Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Large (1–5 mm) Microplastics on the Strandline of a Macrotidal Sandy Beach (Polzeath, Southwest England) and Their Association with Beach-Cast Seaweed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Beach Sand Sampling
2.3. Sieving and Visual Sorting for Microplastics
2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables
3.2. Number and Mass of MPs
3.3. Correlations
3.4. Polymer Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jang, M.; Shim, W.J.; Cho, Y.; Han, G.M.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H. A close relationship between microplastic contamination and coastal area use pattern. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewc, K.; Graca, B.; Dolega, A. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the coastal zone: Characteristics and relationship with meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, C.C.; Zhu, X.S.; Pan, K.; Xu, X.R. Risk of aquaculture-derived microplastics in aquaculture areas: An overlooked issue or a non-issue? Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 923471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.; Turner, A. Microplastics in surface coastal waters around Plymouth, UK, and the contribution of boating and shipping activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mao, X.; Xing, R.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, Q.H.; Liu, H.H.; Wu, Y.N.; Li, Y.S. Microplastics Pollution and Their Potential Impact in Marine Systems: A Case Study in Shandong Peninsula, China. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, L.; Hardesty, B.D.; Leonard, G.H.; Pragnell-Raasch, H.; Mallos, N.; Campbell, I.; Wilcox, C. A global assessment of the relationship between anthropogenic debris on land and the seafloor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Kang, J.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Large accumulation of micro-sized synthetic polymer particles in the sea surface microlayer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9014–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Lyashevska, O.; Joyce, H.; Pagter, E.; Nash, R. Floating microplastics in a coastal embayment: A multifaceted issue. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.K.; Pereira, J.M.; Frias, J.P.G.L.; Ríis, N.; Carriço, R.; Juliano, M.; Rodríquez, Y. Beaches of the Azores archipelago as transitory repositories for small plastic fragments floating in the North-East Atlantic. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263A, 114494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.M.; Monteiro, R.C.P.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Costa, M.F. Do beachrocks affect microplastic deposition on the strandline of sandy beaches? