Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Study
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nano-Included Suspension
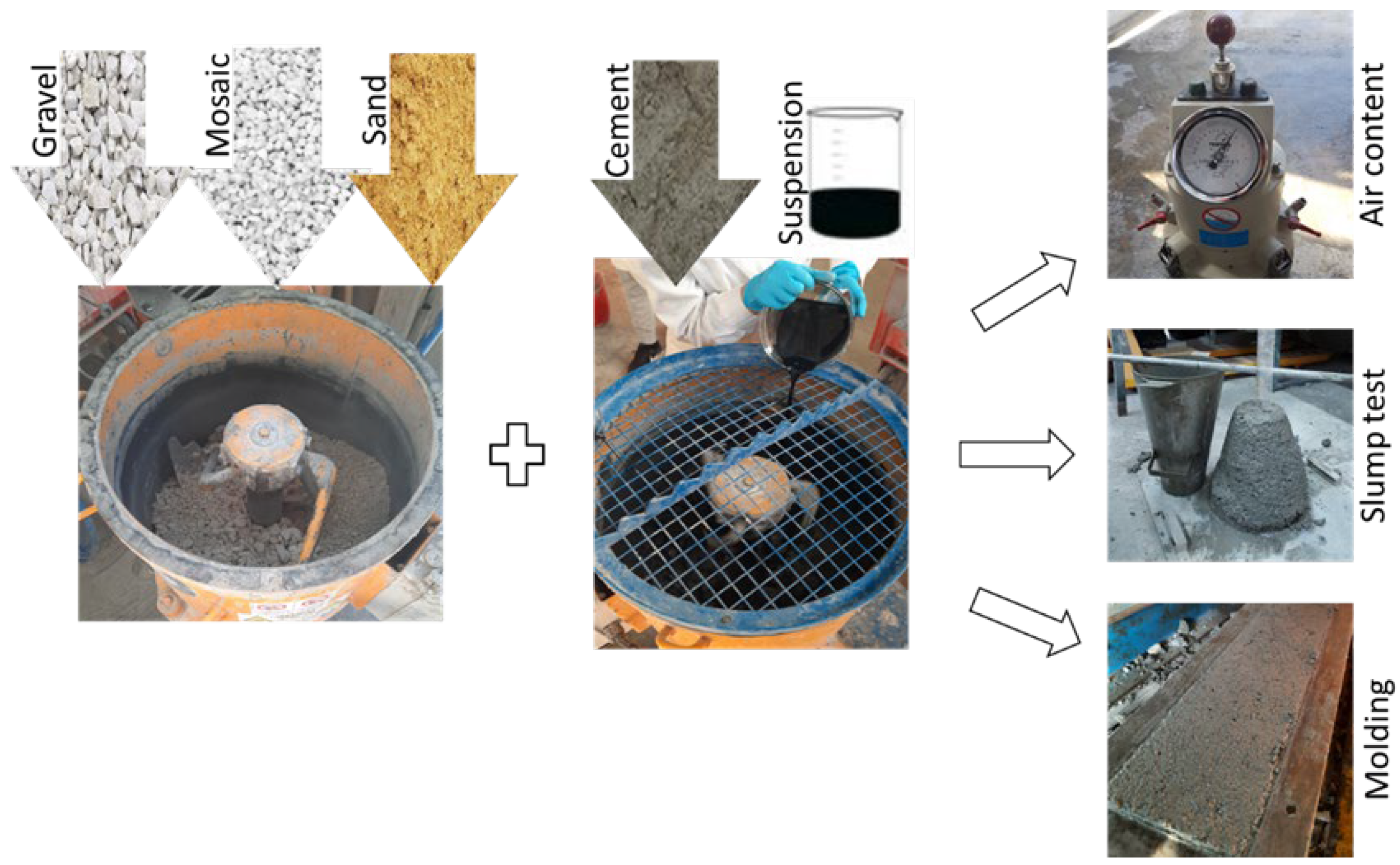
2.3. Procedure of Cement Paste and Concrete Mixtures
2.3.1. Cement Paste
2.3.2. Concrete
2.4. Nondestructive Materials’ Characterization
2.4.1. Thermal Behavior Procedure
2.4.2. Electrical Resistivity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Infrared Thermography
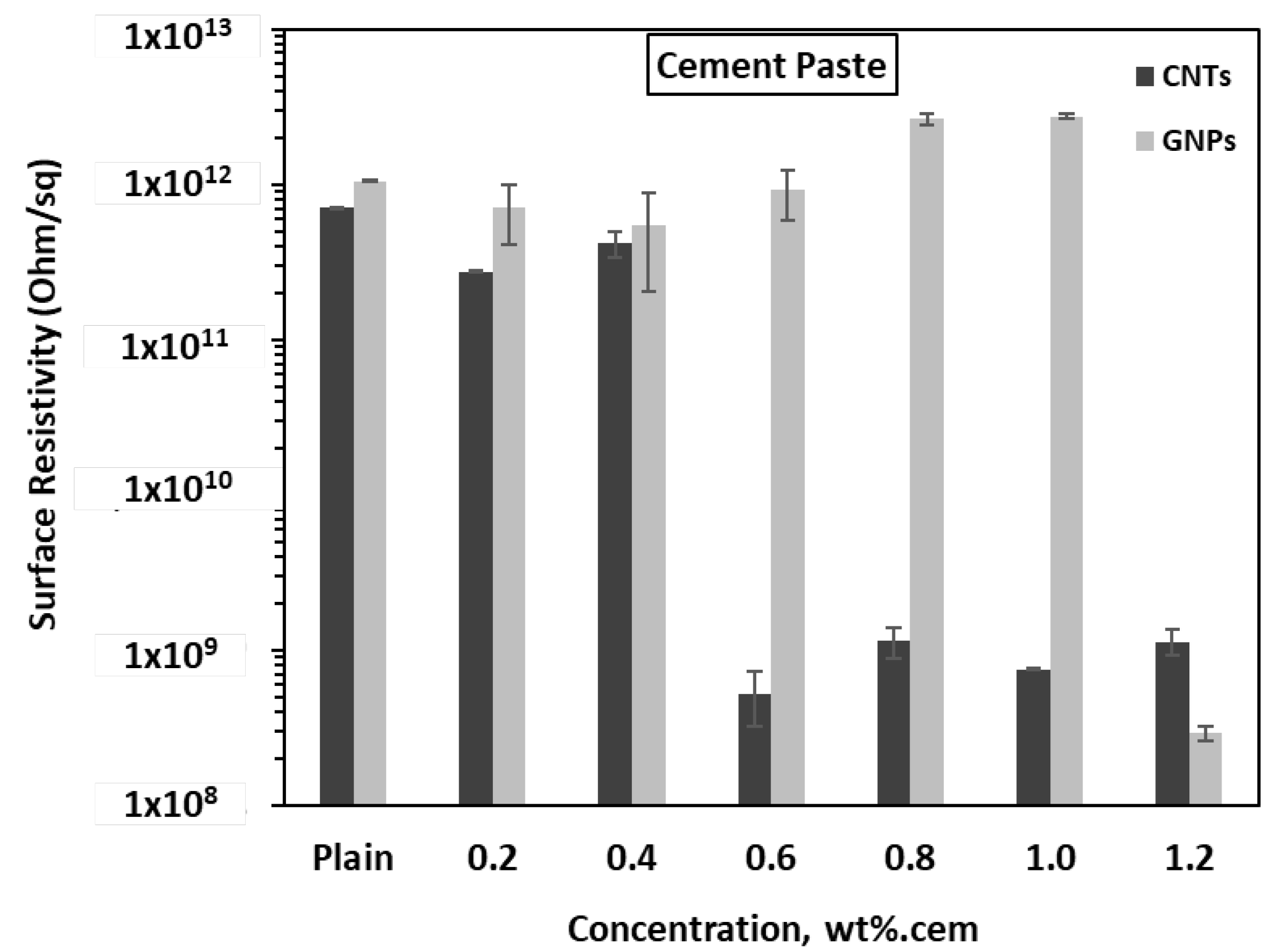
3.2. Electrical Resistivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamal, H.A.; El-Feky, M.; Alharbi, Y.R.; Abadel, A.A.; Kohail, M.J.S. Enhancement of the concrete durability with hybrid nano materials. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.P.; Dalal, P.J.C. Experimental investigation on strength and durability of graphene nanoengineered concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, I.; Shafigh, P.; Abu Hassan, Z.F.B.; Mahyuddin, N.B. Thermal conductivity of concrete—A review. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D. Electrically conductive cement-based materials. Adv. Cem. Res. 2004, 16, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, L.; Gleize, P.J.P. Effect of carbon nanotubes on compressive, flexural and tensile strengths of Portland cement-based materials: A systematic literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragazikis, I.; Dalla, P.; Exarchos, D.; Dassios, K.; Matikas, T. Nondestructive evaluation of the mechanical behavior of cement-based nanocomposites under bending. In Proceedings of the Smart Sensor Phenomena, Technology, Networks, and Systems Integration 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.K.; Mitra, N.J.C. Thermal conductivity of cement paste: Influence of macro-porosity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneto, K.; Tsuruta, M.; Sakai, G.; Cho, W.; Ando, Y. Electrical conductivities of multi-wall carbon nano tubes. Synth. Met. 1999, 103, 2543–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-M.; Liu, S.; Han, Y.; Leng, P. Preparation and durability of cement-based composites doped with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2015, 7, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, J.; Beaudoin, J. Carbon nanotubes and their application in the construction industry. