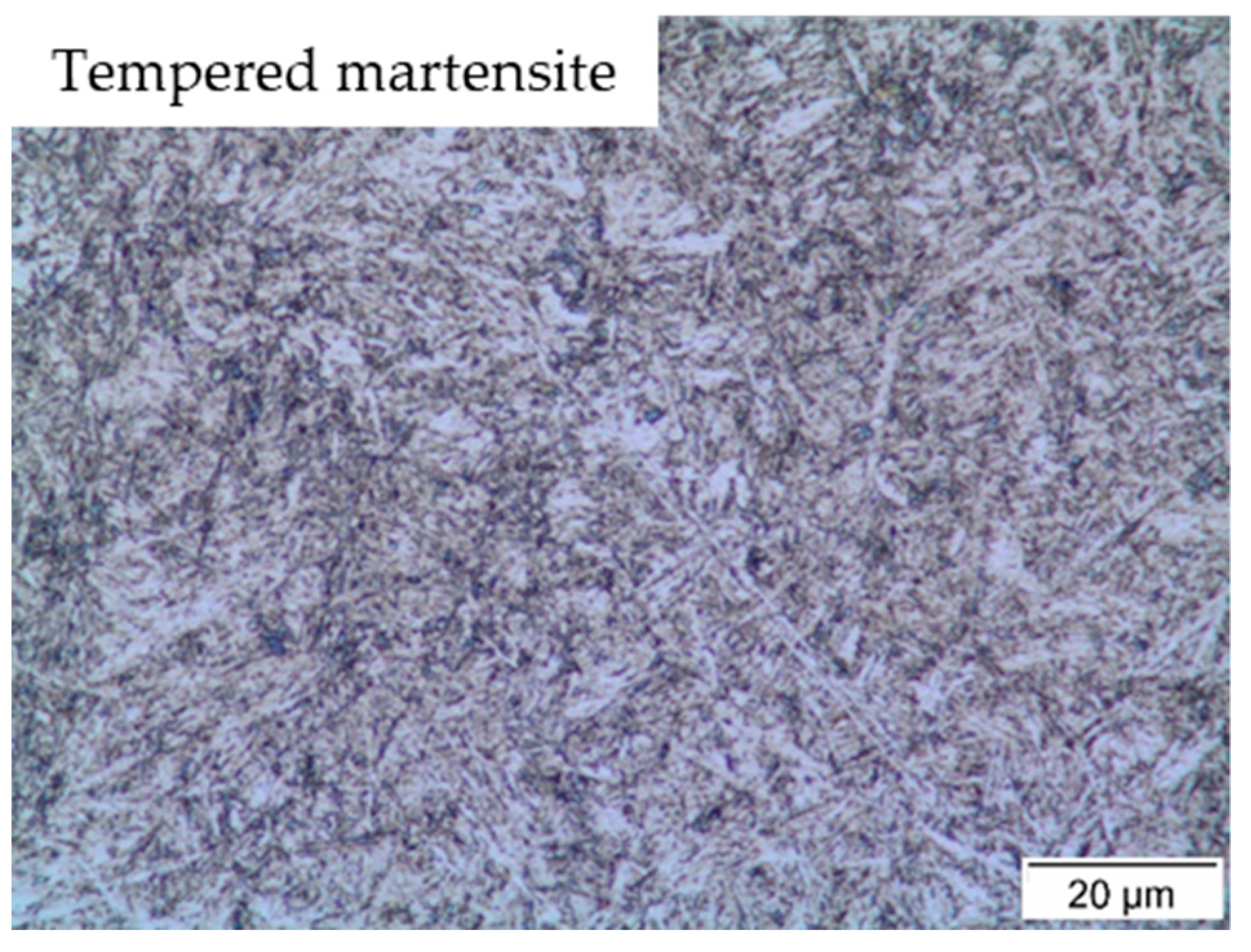
2.1. Steel Characterization
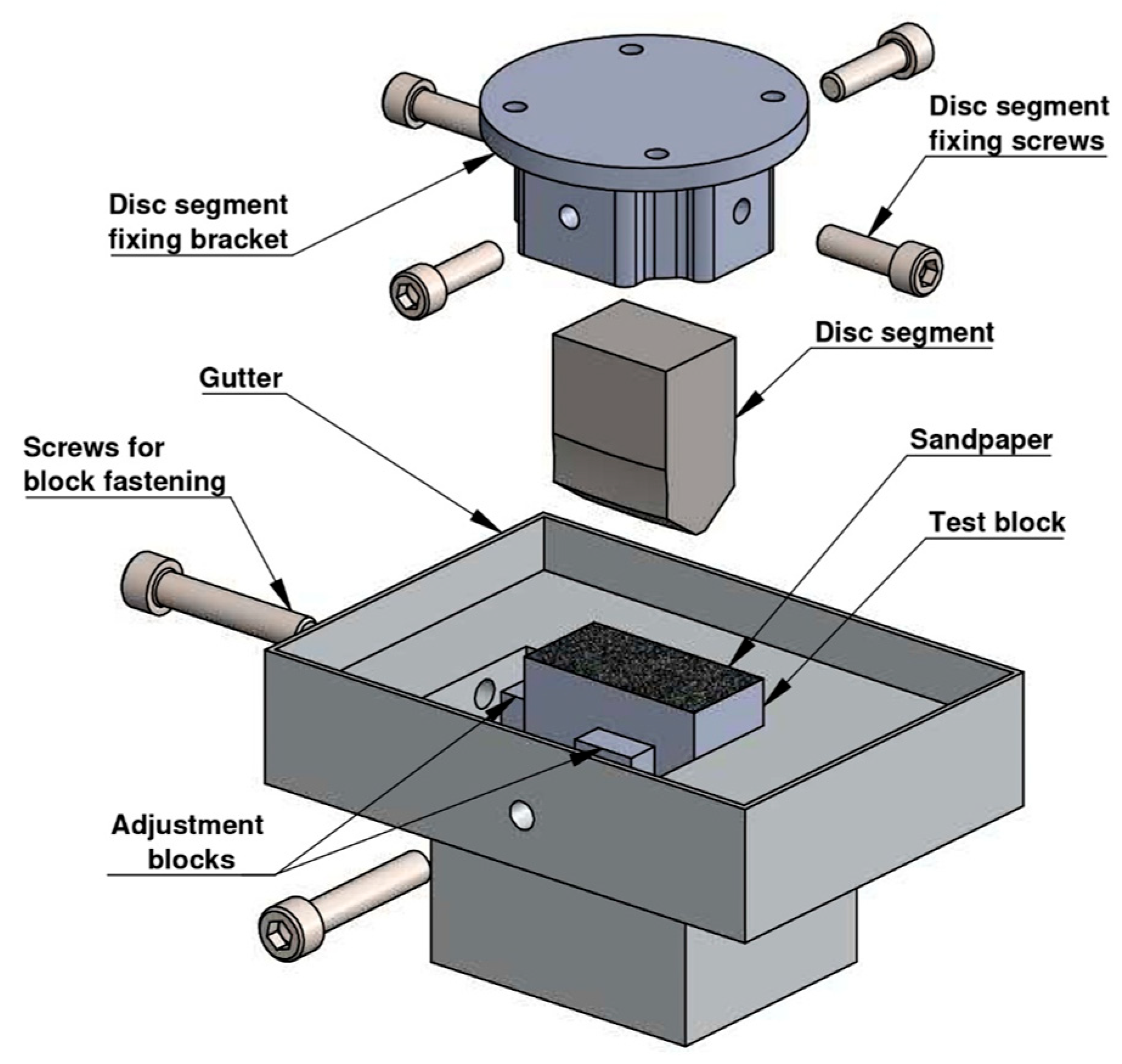
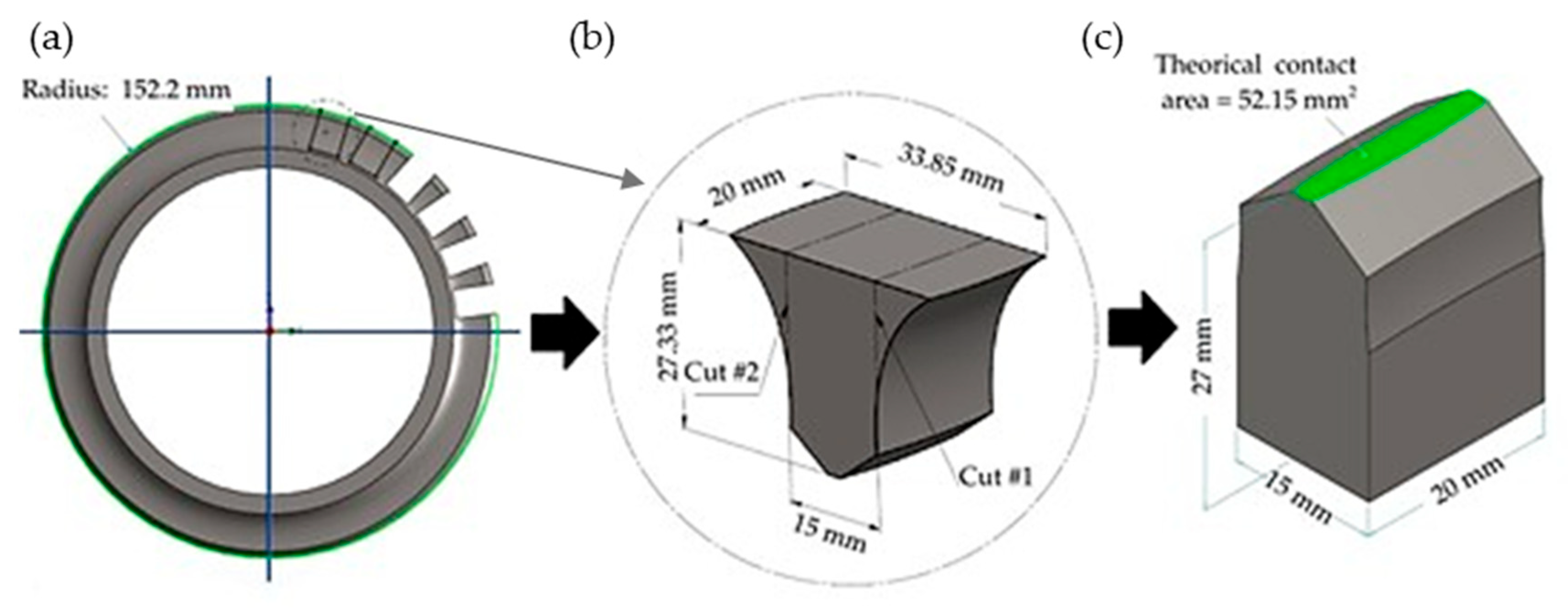
2.2. Test Rig and Specimen Preparation
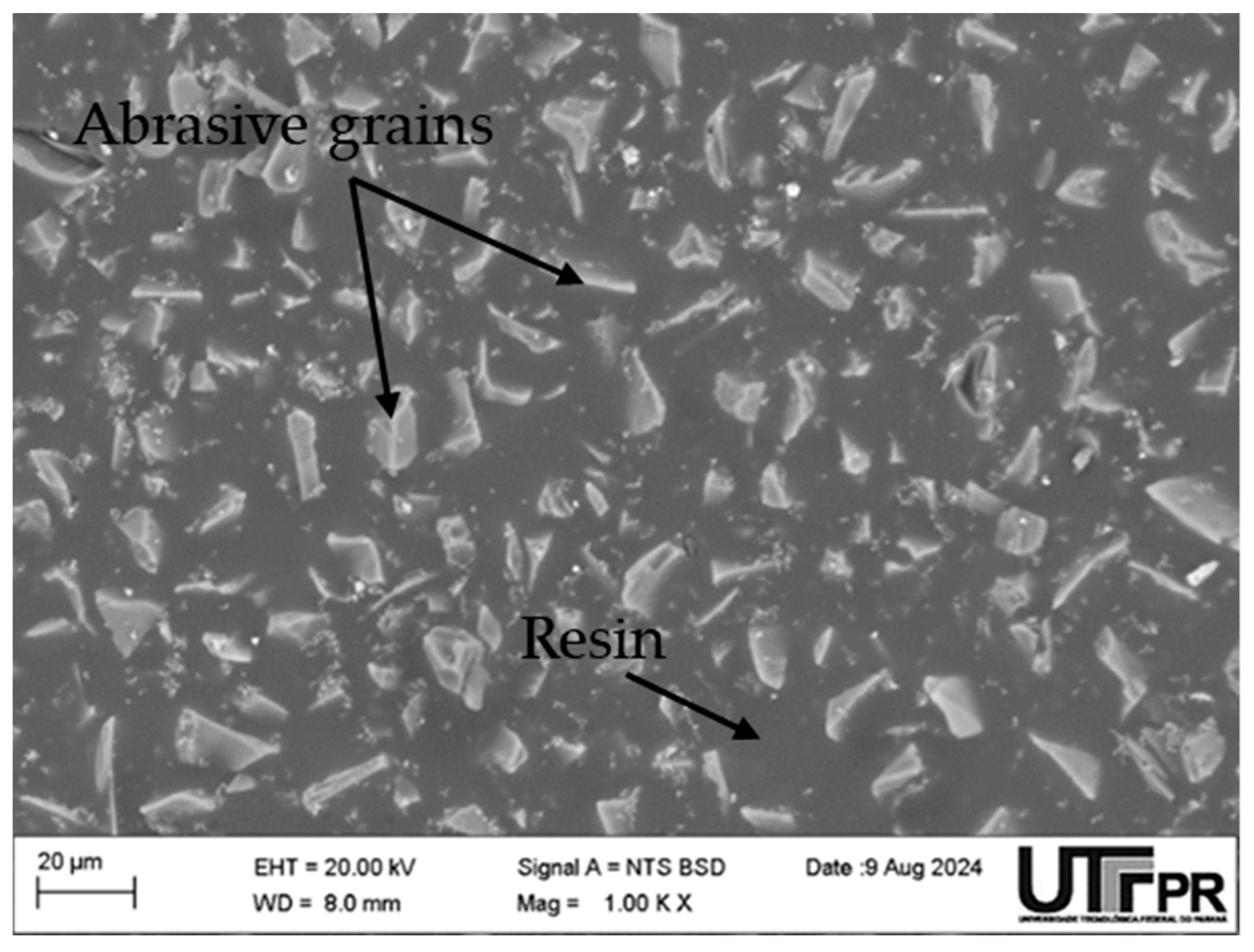
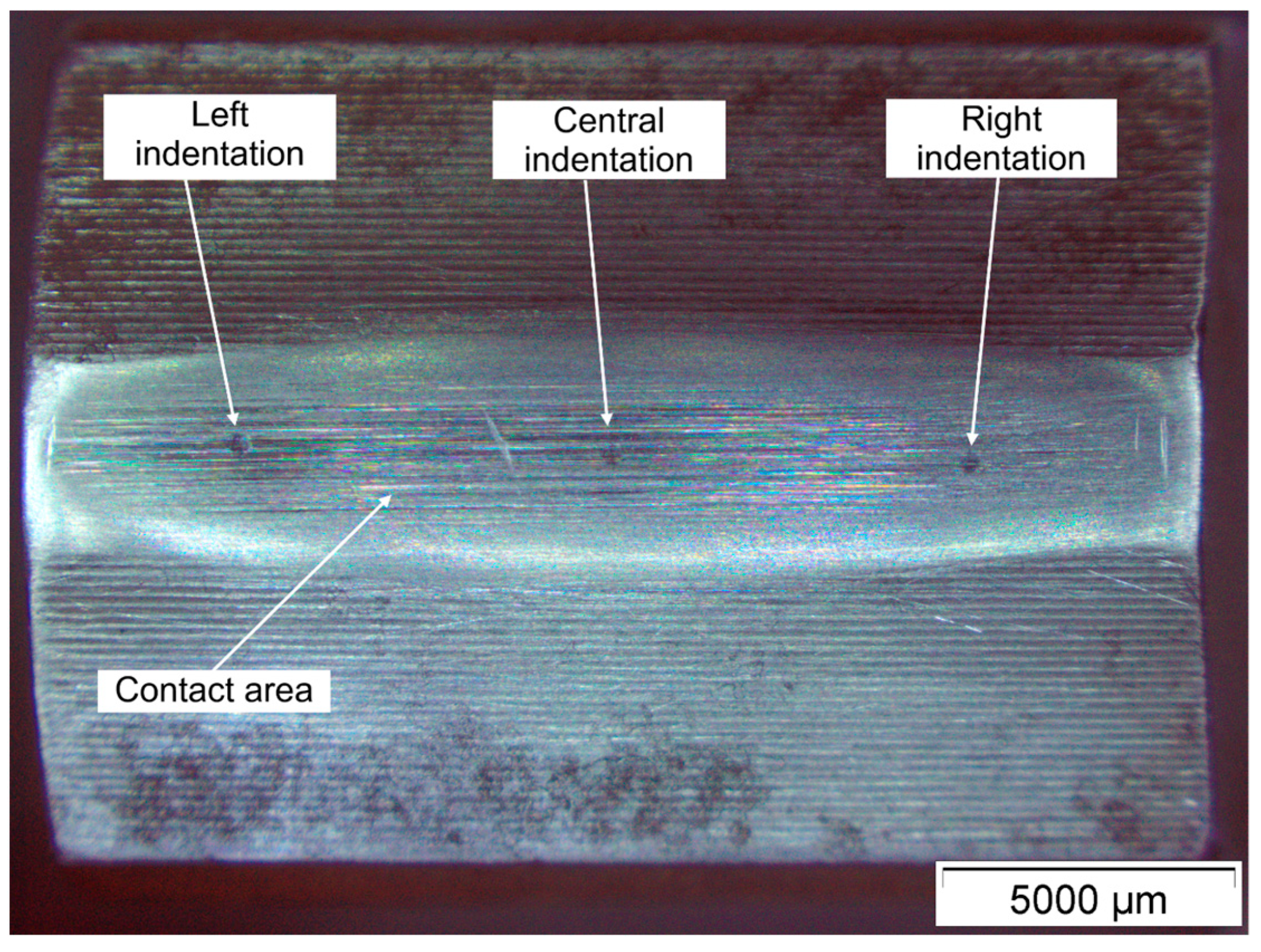
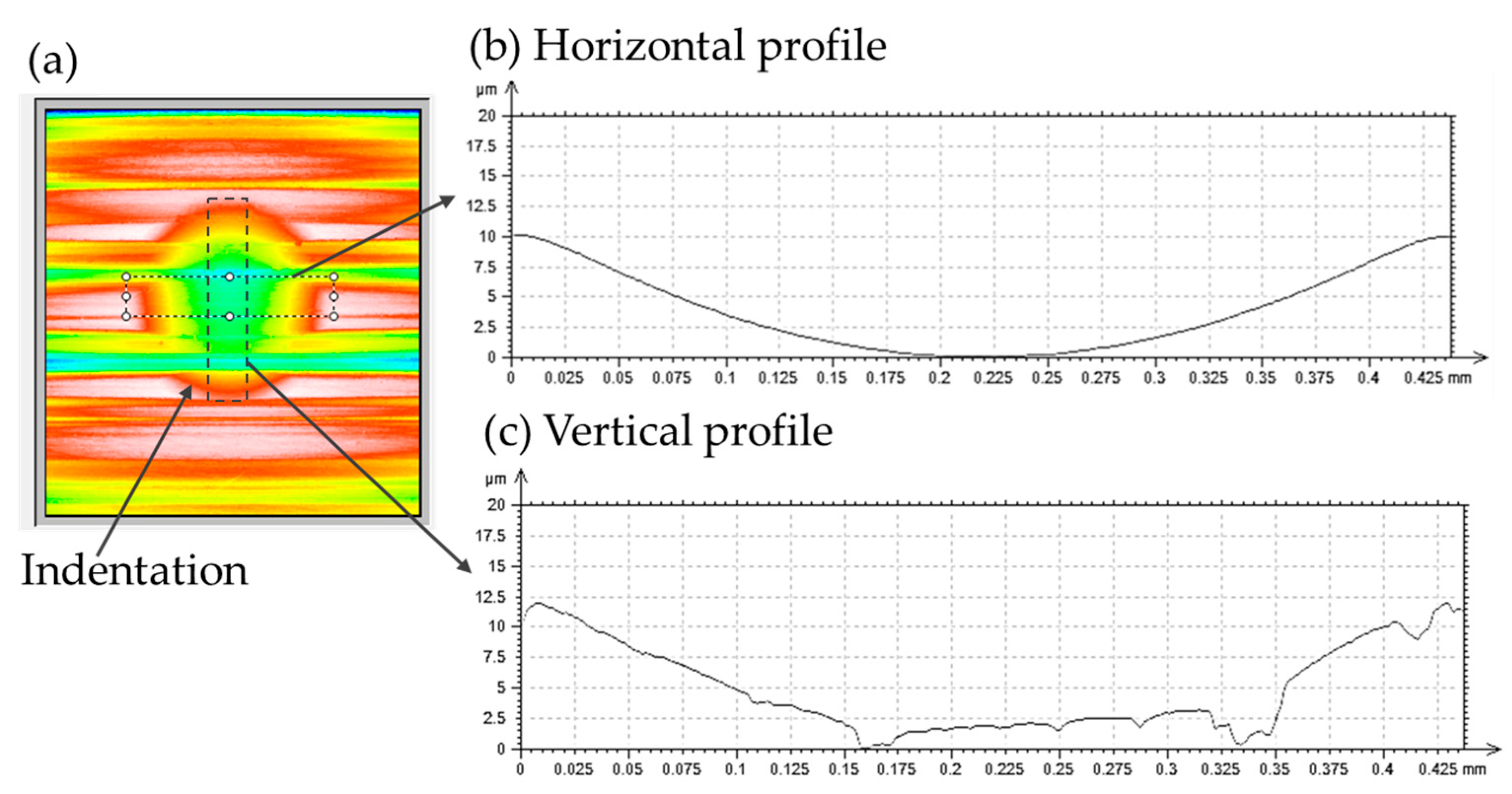
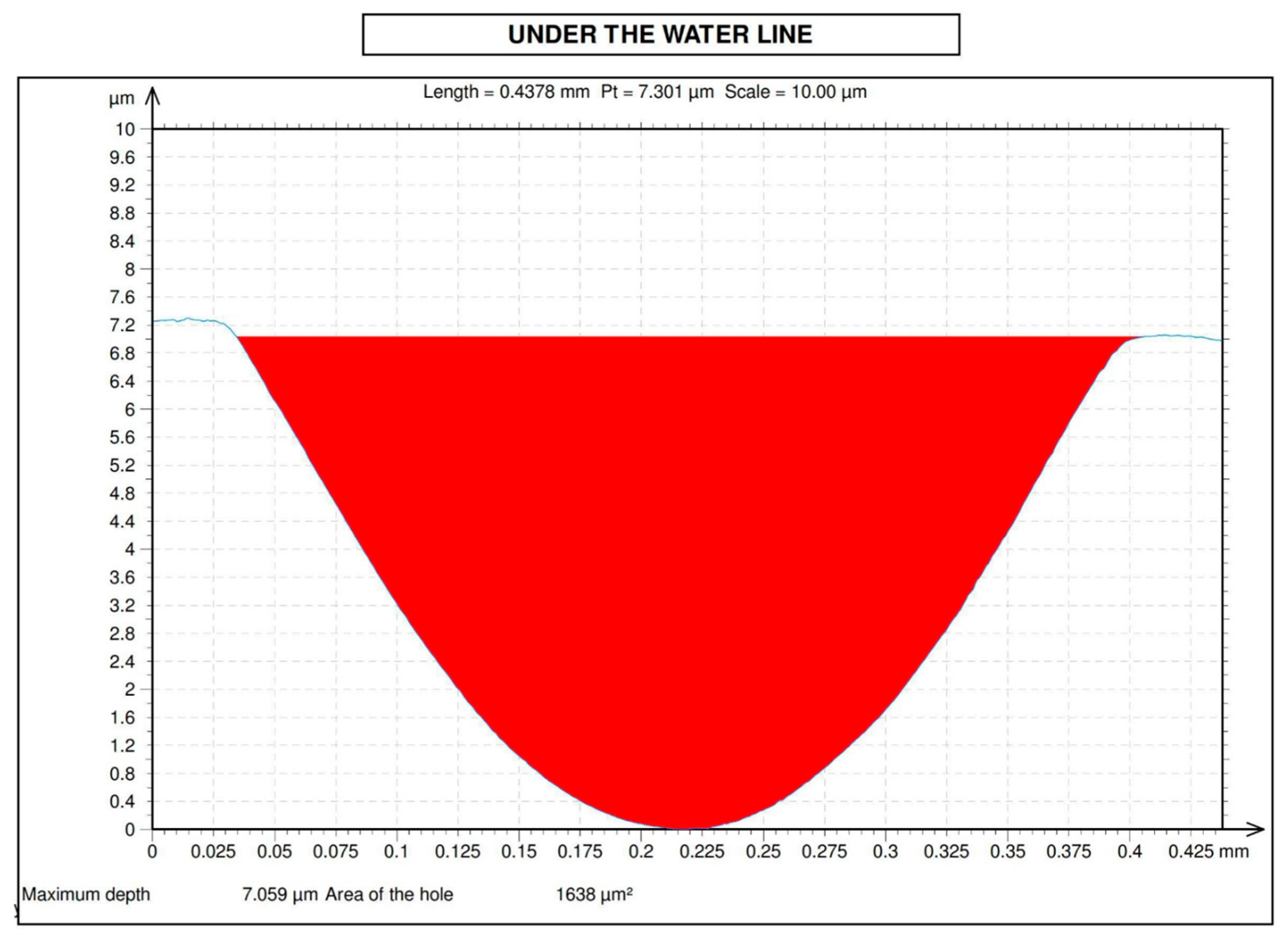
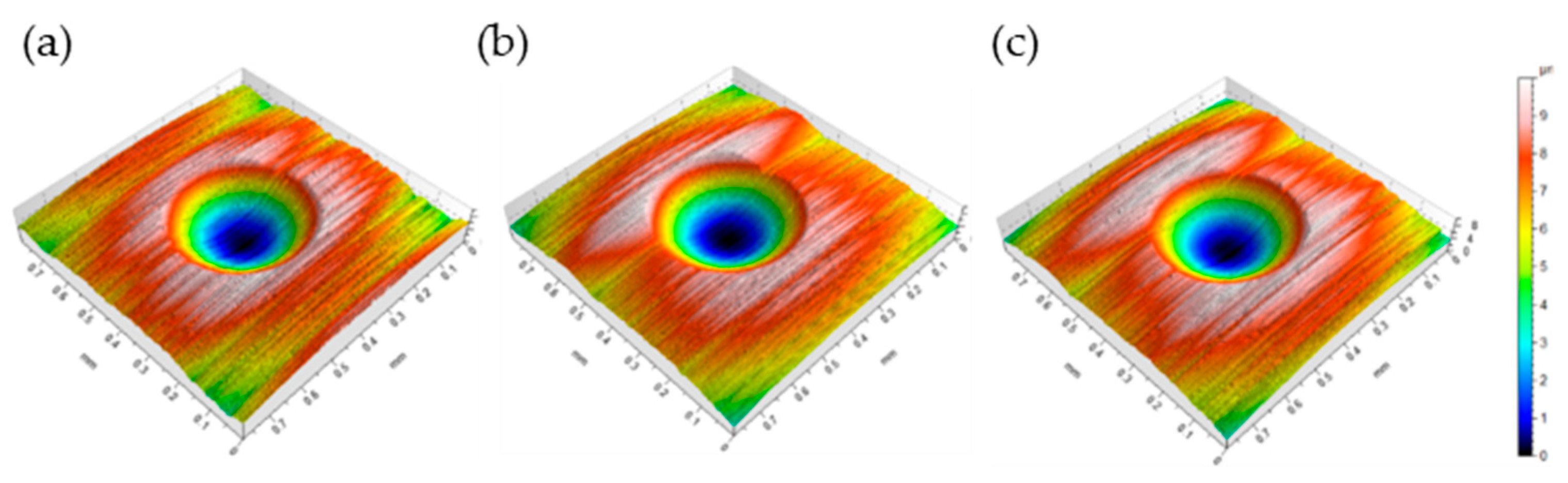
2.3. Wear Measurement Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Descriptive Statistics: Median, mean, mode, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), confidence interval (CI), kurtosis, skewness, and p-values were calculated for all measured parameters. These descriptive metrics provided an initial understanding of the data distribution.
- Sample Size Validation: Based on the Central Limit Theorem, sample size adequacy was confirmed by calculating the confidence intervals for the mean. The maximum error, “e”, of the confidence interval was computed according to Equation (1):where e = CImax − CImin; n = sample size; Z(γ/2) = normal value associated with confidence coefficient; and σ = standard deviation of X.
- Verification of Statistical Differences Between Groups: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied to assess the statistical significance of the differences between the three groups of indentations: central, right, and left. The null hypothesis assumed similar means across the groups, while the alternative hypothesis suggested that at least one mean was different.
- T-Test for Paired Samples: To evaluate the differences in indentation height before and after the wear test, a paired Student’s t-test was conducted. The null hypothesis posited that the means were similar, while the alternative hypothesis suggested a difference.
- Data Visualization: The results were visualized using boxplots to illustrate the distribution and variability of the indentation heights. Additionally, p-values were reported to indicate the statistical significance of the observed differences.
