Abstract
In recent years, much interest has been generated by the idea that nitrosative stress plays a role in the aetiology of human diseases, such as atherosclerosis, inflammation, cancer, and neurological diseases. The chemical changes mediated by reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are detrimental to cell function, because they can cause nitration, which can alter the structures of cellular proteins, DNA, and lipids, and hence, impair their normal function. One of the most potent biological nitrosative agents is peroxynitrite (ONOO−), which is produced when nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (•O2−) are combined at extremely rapid rates. Considering the plethora of oxidations by peroxynitrite, this makes peroxynitrite the most prevalent nitrating species responsible for protein, DNA, and lipids nitration in vivo. There is biochemical evidence to suggest that the interactions of the radicals NO and superoxide result in the formation of a redox system, which includes the reactions of nitrosation and nitration, and is a component of the complex cellular signalling network. However, the chemistry involved in the nitration process with peroxynitrite derivatives is poorly understood, particularly for biological molecules, such as DNA, proteins, and lipids. Here, we review the processes involved in the nitration of biomolecules, and provide a mechanistic explanation for the chemical reactions of NOS and nitrosative stress. This study reveals that these processes are based on a surprisingly simple and straightforward chemistry, with a fascinating influence on cellular physiology and pathology.
1. Introduction
In 1979, an article was published highlighting the role of endothelial cells in the acetylcholine-induced relaxation of arterial smooth muscle, recognising that vasodilation by bradykinin, histamine, and ATP was due to the same relaxing substance, which they called endothelium-derived relaxing factor EDRF [1]. In 1987, Ignarro concluded that EDRF was •NO or a chemically related radical species [2], after Murad suggested that EDRF was an “endogenous nitrovasodilator” [3]. Subsequently, Salvador Moncada’s group revealed that •NO release explains the biological activity of EDRF [4]. These early observations, together with the discovery of the L-arginine/•NO path, led to the subsequent finding of this ubiquitous gas in mammalian physiology [4]. This initial research on •NO and NOS activity was recognized with the 1998 Nobel Prize for Physiology and Medicine, awarded to Drs. Furchgott, Ignarro, and Murad [5].
Nitric oxide •NO is a ubiquitous molecule, generated by cellular signalling systems, found in a variety of cell types and organs, including the vascular endothelium, platelets, macrophages, and neuronal cells, as well as the active species of nitroglycerine [6]. In the cardiovascular system, nitric oxide determines the basal vascular tone and myocardial contractility, inhibits platelet aggregation, limits leukocyte adhesion to the endothelium, and regulates myocardial contractility [7]. It plays a role in the aetiology of cardiovascular disorders, such as essential hypertension, reperfusion injury, atherosclerosis, and myocardial depression associated with septic shock [8]. There is a continuous production of •NO by vascular endothelial cells, and this basal release regulates vascular tone [9].
•NO synthesis occurs from the central nitrogen present in the guanidine group of the amino acid L-arginine, which undergoes oxidation to form L-citrulline and the free radical •NO, in a reaction catalysed by the enzyme •NO synthase NOS [10], Figure 1. •NO is produced via the action of a group of enzymes called nitric oxide synthases. Oxygen and NADPH are necessary cofactors in the reaction. There are three isoforms of NOS, named according to their activity or the type of tissue in which they were first described. The isoforms are neuronal NOS (nNOS), endothelial NOS (eNOS), and inducible NOS (iNOS). These enzymes are also sometimes referred to by their number, so that nNOS is known as NOS1, iNOS is known as NOS2, and eNOS is NOS3. All three isoforms can be found in a wide variety of tissues and cell types. nNOS and eNOS are constitutively expressed in mammalian cells, and synthesise NO in response to increases in intracellular calcium levels. iNOS activity is independent of the level of calcium in the cell, however its activity—like all of the NOS isoforms—is dependent on the binding of calmodulin.
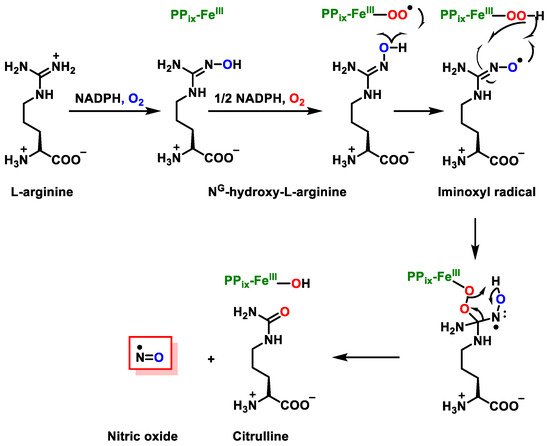
Figure 1.
