Molecular Surveillance of Pyrethroid Resistance Kdr Alleles T917I and L920F in Head and Body Lice from Nigeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Location and Louse Sampling
2.3. Pediculicides and Lice Treatment Methods
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Amplification of the Knockdown Resistance (Kdr) Gene Fragment by Conventional PCR and Sequencing
2.6. Detection of Kdr Alleles Using PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism)
2.7. Nucleotide Sequencing Analysis for SNPs
3. Results
3.1. Kdr-Allele Frequency
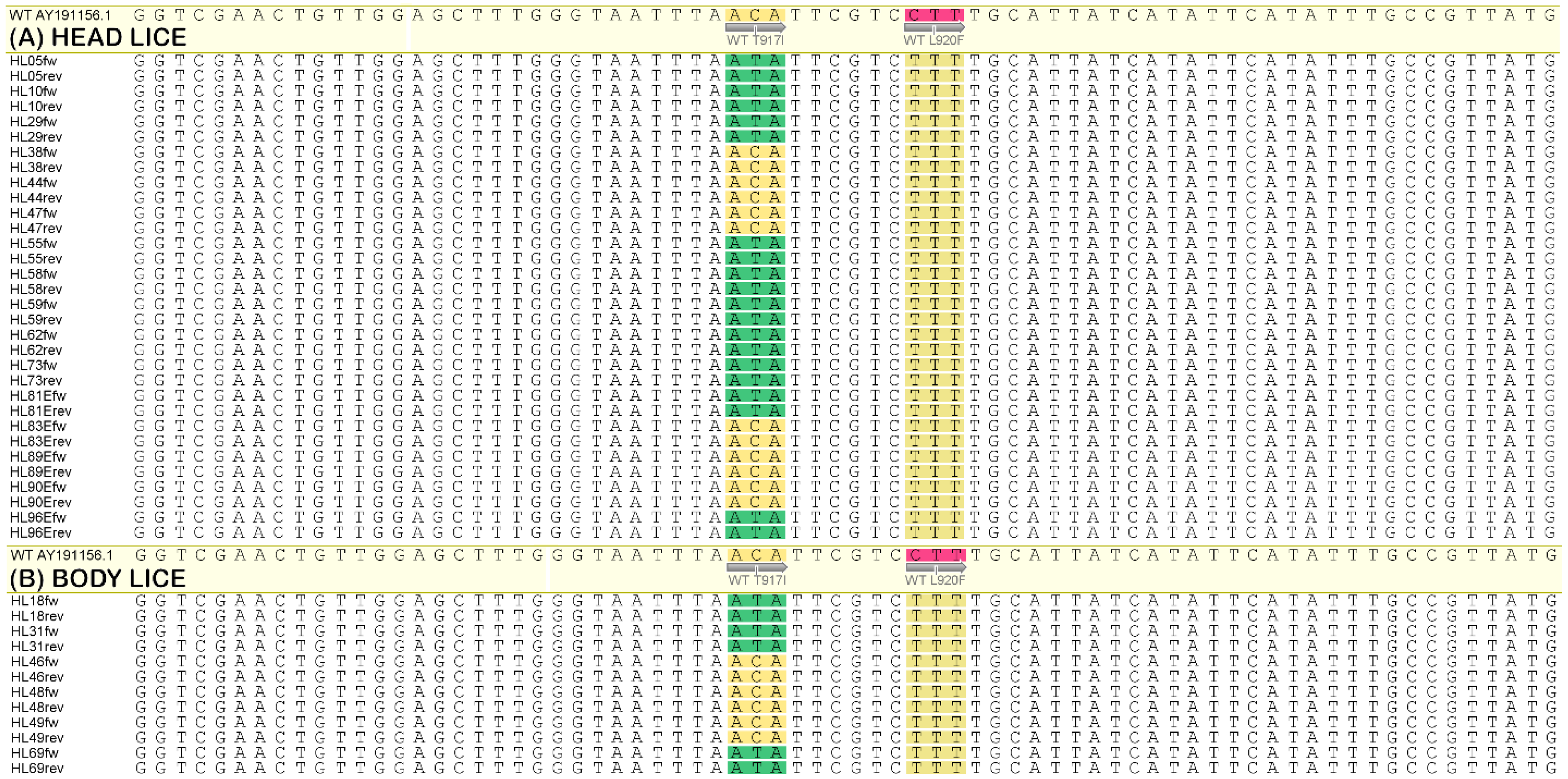
3.2. Sequencing Analysis
3.3. Survey of Pediculicides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, D.L.; Smith, V.S.; Hammond, S.L.; Rogers, A.R.; Clayton, D.H. Genetic Analysis of Lice Supports Direct Contact between Modern and Archaic Humans. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukelbach, J. Management and Control of Head Lice Infestations, 1st ed.; Uni-Med Verlag AG: Bremen, Germany; London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Toups, M.A.; Kitchen, A.; Light, J.E.; Reed, D.L. Origin of Clothing Lice Indicates Early Clothing Use by Anatomically Modern Humans in Africa. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Report of the Tenth Meeting of the WHO Strategic and Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/ntds/strategic-and-advisory-group-on-neglected-tropical-diseases-(stag-ntds)/tenth-ntd-stag-report-2017.pdf?sfvrsn=9ec99065_2 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Toloza, A.; Vassena, C.; Gallardo, A.; González-Audino, P.; Picollo, M.I. Epidemiology of Pediculosis capitis in elementary schools of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, I.F. Human lice and their control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Roux, V. The Body louse as a vector of reemerging human diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 888–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Pollack, R.J.; Reed, D.L.; Barker, S.C.; Gordon, S.; Toloza, A.C.; Picollo, M.I.; Taylan-Ozkan, A.; Chosidow, O.; Habedank, B.; et al. International recommendations for an effective control of head louse infestations. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Previte, D.J.; Yoon, K.S.; Murenzi, E.; Koehler, J.E.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Lee, S.H.; Clark, J.M. Comparison of the proliferation and excretion of Bartonella quintana between body and head lice following oral challenge. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.M. Determination, mechanism and monitoring of knockdown resistance in permethrin-resistant human head lice, Pediculus humanus capitis. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2009, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kristensen, M. Identification of Sodium Channel Mutations in Human Head Louse (Anoplura: Pediculidae) from Denmark. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; McCarroll, L.; Roberts, R.; Karunaratne, P.; Roberts, C.; Casey, D.; Morgan, S.; Touhig, K.; Morgan, J.; Collins, F.; et al. Surveillance of insecticide resistance in head lice using biochemical and molecular methods. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.; Millard, B.; Bouges-Michel, C.; Bruel, C.; Bouvresse, S.; Izri, A. Detection of pyrethroid resistance gene in head lice in schoolchildren from Bobigny, France. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Ishii, N.; Natsuaki, M.; Fukutomi, H.; Komagata, O.; Kobayashi, M.; Tomita, T. Prevalence of kdr-like mutations associated with pyrethroid resistance in human head louse populations in Japan. