Process of Fabricating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Milli-to-Microneedles Using the Bi-Directional Drawing Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
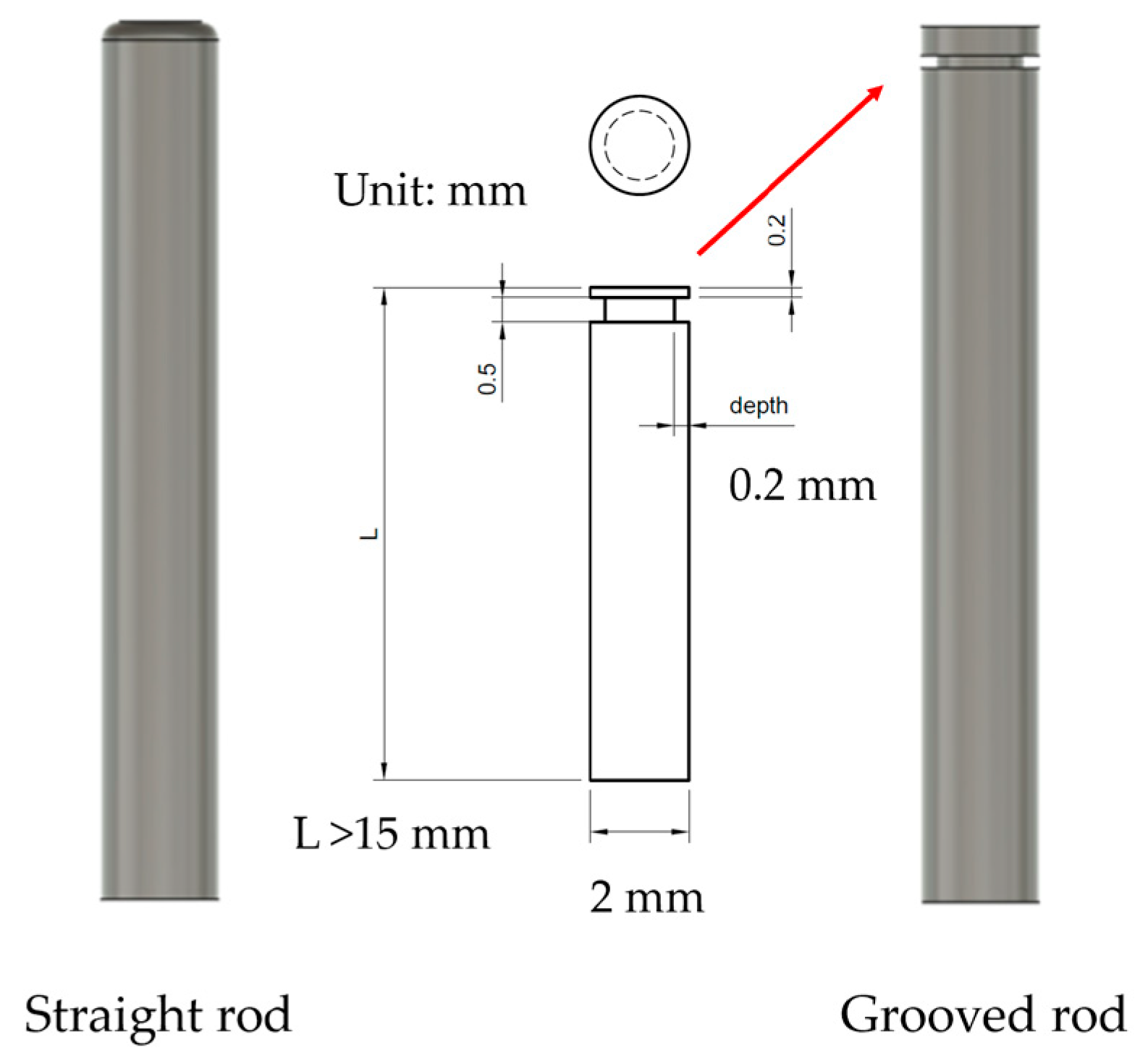
2.1. Preparation of HA Solution for Dissolving Microneedles
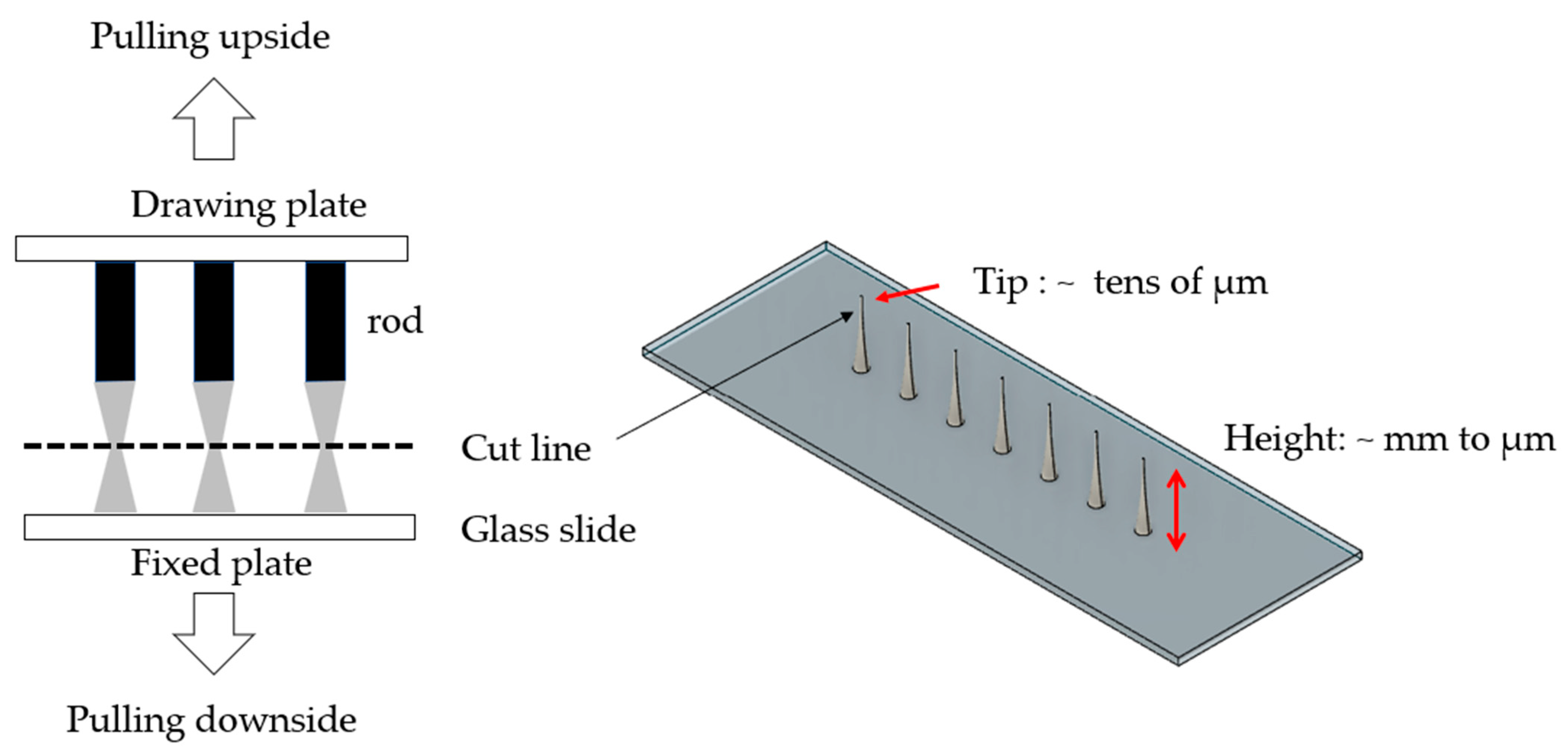
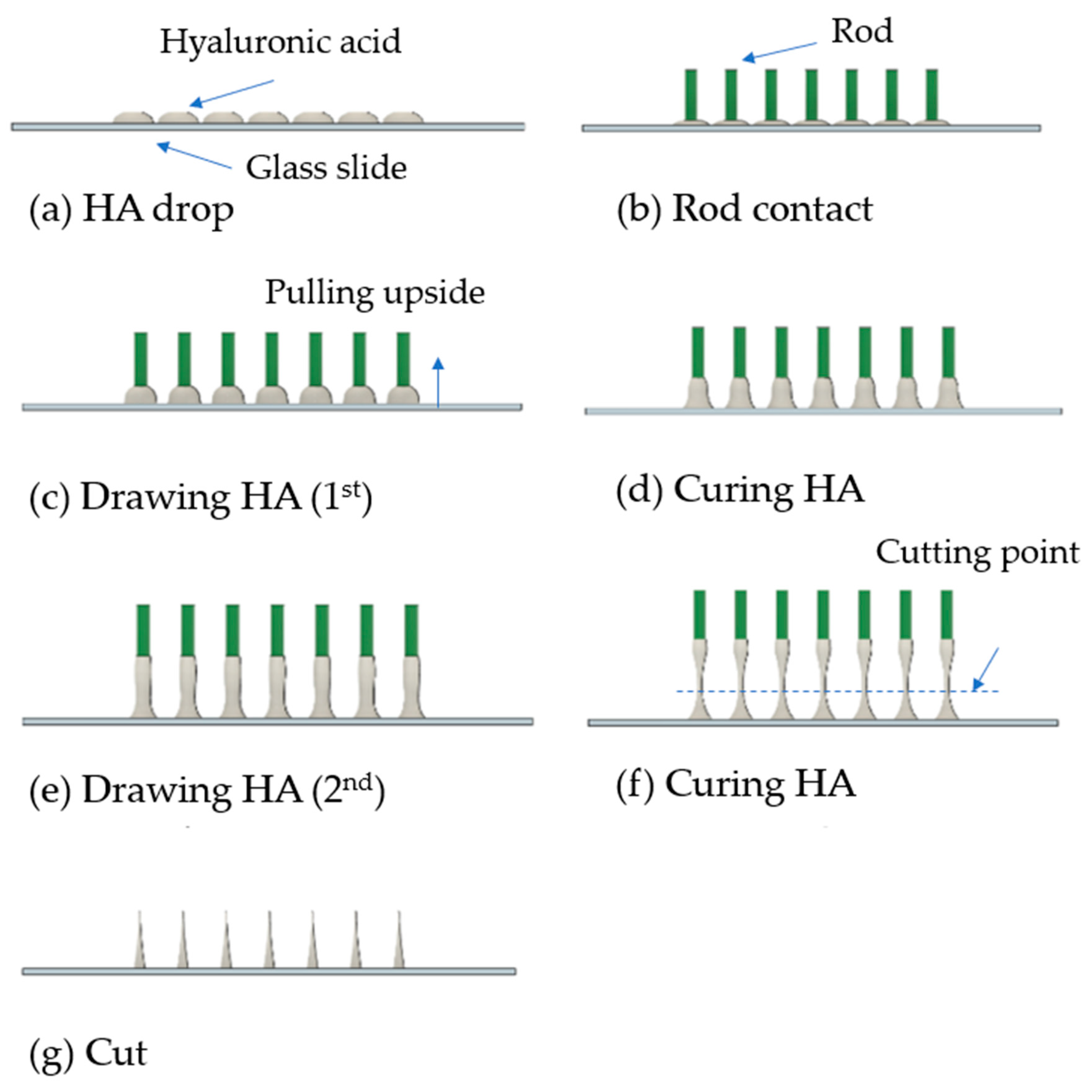
2.2. Design of Drawing Lithography Equipment
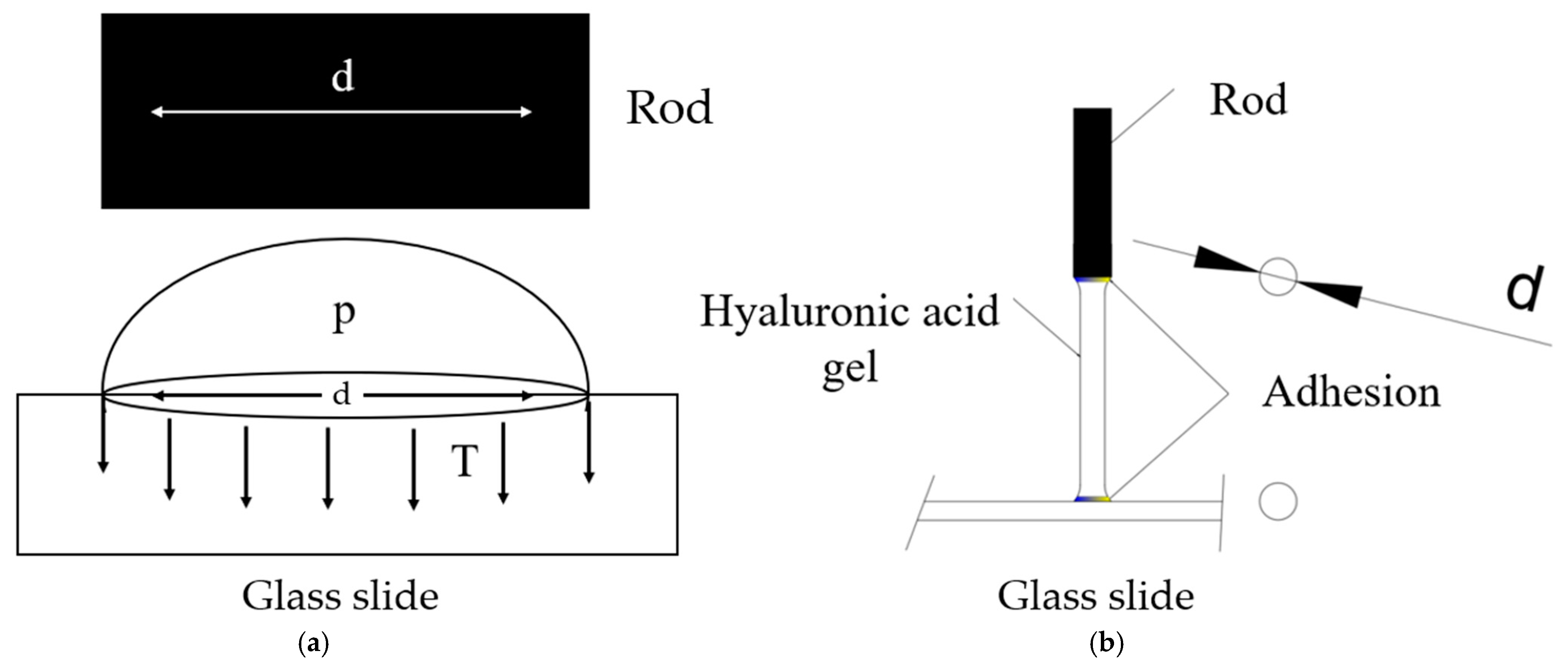
2.3. Mechanical Analysis of Surface Tension
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Liquid Droplet Test
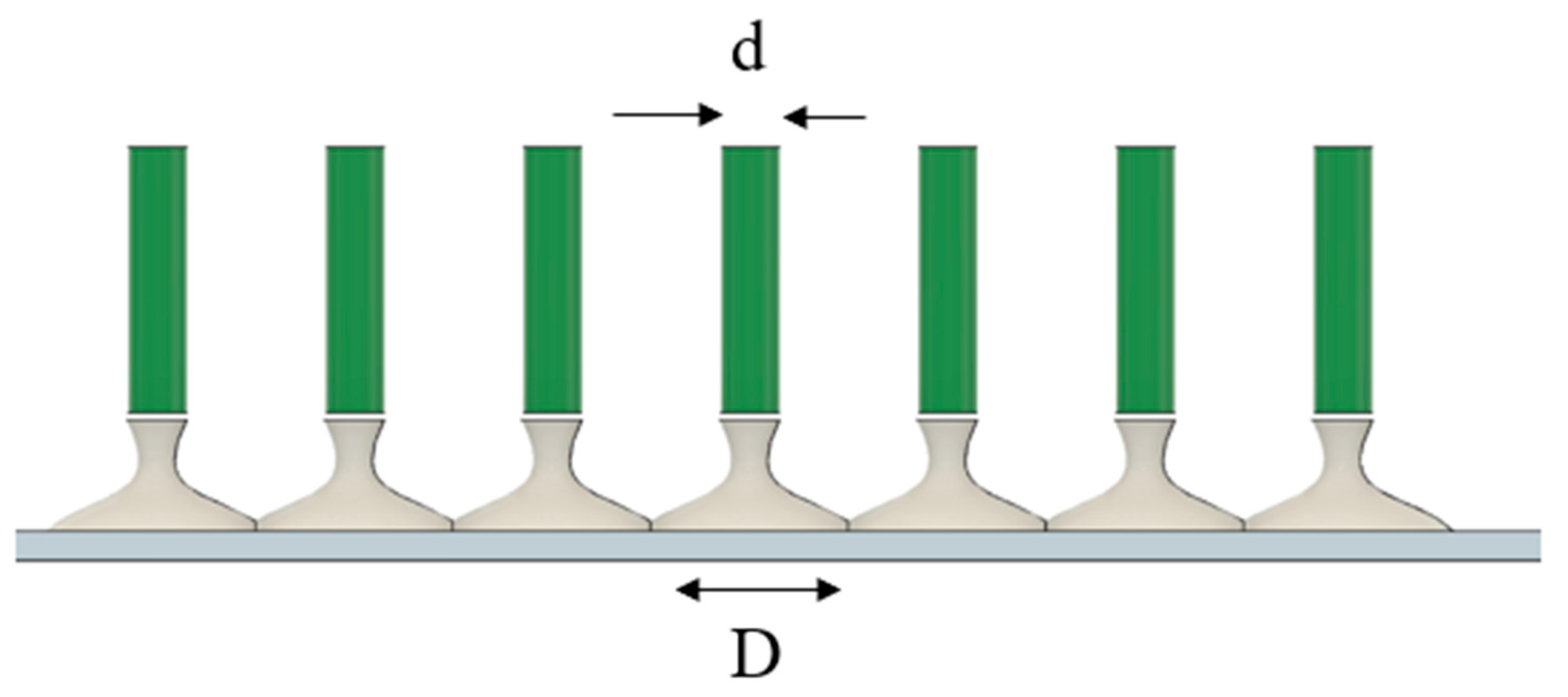
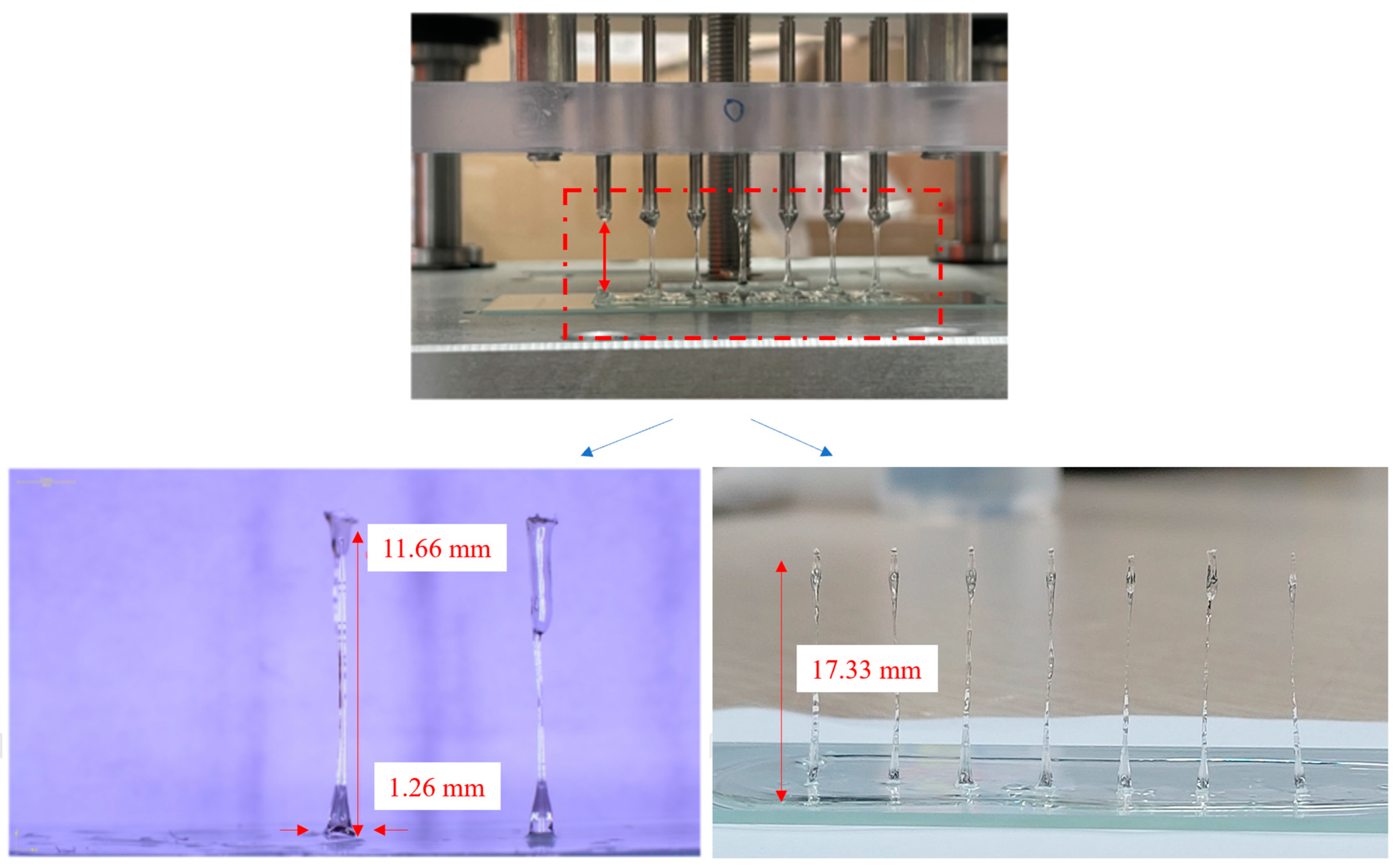
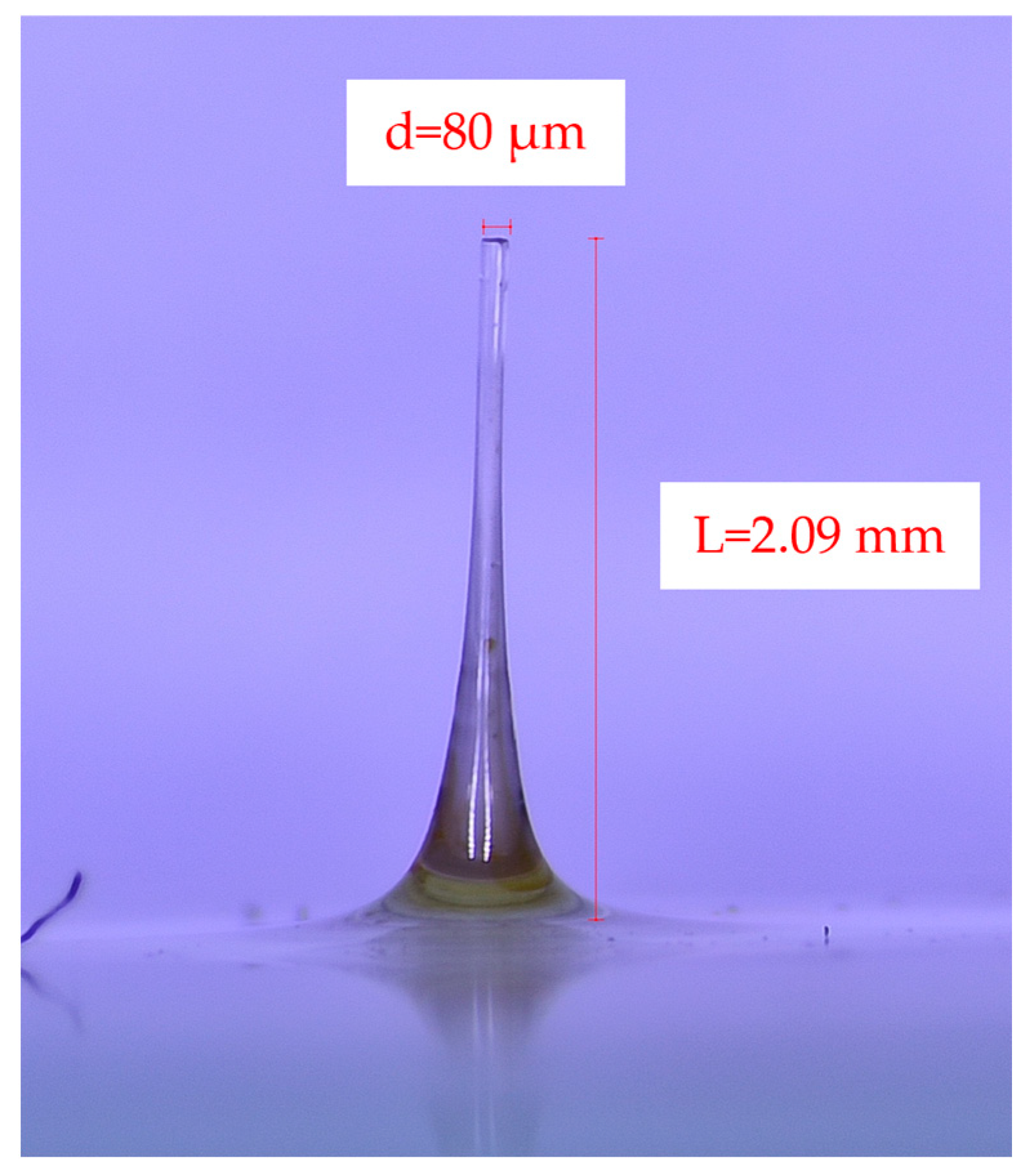
3.2. Unidirectional and Bidirectional Drawing Technique