Synthesis of citrulline and •NO from L-arginine, in a reaction catalysed by the enzyme NOS.
The oxidation of the terminal guanido-nitrogen atoms of L-arginine produces the nitric oxide radical (•NO). Different micro-environments have the ability to convert NO to a variety of additional RNS, including the nitrosonium cation (NO+), the nitroxyl anion (NO−), and the peroxynitrite (ONOO−). Under physiological conditions, endogenous arginine synthesis is sufficient to meet the body’s needs, and no additional supplementation from the diet is required. During childhood, growth, pregnancy, and diseases such as infections and cancer, arginine is synthesised endogenously via the arginine-citrulline cycle [11,12].
This NOS enzyme requires L-arginine and molecular oxygen as substrates, and the presence of several cofactors, including nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide phosphate NADPH, flavin adenine dinucleotide FAD, flavin mononucleotide FMN, and tetrahydrobiopterin BH4 [13]. The cofactor BH4 is an important regulator of NOS function, as it is required to maintain the enzymatic coupling of L-arginine oxidation [13]. The loss or oxidation of BH4 to 7,8-dihydrobiopterin (BH2) is associated with NOS uncoupling, resulting in the production of superoxide instead of •NO. The inhibition of BH4 recycling leads to the uncoupling of eNOS in endothelial cells, even without oxidative stress. Studies indicate that not only the level of BH4 but also its recycling, which regulate its bioavailability, represent real potential therapeutic targets [14]. Endothelial eNOS is mainly expressed in endothelial cells, and its function is to keep blood vessels dilated and control blood pressure, with vasoprotective and anti-atherosclerotic effects. Oxidative stress causes eNOS uncoupling, reduced •NO production, and endothelial dysfunction in the vasculature [15]. Moreover, the endothelial eNOS becomes uncoupled when its co-factor, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), is oxidised by superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, and no longer produces nitric oxide •NO, instead generating the superoxide anion [16,17], Figure 1. As a result of the excess reactive oxygen species (ROS), the inducible NOS isoform (iNOS) is activated, which overproduces •NO. •NO produced by iNOS reacts with the superoxide produced by uncoupled eNOS to form peroxynitrite, which nitrosylates tyrosine residues, inactivating proteins required for cellular energy metabolism and function, and nitrosylates the critical intracellular antioxidant glutathione, forming non-antioxidant S-nitrosyl glutathione, Figure 2.
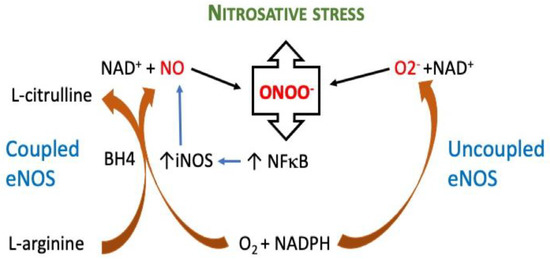
Figure 2.
Pathway mechanism of coupled and uncoupled eNOS. Uncoupling eNOS causes nitrosative stress. By oxidizing its cofactor, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), the endothelial isoform of nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) becomes uncoupled, generating a superoxide anion (O2). Superoxide then reacts with nitric oxide (NO), which is generated by neighbouring, still-coupled eNOS, to form the potent oxidant peroxynitrite (ONOO−), which in turn, increases the activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NFB) in the cell. When the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is activated, the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is expressed, which creates large amounts of NO that combine with eNOS-generated O2 to enhance the synthesis of ONOO−.
All NOS enzymes (eNOS, iNOS and nNOS) contain a zinc–thiolate cluster formed by a zinc ion, with a structural rather than a catalytic function [18].
•NO can also be generated from the inorganic anions nitrate NO3− and nitrite NO2−, particularly in hypoxic states [19]. The oxidation of •NO produces •NO2, and the oxidation in aqueous solution mainly produces nitrite ion NO2− [20], Figure 3.
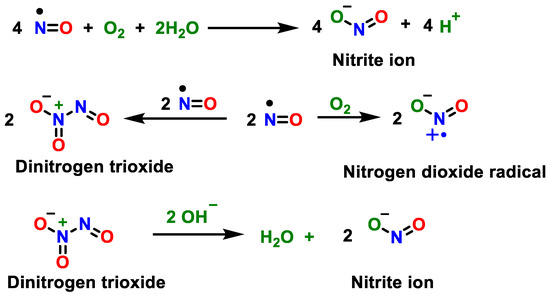
Figure 3.
Oxidation of •NO to •NO2 and oxidation in aqueous solution to nitrite ion NO2−.
