- Article
Geographic Distance as a Driver of Tabanidae Community Structure in the Coastal Plain of Southern Brazil
- Rodrigo Ferreira Krüger,
- Helena Iris Leite de Lima Silva and
- Tiago Kütter Krolow
- + 3 authors
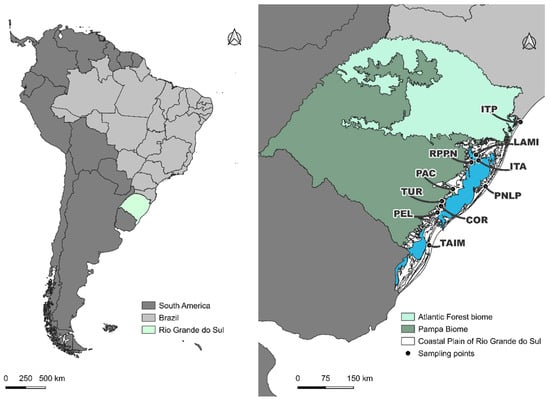
Horse flies (Tabanidae) negatively affect livestock by reducing productivity, compromising animal welfare, and serving as mechanical vectors of pathogens. However, the spatial processes shaping their community organization in southern Brazil’s Coastal Plain of Rio Grande do Sul (CPRS) remain poorly understood. To address this, we conducted standardized Malaise-trap surveys and combined them with historical–contemporary comparisons to examine distance–decay patterns in community composition. We evaluated both abundance-based (Bray–Curtis) and presence–absence (Jaccard) dissimilarities using candidate models. Across sites, Tabanus triangulum emerged as the dominant species. Dissimilarity in community structure increased monotonically with geographic distance, with no evidence of abrupt thresholds. The square-root model provided the best fit for abundance-based data, whereas a linear model best described presence–absence patterns, reflecting dispersal limitation and environmental filtering across a heterogeneous coastal landscape. Sites within riparian forests and conservation units displayed higher diversity, emphasizing the ecological role of protected habitats and the importance of maintaining connected corridors. Collectively, these findings establish a process-based framework for surveillance and landscape management strategies to mitigate vector, host contact. Future directions include integrating remote sensing and host distribution, applying predictive validation across temporal scales.
13 January 2026


![The life cycle of Babesia spp. within the tick vector and the bovine host. Source: Adapted from [41].](https://mdpi-res.com/parasitologia/parasitologia-06-00002/article_deploy/html/images/parasitologia-06-00002-g001-550.jpg)