Abstract
This study performs an analysis of steam penetration through thermal protective fabric materials. Different, multilayered thermal protective fabrics were selected and tested in a laboratory-simulated steam exposure, and their steam protective performance (SPP) was measured in terms of the time required to generate second-degree burns on the bodies of wearers. Additionally, the total transmitted thermal energy (TTTE) through the fabrics during testing was measured. Through statistical analysis, it was established that fabric properties, namely air permeability and thickness, are the key factors that affect the SPP and TTTE; the relationship among the fabric properties, SPP, and TTTE is also summarized. Theoretically, it has been found that heat and mass (steam) transfer occur through fabrics in the course of steam exposure, which mainly affect the SPP and TTTE. This study could help textile/materials engineers to develop high performance thermal protective fabrics for the increased occupational health and safety of firefighters and industrial workers.
1. Introduction
Firefighters and industrial workers often incur burn injuries when they encounter hazardous thermal exposures while performing their job duties [1,2,3]. Contextually, it has been identified that water used by firefighters to put out a fire may convert into steam, which may reach the firefighters [4,5,6,7,8]. Additionally, upstream oil and gas industry workers are often exposed to steam while extracting bitumen from oil sands and producing heavy oil [9,10]. As the performance of thermal protective clothing worn by firefighters and industrial workers depends upon the various thermal exposures these workers face in their occupations [11,12,13,14,15,16,17], it can be inferred that steam has a significant impact on the thermal protective performance of clothing [4,5,6,7,8]. In steam exposure, a significant amount of thermal energy transfer occurs through clothing, which causes burns to workers in these occupations.
In considering thermal protection and steam exposure, many researchers studied the SPP of fabric materials used in thermal protective clothing [4,5,6,7,8,18,19,20,21]. Keiser et al. (2008), Keiser and Rossi (2008), Keiser et al. (2010), Mandal et al. (2013), and Shoda et al. (1998) suggested that imposed high-pressurized steam enters into the fabric structure and gradually condenses [4,5,6,7,8]. After the condensation phase, the steam converts into hot water. This hot water generates burn injuries when it comes into contact with the human body. These researchers identified that a permeable fabric allows more steam transfer toward wearers than an impermeable fabric. As a result, they suggested that thermal protective fabrics should be steam impermeable in nature to provide effective protection from steam exposure. Mandal et al. (2013) further found that the air permeability of the outer layer (shell fabric) is crucial for the SPP of a multilayered thermal protective fabric system (i.e., an assembly of shell fabric, moisture barrier, and/or thermal liner) [7]. They recommended that it is essential to place a moisture barrier with zero air permeability in the outer layer of multilayered fabric systems in order to achieve a high SPP. This air-impermeable moisture barrier will immediately stop the steam penetration through the fabric system, which will considerably decrease the chances of burns on the bodies of wearers [7,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Along with air permeability, Desruelle et al. (2002) indicated that the thickness of the fabric systems has a considerable impact on its steam protective performance [25]. Recently, Su et al. (2018) found that fabric thickness insignificantly improves the steam protective performance in comparison to the air permeability of the fabrics [26].
Although previous researchers extensively studied steam penetration through fabrics by evaluating the SPP, only a few studies focused considerably on the TTTE through fabrics in steam exposure of a certain duration [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. This paper studied experimentally both the SPP and TTTE and identified fabric features affecting both. The SPP is also compared with the flame and radiant heat protective performance of fabrics. Steam penetration through fabric systems was studied based on the theory of heat and mass transfer. This paper will contribute to understanding the mechanisms associated with the heat and mass transfer in fabric systems, and the results obtained could help textile/material engineers to develop fabrics for high performance thermal protective clothing.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, multiple thermal protective fabrics (A–F) were selected for testing (Table 1). These fabrics are commercially available and commonly used in the clothing of firefighters and industrial workers. These fabrics were assembled to produce multilayered fabric systems; these configured fabric systems were A (Fabric-A), B (Fabric-B), AC (Fabric-A + Fabric-C), AE (Fabric-A + Fabric-E), AF (Fabric-A + Fabric-F), FA (Fabric-F + Fabric-A), AFC (Fabric-A + Fabric-F + Fabric-C), AFD (Fabric-A + Fabric-F + Fabric-D), AFE (Fabric-A + Fabric-F + Fabric-E), and FAD (Fabric-F + Fabric-A + Fabric-D). The constructional attributes and physical properties of these fabric systems were measured using the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards (Table 2) [27,28,29,30]. In this context, it is notable that porosity (the ratio of pore volume to the total volume of the fabrics depending upon the open and closed porosity) is an important fabric property that could affect the steam penetration through fabrics. However, it is difficult to accurately characterize the pore volume because the pore system within a fabric typically forms a very complicated pore surface that is geometrically irregular; in fact, it is also not accurate to define the pore size in terms of the diameter considering the different structures of pores existing in the fabric [31,32,33]. Considering this situation, although porosity and air permeability are not the same thing, air permeability is measured as an indirect measurement of porosity and is used for explaining the SPP.

Table 1.
Thermal protective fabrics.

Table 2.
Assembled fabric systems.
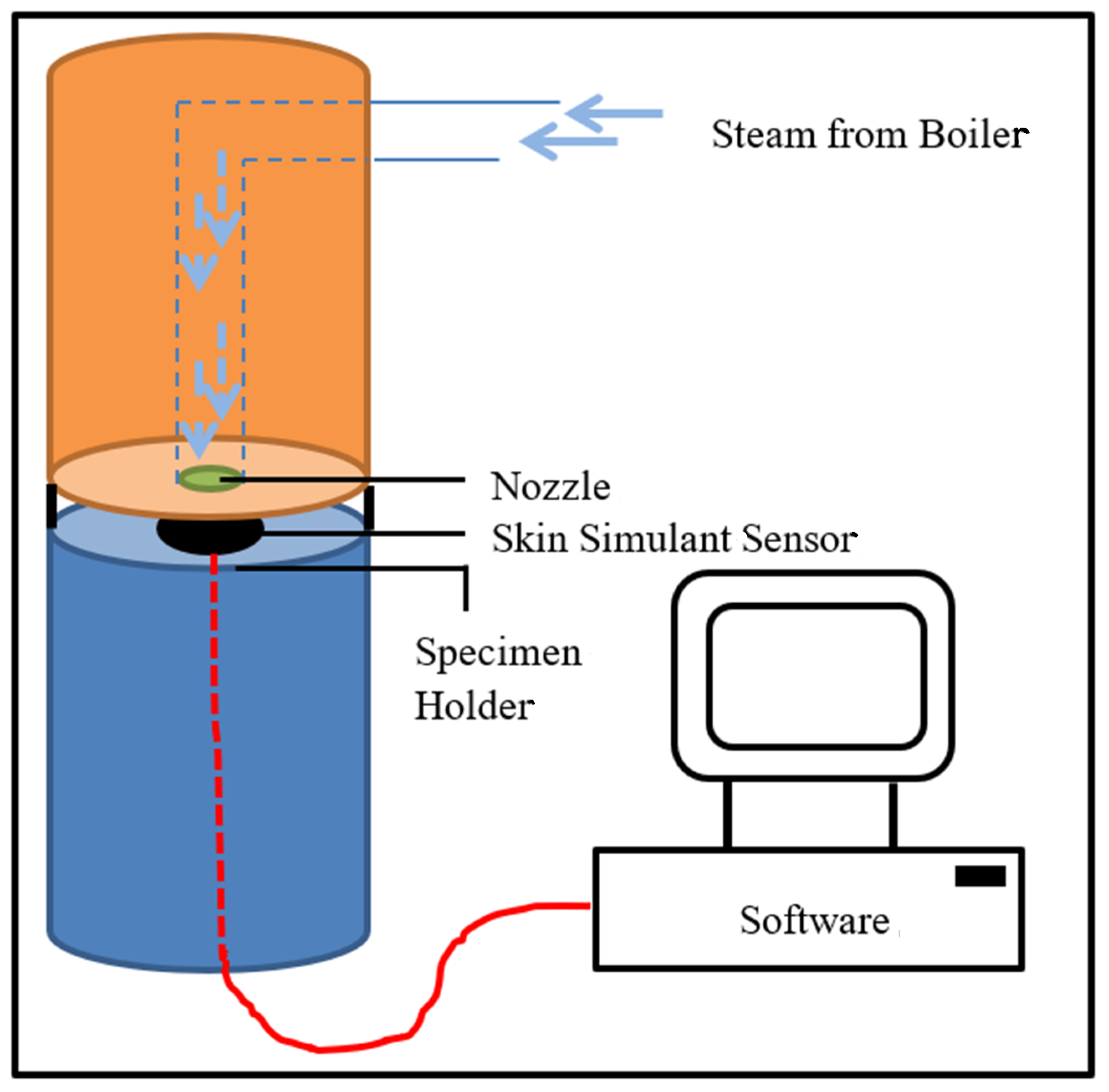
Three specimens (200 mm × 200 mm) of each fabric system were conditioned in a standard atmosphere (21 °C temp. and 65% relative humidity) for 24 h. To understand the steam penetration parameters of the fabric systems, these specimens were tested under steam exposure using the instrument shown in Figure 1. In this test, a specimen of the fabric system was placed on a Teflon-plated specimen holder embedded with a skin simulant sensor. Steam was generated at 150 °C using a 3 kW boiler, and the steam generated was administered at 200 kPa from 50 mm above the specimen through a 4.6 mm nozzle. The skin simulant sensor was used to measure the heat flux, and this heat flux was applied using burn prediction software (programmed according to Henrique’s Burn Integral algorithm) to calculate the time required to generate second-degree skin burns [34]. The skin simulant sensor was developed by the University of Alberta in Canada using inorganic material called ‘colorceron’, which is a mixture of calcium, aluminum, silicate, asbestos fibers, and a binder; and this sensor was calibrated using the standardized Schmidt–Boelter water-cooled sensor [34]. The predicted mean burn time obtained from the three specimens was interpreted as the SPP of the fabric system. The TTTE of the fabric system specimen during (30 s) and after (10 s) of steam exposure was also measured. Subsequently, the fabric properties, SPP, and TTTE values were normalized statistically, and a t-test was carried out using STATCRUNCH software (developed by West of Texas A&M University, USA). The association among the fabric properties, SPP and/or TTTE was inferred based on the sign (+ or −) of the T-stat value obtained from the t-test. p-values obtained from the t-test for all fabric properties were also analyzed. If the p-value for any property was less than 0.05, this property was identified as the key property affecting the SPP/TTTE. Relationship plots were developed among the fabric properties, SPP, and/or TTTE; and the coefficient of determination (R2) of the plots developed was calculated. A R2 value with proximity to 1 was inferred as a strong association among the fabric properties, SPP, and/or TTTE. Inference tests (hypothesis test (p-value) and a 95% confidence interval (upper and lower limits)) were carried out to understand the differences in the SPP/TTTE of various sets of fabric systems.