3. Results and Discussion
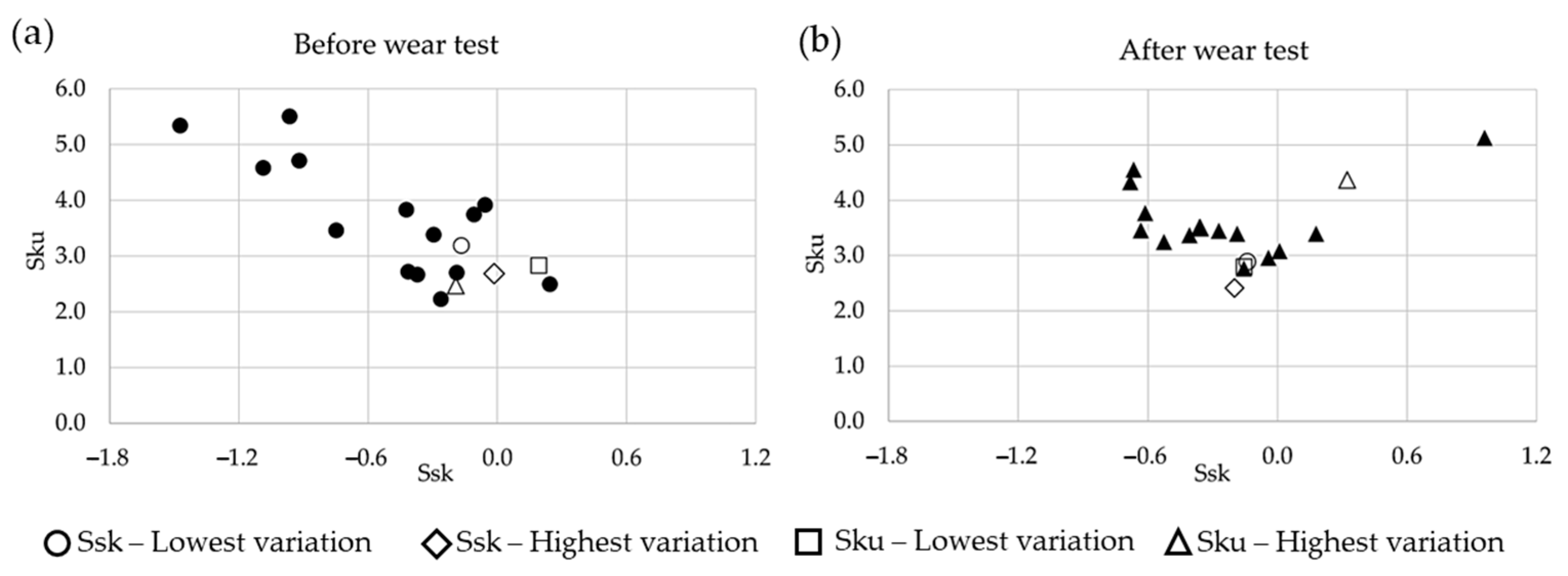
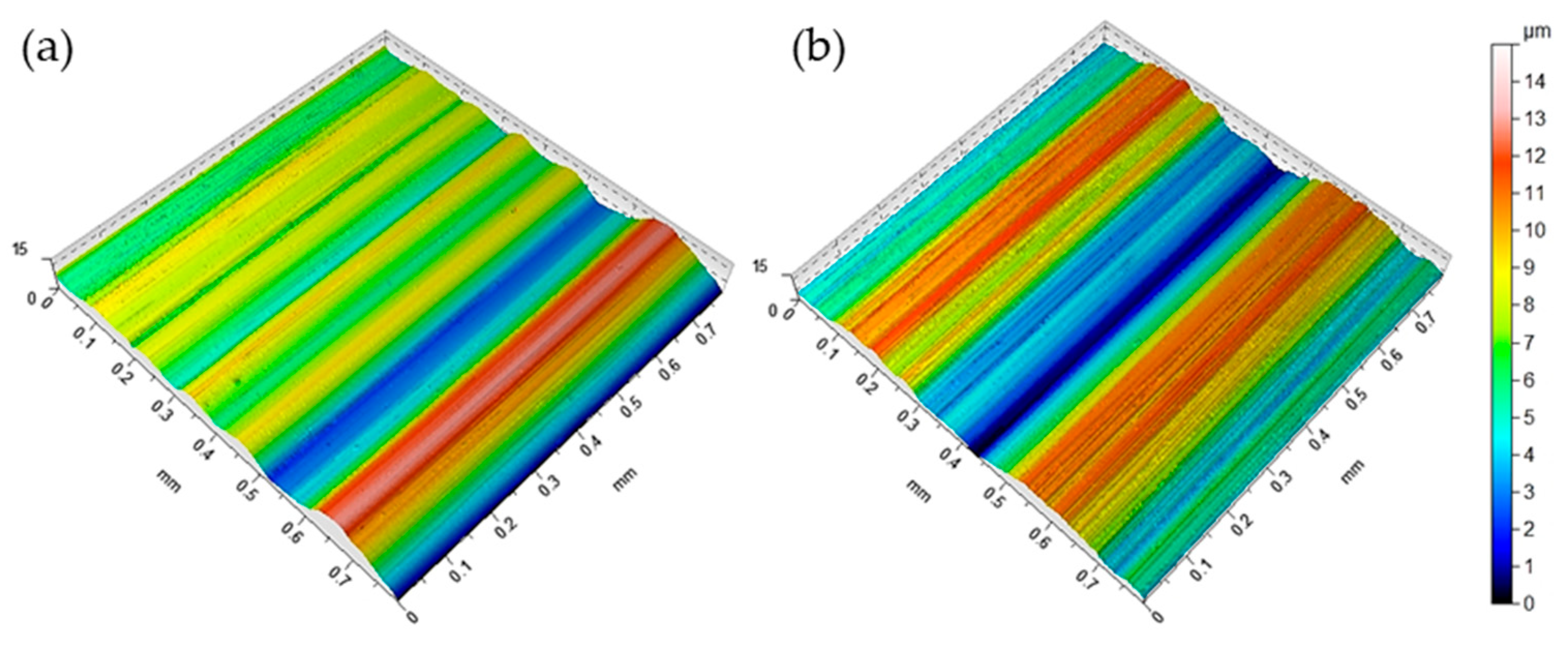
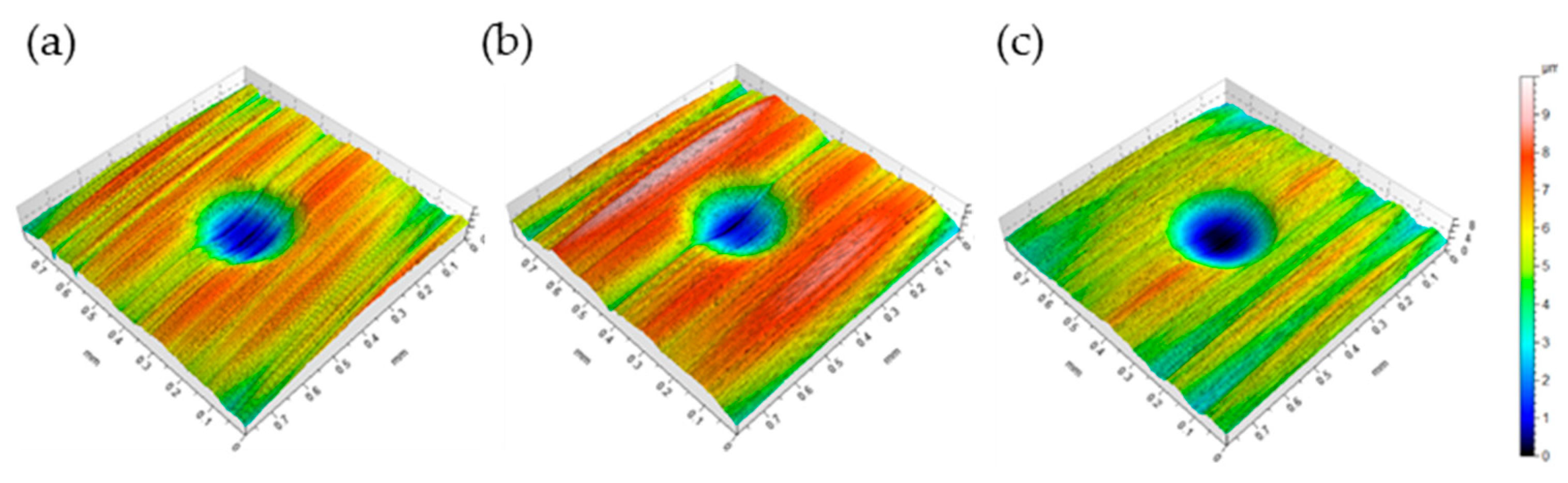
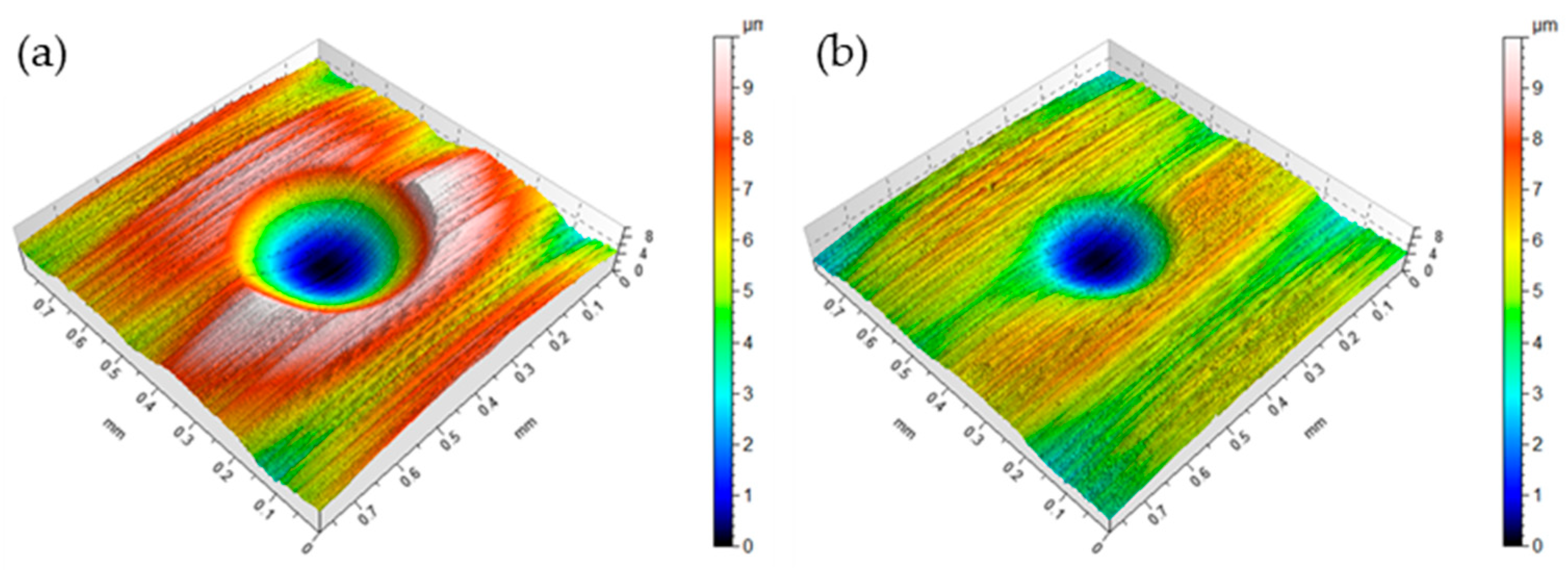
3.1. Surface Roughness Variation
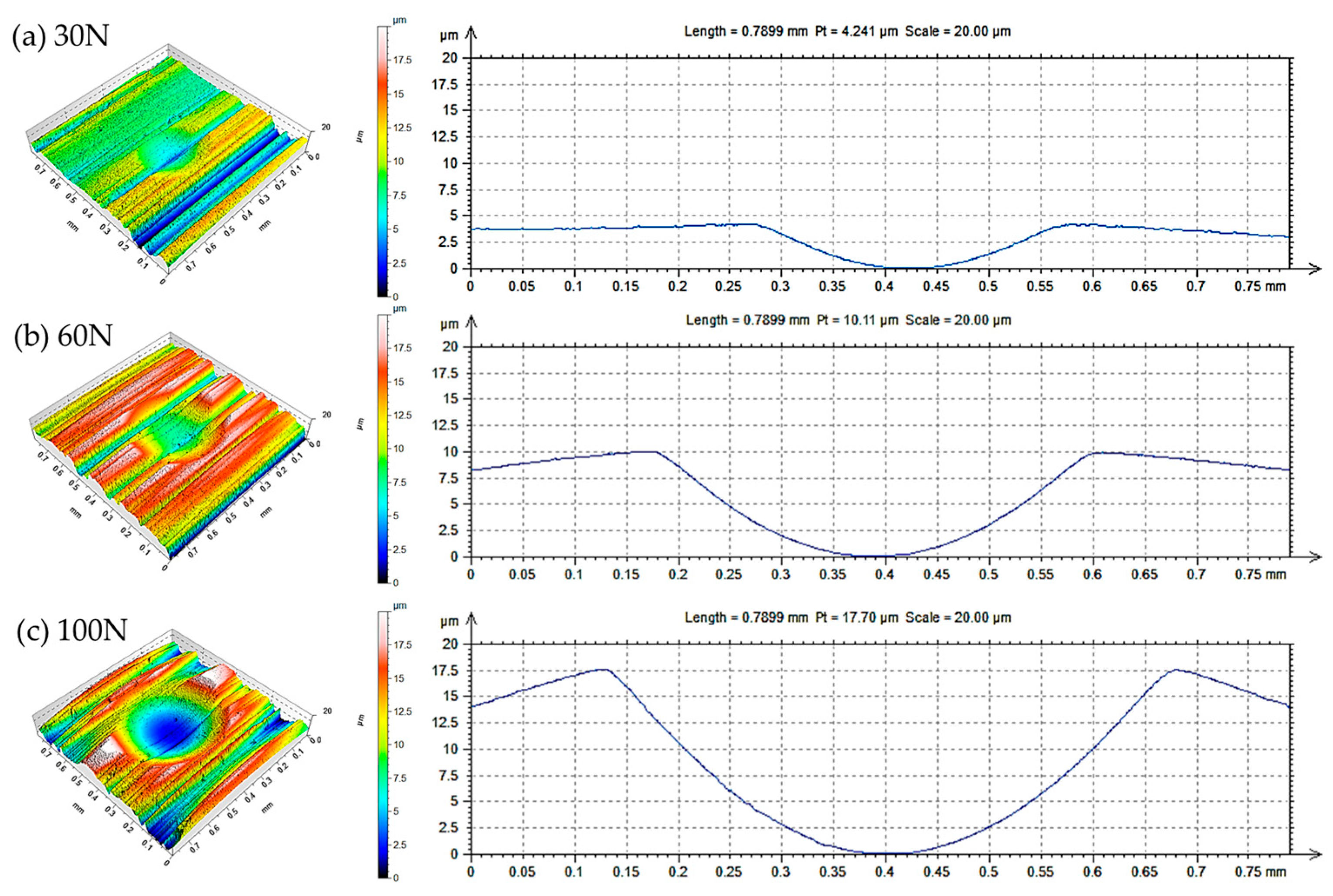
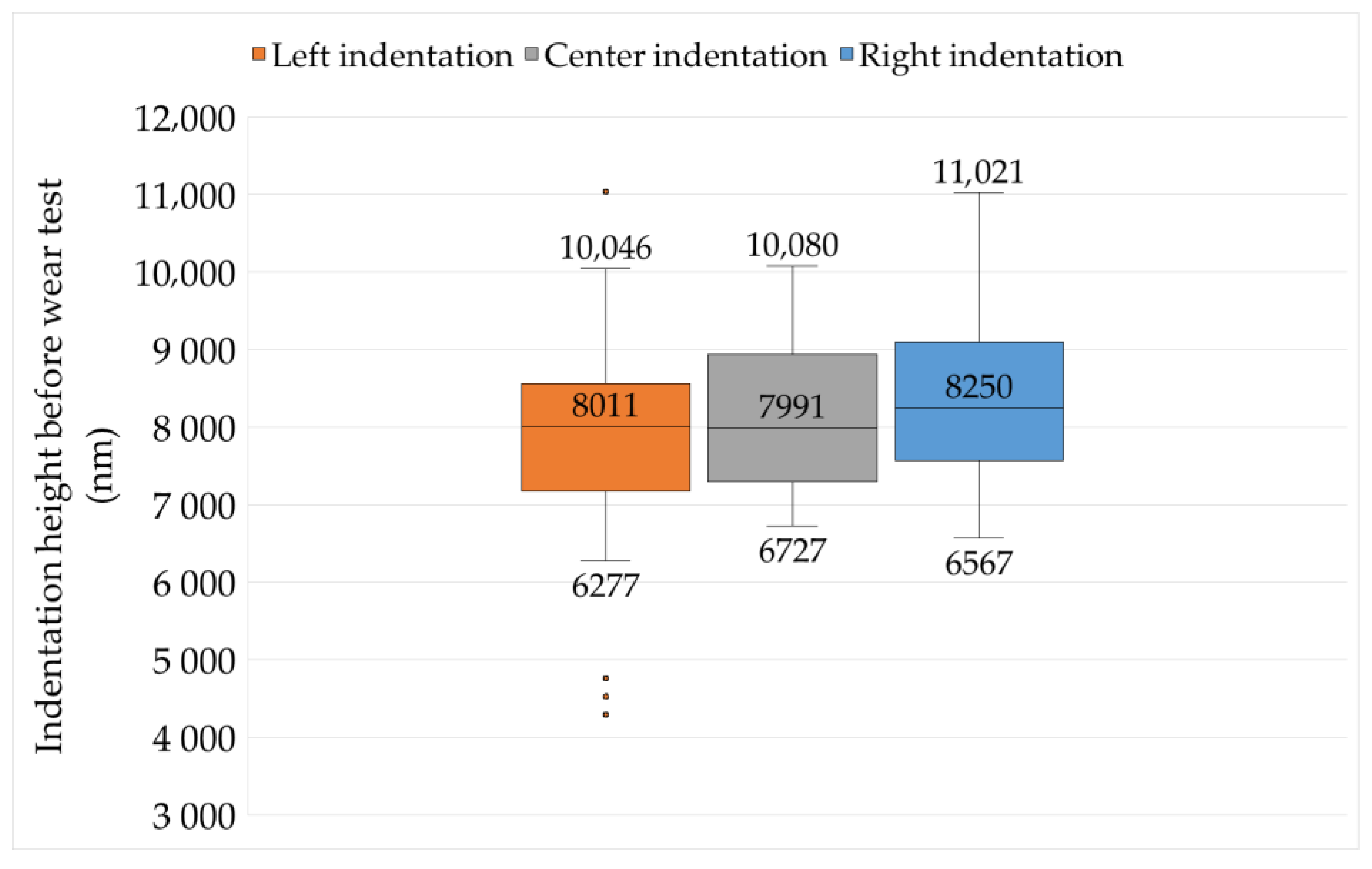
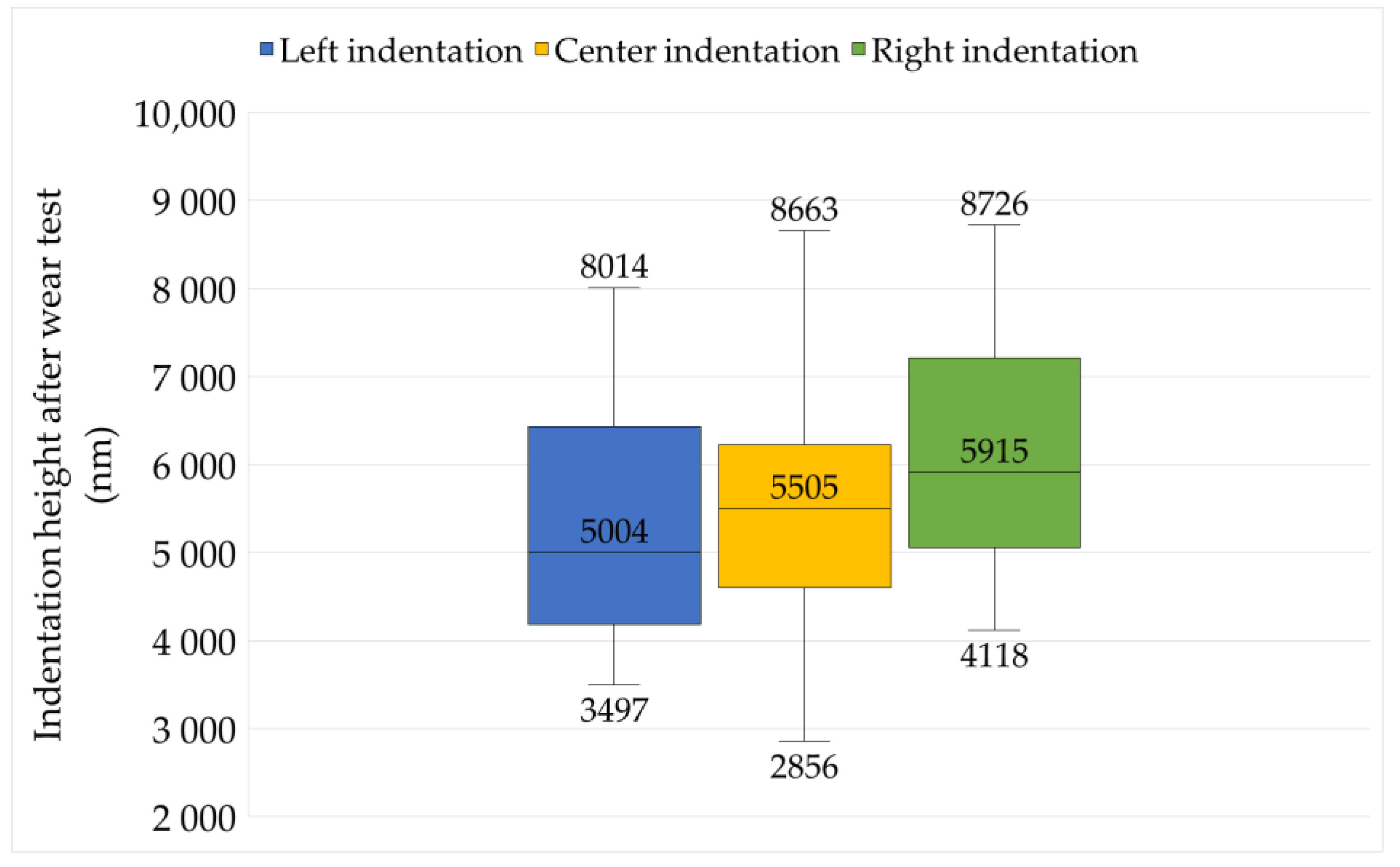
3.2. Wear Measurements
3.3. Reliability of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, W.; Li, X.; Jin, D.; Yang, Y.; Qin, R.; Wang, X. Analysis and prediction of TBM disc cutter wear when tunneling in hard rock strata: A case study of a metro tunnel excavation in Shenzhen, China. Wear 2020, 446–447, 203190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janc, B.; Vižintin, G. Investigation of Disc Cutter Wear in Tunnel-Boring Machines (TBMs): Integration of Photogrammetry, Measurement with a Caliper, Weighing, and Macroscopic Visual Inspection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Hu, M.; Liu, B.; Cao, W.; Xu, B. Full-scale linear cutting tests to study the influence of pre-groove depth on rock-cutting performance by TBM disc cutter. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 122, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y. Development and application of a full-scale mechanical rock-cutting platform for measuring the cutting performance of TBM cutter. Measurement 2022, 204, 112036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzaban, M.; Jamal, R.; Dahl, F.; Francisco, J.; Macias, J. Wear of Cutting Tools in Hard Rock Excavation Process: A Critical Review of Rock Abrasiveness Testing Methods. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 56, 1843–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Mo, J.; Zhang, M.; Su, Y.; Zhou, Z. Cutting performance and contact behavior of partial-wear TBM disc cutters: A laboratory scale investigation. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 137, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, P.J. Applications of Microindentation Methods in Tribology Research. In Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering; STP889-EB; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, A.W. Wear measurements. In ASM Handbook: Friction, Lubrication, and Wear Technolog; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1992; Volume 18, pp. 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Valigi, M.C.; Logozzo, S.; Affatato, S. New challenges in tribology: Wear assessment using 3D optical scanners. Materials 2017, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maculotti, G.; Goti, E.; Genta, G.; Mazza, L.; Galetto, M. Uncertainty-based comparison of conventional and surface topography-based methods for wear volume evaluation in pin-on-disc tribological test. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousseau, T.; Passos, A.G. Methodology for wear mapping error quantification. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2020, 72, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, R.B.; Sinatora, A. Quantification of cylinder bores almost ‘zero-wear’. Wear 2016, 364–365, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, A.A. An Indentation Method for Measuring Wear; Research Paper RP1819; U.S. Department of Commerce National Bureau of Standards: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1947; Volume 39.