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.F.; Sul, J.A.I.D.; Silva-Cavalcanti, J.S.; Araujo, M.C.B.; Spengler, A.; Tourinho, P.S. On the importance of size of plastic fragments and pellets on the strandline: A snapshot of a Brazilian beach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, C.; Rojas, I.J.; Lasserre, J.; Villette, S.; Lecomte, S.; Cachot, J.; Morin, B. Stranded in the high tide line: Spatial and temporal variability of beached microplastics in a semi-enclosed embayment (Arcachon, France). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlino, S.; Locritani, M.; Bernardi, G.; Como, C.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V.; Abbate, M. Spatial and temporal distribution of chemically characterized microplastics within the protected area of Pelagos Sanctuary (NW Mediterranean Sea): Focus on natural and urban beaches. Water 2020, 12, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.V.; Conley, D.C.; Masselink, G.; Leonardi, N.; McCarroll, R.J.; Scott, T.; Valiente, N.G. Wave, Tide and topographical controls on headland sand bypassing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC017053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The River Trust. Sewage Outflow Map, UK, Experience ArcGIS. 2022. Available online: https://experience.arcgis.com/experience/e834e261b53740eba2fe6736e37bbc7b/page/Map/?org=theriverstrust (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Department for Environment, Food, and Rural Affairs and Environmental Agency. Bathing Water Profile for Polzeath Cornwall. 2024. Available online: https://environment.data.gov.uk/bwq/profiles/profile.html?site=ukk3104-33300 (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Tirkey, A.; Upadhyay, L. Microplastics: An overview on separation, identification and characterization of microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Wallerstein, C.; Arnold, R. Identification, origin and characteristics of bio-bead microplastics from beaches in western Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Sierra, J.; Muñoz-Perez, J.J.; Navarro-Pons, M. Beach nourishment effects on sand porosity variability. Coast. Eng. 2014, 83, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M. Man-Made Cellulose Fibre Reinforcements (MMCFR) In Biocomposites for High-Performance Applications; Ray, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2017; pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- GP. General Plastics Manufacturing. 2024. Available online: https://www.generalplastics.com/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Omnexus. Plastics & Elastomers Selector. 2024. Available online: https://omnexus.specialchem.com/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Vinyltec. TPV, Thermoplastic Vulcanizate. 