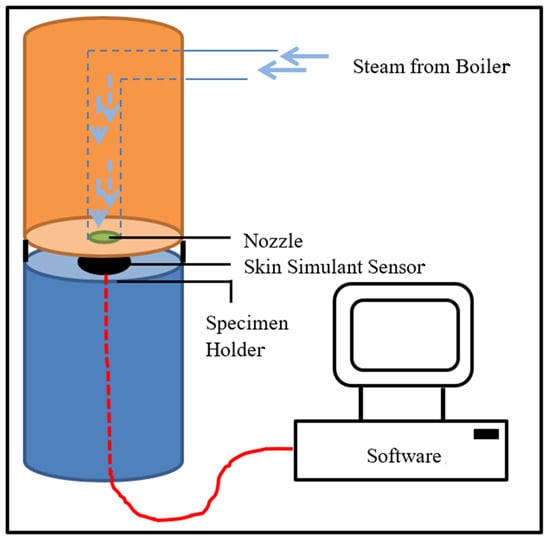
Figure 1.
Steam exposure test.
3. Results and Discussion
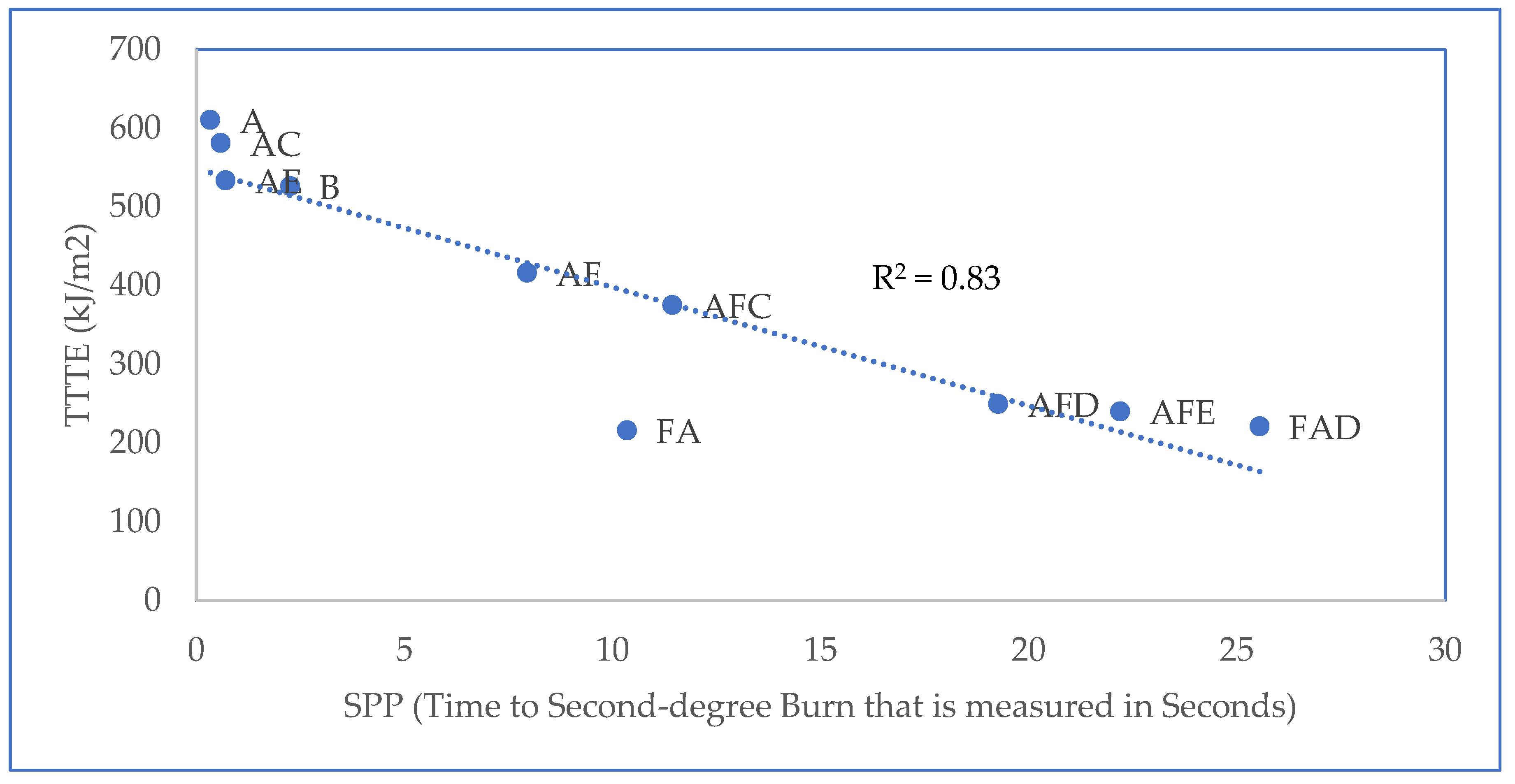
The parameters for steam penetration (SPP and TTTE) through the selected fabric systems (obtained from the steam exposure test) are shown in Table 3. The SPP per unit thickness of each fabric system is also calculated and presented in Table 3. Based on the data shown in Table 3, a relationship plot between the SPP and TTTE is displayed in Figure 2. According to Figure 2, the trend line of the plot is negative, and the R2 value is close to 1; hence, a strong negative relationship exists between the SPP and TTTE. From this, it can be inferred that the TTTE through a fabric system is generally low if the fabric system possesses a high SPP. Mandal et al. (2013) previously evaluated the flame and radiant heat protective performance of the same set of fabric systems mentioned in Table 3, which firefighters often encounter in flame and radiant heat exposures [7]. A comparison of these previous results (Table 4) with the SPP values of Table 3 clearly shows that the protective performances of air-permeable fabric systems are significantly lower in steam exposure. This is because flame and radiant heat exposures mainly involve a heat transfer through the fabric systems toward the bodies of wearers [35]; however, in steam exposure, a hot mass transfer mainly occurs through fabric systems. As the mode of thermal energy transfer differs in these exposures, the performance of the fabric systems lowers under steam exposure. In the following section, the effect of fabric features on the SPP/TTTE is established to characterize the steam penetration through the fabric system.

Table 3.
Steam penetration parameters of fabric systems.
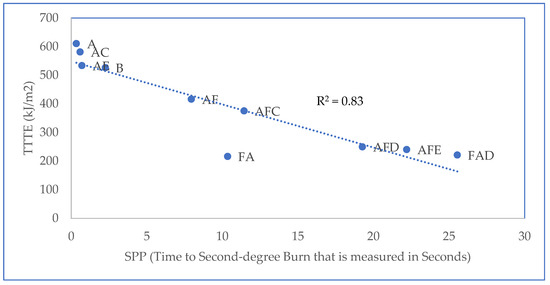
Figure 2.
Relationship plot between SPP and TTTE.

Table 4.
Flame and radiant heat protective performance of selected fabric systems [adapted from Mandal, et al. (2013)] [7].