- Begelinger, A.; De Gee, A. Wear measurements using Knoop diamond indentations. Wear 1977, 43, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Voort, G.F. Operator Errors in the Measurement of Microindentation Hardness; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt, M.; Cappella, B. Comparative analysis of error sources in the determination of wear volumes of oscillating ball-on-plane tests. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Zhang, S.R.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.Q.; Yu, L.C.; Wang, L.X. Prediction model for disc cutter wear during hard rock breaking based on plastic removal abrasiveness mechanism. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, J.C.; Carvalho, M.A.; Xavier, R.R.; Franco, S.D.; De Mello, J.D. Effect of temperature, normal load and pre-oxidation on the sliding wear of multi-component ferrous alloys. Wear 2005, 259, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImageJ Web Site. Available online: https://imagej.net/ij/ (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Alcar. Guide Alcar. 2024. Available online: https://alcar.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Catalogo_Alcar_NOVO.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- ASTM Standard E10. Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials. 2018. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1520/E0010-18 (accessed on 23 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 6 July 2024).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An {R} Companion to Applied Regression; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca (accessed on 6 July 2024).
- Lüdecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Patil, I.; Makowski, D. Extracting, Computing and Exploring the Parameters of Statistical Models using {R}. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlin, R.; Jacobson, S. The particle size effect in abrasion studied by controlled abrasive surfaces. Wear 1999, 224, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, A.C.; Benegra, M.; Pintaude, G. Surface characterization of the seating platform of titanium implant processed with different textures. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shengyu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhu, G. Discrimination of wear performance based on surface roughness parameters arithmetic mean height (Sa) and skewness (Ssk). Wear 2024, 548, 205397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.451 | 0.988 | 0.355 | 5.482 | 1.145 | 0.871 | 0.149 |
| Indentation (ID) | Position 1 | Mean Area (mm2) | Applied Force (N) | Height Before (nm) | Height After (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L | 57.06 | 85.60 | 7498 | 4668 |
| 2 | R | 57.06 | 85.60 | 8263 | 5847 |
| 3 | C | 57.06 | 85.60 | 7110 | 4996 |
| 4 | L | 61.26 | 91.89 | 8134 | 4585 |
| 5 | R | 61.26 | 91.89 | 9792 | 7921 |
| 6 | C | 61.26 | 91.89 | 7297 | 4701 |
| 7 | L | 50.60 | 75.90 | 7739 | 6530 |
| 8 | R | 50.60 | 75.90 | 6954 | 4709 |
| 9 | C | 50.60 | 75.90 | 8493 | 4760 |
| 10 | L | 63.04 | 94.56 | 8118 | 7886 |
| 11 | R | 63.04 | 94.56 | 8827 | 8726 |
| 12 | C | 63.04 | 94.56 | 10,069 | 8663 |
| 13 | L | 56.53 | 84.80 | 4293 | 4138 |
| 14 | R | 56.53 | 84.80 | 10,160 | 4130 |
| 15 | C | 56.53 | 84.80 | 6727 | 5507 |
| 16 | L | 54.31 | 81.46 | 10,046 | 7539 |
| 17 | R | 54.31 | 81.46 | 8642 | 5177 |
| 18 | C | 54.31 | 81.46 | 9091 | 6562 |
| 19 | L | 57.90 | 86.86 | 7744 | 4648 |
| 20 | R | 57.90 | 86.86 | 8104 | 5982 |
| 21 | C | 57.90 | 86.86 | 8643 | 6342 |
| 22 | L | 64.25 | 96.37 | 10,025 | 5340 |
| 23 | R | 64.25 | 96.37 | 7778 | 6716 |
| 24 | C | 64.25 | 96.37 | 9041 | 5881 |
| 25 | L | 51.63 | 77.44 | 4760 | 3497 |
| 26 | R | 51.63 | 77.44 | 6567 | 6365 |
| 27 | C | 51.63 | 77.44 | 7360 | 4556 |
| 28 | L | 60.93 | 91.40 | 9915 | 8014 |
| 29 | R | 60.93 | 91.40 | 9185 | 5122 |
| 30 | C | 60.93 | 91.40 | 7223 | 4108 |
| 31 | L | 57.48 | 86.22 | 4524 | 4317 |
| 32 | R | 57.48 | 86.22 | 6736 | 4376 |
| 33 | C | 57.48 | 86.22 | 10,016 | 7397 |
| 34 | L | 54.83 | 82.24 | 11,037 | 6156 |
| 35 | R | 54.83 | 82.24 | 11,021 | 7243 |
| 36 | C | 54.83 | 82.24 | 10,080 | 2856 |
| 37 | L | 58.90 | 88.35 | 7903 | 3727 |
| 38 | R | 58.90 | 88.35 | 7222 | 7360 |
| 39 | C | 58.90 | 88.35 | 8258 | 6503 |
| 40 | L | 65.25 | 97.88 | 8315 | 7469 |
| 41 | R | 65.25 | 97.88 | 8237 | 5428 |
| 42 | C | 65.25 | 97.88 | 7677 | 5503 |
| 43 | L | 52.63 | 78.95 | 6277 | 3968 |
| 44 | R | 52.63 | 78.95 | 7697 | 7127 |
| 45 | C | 52.63 | 78.95 | 8016 | 5629 |
| 46 | L | 62.93 | 94.40 | 8643 | 5451 |
| 47 | R | 62.93 | 94.40 | 9778 | 7689 |
| 48 | C | 62.93 | 94.40 | 7312 | 4282 |
| 49 | L | 58.48 | 87.72 | 8323 | 5613 |
| 50 | R | 58.48 | 87.72 | 8776 | 4118 |
| 51 | C | 58.48 | 87.72 | 7966 | 5613 |
| 52 | L | 55.83 | 83.75 | 7059 | 3591 |
| 53 | R | 55.83 | 83.75 | 7521 | 5033 |
| 54 | C | 55.83 | 83.75 | 6816 | 4569 |
| 1 | L | 57.06 | 85.60 | 7498 | 4668 |
| 2 | R | 57.06 | 85.60 | 8263 | 5847 |
| 3 | C | 57.06 | 85.60 | 7110 | 4996 |
| 4 | L | 61.26 | 91.89 | 8134 | 4585 |
| 5 | R | 61.26 | 91.89 | 9792 | 7921 |
| 6 | C | 61.26 | 91.89 | 7297 | 4701 |
| 7 | L | 50.60 | 75.90 | 7739 | 6530 |
| 8 | R | 50.60 | 75.90 | 6954 | 4709 |
| 9 | C | 50.60 | 75.90 | 8493 | 4760 |
| 10 | L | 63.04 | 94.56 | 8118 | 7886 |
| 11 | R | 63.04 | 94.56 | 8827 | 8726 |
| 12 | C | 63.04 | 94.56 | 10,069 | 8663 |
| Variable | Median (nm) | Average (nm) | Mode (nm) | SD 1 (nm) | CV 2 | CI 3 Min 95% | CI Max 95% | E 4 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before test | 8110 | 8643 | 8126 | 1455.2 | 17.9 | 7737.9 | 8514.2 | 776.3 |
| After test | 5477 | 5613 | 5641 | 1429.6 | 25.3 | 5260.0 | 6022.7 | 762.6 |
| Variable | Kurtosis | Skewness | Sig (p) | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before test | 0.6117 | −0.3502 | 0.0913 | Normal |
| After test | −0.6878 | 0.3741 | 0.1424 | Normal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piazzetta, G.R.; Zeller, T.M.; Hernandez-Otalvaro, J.M.; Pintaude, G. Revisiting an Indentation Method for Measuring Low Wear Rates Using 3D Interferometry. Metrology 2025, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020035
Piazzetta GR, Zeller TM, Hernandez-Otalvaro JM, Pintaude G. Revisiting an Indentation Method for Measuring Low Wear Rates Using 3D Interferometry. Metrology. 2025; 5(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020035
Chicago/Turabian StylePiazzetta, Gabriela R., Thomas M. Zeller, Juan M. Hernandez-Otalvaro, and Giuseppe Pintaude. 2025. "Revisiting an Indentation Method for Measuring Low Wear Rates Using 3D Interferometry" Metrology 5, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020035
APA StylePiazzetta, G. R., Zeller, T. M., Hernandez-Otalvaro, J. M., & Pintaude, G. (2025). Revisiting an Indentation Method for Measuring Low Wear Rates Using 3D Interferometry. Metrology, 5(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020035







