Harnessing Immunoinformatics for Precision Vaccines: Designing Epitope-Based Subunit Vaccines against Hepatitis E Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
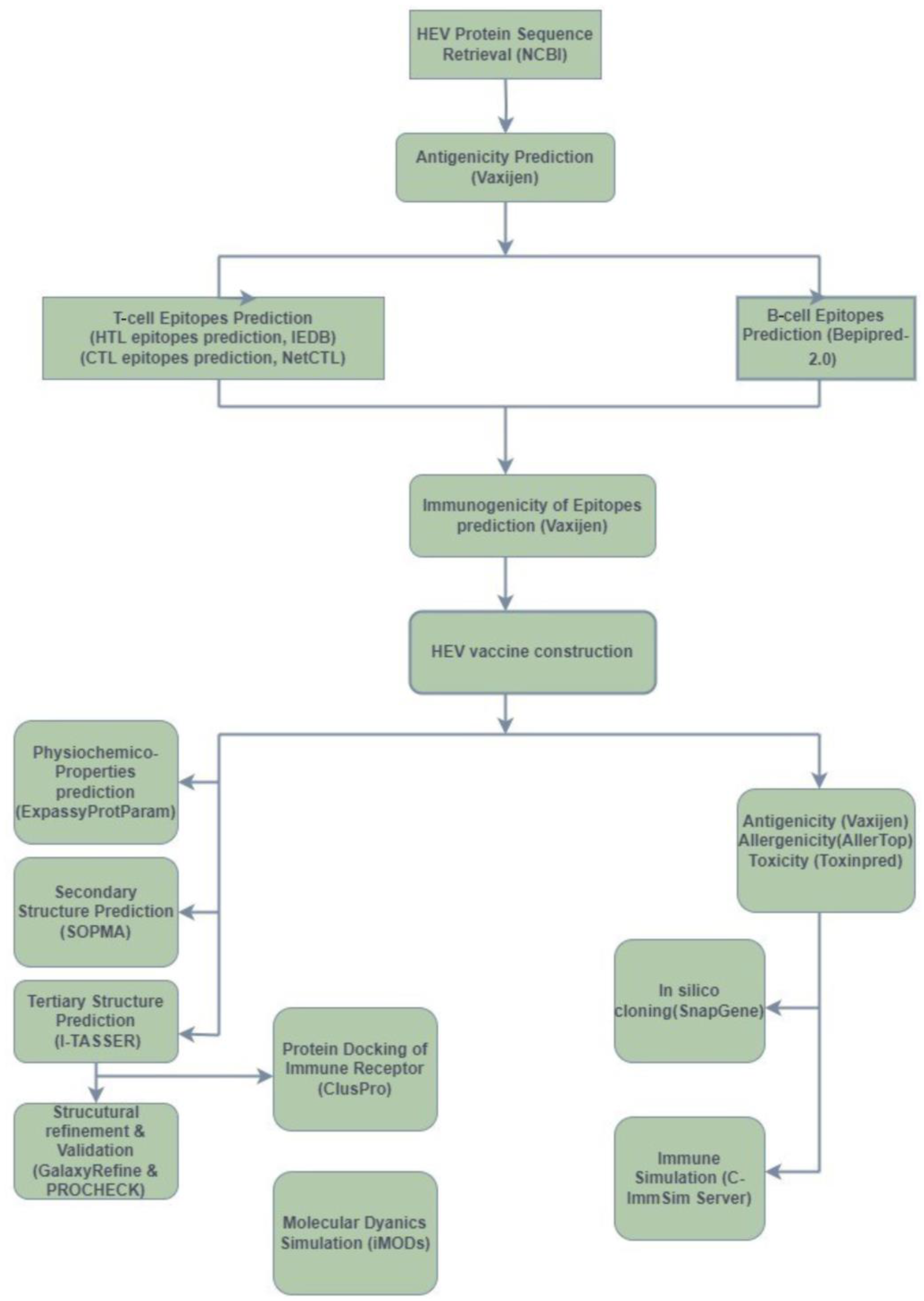
2. Methods
2.1. Retrieval of HEV Protein Sequences
2.2. Antigenicity Testing
2.3. Epitope Predictions
2.3.1. T-Cell Epitope Predictions
2.3.2. B-Cell Epitope Predictions
2.4. Peptide Immunogenicity Predictions
2.5. HEV Vaccine Construction
2.6. Different Physicochemical Properties Prediction of Vaccine Constructs
2.7. Predictions of the Secondary Structures for Vaccine Constructs
2.8. Predictions and Refinement of the Tertiary Structures for Vaccine Constructs
2.9. Predictions of Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Toxicity
2.10. Protein Docking of the Immune Receptor
2.11. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
2.12. In Silico Cloning
2.13. Immune Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Protein Targets
3.2. Predictions of T-Cell Epitopes
3.3. Predictions of B-Cell Epitopes
3.4. HEV Vaccine Sequence Construction
3.5. Physicochemical Properties of the Vaccine
3.6. Predictions of Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Toxicity
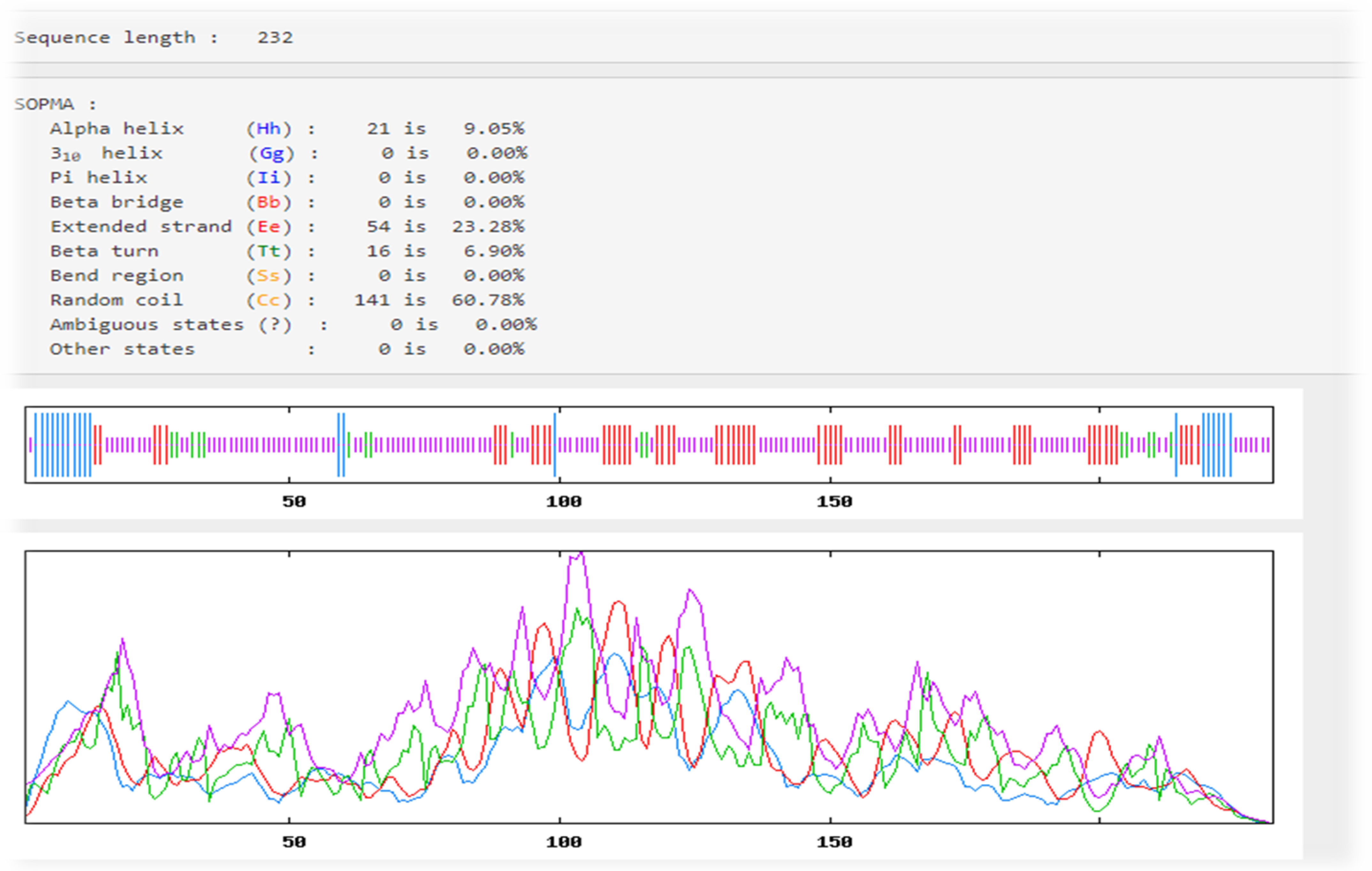
3.7. Predictions of the Secondary Structures
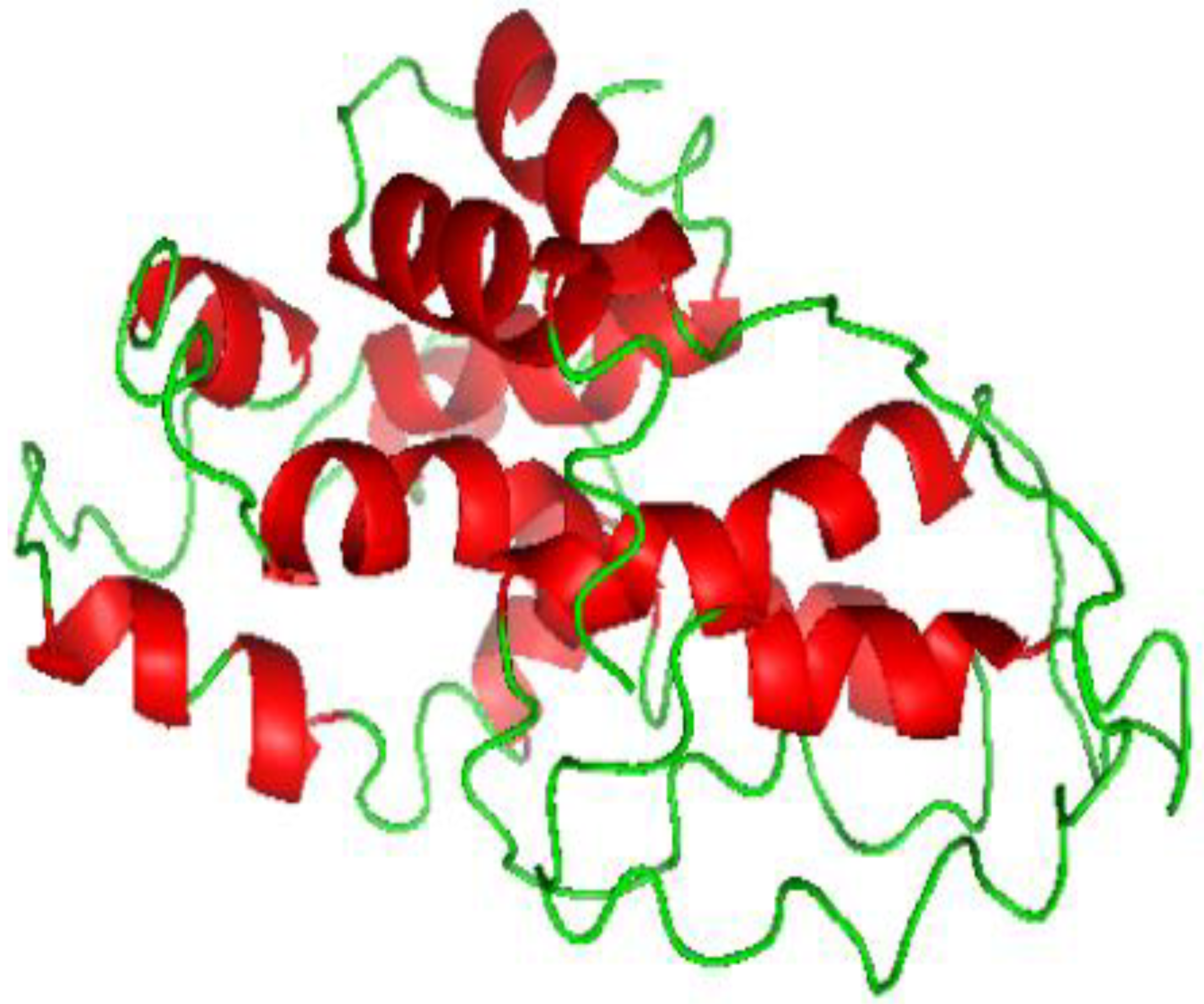
3.8. Three-Dimensional Structure Prediction
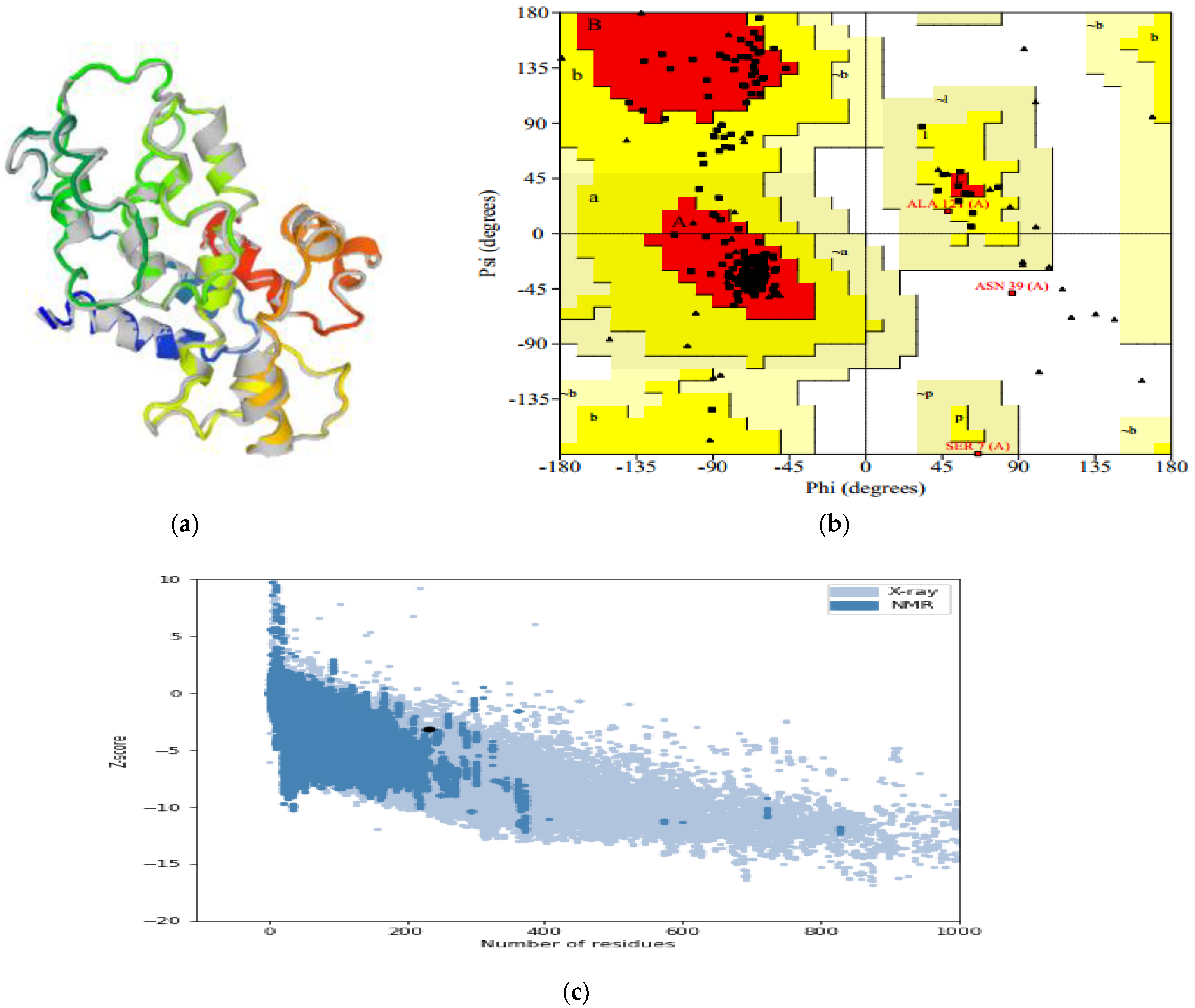
3.9. Three-Dimensional Refinement and Validation
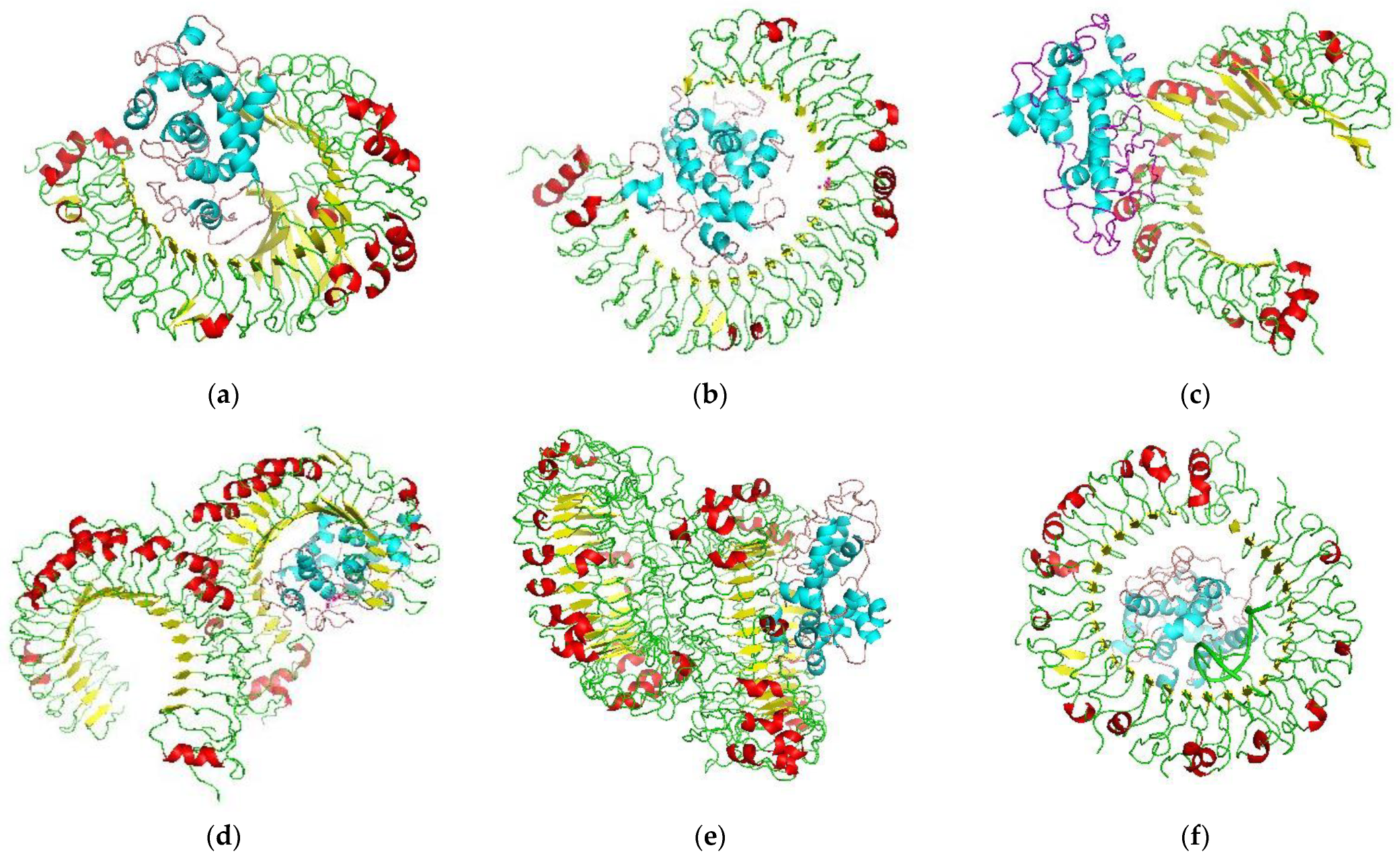
3.10. Protein–Protein Docking of the Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) and Vaccine Construct
3.11. Dynamics Simulation
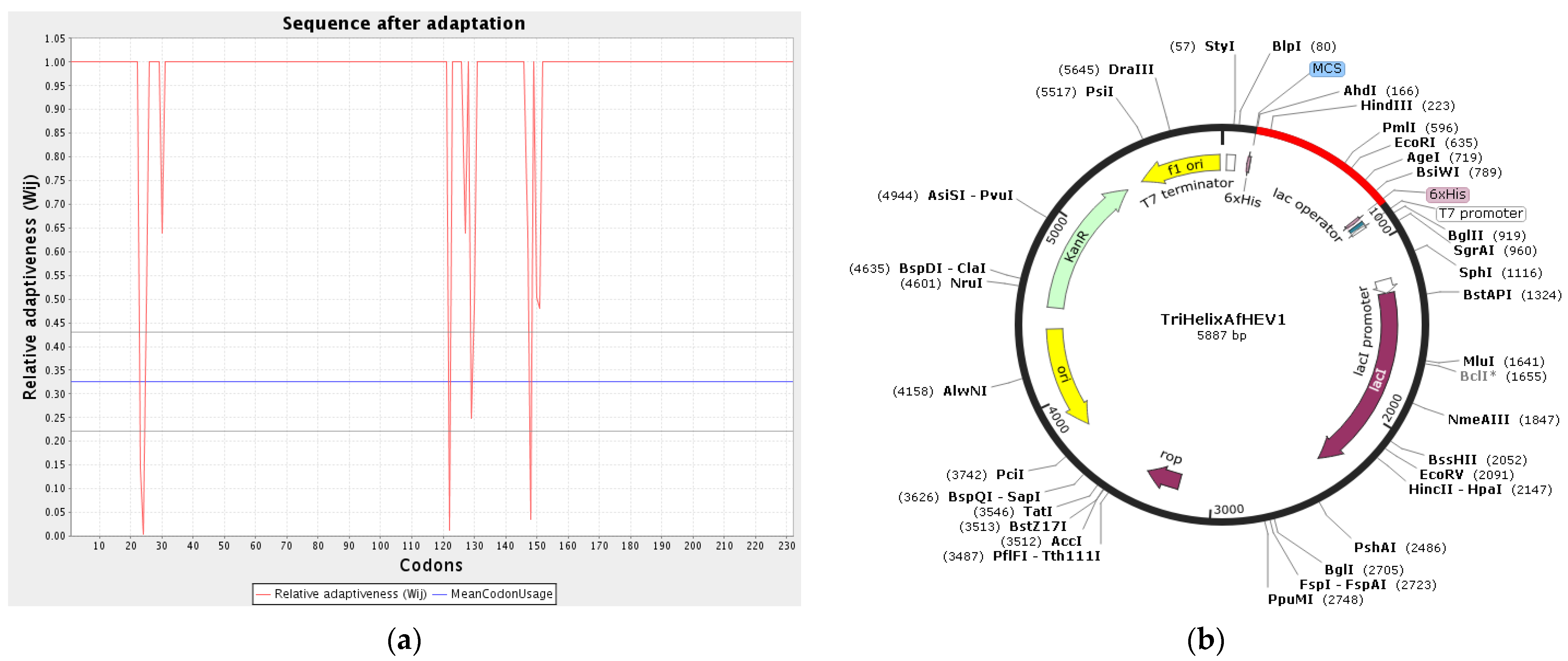
3.12. Codon Adaptation and In Silico Cloning
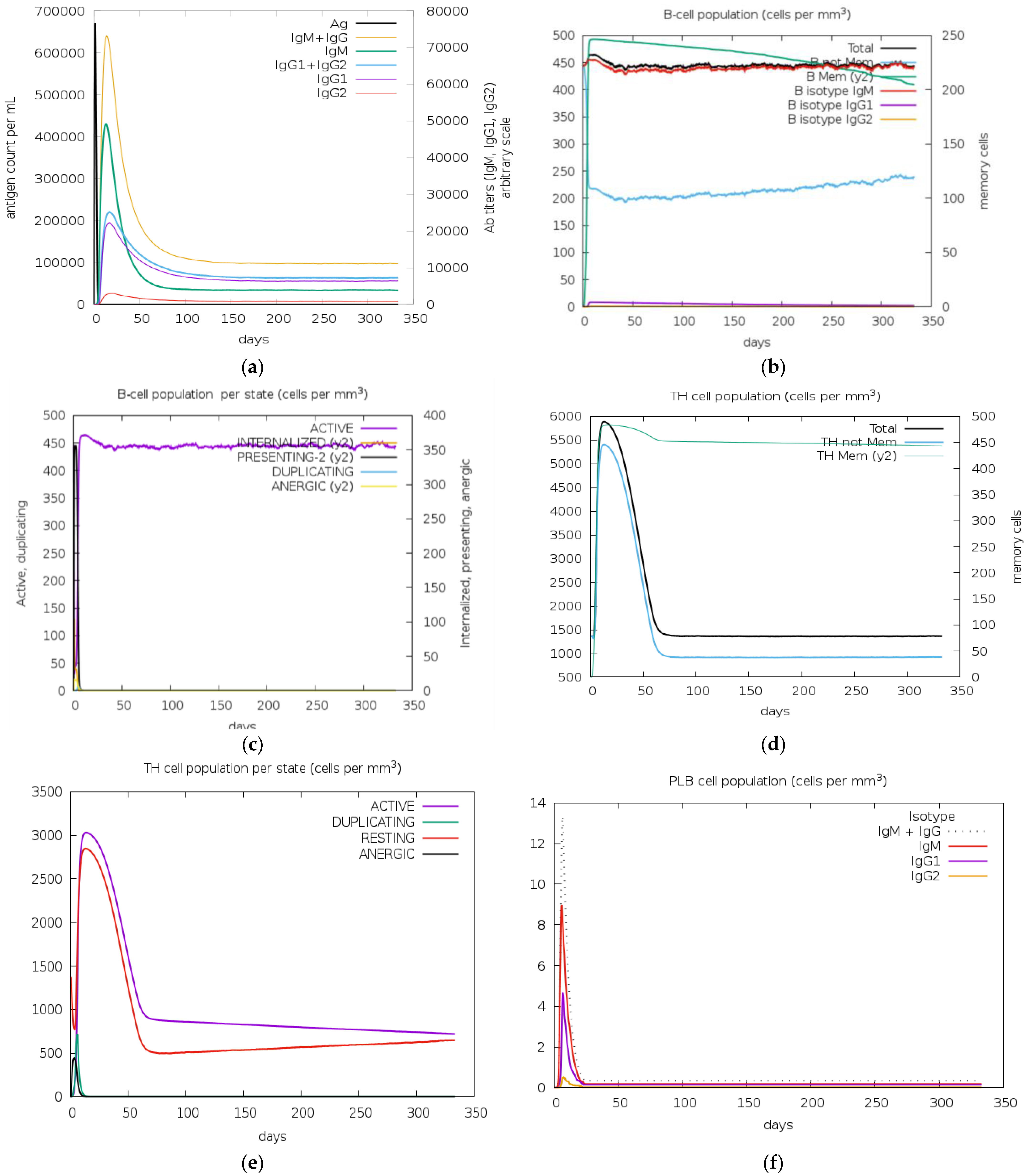
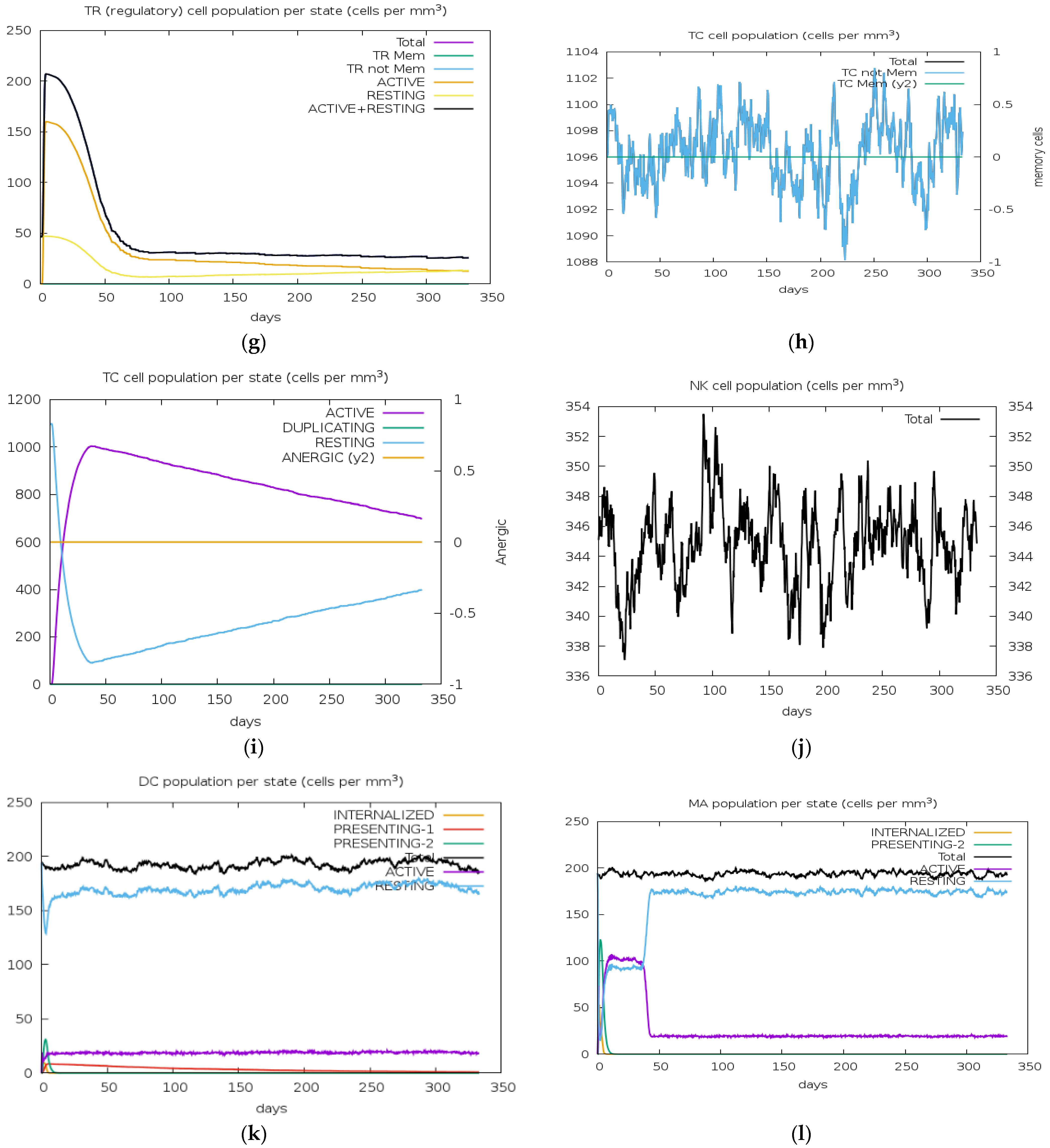
3.13. Immune Simulation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cainelli, F. Liver diseases in developing countries. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Dalton, H.R.