Biochemically, •NO, a free radical (with an unpaired electron), moderately stable in aqueous media, is a biological messenger in physiological solutions, and is able to diffuse easily through biological membranes [21]. Its plasma concentration is approximately 3 nmol/L. The redox biochemistry of nitrogen monoxide is related to its biologically active redox forms, NO+ (nitrosonium), NO− (nitroxyl anion), and the free radical •NO [22]. These •NO redox species interact in a manner analogous to the redox biochemistry of O2, such as the superoxide anion •O2− and O22− (which forms H2O2 in aqueous solution), but unlike •O2− and H2O2, is not cytotoxic. Under physiological conditions, endogenous •NO (or oxidised derivatives such as NO+, N2O3, or nitrosylated metals) reacts in the presence of molecular oxygen with low molecular weight thiol groups to form S-nitrosothiols; significantly more stable in plasma, thus serving as a reservoir. Once •NO is produced, it readily diffuses across cell membranes to interact with specific molecules, and regulates protein activity by reversibly binding, including heme iron and thiols.
2. Superoxide Anion (•O2−) and Peroxynitrite (ONOO−)
Reactive oxygen species ROS are risk factors for the development of diseases such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus DMT2. •O2− is the first step of O2 reduction and this reaction occurs spontaneously, with a negative free Gibbs energy ∆Go: [23].
O2 + e− → O2•− ΔGo = −101.39 Kcal/mol
ROS are mainly produced as a by-product of mitochondrial respiration. A small percentage of the electrons escape complexes I and III, in the electron transport chain ETC [24]. They are also generated in the immune system to eliminate invading micro-organisms, and, in phagocytes, NADPH oxidase produces •O2− in large quantities for the oxygen-dependent destruction of invading pathogens [25]. Consecutive O2 reduction with H+ and e− is a reaction in which the final product is water, with a ∆Go ≤ 0.
O2 + 4e− + 4H+ → 2H2O ΔGo = −1162.76 Kcal/mol
Peroxynitrite derivatives induce lipid peroxidation, the inactivation of enzymes and proteins, and mitochondrial dysfunction. They are in equilibrium with peroxynitrous acid (ONOOH) and, under physiologically pH conditions, both species coexist [26]. Peroxynitrite is an anion derived from the reaction of •NO with •O2−, Figure 4.
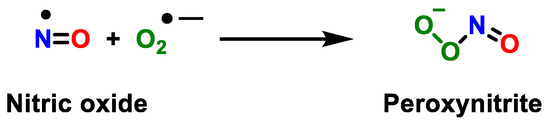
Figure 4.
Reaction between the radical •NO and superoxide anion •O2−, yielding peroxynitrite.
•NO2 is also formed from the decomposition of organic peroxynitrites (RONOO). Due to its oxidising properties, peroxynitrite can damage a wide variety of biomolecules in cells, including lipids, DNA, and proteins, and induces the mitochondrial dysfunction that triggers apoptosis, mediated by calcium-dependent cysteine proteases (calpains) [27]. Peroxynitrite and derivatives are associated with a variety of disease processes, such as atherosclerosis [28], hypertension [29], inflammation [30], cancer [31], neurodegeneration [32], and sepsis [33]. It is a potent oxidising [34] and nitrating agent, with a short half-life of about 10 ms [35,36]. Due to its reduced half-life, it decomposes into oxidising and nitrating species, including the •OH and •NO2 radicals. ONOO− is a highly reactive oxidant, with a very important role in the destruction of foreign pathogens by immune cells, as macrophages [37], because it decomposes easily in the presence of the H+ cation and produces •OH and •NO2 [38].
Metalloproteins such as superoxide dismutase (SOD1 and SOD2) and CO2 generate the •NO2 radical, the cause of the detrimental effects attributed to peroxynitrite (given its very short lifespan). ONOO− can interact with carbon dioxide CO2 to generate nitrosoperoxocarbonate ONOOCO2−, which by homolytic fission, produces •NO2 and anionic carbonate radical •CO3−. Peroxynitrite does not oxidise or nitrate tyrosine directly, but rather oxidises and nitrates it via its radical products. The question of whether peroxynitrite may be generated biologically at levels high enough to play a substantial role in •NO2 dependent disease has stimulated serious debate in the area. Peroxynitrite is a transitory species with a biological half-life (10–20 ms) even shorter than NO (1–30 s), thus its existence must be deduced by analytical, pharmacological, or genetic methods. Further possible reactions of peroxynitrite and derivative radicals are as follows, Figure 5.