Effect of Fabric Features on SPP/TTTE
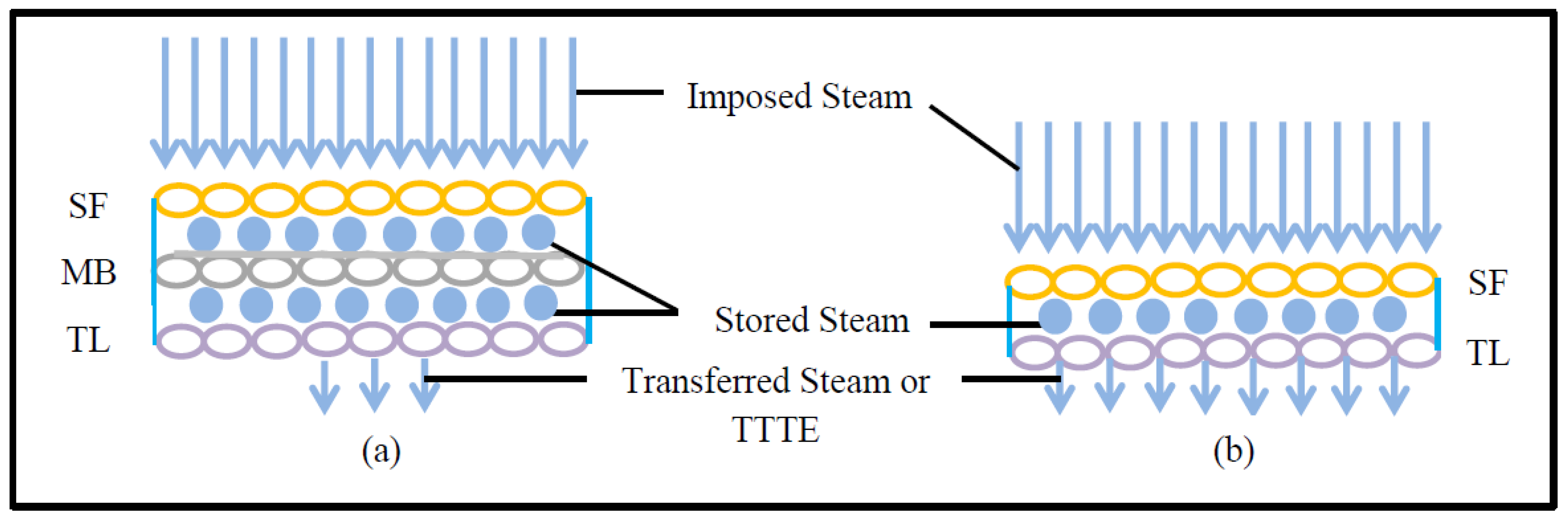
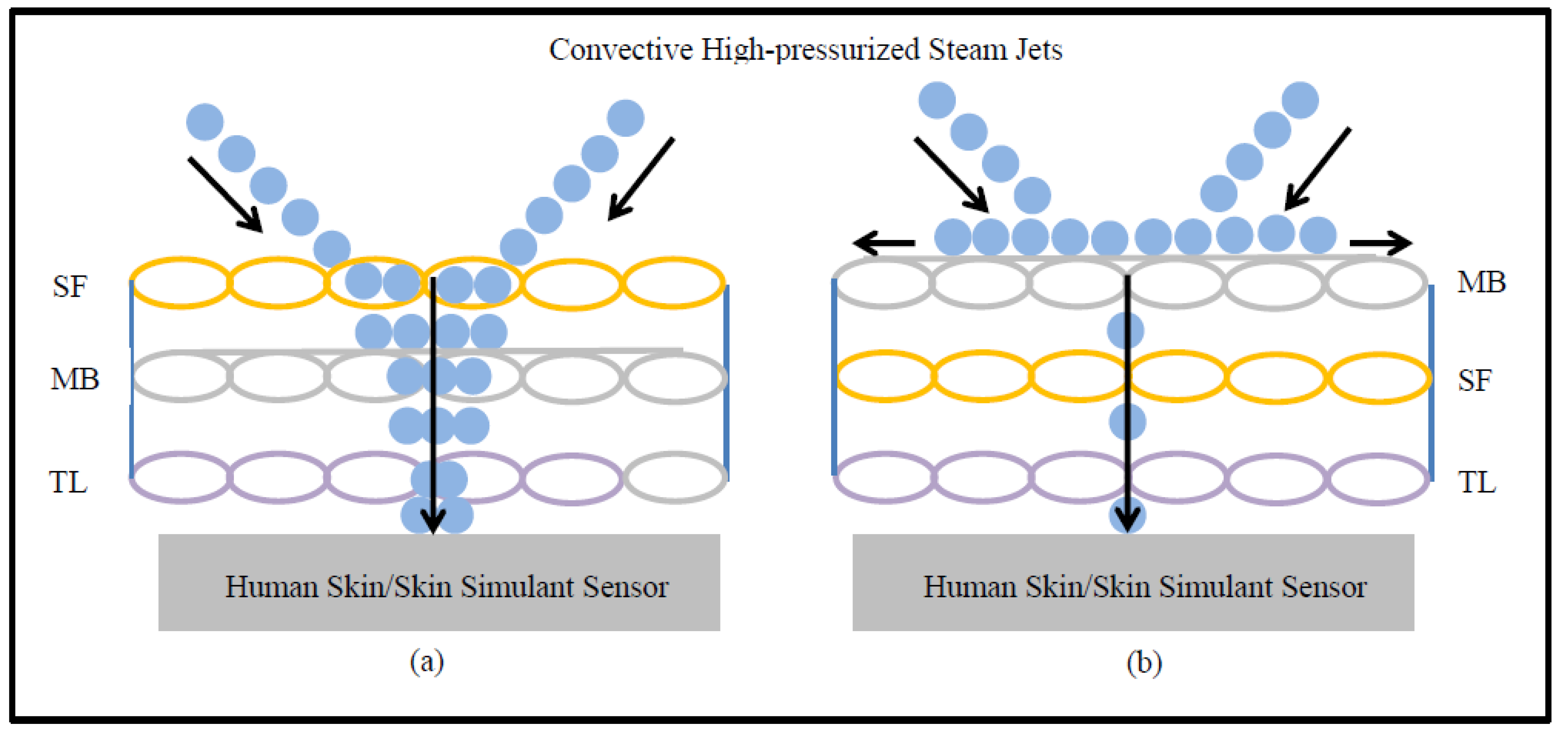
Table 3 shows that the SPP of triple-layered fabric systems is much higher than for single- or double-layered fabric systems. This is because a triple-layered fabric system including a moisture barrier can trap higher amounts of dead air than single- or double-layered fabric systems [36,37,38,39,40]. Consequently, triple-layered fabric systems prove to be more thermally insulated and can provide better protection against steam exposure [7]. In this context, it is necessary to mention that the SPP per unit thickness of a double-layered fabric system incorporating a moisture barrier (e.g., AF or FA) is equivalent or sometimes even higher to triple-layered fabric systems; however, the SPP per unit thickness of a double-layered fabric system not comprising a moisture barrier (e.g., AC or AE) is much lower than triple-layered fabric systems (Table 3). This finding could help to establish that structural differences, such as the presence or absence of moisture barriers in fabric systems, are crucial to the SPP. In fact, only the presence of a moisture barrier in combination with a shell fabric (e.g., FA) could give better protection than a few high thickness triple-layered fabric systems (e.g., AFC, AFD, and AFE). Furthermore, it is evident from Table 3 that the TTTE through triple-layered fabric systems is lower than for single- or double-layered fabric systems. This is because triple-layered fabric systems have increased amounts of empty space (among their constituent shell fabrics (SF), moisture barriers (MB), and thermal liners (TL)), and these empty spaces can store steam within the fabric systems [21]. As the stored steam inside the triple-layered fabric system remains high, the transferred steam or the TTTE through the fabric system is low (Figure 3).
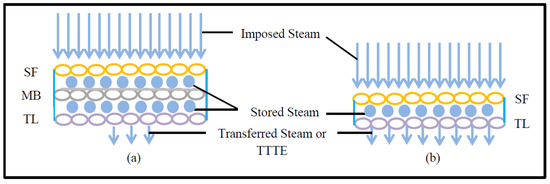
Figure 3.
TTTE through (a) triple-layered and (b) double-layered fabric systems.