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E virus infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 116–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N. Lessons from hepatitis E vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelabu, O.A.; Chuks Iweriebor, B.; Nwodo, U.U.; Obi, L.C.; Okoh, A.I. Incidence and Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus from Swine in Eastern Cape, South Africa. Adv. Virol. 2017, 2017, 1073253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshadpour, F.; Taherkhani, R.; Makvandi, M.; Rajabi Memari, H.; Samarbafzadeh, A.R. Codon Optimized Expression and Purification of Truncated ORF2 Protein of Hepatitis E Virus in Escherichia coli. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, 11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Ding, Q.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, N.S. Hepatitis E: Discovery, global impact, control and cure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7030–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Xia, J. Hepatitis E virus infection during pregnancy. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriarirad, R.; Erfani, A.; Rastegarian, M.; Zeighami, A.; Arefkhah, N.; Ghorbani, F.; Sarvari, J.; Sarkari, B. Seroprevalence of anti-hepatitis E antibodies and antigens among HIV-infected patients in Fars Province, southern Iran. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, R.; Farshadpour, F.; Makvandi, M. Design and production of a multiepitope construct derived from hepatitis E virus capsid protein. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Nelson, K.E.; Panzner, U.; Kasture, Y.; Labrique, A.B.; Wierzba, T.F. A systematic review of the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaço, J.G.; Gardinali, N.R.; de Mello, V.D.M.; Leal, M.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Pinto, M.A. Hepatitis E: Update on Prevention and Control. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 10, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, E.; Rappuoli, R. Vaccines for the future: Learning from human immunology. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patronov, A.; Doytchinova, I. T-cell epitope vaccine design by immunoinformatics. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, M.; Karkhah, A.; Nouri, H.R. Development of a multi-epitope peptide vaccine inducing robust T cell responses against brucellosis using immunoinformatics based approaches. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, Z.; Karim, M.M.; Sen, M.K.; Adhikari, U.K. Structural Basis and Designing of Peptide Vaccine using PE-PGRS Family Protein of Mycobacterium ulcerans–An Integrated Vaccinomics Approach. bioRxiv 2019, 795146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. Hepatitis E: An overview and recent advances in vaccine research. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, R.; Farshadpour, F. A new strategy for development of hepatitis E vaccine: Epitope-based vaccines. Pathog. Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, e933. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis E. 27 July 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, R.; Mahajan, S.; Overton, J.A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Martini, S.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Sette, B.P. The immune Epitope Database (IEDB). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D339–D343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lamberth, K.; Buus, S.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. NetCTL-1.2: Large-scale validation of methods for cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 31, 424. [Google Scholar]
- Jespersen, M.C.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-2.0: Improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W24–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Fundamentals and Methods for T- and B-Cell Epitope Prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 7, 2314–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peele, K.A.; Srihansa, T.; Krupanidhi, S.; Ayyagari, V.S.; Venkateswarulu, T.C. Design of multi-epitope vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2: A in-silico study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1, 0739–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipo, E.K.; Ajayi, A.F.; Onile, O.S.; Ariyo, O.E.; Jimah, E.M.; Ezediuno, L.O.; Adebayo, O.I.; Adebayo, E.T.; Oguntomi, A.S.; Akindiya, O.E.; et al. Designing a conserved peptide-based subunit vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatics approach. In Silico Pharmacol. 