Recent Advances in Lubricant-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhancing Mechanical Lifespan and Electrical Output
Abstract
:1. Introduction
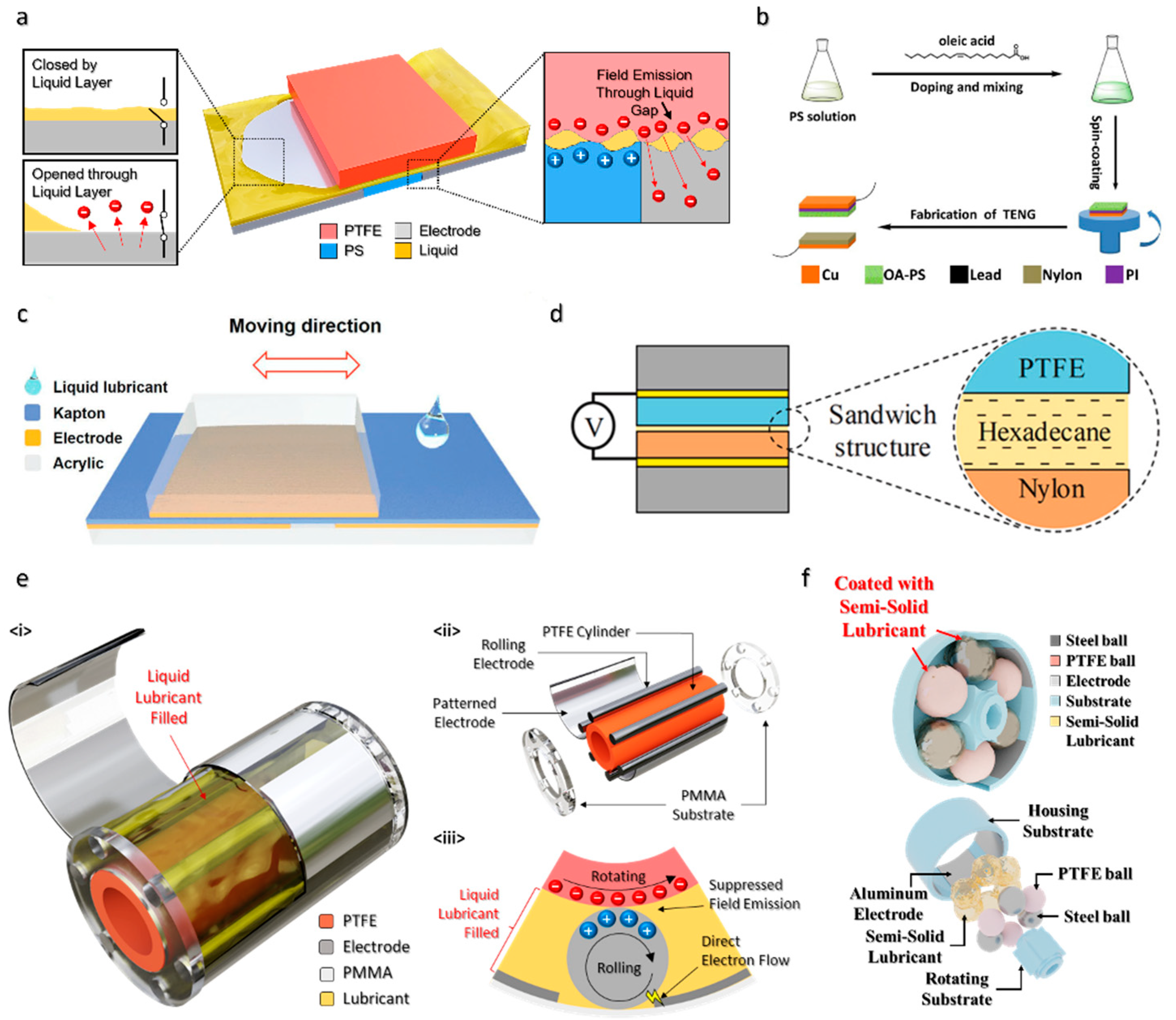
2. Lubricant-Based TENGs
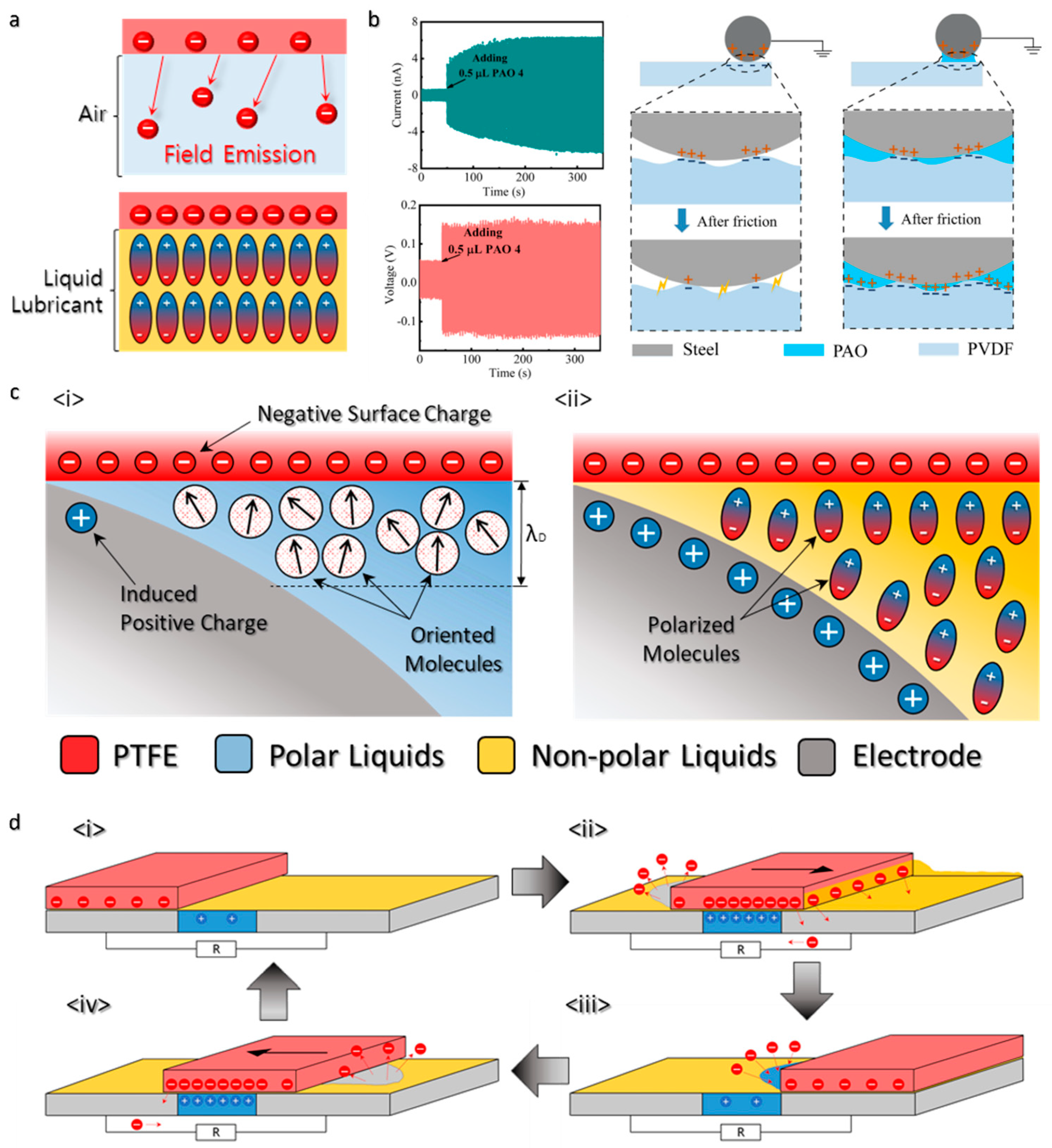
3. Working Mechanism of Lubricant-Based TENGs
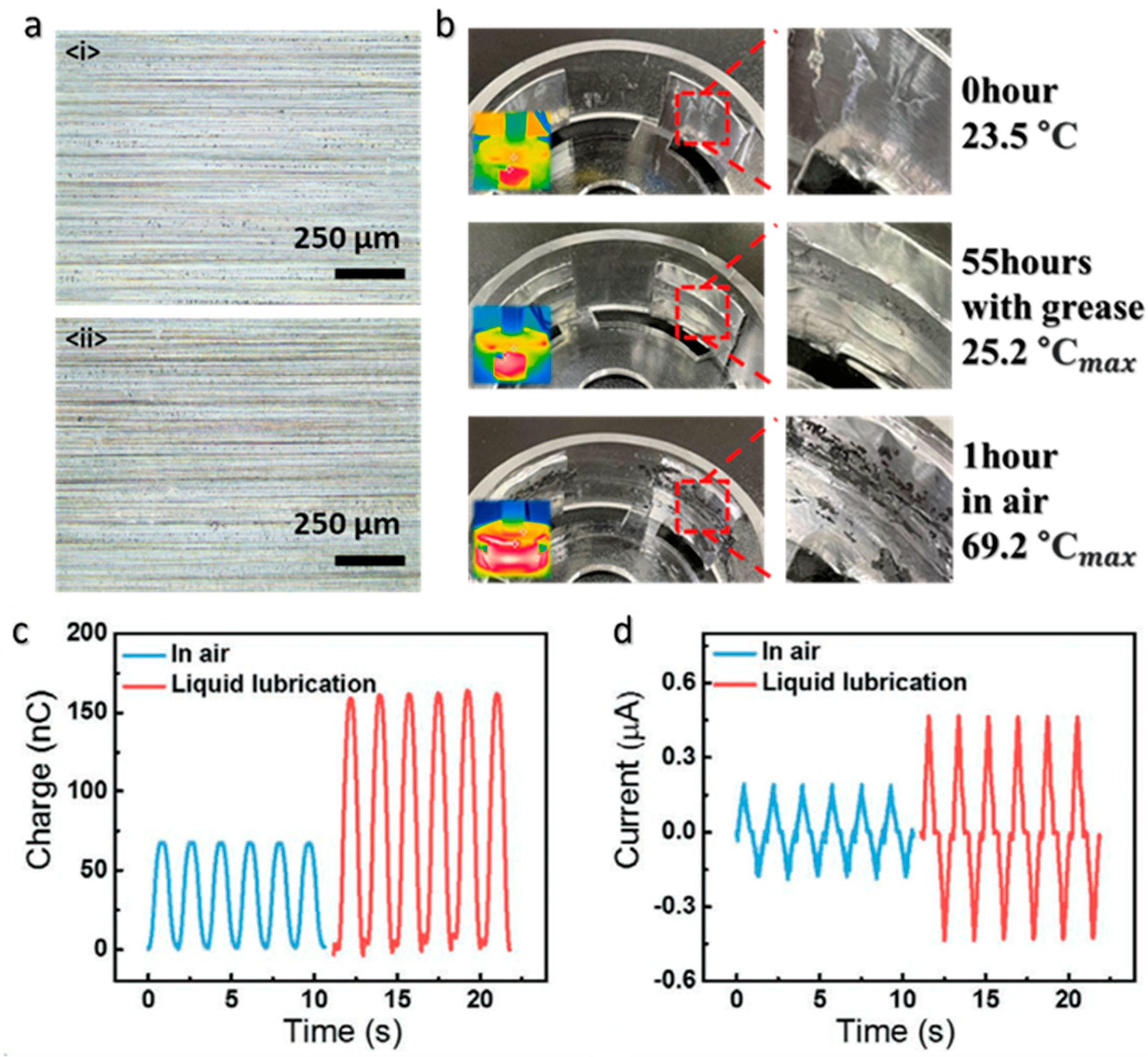
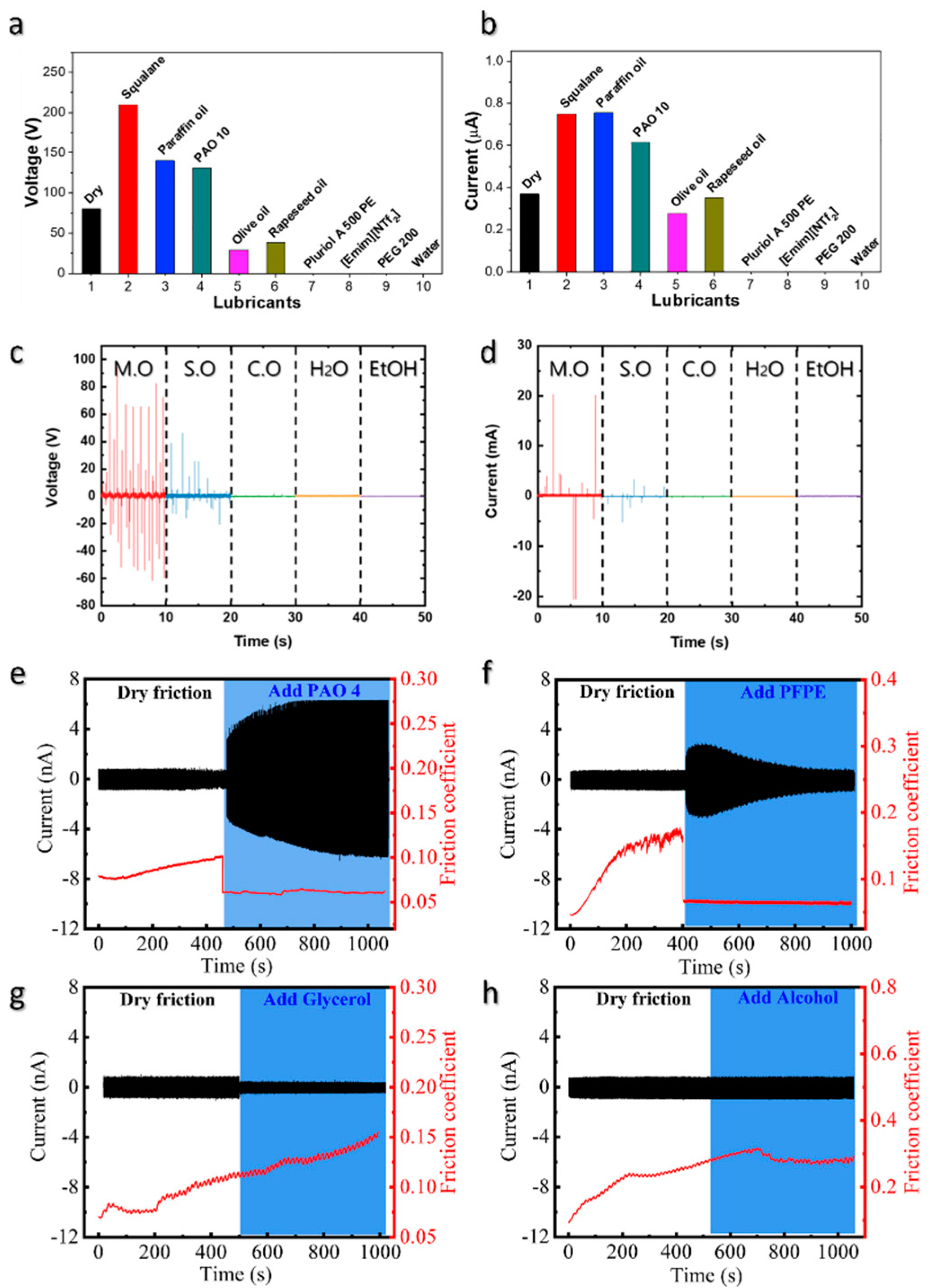
4. Performance of Lubricant-Based TENGs and Relevant Parameters
5. Summary and Perspectives
- (1)
- Optimization of lubricant-based TENG design to withhold more lubricant on the surface during operation and advanced surface design considering lubrication at the design level;
- (2)
- Further quantitative analysis of the relationship between TENGs and lubricant liquids, especially on the EDL formation of lubricant liquids under high surface charge conditions;
- (3)
- Quantitative analysis of various lubricant liquids affecting mechanical lifespan and electrical output of TENG, including commercial synthetic and organic oil;
- (4)
- Long-term influence of lubricant liquids on TENG surfaces and the effect of long-term operation on polymer surfaces.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, S.; Conrad, J.M. A survey of energy harvesting sources for embedded systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Southeastcon, Huntsville, AL, USA, 3–6 April 2008; pp. 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunathan, V.; Kansal, A.; Hsu, J.; Friedman, J.; Srivastava, M. Design considerations for solar energy harvesting wireless embedded systems. In Proceedings of the IPSN 2005, Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Boise, ID, USA, 15 April 2005; pp. 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Abdin, Z.; Alim, M.; Saidur, R.; Islam, M.; Rashmi, W.; Mekhilef, S.; Wadi, A. Solar energy harvesting with the application of nanotechnology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 26, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, A.J.; Lipson, H. Ambient wind energy harvesting using cross-flow fluttering. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.K.; Panda, S.K. Optimized wind energy harvesting system using resistance emulator and active rectifier for wireless sensor nodes. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 26, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.K.; Panda, S.K. Measurement. Self-autonomous wireless sensor nodes with wind energy harvesting for remote sensing of wind-driven wildfire spread. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Yong, H.; Choi, Y.I.; Ryu, J.; Lee, S. Stackable Disk-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Generate Energy from Omnidirectional Wind. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 9, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Chung, J.; Choi, D.; Jung, D.; Cho, M.; Lee, S. Highly reliable wind-rolling triboelectric nanogenerator operating in a wide wind speed range. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrara, M.; Cacan, M.R.; Toussaint, J.; Leamy, M.J.; Ruzzene, M.; Erturk, A. Metamaterial-inspired structures and concepts for elastoacoustic wave energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Alkhateeb, A.; Heath, R.W. Millimeter Wave Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 6048–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younesian, D.; Alam, M.-R. Multi-stable mechanisms for high-efficiency and broadband ocean wave energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2017, 197, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Shin, G.; Chung, S.-H.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Water behavior based electric generation via charge separation. Nano Energy 2020, 82, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Mayaram, K.; Fiez, T. Efficient Far-Field Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting for Passively Powered Sensor Networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, D.; Costanzo, A.; Del Prete, M.; Rizzoli, V. Genetic-based design of a tetra-band high-efficiency radio-frequency energy harvesting system. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zungeru, A.M.; Ang, L.-M.; Prabaharan, S.; Seng, K.P. Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting and Management for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Green Mobile Devices and Networks: Energy Optimization and Scavenging Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 341–368. [Google Scholar]
- Beeby, S.P.; Torah, R.N.; Tudor, M.J.; Glynne-Jones, P.; O’Donnell, T.; Saha, C.R.; Roy, S. A micro electromagnetic generator for vibration energy harvesting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 17, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, E.; Badel, A.; Richard, C.; Petit, L.; Guyomar, D. A comparison between several vibration-powered piezoelectric generators for standalone systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 126, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-Generator-Driven Pulse Electrodeposition for Micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoscale Triboelectric-Effect-Enabled Energy Conversion for Sustainably Powering Portable Electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, S.; Joung, Y.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.; Ra, Y.; Kim, M.; Ahn, D.; Lin, Z.-H.; Choi, D. Charge transfer accelerating strategy for improving sensitivity of droplet based triboelectric sensors via heterogeneous wettability. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ra, Y.; Cho, S.; Jang, S.; Kam, D.; Yun, Y.; Kim, H.; Choi, D. Geometric gradient assisted control of the triboelectric effect in a smart brake system for self-powered mechanical abrasion monitoring. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Cho, H.; Yong, H.; Heo, D.; Rim, Y.S.; Lee, S. Versatile surface for solid–solid/liquid–solid triboelectric nanogenerator based on fluorocarbon liquid infused surfaces. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, Y.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.; Yun, Y.; Cho, S.; Choi, J.H.; Jang, S.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D.; Kim, J.-G.; et al. Triboelectric signal generation and its versatile utilization during gear-based ordinary power transmission. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Tang, Q.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, C. Quantifying contact status and the air-breakdown model of charge-excitation triboelectric nanogenerators to maximize charge density. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Shin, G.; Choi, D.; Choi, K.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Ion-Enhanced Field Emission Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Chung, S.; Lee, G.; Hwang, P.T.J.; Kim, M.; Jung, H.; Jin, Y.; Hong, J.; et al. AC/DC Convertible Pillar-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Output Current Amplified by the Design of the Moving Electrode. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Lee, K.-S.; Niazi, M.U.K.; Park, H.-S. Triboelectric nanogenerator integrated origami gravity support device for shoulder rehabilitation using exercise gaming. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.; Park, H.; Bhatia, D.; Jee, E.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, D. An ultra-mechanosensitive visco-poroelastic polymer ion pump for continuous self-powering kinematic triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Song, M.; Chung, S.-H.; Hwang, P.T.; Kim, D.; Koo, B.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Lightweight mobile stick-type water-based triboelectric nanogenerator with amplified current for portable safety devices. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2022, 23, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-H.; Heo, D.; Song, Y.; Chung, J.; Kim, B.; Nam, W.; Hwang, P.T.; Kim, D.; Koo, B.; Hong, J.; et al. Highly reliable triboelectric bicycle tire as self-powered bicycle safety light and pressure sensor. Nano Energy 2021, 93, 106797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Cha, K.; Lin, Z.-H.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. A portable device for water-sloshing-based electricity generation based on charge separation and accumulation. Iscience 2021, 24, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Song, M.; Chung, S.-H.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.-H.