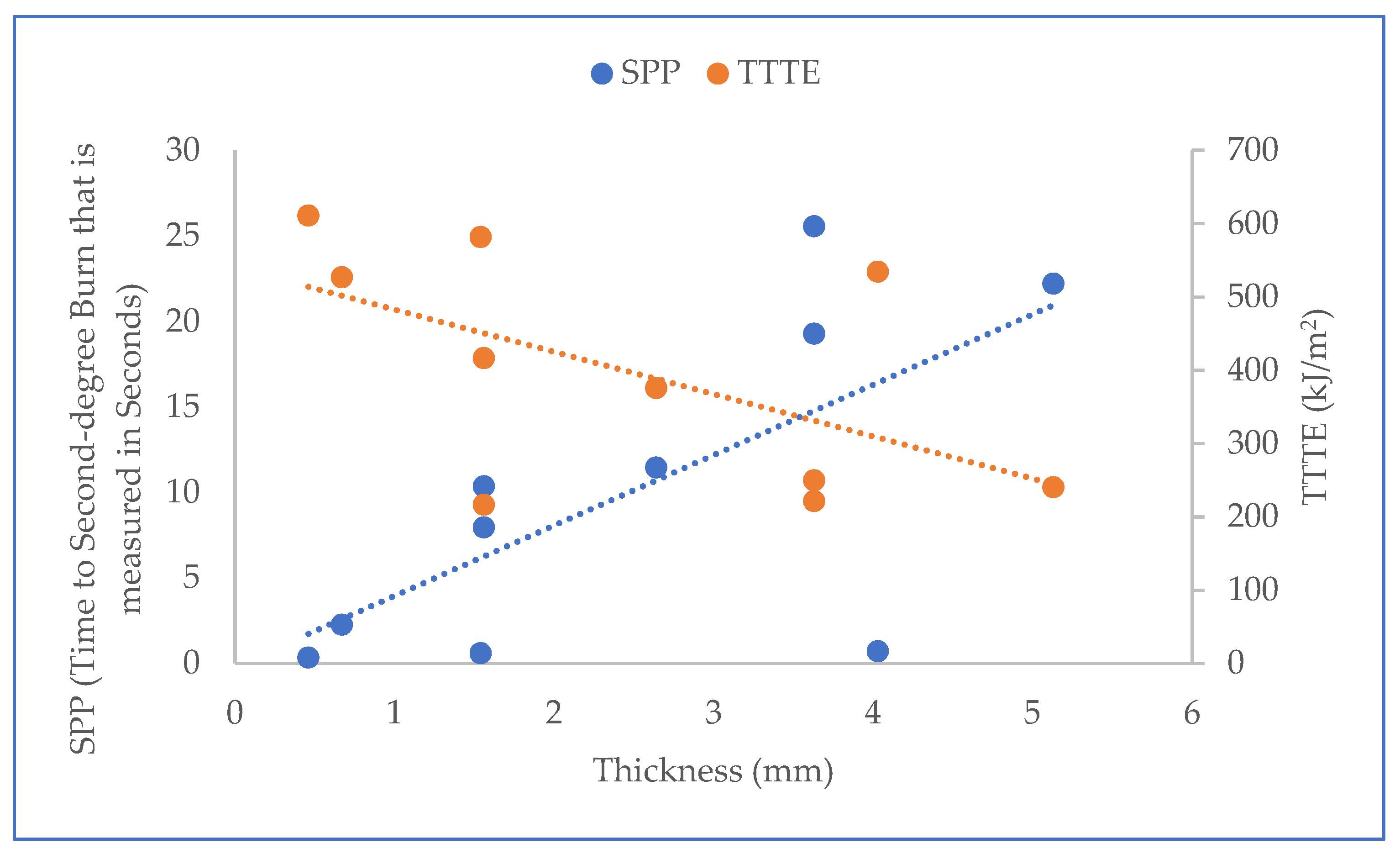
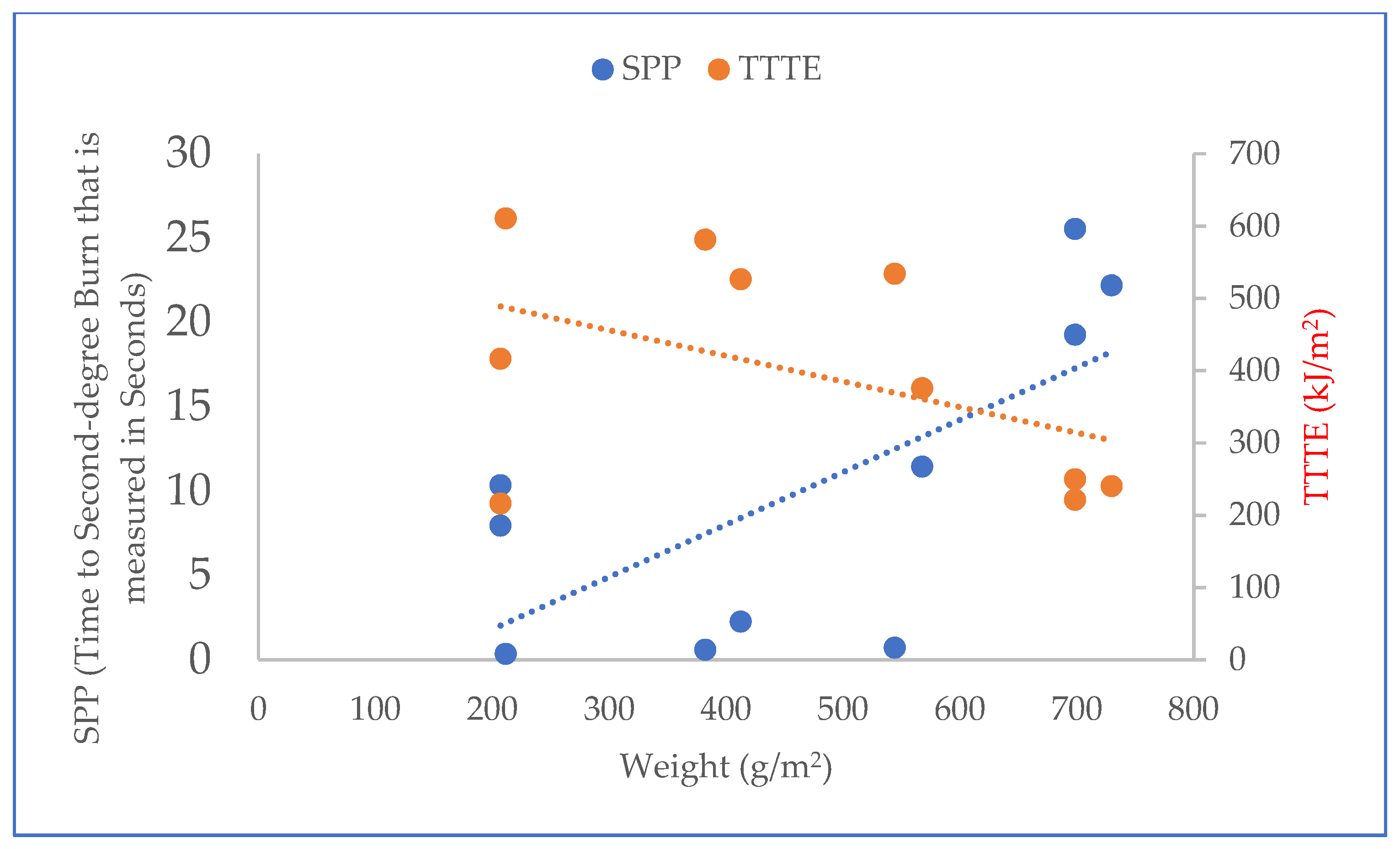
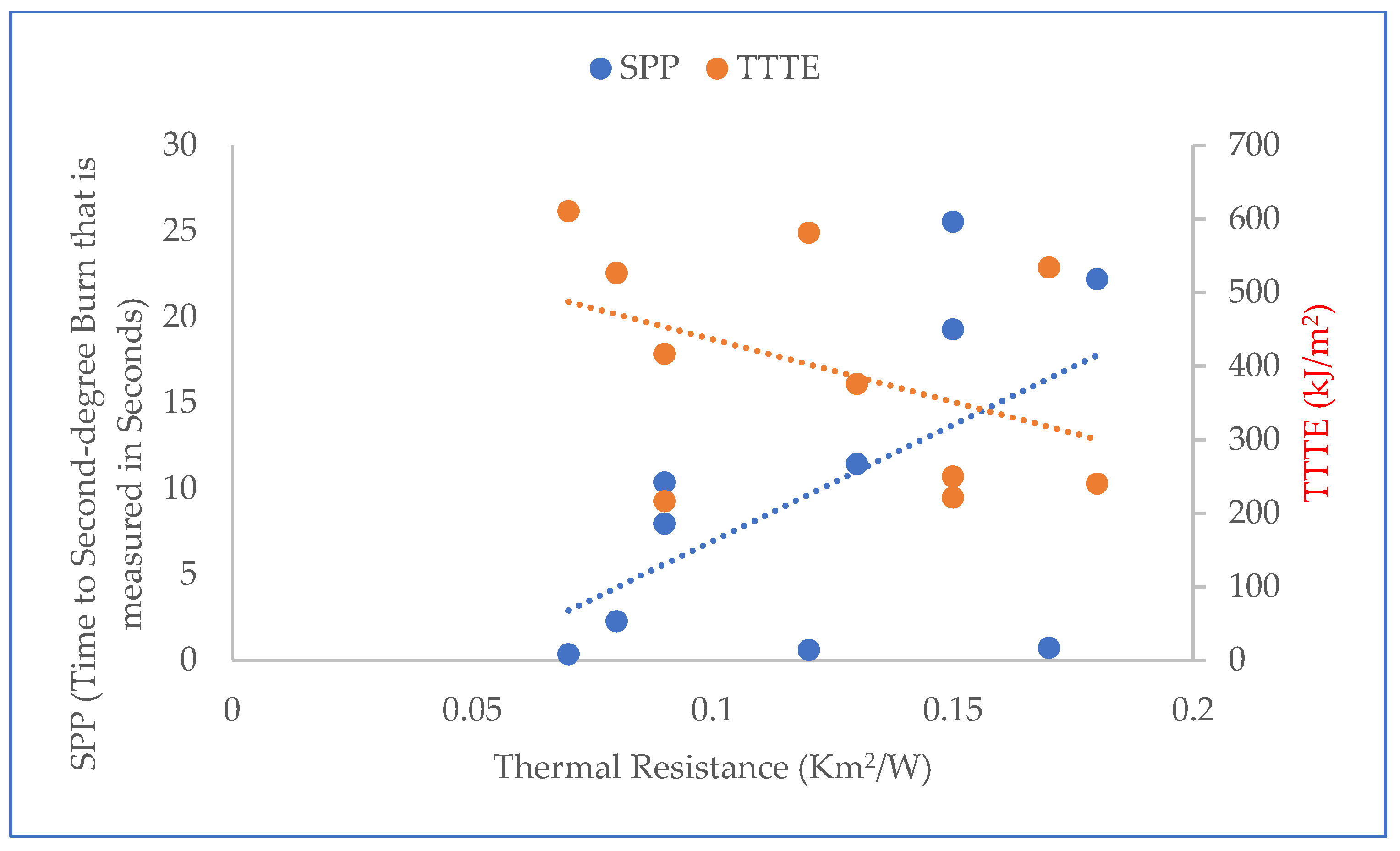
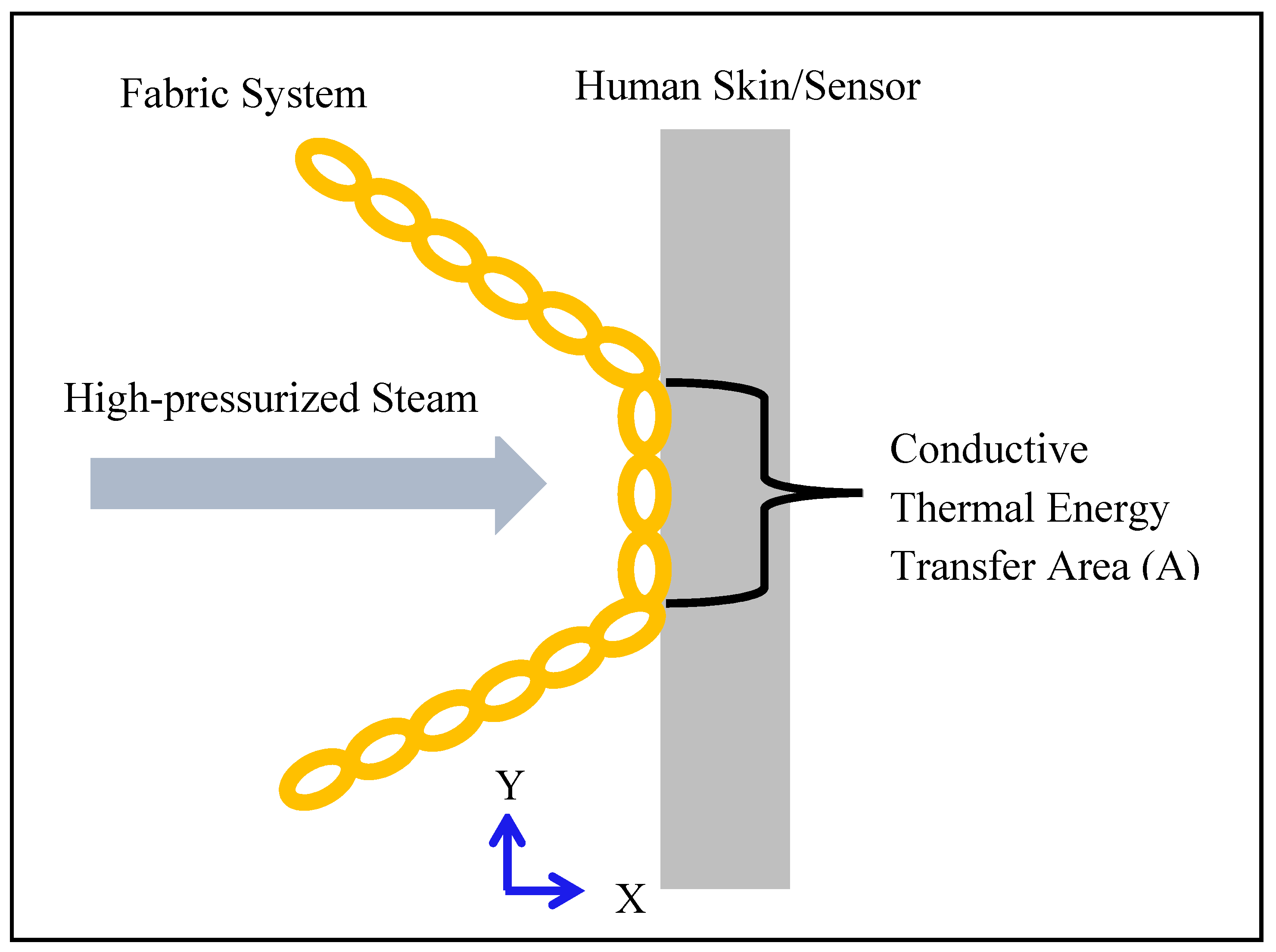
Furthermore, the results of the t-test (T-stat and P-value) between normalized values of the fabric system properties (Table 2) and SPP/TTTE (Table 3) are shown in Table 5. In Table 5, the T-stat values of thickness, weight, and thermal resistance with SPP are positive, whereas the T-stat values of these properties with TTTE are negative. This indicates that these properties possess a positive and negative relationship with the SPP and TTTE, respectively. The relationship plots of these properties with SPP and TTTE, shown in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, suggest that a moderate relationship exists between each of them and the SPP/TTTE. These relationships can be further explained by the theory of heat transfer through fabric systems [14,18,20]. In a high-pressurized steam exposure, intimate contact occurs between fabric systems and the skin of the wearers (skin simulant sensor) (Figure 7). Consequently, a conductive thermal energy transfer proceeds from the fabric systems toward the skin. In this situation, a fabric with high weight and thickness can trap more insulative dead air, which can augment the thermal resistance of the fabric. This highly thermally insulated and resistive fabric can enhance the SPP by slowly transferring conductive thermal energy and generating slower burns on