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Microneedles: Materials, Fabrication, and Biomedical Applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2023, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, N.; Ashraf, M.W.; Tayyaba, S. A Review on Solid Microneedles for Biomedical Applications. J. Pharm. Innov. 2022, 17, 1464–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, K.M.; Rad, Z.F. Sampling Dermal Interstitial Fluid Using Microneedles: A Review of Recent Developments in Sampling Methods and Microneedle-Based Biosensors. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-H.; Jin, S.-G. Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Current Trends and Fabrication. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Ahmad, R.; Khan, H.; Arshad, M.S.; Rasekh, M.; Hussain, A.; Walsh, S.; Li, X.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z. Microneedle Coating Techniques for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, I.; Rai, V.K. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Microneedle Array: Recent Applications in Drug Delivery and Cosmetology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Lin, R.; Yao, M.; Han, Y.; Han, J. The Most Promising Microneedle Device: Present and Future of Hyaluronic Acid Microneedle Patch. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3087–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Peng, W.; Su, W.; Yi, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Guo, B.; Li, X. Delicate Assembly of Ultrathin Hydroxyapatite Nanobelts with Nanoneedles Directed by Dissolved Cellulose. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 4516–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, W.; Liang, L. Fabrication of a Ti Porous Microneedle Array by Metal Injection Molding for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, G.M. Porous Polymer Coatings on Metal Microneedles for Enhanced Drug Delivery. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Laffitte, Y.; Schmill, U.; Hu, W.; Kaddoura, M.; Blondeel, E.J.M.; Cui, B. Fabrication of Sharp Silicon Hollow Microneedles by Deep-Reactive Ion Etching Towards Minimally Invasive Diagnostics. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo-Martínez, Á.; Mallon, B.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Vora, L.K.; Anjani, Q.K.; Donnelly, R.F. Hollow microneedles: A perspective in biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Sun, J.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D. Microneedle System for Transdermal Drug and Vaccine Delivery: Devices, Safety, and Prospects. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 17, 1559325819878585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K.J.B. Dissolving Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Advances and Challenges. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 93, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, C.S.; Banga, A.K.J. Characterization of Solid Maltose Microneedles and Their Use for Transdermal Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Prow, T.W.; Crichton, M.L.; Jenkins, D.W.; Roberts, M.S.; Frazer, I.H.; Fernando, G.J.; Kendall, M.A. Dry-Coated Microprojection Array Patches for Targeted Delivery of Immunotherapeutics to the Skin. J. Control. Release 2009, 139, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Gao, Y. Controllable Coating of Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 41, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, R.; Singh, M.; Nguyen, H.X.; Jonnalagadda, S. A Review of Recent Advances in Microneedle Technology for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, M.; Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. A Review of 3D-Printing of Microneedles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Jung, H. Drawing Lithography for Microneedles: A Review of Fundamentals and Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7309–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiji, S.; Dangol, M.; Jung, H. A Patchless Dissolving Microneedle Delivery System Enabling Rapid and Efficient Transdermal Drug Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.W.; Nam, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Min, H.S.; Yang, H.; Cho, Y.; Hwang, S.; Son, J.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Minocycline-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle: Innovation in Local Minocycline Delivery for Periodontitis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 349, 122976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Yamagishi, R.; Ando, M.; Hachikubo, Y.