Intestinal Microbial Eukaryotes at the Human, Animal and Environment Interface in Rural Iraq
Abstract
1. Introduction
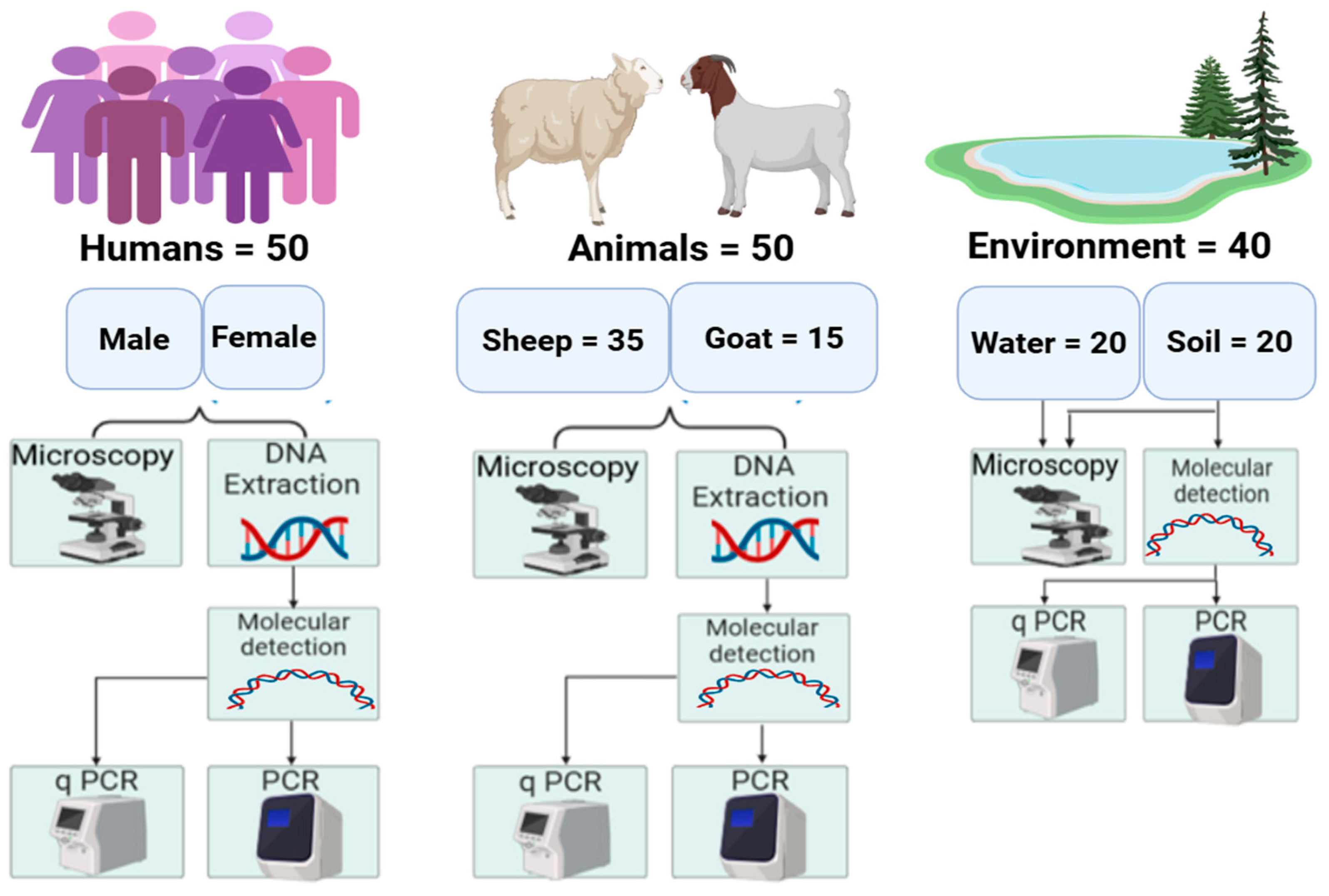
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Microscopic Examination
2.5. DNA Extraction and Molecular Detection
| Parasite of Interest | Target Gene | Detection Method | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Amplification Condition | Amplicon Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptosporidium spp. | SSU | nPCR | CRY-SSU-F1: GATTAAGCCATGCATGTCTAA | 95 °C: 2 min; 24 cycles: 94 °C: 50 s 53 °C: 50 s 72 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 10 min | 723 bp | [14,16] |
| CRY-SSU-R1: CTTGAATACTCCAGCATGGAA | ||||||
| CRY-SSU- F2: CAGTTATAGTTTACTTGATAATC | 94 °C: 2 min; 30 cycles: 94 °C: 50 s 56 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 10 min | 631 bp | ||||
| CRY-SSU- R2: GAAAATTAGAGTGCTTAAAGCAGG | ||||||
| GP60 | nPCR | F1: AL3531: ATAGTCTCCGCTGTATTC | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 45 s 50 °C: 45 s 72 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 7 min | 1000 bp | [16,17] | |
| R1: AL3535: GCAAGGAACGATGTATCT | ||||||
| F2 AL3532: TCCGCTGTATTCTCAGCC | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 45 s 50 °C: 45 s 72 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 7 min | 850 bp | ||||
| R2 AL3534: GCAGAGGAACCAGCATC | ||||||
| Giardia duodenalis | SSU | qPCR | GIARDIA-80-F: GACGGCTCAGGACAACGGTT | 95 °C: 2 min; 50 cycles: 95 °C: 15 s 58 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 30 s | 62 bp | [14,18,19] |
| GIARDIA-127-R: TTGCCAGCGGTGTCCG | ||||||
| Probe: FAM: CCCGCGGCGGTCCCTGCTAG | ||||||
| Bg beta-giardin | nPCR | F1(G7F): AAGCCCGACCTCACCCGCAGTGC | 94 °C: 5 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 30 s 66 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 7 min | 753 bp | [20] | |
| F2(G376): CATAAGGACGCCATCGCGGCTCTGAGG | 94 °C: 3 min; 30 cycles: 94 °C: 30 s 65 °C: 15 s 72 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 7 min | 292 bp | ||||
| R (G759R): GAGGCCGCCCTGGATCTTCGAGACGAC | ||||||
| Tpi triosephosphate isomerase | nPCR | Tpi_AL3543_F1: AAAT/IDEOXYL/ATGCCTGGTCG | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 45 s, 50 °C: 35 s 72 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 10 min | 530 bp | [21] | |
| Tpi_AL3546_R1: CAAACCTT/IDEOXYL/TCCGCAAACC | ||||||
| Tpi_AL3544_F2: CCCTTGATCGG/IDEXYL/GGTAACTT | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 35 s 47 °C: 35 s 72 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 10 min | 332 bp | ||||
| Tpi_AL3545_R2: GTGGCCACCAC/IDEOXYL/CCCGTGCC | ||||||