the bodies of wearers. Turning our attention to Figure 7, Equations (1) and (2) represent in analytical and mathematical terms the conservation of conductive thermal energy for a one-dimensional rectangular coordinate, X and Y coordinates-based fabric system [41]. Based on Equation (2), it can be inferred that the behavior of the TTTE through a fabric system is dependent upon the area of the fabric system (A in cm2), gradient of temperature along the x direction of the fabric system (δT/δx in °C/cm), rate of energy generation per unit volume of the fabric system (qg in W/cm3), density of the fabric system (ρ in g/cm3), thickness of the fabric system (dx in cm), specific heat of the fabric system (Cp in J/gm. °C), total steam exposure time (t in s), and thermal conductivity of the fabric system (kf in W/m.K).
Thermal energy conduction into the fabric system + Thermal energy generation inside the fabric system = Thermal energy conduction out of the fabric system + Thermal energy storage inside the fabric system

Table 5.
Results of t-test.
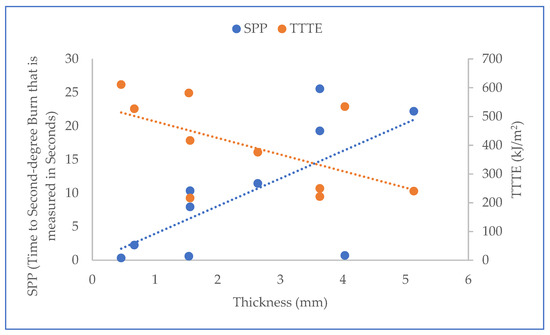
Figure 4.
Relationship plot of thickness with SPP and TTTE.
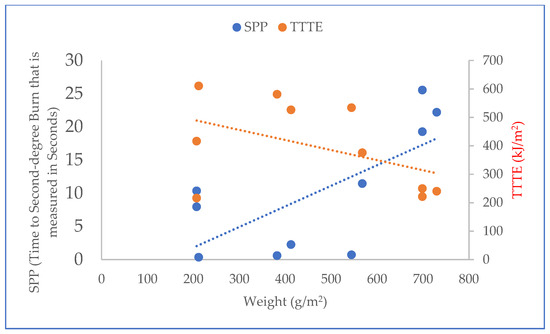
Figure 5.
Relationship plot of weight with SPP and TTTE.
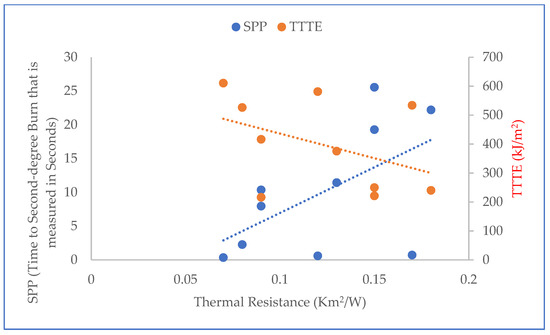
Figure 6.
Relationship plot of thermal resistance with SPP and TTTE.
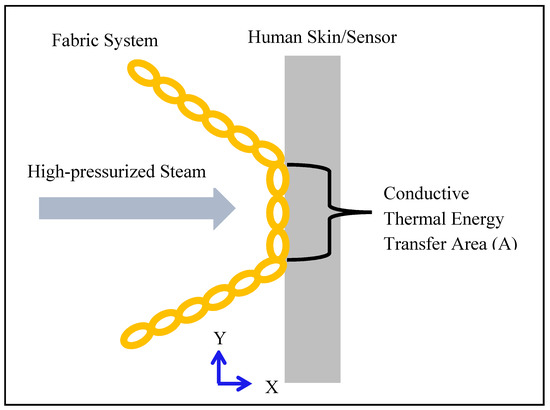
Figure 7.
Conductive thermal energy transfer through a fabric system under steam exposure.
