Modelling of Auxetic Woven Structures for Composite Reinforcement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
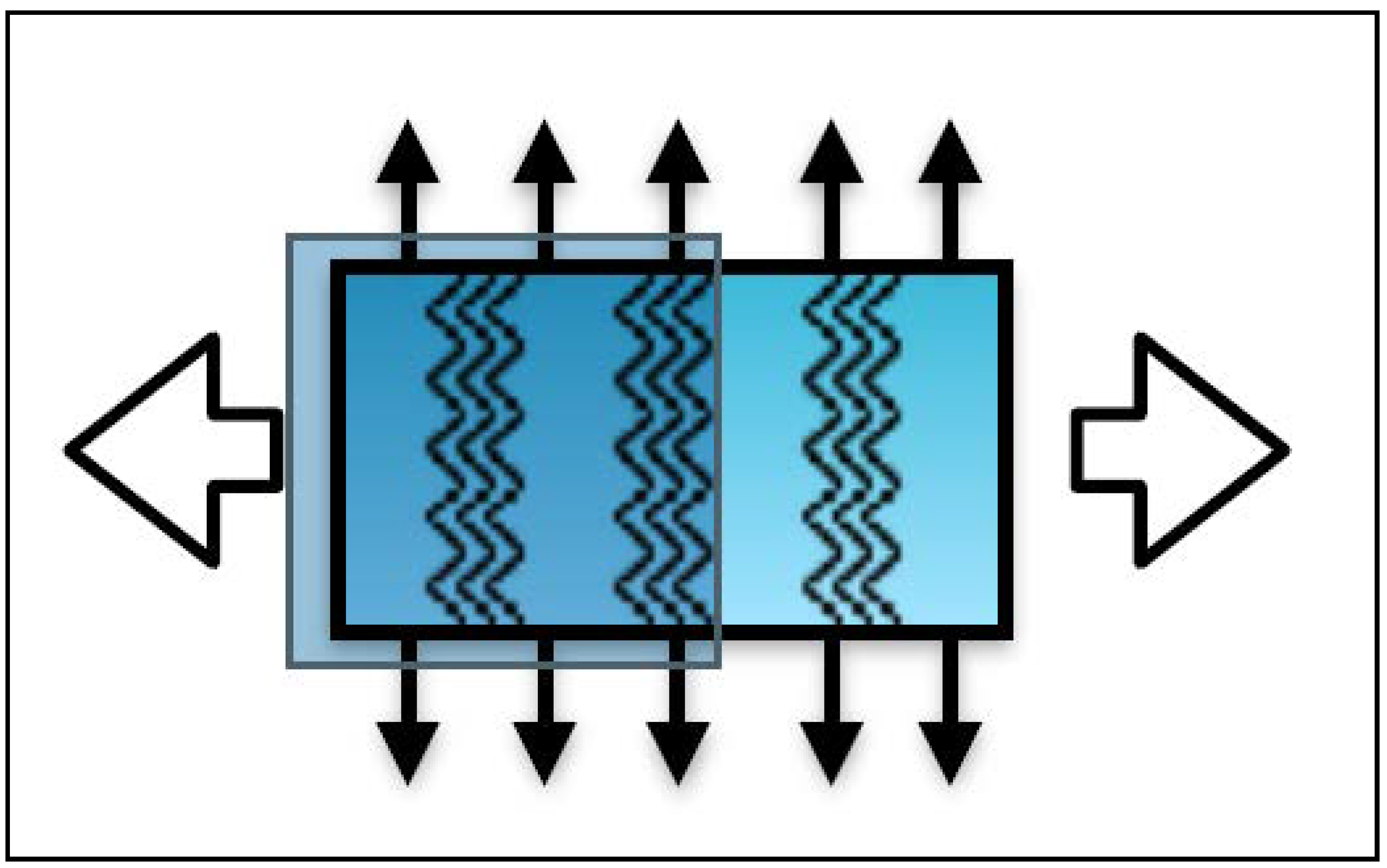
2. Analytical Model
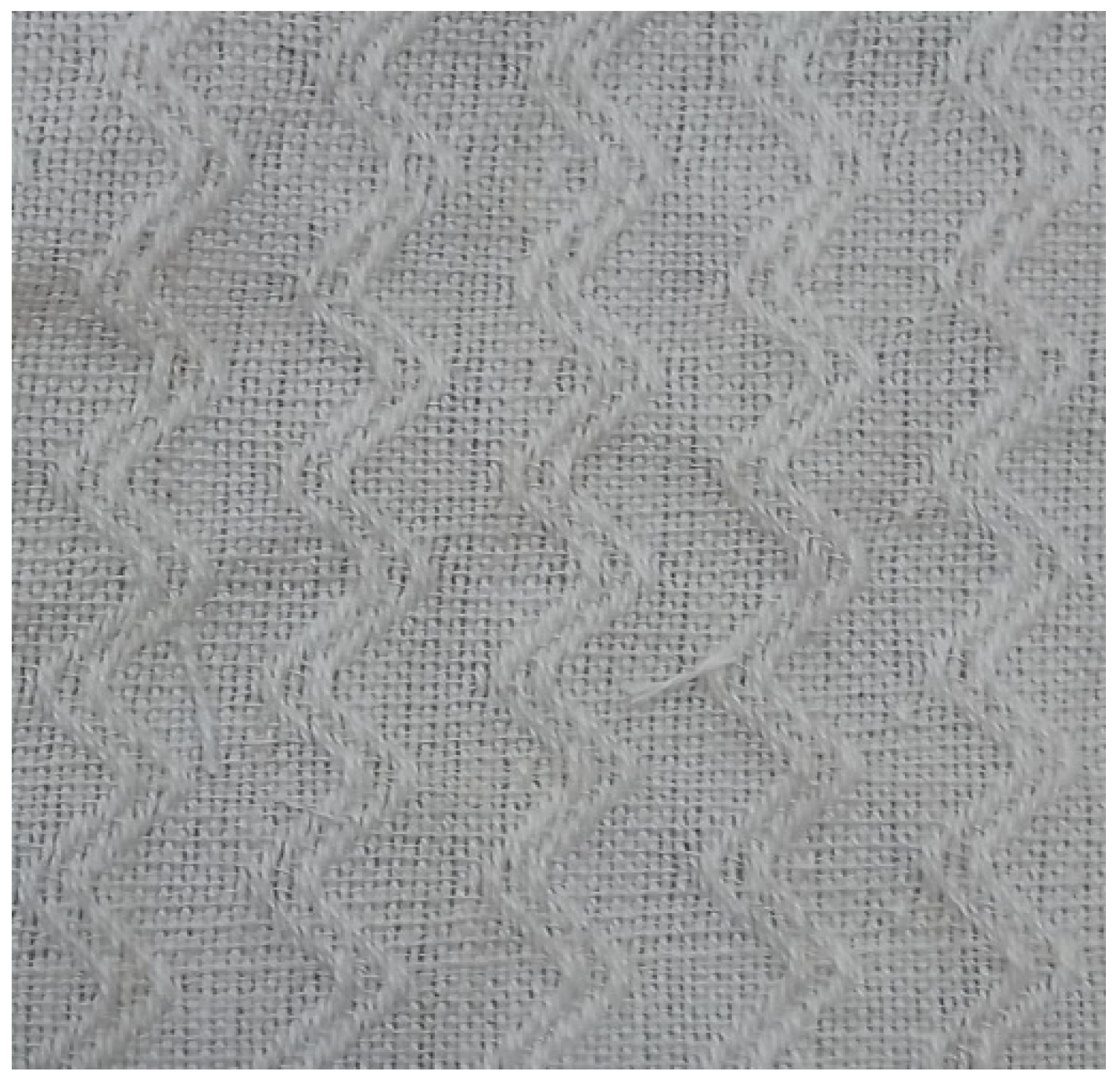
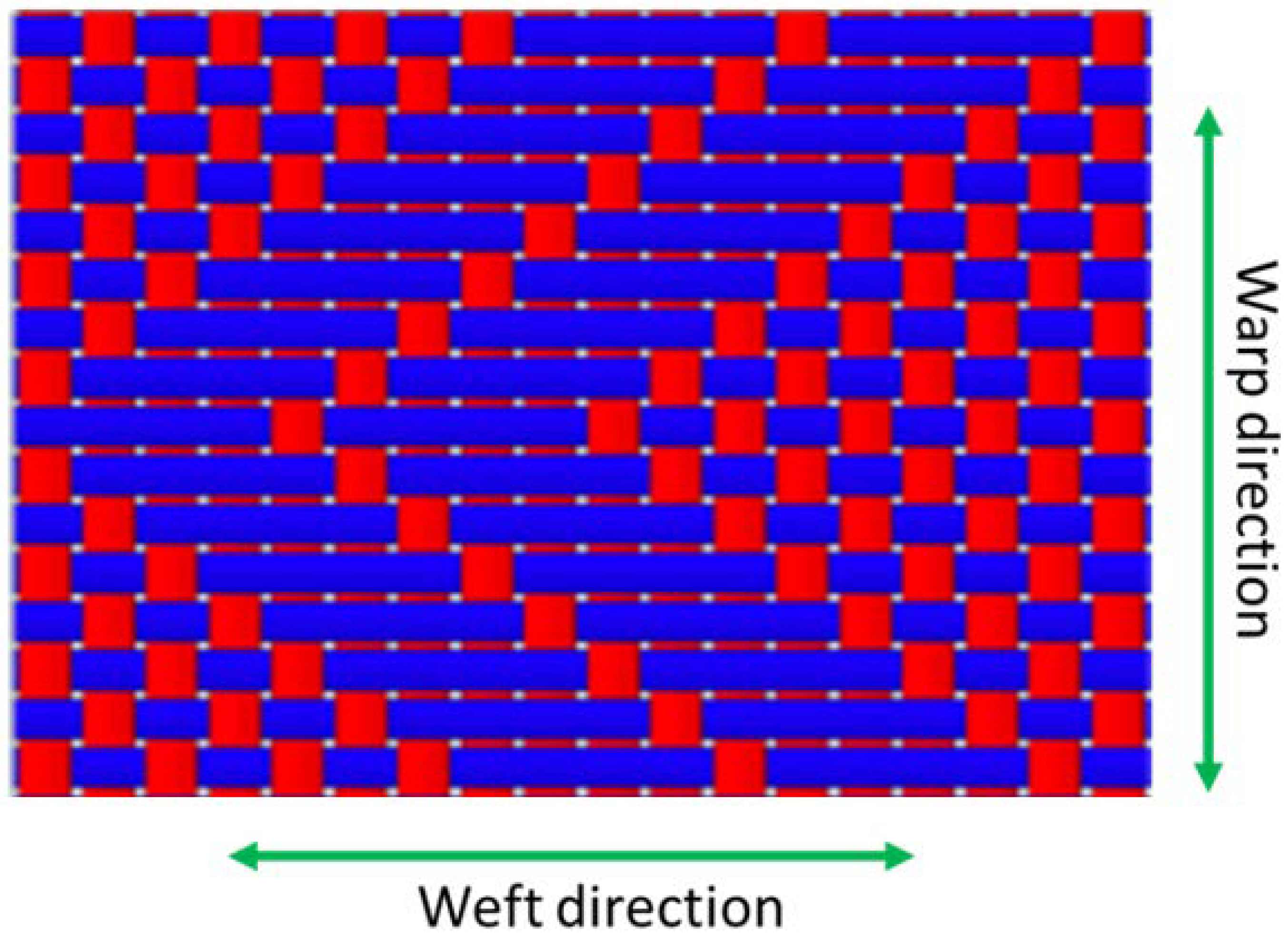
2.1. Material
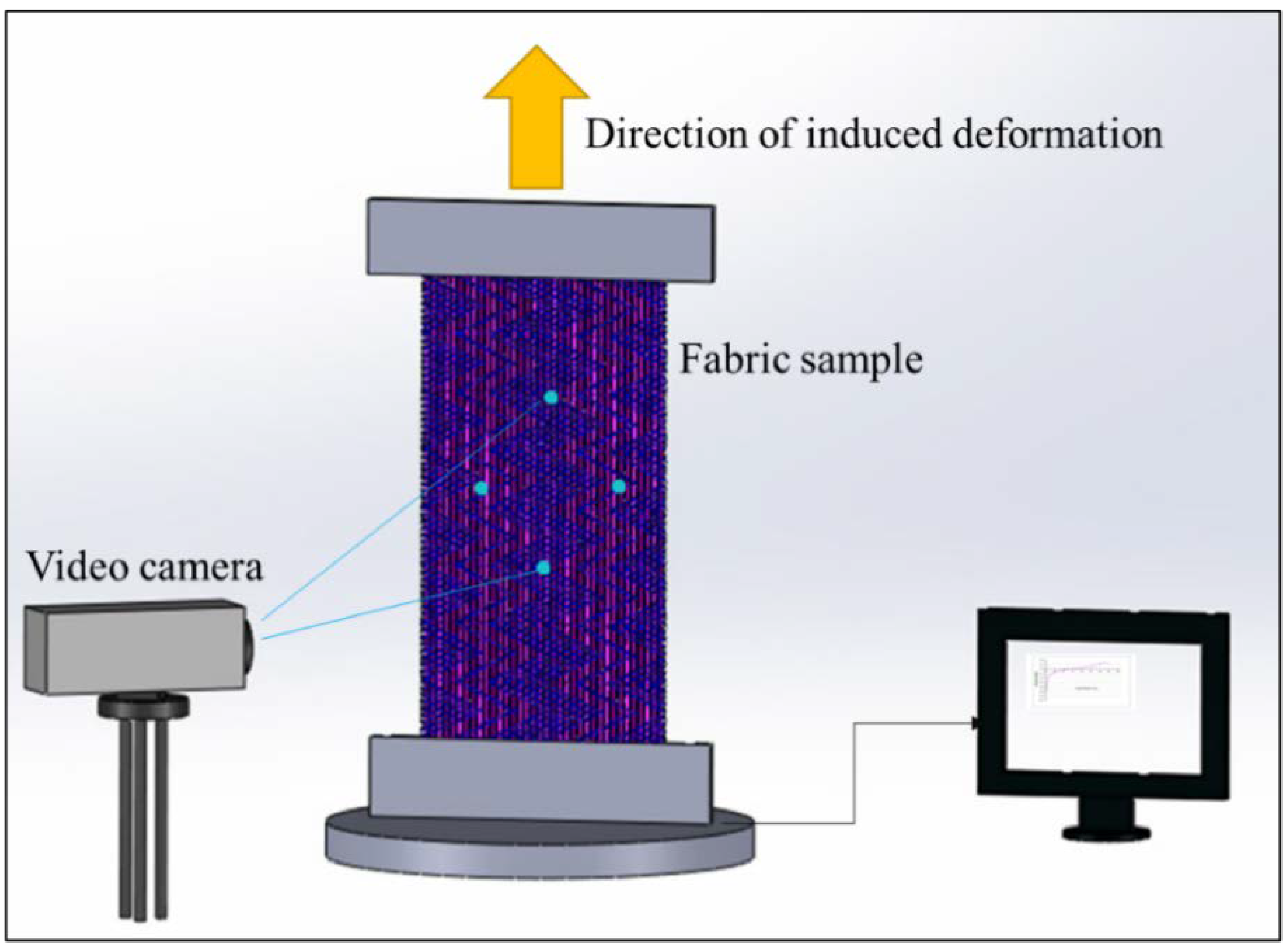
2.2. Test Method
3. Computational Model
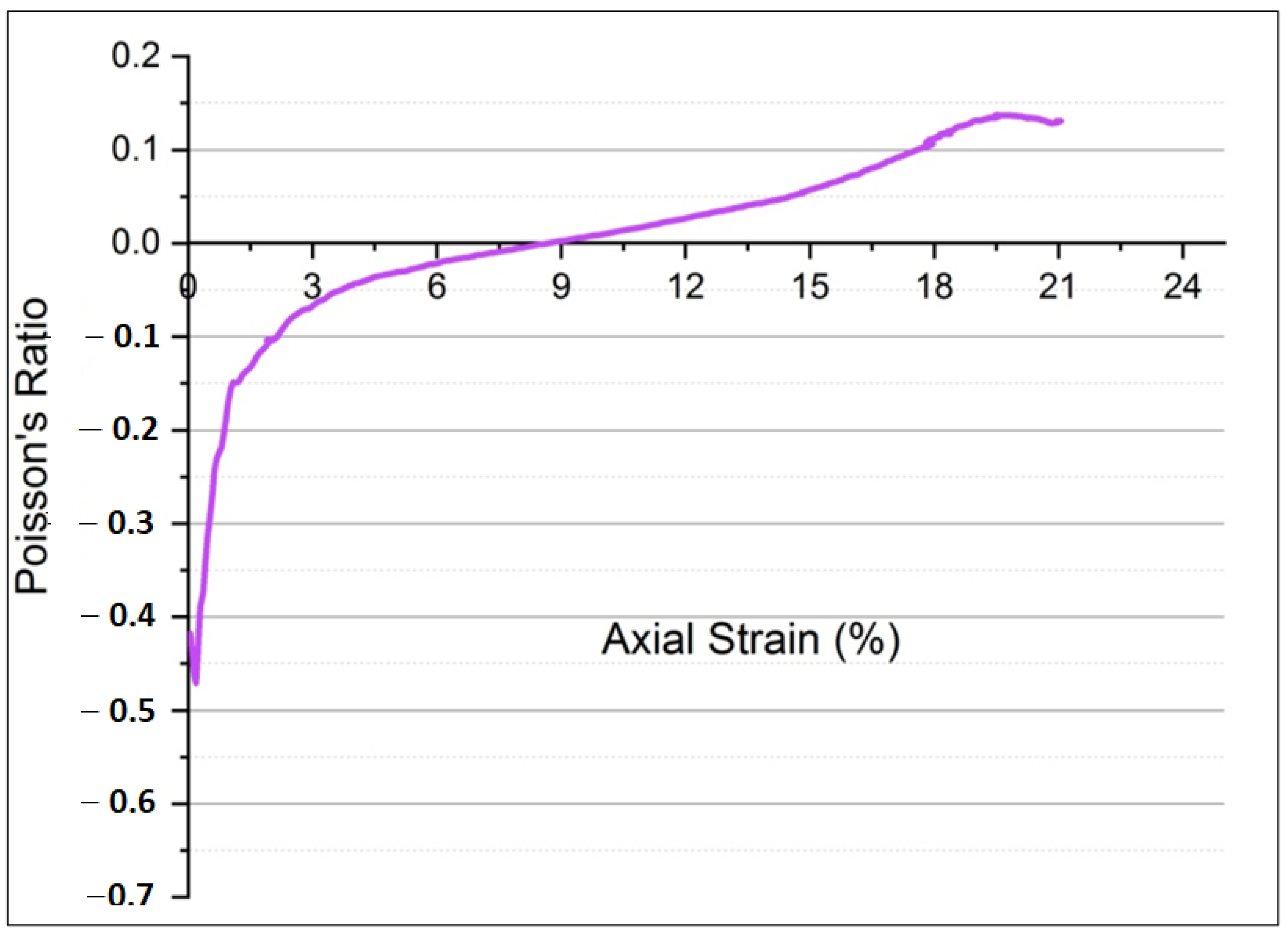
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Results
4.2. Analytical Model Results
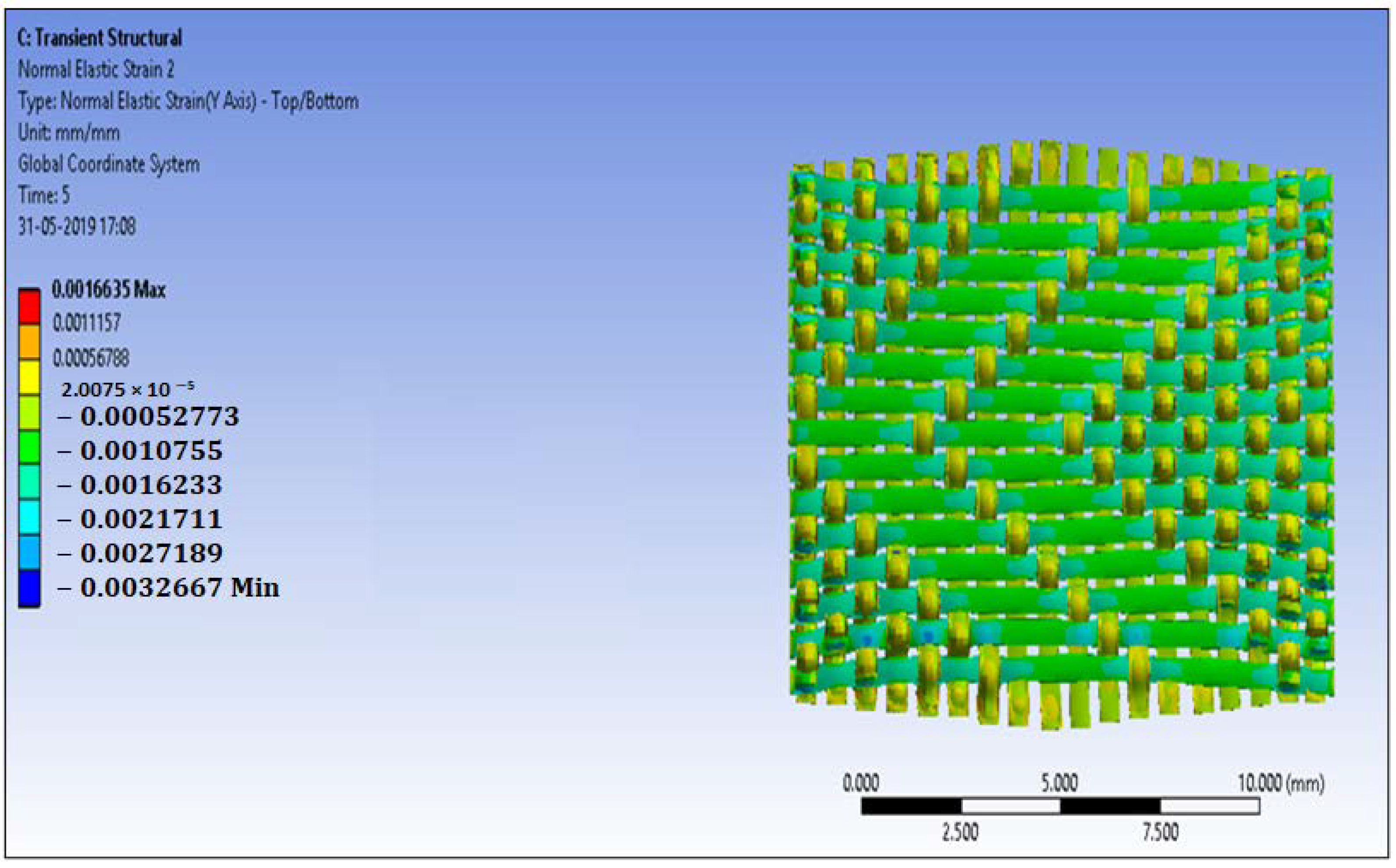
4.3. Computational Model Results
4.4. Comparison of the Computational and Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carneiro, V.H.; Meireles, J.; Puga, H. Auxetic materials—A review. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2013, 31, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C. Mechanics of Metamaterials with Negative Parameters; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodtsov, V.A.; Lisovenko, D.S. Auxetics among Materials with Cubic Anisotropy. Mech. Solids 2020, 55, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.C. Auxetic Materials and Structures; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.V.; Gorodtsov, V.A.; Lisovenko, D.S. Classification of cubic auxetics. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 2013, 250, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Q. Microstructural design of connective base cells for functionally graded materials. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4022–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.V.; Gorodtsov, V.A.; Lisovenko, D.S.; Volkov, M.A. Auxetics among 6-constant tetragonal crystals. Lett. Mater. 2015, 5, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, R.; Lisovenko, D.S.; Chentsov, A.; Lavrentyev, S.Y. Experimental study of auxetic behavior of re-entrant honeycomb with curvilinear elements. Lett. Mater. 2017, 7, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakes, R. Foam Structures with a Negative Poisson’s Ratio. Science 1987, 235, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.W. Two-Dimensional Isotropic System with a Negative Poisson Ratio. Phys. Lett. A 1989, 137, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.W.; Tretiakov, K.V.; Kowalik, M. Elastic properties of dense solid phases of hard cyclic pentamers and heptamers in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 036121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, R.V.; Gorodtsov, V.A.; Lisovenko, D.S. Auxetic mechanics of crystalline materials. Mech. Solids 2010, 45, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Shacklette, J.M.; Zakhidov, A.; Stafström, S. Negative Poisson’s ratios as a common feature of cubic metals. Nature 1998, 392, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Lewis, J.L. Properties and an anisotropic model of cancellous bone from the proximal tibial epiphysis. J. Biomech. Eng. 1982, 104, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolich, L.M.; LaBarbera, M.; Stevens, W.P. Poisson’s ratio of a crossed fibre sheath: The skin of aquatic salamanders. J. Zool. 1994, 232, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikhitsa, P.V. Architecture of cylinders with implications for materials with negative Poisson ratio. Phys. Status Solidi B-Basic Solid State Phys. 2007, 244, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, H. Auxetic materials and their potential applications in textiles. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, A.E.H. A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity. Nature 1920, 105, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, J.N.; Gatt, R.; Zammit, V.; Williams, J.J.; Evans, K.E.; Alderson, A.; Walton, R.I. Natrolite: A zeolite with negative Poisson’s ratios. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 086102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, S.K. Three decades of auxetic polymers: A review. e-Polymers 2015, 15, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunton, D.J.; Saunders, G.A. The Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of arsenic, antimony and bismuth. J. Mater. Sci. 1972, 7, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. The anisotropic behavior of Poisson’s ratio, Young’s modulus, and shear modulus in hexagonal materials. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Res. 1976, 38, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh-Haeri, A.; Weidner, D.J.; Parise, J.B. Elasticity of α-cristobalite: A silicon dioxide with a negative poisson’s ratio. Science 1992, 257, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Literature Review: Materials with Negative Poisson’s Ratios and Potential Applications to Aerospace and Defence; Defence Science and Technology Organisation: Canberra, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, N.; Mcleod, A.; Booth, F.; Scott, L.; Duncan, S.; Droubi, G. Auxetic Structures for Marine Safety Applications (Rope, Sandwich Panel). Presented at the The Institute of Marine Engineering, Science and Technology (IMarEST), Londin, UK, 28 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, M. Mechanical Properties of Auxetic and Conventional Polypropylene Random Short Fibre Reinforced Composites. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 5, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.; Ren, Z.; Smith, C.; Evans, K. A negative Poisson’s ratio carbon fibre composite using a negative Poisson’s ratio yarn reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-T.; Wang, B.; Wen, Z.-H.; Ma, L. Fabrication and mechanical properties of CFRP composite three-dimensional double-arrow-head auxetic structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 164, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozniak, A.; Wojciechowski, K.W.; Grima, J.; Mizzi, L. Planar auxeticity from elliptic inclusions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 94, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narojczyk, J.W.; Wojciechowski, K.W. Poisson’s Ratio of the f.c.c. Hard Sphere Crystals with Periodically Stacked (001)-Nanolayers of Hard Spheres of Another Diameter. Materials 2019, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brańka, A.C.; Heyes, D.M.; Wojciechowski, K.W. Auxeticity of cubic materials under pressure. Phys. Status Solidi B 2011, 248, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. Auxetic Textile Materials—A review. J. Text. Eng. Fash. Technol. 