A Machine Learning-Empowered Workflow to Discriminate Bacillus subtilis Motility Phenotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacillus subtilis
2.2. Bioimaging Strategies
2.2.1. Motility Assay and Swarming Monitoring
2.2.2. Colony Shape Typization Assay
2.3. Computational Methods
2.3.1. Image Processing
2.3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3.3. Density-Based Spatial Clustering Applications with Noise (DBSCAN)
3. Results and Discussion
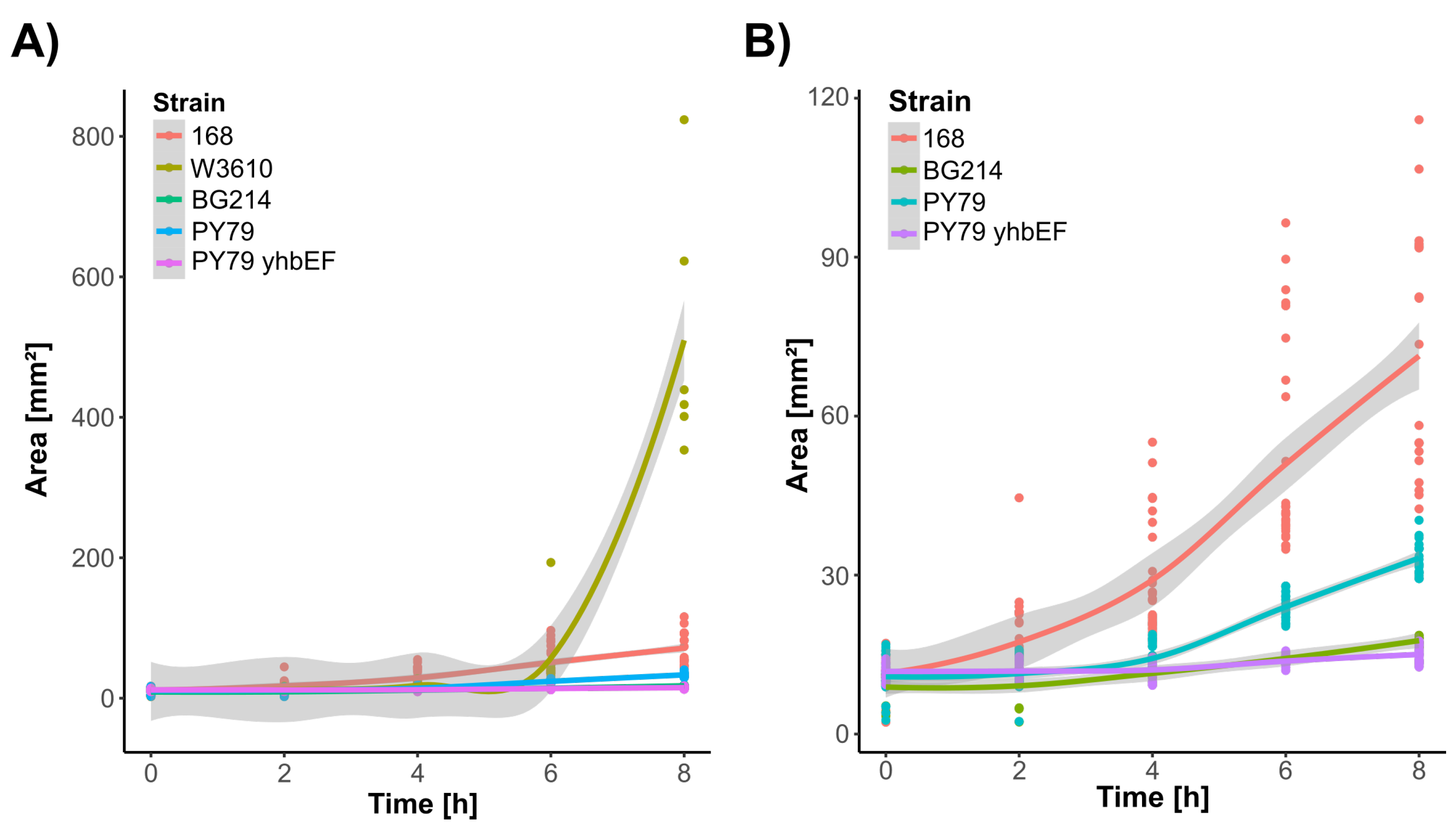
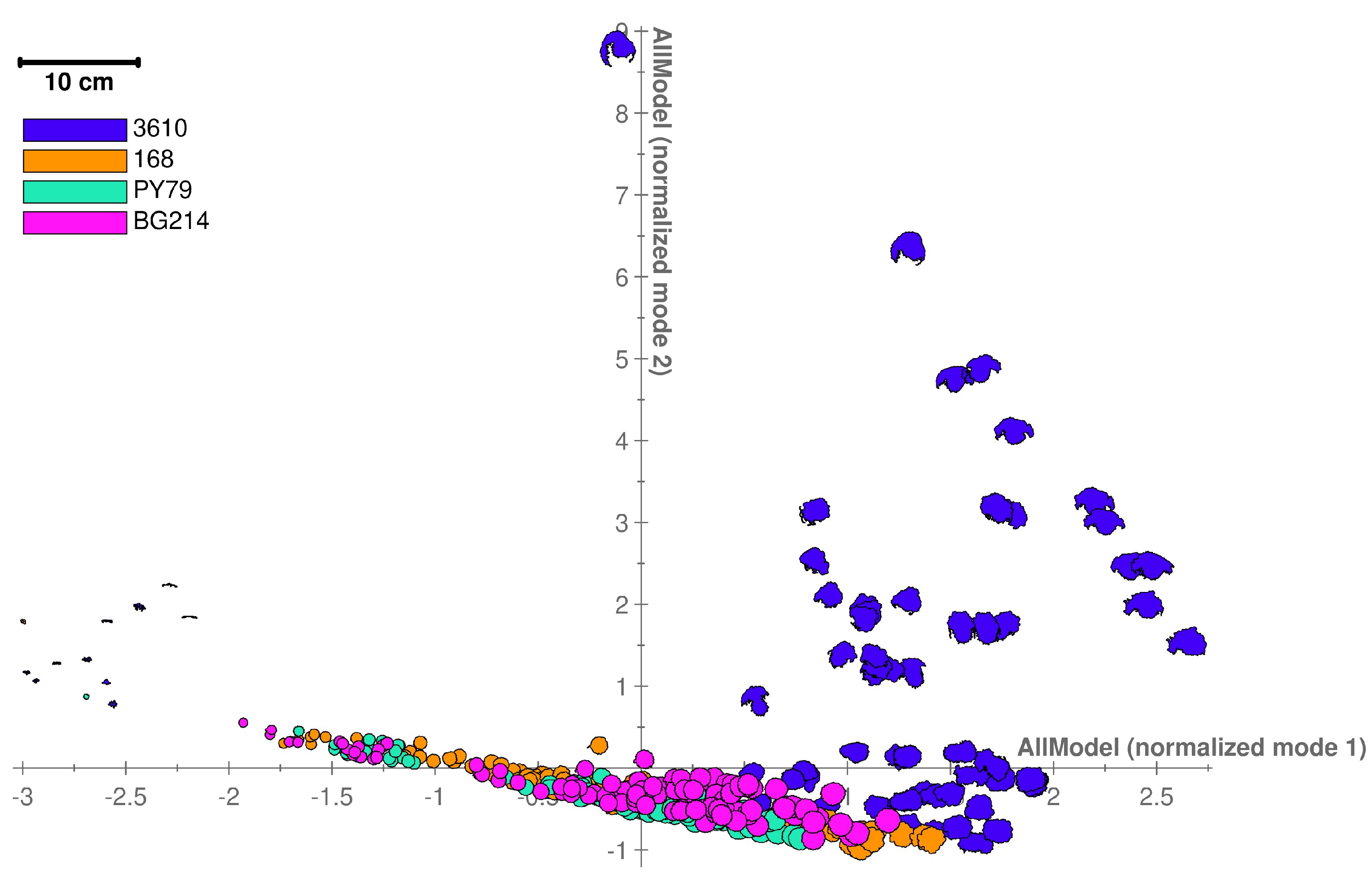
3.1. Commonly Used B. subtilis Strains Show Distinct Colony Shape Phenotypes
3.2. Strain-Specific Colony Formation Growth Patterns Contain Characteristic Colony Formation Shapes
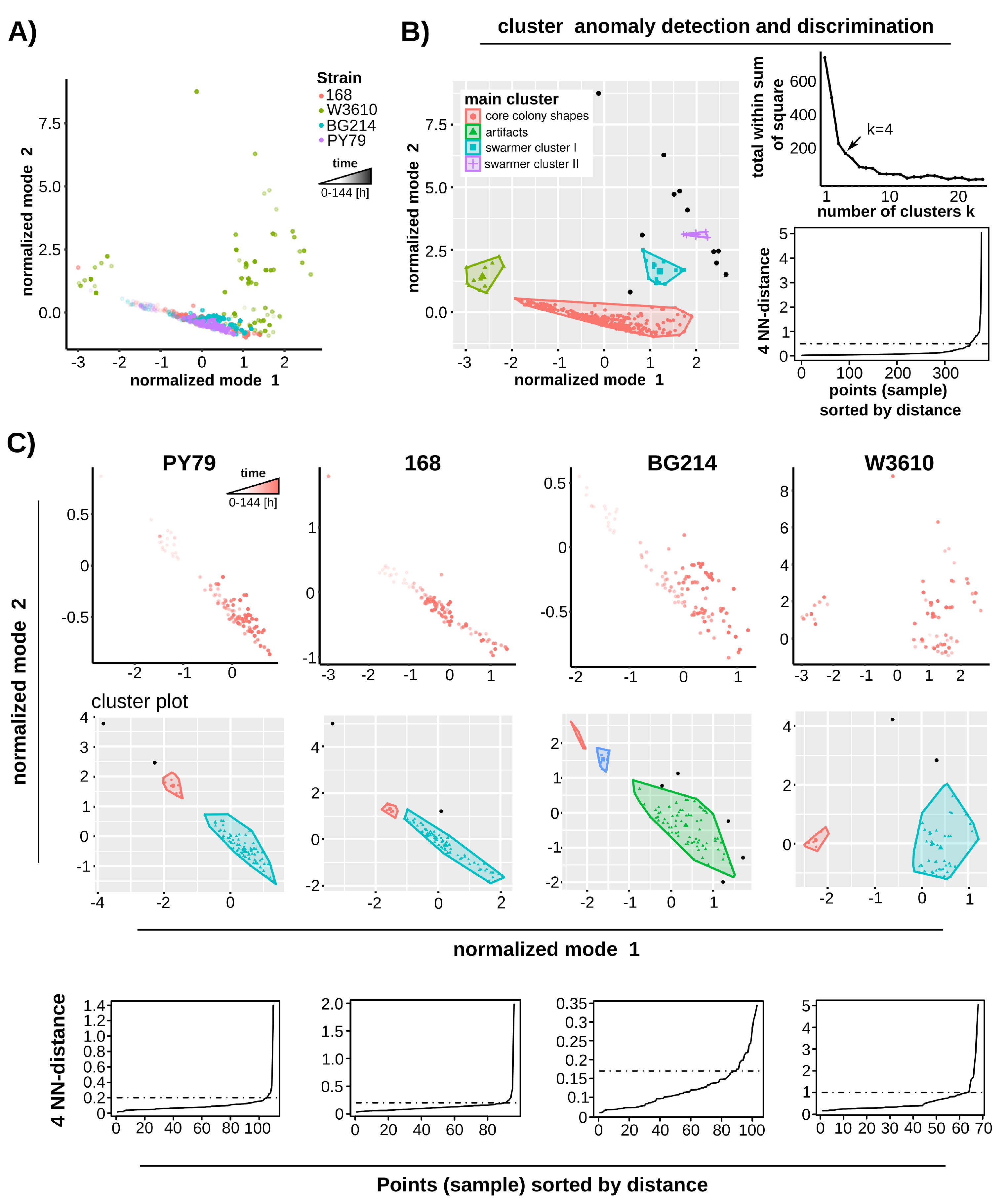
3.3. Phenotypes Can Be Discriminated According to Their Swarming Behavior
3.4. Spatial Clustering Is Capable of Detecting Anomalous Colony Formation
4. Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| DBSCAN | density-based spatial clustering applications with noise |
| epsilon-/eps-parameter | |
| IJ | ImageJ |
| k-NN | k-nearest neighbor |
| ml | machine learning |
| LOESS | locally estimated scatterplot smoothing |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
References
- Steenken, W.; Oatway, W., Jr.; Petroff, S. Dissociation and pathogenicity of the R and S variants of the human tubercle bacillus (H37). J. Exp. Med. 1934, 60, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithburn, K.C. The colony morphology of tubercle bacilli: I. The Presence of Smooth Colonies in Strains Recently Isolated from Sources Other than Sputum. J. Exp. Med. 1935, 61, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantratita, N.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Boonbumrung, K.; Tiyawisutsri, R.; Vesaratchavest, M.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Chierakul, W.; Wongratanacheewin, S.; Pukritiyakamee, S.; White, N.J.; et al. Biological relevance of colony morphology and phenotypic switching by Burkholderia pseudomallei. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtrup, S.; Graumann, P.L. Strain-dependent motility defects and suppression by a flhO mutation for B. subtilis bactofilins. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, J.E.; Kearns, D.B. Swarming motility and the control of master regulators of flagellar biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttenplan, S.B.; Kearns, D.B. Regulation of flagellar motility during biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 849–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, D.B.; Losick, R. Swarming motility in undomesticated Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science 1966, 153, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, H.J. The identity of Bacillus subtilis. J. Infect. Dis. 1930, 46, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, P.; Perkins, J.B.; Losick, R. Construction of a cloning site near one end of Tn917 into which foreign DNA may be inserted without affecting transposition in Bacillus subtilis or expression of the transposon-borne erm gene. Plasmid 1984, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Andari, J.; Altegoer, F.; Bange, G.; Graumann, P.L. Bacillus subtilis bactofilins are essential for flagellar hook-and filament assembly and dynamically localize into structures of less than 100 nm diameter underneath the cell membrane. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, P.R.; Giles, N.H., Jr. Induced biochemical mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Am. J. Bot. 1947, 34, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizizen, J. Transformation of biochemically deficient strains of Bacillus subtilis by deoxyribonucleate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1958, 44, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, Z.; Theriot, J. Comparison of quantitative methods for cell-shape analysis. J. Microsc. 2007, 227, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, F.J. Ueber Bacterien, die Kleinsten Lebenden Wesen; CG Lüderitz: Berlin, Germany, 1872; Volume 165. [Google Scholar]