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Oshima, M.; Goo, S.L.; Hayashi, H.; et al. Fabrication and Evaluation of Dissolving Hyaluronic Acid Microneedle Patches for Minimally Invasive Transdermal Drug Delivery by Nanoimprinting. Gels 2025, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

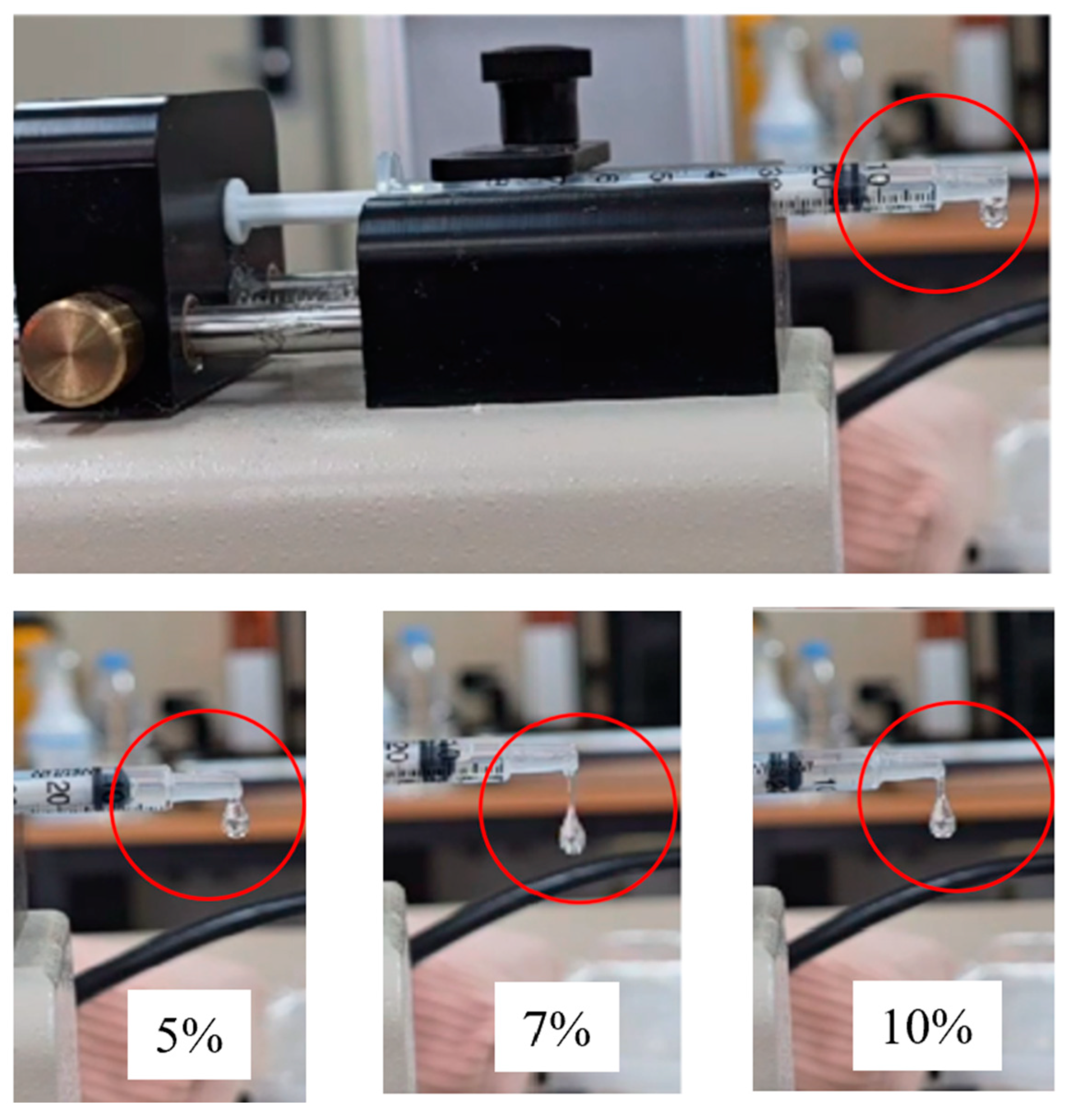
| 5% | 7% | 10% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (cp) | 4333 | 25,330 | 249,700 |
| Drop falling time (sec) | 16 | 59 | 59 |
| Drop mass (mg) | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.-K.; Lee, K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, B. Process of Fabricating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Milli-to-Microneedles Using the Bi-Directional Drawing Method. Micro 2025, 5, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020022
Kang J-K, Lee K, Choi Y, Kim S-G, Kim B. Process of Fabricating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Milli-to-Microneedles Using the Bi-Directional Drawing Method. Micro. 2025; 5(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Joon-Koo, Kihak Lee, Yein Choi, Se-Gie Kim, and Bonghwan Kim. 2025. "Process of Fabricating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Milli-to-Microneedles Using the Bi-Directional Drawing Method" Micro 5, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020022
APA StyleKang, J.-K., Lee, K., Choi, Y., Kim, S.-G., & Kim, B. (2025). Process of Fabricating Hyaluronic Acid-Based Milli-to-Microneedles Using the Bi-Directional Drawing Method. Micro, 5(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020022