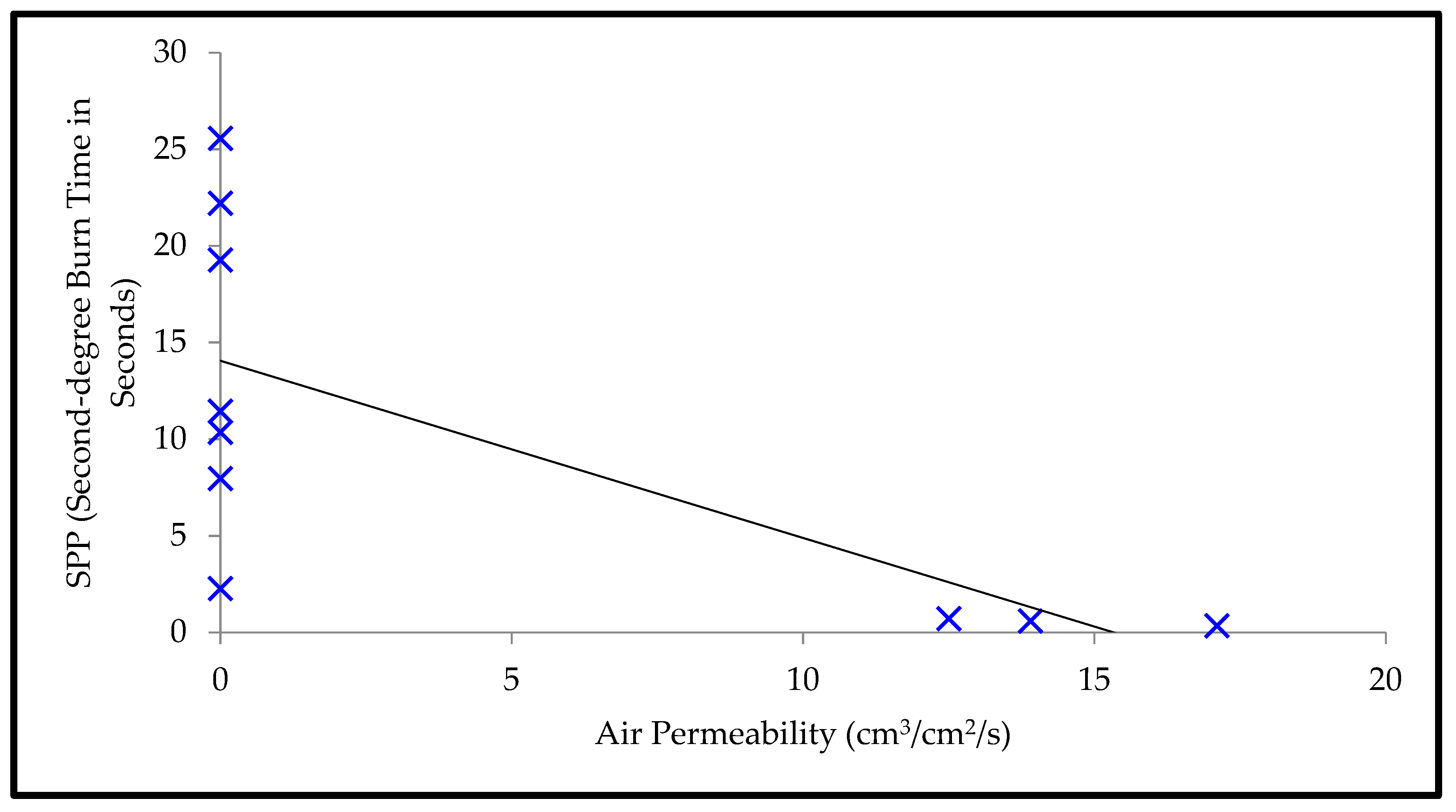
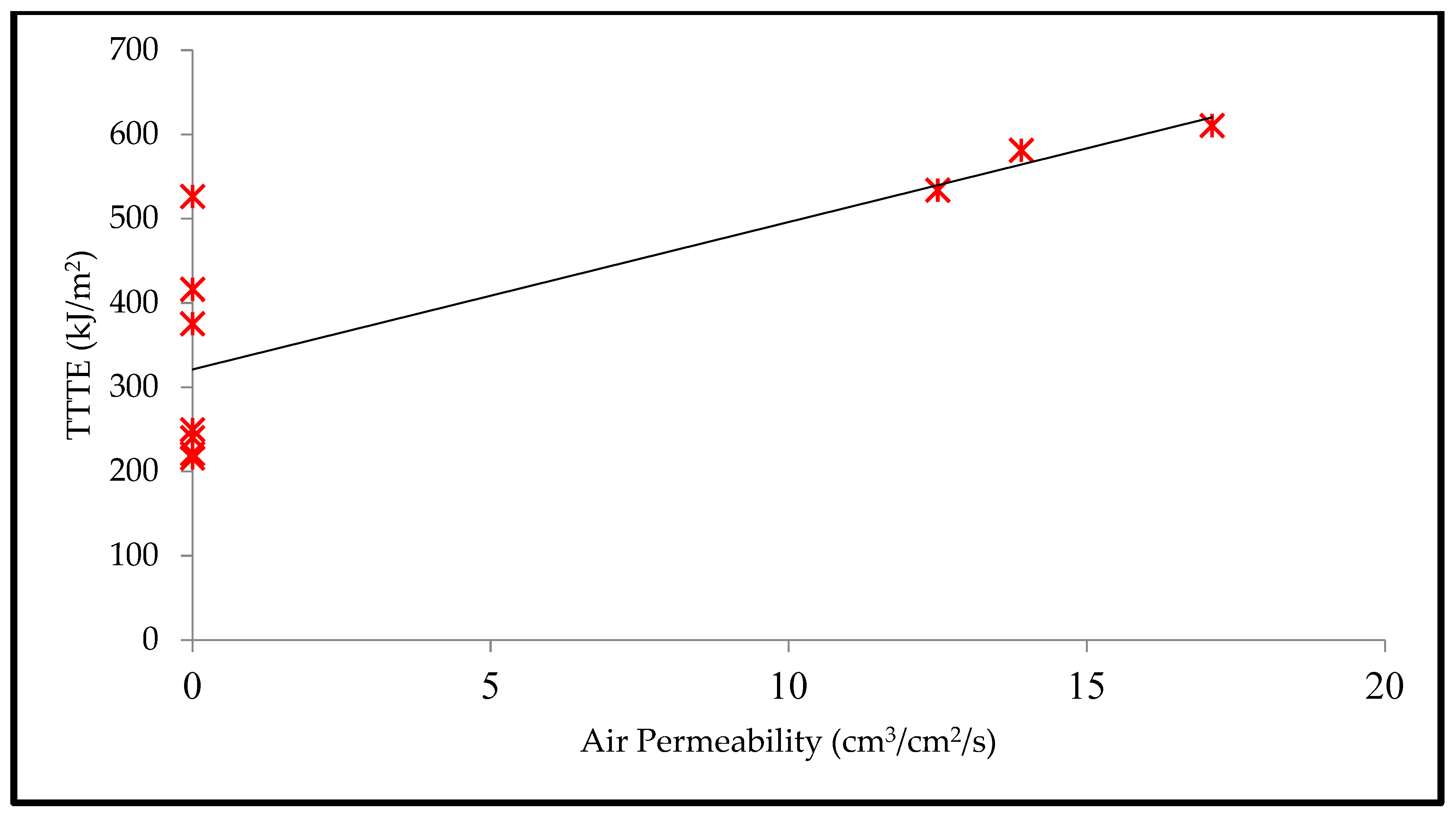
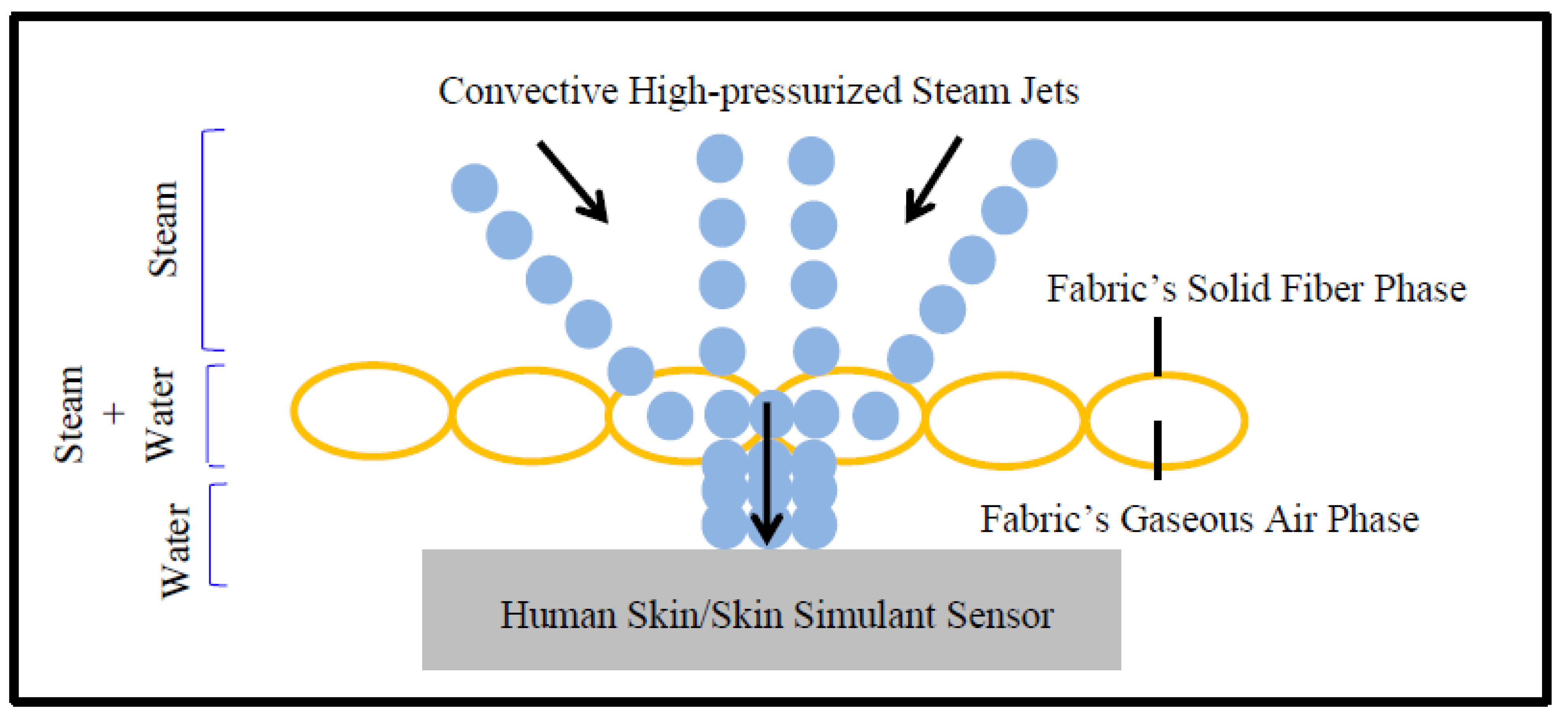
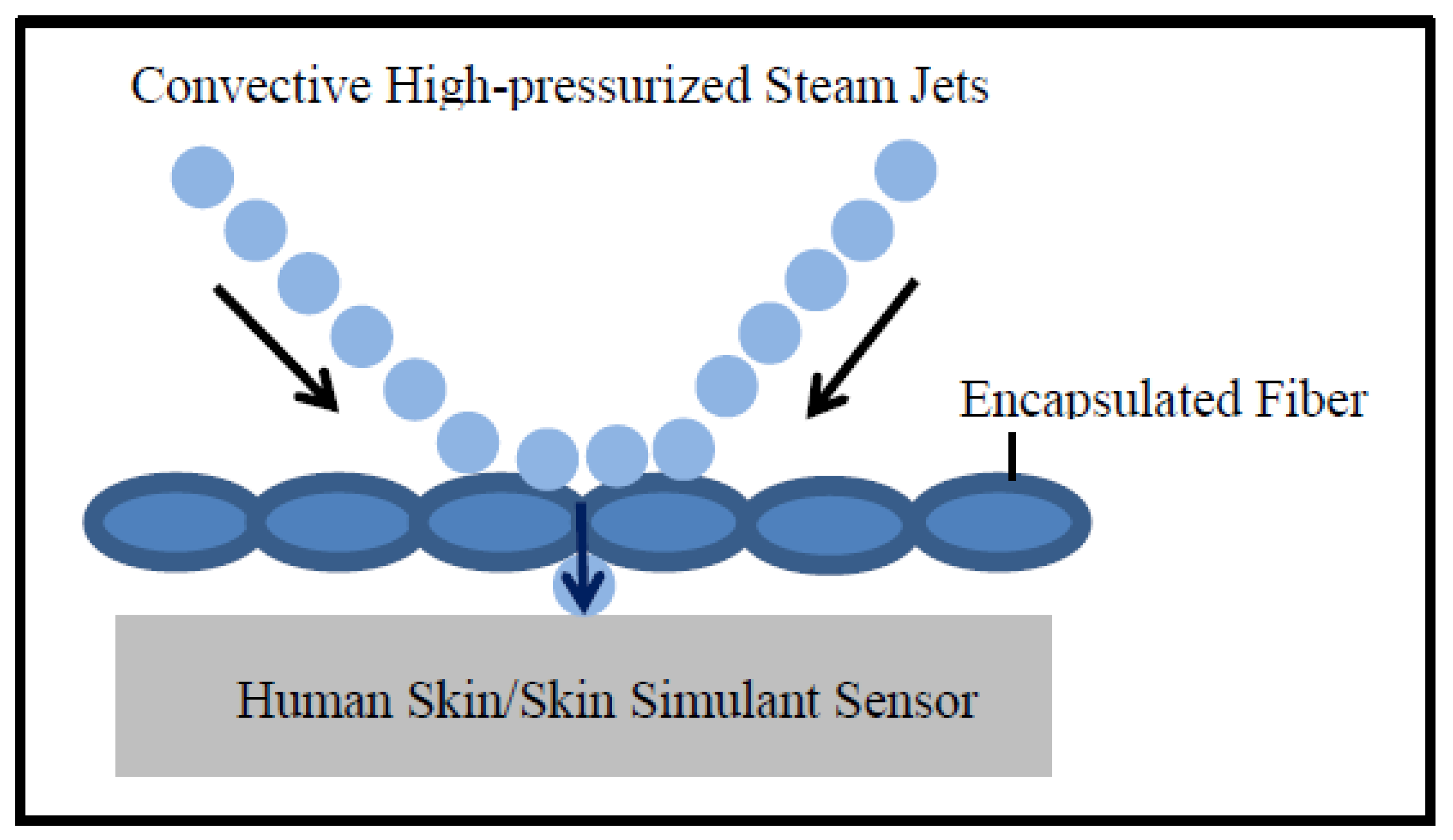
Moreover, Table 5 shows that the T-stat value of air permeability is negative with respect to the SPP; however, the T-stat value of air permeability is positive with respect to the TTTE. This implies that air permeability has a negative and positive relationship with the SPP and TTTE, respectively (Figure 8 and Figure 9). In addition, the p-values (0.001 and 0.007) of air permeability are least among all fabric properties and are below 0.05. This means that air permeability is the most important and significant property to understand the SPP of or the TTTE through fabric systems. This finding can be explained comprehensively by the theory of mass (steam) transfer through fabric systems [11,12,13,14,15]. In this context, it is notable that a regular fabric is a multiphase, porous media, which comprises both solid fiber and gaseous air phases (Figure 10); and Darcy’s law states that the mass transfer through porous media depends upon the permeability of that media (Equation (3). According to this law, a fabric with high air permeability can quickly transfer thermal energy in the form of convective steam jets through its air phase; eventually, the SPP and TTTE become low and high, respectively. Here, steam that has entered the fabric system gradually condenses and produces a mixture of steam and hot water; this hot water mainly transfers through the fabric system toward the bodies of wearers and generates burns (Figure 10). In the steam condensation process, a considerable amount of thermal energy is released, which also causes burns on the bodies of wearers [34,37]. Through inference testing (hypothesis and a 95% confidence interval) of the dataset shown in Table 3, it has been found that a significant difference exists between the TTTE of air-impermeable and air-permeable fabrics (p-value < 0.05), and this difference always remains negative. This