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloza, A.C.; Ascunce, M.S.; Reed, D.; Picollo, M.I. Geographical distribution of pyrethroid resistance allele frequency in head lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) from Argentina. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellatly, K.J.; Krim, S.; Palenchar, D.J.; Shepherd, K.; Yoon, K.S.; Rhodes, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Clark, J.M. Expansion of the knockdown resistance frequency map for human head lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) in the United States Using Quantitative Sequencing. J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Capps, D.; Winful, E.B.; Warang, S.S.; Braswell, S.E.; Tokarevich, N.K.; Bonilla, D.L.; Durden, L.A. Molecular Markers of Pesticide Resistance and Pathogens in Human Head Lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) from Rural Georgia, USA. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Acevedo, G.; Del Solar Kupfer, C.P.; Dressel Roa, P.; Toloza, A.C. First determination of pyrethroid knockdown resistance alleles in human head lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) from Chile. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, K.; Rodriguez, C.A.; Jamani, S.; Fronza, G.; Roca-Acevedo, G.; Sanchez, A.; Toloza, A.C. First evidence of the mutations associated with pyrethroid resistance in head lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) from Honduras. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahvechi Khaligh, F.; Djadid, N.D.; Farmani, M.; Asadi Saatlou, Z.; Frooziyan, S.; Abedi Astaneh, F.; Farnoosh, F.; Sofizadeh, A.; Naseri, F.; Adib, D.; et al. Molecular monitoring of knockdown resistance in head louse (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) populations in Iran. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkouiten, S.; Drali, R.; Badiaga, S.; Veracx, A.; Giorgi, R.; Raoult, D.; Brouqui, P. Effect of Permethrin–Impregnated Underwear on Body Lice in Sheltered Homeless Persons. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yoon, K.-S.; Williamson, M.S.; Goodson, S.J.; Takano-Lee, M.; Edman, J.D.; Devonshire, A.L.; Clark, J.M. Molecular analysis of kdr-like resistance in permethrin-resistant strains of head lice, Pediculus capitis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 66, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.S.; Symington, S.B.; Lee, H.S.; Soderlund, D.M.; Clark, J.M. Three mutations identified in the voltage-sensitive sodium channel alpha-subunit gene of permethrin-resistant human head lice reduce the permethrin sensitivity of house fly Vssc1 sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enechukwu, N.A.; Ezejiofor, O.I.; Anaje, C.C.; Ozoh, G.O.; Ogunbiyi, A.O. Human head lice infestation in Nigeria: Observations and review of relevant literature. Niger. J. Dermatol. 2020, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Okoh, B.A.N.; Alikor, E.A.D. Prevalence of head lice infestation in primary school children in port Harcourt. East Afr. Med. J. 2013, 90, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Abah, A.E.; Owens, P.; Maduike, E. Reemergence of head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) among a university community in Southern Nigeria. Egypt. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 43, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, L.A. Lice, the Phthiraptera. In Biology of Disease Vectors; Marquardt, W.H., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, K.; Larkin, K.; Sanchez, A. Global Trends in Genetic Markers of Pediculus humanus capitis Resistance Mechanisms. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2020, 7, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgdon, H.E.; Yoon, K.S.; Previte, D.J.; Kim, H.J.; Aboelghar, G.E.; Lee, S.H.; Clark, J.M. Determination of knockdown resistance allele frequencies in global human head louse populations using the serial invasive signal amplification reaction. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, N.; Sunantaraporn, S.; Phadungsaksawasdi, K.; Seatamanoch, N.; Kongdachalert, S.; Phumee, A.; Siriyasatien, P. Presence of the knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in the head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) collected from primary school children of Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firooziyan, S.; Sadaghianifar, A.; Taghilou, B.; Galavani, H.; Ghaffari, E.; Gholizadeh, S. Identification of novel voltage-gated sodium channel mutations in human head and body lice (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, E.; Daliri, S.; Yazdani, Z.; Mohseni, S.; Mohammadyan, G.; Seyed Hosseini, S.N.; Haghighi, R.N. Evaluation of resistance of human head lice to pyrethroid insecticides: A meta-analysis study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.; Bouvresse, S.; Berdjane, Z.; Izri, A.; Chosidow, O.; Clark, J.M. Insecticide resistance in head lice: Clinical, parasitological and genetic aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Strategy to Respond to Antimalarial Drug Resistance in Africa; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9789240060265. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.; Alonso, P.; Ringwald, P. Current and emerging strategies to combat antimalarial resistance. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynagh, T.; Lynch, J.W. Ivermectin binding sites in human and invertebrate Cys-loop receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Population | No. of Lice Analyzed (No. of Affected Subjects) | Genotype a | Resistance Allele Frequency (%) | H-W b (χ2) | FIS c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/S | R/S | R/R | |||||
| Maiduguri | HL 46 (35) | 3 (6.52) | 16 (34.78) | 27 (58.70) | 76.08 | 0.0897 | 0.055 |
| BL 22 (22) | 1 (4.54) | 0 (0) | 21 (95.46) | 95.45 | 22 * | 1 | |
| Yunusari | HL 12 (10) | 9 (75) | 1 (8.33) | 2 (16.67) | 20.83 | 6.702 * | 0.766 |
| BL 5 (5) | 4 (80) | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 10 | 0.0617 | - | |
| Total | 85 (72) | 17 (20) | 18 (21.18) | 50 (58.82) | 69.41 | 21.361 * | 0.232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamani, J.; Harrus, S.; Laminu, B.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Shand, M.; Roca-Acevedo, G.; Toloza, A.C. Molecular Surveillance of Pyrethroid Resistance Kdr Alleles T917I and L920F in Head and Body Lice from Nigeria. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040057
Kamani J, Harrus S, Laminu B, Nachum-Biala Y, Shand M, Roca-Acevedo G, Toloza AC. Molecular Surveillance of Pyrethroid Resistance Kdr Alleles T917I and L920F in Head and Body Lice from Nigeria. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamani, Joshua, Shimon Harrus, Bukar Laminu, Yaarit Nachum-Biala, Mike Shand, Gonzalo Roca-Acevedo, and Ariel Ceferino Toloza. 2025. "Molecular Surveillance of Pyrethroid Resistance Kdr Alleles T917I and L920F in Head and Body Lice from Nigeria" Parasitologia 5, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040057
APA StyleKamani, J., Harrus, S., Laminu, B., Nachum-Biala, Y., Shand, M., Roca-Acevedo, G., & Toloza, A. C. (2025). Molecular Surveillance of Pyrethroid Resistance Kdr Alleles T917I and L920F in Head and Body Lice from Nigeria. Parasitologia, 5(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5040057