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Nanotechnology in Construction, National Research Council Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchos, D.; Dalla, P.; Tragazikis, I.; Alafogianni, P.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Paipetis, A.; Dassios, K.; Matikas, T. Thermal and electrical behavior of nano-modified cement mortar. In Proceedings of the Smart Sensor Phenomena, Technology, Networks, and Systems Integration 2014, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dalla, P.; Tragazikis, I.; Exarchos, D.; Dassios, K.; Matikas, T. Cement-based materials with graphene nanophase. In Proceedings of the Smart Materials and Nondestructive Evaluation for Energy Systems 2017, Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavi, T.C.; Pavithra, P.; Singh, S.B.; Raj, S.B.V. Effect of multiwalled carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of concrete. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hilding, J.; Grulke, E.A.; Zhang, Z.G.; Lockwood, F. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes in liquids. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H.-P.; Clauss, A.; Fischer, G.; Hofmann, U. Surface properties of extremely thin graphite lamellae. In Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Carbon, the Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 19–23 June 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. UK scientists demonstrate ultra-sensitive graphene-based gas sensor. Sens. Rev. 2008, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.C.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M. Drawing conclusions from graphene. Phys. World 2006, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, V.U.; Sapuan, S.M.; Hassan, M.R. Innovative dispersion techniques of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) through mechanical stirring and ultrasonication: Impact on morphological, mechanical, and thermal properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Def. Technol. 