| Blastocystis | SSU | nPCR | RD3—F1: GGGATCCTGA TCCTTCCGCAGGTTCACCTAC | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycles: 94 °C: 1 min 60 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 100 s 72 °C: 7 min. | 600 bp | [15,22] |
| RD5—R1: GGAAGC TTATCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGTA | ||||||
| BsRD5F—F2: ATCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT | 94 °C: 3 min; 35 cycle: 94 °C: 1 min 60 °C: 1 min 72 °C: 100 s 72 °C: 10 min | 650 bp | ||||
| BhRDr—R2: GAGCTTTTTAACTGCAACAACG | ||||||
| Entamoeba histolytica | SSU | qPCR | End-239F: ATTGTCGTGGCATCCTAACTCA | 95 °C: 2 min; 50 cycles: 95 °C: 15 s 58 °C: 30 s 72 °C: 30 s | 172 bp | [19] |
| End-88R: GCGGACGGCTCATTATAACA | ||||||
| Probe: VIC-TCATTGAATGAATTGGCCATTT′-NFQ | ||||||
| Enterocytozoonbieneusi | ITS | nPCR | EBITS3: GGTCATAGGGATGAAGAG | 95 °C 5 min; 35 Cycles: 94 °C: 40 s 53 °C: 45 s 72 °C: 45 s 72 °C: 4 min | 435 bp | [23,24] |
| EBITS4: TTCGAGTTCTTTCGCGCTC | ||||||
| EBITS1: GCTCTGAATATCTATGGCT | 95 °C 5 min; 30 Cycles: 94 °C: 35 s 55 °C: 40 s 72 °C: 40 s 72 °C: 5 min | 390 bp | ||||
| EBITS2.4: ATCGCCGACGGATCCAAGTG |
2.6. Sequencing Analysis
3. Results
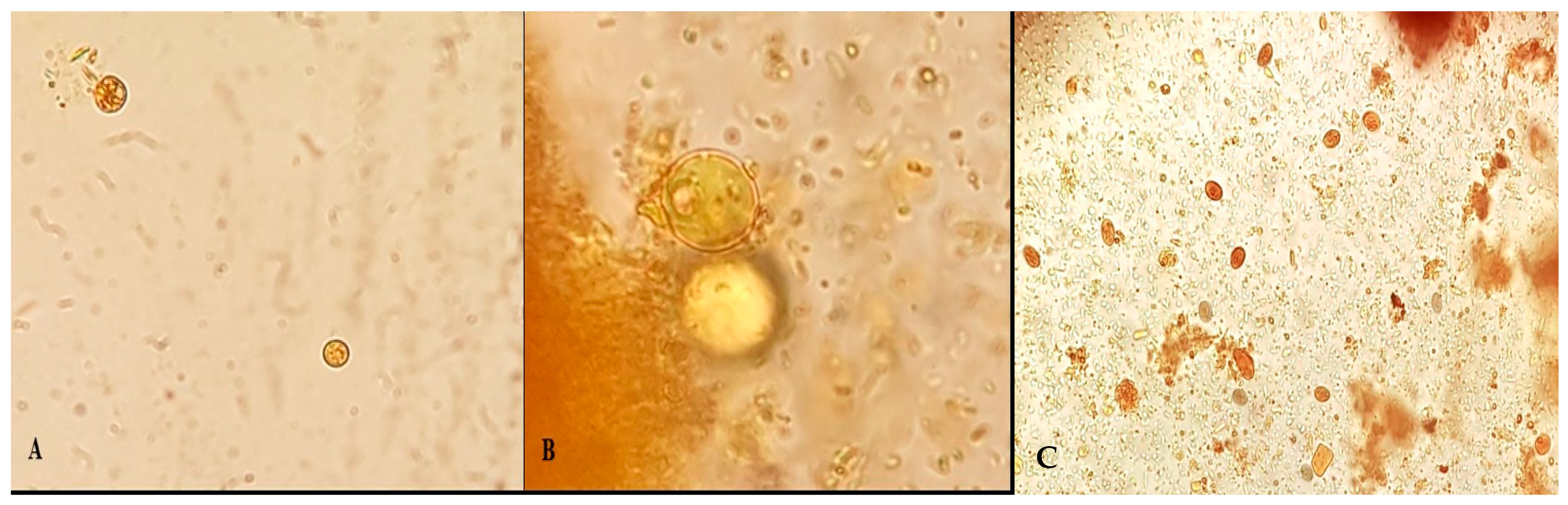
3.1. Light Microscopy
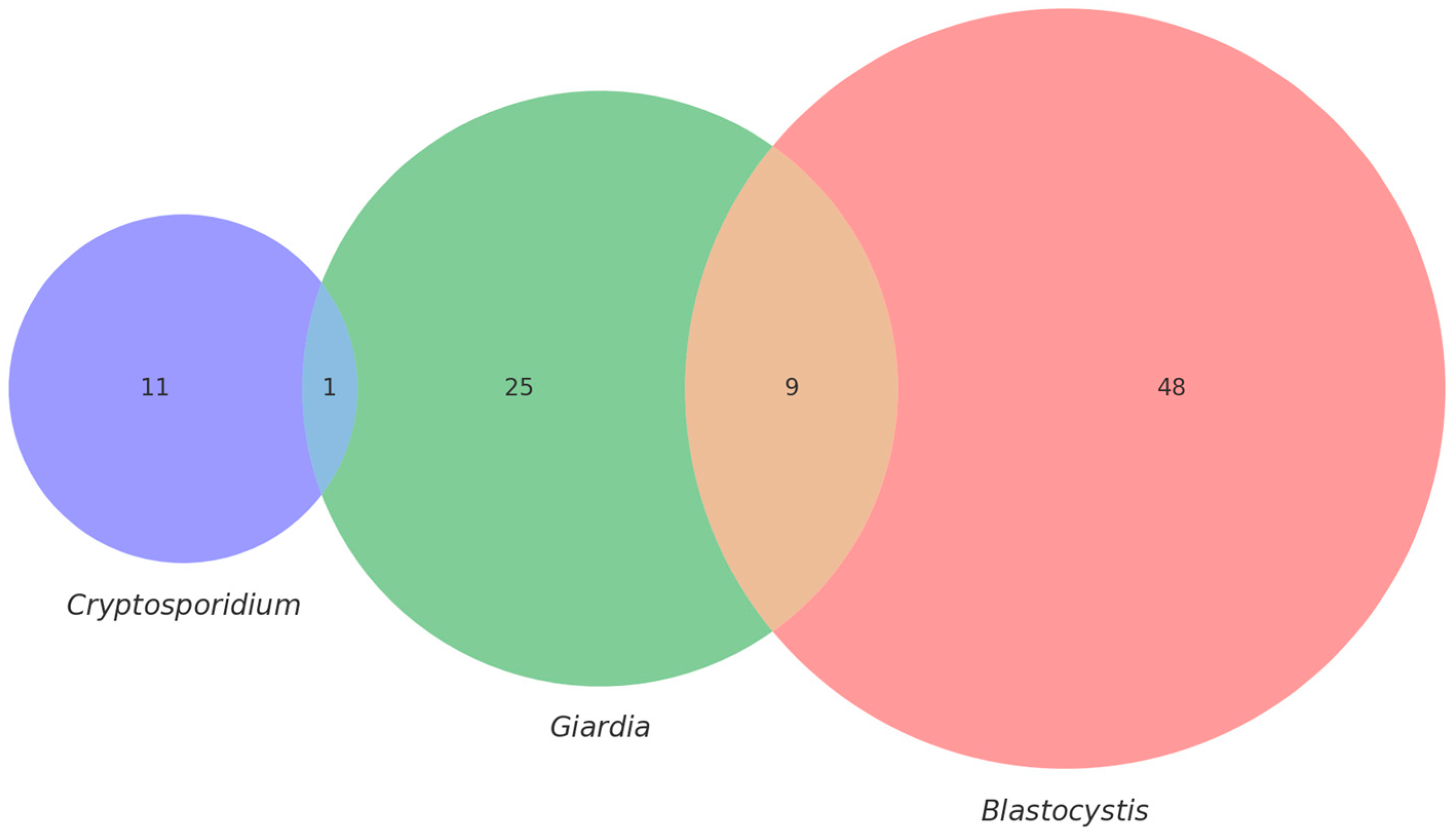
3.2. Molecular Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdoli, A.; Olfatifar, M.; Eslahi, A.V.; Moghadamizad, Z.; Nowak, O.; Pirestani, M.; Karimipour-Saryazdi, A.; Badri, M.; Karanis, P. Prevalence of intestinal protozoan parasites among Asian schoolchildren: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2024, 52, 2097–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebremichael, S.T.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Andegiorgish, A.K.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, J.; Li, T.; Bao, J.; Zhou, Z.; et al. First identification and coinfection detection of Enterocytozoon bieneusi, Encephalitozoon spp., Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in diarrheic pigs in Southwest China. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Palit, P.; Haque, A.; Levine, M.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Nasrin, D.; Hossain, M.J.; Sur, D.; Ahmed, T.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Symptomatic and asymptomatic enteric protozoan parasitic infection and their association with subsequent growth parameters in under five children in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, D.C.; Vanopdenbosch, E.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Abbassi, H.; E Peeters, J. A review of the importance of cryptosporidiosis in farm animals. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1269–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Liang, G.; Su, N.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Kang, X.; Guo, K. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Diarrheic and Non-Diarrheic Calves from Ningxia, Northwestern China. Animals 2023, 13, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Liang, C.; Chi, S.-C.; Lee, K.-J.; Chou, C.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yang, W.-Y. An Epidemiological Assessment of Cryptosporidium and Giardia spp. Infection in Pet Animals from Taiwan. Animals 2023, 13, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Huston, C.D.; Hughes, M.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A. Amebiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykur, M.; Malatyalı, E.; Demirel, F.; Cömert-Koçak, B.; Gentekaki, E.; Tsaousis, A.D.; Dogruman-Al, F. Blastocystis: A Mysterious Member of the Gut Microbiome. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, C.J.; Garófalo, M.P.; Perazzo, J.; Epelbaum, C.; Castro, G.; Sicilia, P.; Barnes, A.; Guasconi, L.; Burstein, V.L.; Beccacece, I.; et al. Enterocytozoon bieneusi Infection after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant in Child, Argentina. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedair, N.H.; Zeki, I.N. Prevalence of Some Parasitic Infections in Iraq from 2019 to 2020. Iraqi J. Sci. 2023, 64, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberfkani, M.I. Molecular characterization of Blastocystis hominis in irritable bowel syndrome patients and nursing staff in public and private clinic in Iraq. Ann. Parasitol. 2022, 68, 715–720. [Google Scholar]
- Hafidh, A.-S.; Aevan, A.-M. Microsporidial infection in some domesticand laboratory animals in Iraq. Int. J. Basic Appl. Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fadl, S.R. Prevalence of Parasitic Infection in Sheep From different Regions in Baghdad. Iraqi J. Veter-Med. 2011, 35, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxamhud, S.; Reghaissia, N.; Laatamna, A.; Samari, H.; Remdani, N.; Gentekaki, E.; Tsaousis, A.D. Molecular Identification of Cryptosporidium spp., and Giardia duodenalis in Dromedary Camels (Camelus dromedarius) from the Algerian Sahara. Parasitologia 2023, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinatham, V.; Maxamhud, S.; Popluechai, S.; Tsaousis, A.D.; Gentekaki, E. Blastocystis One Health Approach in a Rural Community of Northern Thailand: Prevalence, Subtypes and Novel Transmission Routes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 746340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindergard, G.; Nydam, D.V.; Wade, S.E.; Schaaf, S.L.; Mohammed, H.O. The sensitivity of PCR detection of cryptosporidium oocysts in fecal samples using two DNA extraction methods. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 7, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, P.