Implementation of Automatic Segmentation Framework as Preprocessing Step for Radiomics Analysis of Lung Anatomical Districts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
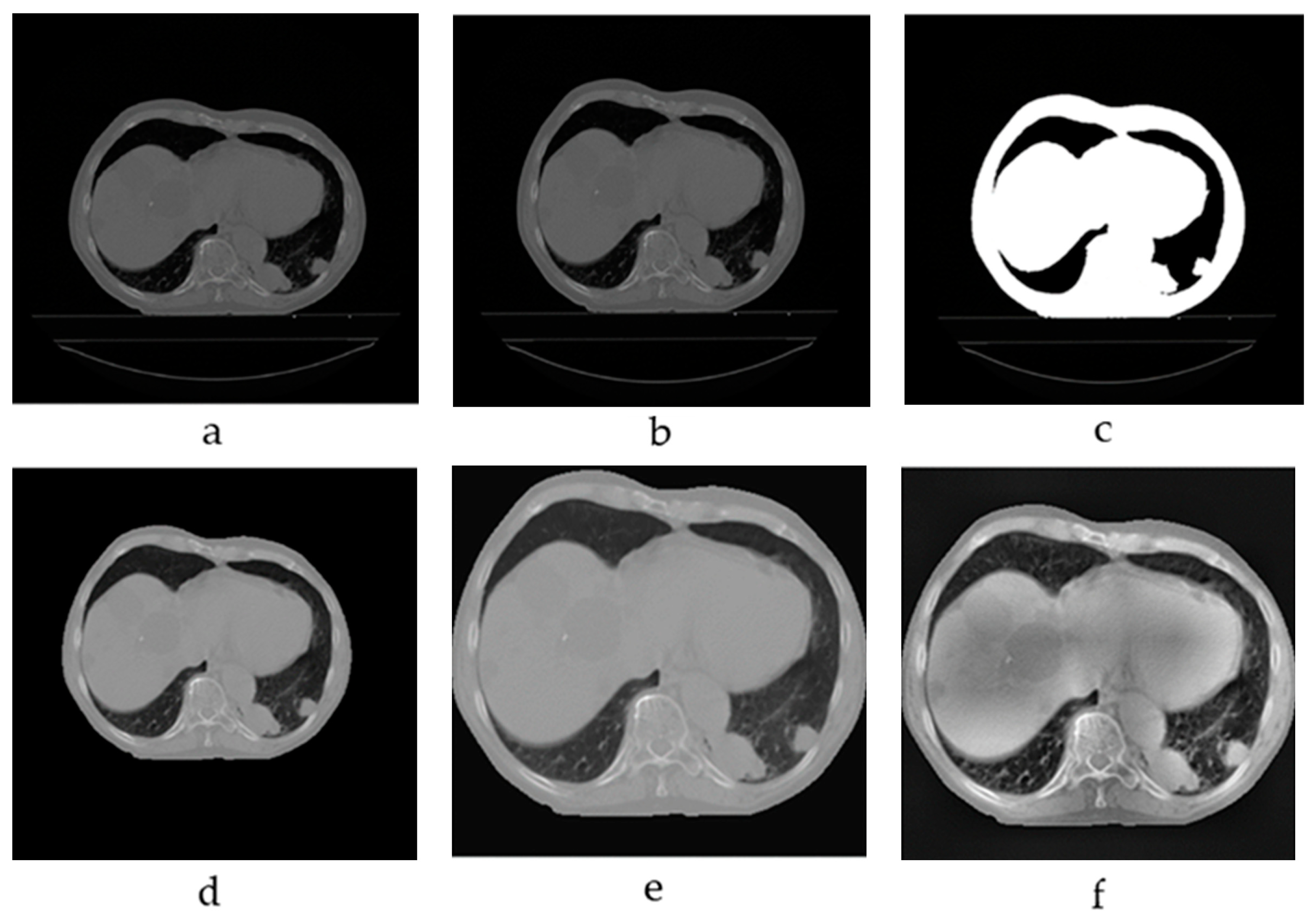
2.1. Image Preprocessing
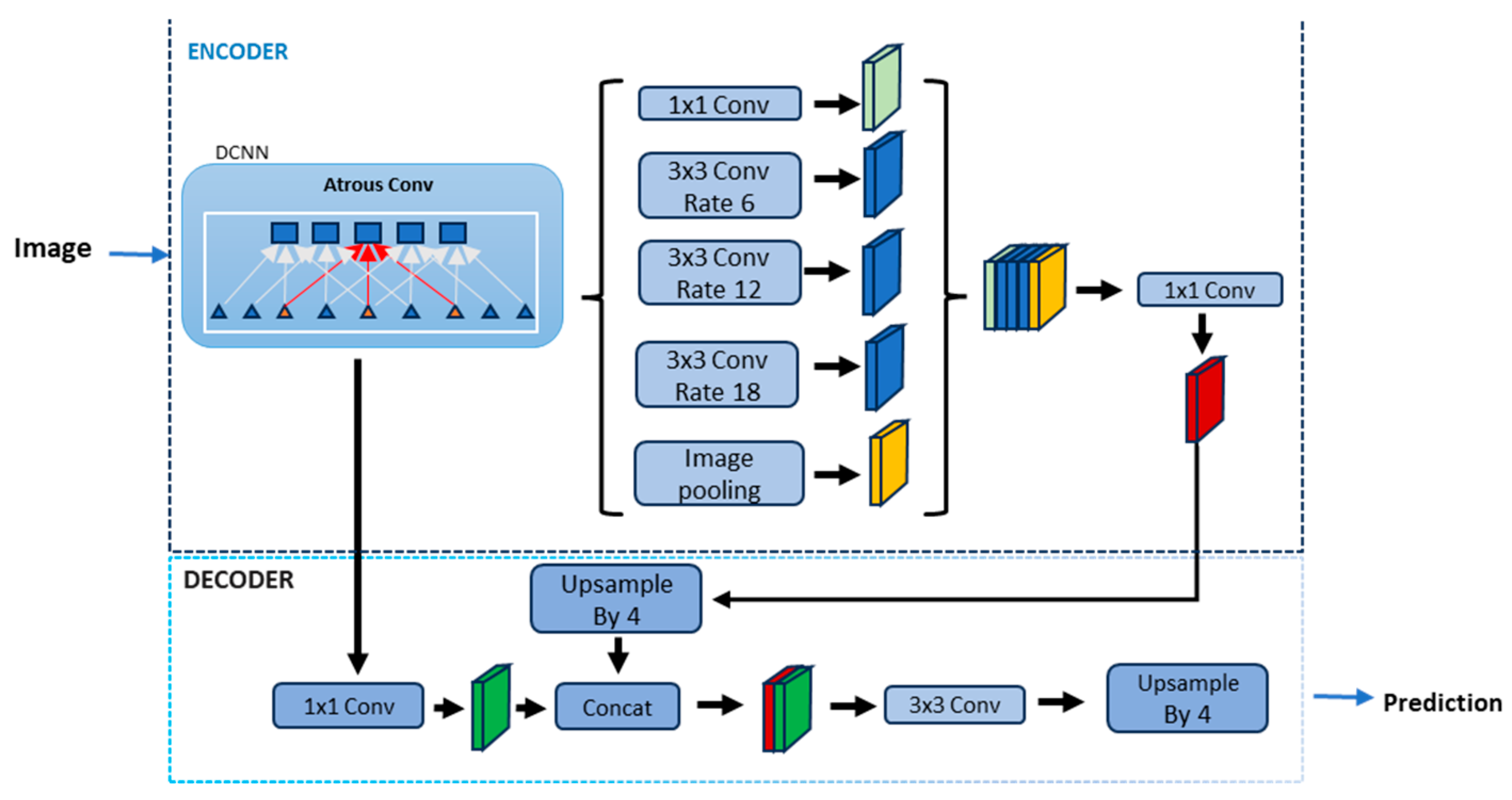
2.2. Lung Segmentation Using Deep Learning and Transfer Learning
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Loss Function and Evaluation Metrics
2.5. Dataset Introduction
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Preprocessing Results
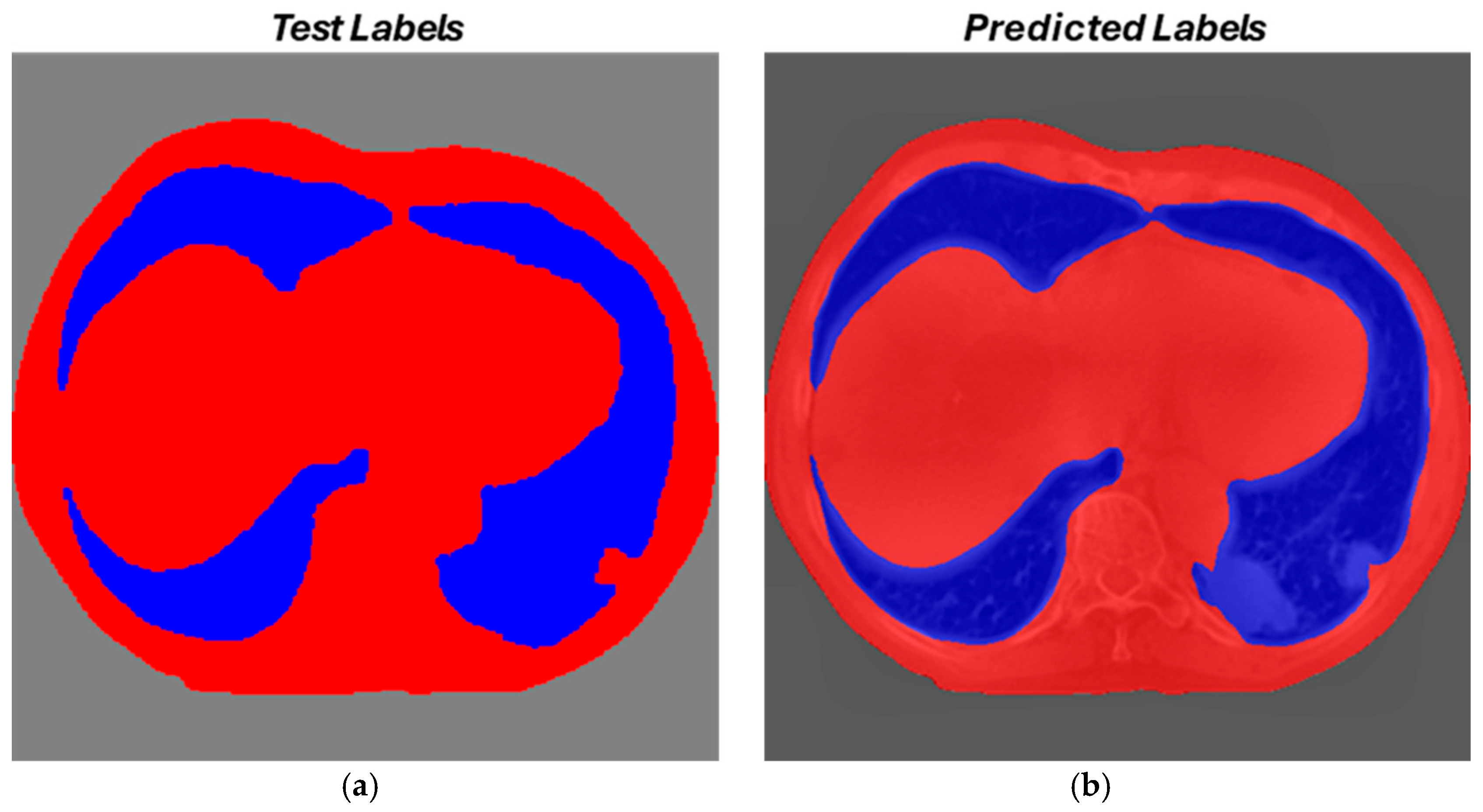
3.3. Segmentation Results
Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Final Considerations on Segmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From Qualitative to Quantitative Imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in Medical Imaging—“How-to” Guide and Critical Reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piorkowski, A.; Obuchowicz, R.; Najjar, R. Redefining Radiology: A Review of Artificial Intelligence Integration in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Mithun, S.; Sherkhane, U.B.; Dwivedi, P.; Puts, S.; Osong, B.; Traverso, A.; Purandare, N.; Wee, L.; Rangarajan, V.; et al. Emerging Role of Quantitative Imaging (Radiomics) and Artificial Intelligence in Precision Oncology. Open Explor. 2023, 4, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; De Jong, E.E.C.; Van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The Bridge between Medical Imaging and Personalized Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A. Challenges and Limitations in Applying Radiomics to PET Imaging: Possible Opportunities and Avenues for Research. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 179, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Jin, Q. Radiomics and Its Feature Selection: A Review. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.T.; Li, B.; Teng, X.Z.