2021, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.M. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Deléage, G. ALIGNSEC: Viewing protein secondary structure predictions within large multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3991–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Alauddin, S.M.; Al Amin, M.; Nur, S.M.; Mannan, A. In Silico Molecular Characterization of Cysteine Protease YopT from Yersinia pestis by Homology Modeling and Binding Site Identification. Drug Target Insights 2014, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP-a server for in silico prediction of allergens. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein-protein docking. Nat Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JR López-Blanco, J.I.; Aliaga, E.S.; Quintana-Ortí, P. iMODS. Chacón. Internal coordinates normal mode analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W271–W276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Münch, R.; Nörtemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, O.; Lund, O.; Bernaschi, M.; Castiglione, F. Computational Immunology Meets Bioinformatics: The Use of Prediction Tools for Molecular Binding in the Simulation of the Immune System 2010. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shey, R.A.; Ghogomu, S.M.; Esoh, K.K.; Nebangwa, N.D.; Shintouo, C.M.; Nongley, N.F.; Asa, B.F.; Ngale, F.N.; Vanhamme, L.; Souopgui, J. In-silico design of a multi-epitope vaccine candidate against onchocerciasis and related filarial diseases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Joshi, M.D.; Singhania, S.; Ramsey, K.H.; Murthy, A.K. Peptide Vaccine: Progress and Challenges. Vaccines 2014, 2, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, K.K.; Luke, G.A.; Knox, C.; Kumar, P.; Pletschke, B.I.; Singh, P.K.; Shukla, P. Vaccine and antibody production in plants: Developments and computational tools. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2018, 17, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Bing, Z.; Guan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Development of new hepatitis E vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashair, A.A.; Yassir, A.; Khoubieb, A.; Elsideeq, E.M. Identification of Novel Multi Epitopes Vaccine against the Capsid Protein (ORF2) of Hepatitis E Virus. Am. J. Infect. Dis. Microbiol. 