- Julkowska, D.; Obuchowski, M.; Holland, I.B.; Séror, S.J. Comparative Analysis of the Development of Swarming Communities of Bacillus subtilis 168 and a Natural Wild Type: Critical Effects of Surfactin and the Composition of the Medium. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis I: The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1951, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. LOWESS: A program for smoothing scatterplots by robust locally weighted regression. Am. Stat. 1981, 35, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J. Locally weighted regression: An approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC., Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L., Jr. Python Reference Manual; Department of Computer Science [CS]. Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica Amsterdam, The Netherlands (CWI). Available online: https://www.python.org/downloads/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Xie, Y. knitr: A General-Purpose Package for Dynamic Report Generation in R. R Package Version 1.39. 2022. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/knitr/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Xie, Y. Dynamic Documents with R and Knitr, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1498716963. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Knitr: A Comprehensive Tool for Reproducible Research in R. In Implementing Reproducible Computational Research; Stodden, V., Leisch, F., Peng, R.D., Eds.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1466561595. [Google Scholar]
- Allaire, J.; Horner, J.; Xie, Y.; Marti, V.; Porte, N. Markdown: Render Markdown with the C Library ’Sundown’. R Package Version 1.1. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=markdown (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Rueden, C.T.; Hiner, M.C.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 1.0.10. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, W. Operations Useful for Similarity-Invariant Pattern Recognition. J. ACM 1962, 9, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvas, I.; Chernov, A.; Butakova, M.; Chaikalis, C. Increasing the quality and performance of n-dimensional point anomaly detection in traffic using pca and dbscan. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 20–21 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.; Jinhang, S. The analysis and research of clustering algorithm based on PCA. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Yangzhou, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinath Krishna, V.; Weaver, G.A.; Sanders, W.H. PCA-based method for detecting integrity attacks on advanced metering infrastructure. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Quantitative Evaluation of Systems, Madrid, Spain, 1–3 September 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 70–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Kdd, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; Volume 96, pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hahsler, M.; Piekenbrock, M.; Doran, D. dbscan: Fast Density-Based Clustering with R. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 91, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, C. fpc: Flexible Procedures for Clustering. R Package Version 2.2-5. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fpc (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Dowle, M.; Srinivasan, A. data.table: Extension of ‘data.frame’. R Package Version 1.14.2. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.table (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K. Cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions. R Package Version 2.1.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cluster (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Wickham, H. Stringr: Simple, Consistent Wrappers for Common String Operations. R package Version 1.4.1. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=stringr (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Schubert, E.; Sander, J.; Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. DBSCAN revisited, revisited: Why and how you should (still) use DBSCAN. ACM Trans. Database Syst. (TODS) 2017, 42, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, E.; Hodges, J.L., Jr. Discriminatory Analysis-Nonparametric Discrimination: Small Sample Performance; Technical Report; California Univ Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.; Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. Density-based clustering in spatial databases: The algorithm gdbscan and its applications. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Fujikawa, H. Diffusion-limited growth in bacterial colony formation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1990, 168, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasbin, R.E.; Fields, P.I.; Andersen, B.J. Properties of Bacillus subtilis 168 derivatives freed of their natural prophages. Gene 1980, 12, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Schwan, M.; Thormann, K.M.; Graumann, P.L. Antibiotic Drug screening and Image Characterization Toolbox (ADICT): A robust imaging workflow to monitor antibiotic stress response in bacterial cells in vivo. F1000Research 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strain | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| W3610 | B. subtilis wild-type isolate | [9] |
| PY79 | B. subtilis lab strain trpC2 | [10] |
| PY79yhbEF | B. subtilis lab strain PY79, yhbEF::kan | [11] * |
| 168 | B. subtilis lab strain trpC2 | [12,13] |
| BG214 | B. subtilis lab strain | ∘ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayer, B.; Holtrup, S.; Graumann, P.L. A Machine Learning-Empowered Workflow to Discriminate Bacillus subtilis Motility Phenotypes. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 565-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2040036
Mayer B, Holtrup S, Graumann PL. A Machine Learning-Empowered Workflow to Discriminate Bacillus subtilis Motility Phenotypes. BioMedInformatics. 2022; 2(4):565-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayer, Benjamin, Sven Holtrup, and Peter L. Graumann. 2022. "A Machine Learning-Empowered Workflow to Discriminate Bacillus subtilis Motility Phenotypes" BioMedInformatics 2, no. 4: 565-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2040036
APA StyleMayer, B., Holtrup, S., & Graumann, P. L. (2022). A Machine Learning-Empowered Workflow to Discriminate Bacillus subtilis Motility Phenotypes. BioMedInformatics, 2(4), 565-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2040036