2025, 43, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, S.K.; Rudzionis, Z.; Ghosh, R. Influence of CNT, graphene nanoplate and CNT-graphene nanoplate hybrid on the properties of lightweight concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 1979–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, P.T.; Tragazikis, I.K.; Trakakis, G.; Galiotis, C.; Dassios, K.G.; Matikas, T.E. Multifunctional Cement Mortars Enhanced with Graphene Nanoplatelets and Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2021, 21, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafogianni, P.; Dassios, K.; Farmaki, S.; Antiohos, S.K.; Matikas, T.E.; Barkoula, N.M. On the efficiency of UV–vis spectroscopy in assessing the dispersion quality in sonicated aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 495, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, K.; Dixit, A.R. A review on the mechanical properties of polymer composites reinforced by carbon nanotubes and graphene. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.S.; Panesar, D.K. Nano reinforced cement paste composite with functionalized graphene and pristine graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 197, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.; Loh, K. Nanoengineering ultra-high-performance concrete with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2142, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, L.; Buoso, A.; Corazza, F. Electrical properties of carbon nanotubes cement composites for monitoring stress conditions in concrete structures. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 82, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Fangueiro, R.; Correia, A.G. An effective method for hybrid CNT/GNP dispersion and its effects on the mechanical, microstructural, thermal, and electrical properties of multifunctional cementitious composites. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 6749150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Sobolev, K. Nanotechnology in concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Collins, F.G.; MacLeod, A.J.N.; Pan, Z.; Duan, W.H.; Wang, C.M. Carbon nanotube–cement composites: A retrospect. IES J. Part A Civ. Struct. Eng. 2011, 4, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Mehta, A. Effect of carbon nanotubes on properties of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Ram, M.K.; Zayed, A.; Kamal, R.; Shanahan, N. Investigation of physical properties of graphene-cement composite for structural applications. Open J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 4, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasena, M. Investigation on strength properties of graphene oxide concrete. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. Res. Dev. 2015, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Gotzamanis, A.; Farmaki, S.; Tsimpoukas, T.; Konstantinidis, A.; Dalla, P.; Exarchos, D.; Galiotis, C.; Dassios, K.; Matikas, T. Advanced nano-reinforced concrete for exotic applications. In Proceedings of the NDE 4.0, Predictive Maintenance, and Communication and Energy Systems in a Globally Networked World, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6 March–11 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, W.G.; Li, C.Y.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Duan, W.H.; Li, Z. Effects of graphene oxide agglomerates on workability, hydration, microstructure and compressive strength of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsaei, E.; Souza, F.B.; Yao, X.; Benhelal, E.; Akbari, A.; Duan, W. Graphene-based nanosheets for stronger and more durable concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, S.; Pan, Z.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Nano reinforced cement and concrete composites and new perspective from graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, K.L.; Takhistov, P.T.; Miltz, J. Intelligent packaging: Concepts and applications. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, R1–R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 196-1:2005; Methods of Testing Cement, in Part 1: Determination of Strength. BSI Standards Limited: London, UK, 2005.