2024. Available online: https://vic.co.th/en/tpv-thermoplastic-valcanizate-eng/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Wilson, D.R.; Godley, B.J.; Haggar, G.L.; Santillo, D.; Sheen, K.L. The influence of depositional environment on the abundance of microplastic pollution on beaches in the Bristol Channel, UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T.M.; Arneborg, L.; Broström, G.; Almroth, B.C.; Gipperth, L.; Hassellöv, M. The unaccountability case of plastic pellet pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumhansl, K.A.; Scheibling, R.E. Production and fate of kelp detritus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 467, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutow, L.; Eckerlebe, A.; Giménez, L.; Saborowski, R. Experimental evaluation of seaweeds as a vector for microplastics into marine food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, C.; Fisher, J.; Turner, A. Biomonitoring of microplastics, anthropogenic microfibres and glass retroreflective beads by marine macroalgae. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, M.; Zimmer, M.; Jelinski, D.E.; Mews, M. wrack deposition on different beach types: Spatial and temporal variation in the pattern of subsidy. Ecology 2005, 86, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onink, V.; Kaandorp, M.L.A.; van Sebille, E.; Laufkötter, C. Influence of particle size and fragmentation on large-scale microplastic transport in the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15528–15540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Schüttrumpf, H. Infiltration behavior of microplastic particles with different densities, sizes, and shapes—From glass spheres to natural sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9366–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, P.G.; Weideman, E.A.; Perold, V.; Moloney, C.L. Towards balancing the budget: Surface macro-plastics dominate the mass of particulate pollution stranded on beaches. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 575395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. Foamed polystyrene in the marine environment: Sources, additives, transport, behavior, and impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10411–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Mahanwar, P. A brief discussion on advances in polyurethane applications. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.S.; Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Potential microplastic release from beached fishing gear in Great Britain’s region of highest fishing litter density. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173B, 1131145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, O.J.; Walklett, E.J.; Turner, A. Relationships between sediment size distribution and microplastic abundance and characteristics along the strandline of a sandy embayment (Whitsand, southwest England). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 213, 117686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrell, W.R. A simple model of wind-blown tidal strandlines: How marine litter is deposited on a mid-latitude, macro-tidal shelf sea beach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Arnold, R.; Williams, T. Weathering and persistence of plastic in the marine environment. Lessons from LEGO. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Amos, S.L.; Williams, T. Coastal dunes as a sink and secondary source of marine plastics: A study at Perran Beach, southwest England. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Chen, T.H. Spatial and seasonal distribution of microplastics on sandy beaches along the coast of the Hengchun Peninsula, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lots, F.A.E.; Behrens, P.; Vijver, M.G.; Horton, A.A.; Bosker, T. A large-scale investigation of microplastic contamination: Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in European beach sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.J.; Turner, A. Microplastic transport and deposition in a beach-dune system (Saunton Sands-Braunton Burrows, southwest England). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, R.F.; Vincent, A.E.S.; Hoellein, T.J. Trash dance: Anthropogenic litter and organic matter co-accumulate on urban beaches. Geosciences 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaski, B.P.; Sikes, D.S.; Konar, B. Beach-cast and drifting seaweed wrack is an important resource for marine and terrestrial macroinvertebrates in high latitudes. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 187, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
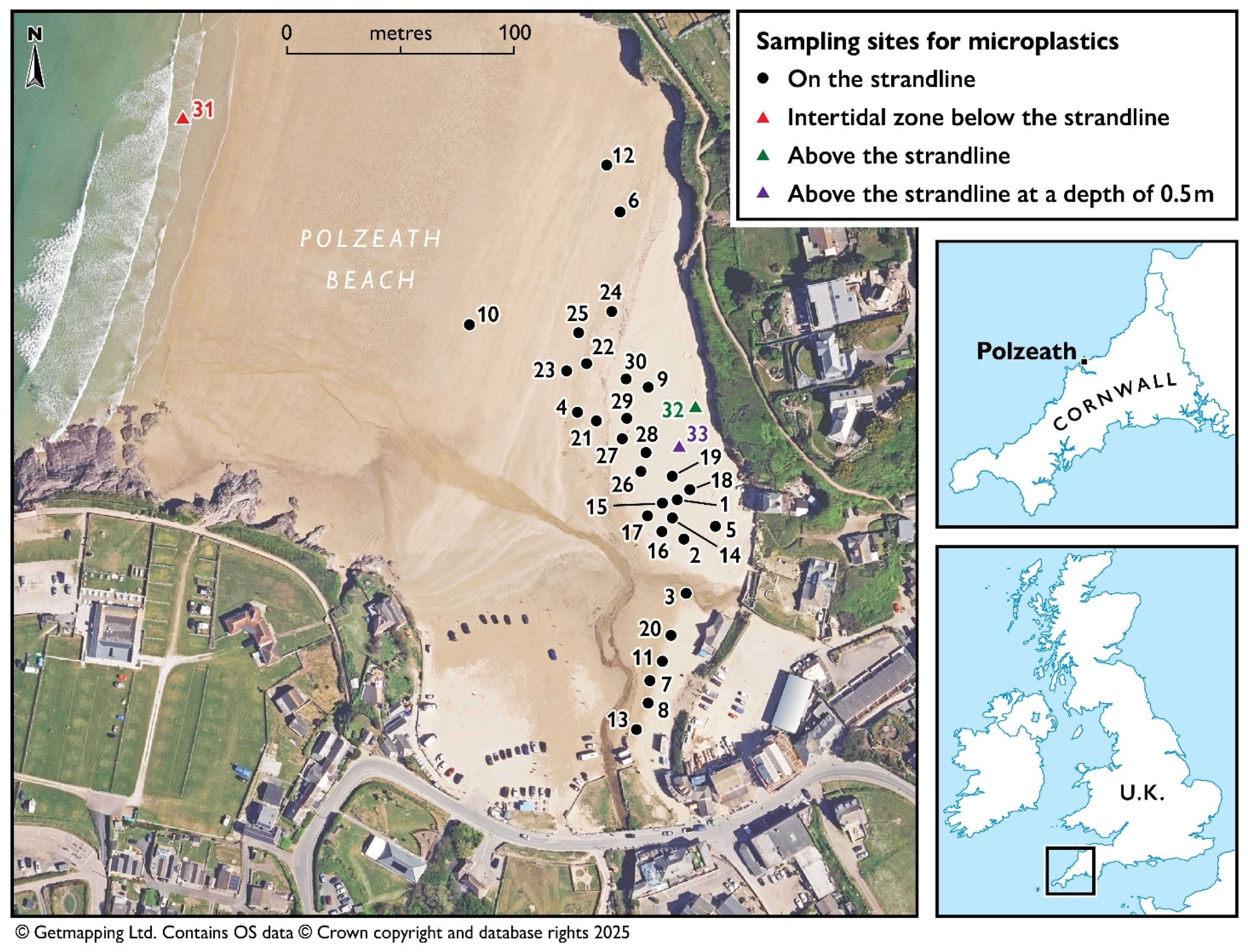
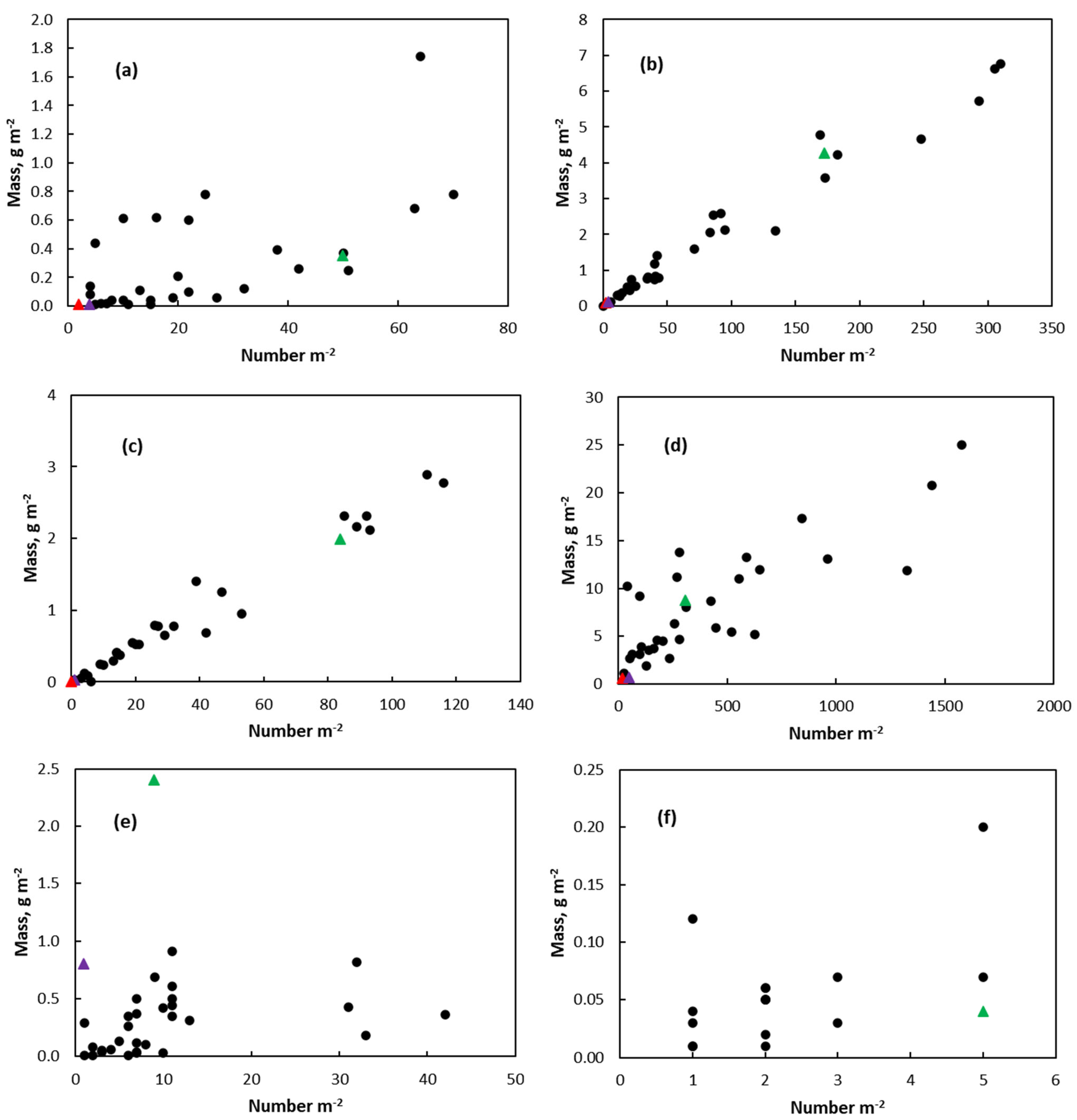
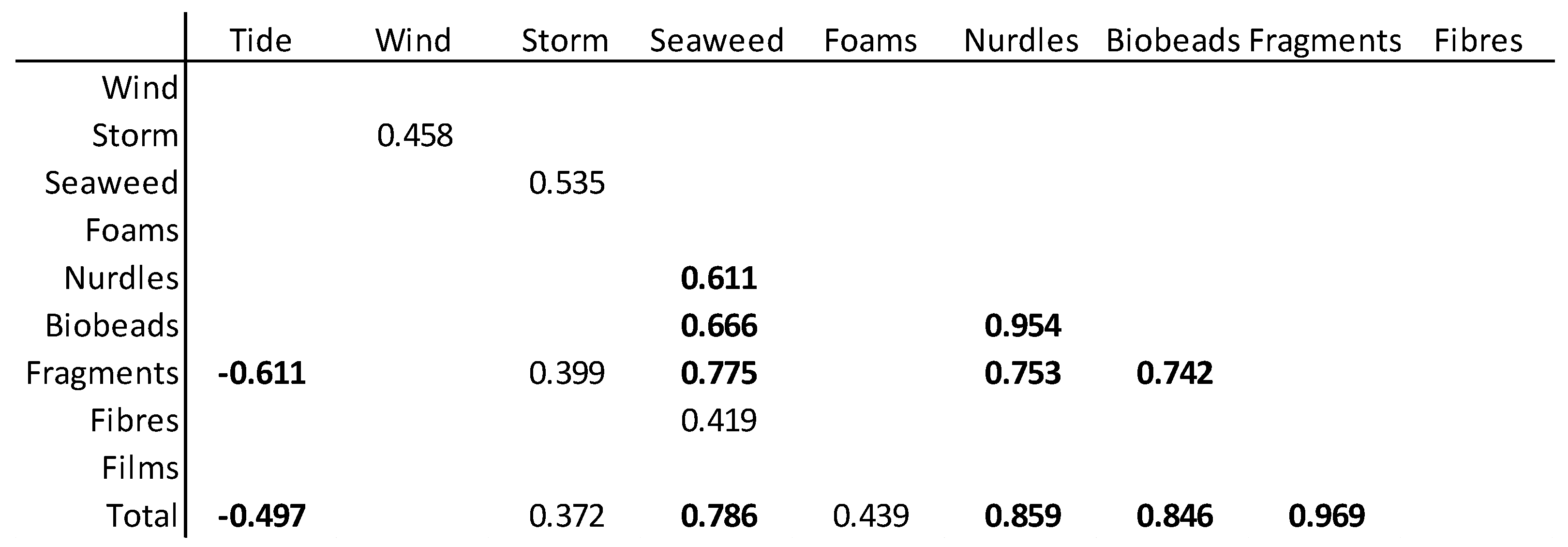
| Sampling | Date | Tidal Range, m | Wind Speed, mph | Storm Activity | Sample Number | Seaweed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 17 June 2023 | 5.2 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 | |||||
| B | 24 June 2023 | 3.9 | 14 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | |||||
| C | 19 July 2023 | 5.1 | 12 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 3 | |||||
| D | 4 August 2023 | 7.2 | 13 | 0 | 7 | 3 |
| 8 | 0 | |||||
| E | 11 August 2023 | 2.8 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 8 |
| F | 14 August 2023 | 4.6 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 5 |
| 11 | 9 | |||||
| 12 | 4 | |||||
| G | 15 August 2023 | 4.8 | 12 | 1 | 13 | 7 |