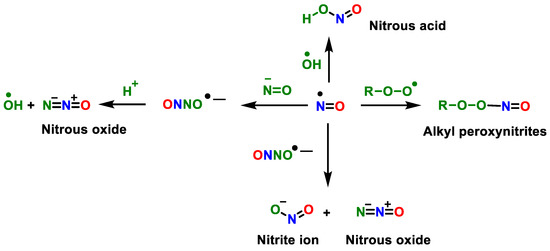
Figure 5.
Secondary reactions of peroxynitrite and another radical.
ONOO− is a highly reactive oxidant, with a very important role in the destruction of foreign pathogens by immune cells such as macrophages. If its production is deregulated, it contributes to various cardiovascular, neurological diseases, and cancer. Its formation occurs in those cellular compartments where superoxide anion is produced [39]. Peptide glutathione (GSH) reaches millimolar concentrations inside cells, and for some time, was considered a peroxynitrite scavenger. However, the reaction is slow and does not prevail over other in vivo secondary reactions, being mainly a target for derived peroxynitrite radicals. Since peroxynitrite can initiate various unwanted biological oxidations, cells use the superoxide dismutase pathway, SOD, to prevent the formation of peroxynitrite and its side reactions [40]. Peroxynitrite radical scavenging is a useful tool to assess the antioxidant potential of polyphenols [41]. These free radicals increase protein S-nitrosylation and nitration, resulting in nitrosative stress, which can alter the structures of proteins, and hence impair their normal function. Additionally, nitrosative stress can damage membrane fatty acids, DNA, and its repair mechanism. Protein activity is disrupted, and organelle function is unsettled under such stress conditions, resulting in reduced cell mitosis and increased apoptosis.
Metalloproteins such as superoxide dismutase (SOD1 and SOD2) and CO2 generate the •NO2 radical, the cause of the detrimental effects attributed to peroxynitrite (given its very short lifespan). ONOO− can interact with carbon dioxide CO2 to generate nitrosoperoxocarbonate ONOOCO2−, which via homolytic fission, produces •NO2 and anionic carbonate radical •CO3−. Secondary reactions of peroxynitrite depend on interaction with H+, CO2, and metalloproteins, Figure 6.
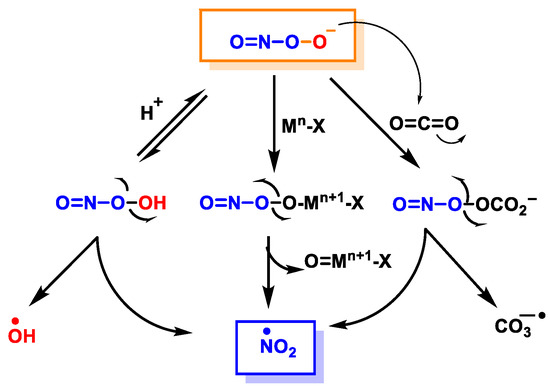
Figure 6.
Secondary reactions of peroxynitrite to •NO2, •OH and •CO3−. Mn-X represents a metalloprotein, in which the co-ordinate metal moves up one valence to Mn+1-X, as is the case for the superoxide dismutase SOD1.
3. Protein Nitration
Peroxynitrite derivatives can modify proteins, promoting changes in protein function through oxidation/nitration mechanisms, with biological relevance, by producing new functions, protein aggregation, turnover, signalling, and immunological processes [42]. Peroxynitrite is involved in cell signalling processes, and some peroxynitrite-modified proteins have been found to be immunogenic, and implicated in the aetiology of several diseases. Among the molecular after-effects of peroxynitrite, the tyrosine-nitrated proteins are of prime relevance [43]. The nitration of tyrosine residues has been observed in a variety of processes, including those associated with oxidative stress, such as inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and cardiovascular diseases [44]. The oxidative inflammatory environment dictates the production and pro-oxidative reactivity of NO metabolites, as well as the pro- and antioxidant activity of •NO itself. Proteins and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) can be oxidised, nitrosated, or nitrated, depending on the redox state. The nitration of protein tyrosine residues has been identified as one of the primary characteristics of peroxynitrite and peroxynitrite-derived species’ interactions with biomolecular targets. The chemical reactions involved in protein oxidation and nitration are outlined below, in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
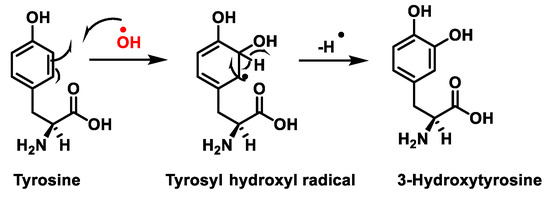
Figure 7.