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Triangulated Cylinder Origami-Based Piezoelectric/Triboelectric Hybrid Generator to Harvest Coupled Axial and Rotational Motion. Research 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-H.; Chung, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. Screw Pump-Type Water Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Active Water Flow Control. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 23, 2000758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Silva, S. Towards optimized triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Hong, H.; Cho, B.G.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, U.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.; Chung, K.-B.; Choi, D. Band well structure with localized states for enhanced charge accumulation on Triboelectrification. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Ra, Y.; Cho, S.; La, M.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. Electrical charge storage effect in carbon based polymer composite for long-term performance enhancement of the triboelectric nanogenerator. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 207, 108680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.; Chung, J.; Shin, G.; Seok, M.; Lee, C.; Lee, S. Yo-Yo Inspired Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Energies 2021, 14, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yuan, C.; Liang, X.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bowen, C. Triboelectric and Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Future Soft Robots and Machines. Iscience 2020, 23, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Segmentally Structured Disk Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Rotational Mechanical Energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, L.; Shi, B.; Li, Z. A size-unlimited surface microstructure modification method for achieving high performance triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2016, 28, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wong, M.C.; Hao, J. Strategies and progress on improving robustness and reliability of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 55, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tao, X.-M.; Peng, Z. Upper limits for output performance of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerator systems. Nano Energy 2018, 57, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Wu, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z.L. Maximized Effective Energy Output of Contact-Separation-Triggered Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Limited by Air Breakdown. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Dai, K.; Yi, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; You, Z. Optimization of triboelectric nanogenerator load characteristics considering the air breakdown effect. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, L. Micro/nano-structures-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerators by femtosecond laser direct writing. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y. Effects of surface micro-structures on capacitances of the dielectric layer in triboelectric nanogenerator: A numerical simulation study. Nano Energy 2020, 79, 105432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Enhancing output performance of direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator under controlled atmosphere. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seol, M.-L.; Han, J.-W.; Moon, D.-I.; Meyyappan, M. Triboelectric nanogenerator for Mars environment. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Quantitative Measurements of Vibration Amplitude Using a Contact-Mode Freestanding Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12004–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. From contact-electrification to triboelectric nanogenerators. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 096502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Chung, J.; Shin, G.; Sim, J.-Y.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, W. Toward sustainable output generation of liquid–solid contact triboelectric nanogenerators: The role of hierarchical structures. Nano Energy 2018, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Heo, D.; Kim, B.; Lee, S. Superhydrophobic Water-Solid Contact Triboelectric Generator by Simple Spray-On Fabrication Method. Micromachines 2018, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Chung, J.; Moon, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Elastic spiral triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-charging case for portable electronics. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.; Kim, T.; Yong, H.; Yoo, K.T.; Lee, S. Sustainable oscillating triboelectric nanogenerator as omnidirectional self-powered impact sensor. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of Sliding-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6184–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical modeling of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Yong, H.; Moon, H.; Van Duong, Q.; Choi, S.T.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Hand-Driven Gyroscopic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Recharging Portable Devices. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, D.Y.; Yun, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.J.N.E. Direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator via water electrification and phase control. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Yong, H.; Moon, H.; Choi, S.T.; Bhatia, D.; Choi, D.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Capacitor-Integrated Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Metal-Metal Contact for Current Amplification. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, D.H.; Ribatski, G.; Filho, E.P.B. Experimental evaluation of thermal conductivity, viscosity and breakdown voltage AC of nanofluids of carbon nanotubes and diamond in transformer oil. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 58, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Chung, S.-H.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jin, Y.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Dielectric liquid-based self-operating switch triboelectric nanogenerator for current amplification via regulating air breakdown. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, D. Oleic-acid enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator with high output performance and wear resistance. Nano Energy 2019, 69, 104435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Simultaneously Enhancing Power Density and Durability of Sliding-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Interface Liquid Lubrication. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Yi, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J. Hexadecane-containing sandwich structure based triboelectric nanogenerator with remarkable performance enhancement. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Chung, J.; Song, M.; Kim, S.; Shin, D.; Lin, Z.H.; Koo, B.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Nonpolar Liquid Lubricant Submerged Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Current Amplification via Direct Electron Flow. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Chung, J.; Chung, S.-H.; Cha, K.; Heo, D.; Kim, S.; Hwang, P.T.; Kim, D.; Koo, B.; Hong, J.; et al. Semisolid-lubricant-based ball-bearing triboelectric nanogenerator for current amplification, enhanced mechanical lifespan, and thermal stabilization. Nano Energy 2021, 93, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hu, Y.-Z. The study of transition from elastohydrodynamic to mixed and boundary lubrication. The advancing frontier of engineering tribology. In Proceedings of the 1999 STLE/ASME HS Cheng Tribology Surveillance, New York, NY, USA; 1999; pp. 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Fisher, J. Tribology in Joint Replacement. In Joint Replacement Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 31–61. [Google Scholar]
- Höglund, E. Influence of lubricant properties on elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Wear 1999, 232, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.T.; Barbosa, J.R., Jr. Role of the thermodynamics, heat transfer, and fluid mechanics of lubricant oil in hermetic reciprocating compressors. Heat Transf. Eng. 2009, 30, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Kojima, H.; Hayakawa, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Kato, T.; Rokunohe, T. Influence of space charge by primary and secondary streamers on breakdown mechanism under non-uniform electric field in air. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Des Moines, IA, USA, 19–22 October 2014; pp. 