| H | 26 August 2023 | 2.7 | 6 | 1 | 14 | 4 |
| 15 | 6 | |||||
| 16 | 9 | |||||
| 17 | 10 | |||||
| I | 30 September 2023 | 7.6 | 23 | 2 | 18 | 6 |
| 19 | 7 | |||||
| 20 | 9 | |||||
| J | 22 October 2023 | 3.0 | 18 | 0 | 21 | 4 |
| 22 | 4 | |||||
| 23 | 6 | |||||
| 24 | 5 | |||||
| 25 | 8 | |||||
| K | 4 November 2023 | 2.8 | 19 | 2 | 26 | 5 |
| 27 | 9 | |||||
| 28 | 10 | |||||
| 29 | 10 | |||||
| 30 | 8 | |||||
| (31) | (0) | |||||
| (32) | (3) | |||||
| (33) | (0) |
| Sample Number | Number of MPs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foams | Nurdles | Biobeads | Fragments | Fibres | Films | Total | |
| 1 | 15 | 183 | 89 | 280 | 3 | 0 | 570 |
| 2 | 11 | 169 | 93 | 270 | 6 | 0 | 549 |
| 3 | 4 | 83 | 27 | 108 | 10 | 0 | 232 |
| 4 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 7 | 5 | 129 |
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 1 | 52 | 11 | 0 | 89 |
| 6 | 64 | 92 | 26 | 40 | 10 | 5 | 237 |
| 7 | 20 | 13 | 4 | 63 | 6 | 0 | 106 |
| 8 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 35 |
| 9 | 13 | 42 | 29 | 310 | 7 | 0 | 401 |
| 10 | 50 | 305 | 85 | 845 | 6 | 2 | 1293 |
| 11 | 25 | 35 | 15 | 257 | 11 | 0 | 343 |
| 12 | 0 | 22 | 5 | 97 | 2 | 0 | 126 |
| 13 | 63 | 86 | 53 | 425 | 13 | 2 | 642 |
| 14 | 10 | 13 | 3 | 178 | 11 | 2 | 217 |
| 15 | 7 | 19 | 13 | 280 | 11 | 2 | 332 |
| 16 | 4 | 95 | 39 | 590 | 32 | 1 | 761 |
| 17 | 8 | 134 | 42 | 650 | 42 | 2 | 878 |
| 18 | 5 | 40 | 19 | 164 | 3 | 2 | 233 |
| 19 | 38 | 25 | 20 | 141 | 33 | 1 | 258 |
| 20 | 19 | 34 | 14 | 204 | 11 | 0 | 282 |
| 21 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 128 | 1 | 0 | 151 |
| 22 | 6 | 21 | 9 | 236 | 2 | 3 | 277 |
| 23 | 27 | 43 | 21 | 520 | 7 | 0 | 618 |
| 24 | 22 | 40 | 10 | 450 | 7 | 2 | 531 |
| 25 | 70 | 41 | 14 | 628 | 8 | 1 | 762 |
| 26 | 15 | 71 | 32 | 554 | 4 | 1 | 677 |
| 27 | 32 | 248 | 116 | 1439 | 5 | 0 | 1840 |
| 28 | 42 | 310 | 111 | 1575 | 7 | 3 | 2048 |
| 29 | 22 | 293 | 92 | 1325 | 9 | 2 | 1743 |
| 30 | 51 | 173 | 47 | 962 | 31 | 1 | 1265 |
| (31) | (2) | (2) | (1) | (21) | (0) | (0) | (26) |
| (32) | (50) | (173) | (84) | (310) | (9) | (5) | (631) |
| (33) | (4) | (4) | (0) | (52) | (1) | (0) | (61) |
| total | 674 | 2662 | 1037 | 12,898 | 317 | 37 | 17,625 |
| mean | 22.5 | 88.7 | 34.6 | 430 | 10.6 | 1.2 | 588 |
| sd | 20.1 | 94.8 | 35.2 | 421 | 10.2 | 1.4 | 542 |
| median | 15.5 | 41.5 | 20.5 | 275 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 372 |
| min | 0 | 0 | 1 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 35 |
| max | 70 | 310 | 116 | 1575 | 42 | 5 | 2048 |
| Sample Number | Mass of MPs, g | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foams | Nurdles | Biobeads | Fragments | Fibres | Films | Total | |
| 1 | 0.01 | 4.22 | 2.16 | 13.75 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 20.18 |