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Hoque, S.; Hammouma, O.; Leruste, H.; Détriché, S.; Canniere, E.; Daandels, Y.; Dellevoet, M.; Roemen, J.; et al. Cross-Border Investigations on the Prevalence and Transmission Dynamics of Cryptosporidium Species in Dairy Cattle Farms in Western Mainland Europe. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hove, R.T.; Schuurman, T.; Kooistra, M.; Möller, L.; van Lieshout, L.; Verweij, J.J. Detection of diarrhoea-causing protozoa in general practice patients in The Netherlands by multiplex real-time PCR. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Blangé, R.A.; Templeton, K.; Schinkel, J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; van Rooyen, M.A.A.; van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Simultaneous Detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium parvum in Fecal Samples by Using Multiplex Real-Time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciò, S.M.; De Giacomo, M.; Pozio, E. Sequence analysis of the β-giardin gene and development of a polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism assay to genotype Giardia duodenalis cysts from human faecal samples. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Fayer, R.; Bern, C.; Gilman, R.H.; Trout, J.M.; Schantz, P.M.; Das, P.; Lal, A.A.; Xiao, L. Triosephosphate Isomerase Gene Characterization and Potential Zoonotic Transmission of Giardia duodenalis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, S.M.; Tawari, B.; Clark, C.G. DNA Barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist 2006, 157, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadica, A.S.; Messa, A.E.; Dashti, A.; Balasegaram, S.; Santin, M.; Manjate, F.; Chirinda, P.; Garrine, M.; Vubil, D.; Acácio, S.; et al. First identification of genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microsporidia) among symptomatic and asymptomatic children in Mozambique. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckholt, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Tzipori, S. Prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in swine: An 18-month survey at a slaughter-house in Massachusetts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2595–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hraiga, B.A. Investigation of Cryptosporidium infection in Lambs and Goat Kids at Al-kut city, wasit province. J. Health Med. Nurs. 2017, 43, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhaled, M.J.A. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in sheep and goat in Al-Qadisiyah province/Iraq. Iraqi J. Veter-Med. 2017, 41, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Ahmadpour, E.; Carmena, D.; Spotin, A.; Bangoura, B.