2019, 7, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Bari, A.; Adeel, M.M.; Maryam, A.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Du, X.; Muneer, I.; Ahmad, H.I.; Wang, J. Peptide vaccine against chikungunya virus: Immuno-informatics combined with molecular docking approach. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.P.; Sharma, M.; Tripathy, A.S. Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in Hepatitis E Recovered Individuals, 1–30 Years Post Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiliang, M.; Chengwei, W.; Xinru, M.; Yi, H. Cell Dysfunction Associated with Aging and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Amanna, I.J.; Slifka, M.K. Contributions of humoral and cellular immunity to vaccine-induced protection in humans. Virology 2011, 411, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J.E. Prevention of Fetal and Early Life Infections Through Maternal–Neonatal Immunization. Infect. Dis. Fetus Newborn 2011, 1, 1212–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Livingston, B.; Crimi, C.; Newman, M.; Higashimoto, Y.; Appella, E.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A. A Rational Strategy to Design Multiepitope Immunogens Based on Multiple Th Lymphocyte Epitopes. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5499–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezafat, N.; Karimi, Z.; Eslami, M.; Mohkam, M.; Zandian, S.; Ghasemi, Y. Designing an efficient multi-epitope peptide vaccine against Vibrio cholerae via combined immunoinformatics and protein interaction based approaches. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 62, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Ueda, H.; Kitayama, A.; Kamiya, N.; Nagamune, T. Design of the linkers which effectively separate domains of a bifunctional fusion protein. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2001, 14, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenUrlPandey, R.K.; Narula, A.; Naskar, M.