Exploratory Toxicogenomic Analysis of Parasite-Related Th2 Immune Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Selection
2.2. Chemical Data Source and Chemical–Gene Interactions
2.3. Chemical Intersection, Chemical Classification and Expression Profile
2.4. Enriched Diseases
3. Results
3.1. Chemical–Gene Interactions
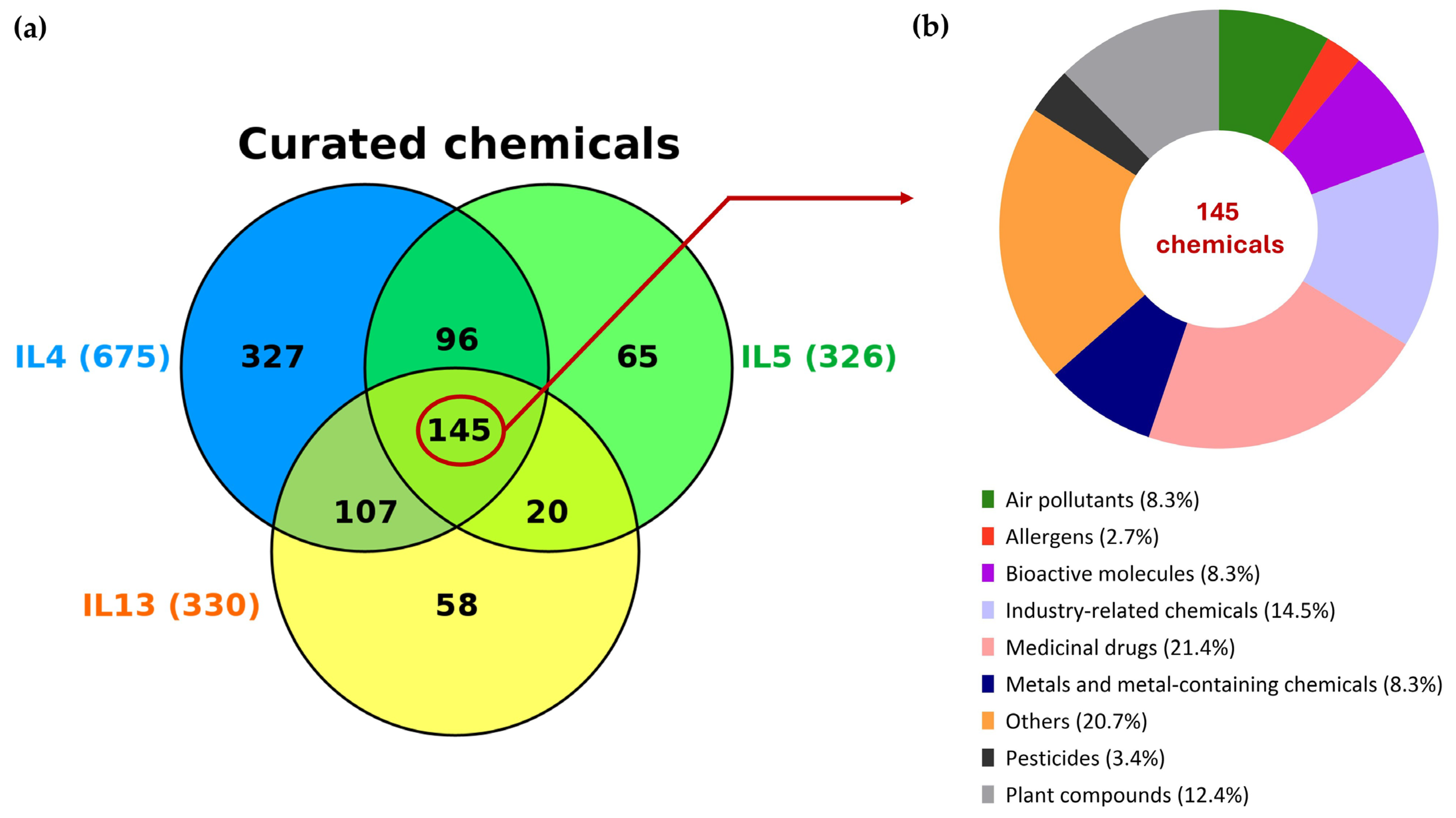
3.2. Chemical Intersection, Chemical Classification and Expression Profile
3.3. Enriched Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grencis, R. Immunity to Helminths: Resistance, Regulation, and Susceptibility to Gastrointestinal Nematodes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Ziliotto, M.; Kulmann-Leal, B.; Chies, J.A.B. Iron deficiency and soil-transmitted helminth infection: Classic and neglected connections. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, J.; Charlier, J.; Van Dijk, J.; Morgan, E.R.; Geary, T.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Claerebout, E. Control of helminth ruminant infections by 2030. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanebeck, K.M.; Besson, A.A.; Lagrue, C.; Green, S.J. The energetic costs of sub-lethal helminth parasites in mammals: A meta-analysis. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1886–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, D.J.; Albery, G.F.; Kessler, M.K.; Lunn, T.J.; Falvo, C.A.; Czirják, G.Á.; Martin, L.B.; Plowright, R.K. Macroimmunology: The drivers and consequences of spatial patterns in wildlife immune defence. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 972–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vineis, P.; Robinson, O.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Dehghan, A.; Mudway, I.; Dagnino, S. What is new in the exposome? Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliotto, M.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Soil-Transmitted Parasites and Non-Pathogenic Nematodes in Different Regions of Porto Alegre City, Brazil: A Comparison between Winter and Summer. Parasitologia 2024, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Allen, J.E. Mapping immune response profiles: The emerging scenario from helminth immunology. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, A.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Esteban, J.G.; Toledo, R. Th2 and Th1 Responses: Clear and Hidden Sides of Immunity Against Intestinal Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, F.D.; Wynn, T.A.; Donaldson, D.D.; Urban, J.F. The role of IL-13 in helminth-induced inflammation and protective immunity against nematode infections. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1999, 11, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marillier, R.G.; Michels, C.; Smith, E.M.; Fick, L.C.; Leeto, M.; Dewals, B.; Horsnell, W.G.; Brombacher, F. IL-4/IL-13 independent goblet cell hyperplasia in experimental helminth infections. BMC Immunol. 2008, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Nutman, T.B. Immune Responses to Helminth Infection. In Clinical Immunology, 5th ed.; Rich, R.R., Fleisher, T.A., Shearer, W.T., Schroeder, H.W., Frew, A.J., Weyand, C.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 437–447. ISBN 9780702068966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Rutitzky, L.I.; Urban, J.F.; Stadecker, M.J.; Gause, W.C. Protective immune mechanisms in helminth infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitre, E.; Klion, A.D. Eosinophils and helminth infection: Protective or pathogenic? Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Toxicogenomics of the C–C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5): Exploring the potential impacts of chemical-CCR5 interactions on inflammation and human health. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 186, 114511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, N.E.; Carlsten, C. Interplay of air pollution and asthma immunopathogenesis: A focused review of diesel exhaust and ozone. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B.; Ellwange, J.H. Toxicogenomics of persistent organic pollutants: Potential impacts on biodiversity and infectious diseases. Anthropocene 2024, 48, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CTD—The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. Available online: https://ctdbase.org/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Davis, A.P.; Wiegers, T.C.; Sciaky, D.; Barkalow, F.; Strong, M.; Wyatt, B.; Wiegers, J.; McMorran, R.; Abrar, S.; Mattingly, C.J. Comparative Toxicogenomics Database’s 20th anniversary: Update 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1328–D1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CTD—The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. VennViewer. Available online: https://ctdbase.org/tools/vennViewer.go (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- NIH—National Institutes of Health. National Library of Medicine. PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2025 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1516–D1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CTD—The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. Set Analyzer. Available online: https://ctdbase.org/tools/analyzer.go (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Zhu, J.; Yamane, H.; Cote-Sierra, J.; Guo, L.; Paul, W.E. GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: Induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M.A.; Perelson, A.S. Th1/Th2 Cross Regulation. J. Theor. Biol. 1994, 170, 25–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Kaplan, M.H. Transcriptional regulation by STAT6. Immunol. Res. 2011, 50, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Whitelaw, M.L. The emerging role of AhR in physiology and immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Juan, A.; Tabtim-On, D.; Coillard, A.; Becher, B.; Goudot, C.; Segura, E. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor shapes monocyte transcriptional responses to interleukin-4 by prolonging STAT6 binding to promoters. Sci. Signal. 2024, 17, eadn6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, V.; Aguilera, J.; Prunicki, M.; Nadeau, K.C. Mechanisms of climate change and related air pollution on the immune system leading to allergic disease and asthma. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 67, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.J.; Chico, M.E.; Guadalupe, I.; Sandoval, C.A.; Mitre, E.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Barreto, M.L.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Strachan, D.P.; Griffin, G.E. Impact of early life exposures to geohelminth infections on the development of vaccine immunity, allergic sensitization, and allergic inflammatory diseases in children living in tropical Ecuador: The ECUAVIDA birth cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrais, M.; Maricoto, T.; Nwaru, B.I.; Cooper, P.J.; Gama, J.M.R.; Brito, M.; Taborda-Barata, L. Helminth infections and allergic diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the global literature. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 2139–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, G.A.W. Hygiene Hypothesis and Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, G.A.W. The old friends hypothesis: Evolution, immunoregulation and essential microbial inputs. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1220481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Immunologic influences on allergy and the TH1/TH2 balance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.H.; Hwang, J.; Kwon, R.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; GBD 2019 Allergic Disorders Collaborators; Shin, J.I.; Yon, D.K. Global, regional, and national burden of allergic disorders and their risk factors in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Allergy 2023, 78, 2232–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y. Global burden of soil-transmitted helminth infections, 1990–2021. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2024, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B. Toxicogenomics of Arsenic, Lead and Mercury: The Toxic Triad. Pollutants 2025, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IL4 (n = 675 Interacting Chemicals) | IL5 (n = 326 Interacting Chemicals) | IL13 (n = 330 Interacting Chemicals) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top 20 Chemicals | Number of Chemical–Gene Interactions | Organism Number | Top 20 Chemicals | Number of Chemical–Gene Interactions | Organism Number | Top 20 Chemicals | Number of Chemical–Gene Interactions | Organism Number |
| Poly I-C | 111 | 2 | Ovalbumin | 97 | 2 | Ovalbumin | 107 | 1 |
| Ovalbumin | 104 | 2 | Toluene 2,4-diisocyanate | 34 | 2 | Particulate matter | 46 | 4 |
| Lipopolysaccharides | 85 | 4 | Dexamethasone | 26 | 2 | Ozone | 38 | 3 |
| Toluene 2,4-diisocyanate | 83 | 3 | Antigens, dermatophagoides | 25 | 3 | Lipopolysaccharides | 35 | 4 |
| Tetradecanoylphorbol acetate | 60 | 5 | Particulate matter | 24 | 2 | Toluene 2,4-diisocyanate | 28 | 1 |
| Ionomycin | 50 | 5 | Ozone | 22 | 3 | Antigens, dermatophagoides | 24 | 1 |
| Mercuric chloride | 45 | 4 | Tetradecanoylphorbol acetate | 16 | 3 | Vehicle emissions | 21 | 3 |
| Particulate matter | 45 | 3 | Vehicle emissions | 15 | 2 | Metformin | 19 | 1 |
| Bisphenol A | 39 | 3 | Bisphenol A | 14 | 3 | Dexamethasone | 18 | 4 |
| 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium | 35 | 1 | Lipopolysaccharides | 14 | 3 | Tetradecanoylphorbol acetate | 18 | 3 |
| Dinitrochlorobenzene | 28 | 1 | Calcimycin | 12 | 1 | Nanotubes, carbon | 14 | 2 |
| Ketoconazole | 28 | 1 | 1-Methyl-3-isobutylxanthine | 11 | 1 | Dinitrophenyl-bovine serum albumin | 12 | 1 |
| Dexamethasone | 26 | 3 | Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin | 11 | 3 | Air pollutants | 11 | 2 |
| Antigens, dermatophagoides | 25 | 2 | Bucladesine | 10 | 1 | Calcimycin | 11 | 3 |
| 4-(5H-dibenzo(a,d)cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-1-(4-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)butyl)piperidine | 24 | 1 | Colforsin | 10 | 1 | Dust | 11 | 2 |
| Itraconazole | 23 | 1 | Itraconazole | 10 | 1 | Alisol B 23-acetate | 10 | 1 |
| Terbinafine | 23 | 1 | Ketoconazole | 10 | 1 | Calcitriol | 10 | 1 |
| Vehicle emissions | 22 | 3 | Miconazole | 10 | 1 | Fidarestat | 10 | 2 |
| Calcimycin | 21 | 2 | Nanotubes, carbon | 10 | 2 | Plant extracts | 10 | 2 |
| Dinitrophenyl-human serum albumin conjugate | 21 | 1 | Terbinafine * and Tolnaftate * | 10 | 1 | Resveratrol | 10 | 3 |
| Disease | Corrected p-Value | Annotated Genes Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Parasitic diseases | 4.65 × 10−42 | 62 |
| Protozoan infections | 6.18 × 10−29 | 44 |
| Malaria | 1.22 × 10−13 | 23 |
| Euglenozoa infections | 3.47 × 10−12 | 21 |
| Leishmaniasis | 3.47 × 10−12 | 21 |
| Skin diseases, parasitic | 1.51 × 10−8 | 16 |
| Leishmaniasis, visceral | 2.30 × 10−6 | 13 |
| Helminthiasis | 1.23 × 10−5 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B.; Ellwanger, J.H. Exploratory Toxicogenomic Analysis of Parasite-Related Th2 Immune Response. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040058
Ziliotto M, Chies JAB, Ellwanger JH. Exploratory Toxicogenomic Analysis of Parasite-Related Th2 Immune Response. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiliotto, Marina, José Artur Bogo Chies, and Joel Henrique Ellwanger. 2025. "Exploratory Toxicogenomic Analysis of Parasite-Related Th2 Immune Response" Parasitologia 5, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040058
APA StyleZiliotto, M., Chies, J. A. B., & Ellwanger, J. H. (2025). Exploratory Toxicogenomic Analysis of Parasite-Related Th2 Immune Response. Parasitologia, 5(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040058