Tyrosine oxidation with hydroxyl radical •OH to hydroxytyrosine.
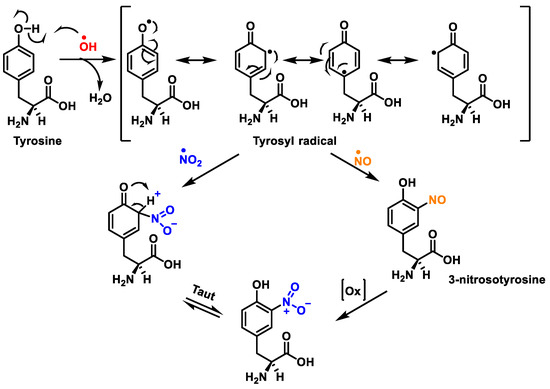
Figure 8.
Tyrosine nitration with •NO2 and nitrosation with •NO to nitrotyrosine.
Protein nitration in tyrosine residue is a covalent protein modification from the addition of a nitro •NO2 group adjacent to the hydroxyl group on the aromatic ring. A stable product 3-nitrotyrosine is formed via the addition of •NO2 to the ortho position of tyrosine, Figure 8. The proximity of catalytic metal centres appears to be of critical relevance in the process of Tyr-nitration. This allows for more selectivity and, in certain cases, greater specificity in the nitration of the Tyr residue.
The nitration of tyrosine residues has been observed in a variety of processes, including those associated with oxidative stress, such as inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and cardiovascular diseases [44]. A key role in cellular defence against oxidative stress is played by Mn superoxide dismutase MnSOD or SOD2. Several residues of MnSOD (including Tyr34, Tyr9 and Tyr11) are susceptible to nitration, and the loss of MnSOD activity on Tyr34 nitration implies its inactivation [45]. Some amino acids can react directly with peroxynitrite: cysteine, methionine, and tryptophan, and others do not react directly with peroxynitrite (e.g., tyrosine, phenylalanine, and histidine), but can be modified through secondary species, such as hydroxyl, carbonate, and nitrogen dioxide radicals. In contrast to tyrosine, tryptophan has many sites to be nitrated.
4. Lipid Nitration
Lipid peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation and nitration, including cell membranes and lipoproteins, lead to the formation of new signalling modulators, modifying the role of key lipid-metabolising enzymes [46]. The chemical reactions on lipid oxidation and nitration are outlined below, Figure 9. It is believed that NO2-FAs are formed by the non-enzymatic interaction of unsaturated fatty acids with NO-derived species, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrite (•NO2), or peroxynitrite (ONOO−); nevertheless, the exact process by which fatty acids are nitrated in vivo is unclear as yet [47]. However, nitrated unsaturated fatty acids have chemically electrophilic characteristics that allow them to facilitate reversible nitroalkylation reactions (Michael reaction), with deprotonated thiolate anions such as cysteine thiol groups in proteins, or peptides such as glutathione. Furthermore, the formation of NO2-FAs in a lipophilic environment, such as the bilayer of cellular membranes, provides a suitable signal transduction pathway. Nitrated lipids also serve as signalling molecules, since modest quantities of these molecules can act as effective mediators for signal-transduction cascades when present in high concentrations.
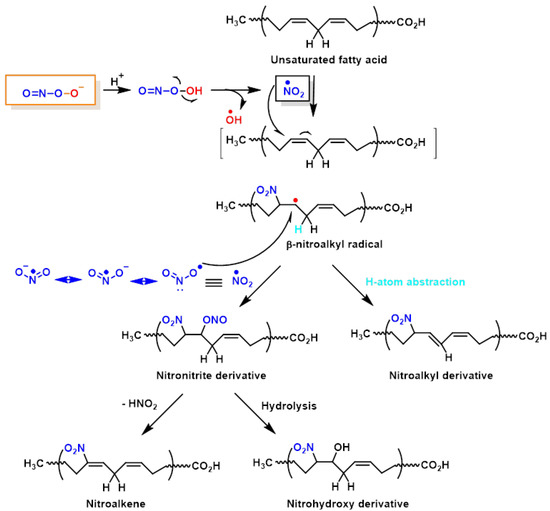
Figure 9.
Lipid oxidation and nitration to nitrohydroxyderivatives.
5. DNA Nitration
Peroxynitrite can cause DNA strand breaks and even react with DNA, causing damage to both the sugar and the bases in the nucleus. Of the four DNA bases, guanine has the lowest oxidation potential (E° = 0.81 V) and is the most reactive, giving 8-oxoguanine and 8-nitroguanine, oxazolone, and its precursor, imidazolone [48]. The chemical reactions on guanine oxidation and nitration are outlined below, Figure 10.