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Improved Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Fast Accumulation Process of Surface Charges. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, P.; Yin, X.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Surface charge density of triboelectric nanogenerators: Theoretical boundary and optimization methodology. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 18, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, Z.L. Maximum Surface Charge Density for Triboelectric Nanogenerators Achieved by Ionized-Air Injection: Methodology and Theoretical Understanding. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6720–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, A.; Capan, R.; Bechev, D.; Sauer, B. The Influence of Lubricant Conductivity on Bearing Currents in the Case of Rolling Bearing Greases. Lubricants 2019, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, M.; Luo, N.; Wang, D. Influence of interface liquid lubrication on triboelectrification of point contact friction pair. Tribol. Int. 2021, 165, 107323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Da, P.; Xu, M.; Wu, H.; Zheng, G. Silicon Nanowires for Biosensing, Energy Storage, and Conversion. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5177–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Narayanan, S.R.; Wu, W. Field-Assisted Splitting of Pure Water Based on Deep-Sub-Debye-Length Nanogap Electrochemical Cells. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8421–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xi, Y.; Shi, Y. Toward wear-resistive, highly durable and high performance triboelectric nanogenerator through interface liquid lubrication. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, S.-H.; Chung, J.; Lee, S. Recent Advances in Lubricant-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhancing Mechanical Lifespan and Electrical Output. Nanoenergy Adv. 2022, 2, 210-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2020009
Chung S-H, Chung J, Lee S. Recent Advances in Lubricant-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhancing Mechanical Lifespan and Electrical Output. Nanoenergy Advances. 2022; 2(2):210-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Seh-Hoon, Jihoon Chung, and Sangmin Lee. 2022. "Recent Advances in Lubricant-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhancing Mechanical Lifespan and Electrical Output" Nanoenergy Advances 2, no. 2: 210-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2020009
APA StyleChung, S.-H., Chung, J., & Lee, S. (2022). Recent Advances in Lubricant-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Enhancing Mechanical Lifespan and Electrical Output. Nanoenergy Advances, 2(2), 210-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2020009