| 2 | 0.01 | 4.78 | 2.12 | 11.20 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 18.12 |
| 3 | 0.14 | 2.06 | 0.78 | 3.91 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 6.92 |
| 4 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 9.16 | 0.37 | 0.20 | 10.37 |
| 5 | 0.61 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 2.67 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 4.29 |
| 6 | 1.74 | 2.58 | 0.79 | 10.20 | 0.42 | 0.07 | 15.80 |
| 7 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 3.08 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 4.09 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 1.13 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 1.55 |
| 9 | 0.11 | 1.40 | 0.65 | 8.08 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 10.74 |
| 10 | 0.37 | 6.63 | 2.31 | 17.33 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 26.91 |
| 11 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.38 | 6.30 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 8.72 |
| 12 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 0.09 | 3.09 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 3.92 |
| 13 | 0.68 | 2.54 | 0.95 | 8.67 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 13.20 |
| 14 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 4.55 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 5.33 |
| 15 | 0.02 | 0.53 | 0.29 | 4.71 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 6.10 |
| 16 | 0.08 | 2.12 | 1.40 | 13.22 | 0.82 | 0.04 | 17.68 |
| 17 | 0.04 | 2.10 | 0.69 | 11.91 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 15.15 |
| 18 | 0.44 | 1.17 | 0.55 | 3.76 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 5.97 |
| 19 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 3.54 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 5.21 |
| 20 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.41 | 4.50 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 6.64 |
| 21 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 1.91 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 2.24 |
| 22 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 2.65 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 3.50 |
| 23 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 0.52 | 5.46 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 6.86 |
| 24 | 0.10 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 5.87 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 7.02 |
| 25 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.41 | 5.23 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 7.47 |
| 26 | 0.04 | 1.59 | 0.78 | 10.98 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 13.48 |