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium infections in terrestrial ungulates with focus on livestock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehena, J.; Bin Harun, A.; Karim, R. Epidemiology of Blastocystis in farm animals: A review. Veter-Parasitol. 2024, 334, 110382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, R.; Haghighi, A.; Stensvold, C.R.; Kheirandish, F.; Azargashb, E.; Raeghi, S.; Kohansal, C.; Bahrami, F. Prevalence and subtype identification of Blastocystis isolated from humans in Ahvaz, Southwestern Iran. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2017, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Rahimi, H.M.; Rezaeian, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Badri, M.; Mirjalali, H. Detection and molecular characterization of Blastocystis sp., Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Giardia duodenalis in asymptomatic animals in southeastern Iran. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, I.; Bozorg-Ghalati, F.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Manfredi, M.T.; Motazedian, M.H.; Mohammadpour, N. First molecular subtyping and phylogeny of Blastocystis sp. isolated from domestic and synanthropic animals (dogs, cats and brown rats) in southern Iran. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Wang, F.; Chang, S.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L. Predominance of the Blastocystis subtype ST5 among free-living sympatric rodents within pig farms in China suggests a novel transmission route from farms. One Health 2024, 18, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.-H.; Yen, T.-Y.; Tung, H.-H.; Ho, A.; Chien, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Kang, S.-W.; Juan, N.-N.; Lin, F.-L. Surveillance of Emerging Rodent-Borne Pathogens in Wastewater in Taiwan: A One Health Approach. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, M.; Bahrami, A.M.; Mousivand, A.; Shamsi, L.; Asghari, A.; Shahabi, S.; Sadrebazzaz, A. First molecular characterization of Blastocystis subtypes from domestic animals (sheep and cattle) and their animal-keepers in Ilam, western Iran: A zoonotic concern. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2024, 71, e13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhum, R.W.; Jaber, N.; Al-Asadi, H.; Abbas, Z.; Al-Maliki, J. Study the prevalence of entamoeba species in children and farm animals in waist province. Web Sci. Sch. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2022, 2, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dabbagh, S.M.K.; Alseady, H.H.; Alhadad, E.J. Molecular identification of Entamoeba spp. in humans and cattle in Baghdad, Iraq. Veter-World 2024, 17, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, S.R.; Al-Hasnawy, M.H. Microscopic and Molecular Diagnosis of Giardia Duodenalis in Human in Babylon Province, Iraq. Int. J. Pharm. Bio-Med. Sci. 2023, 3, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, D.A.; Alobaidii, W.A.; Alkateb, Y.N.M.; Ali, F.F.; Ola-Fadunsin, S.D.; Gimba, F.I. Molecular detection and prevalence of human-pathologic Enterocytozoon bieneusi among pet birds in Mosul, Iraq. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 95, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, T.P.; Raju, G.P.; Rao, I.S.; Kumar, A.P. Data collection, statistical analysis and machine learning studies of cancer dataset from North Costal Districts of AP, India. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 48, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R. Blastocystis in stool: Friend, foe or both? J. Travel Med. 2025, 32, taaf011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousis, A.D.; Gentekaki, E.; Stensvold, C.R. Advancing research on Blastocystis through a One Health approach. Open Res. Eur. 2024, 4, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Source | Humans | Animals | Soil | Water | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of Parasites | Number of Positive | % | Number of Positive | % | Number of Positive | % | Number of Positive | % | Number of Positive | % |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 6 | 12% | 13 | 26% | 1 | 5% | 3 | 15% | 23 | 19.16% |
| Blastocystis sp. | 8 | 16% | 39 | 78% | 9 | 45% | 1 | 5% | 57 | 47.5% |
| Goat: 8 | 4% | |||||||||
| Giardia duodenalis | 5 | 10% | 4 | 8% | - | - | - | - | 9 | 7.5% |
| Total | 19 | 56 | 10 | 4 | 89 | 63.57% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salman Al-Adilee, Y.M.; Shather, M.M.; Kalef, D.A.; Maxamhud, S.; Akdur Öztürk, E.; Gentekaki, E.; Tsaousis, A.D. Intestinal Microbial Eukaryotes at the Human, Animal and Environment Interface in Rural Iraq. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030034
Salman Al-Adilee YM, Shather MM, Kalef DA, Maxamhud S, Akdur Öztürk E, Gentekaki E, Tsaousis AD. Intestinal Microbial Eukaryotes at the Human, Animal and Environment Interface in Rural Iraq. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalman Al-Adilee, Yaseen Majid, Maulood M. Shather, Dalia A. Kalef, Sadiya Maxamhud, Eylem Akdur Öztürk, Eleni Gentekaki, and Anastasios D. Tsaousis. 2025. "Intestinal Microbial Eukaryotes at the Human, Animal and Environment Interface in Rural Iraq" Parasitologia 5, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030034
APA StyleSalman Al-Adilee, Y. M., Shather, M. M., Kalef, D. A., Maxamhud, S., Akdur Öztürk, E., Gentekaki, E., & Tsaousis, A. D. (2025). Intestinal Microbial Eukaryotes at the Human, Animal and Environment Interface in Rural Iraq. Parasitologia, 5(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030034