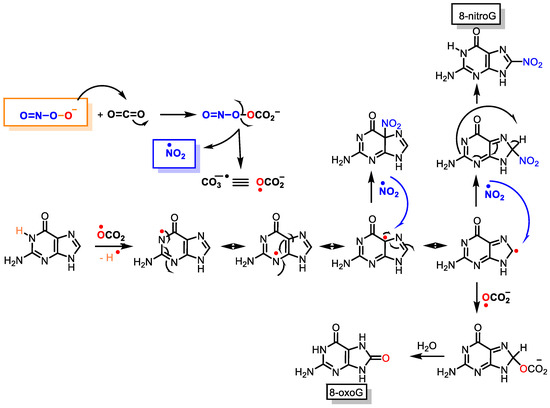
Figure 10.
Guanine reactions with peroxynitrite to 8-oxoguanine and 8-nitroguanine.
6. Role of •NO as a Potential Treatment against COVID-19
COVID-19 is both a respiratory and a vascular disease, especially for patients with severe symptoms [49]. The virus SARS-CoV-2, with a size of 80–100 nm, infects and replicates in endothelial cells EC before infecting the underlying tissue, as the EC is the major source of •NO synthesis in mammals. •NO is an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory molecule that plays an important role in vascular and pulmonary function against viral infections [50]. In the case of the SARS-CoV-1 virus, it caused the severe acute respiratory outbreak in 2003, •NO inhibited viral replication through cytotoxic reactions via intermediates such as peroxynitrite [51]. •NO derivatives are antimicrobial, with key roles in pulmonary vascular function in the context of viral infections and pulmonary diseases. At this point, •NO emerges as a potential treatment against COVID-19 [52].
Reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide anion •O2−, serve as the host defence and are generated during viral infection. Excess ROS activate M1 macrophages, recruit neutrophils, and increase peroxynitrite production [53], which act as a potent response to the invading virus, but induce collateral damage, such as endothelial dysfunction, vessel permeabilisation, and lipid membrane peroxidation. Factors that contribute to regulating the inflammatory and immune response include the nitric oxide/reactive oxygen species •NO/ROS ratio, M1 macrophage activation, and induced red blood cell RBC damage [54]. Inducible NOS is commonly elevated during infection by viruses, as in SARS-CoV-1 infection [31]. •NO generated from endothelial eNOS decreases with age, and patients with chronic vascular inflammation, such as diabetes mellitus type 2, metabolic syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, hypertension, autoimmune disorders, and haemoglobinopathies, may produce less eNOS. Simultaneously, this enzyme, under oxidative stress, reduces its expression and •NO production [55].
The •NO-deprived vasculature suffers from persistent inflammation, reduced oxygen supply, and the elimination of toxic by-products generated during infection, due to reduced blood flow to and from the hypoxic tissue. Both NO and its generated RNS can have substantial impacts on mitochondrial activity. Nitric oxide interacts strongly with all heme moieties, reducing the activity of iron-containing enzymes, such as cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV). The electron transport chain is inhibited by nanomolar •NO, which competes with O2 for electrons. Supplementation with •NO-generating compounds prevents cytokine storming, and restores functional capillary density, which is crucial for oxygen supply to organs that are sensitive to oxygen deprivation, such as the kidneys [56]. Older people with vascular stressors may have low levels of vascular •NO, increasing their vulnerability. The supplementation of arginine for specific patient populations may be a treatment that reduces viral load in the lungs and prevents the cascade of negative events associated with infection [57], but above all, restoring •NO bioavailability may be a genuine preventive or early treatment option for COVID-19 [58].