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, P.; Malik, R. Exploring dual inhibitory role of febrifugine analogues against Plasmodium utilizing structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.; Shen, W. Fusion Protein Linkers: Property, Design and Functionality. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2014, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, F.; Cohan, R.A.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Samimi, H.; Haghpanah, V. An in-silico approach to develop of a multi-epitope vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein. Res. Sq. 2020, 1, 0374. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipo, E.K.; Olufemi, S.E.; Ojo, T.O.; Adediran, D.A.; Idowu, A.F.; Idowu, U.A.; Onyeaka, H. Africa (COVID-19) Vaccine Technology Transfer: Where Are We? Life 2023, 13, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Pandey, R.K.; Khatoon, N.; Narula, A.; Mishra, A.; Prajapati, V.K. Exploring dengue genome to construct a multi-epitope based subunit vaccine by utilizing immunoinformatics approach to battle against dengue infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladipo, E.K.; Akindiya, O.E.; Oluwasanya, G.J.; Akanbi, G.M.; Olufemi, S.E.; Adediran, D.A.; Bamigboye, F.O.; Aremu, R.O.; Kolapo, K.T.; Oluwasegun, J.A.; et al. Bioinformatics analysis of structural protein to approach a vaccine candidate against Vibrio cholerae infection. Immunogenetics 2023, 75, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meza, B.; Ascencio, F.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.P.; Torres, J.; Angulo, C. A novel design of a multi-antigenic, multistage and multi-epitope vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: An in-silico approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladipo, E.K.; Ajayi, A.F.; Ariyo, O.E.; Onile, S.O.; Jimah, E.M.; Ezediuno, L.O.; Adebayo, O.I.; Adebayo, E.T.; Odeyemi, A.N.; Oyeleke, M.O.; et al. Exploration of surface glycoprotein to design a multi-epitope vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19. Inf. Med. Unlocked 2020, 21, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhovny, D.