2017, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argatov, I.; Guinovart-Díaz, R.; Sabina, F. On local indentation and impact compliance of isotropic auxetic materials from the continuum mechanics viewpoint. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 54, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Z.-M.; Shi, W.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. On auxetic materials: Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3269–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Alderson, K.L. Auxetic materials: The positive side of being negative. Eng. Sci. Educ. J. 2000, 9, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, K.L.; Alderson, A.; Smart, G.; Simkins, V.R.; Davies, P.J. Auxetic polypropylene fibres: Part 1—Manufacture and characterisation. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2002, 31, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakes, R.S.; Witt, R. Making and Characterizing Negative Poisson’s Ratio Materials. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. 2002, 30, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorato, A.; Innocenti, P.; Scarpa, F.; Alderson, A.; Alderson, K.; Zied, K.; Ravirala, N.; Miller, W.; Smith, C.; Evans, K. The transverse elastic properties of chiral honeycombs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ali, M.N.; Sami, J.; Ansari, U. Review of Mechanics and Applications of Auxetic Structures. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alderson, K.; Webber, R.; Mohammed, U.; Murphy, E.; Evans, K. An experimental study of ultrasonic attenuation in microporous polyethylene. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 50, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darja, R.; Tatjana, R.; Alenka, P.Č. Auxetic textiles. Acta Chim. Slov. 2013, 60, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.S.; Hu, H. Woven fabrics made of auxetic plied yarns. Polymers 2018, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sloan, M.; Wright, J.; Evans, K. The helical auxetic yarn—A novel structure for composites and textiles; Geometry, manufacture and mechanical properties. Mech. Mater. 2011, 43, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Hook, P.; Smith, C.W.; Wang, X.; Evans, K.E. The manufacture and characterisation of a novel, low modulus, negative Poisson’s ratio composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chalivendra, V.B.; Kim, Y.K. Impact behaviour of auxetic Kevlar®/epoxy composites. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Akram, J.; Umair, M.; Hamdani, S.T.A.; Shaker, K.; Nawab, Y.; Zeeshan, M. Development of composites, reinforced by novel 3D woven orthogonal fabrics with enhanced auxeticity. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 49, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, F.; Chalivendra, V.; Kim, Y. Dynamic constitutive response of novel auxetic Kevlar®/epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 195, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. Auxetic fibre–reinforced composites. Auxetic Text. 2019, 1, 285–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.; Hu, H. Auxetic composites made of 3D textile structure and polyurethane foam. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 2016, 253, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N. Analysis of woven fabric strengths: Prediction of fabric strength under uniaxial and biaxial extensions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Zulifqar, A.; Hua, T.; Hu, H. Bi-stretch auxetic woven fabrics based on foldable geometry. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 2694–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, J.N.; Ravirala, N.; Galea, R.; Ellul, B.; Attard, D.; Gatt, R.; Alderson, A.; Rasburn, J.; Evans, K.E. Modelling and testing of a foldable macrostructure exhibiting auxetic behaviour. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 2011, 248, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, J.D.; Chapman, C.D.; Tang, X. Derivation of boundary conditions for micromechanics analyses of plain. J. Compos. Mater. 2000, 34, 724–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvelli, V.; Corazza, C.; Poggi, C. Mechanical modelling of monofilament technical textiles. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 42, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| S.No | Yarn Fineness | Tenacity at Breaking Extension (cN/tex) | Breaking Extension (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Cotton (30/2 tex) | 13.608 | 6.304 |