7. Conclusions
In recent years, there has been considerable interest in the idea that chronic oxidative/nitrosative stress plays a role in the aetiology of a variety of human illnesses. Oxidative/nitrosative stress is caused by an imbalance in the oxidant/antioxidant system, as shown by an increase in the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. NO is an important oxidative biological signalling molecule involved in a variety of physiological processes, such as neurotransmission, blood pressure control, defence mechanisms, smooth muscle relaxation, and immunological modulation. In the extracellular environment, •NO reacts with oxygen and water to form nitrate and nitrite anions. A major route of •NO degradation is the rapid interaction of NO with superoxide anions to produce the highly reactive product peroxynitrite (ONOO–). The •NO2 radical is a key radical in cellular nitrosative stress. Many metabolic processes involving cellular proteins (e.g., nitration, nitrosylation, oxidation), DNA (e.g., deamination), and lipids are driven by these extremely reactive RNS (e.g., nitration, oxidation). Typically, the result is a biomolecule’s loss of function. A basic principle of the nitrosative stress conceptual framework is that these RNS-mediated chemical changes are detrimental to cellular function. In this review, we provide a theoretical study of the chemical equations of nitration, due to peroxynitrite anion derivatives on lipids, proteins, and DNA being presented, which are of particular importance due to the negative side effects on health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A.J. and E.P.-L.; investigation, C.A.J. and E.P.-L.; writing—review and editing, C.A.J.; J.M.P.d.l.L. and F.J.P.; supervision, C.A.J. and J.M.P.d.l.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by “Junta de Castilla y León”, projects FEDER-VA115P17, and VA149G18); by project APOGEO (Cooperation Program INTERREG-MAC 2014–2020, with European Funds for Regional Development-FEDER. “Agencia Canaria de Investigación, Innovación y Sociedad de la Información (ACIISI) del Gobierno de Canarias”, project ProID2020010134, Caja Canarias, project 2019SP4 and Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Grant PID2019-105838RB-C31).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Murad, F.; Arnold, W.P.; Mittal, C.K.; Braughler, J.M. Properties and regulation of guanylate cyclase and some proposed functions for cyclic GMP. Natl. Libr. Med. 1979, 11, 175–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Buga, G.M.; Wood, K.S.; Byrns, R.E.; Chaudhuri, G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9265–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murad, F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, R.G.; Palacios, M.; Palmer, R.M.; Moncada, S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: A transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5159–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- SoRelle, R. Nobel Prize Awarded to Scientists for Nitric Oxide Discoveries. Circulation 1998, 98, 2365–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsuki, S.; Arnold, W.; Mittal, C.; Murad, F. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin and nitric oxide in various tissue preparations and comparison to the effects of sodium azide and hydroxylamine. J. Cycl. Nucleotide Res. 1977, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoo, A.; van Zanten, J.V.; Metsios, G.S.; Carroll, D.; Kitas, G.D. The endothelium and its role in regulating vascular tone. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2010, 4, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibel, A.; Lukinac, A.M.; Dambic, V.; Juric, I.; Selthofer-Relatic, K. Oxidative Stress in Ischemic Heart Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Leung, S.W. Vascular nitric oxide: Beyond eNOS. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reedijk, J.; Poeppelmeier, K. Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II: From Elements to Applications; V1 Main-Group Elem., Incl. Noble Gases V2 Transition Elem., Lanthanides and Actinides V3 Bioinorganic Fundam. and Appl.: Metals in Nat. Living Syst. and Metals in Toxicology and Med. V4 Solid-State Mater., Incl. Ceramics and Minerals V5 Porous Mater. and Nanomaterials V6 Homogeneous Catal. Appl. V7 Surf. Inorganic Chem. and Heterog. Catal. V8 Coord. and Organometallic Chem. V9 Theory and Methods; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–7196. [Google Scholar]
- Husson, A.; Brasse-Lagnel, C.; Fairand, A.; Renouf, S.; Lavoinne, A. Argininosuccinate synthetase from the urea cycle to the citrulline–NO cycle. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, H.; Sustmann, R.; Thater, C.; Butler, A.; Ingold, K. On the mechanism of the nitric oxide synthase-catalyzed conversion of N omega-hydroxyl-L-arginine to citrulline and nitric oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17776–17779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crabtree, M.J.; Channon, K.M. Synthesis and recycling of tetrahydrobiopterin in endothelial function and vascular disease. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jerkic, M.; Letarte, M. Contribution of oxidative stress to endothelial dysfunction in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manukhina, E.; Downey, H.F.; Mallet, R.T. Role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular adaptation to intermittent hypoxia. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 231, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B. Teaching the basics of redox biology to medical and graduate students: Oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmens, B.; Goessler, W.; Schmidt, K.; Mayer, B. Role of Bound Zinc in Dimer Stabilization but Not Enzyme Activity of Neuronal Nitric-oxide Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35786–35791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N.; Chandra, M.; Tuteja, R.; Misra, M.K. Nitric Oxide as a Unique Bioactive Signaling Messenger in Physiology and Pathophysiology. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2004, 2004, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.B.; Bryan, N.S.; Bian, K.; Murad, F. Discovery of the nitric oxide signaling pathway and targets for drug development. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.S.; Singel, D.J.; Loscalzo, J. Biochemistry of Nitric Oxide and Its Redox-Activated Forms. Science 1992, 258, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés Juan, C.; Pérez de Lastra, J.M.; Plou Gasca, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J. An Update on Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, F.; Mattevi, A. Structure and mechanisms of ROS generation by NADPH oxidases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 59, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Campolo, N.; Trujillo, M.; Bartesaghi, S.; Carballal, S.; Romero, N.; Alvarez, B.; Radi, R. Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1338–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteman, M.; Armstrong, J.S.; Cheung, N.S.; Siau, J.L.; Rose, P.; Schantz, J.T.; Jones, D.P.; Halliwell, B. Peroxynitrite mediates calcium-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death via activation of calpains. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1395–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Brock, T.A.; Chang, L.Y.; Crapo, J.; Briscoe, P.; Ku, D.; Bradley, W.A.; Gianturco, S.H.; Gore, J.; Freeman, B.A. Superoxide and peroxynitrite in atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, R.P.; Kubant, R.; Jacob, R.F.; Walter, M.F.; Boychuk, B.; Malinski, T. Effect of Nebivolol on Endothelial Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite Release in Hypertensive Animals: Role of Antioxidant Activity. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 48, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, C. The pathophysiological role of peroxynitrite in shock, inflammation, and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock 1996, 6, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torreilles, F.; Salman-Tabcheh, S.; Guérin, M.-C.; Torreilles, J. Neurodegenerative disorders: The role of peroxynitrite. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 30, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryglewski, R.J.; Palmer, R.M.J.; Moncada, S. Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature 1986, 320, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrocq, C.; Blanchard, B.; Pignatelli, B.; Ohshima, H. Peroxynitrite: An endogenous oxidizing and nitrating agent. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R.; Peluffo, G.; Alvarez, M.N.; Naviliat, M.; Cayota, A. Unraveling peroxynitrite formation in biological systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolo, C.; Alvarez, M.N.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite, a potent macrophage-derived oxidizing cytotoxin to combat invading pathogens. BioFactors 2013, 40, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lymar, S.V.; Khairutdinov, R.F.; Hurst, J.K. Hydroxyl Radical Formation by O−O Bond Homolysis in Peroxynitrous Acid. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 5259–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafirovich, V.; Lymar, S.V. Nitroxyl and its anion in aqueous solutions: Spin states, protic equilibria, and reactivities toward oxygen and nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7340–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trujillo, M.; Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite Detoxification and Its Biologic Implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, P.; León, R. When It Comes to an End: Oxidative Stress Crosstalk with Protein Aggregation and Neuroinflammation Induce Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R. Protein Tyrosine Nitration: Biochemical Mechanisms and Structural Basis of Functional Effects. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.R.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, K.P. Role of protein tyrosine nitration in neurodegenerative diseases and atherosclerosis. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2009, 32, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeli, N.B.; Litterman, N.K.; Miller, A.-F.; Groves, J.T. Peroxynitrite Mediates Active Site Tyrosine Nitration in Manganese Superoxide Dismutase. Evidence of a Role for the Carbonate Radical Anion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17174–17185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubbo, H.; Trostchansky, A.; O’Donnell, V.B. Peroxynitrite-mediated lipid oxidation and nitration: Mechanisms and consequences. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 484, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbo, H. Nitro-fatty acids: Novel anti-inflammatory lipid mediators. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, N.; Prolo, C.; Álvarez, M.N.; Piacenza, L.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite Formation and Detection in Living Cells. In Nitric Oxide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, H.K.; Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M. COVID-19—A vascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, N.C.; Zhang, D.; Friedman, J.M.; Friedman, A.J. Harnessing nitric oxide for preventing, limiting and treating the severe pulmonary consequences of COVID-19. Nitric Oxide 2020, 103, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerström, S.; Gunalan, V.; Keng, C.T.; Tan, Y.-J.; Mirazimi, A. Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: Viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected. Virology 2009, 395, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, W.; Jiang, J.; Su, L.; Shu, T.; Liu, H.; Lai, S.; Ghiladi, R.A.; Wang, J. The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 163, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H.R.; Gao, D.; Pararasa, C. Redox regulation in metabolic programming and inflammation. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejero, J.; Shiva, S.; Gladwin, M.T. Sources of Vascular Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 311–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Gori, T.; Münzel, T. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.R.; Tyagi, S.C. Myocardial redox stress and remodeling in metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and congestive heart failure. Med. Sci. Monit. 2003, 9, SR35–SR52. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, C.A.; Rostad, C.A.; Mantus, G.; Anderson, E.J.; Chahroudi, A.; Jaggi, P.; Wrammert, J.; Ochoa, J.B.; Ochoa, A.; Basu, R.K. Altered amino acid profile in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101708118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J. Lifestyle-mediated nitric oxide boost to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection: A perspective. Nitric Oxide 2021, 115, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).