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. Efficient Unbound Docking of Rigid Molecules; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 2452, pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IT Desta, K.A.; Porter, B.; Xia, D.; Kozakov, S. Vajda Performance and its limits in rigid body protein-protein docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwagbemi, O.O.; Oladipo, E.K.; Dairo, E.O.; Ayeni, A.E.; Irewolede, B.A.; Jimah, E.M.; Oyewole, M.P.; Olawale, B.M.; Adegoke, H.M.; Ogunleye, A.J.; et al. Computational construction of a glycoprotein multi-epitope subunit vaccine candidate for old and new South-African SARS-CoV-2 virus strains. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 28, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J.A.; Chacón, P.; Abagyan, R. Predictions of protein flexibility: First-order measures. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2004, 56, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopéz-Blanco, J.R.; Garzón, J.I.; Chacón, P. iMod: Multipurpose normal mode analysis in internal coordinates. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Rao, K.K.; Balaji, P.V. Monomerization alters the dynamics of the lid region in Campylobacter jejuni CstII: An MD simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct Dyn. 2016, 34, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, F.; Obaid, A.; Ikram, A.; Janjua, H. Mutation-structure-function relationship based integrated strategy reveals the potential impact of deleterious missense mutations in autophagy related proteins on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A comprehensive informatics approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, P.; Padhi, A.K.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Tripathi, T. Design of a peptide-based subunit vaccine against novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb Pathog. 2020, 145, 104236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, A.; Longhi, R.; Peri, C.; Colombo, G. Peptides for immunological purposes: Design, strategies and applications. Amino Acids. 2013, 45, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherkhani, R.; Makvandi, M.; Farshadpour, F. Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using 2 truncated ORF2 proteins for detection of IgG antibodies against hepatitis E virus. Ann. Lab. Med. 2014, 34, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, S.B.; Nain, Z.; Khan, M.S.A.; Abdulla, F.; Tasmin, R.; Adhikari, U.K. Exploring Lassa Virus Proteome to Design a Multi-epitope Vaccine Through Immunoinformatics and Immune Simulation Analyses. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2089–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oladipo, E.K.; Dairo, E.O.; Bamigboye, C.O.; Ajayi, A.F.; Onile, O.S.; Ariyo, O.E.; Jimah, E.M.; Oyawoye, O.M.; Oloke, J.K.; Iwalokun, B.A.; et al. Harnessing Immunoinformatics for Precision Vaccines: Designing Epitope-Based Subunit Vaccines against Hepatitis E Virus. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 1620-1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030088
Oladipo EK, Dairo EO, Bamigboye CO, Ajayi AF, Onile OS, Ariyo OE, Jimah EM, Oyawoye OM, Oloke JK, Iwalokun BA, et al. Harnessing Immunoinformatics for Precision Vaccines: Designing Epitope-Based Subunit Vaccines against Hepatitis E Virus. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(3):1620-1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030088
Chicago/Turabian StyleOladipo, Elijah Kolawole, Emmanuel Oluwatobi Dairo, Comfort Olukemi Bamigboye, Ayodeji Folorunsho Ajayi, Olugbenga Samson Onile, Olumuyiwa Elijah Ariyo, Esther Moradeyo Jimah, Olubukola Monisola Oyawoye, Julius Kola Oloke, Bamidele Abiodun Iwalokun, and et al. 2024. "Harnessing Immunoinformatics for Precision Vaccines: Designing Epitope-Based Subunit Vaccines against Hepatitis E Virus" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 3: 1620-1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030088
APA StyleOladipo, E. K., Dairo, E. O., Bamigboye, C. O., Ajayi, A. F., Onile, O. S., Ariyo, O. E., Jimah, E. M., Oyawoye, O. M., Oloke, J. K., Iwalokun, B. A., Ajani, O. F., & Onyeaka, H. (2024). Harnessing Immunoinformatics for Precision Vaccines: Designing Epitope-Based Subunit Vaccines against Hepatitis E Virus. BioMedInformatics, 4(3), 1620-1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030088