| 27 | 0.12 | 4.66 | 2.78 | 20.76 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 28.45 |
| 28 | 0.26 | 6.76 | 2.89 | 25.04 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 35.10 |
| 29 | 0.60 | 5.73 | 2.31 | 11.87 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 21.26 |
| 30 | 0.25 | 3.57 | 1.25 | 13.09 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 18.60 |
| (31) | (0.01) | (0.09) | (0.02) | (0.56) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) |
| (32) | (0.35) | (4.26) | (1.98) | (8.70) | (2.40) | (0.04) | (17.73) |
| (33) | (0.01) | (0.11) | (0.00) | (0.65) | (0.80) | (0.00) | (1.57) |
| total | 8.59 | 59.5 | 25.78 | 247.62 | 8.50 | 0.88 | 350.87 |
| mean | 0.29 | 1.98 | 0.86 | 8.25 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 11.70 |
| sd | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.88 | 5.82 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 8.48 |
| median | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 6.09 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 8.10 |
| min | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 1.55 |
| max | 1.74 | 6.76 | 2.89 | 25.04 | 0.91 | 0.20 | 35.10 |
| Polymer (Density) | PE (0.91–0.97) | PP (0.90) | EPS (0.02–0.04) | FPU (0.05–0.96) | RY (1.53) | TPV (0.96) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foams | 3 | 2 | ||||
| Nurdles | 4 | 1 | ||||
| Biobeads | 5 | |||||
| Fragments | 3 | 2 | ||||
| Fibres | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Films | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Total | 17 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beale, C.; Turner, A. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Large (1–5 mm) Microplastics on the Strandline of a Macrotidal Sandy Beach (Polzeath, Southwest England) and Their Association with Beach-Cast Seaweed. Micro 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5030043
Beale C, Turner A. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Large (1–5 mm) Microplastics on the Strandline of a Macrotidal Sandy Beach (Polzeath, Southwest England) and Their Association with Beach-Cast Seaweed. Micro. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeale, Catherine, and Andrew Turner. 2025. "Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Large (1–5 mm) Microplastics on the Strandline of a Macrotidal Sandy Beach (Polzeath, Southwest England) and Their Association with Beach-Cast Seaweed" Micro 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5030043
APA StyleBeale, C., & Turner, A. (2025). Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Large (1–5 mm) Microplastics on the Strandline of a Macrotidal Sandy Beach (Polzeath, Southwest England) and Their Association with Beach-Cast Seaweed. Micro, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5030043