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.R.; Sheng, J.B.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Radiomics Study in Cancer: The Role of Feature Engineering and Modeling. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, A.; Stirling, D.; Field, M.; Ros, M.; Ritz, C.; Carolan, M.; Holloway, L.; Miller, A.A. The Role of Deep Learning and Radiomic Feature Extraction in Cancer-Specific Predictive Modelling: A Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, A.; Stefano, A.; Coronnello, C.; Russo, G.; Vernuccio, F.; Cannella, R.; Salvaggio, G.; Lagalla, R.; Barone, S. Radiomics: A New Biomedical Workflow to Create a Predictive Model. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1248, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, G.; Bini, F.; Russo, G.; Comelli, A.; Marinozzi, F.; Stefano, A. MatRadiomics: A Novel and Complete Radiomics Framework, from Image Visualization to Predictive Model. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamnitsas, K.; Ledig, C.; Newcombe, V.F.J.; Simpson, J.P.; Kane, A.D.; Menon, D.K.; Rueckert, D.; Glocker, B. Efficient Multi-Scale 3D CNN with Fully Connected CRF for Accurate Brain Lesion Segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 36, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressem, K.K.; Adams, L.C.; Erxleben, C.; Hamm, B.; Niehues, S.M.; Vahldiek, J.L. Comparing Different Deep Learning Architectures for Classification of Chest Radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primakov, S.P.; Ibrahim, A.; van Timmeren, J.E.; Wu, G.; Keek, S.A.; Beuque, M.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Lavrova, E.; Scrivener, M.; Sanduleanu, S.; et al. Automated Detection and Segmentation of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Computed Tomography Images. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens-Helthineers Instructions for Use—AI-Rad Companion (Pulmonary) VA31. Available online: https://content.doclib.siemens-healthineers.com/rest/v1/view?document-id=930870 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Siemens Helthineers AI-Rad Companion Chest CT VA20 Whitepaper—April 2022. Available online: https://marketing.webassets.siemens-healthineers.com/d4d8b5ba29e6d49e/e8eba575c238/siemens-healthineers-dh-AI-rad_chest_ct_whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, 3DV 2016, Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman, M.; Arabnia, H.R.; Rasheed, K. A Review of Deep Transfer Learning and Recent Advancements. Technologies 2023, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Y.; Alsheikhy, A.A.; Shawly, T.; Lahza, H. Medical Images Segmentation for Lung Cancer Diagnosis Based on Deep Learning Architectures. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudoukhani, N.; Elberrichi, Z.; Oulladji, L.; Dif, N. New Attention-Gated Residual Deep Convolutional Network for Accurate Lung Segmentation in Chest x-Rays. Evol. Syst. 2024, 15, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M.; Bourisly, A.K.; Prakash, N.B.; Sumithra, M.G.; Acharya, U.R. Automated Semantic Lung Segmentation in Chest CT Images Using Deep Neural Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 15343–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayed, M.E.; Islam, S.M.S.; Niha, S.I.; Jim, J.R.; Kabir, M.M.; Mridha, M.F. Deep Learning for Medical Image Segmentation: State-of-the-Art Advancements and Challenges. Inf. Med. Unlocked 2024, 47, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11211, pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahni, A.A.; Mohamed Fuzaie, M.F.; Al Irr, O.I. Automated Bed Detection and Removal from Abdominal CT Images for Automatic Segmentation Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, IECBES 2018—Proceedings, Sarawak, Malaysia, 3–6 December 2018; pp. 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanagavarapu, S.; Sridhar, S.; Gopal, T.V. COVID-19 Identification in CLAHE Enhanced CT Scans with Class Imbalance Using Ensembled ResNets. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference, IEMTRONICS 2021—Proceedings, Toronto, ON, Canada, 21–24 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaalouk, A.M.; Ebrahim, G.A.; Mohamed, H.K.; Hassan, H.M.; Zaalouk, M.M.A. A Deep Learning Computer-Aided Diagnosis Approach for Breast Cancer. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.N.; Lee, C.C.; Liang, C.M.; Pao, S.I.; Huang, K.H.; Lin, K.F. General Deep Learning Model for Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Cavalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding Tumour Phenotype by Noninvasive Imaging Using a Quantitative Radiomics Approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.S.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lombardo, E.; Huang, L.; Avanzo, M.; Fanetti, G.; Franchin, G.; Zschaeck, S.; Weingärtner, J.; Belka, C.; Riboldi, M.; et al. Comparison of Deep Learning Networks for Fully Automated Head and Neck Tumor Delineation on Multi-Centric PET/CT Images. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, G.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zeng, W.; Guo, J.; Tang, W. Automatic Classification and Segmentation of Multiclass Jaw Lesions in Cone-Beam CT Using Deep Learning. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2024, 53, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Huber, S.; Arora, S.; Ze’evi, T.; Haider, S.P.; Kucukkaya, A.S.; Iseke, S.; Kuhn, T.N.; Gebauer, B.; Michallek, F.; et al. Automated MRI Liver Segmentation for Anatomical Segmentation, Liver Volumetry, and the Extraction of Radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 5056–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, A.M.; Heidenreich, J.F.; Metz, C.; Veldhoen, S.; Bley, T.A.; Wech, T. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation of the Lung in MR-Images Acquired by a Stack-of-Spirals Trajectory at Ultra-Short Echo-Times. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gite, S.; Mishra, A.; Kotecha, K. Enhanced Lung Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 22839–22853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Site | Patients | Type of Cancer | Images | Resolution [Pixel] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | 422 | Non-Small cells | 47,919 | 512 × 512 |
| Total 2D Images | Training | Validation | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 47,919 | 29,187 | 9312 | 9420 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefano, A.; Bini, F.; Lauciello, N.; Pasini, G.; Marinozzi, F.; Russo, G. Implementation of Automatic Segmentation Framework as Preprocessing Step for Radiomics Analysis of Lung Anatomical Districts. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 2309-2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040125
Stefano A, Bini F, Lauciello N, Pasini G, Marinozzi F, Russo G. Implementation of Automatic Segmentation Framework as Preprocessing Step for Radiomics Analysis of Lung Anatomical Districts. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(4):2309-2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040125
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefano, Alessandro, Fabiano Bini, Nicolò Lauciello, Giovanni Pasini, Franco Marinozzi, and Giorgio Russo. 2024. "Implementation of Automatic Segmentation Framework as Preprocessing Step for Radiomics Analysis of Lung Anatomical Districts" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 4: 2309-2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040125
APA StyleStefano, A., Bini, F., Lauciello, N., Pasini, G., Marinozzi, F., & Russo, G. (2024). Implementation of Automatic Segmentation Framework as Preprocessing Step for Radiomics Analysis of Lung Anatomical Districts. BioMedInformatics, 4(4), 2309-2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4040125