demonstrates that the TTTE through an air-impermeable fabric is much lower than an air-permeable fabric, because air-impermeable fabrics do not allow a steam transfer, lowering the TTTE [42,43]. In the case of multilayered, impermeable fabric systems (shown in Table 3), a fabric system including a moisture barrier in its outer layer has less TTTE (or high SPP) than a fabric system including a moisture barrier in its inner (middle) layer. This is because the presence of a polyurethane-coated (smooth surfaced) moisture barrier in its outer layer can immediately stop the steam transfer through the fabric system during exposure; as a result, the TTTE becomes lower, or the SPP enhances (Figure 11). This immediate stop of the steam transfer is less prominent in a fabric system with a moisture barrier in its inner layer. In this context, it is also notable that Fabric-B (in Table 3) is an air-impermeable, single-layered fabric (without any moisture barrier) that possesses a moderately acceptable SPP. This is because Fabric-B has encapsulated fiber finishing that did not allow a transfer of steam through its structure; as a consequence, the SPP enhances (Figure 12).
where Q = the total discharge of steam per unit time (m3/s), K = fabric permeability (m2), A = cross sectional area of mass flow (m2), Pa = pressure of the steam jet (Pa), Pb = pressure of steam jet after passing through the fabric system (Pa), μ = viscosity (Pa·s), and L = thickness of the fabric systems (m).
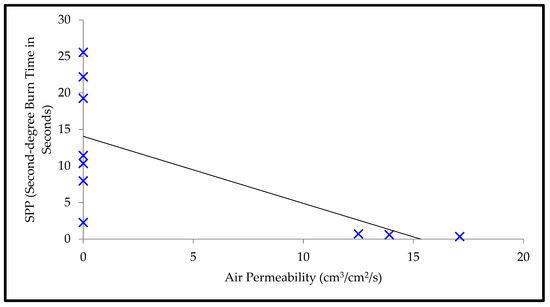
Figure 8.
Relationship plot of air permeability and SPP.
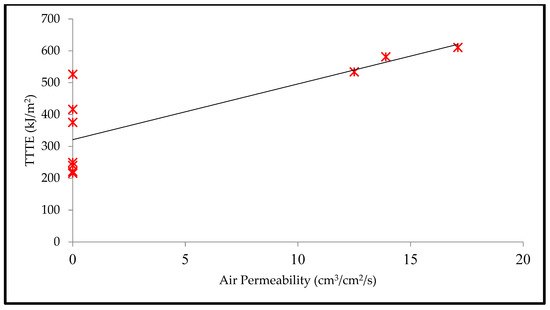
Figure 9.
Relationship plot of air permeability and TTTE.
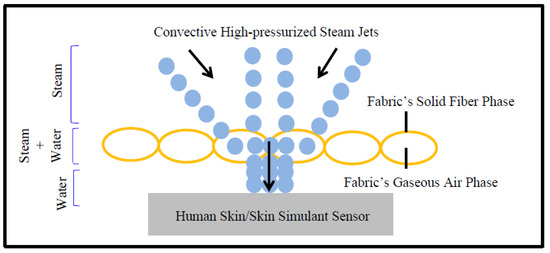
Figure 10.
Steam transfer mechanisms through regular fabrics.
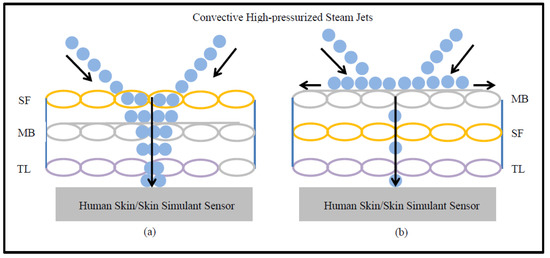
Figure 11.
High-pressurized steam transfer through (a) a triple-layered fabric with SF in the outer layer, and (b) a triple-layered fabric with MB in the outer layer.
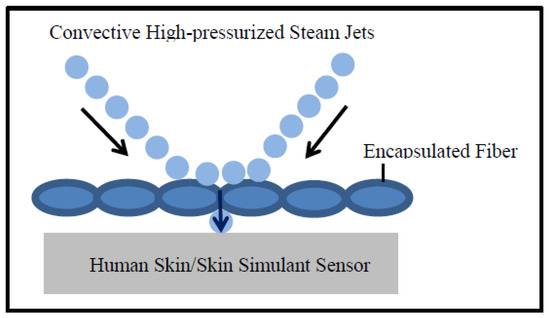
Figure 12.