| B | Cotton (20 tex) | 11.890 | 3.404 |
| C | Core spun spandex 38 tex | 5.674 | 63.24 |
| Parameters | Warp | Weft |
|---|---|---|
| Yarn spacing (mm) | 0.635 | 0.635 |
| Crimp (%) | 8 | 7.1 |
| Bending modulus (MPa) | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| Coefficient of friction | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Direction | Plain Weave | Float |
|---|---|---|
| Weft (Axial strain %) | 1.1660 | 0.5253 |
| Warp (Transverse strain %) | 0.5268 | 0.3909 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shukla, S.; Behera, B.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Tichý, M.; Kolář, V.; Müller, M. Modelling of Auxetic Woven Structures for Composite Reinforcement. Textiles 2022, 2, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010001
Shukla S, Behera BK, Mishra RK, Tichý M, Kolář V, Müller M. Modelling of Auxetic Woven Structures for Composite Reinforcement. Textiles. 2022; 2(1):1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleShukla, Shivangi, Bijoya Kumar Behera, Rajesh Kumar Mishra, Martin Tichý, Viktor Kolář, and Miroslav Müller. 2022. "Modelling of Auxetic Woven Structures for Composite Reinforcement" Textiles 2, no. 1: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010001
APA StyleShukla, S., Behera, B. K., Mishra, R. K., Tichý, M., Kolář, V., & Müller, M. (2022). Modelling of Auxetic Woven Structures for Composite Reinforcement. Textiles, 2(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2010001