- BS EN 206:2013+A2:2021; Concrete—Specification, Performance, Production and Conformity. BSI Standards Limited: London, UK, 2021.
- ASTM C143/C143M-20; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C231/C231M-17a; Standard Test Method for Air Content of Freshly Mixed Concrete by the Pressure Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
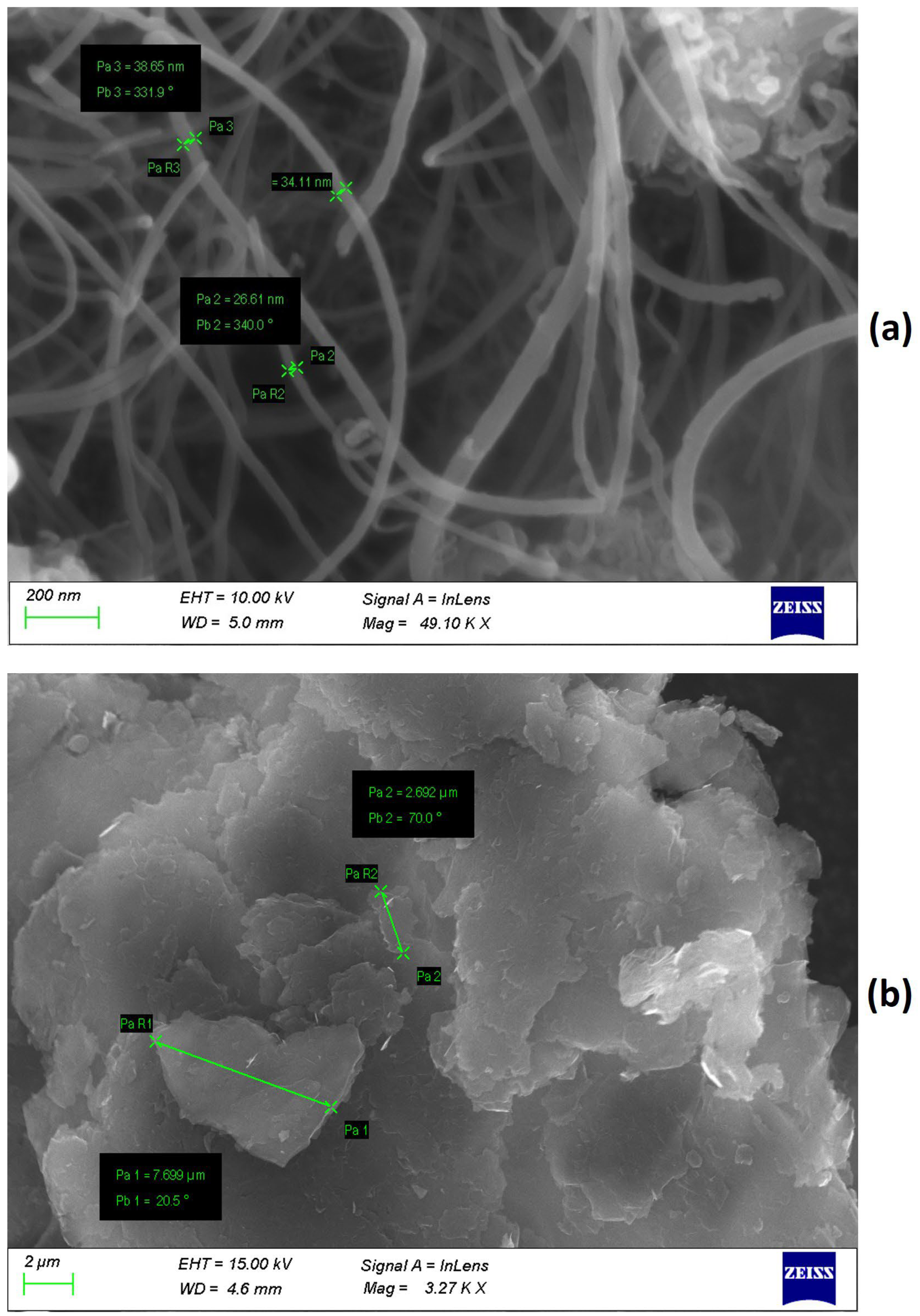








| Properties | |
|---|---|
| CNTs | GNPs |
| Elastic Modulus: 950 GPa [35,36] | Elastic Modulus: 950 GPa [35,36] |
| Tensile Strength: 11–63 GPa [35,36] | Tensile Strength: ~130 GPa [35,36] |
| Diameter/Thickness: 15–40 nm | Diameter/Thickness: ~0.08 nm |
| Electron Conductivity: 6.3 × 107 S/m | Electron Conductivity: 107–108 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity: 406 Wm−1K−1 | Thermal Conductivity: 3000–5300 Wm−1K−1 |
| Main Range of Diameter: 40–60 nm | Lateral Size (LD50): 7.2 μm |
| Purity: ≥95% | Average Thickness: 3 nm |
| Ash: <3% | Oxygen Content (XPS): <1% |
| Length: 5–15 μm | Average Number of Layers: 5–10 |
| Special Surface Area: 40–300 m2/g | BET: 70 m2/g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farmaki, S.G.; Dalla, P.T.; Exarchos, D.A.; Dassios, K.G.; Matikas, T.E. Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions. Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030013
Farmaki SG, Dalla PT, Exarchos DA, Dassios KG, Matikas TE. Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions. Nanomanufacturing. 2025; 5(3):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarmaki, Spyridoula G., Panagiota T. Dalla, Dimitrios A. Exarchos, Konstantinos G. Dassios, and Theodore E. Matikas. 2025. "Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions" Nanomanufacturing 5, no. 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030013
APA StyleFarmaki, S. G., Dalla, P. T., Exarchos, D. A., Dassios, K. G., & Matikas, T. E. (2025). Thermal and Electrical Properties of Cement-Based Materials Reinforced with Nano-Inclusions. Nanomanufacturing, 5(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5030013