High-pressurized steam transfer through a single-layered encapsulated fiber finished fabric.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In this study, it has been found that a fabric system with a low total transmitted thermal energy (TTTE) generally possesses high steam protective performance (SPP). The SPP/TTTE are mainly dependent upon the constructional attributes and physical properties of fabric systems. Usually, multilayered fabric systems comprising a moisture barrier are highly thermally insulated due to higher amounts of dead air trapped in their structures, and they can store steam in the empty spaces present among their constituent layers. Consequently, multilayered fabric systems have a high SPP and a low TTTE. It can also be concluded from this study that moisture barriers present in fabric structures play a crucial role in achieving a high SPP and low TTTE, by minimizing mass transfer through fabric systems toward the bodies of wearers. Altogether, it can be suggested that designing a thermal protective fabric system comprising a moisture barrier and considerable empty space may be useful to provide adequate protection against steam.
Furthermore, it was found that intimate contact occurs between fabric systems and the bodies of wearers in high-pressurized steam exposure; as a result, conductive thermal energy transfers through fabric systems toward the bodies of wearers. In this case, a thick, weighty, and thermally resistive fabric system can reduce the conductive thermal energy transfer, lower the TTTE, and enhance the SPP. Along with the physical properties of fabrics (e.g., weight and thickness), thermal properties (thermal conductivity, specific heat, and density) also contribute equally to the TTTE/SPP. Sometimes, thermophysical properties (e.g., weight, thickness, thermal conductivity, specific heat, and density) of fabric systems may change due to the compression exerted on them by high-pressurized steam; this situation can lower the SPP. Thus, it is expected that anticompression-based fabric systems could provide better protection from steam by achieving a high SPP. Furthermore, it can be concluded that the air permeability of a fabric is the most important property that affects the SPP/TTTE. As fabric is a porous medium comprising both solid fibers and gaseous air phases, a highly air-permeable fabric can transfer steam quickly in its air phase, resulting in a lower SPP. Generally, an air-impermeable fabric system can be used effectively to achieve a high SPP or a low TTTE. In the case of multilayered, impermeable fabric systems, it is suggested to place a moisture barrier in their outer layers. This configuration can effectively reduce the overall air permeability of these fabric systems; eventually, their mass transfer may decline and result in a lower TTTE and a higher SPP.
Overall, the findings obtained from this study can be useful for textile/material engineers to develop high performance thermal protective fabrics that increase the occupational health and safety of firefighters and industrial workers. This study can be further extended by analyzing the heat flux profile through fabric systems in the steam exposure of a certain duration.
Author Contributions
S.M., conceptualization, designing and performing experiments, writing, and data analysis; G.S., conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the University of Alberta, Canada, by an Izaak Walton Killam Memorial Scholarship to Sumit Mandal and Oklahoma State University, USA, by a start-up grant to Sumit Mandal.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate technical support from Mark Ackerman (Adjunct Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Alberta, Canada) and Stephen Paskaluk (Research Engineer, Department of Human Ecology, University of Alberta, Canada).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karter, M.J.; Molis, J.L. U.S. Firefighter Injuries—2011; National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): Quincy, MA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.tkolb.net/firereports/2012/2011ff_injuries.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2013).
- Fahy, R.F.; LeBlanc, P.R.; Molis, J.L. Firefighter Fatalities in the United States—2011; National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): Quincy, MA, USA, 2012; Available online: https://kstp.com/kstpImages/repository/cs/files/FirefighterFatalities.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2013).
- Mian, M.A.H.; Mullins, R.F.; Alam, B.; Brandigi, C.; Friedman, B.C.; Shaver, J.R.; Hassan, Z. Workplace-related burns. Ann. Burns. Fire. Disasters 2011, 24, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, C.; Becker, C.; Rossi, R.M. Moisture Transport and Absorption in Multilayer Protective Clothing Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, C.; Rossi, R.M. Temperature Analysis for the Prediction of Steam Formation and Transfer in Multilayer Thermal Protective Clothing at Low Level Thermal Radiation. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, C, Wyss, P, Rossi, RM. Analysis of steam formation and migration in firefighters’ protective clothing using x-ray radiography. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2010, 16, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G.; Ackerman, M.; Paskaluk, S.; Gholamreza, F. Characterization of textile fabrics under various thermal exposures. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, P. Simulation of constant pressure steam injection in a porous medium. Int. Commun. Heat. Mass. 1998, 25, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalbani, S.; Ackerman, M.; Crown, E.; Keulen, M.; Song, G. Performance of Protective Clothing and Equipment: Emerging Issues and Technologies STP-1544; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 9, p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, B.P. Epidemiology and man-days loss in burn injuries amongst workers in an oil industry. Burns 2001, 27, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.A.; Patel, J.H.; Lentz, C.W.; Bell, D.E. Firefighter Burn Injuries: Predictable Patterns Influenced by Turnout Gear. J. Burn. Care. Res. 2012, 33, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R. Fire fighting and its influence on the body. Ergonomics. 2003, 46, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev, I.; Barker, R.L. Analysis of Heat Transfer Characteristits of Fabrics in an Open Flame Exposure. Text. Res. J. 1983, 53, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Paskaluk, S.; Sati, R.; Crown, E.M.; Dale, D.J.; Ackerman, M. Thermal protective performance of protective clothing used for low radiant heat protection. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G. An Empirical Analysis of Thermal Protective Performance of Fabrics Used in Protective Clothing. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2014, 58, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Yoo, H.S.; Zhang, X.S.; Pan, N. Radiant Protective and Transport Properties of Fabrics Used by Wildland Firefighters. Text. Res. J. 2000, 70, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G.; Gholamreza, F. A novel protocol to characterize the thermal protective performance of fabrics in hot-water exposure. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G. Characterization of protective textile material for thermal hazard. In Proceedings of the Fiber Society Spring Conference, Hung Hum, Hong Kong, 23–25 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S.; Lu, Y.; Song, G. Characterization of thermal protective clothing under hot-water and pressurized steam exposure. In Proceedings of the The 2013 Herman and Myrtle Goldstein Student Paper Competition organized by American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC), Greenville, SC, USA, 9–11 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.; Indelicato, E.; Bolli, W. Hot Steam Transfer Through Heat Protective Clothing Layers. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2004, 10, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mandal, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Song, G. Characterization of Thermal Protective Clothing under Hot Water and Pressurized Steam Exposure. AATCC J. Res. 2014, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, R.; Song, G.; Dong, H. Thermal Protective Performance of Membrane material Used in Protective Clothing against Hot Water and Steam; Iowa State University Digital Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2017; Volume 74, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J. Quantification of the energy storage caused dual performance of thermal protective clothing containing with moisture exposed to hot steam. Energy Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 2585–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sun, L.; Lu, Y. Effects of Radiant Heat and Frictional Abrasion on Thermal Protective Performance of Clothing Against High Pressurized Steam. Cloth. Text. Res. J. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desruelle, A.; Schmid, B.; Montmayeur, A. Technical Report. 2002. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/citations/ADP012415 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Su, Y.; Li, R.; Song, G.; Li, J.; Xiang, C. Modeling steam heat transfer in thermal protective clothing under hot steam exposure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 120, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 1777; Standard Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996.
- ASTM D 3776; Standard Test Method for Mass per Unit Area (Weight) of Fabric. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- ASTM D 1518; Standard Test Method for Thermal Resistance of Batting Systems Using A Hot Plate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM D 737; Standard Test Method for Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Epps, H.H.; Leonas, K.K. Pore Size and Air Permeability of Four Nonwoven Fabrics. Int. Nonwovens J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, E. The Three P’s: Porosity, Permeability and Permeance. Available online: https://thefiberwire.com/2016/04/07/the-three-ps-porosity-permeability-and-permeance/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Scheidegger, A.L. The Physics of Flow Through Porous Media; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, S.; Song, G. Thermal sensors for performance evaluation of protective clothing against heat and fire: A review. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Camenzind, M.; Annaheim, S.; Rossi, R.M. Evaluation of heat and flame protective performance of clothing using manikins. In Manikins Textile Evaluation; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Annaheim, S.; Camenzind, M.; Li, J.; Mandal, S.; Psikuta, A.; Rossi, R.M. Moisture transfer of the clothing–human body system during continuous sweating under radiant heat. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 4537–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Annaheim, S.; Camenzind, M.; Rossi, R.M. Characterization and modelling of thermal protective performance of fabrics under different levels of radiant-heat exposures. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 48, 1184–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Psikuta, A.; Camenzind, M.; Li, J.; Mandal, S.; Michel Rossi, R.; Annaheim, S. Effect of perspired moisture and material properties on evaporative cooling and thermal protection of the clothed human body exposed to radiant heat. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Annaheim, S.; Capt, A.; Greve, J.; Camenzind, M.; Rossi, R.M. A categorization tool for fabric systems used in firefighters’ clothing based on their thermal protective and thermo-physiological comfort performances. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 3244–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, C. Steam Burns Moisture Management in Firefighter Protective Clothing. Ph.D. Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology ETH, Zurich, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard, J.H.; Lienhard, J.H. A Heat Transfer Textbook, 4th ed.; Dover Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 111–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.; Traugott, Z. Influence of humidity on the radiant, convective and contact heat transmission through protective clothing materials. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Performance of Protective Clothing: Improvement through Innovation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–27 January 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, G.; Batcheller, J.; Crown, E.M.; Ackerman, M.Y. Development of thermal protective fabrics for steam and hot water protection. In Proceedings of the 108th Institute of Textile Science Scientific Session, Qubec, QC, Canada, 21 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).